Pre-Trained Transformer-Based Models for Text Classification Using Low-Resourced Ewe Language
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We developed and preprocessed a low-resource EWE dataset for news classification. The Ewe news dataset consists of 4264 news articles with six distinct classes. Each news article comprises an average of 400 words;
- Based on the Ewe news dataset, we developed a word embedding process for exploiting the semantic representation in the low-resource language. We further fine-tuned seven transformer-based language models using the proposed Ewe dataset to explore its semantic representation for text classification;
- We evaluated the robustness and stability of our fine-tuned models in capturing the exact semantic representation of the low-resourced Ewe text. State-of-the-art results were achieved with the fine-tuned language models in each class. A deep comparative study analyzed each model’s ability to capture strong semantic Ewe information.
2. Related Work
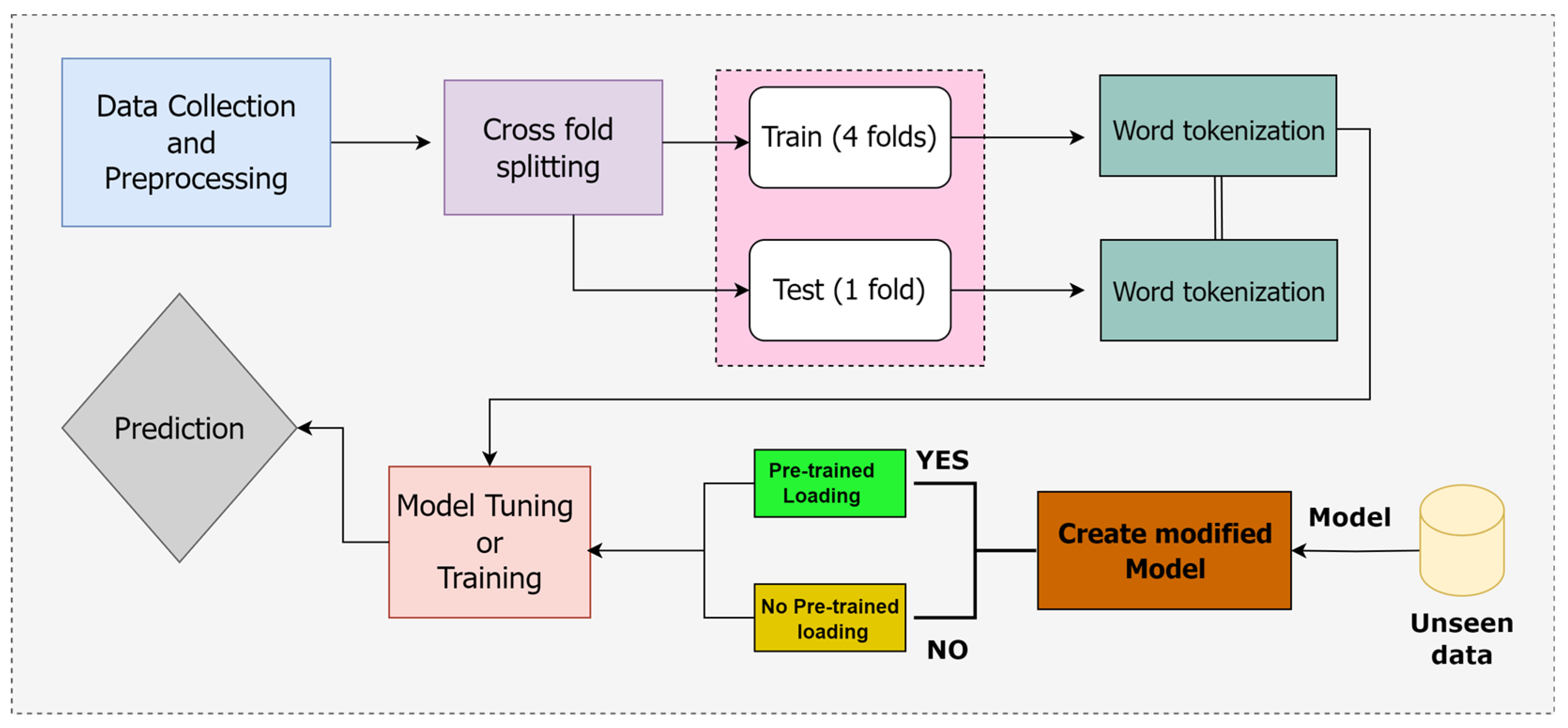
3. Materials and Methodology
3.1. Ewe Dataset Formation
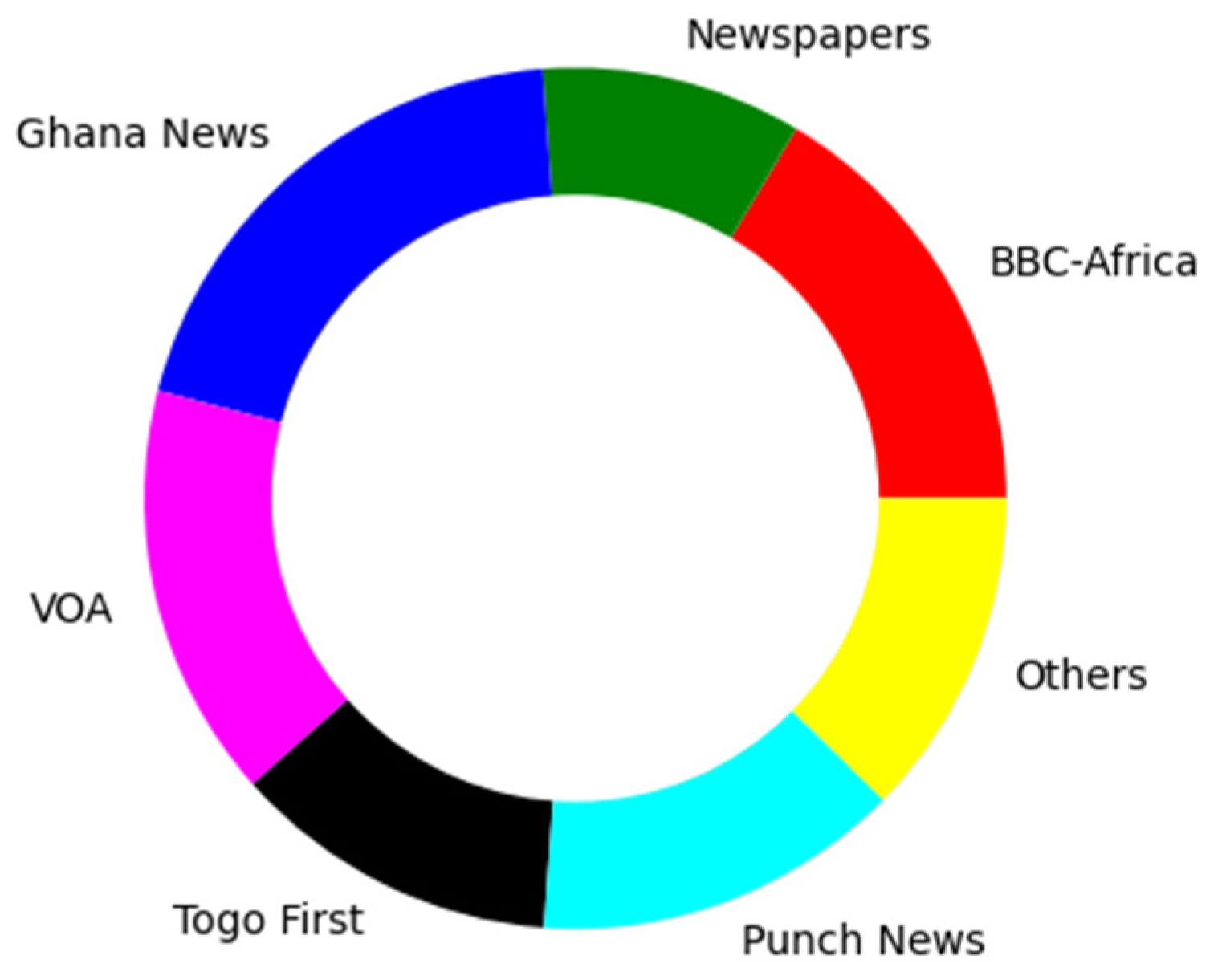
3.1.1. Data Collection
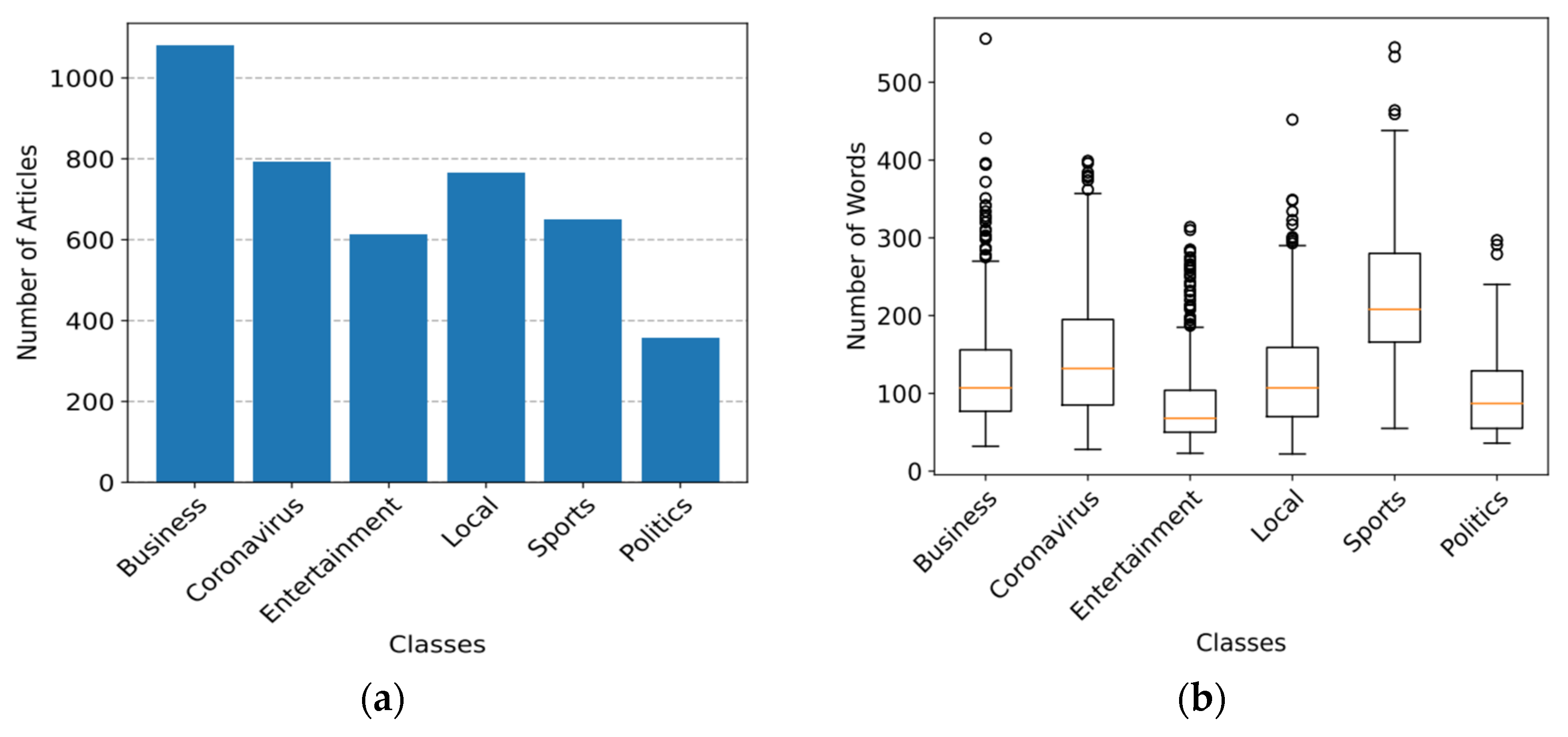
3.1.2. Ewe News Dataset Description
3.2. Preprocessing and Word Embedding
Word Embedding
3.3. Methodology
3.3.1. Reason for Choosing These Transformer-Based Models
3.3.2. BERT Model
3.3.3. DistilBERT Model
3.3.4. RoBERTa and DistilRoBERTa Models
3.3.5. DeBERTa Model
3.3.6. Fine-Tuning
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Evaluation Metric
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Results and Discussion
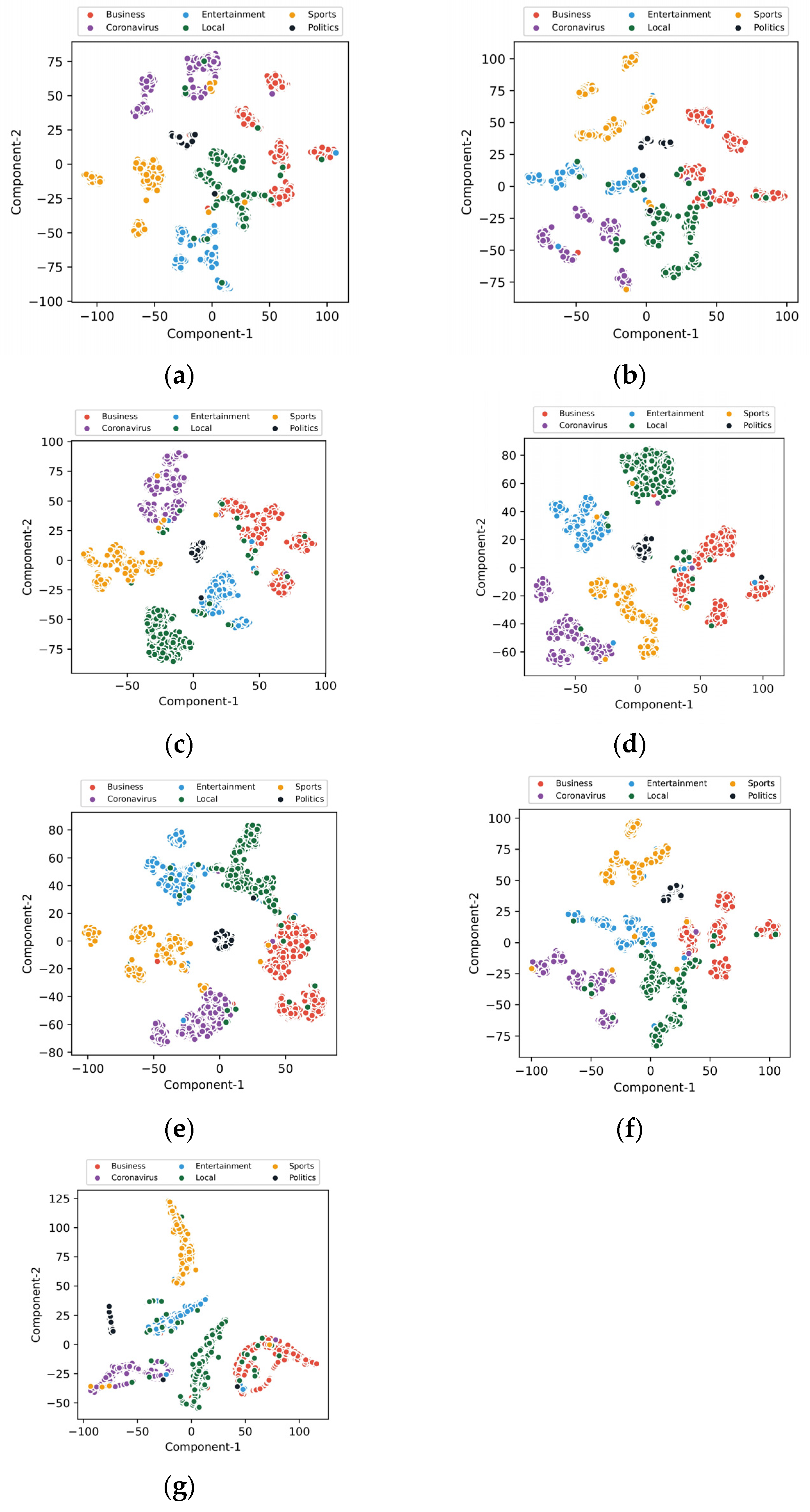
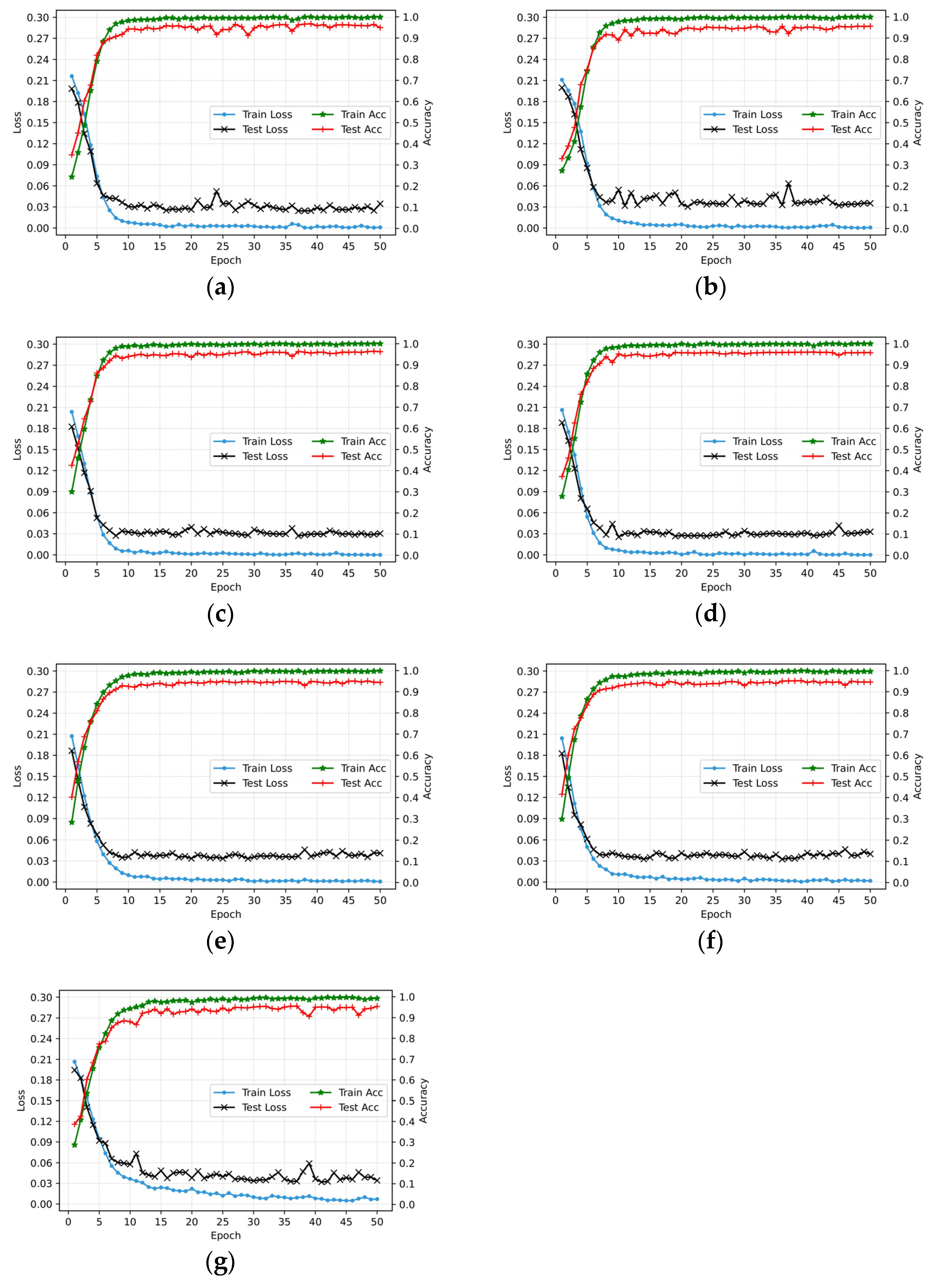
4.3.1. Visualization of Class Feature Separability
4.3.2. Models’ Performance Comparison
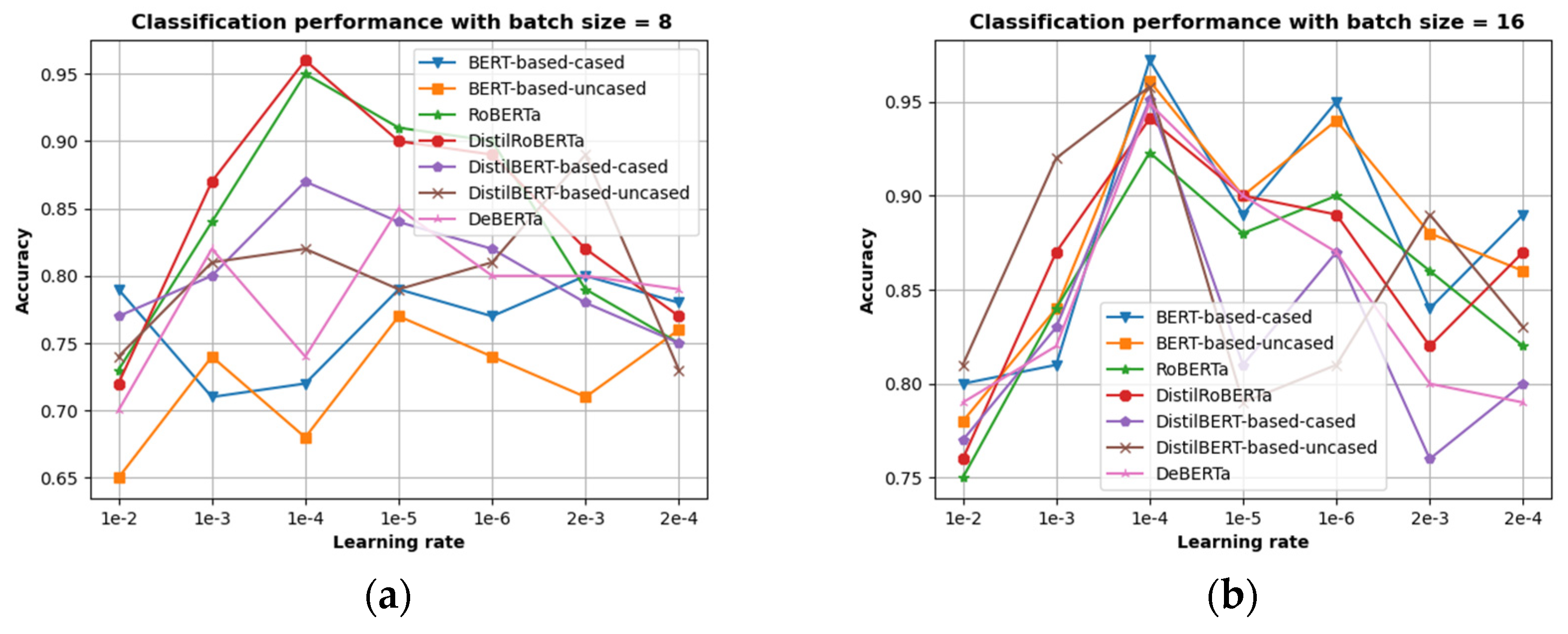
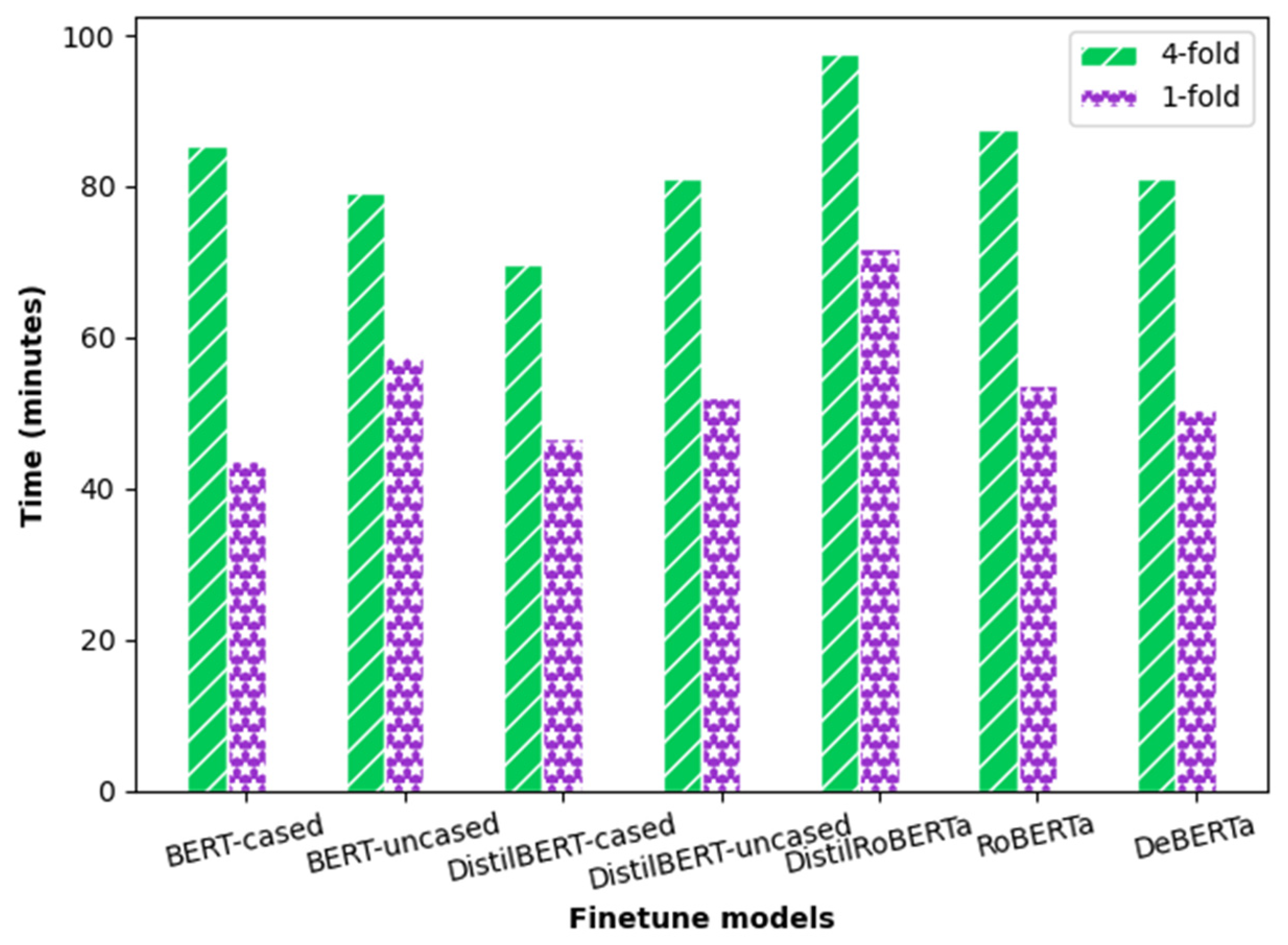
4.3.3. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | http://qwone.com/~jason/20Newsgroups/ (accessed on 11 November 2021) |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | https://ghananewsonline.com.gh/ (accessed on 20 October 2021) |
| 5 | https://www.voaafrica.com/ (accessed on 17 January 2022) |
| 6 | https://www.togofirst.com/en (accessed on 19 January 2022) |
| 7 | https://punchng.com/ (accessed on 16 January 2022) |
| 8 | https://www.bbc.com/news/world/africa (accessed between 11 January to February 23 2022) |
