Biochip Systems for Intelligence and Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biochip Working Mechanism and Industrial Value
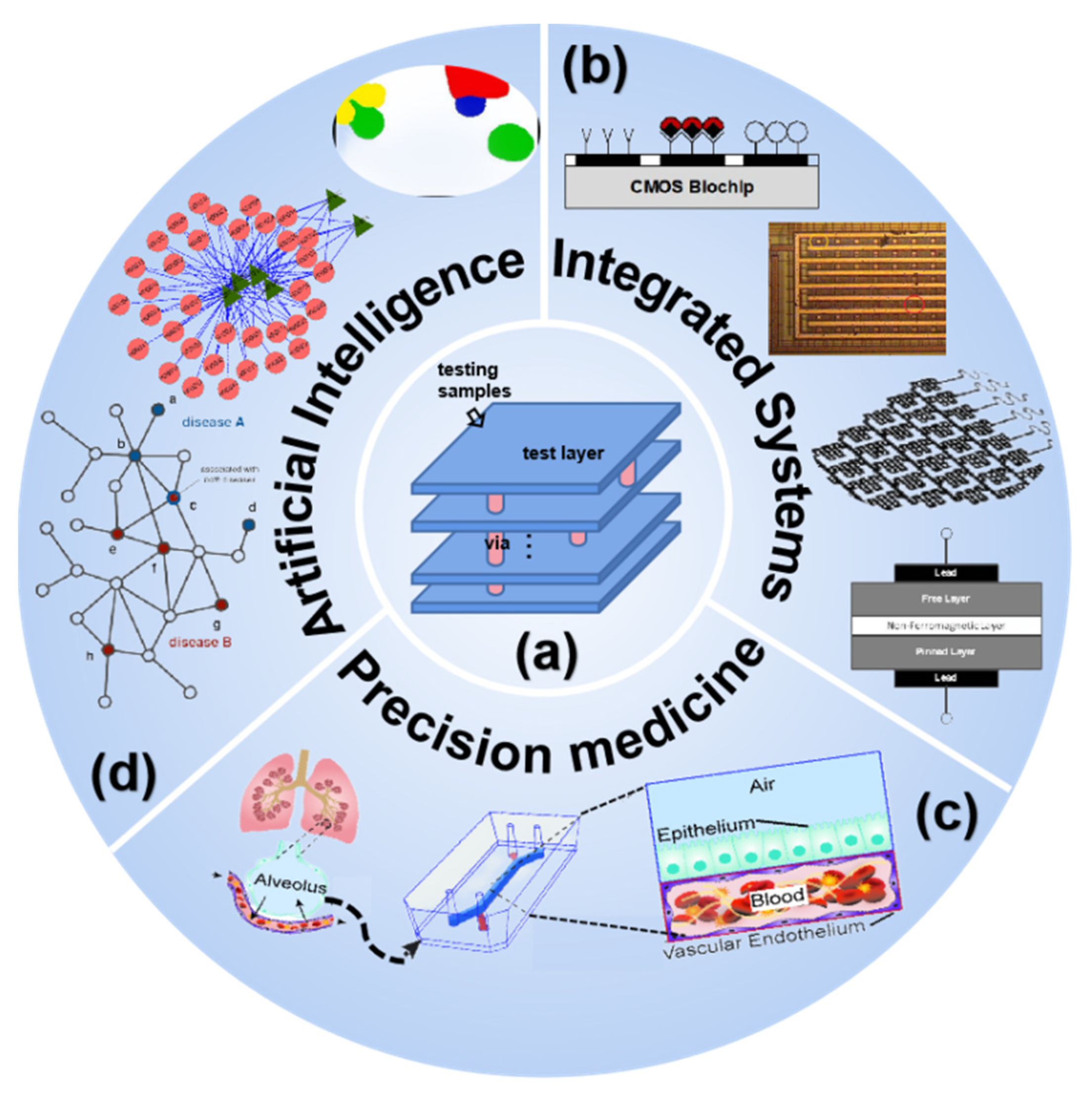
3. Intelligent? Integrated? A Part of the Human Body? The Infinite Possibilities of Biochip Systems
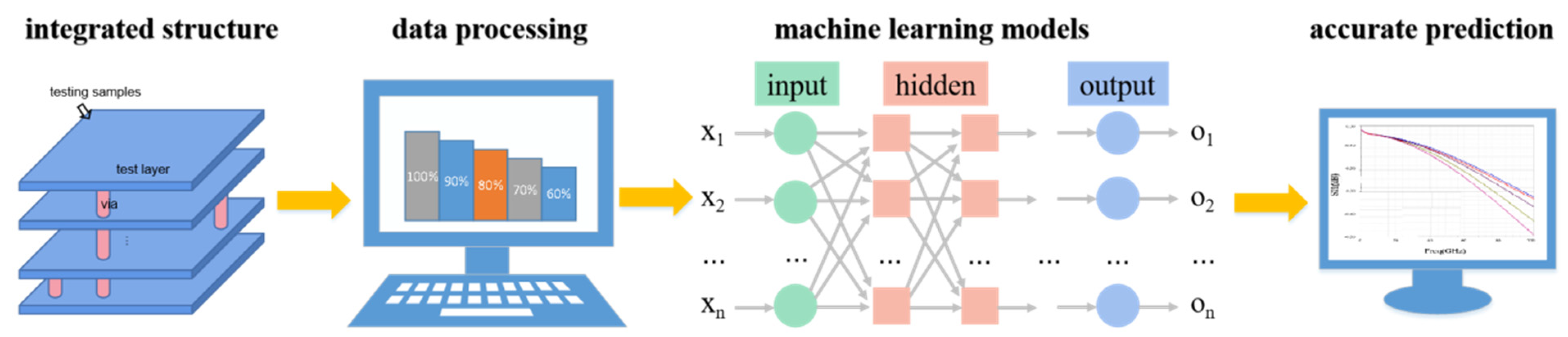
3.1. Machine Learning Is a Prerequisite for Efficient Chip Detection
3.2. Integrated Technologies Are the Basis on Which Biochip Architectures Are Built
3.3. Precision Medicine Is a Specific Application Scenario for Biochips
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance Sensing
4.2. System Integration
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rebekah, F.; William, H.; Kira, C.; Debra, O.; Mary, L.; Linda, V.; Raymond, H.; Joseph, A.; Carol, R. One Health Core Competency Domains. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, E.P.J. The evolution of One Health: A decade of progress and challenges for the future. Vet. Rec. 2014, 174, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, C.J.; Heise, M.T.; Bachelder, E.M.; Ainslie, K.M. Vaccine formulations in clinical development for the prevention of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 169, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlBalwi, M.A.; Khan, A.; AlDrees, M.; Gk, U.; Manie, B.; Arabi, Y.; Alabdulkareem, I.; AlJohani, S.; Alghoribi, M.; AlAskar, A.; et al. Evolving sequence mutations in the middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morens, D.M.; Folkers, G.K.; Fauci, A.S. The challenge of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2004, 430, 242–249, Erratum in Nature 2010, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.; Angulo, A.; Amaratunga, D.; Guo, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wan, J.S.; Bittner, A.; Frueh, K.; Jackson, M.R.; Peterson, P.A.; et al. DNA microarrays of the complex human cytomegalovirus genome: Profiling kinetic class with drug sensitivity of viral gene expres-sion. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5757–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Coscoy, L.; Zylberberg, M.; Avila, P.C.; Boushey, H.A.; Ganem, D.; DeRisi, J.L. Microarray-based detection and genotyping of viral pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15687–15692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, H.; Johansson, P.; Li, Q.-G.; Lundkvist, A.; Nilsson, P.; Elgh, F. Microarray technology for identification and distinction of hantaviruses. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, P.; Wilson, J. HIV genotyping by chip technology. Am. Clin. Lab. 2000, 19, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- All Optical Biophotonic and Microfluidics Circuits for Photo Thermal Bacterial Killing Based on Localised Plasmon Resonances of Gold Nanoparticles. Available online: https://research.uniroma1.it/all-optical-biophotonic-and-microfluidics-circuits-photo-thermal-bacterial-killing-based-localised (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Using Gold Nanoparticles to Destroy Viruses. Available online: https://actu.epfl.ch/news/using-gold-nanoparticles-to-destroy-viruses/ (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; Li, S.; Hou, Q.; Jiang, X. Modulating the antibacterial activity of gold nanopar-ticles by balancing their monodispersity and aggregation. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminu, S.I.; Mustapha, A.N.; Kabir, M.M.; Abubakar, M.; Sha’arani, Y.M.; Ashir, Y.A.; Murtala, M.; Yusuf, B.D.; Abdullahi, S.S.; Seed, A.M.; et al. Innovative Nanotechnology a Boon for Fight Against Pandemic COVID–19. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3, 651308. [Google Scholar]
