Urban Networks in the Yangtze River Delta from the Perspective of Transaction Linkages in Manufacturing Industries: Characteristics, Determinants, and Strategies for Intercity Integration Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. From WCN Research to Urban Networks of MCRs
2.2. Analytical Perspectives of Urban Network Reaserch of Mega-City Regions
2.3. Research Method of Urban Networks of Maga-City Region
2.4. Urban Network Governance in Mega-City Regions
2.5. Research Gap
3. Materials and Methods
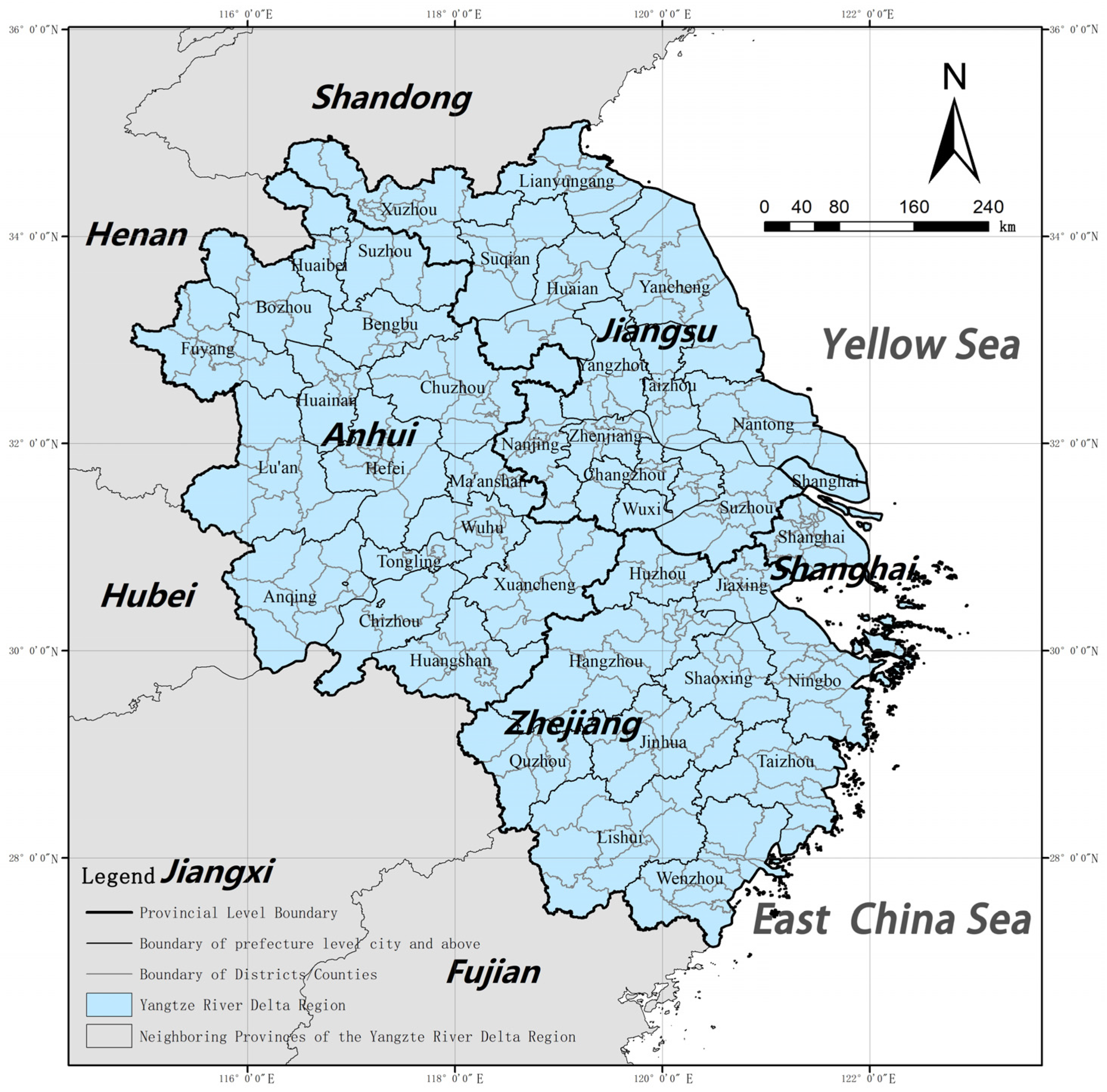
3.1. Research Area
3.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
3.3. Research Methods
3.3.1. Social Network Analysis (SNA)
- Degree centrality
- Betweenness centrality
- Linkage value between cities
- Community Detection
3.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation
3.3.3. Quadratic Assignment Procedure (QAP)
3.3.4. Stepwise Regression Method
4. Results
4.1. Nodal Centralities, City Dyads, and Their Geographical Distribution
4.2. Community Structure and Geographical Distribution
4.3. Determinants of the Urban Networks
4.3.1. Determinants of Interurban Links
4.3.2. Determinants of Nodal Centralities
5. Discussion
5.1. Urban Networks Led by Transaction Linkages in Manufacturing Industries and Other Related Dimensions
5.2. Implications for Policy and Regional Planning toward the Integrated Development of Manufacturing Industries in MCRs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kordos, M.; Vojtovic, S. Transnational corporations in the global world economic environment. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on New Challenges in Management and Organization: Organization and Leadership, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2 May 2016; pp. 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Dachs, B.; Kinkel, S.; Jager, A.; Palcic, I. Backshoring of production activities in European manufacturing. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2019, 25, 100531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentoft, J.; Olhager, J.; Heikkila, J.; Thoms, L. Manufacturing backshoring: A systematic literature review. Oper. Manag. Res. 2016, 9, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sheng, J.C.; Huang, F. China’s future investments in environmental protection and control of manufacturing industry: Lessons from developed countries. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokan, T.; Kuroiwa, I.; Laksanapanyakul, N.; Ueki, Y. Spatial structures of manufacturing clusters in Thailand, Cambodia and Lao People’s Democratic Republic. J. Asia Pac. Econ. 2020, 25, 418–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyen, L. Internal Factors Influencing Firm Profitability in the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Empirical Evidence from Vietnam. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2022, 9, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, J. The Changing Geography of Domestic Financial City Network in China, 1995–2015. Growth Change 2018, 49, 490–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigler, T.J.; Martinus, K. Extending beyond “world cities” in World City Network (WCN) research: Urban positionality and economic linkages through the Australia-based corporate network. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2017, 49, 2916–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, S.; Sillig, C.; Ghiara, H. Advanced Logistics in Italy: A City Network Analysis. Tijdschr. Voor Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2017, 108, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, A.S.; Beckfield, J. Power and position in the world city system. Am. J. Sociol. 2004, 109, 811–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, W.; Koster, H.; Hall, P. The Location and Global Network Structure of Maritime Advanced Producer Services. Urban Stud. 2011, 48, 2749–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J.; Catalano, G.; Walker, D.R.F. Measurement of the world city network. Urban Stud. 2002, 39, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J.; Catalano, G.; Gane, N. A geography of global change: Cities and services, 2000–2001. Urban Geogr. 