| 9 | https://www.myjoyonline.com/ (accessed between 11 December 2021 to 30 January 2022) |
| 10 | https://citinewsroom.com/ (accessed on 25 February 2022) |
| 11 | beautifulsoup4·PyPI |
References
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Sun, S.; Luo, X. BERT-based chinese text classification for emergency management with a novel loss function. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 10417–10428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, S.; Iglesias, C.A. A text classification approach to detect psychological stress combining a lexicon-based feature framework with distributional representations. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 103011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjali, A.; Magnéli, M.; Shin, D.; Malchau, H.; Muratoglu, O.K.; Varadarajan, K.M. Natural language processing with deep learning for medical adverse event detection from free-text medical narratives: A case study of detecting total hip replacement dislocation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 129, 104140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, K.; Khan, M.A.; Saeed, U.; Al Ghamdi, M.A.; Asif, M.; Arfan, M. Semantic Analysis to Identify Students’ Feedback. Comput. J. 2022, 65, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, V.; Alharithi, F.S.; Álvarez, R.M.; Singh, A.; Qahtani, A.M. NLP-Based Application for Analyzing Private and Public Banks Stocks Reaction to News Events in the Indian Stock Exchange. Systems 2022, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhady, N.; Elsemman, I.E.; Farghally, M.F.; Soliman, T.H.A. Developing Analytical Tools for Arabic Sentiment Analysis of COVID-19 Data. Algorithms 2023, 16, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Inuzuka, M.; Kuroyanagi, I.; Segawa, O. Spontaneous Speech Summarization: Transformers All The Way Through. In Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 23–27 August 2021; pp. 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivinayagam, A.; El-Bayeh, C.Z.; Damaševičius, R. Twenty Years of Machine-Learning-Based Text Classification: A Systematic Review. Algorithms 2023, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbesi, V.K.; Chen, W.; Gizaw, S.M.; Ukwuoma, C.C.; Ameneshewa, A.S.; Ejiyi, C.J. Attention Based BiGRU-2DCNN with Hunger Game Search Technique for Low-Resource Document-Level Sentiment Classification. In ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; 2023; pp. 48–54. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Xia, C.; Yang, R.; Sun, L.; Yu, P.S.; He, L. A Survey on Text Classification: From Traditional to Deep Learning. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2022, 13, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, F.; Reynolds, D.; Dehak, N. Deep neural network approaches to speaker and language recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 1671–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggilla, C. Discrimination between Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects using {CNN}- and {LSTM}-based Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Third Workshop on {NLP} for Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects ({V}ar{D}ial3), Osaka, Japan; 2016; pp. 185–4824. [Google Scholar]
- Agbesi, V.K.; Chen, W.; Odame, E.; Browne, J.A. Efficient Adaptive Convolutional Model Based on Label Embedding for Text Classification Using Low Resource Languages. In Proceedings of the 2023 7th International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Metaheuristics & Swarm Intelligence, Virtual, 23–24 April 2023; pp. 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; van Merriënboer, B.; Bahdanau, D.; Bengio, Y. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder–decoder approaches. In Proceedings of the SSST 2014-8th Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation, Doha, Qatar, 25 October 2014; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.; Ruder, S. Universal language model fine-tuning for text classification. In Proceedings of the ACL 2018-56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Proceedings of the Conference (Long Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; pp. 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. Homol. Homotopy Appl. 2007, 9, 399–438. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the NAACL HLT 2019-2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies-Proceedings of the Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Nassiri, K.; Akhloufi, M. Transformer models used for text-based question answering systems. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 10602–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.C.B.; Cheng, C. Establishing Baselines for Text Classification in Low-Resource Languages. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.02068. [Google Scholar]