- Shoujun, X.; Ling, C.; Ning, X. Biochip Development. Prog. Chem. 2009, 21, 2397–2410. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.M.; Sanders, J.Z.; Kaiser, R.J.; Hughes, P.; Dodd, C.; Connell, C.R.; Heiner, C.; Kent, S.B.H.; Hood, L.E. Fluo-rescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature 1986, 321, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortina, P.; Graves, D.; Stoeckert, C., Jr.; McKenzie, S. Surrey in Biochip Technology; Cheng, J., Kricka, L.J., Eds.; Technology Options and Applications of DNA Microarrays, Harwood Academic Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 185–216. [Google Scholar]
- Livingston, A.D.; Campbell, C.J.; Wagner, E.K.; Ghazal, P. Biochip sensors for the rapid and sensitive detection of viral disease. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teixeira, R.; Doetsch, J. The multifaceted role of mobile technologies as a strategy to combat COVID-19 pandemic. Epidemiology Infect. 2020, 148, e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murg, S.; Moore, B.; Lovell, M.; Wolf, R.; Bejjany, B.A.; Wu, A.H.B.; Kelles, S. Business Strategy for Molecular Diagnostics in the Lab, Report Summary, 2nd ed.; Washington G-2 Reports; Kennedy Information: Peterborough, NH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, M.; Scoones, I. The social and political lives of zoonotic disease models: Narratives, science and policy. Soc. Sci. Med. 2013, 88, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Lim, C.Y.; Ren, J.; Zhou, J.; Pu, K.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Mao, H.; Lam, Y.C.; Duan, H. Magnetic nanochain integrated microfluidic biochips. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, H.H.; Tran, N.K.; Betts, E.V.; Howell, L.P.; Green, R. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Pathology: The Present Landscape of Supervised Methods. Acad. Pathol. 2019, 6, 2374289519873088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culhane, A.; Buehler, L.K.; Rashidi, H.H. Bioinformatics Basics: Applications in Biological Science and Medicine. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 2006, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalik, E.L.; Henao, R.; Montgomery, J.L.; Nawrocki, J.W.; Aydin, M.; Lydon, E.C.; Ko, E.R.; Petzold, E.; Nicholson, B.P.; Cairns, C.B.; et al. Discriminating Bacterial and Viral Infection Using a Rapid Host Gene Expression Test*. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 1651–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AI and Organ-on-a-Chip Technologies Stand Out at BIO 2019. Available online: https://www.biocompare.com/Editorial-Articles/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Zitnik, M.; Nguyen, F.; Wang, B.; Leskovec, J.; Goldenberg, A.; Hoffman, M.M. Machine learning for integrating data in biology and medicine: Principles, practice, and opportunities. Inf. Fusion 2018, 50, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, J.; Gao, L. Drug repositioning based on triangularly balanced structure for tissue-specific diseases in in-complete interactome. Artif. Intell. Med. 2017, 77, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, B.; Ma, X.; Gao, L. The extraction of drug-disease correlations based on module distance in incomplete human interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2016, 10, 111–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Javani, A.; Park, J.; Velasco, V.; Xu, B.; Razorenova, O. A Machine Learning-Assisted Nanoparticle-Printed Biochip for Real-Time Single Cancer Cell Analysis. Adv. Biosyst. 