Does Green Transformational Leadership Develop Green Absorptive Capacity? The Role of Internal and External Environmental Orientation
Abstract
1. Introduction
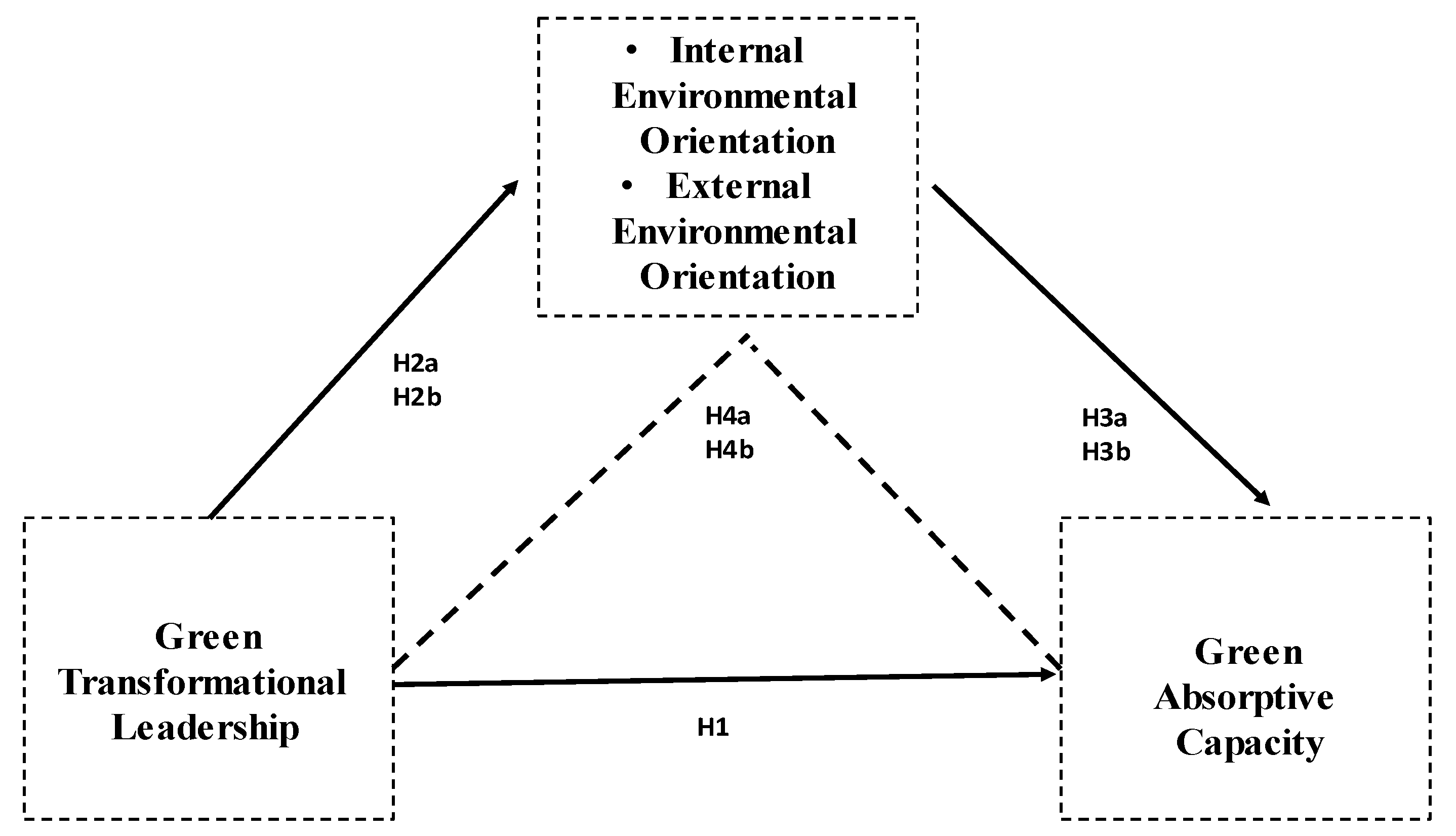
2. Theoretical Development and Hypothesis Presentation
2.1. Green Transformational Leadership and Green Absorptive Capacity
2.2. Green Transformational Leadership and Environmental Orientation
2.3. Environmental Orientation and Green Absorptive Capacity
2.4. The Mediating Role of Environmental Orientation
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Sample and Data Collection
3.2. Measure of Constructs
4. Analysis and Results
4.1. Measurement Model Assessment
4.2. Structural Model Assessment
5. Discussion, Contributions, and Limitations
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Theoretical Contributions
5.3. Managerial Implications
5.4. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Green Transformational Leadership
Appendix A.2. Green Absorptive Capacity
Appendix A.3. Internal Environmental Orientation
Appendix A.4. External Environmental Orientation
References
- Hamann, R.; Smith, J.; Tashman, P.; Marshall, R.S. Why do SEs go green? An analysis of wine firms in South Africa. Bus. Soc. 2017, 56, 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; O’Dowd, P.; Dimache, A. Environmental challenges for European manufacturing SMEs. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2020, 13, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.P. Knowledge acquisition and development in sustainability-oriented small and medium-sized enterprises: Exploring the practices, capabilities and cooperation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3769–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, D.A.D.J.; ten Caten, C.S.; Jung, C.F.; Ribeiro, J.L.D.; Navas, H.V.G.; Cruz-Machado, V.A. Eco-innovation determinants in manufacturing SMEs: Systematic review and research directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, S. Ecodesign Practices in Industry: An Appraisal of Product Life Cycle Design İnitiatives in SMEs. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Engineering Management Conference, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 13 September 2005; Volume 2, pp. 475–479. [Google Scholar]
- Mady, K.; Halim, M.A.S.A.; Omar, K.; Abdelkareem, R.S.; Battour, M. Institutional pressure and eco-innovation: The mediating role of green absorptive capacity and strategically environmental orientation among manufacturing SMEs in Egypt. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2022, 9, 206425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Lin, S.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Hung, S.T.; Chang, C.W.; Huang, C.W. Improving green product development performance from green vision and organizational culture perspectives. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelmaged, M.; Hashem, G. Absorptive capacity and green innovation adoption in SMEs: The mediating effects of sustainable organizational capabilities. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, L.M.; Alves, M.F.R.; Liboni, L.B. Green absorptive capacity: A mediation-moderation model of knowledge for innovation. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2018, 27, 1502–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Govindan, K.; Xie, X.; Yan, L. How to drive green innovation in China’s mining enterprises? Under the perspective of environmental legitimacy and green absorptive capacity. Resour. Policy 2021, 72, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, H. Green Innovation Sustainability: How Green Market Orientation and Absorptive Capacity Matter? Sustainability 2022, 14, 8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, Y.H. The determinants of green radical and incremental innovation performance: Green shared vision, green absorptive capacity, and green organizational ambidexterity. Sustainability 2014, 6, 7787–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, C.W. Enhancing green absorptive capacity, green dynamic capacities and green service innovation to improve firm performance: An analysis of structural equation modeling (SEM). Sustainability 2015, 7, 15674–15692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirun, T.; Makhloufi, L.; Hassan, M.G. Environmental Outcomes of Green Entrepreneurship Harmonization. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Khan, A.; Yahya, S.; Zafar, A.B.; Shahzad, M. Green core competencies to prompt green absorptive capacity and bolster green innovation: The moderating role of organization’s green culture. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2021, 5, 536–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Wu, W. How does green innovation improve enterprises’ competitive advantage? The role of organizational learning. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.D.T.; Paillé, P.; Halilem, N. Systematic review on environmental innovativeness: A knowledge-based resource view. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Shafique, I.; Qammar, A.; Ercek, M.; Kalyar, M.N. Prompting green product and process innovation: Examining the effects of green transformational leadership and dynamic capabilities. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouaibi, S.; Chouaibi, J.; Rossi, M. ESG and Corporate Financial Performance: The Mediating Role of Green Innovation: UK Common Law versus Germany Civil Law. Euro. Med. J. Bus. 2021, 17, 46–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxborrow, L.; Brindley, C. Adoption of ‘eco advantage’ by SMEs: Emerging opportunities and constraints. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2013, 16, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, I.; Takeuchi, H. The Knowledge Creating; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Naqshbandi, M.M.; Tabche, I. The interplay of leadership, absorptive capacity, and organizational learning culture in open innovation: Testing a moderated mediation model. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 133, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Anderson, M. The combined influence of top and middle management leadership styles on absorptive capacity. Manag. Learn. 2012, 43, 25–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Morales, V.J.; Matías-Reche, F.; Hurtado-Torres, N. Influence of transformational leadership on organizational innovation and performance depending on the level of organizational learning in the pharmaceutical sector. J. Organ. Change Manag. 2008, 21, 188–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, T.-K.; Zeng, J.; Rezaei Zadeh, M.; Haak-Saheem, W. Organizational learning of Absorptive Capacity and Innovation: Does Leadership Matter? Eur. Manag. Rev. 2020, 17, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatten, T.; Adams, D.; Brettel, M. Fostering absorptive capacity through leadership: A cross-cultural analysis. J. World Bus. 2015, 50, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Zadeh, M.; Hackney, R.; Zeng, J. Augmenting learning processes of absorptive capacity for innovation: Insights for effective leadership within global pharmaceutical companies. Eur. Manag. Rev. 2021, 19, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xu, A.; Lin, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, W. Environmental Leadership, Green Innovation Practices, Environmental Knowledge Learning, and Firm Performance. Sage Open 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogus, T.J.; Sutcliffe, K.M. Organizational mindfulness and mindful organizing: A reconciliation and path forward. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2012, 11, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Xia, E.; Ali, F.; Awan, U.; Ashfaq, M. Achieving green product and process innovation through green leadership and creative engagement in manufacturing. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022, 33, 656–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.X.; Wang, J.R.; Zhou, C. Exploring the linkages of green transformational leadership, organizational green learning, and radical green innovation. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulraj, A. Understanding the relationships between internal resources and capabilities, sustainable supply management, and organizational sustainability. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2011, 47, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelmaged, M. Direct and indirect effects of eco-innovation, environmental orientation and supplier collaboration on hotel performance: An empirical study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zameer, H.; Wang, Y.; Yasmeen, H.; Mubarak, S. Green innovation as a mediator in the impact of business analytics and environmental orientation on green competitive advantage. Manag. Decis. 2020, 60, 488–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.Y.K.; He, H.; Chan, H.K.; Wang, W.Y.C. Environmental orientation and corporate performance: The mediation mechanism of green supply chain management and moderating effect of competitive intensity. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2012, 41, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabler, C.B.; Richey, R.G.; Rapp, A. Developing an eco-capability through environmental orientation and organizational innovativeness. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 45, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnenluecke, M.; Griffiths, A. Corporate sustainability and organizational culture. J. World Bus. 2010, 45, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.Y.; Ma, K.H. How and when environmental orientation drives corporate sustainable development in a cross-national buyer-supplier dyad. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 30, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari, D.; Wright, G.; Peattie, K. Green and competitive: Influences on environmental new product development performance. J. Bus. Res. 2003, 56, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.S.; Jakhar, S.K. The Effect of Environmental Regulations, Top Management Commitment, and Organizational Learning on Green Product Innovation: Evidence from Automobile Industry. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 3907–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Stepchenkova, S. Does environmental leadership affect market and eco performance? Evidence from Korean franchise firms. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2018, 33, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurner, T.W.; Roud, V. Greening strategies in Russia’s manufacturing—From compliance to opportunity. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2851–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Pascual, L.; Curado, C.; Galende, J. The triple bottom line on sustainable product innovation performance: A mixed methods approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.A.; George, G. Absorptive capacity: A review, reconceptualisation and extension. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2002, 27, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghfous, A. Absorptive capacity and the implementation of knowledge-intensive best practices. S.A.M. Adv. Manag. J. 2004, 69, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kavanagh, M.; Ashkanasy, N. The Impact of Leadership and Change Management Strategy on Organizational Culture and Individual Acceptance of Change During a Merger. Br. J. Manag. 2006, 17, S83–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Bai, X.; Li, J.J. The influence of leadership on product and process innovations in China: The contingent role of knowledge acquisition capability. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 50, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chang, C.H. The determinants of green product development performance: Green dynamic capabilities, green transformational leadership, and green creativity. J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 116, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Learning Theory; General Learning Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Deichmann, D.; Stam, D. Leveraging transformational and transactional leadership to cultivate the generation of organization-focused ideas. Leadersh. Q. 2015, 26, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L. The nature, measurement and nomological network of environmentally specific transformational leadership. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 5, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinkenaite, I.; Breunig, K.J. The emergence of absorptive capacity through micro-macro level interactions. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bhutto, T.A.; Xuhui, W.; Maitlo, Q.; Zafar, A.U.; Bhutto, N.A. Unlocking employees’ green creativity: The effects of green transformational leadership, green intrinsic, and extrinsic motivation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, L.M.; Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q. How transformational leadership and employee motivation combine to predict employee pro-environmental behaviours in China. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 35, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yin, K.; Hou, N.; Zou, Y.; Nie, Q. How to facilitate employee green behavior: The joint role of green transformational leadership and green human resource management practice. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2020, 52, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.B.; Ting, C.-W.; Fei, Y.-M. A Multilevel Model of Environmentally Specific Social Identity in Predicting Environmental Strategies: Evidence from Technology Manufacturing Businesses. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ting, C.