- Alzanin, S.M.; Azmi, A.M.; Aboalsamh, H.A. Short text classification for Arabic social media tweets. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 6595–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cong, P.; Lv, S. A Long-Text Classification Method of Chinese News Based on BERT and CNN. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 34046–34057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.I.; Islam, M.S.; Amin, M.R. Sentiment analysis in Bengali via transfer learning using multi-lingual BERT. In Proceedings of the ICCIT 2020-23rd International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, Proceedings, Virtual, 19–21 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhurayyif, Y.; Sait, A.R.W. A comprehensive survey of techniques for developing an Arabic question answering system. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, W.; Mangaravite, V.; Gomes, C.; Canuto, S.; Resende, E.; Nascimento, C.; Viegas, F.; França, C.; Martins, W.S.; Almeida, J.M.; et al. On the cost-effectiveness of neural and non-neural approaches and representations for text classification: A comprehensive comparative study. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jang, S.; Park, E.; Choi, S. Text classification using capsules. Neurocomputing 2020, 376, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbesi, V.K.; Wenyu, C.; Kuadey, N.A.; Maale, G.T. Multi-Topic Categorization in a Low-Resource Ewe Language: A Modern Transformer Approach. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Wuhan, China, 22–25 April 2022; pp. 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Azunre, P.; Osei, S.; Addo, S.; Adu-Gyamfi, L.A.; Moore, S.; Adabankah, B.; Opoku, B.; Asare-Nyarko, C.; Nyarko, S.; Amoaba, C.; et al. NLP for Ghanaian Languages. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.15475. [Google Scholar]
- Marivate, V.; Sefara, T.; Chabalala, V.; Makhaya, K.; Mokgonyane, T.; Mokoena, R.; Modupe, A. Investigating an approach for low resource language dataset creation, curation and classification: Setswana and Sepedi. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04986. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, J.C.B.; Cheng, C. Evaluating Language Model Finetuning Techniques for Low-resource Languages. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.00409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.N.; Ghani, M.U.