2020, 4, 2000160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelebi, F.; Tasdemir, K.; Icoz, K. Deep learning based semantic segmentation and quantification for MRD biochip images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 77, 103783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, J.; Gao, L. Predicting Potential Drugs for Breast Cancer based on miRNA and Tissue Specificity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzan, R.N.; McMorrow, M.L.; Patrick Kachur, S. Diagnosis of Malaria: Challenges for Clinicians in Endemic and Non-Endemic Regions. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2008, 12, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, I.W.; Busta, H.H.; Schroeder, D.; Yuchun, W. Three Dimensional Integrated Circuits: US. U.S. Patent US7091604 B2, 15 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, C.; Geng, J.; Shi, X.; Gao, Y.; Chang, Z.; Qian, H. Silicon-based Integrated Microarray Biochips for Biosensing and Biodetection Applications. In Biosensors-Micro and Nanoscale Applications; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J. A Fully Automated IVD System Based on MTJ arrays and Superparamagnetic Particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07B315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.A.; Gaster, R.S.; Makinwa, K.A.A.; Wang, S.X.; Murmann, B. A 256 Pixel Magnetoresistive Biosensor Microarray in 0.18 µm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hassibi, A.; Scherer, A.; Hajimiri, A. A Frequency-shift CMOS Magnetic Biosensor Array with Sin-gle-bead Sensitivity and No External Magnet. In Proceedings of the IEEE ISSCC Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2009; pp. 438–439. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Jia, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, T.; Mak, P.-I.; Vai, M.-I.; Martins, R.P. A 3D microblade structure for precise and parallel droplet splitting on digital microfluidic chips. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chakrabarty, K.; Pamula, V.K. Design and optimization of a digital microfluidic biochip for protein crystalliza-tion. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 10–13 November 2008; pp. 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, D.; Kim, H.J.; Fraser, J.P.; Shea, D.E.; Khan, M.; Bahinski, A.; Hamilton, G.A.; Ingber, D.E. Microfabrication of human or-gans-on-chips. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2135–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, D.; Matthews, B.D.; Mammoto, A.; Montoya-Zavala, M.; Hsin, H.Y.; Ingber, D.E. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science 2010, 328, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Barrile, R.; van der Meer, A.D.; Mammoto, A.; Mammoto, T.; De Ceunynck, K.; Aisiku, O.; Otieno, M.A.; Louden, C.S.; Hamilton, G.A.; et al. Primary Human Lung Alveolus-on-a-chip Model of Intravascular Thrombosis for Assessment of Therapeutics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 103, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wei, W.; Chen, Z.; Lin, B.; Zhao, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. Engineered Liver-On-A-Chip Platform to Mimic Liver Functions and Its Biomedical Applications: A Review. Micromachines 2019, 10, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, S.R.; Ozdalgic, B.; Mustafaoglu, N.; Tasoglu, S. Three-Dimensional-Bioprinted Liver Chips and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H. Fabrication and Biomedical Applications of Heart-on-a-chip. Int. J. Bioprinting 2021, 7, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Ingber, D.E. Gut-on-a-Chip microenvironment induces human intestinal cells to undergo villus differentiation. Integr. Biol. 