2003, 24, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Taylor, P.J.; Witlox, F.; Catalano, G. Hierarchical tendencies and regional patterns in the world city network: A global urban analysis of 234 cities. Reg. Stud. 2003, 37, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J. Leading world cities: Empirical evaluations of urban nodes in multiple networks. Urban Stud. 2005, 42, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vind, I.; Fold, N. Multi-level modularity vs. hierarchy: Global production networks in Singapore’s electronics industry. Geogr. Tidsskr. Dan. J. Geogr. 2007, 107, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vind, I.; Fold, N. City networks and commodity chains: Identifying global flows and local connections in Ho Chi Minh City. Glob. Netw. J. Transnatl. Aff. 2010, 10, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraetke, S. How manufacturing industries connect cities across the world: Extending research on ‘multiple globalizations’. Glob. Netw. J. Transnatl. Aff. 2014, 14, 121–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonts, M.; Taylor, M. Corporate Location, Concentration and Performance: Large Company Headquarters in the Australian Urban System. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 2641–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyler, M.; Watson, A. Framing city networks through temporary projects: (Trans)national film production beyond “Global Hollywood”. Urban Stud. 2019, 56, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Zhao, S.X.B.; Wojcik, D. The rise of venture capital centres in China: A spatial and network analysis. Geoforum 2016, 75, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Bi, W.; Lenzer, J.; Zhao, S. Mapping urban networks through inter-firm service relationships: The case of China. Urban Stud. 2017, 54, 3639–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Cao, Y.; Wu, W.; Gao, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W. International Freight Forwarding Services Network in the Yangtze River Delta, 2005–2015: Patterns and Mechanisms. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Jiao, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, J. Evolving Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Network Structure in Yangtze River Delta, China: The Perspective of Passenger Flows. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2020, 13, 925–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wu, K.; Yang, S.; Liu, Q. The Asymmetric Pattern of Population Mobility during the Spring Festival in the Yangtze River Delta Based on Complex Network Analysis: An Empirical Analysis of “Tencent Migration” Big Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Niu, X. Delineation of the Shanghai Megacity Region of China from a Commuting Perspective: Study Based on Cell Phone Network Data in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2021, 147, 04021022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Phelps, N.A. Articulating China’s Science and Technology: Knowledge Collaboration Networks Within and Beyond the Yangtze River Delta Megalopolis in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Niu, C.; Han, J. Spatial Dynamics of Intercity Technology Transfer Networks in China’s Three Urban Agglomerations: A Patent Transaction Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, I.; Sonn, J.W. The persistence of inter-regional hierarchy in technology transfer networks: An analysis of Chinese patent licensing data. Growth Change 2019, 50, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.Z.; Wu, H.Y.; Yin, D.S.; Zhang, Y.P. Macroeconomic uncertainty and the spatiotemporal evolution of innovation networks: Evidence from China’s urban technology supply chain. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2021, 34, 598–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Derudder, B.; Wang, J.; Witlox, F. An Analysis of the Determinants of the Multiplex Urban Networks in the Yangtze River Delta. Tijdschr. Voor Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2020, 111, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Miao, C.; Yu, H.; Li, C. Research on the characteristics and influencing factors of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban network structure from the perspective of listed manufacturing enterprises. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, E.; Miao, C. The characteristics of China’s urban network based on the supply chain system of automobile industry. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 370–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Lin, B.; Ning, Y. Spatial organization and Influencing Factors of Apple’s Component Supply Chain in China. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Hanssens, H.; Derudder, B.; Van Aelst, S.; Witlox, F. Assessing the Functional Polycentricity of the Mega-City-Region of Central Belgium Based on Advanced Producer Service Transaction Links. Reg. Stud. 2014, 48, 1939–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.C.; Beaverstock, J.V.; Taylor, P.J. Transaction links through cities: ‘decision cities’ and ‘service cities’ in outsourcing by leading Brazilian firms. Geoforum 2007, 38, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.H.; Bi, W.K.; Liu, X.J.; Sigler, T. Exploring financial centre networks through inter-urban collaboration in high-end financial transactions in China. Reg. Stud. 2020, 54, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.M.; Wu, S.Y.; Liu, C.L. Comparing China’s urban aviation and innovation networks. Growth Change 2022, 53, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Q.C.; Du, D.B.; Liu, C.L. The geography of intercity technology transfer networks in China. Reg. Stud. Reg. Sci. 2019, 6, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.T.; Grimes, S. The actors and relations in evolving networks: The determinants of inter-regional technology transaction in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 125, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.J.; Meijers, E.J.; Van Oort, F.G. Multiple Perspectives on Functional Coherence: Heterogeneity and Multiplexity in the Randstad. Tijdschr. Voor Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2014, 105, 444–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Chong, Z.H.; Li, X.J.; Nie, G.B. Spatial patterns and determinant factors of population flow networks in China: Analysis on Tencent Location Big Data. Cities 2020, 99, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ning, Y.M.; Lou, X.Y. The evolutionary mechanism of China’s urban network from 1997 to 2015: An analysis of air passenger flows. Cities 2021, 109, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.B.; Wu, G.D.; Han, Y.L.; Niu, Y.L. Unraveling the dynamic changes of high-speed rail network with urban development: Evidence from China. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 85, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.W.; Liu, C.X.; Li, Y.C. Directional and Weighted Urban Network Analysis in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle from the Perspective of New Media Information Flow. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.C. Spatial evolution and growth mechanism of urban networks in western China: A multi-scale perspective. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, E. Polycentric urban regions and the quest for synergy: Is a network of cities more than the sum of the parts? Urban Stud. 2005, 42, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.L.; Zhang, J.X. Planning the competitive city-region—The emergence of strategic development plan in China. Urban Aff. Rev. 2007, 42, 714–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, Z.; Derudder, B.; Liu, X.J. Using urban networks to gain new insight into old questions: Community, economy, bureaucracy. J. Urban Aff. 2021, 43, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.L.; Shen, J.F. A study on inter-city cooperation in the Yangtze river delta region, China. Habitat Int. 2009, 33, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, S. The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Knoke, D. Political Networks: The Structural Perspective; Cambridge University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994; p. 308. [Google Scholar]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E.J. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosvall, M.; Bergstrom, C.T. Maps of random walks on complex networks reveal community structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, L.; Schultz, J. Quadratic Assignment as a General Data—Analysis Strategy. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 1976, 29, 190–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulier, G.; Lemoine, F.; Ünal-Kesenci, D. China’s Integration in East Asia: Production Sharing, FDI & High-Tech Trade. Econ. Change Restruct. 2007, 40, 27–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, K.; Li, Y.; Xu, J. Applicability and prospect of China’s development zone model in Africa. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.C.K.; Xian, S. Assessing the incentives in regional city-to-city cooperation: A case study of Jiangyin-Jingjiang Industrial Park of Jiangsu Province in the Yangtze River Delta region. Asia Pac. Viewp. 2012, 53, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattiker, T.F.; Huang, X.; Schwarz, J.L. Negotiation, email, and Internet reverse auctions: How sourcing mechanisms deployed by buyers affect suppliers’ trust. J. Oper. Manag. 2007, 25, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkina, E.; Van Assche, A.; Kali, R. Structure and evolution of global cluster networks: Evidence from the aerospace industry. J. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 16, 1211–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Liu, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, M. Impact of Polycentric Urban Network on Industrial Structure Upgrades: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2022, 148, 04022024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, K.; Van Hamme, G.; Vinciguerra, S.; David, Q. Global networks, cities and economic performance: Observations from an analysis of cities in Europe and the USA. Urban Stud. 2016, 53, 1137–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, H. Study on the harmony between Beijing manufacturing’s competitiveness and technology innovation. Sci. Res. Manag. 2007, 28, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Eisingerich, A.B.; Bell, S.J.; Tracey, P. How can clusters sustain performance? The role of network strength, network openness, and environmental uncertainty. Res. Policy 2010, 39, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C. Explore the Effects of Interfirm Cooperation and Collaboration Between Supply Chain Integration and Service Innovation Performance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management IEEM, Singapore, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 559–563. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Choi, S.O.; Lee, S. The Effect of a Financial Support on Firm Innovation Collaboration and Output: Does Policy Work on the Diverse Nature of Firm Innovation? J. Knowl. Econ. 2021, 12, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.J.; Van der Knaap, B.; Wall, R.S. Polycentricity and the Multiplexity of Urban Networks. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2014, 22, 816–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; LeGates, R. China’s hybrid global city region pathway: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta. Cities 2018, 77, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Chen, W.; Yu, Z. Uncovering Spatial Structures of Regional City Networks from Expressway Traffic Flow Data: A Case Study from Jiangsu Province, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Z. Production Industry Chain, Production Matching Radius and Self-development Capability of an Enterprise. China Ind. Econ. 2005, 2, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C. Interurban Consumption Flows of Urban Agglomeration in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River: A Network Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, D.; Huang, J. Inter-city connections in China: High-speed train vs. inter-city coach. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 82, 102619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Lu, L.; Yang, L. Network analysis of tourist flows: A cross-provincial boundary perspective. Tour. Geogr. 2016, 18, 561–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, D. Regional Integration in the Inter-City Technology Transfer System of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Derudder, B.; Wang, J.; Shen, W.; Witlox, F. Using Location-Based Social Media to Chart the Patterns of People Moving between Cities: The Case of Weibo-Users in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Urban Technol. 2016, 23, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Derudder, B.; Wang, J.; Shen, W. Regionalization in the Yangtze River Delta, China, from the perspective of inter-city daily mobility. Reg. Stud. 2018, 52, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Zang, Y.; Duan, J. Understanding the Regional Integration Process from the Perspective of Agglomeration and Urban Networks: Case Study in Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Supplier | Province | City | Sub-City Division | Purchase Time | Purchase Amount (Ten Thousand Yuan) | Percentage of Current Year’s Purchases (%) | Source of Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai Yufei Metal Product Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Pudong New Area | 1 April 2020 | 967.51 | 6.14 | annual report |
| Xiandeng HI-TECH Electric Co., Ltd. | Zhejiang | Huzhou | Wuxing District | 1 April 2020 | 662.45 | 4.21 | annual report |
| Suzhou Liangji Motor Co., Ltd. | Jiangsu | Suzhou | Changshu City | 1 April 2020 | 571.26 | 3.63 | annual report |
| Shanghai Bingte Electromechanical Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Fengxian District | 1 April 2020 | 515.94 | 3.28 | annual report |
| Shanghai Yingdu Information Technology Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Yangpu District | 1 April 2019 | 3791.07 | 21.33 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Yufei Metal Product Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Pudong New Area | 1 April 2019 | 1200.87 | 6.76 | prospectus |
| Wujiang Ruifeng Machinery Co., Ltd. | Jiangsu | Suzhou | Wujiang District | 1 April 2019 | 648.28 | 3.65 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Bingte Electromechanical Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Fengxian District | 1 April 2019 | 648.5 | 3.65 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Yingdu Information Technology Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Yangpu District | 1 April 2018 | 1903.9 | 13.11 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Yufei Metal Product Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Pudong New Area | 1 April 2018 | 1297.66 | 8.94 | prospectus |
| Jiangsu Yanling Electric Appliance Factory | Jiangsu | Taizhou | Taixing City | 1 April 2018 | 1278.15 | 8.8 | prospectus |
| Suzhou Goldway Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. | Jiangsu | Suzhou | Wujiang District | 1 April 2018 | 764.82 | 5.27 | prospectus |
| Suzhou Goldway Electromechanical Technology Co., Ltd. | Jiangsu | Suzhou | Wujiang District | 1 April 2017 | 1969.63 | 18.92 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Yufei Metal Product Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Pudong New Area | 1 April 2017 | 1015.9 | 9.76 | prospectus |