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Mahmood, W.; Dengel, A.; Ahmed, S. Benchmarking performance of machine and deep learning-based methodologies for Urdu text document classification. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 5437–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanan, T.; Hawashin, B.; Alzubi, S.; Almaita, E.; Alkhatib, A.; Maria, K.A.; Elbes, M. Improving Arabic Text Classification Using P-Stemmer. Recent Adv. Comput. Sci. Commun. 2020, 15, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnahas, A.; Elfishawy, N.; Nour, M.; Tolba, M. Machine Learning and Feature Selection Approaches for Categorizing Arabic Text: Analysis, Comparison, and Proposal. Egypt. J. Lang. Eng. 2020, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh, T.N.P.; Kha, H.H. Vietnamese News Articles Classification Using Neural Networks. J. Adv. Inf. Technol. 2021, 12, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, M.; Madbouly, M.M.; El-Zoghby, A. Classifying Arabic text using deep learning. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2019, 97, 3412–3422. [Google Scholar]
- Elnagar, A.; Al-Debsi, R.; Einea, O. Arabic text classification using deep learning models. Inf. Process. Manag. 2020, 57, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, G.; Kong, M.; Yin, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Developing Multi-Labelled Corpus of Twitter Short Texts: A Semi-Automatic Method. Systems 2023, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjeisah, M.; Liu, G.; Nortey, R.N.; Song, J.; Lamptey, K.O.; Frimpong, F.N. Twi corpus: A massively Twi-to-handful languages parallel bible corpus. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking, Exeter, UK, 17–19 December 2020; pp. 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: Smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Le, Q.V. XLNet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 2019, 5753–5763. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.M.; Bravo-Marquez, F.; Salameh, M.; Kiritchenko, S. SemEval-2018 Task 1: Affect in Tweets. In Proceedings of the NAACL HLT 2018-International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, SemEval 2018-Proceedings of the 12th Workshop, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–6 June 2018; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyozov, E.; Salaev, U.; Matlatipov, S.; Matlatipov, G. Text classification dataset and analysis for Uzbek language. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.14494. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, T.A.; Shahzad, W.; Arshad, U. Hierarchical Text Classification of Urdu News using Deep Neural Network. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03141. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafoor, A.; Imran, A.S.; Daudpota, S.M.; Kastrati, Z.; Batra, R.; Wani, M.A. The Impact of Translating Resource-Rich Datasets to Low-Resource Languages through Multi-Lingual Text Processing. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 124478–124490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, Z. Scalable multi-channel dilated CNN–BiLSTM model with attention mechanism for Chinese textual sentiment analysis. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 118, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.; Debut, L.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C.; Moi, A.; Cistac, P.; Rault, T.; Louf, R.; Funtowicz, M.; et al. Transformers: State-of-the-Art Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, W. DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.03654. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Huang, L.; Qiu, X. Utilizing BERT for aspect-based sentiment analysis via constructing auxiliary sentence. In Proceedings of the NAACL HLT 2019-2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies-Proceedings of the Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 380–385. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5999–6009. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, M.; Goodman, S.; Gimpel, K.; Sharma, P.; Soricut, R. ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11942. [Google Scholar]
- Conneau, A.; Khandelwal, K.; Goyal, N.; Chaudhary, V.; Wenzek, G.; Guzmán, F.; Grave, E.; Ott, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Unsupervised cross-lingual representation learning at scale. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 8440–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapire, R.E.; Singer, Y. Improved boosting algorithms using confidence-rated predictions. Mach. Learn. 1999, 37, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, D.J.; Till, R.J. A Simple Generalisation of the Area Under the ROC Curve for Multiple Class Classification Problems. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Class | Ewe Text | English Meaning | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coronavirus | Le numekukuwo nu la, ame siwo wu 770,000 ye xɔ COVID-19 le Ghana. | According to research, more than 770,000 people were infected by COVID-19 in Ghana. | 794 |