2013, 5, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Hinojosa, C.D.; Ingber, D.E.; Kim, H.J. Human Intestinal Morphogenesis Controlled by Transepithelial Morphogen Gradient and Flow-Dependent Physical Cues in a Microengineered Gut-on-a-Chip. Iscience 2019, 15, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyilot, M.C.; Natarajan, P.; Hunt, C.R.; Sivarajkumar, S.; Roy, R.; Joglekar, S.; Pandita, S.; Tong, C.W.; Marakkar, S.; Subramanian, L.; et al. Breakthroughs and Applications of Organ-on-a-Chip Technology. Cells 2022, 11, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somnath, G. Three-dimensional microplate formation with evaporating nanoparticle suspensions on superhydrophobic surfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 901–906. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, Z. Atmospheric Corrosion; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Furlow, B. Information overload and unsustainable workloads in the era of electronic health records. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauglitz, G. Artificial vs. human intelligence in analytics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5631–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Managed Healthcare Executive. Available online: https://www.managedhealthcareexecutive.com/view/limits-ai-healthcare (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Futurelearn. Available online: https://www.futurelearn.com/info/courses/how-artificial-intelligence-can-support-healthcare/0/steps/277380 (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Duan, Y.; Zhao, D. Multiple dimension security assessment of Web service. J. China Med. Univ. 2013, 37, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Materials | Advantages | Disadvantages | Main Function | Processing Technology | Culturing Cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung chips [41,42] | PDMS | Low cost; High throughput | Bacterial contamination; Limitation | Pneumonia model; Nano-particle toxicity; Alveolar respiratory process | Cast molding | Alveolar epithelial cells |
| Liver chips [43,44] | Glass PDMS PCL COC Glass+PDMS | Alternative | Poor absorption; Difficult to industrialise | Drug metabolism; Hepatic lobule structure; Drug Hepatotoxicity Testing | Cast molding; 3D printing; Photo-lithography | Hepatoma cells; Liver parenchymal cells |
| Heart chips [45] | PDMS Glass+PDMS Hydrogel PLA ABS | Low cell volume; Low consumption; Dynamic culture | Technical stability; Manufacturing materials | Drug testing; Myocardial ischemic response; Cell contractility measurement; Cell beat frequency measurement | Cast molding; 3D printing; Laser corrosion | Cardiomyocytes; Fibroblasts |
| Intestinal chips [46,47] | PDMS Hydrogel | Stability Continuity | Long incubation time | Intestinal absorption; Intestinal motility; Intestinal villus structure | Cast molding | Colorectal adenocarcinoma cells |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Sun, B.; Zhu, Z. Biochip Systems for Intelligence and Integration. Systems 2023, 11, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11010043
Wang J, Sun B, Zhu Z. Biochip Systems for Intelligence and Integration. Systems. 2023; 11(1):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11010043
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junhao, Bihao Sun, and Zhiyuan Zhu. 2023. "Biochip Systems for Intelligence and Integration" Systems 11, no. 1: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11010043
APA StyleWang, J., Sun, B., & Zhu, Z. (2023). Biochip Systems for Intelligence and Integration. Systems, 11(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems11010043