| Xiandeng HI-TECH Electric Co., Ltd. | Zhejiang | Huzhou | Wuxing District | 1 April 2017 | 700.63 | 6.73 | prospectus |
| Jiangsu Yanling Electric Appliance Factory | Jiangsu | Taizhou | Taixing City | 1 April 2017 | 700.91 | 6.73 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Greenwoods Electric MOTOR Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Chongming District | 1 April 2017 | 637.42 | 6.12 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Yufei Metal Product Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Pudong New Area | 1 April 2016 | 848.36 | 10 | prospectus |
| Jiangsu Yanling Electric Appliance Factory | Jiangsu | Taizhou | Taixing City | 1 April 2016 | 615.49 | 8 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Hualong Longbao Electrician Equipment Co., Ltd. | Shanghai | Shanghai | Minhang District | 1 April 2016 | 654.36 | 8 | prospectus |
| Yixing Nuofu Electrical Materials Co., Ltd. | Jiangsu | Wuxi | Yixing District | 1 April 2016 | 577.74 | 7 | prospectus |
| Shanghai Dishan Lamps & Lanterns Factory | Shanghai | Shanghai | Pudong New Area | 1 April 2016 | 422.41 | 5 | prospectus |
| Meaning of Index | Selection of Index | Variable Symbol | Interpretation of Index | Construction of Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geographical adjacency | Geographical proximity | Geoproximity | Whether the two cities are administratively adjacent | If the two cities are geographically adjacent, the value is 1, otherwise 0 |
| Driving distance a | Drivingdis | Minimum driving distance between two cities | Symmetric matrix formed by the driving distance between any two cities | |
| Administrative district economy | Admineco | Whether the two cities are in the same province | If the two cities are in the same province, the value is 1, otherwise 0 | |
| Administrative resources | National-level development zones | Developmentzone | Differences in the number of national-level development zones (economic and technological development zones, high-tech industrial development zones, and special customs supervision areas) between cities | Symmetric matrix of the difference in the number of national-level development zones between two cities |
| Cooperation parks b | Copark | Number of cooperation parks between two cities | Symmetric matrix of the number of cooperation parks between cities | |
| Administrative level | Adminlevel | Differences in administrative levels between two cities | If the two cities are municipalities directly under the central government, provincial capitals, or cities specifically designated in the state plan, the value is 1, otherwise 0 | |
| People mobility | HSR linkage c | Highspeedrail | Daily HSR service between two cities | Symmetric matrix formed by the daily HSR service between cities |
| Innovation cooperation | Paper co-authorship | Coauthorship | Number of collaborative papers between two cities in Web of Science (total number of papers for the period 2016–2021) | Symmetric matrix of the number of collaborative papers between cities |
| Technological base | Industry structure d | Industrystruc | Similarity of the industry structure between two cities | Symmetric matrix based on the industrial structural similarity coefficient between cities |
| Type | Symbols | Definition of Variables | Implication of Variables | Observed Value | Average Value | Standard Deviation (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Degree centrality of cities | Influence in network | 41 | 5.3607 | 1.0551 | |
| Independent variables | Population in urban areas | Population size | 41 | 5.1061 | 0.7406 | |
| GDP per capita | Economic level | 41 | 11.2025 | 0.5443 | ||
| Advanced degree of industry structure (ratio of tertiary industry GDP to secondary industry GDP) | Industry level | 41 | 0.0684 | 0.2649 | ||