| Political | Ghana Dukplɔla yɔ demokrasi-dukɔmeviwo ƒe habɔbɔa be woƒe tagbɔ kɔ wu wo hatiwo. | The Ghanaian President called the democratic–republican community to be more intelligent than its peers. | 358 |
| Business | Habɔbɔ aɖe si xɔa ame ɖe agbe tso nya me be yeana hehe Ghanatɔ ewo. | A life-saving organization has decided to train ten Ghanaians. | 1082 |
| Local | Nigeria dziɖuɖua wɔ afɔɖeɖe sesẽwo ɖe mɔdododzifɔkuwo ŋu. | The Nigerian government has taken drastic measures against road accidents. | 614 |
| Entertainment | Srɔã ɖee fia be dɔléle sesẽ aɖe le fu ɖem na Olu Jacob. | Olu Jacob is suffering from a severe ailment, his wife disclosed. | 766 |
| Sports | Xexeame ƒe Lãmesẽ Habɔbɔ ɖo lɛta ɖe Ghana be woado go ame alafa ɖeka hena hehexɔxɔ. | The World Health Organization (WHO) has sent a letter to Ghana to meet a hundred people for training purposes. | 650 |
| Total size | 4264 | ||
| Class | No. of Articles | No. of Sentences | No. of Tokens | No. of Tokens after Lemmatization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coronavirus | 794 | 4596 | 7734 | 7121 |
| Political | 358 | 1674 | 5009 | 4701 |
| Business | 1082 | 6338 | 11,441 | 10,506 |
| Local | 614 | 4230 | 9273 | 8513 |
| Entertainment | 766 | 2880 | 6456 | 5887 |
| Sports | 650 | 5436 | 11,736 | 7121 |
| Mean (μ) | 710.67 | 4192.33 | 8608.16 | 308.17 |
| Standard deviation (σ) | 238.70 | 1695.83 | 2705.56 | 2028.05 |
| Class | BERT-Based-Cased | BERT-Based-Uncased | RoBERTa | DistilRoBERTa | DistilBERT-Based-Cased | DistilBERT-Based-Uncased | DeBERTa | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business | 99.07 | 97.22 | 97.22 | 94.44 | 95.37 | 96.30 | 100.00 | 97.09(5) |
| Coronavirus | 98.73 | 96.84 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 98.73 | 96.20 | 100.00 | 98.64(3) |
| Entertainment | 97.54 | 98.36 | 96.72 | 94.26 | 98.36 | 100.00 | 96.72 | 97.42(4) |
| Local | 97.39 | 92.16 | 92.16 | 96.08 | 97.39 | 97.39 | 90.85 | 94.77(6) |
| Sports | 97.67 | 100.00 | 98.45 | 98.45 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 96.90 | 98.78(2) |