| Science and technology input from city government | Technology input | 41 | 12.0378 | 1.1519 | ||
| Number of granted patents of city | Technology capabilities | 41 | 9.1889 | 1.2208 | ||
| Number of industrial enterprises in the city | Industrial clustering | 41 | 7.6024 | 0.8333 | ||
| Number of employees in the traffic, transport, storage, and post | Production services | 41 | 9.8620 | 1.0649 | ||
| Number of employees in financial intermediation | Production services | 41 | 10.0209 | 0.8203 |
| Level | Degree Centrality | Betweenness Centrality | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Cities | Cities | Number of Cities | Cities | |
| Level 1 | 5 | Nanjing, Hangzhou, Shanghai, Suzhou (Jiangsu province), Taizhou (Zhejiang province) | 7 | Nanjing, Hangzhou, Suzhou (Jiangsu province), Shanghai, Chuzhou, Hefei, Bengbu |
| Level 2 | 15 | Chuzhou, Huzhou, Changzhou, Ningbo, Hefei, Bengbu, Jiaxing, Wuxi, Anqing, Wuhu, Shaoxing, Nantong, Wenzhou, Taizhou (Jiangsu province), Yangzhou | 10 | Anqing, Changzhou, Ningbo, Taizhou (Zhejiang province), Wuxi, Shaoxing, Xuzhou, Wenzhou, Huzhou, Taizhou (Jiangsu province) |
| Level 3 | 11 | Xuancheng, Huaian, Xuzhou, Zhenjiang, Jinhua, Yancheng, Lianyungang, Quzhou, Huangshan, Ma’anshan, Tongling | 7 | Jiaxing, Yangzhou, Xuancheng, Huaian, Nantong, Wuhu, Jinhua |
| Level 4 | 8 | Suqian, Lishui, Suzhou (Anhui province), Lu’an, Fuyang, Chizhou, Bozhou, Zhoushan | 11 | Zhenjiang, Ma’anshan, Tongling, Yancheng, Quzhou, Suizhou, Lishui, Huangshan, Suqian, Fuyang, Bozhou |
| Level 5 | 2 | Huaibei, Huainan | 6 | Chizhou, Lianyungang, Huaibei, Lu’an, Huainan, Zhoushan |
| Variable Symbol | Correlation Coefficient | Standardized Regression Coefficient | P (Large) | P (Small) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geoproximity | 0.2322 *** | 0.07481 ** | 0.01000 | 0.99050 |
| Drivingdis | −0.2919 *** | −0.09057 ** | 0.98101 | 0.01949 |
| Admineco | 0.0809 ** | −0.08506 *** | 0.99800 | 0.00250 |
| Developmentzone | 0.2731 ** | 0.12000 ** | 0.03448 | 0.96602 |
| Copark | 0.1269 ** | 0.02403 | 0.10595 | 0.89455 |
| Adminlevel | 0.2292 *** | −0.06936 ** | 0.98401 | 0.01649 |
| Highspeedrail | 0.7109 *** | 0.59425 *** | 0.00050 | 1.00000 |
| Coauthorship | 0.4722 *** | 0.11129 ** | 0.01099 | 0.98951 |
| Industrystruc | −0.2584 *** | −0.05324 * | 0.91554 | 0.08496 |
| R-Square | 0.546 | |||
| Dependent Variable and Independent Variables | Standardized Coefficients and Significance | VIF | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| −0.250 ** | 2.003 | 0.919 | |
| 0.578 *** | 2.253 | ||
| 0.368 *** | 4.335 | ||
| 0.601 *** | 2.884 | ||
| −8.834 | —— |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, X. Urban Networks in the Yangtze River Delta from the Perspective of Transaction Linkages in Manufacturing Industries: Characteristics, Determinants, and Strategies for Intercity Integration Development. Systems 2023, 11, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11080401
Yan Y, Li K, Wang X. Urban Networks in the Yangtze River Delta from the Perspective of Transaction Linkages in Manufacturing Industries: Characteristics, Determinants, and Strategies for Intercity Integration Development. Systems. 2023; 11(8):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11080401
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yiran, Kailun Li, and Xingping Wang. 2023. "Urban Networks in the Yangtze River Delta from the Perspective of Transaction Linkages in Manufacturing Industries: Characteristics, Determinants, and Strategies for Intercity Integration Development" Systems 11, no. 8: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11080401
APA StyleYan, Y., Li, K., & Wang, X. (2023). Urban Networks in the Yangtze River Delta from the Perspective of Transaction Linkages in Manufacturing Industries: Characteristics, Determinants, and Strategies for Intercity Integration Development. Systems, 11(8), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11080401