| Politics | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 93.55 | 99.08(1) |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Macro | F1-Micro | Average | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BERT-based-cased | 0.972 | 0.969 | 0.970 | 0.972 | 0.968 | 0.970 | 0.021 |
| BERT-based-uncased | 0.964 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.963 | 0.960 | 0.962 | 0.037 |
| RoBERTa | 0.959 | 0.957 | 0.949 | 0.953 | 0.956 | 0.955 | 0.049 |
| DistilRoBERTa | 0.960 | 0.959 | 0.960 | 0.961 | 0.958 | 0.960 | 0.039 |
| DistilBERT-based-cased | 0.963 | 0.962 | 0.961 | 0.962 | 0.964 | 0.962 | 0.033 |
| DistilBERT-based-uncased | 0.968 | 0.964 | 0.966 | 0.967 | 0.965 | 0.966 | 0.023 |
| DeBERTa | 0.961 | 0.958 | 0.959 | 0.961 | 0.957 | 0.960 | 0.031 |
| Model | ROC-AUC | ROC-AUC Weight | HL |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERT-based-cased | 0.995 | 0.994 | 0.029 |
| BERT-based-uncased | 0.993 | 0.989 | 0.040 |
| RoBERTa | 0.973 | 0.971 | 0.041 |
| DistilRoBERTa | 0.985 | 0.983 | 0.043 |
| DistilBERT-based-cased | 0.989 | 0.984 | 0.037 |
| DistilBERT-based-uncased | 0.994 | 0.992 | 0.034 |
| DeBERTa | 0.984 | 0.983 | 0.038 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agbesi, V.K.; Chen, W.; Yussif, S.B.; Hossin, M.A.; Ukwuoma, C.C.; Kuadey, N.A.; Agbesi, C.C.; Abdel Samee, N.; Jamjoom, M.M.; Al-antari, M.A. Pre-Trained Transformer-Based Models for Text Classification Using Low-Resourced Ewe Language. Systems 2024, 12, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12010001
Agbesi VK, Chen W, Yussif SB, Hossin MA, Ukwuoma CC, Kuadey NA, Agbesi CC, Abdel Samee N, Jamjoom MM, Al-antari MA. Pre-Trained Transformer-Based Models for Text Classification Using Low-Resourced Ewe Language. Systems. 2024; 12(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgbesi, Victor Kwaku, Wenyu Chen, Sophyani Banaamwini Yussif, Md Altab Hossin, Chiagoziem C. Ukwuoma, Noble A. Kuadey, Colin Collinson Agbesi, Nagwan Abdel Samee, Mona M. Jamjoom, and Mugahed A. Al-antari. 2024. "Pre-Trained Transformer-Based Models for Text Classification Using Low-Resourced Ewe Language" Systems 12, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12010001
APA StyleAgbesi, V. K., Chen, W., Yussif, S. B., Hossin, M. A., Ukwuoma, C. C., Kuadey, N. A., Agbesi, C. C., Abdel Samee, N., Jamjoom, M. M., & Al-antari, M. A. (2024). Pre-Trained Transformer-Based Models for Text Classification Using Low-Resourced Ewe Language. Systems, 12(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12010001