-W.; Li, M.-W. The effects of green transformational leadership on adoption of environmentally proactive strategies: The mediating role of green engagement. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, B.; Xu, F. Promoting Green Product Development Performance via Leader Green Transformationality and Employee Green Self-Efficacy: The Moderating Role of Environmental Regulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, K.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. Measuring Green Creativity for Employees in Green Enterprises: Scale Development and Validation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, Y.H. Green transformational leadership and green performance: The mediation effects of green mindfulness and green self-efficacy. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6604–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Nisar, Q.A.; Shoukat, M.; Ikram, M. Green transformational leadership and green performance: The mediating role of green mindfulness and green self-efficacy. Int. J. Manag. Excell. 2017, 9, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Cop, S.; Olorunsola, V.O.; Alola, U.V. Achieving environmental sustainability through green transformational leadership policy: Can green team resilience help? Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Dhar, R.L. Effect of green transformational leadership on green creativity: A study of tourist hotels. Tour. Manag. 2016, 57, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Liang, H. Interorganizational learning, green knowledge integration capability and green innovation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 24, 1292–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.A.; Shahzad, K.; Nadeem, S. Transformational Leadership and Employee Voice for Product and Process Innovation in SMEs. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2021, 18, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E.; Trevino, L.K.; Harrison, D. Ethical leadership: A social learning perspective for construct development and testing. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2005, 97, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Janssen, O.; Shi, K. Transformational leadership and follower creativity: The mediating role of follower relational identification and the moderating role of leader creativity expectations. Leadersh. Q. 2015, 26, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.B.; Iyer, E.S.; Kashyap, R.K. Corporate environmentalism: Antecedents and influence of industry type. J. Mark. 2003, 67, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.B. Corporate environmentalism: The construct and its measurement. J. Bus. Res. 2002, 55, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxas, B.; Chadee, D. Environmental sustainability orientation and financial resources of small manufacturing firms in the Philippines. Soc. Responsib. J. 2012, 8, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huo, B. The impact of environmental orientation on supplier green management and financial performance: The moderating role of relational capital. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, T.; Garrido-Morgado, A. Corporate Reputation: A Combination of Social Responsibility and Industry. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2012, 19, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, D.; Javidan, M.; Varella, P. Charismatic leadership at the strategic level: A new application of upper echelons theory. Leadersh. Q. 2004, 15, 355–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong, S. Upper echelons theory revisited: The need for a change from casual description to casual explanation. Management 2014, 19, 169–183. [Google Scholar]
- Juravich, M.; Salaga, S.; Babiak, K. Upper echelons in professional sport: The impact of NBA general managers on team performance. J. Sport Manag. 2017, 31, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Jackson, J.; Tudor, T.; Bates, M. Strategies to enhance waste minimization and energy conservation within organizations: A case study from the UK construction sector. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, A.; Kurey, B. Creating a culture of quality. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2014, 92, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, M.F.Y.; Wong, C. Transformational leadership, leaders support, and employee creativity. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2011, 32, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A. Leadership in Sustainable Urban Water Management: An Investigation of the Champion Phenomenon. In Industry Report. Melbourne, Victoria: National Urban Water Governance Program; Monash University: Clayton, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, Y.S.; Garg, R. The simultaneous effect of green ability-motivation-opportunity and transformational leadership in environment management: The mediating role of green culture. Benchmarking Int. J. 2021, 28, 830–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramus, C.A. Encouraging Innovative Environmental Actions: What Companies and Managers Must Do. J. World Bus. 2002, 37, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.; Samson, D. Environmental strategy and low waste operations: Exploring complementarities. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2010, 19, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Barling, J. Greening organizations through leaders’ influence on employees’ pro-environmental behaviors. J. Organ. Behav. 2013, 34, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.R. Human Resource Management for Organizational Sustainability; Business Expert Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, W.E.; Sinkula, J.M. Environmental marketing strategy and firm performance: Effects on new product performance and market share. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2005, 33, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.B. Managerial Perceptions of Corporate Environmentalism: Interpretations from Industry and Strategic Implications for Organizations. J. Manag. Stud. 2001, 38, 489–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraj, E.; Martínez, E.; Matute, J. Green marketing strategy and the firm’s performance: The moderating role of environmental culture. J. Strateg. Mark. 2011, 19, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Kulangara, N.; Foster, K.; Shang, J. Green Market Orientation, Green Supply Chain Relationship Quality, and Green Absorptive Capacity to Enhance Green Competitive Advantage in the Green Supply Chain. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.L. A natural-resource-based view of the firm. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995, 20, 986–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karna, J.; Hansen, E.; Juslin, H. Social responsibility in environmental marketing planning. Eur. J. Mark. 2003, 37, 848–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, D.C. Institutions, Institutional Change, and Economic Performance, Cambridge; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mariadoss, B.J.; Chi, T.; Tansuhaj, P.; Pomirleanu, N. Influences of Firm Orientations on Sustainable Supply Chain Management. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Dang, W.V.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q. Environmental Orientation, Green Supply Chain Management, and Firm Performance: Empirical Evidence from Chinese Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; He, X. Institutional forces and environment management strategy: Moderating effects of environmental orientation and innovation capability. Manag. Organ. Rev. 2018, 14, 577–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Ashfaq, M.; Xia, E.; Awan, U. Does green transformational leadership lead to green innovation? The role of green thinking and creative process engagement. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 31, 580–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillman, D.A.; Smyth, J.D.; Christian, L.M. Internet, Phone, Mail, and Mixed Mode Surveys: The Tailored Design Method, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, T.-K.; Henseler, J. Consistent Partial Least Squares Path Modeling. Manag. Inf. Systems. Q. 2015, 39, 297–316. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/26628355 (accessed on 30 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Wetzels, M.; Odekerken-Schroder, G.; van Oppen, C. Using PLS Path Modeling for Assessing Hierarchical Construct Models: Guidelines and Empirical Illustration. MIS Q. 2009, 33, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Hubona, G.; Ray, P.A. Using PLS Path Modeling in New Technology Research: Updated Guidelines. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2016, 116, 54886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to Use and How to Report the Results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latan, H.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Jabbour, A.B.L.S.; Wamba, S.F.; Shahbaz, M. Effects of Environmental Strategy, Environmental Uncertainty and Top Management’s Commitment on Corporate Environmental Performance: The Role of Environmental Management Accounting. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, J.L.; Sánchez-Franco, M.J. Variance-Based Structural Equation Modeling: Guidelines for using Partial Least Squares in Information Systems Research. In Research Methodologies, Innovations and Philosophies in Software Systems Engineering and Information Systems; Mora, M., Gelman, O., Steenkamp, A.L., Raisinghani, M., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 193–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Lynch, G.J.; Chen, Q. Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: Myths and Truths about Mediation Analysis. J. Consum. Res. 2010, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreras Méndez, J.L.; Sanz Valle, R.; Alegre, J. Transformational leadership and absorptive capacity: An analysis of the organizational catalysts for this relationship. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2017, 30, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jie, X. Can Manager’s Environmentally Specific Transformational Leadership Improve Environmental Performance? AG ICMSEM2019 AISC; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1002, pp. 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharin, F.H.; Hanafi, M.I.M.; Ahmad, W.A.A.W. Proactive Environmental Strategy and Environmental Performance: The Role of Green Transformational Leadership. Solid State Technol. 2020, 63, 3346. [Google Scholar]
- Khoja, F.; Maranville, S. How do firms nurture absorptive capacity? J. Manag. Issues 2010, 22, 262–278. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20798908 (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Dibrell, C.; Craig, J.; Hansen, E. Natural Environment, Market Orientation, and Firm Innovativeness: An Organizational Life Cycle Perspective. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2011, 49, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrick, D.C.; Mason, P.A. Upper Echelons: The Organization as a Reflection of Its Top Managers. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1984, 9, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, D.E.; Morrow, P.C.; Montabon, F. Engagement in environmental behaviors among chain management employees: An organizational support theoretical perspective. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2012, 48, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.G.; Klewitz, J. The role of an SME’s green strategy in public-private eco-innovation initiatives: The case of ecoprofit. J. Small Bus. Entrep. 2012, 25, 451–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suddaby, R.; Seidl, D.; Le, J. Strategy-as-practice meets neoinstitutional theory. Strateg. Organ. 2013, 11, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Ananthram, S. A neo-institutional perspective on ethical decision-making. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2020, 37, 227–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubham; Charan, P.; Murty, L.S. Organizational adoption of sustainable manufacturing practices in India: Integrating institutional theory and corporate environmental responsibility. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2018, 25, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkse, J.; Kuss, M.J.; Hoffmann, V.H. On the Implementation of ‘Global’ Environmental Strategy: The Role of Absorptive Capacity. Int. Bus. Rev. 2010, 19, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.G.; Roh, J.J.; Kang, M. The role of strategic environmental orientation in environmental design practices. Manag. Decis. 2020, 59, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Jia, Y.; Zou, H. Is institutional pressure the mother of green innovation? Examining the moderating effect of absorptive capacity. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Eweje, G.; He, Q.; Lin, Z. Turning motivation into action: A strategic orientation model for green supply chain management. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 29, 2908–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Demographics | Number of Respondents | % |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Business | ||
| Textile | 80 | 21.44 |
| Construction | 73 | 19.57 |
| Automotive | 67 | 17.96 |
| Chemical | 51 | 13.67 |
| Energy | 38 | 10.18 |
| Food | 32 | 8.57 |
| Plastic | 21 | 5.63 |
| Packaging | 11 | 2.94 |
| Number of employees | ||
| Less than 10 | 8 | 2.14 |
| 11–49 | 123 | 32.97 |
| 50–249 | 242 | 64.87 |
| Constructs | Indicators | Factor Loadings | p-Values | Cronbach’s Alpha | rho_A | Composite Reliability | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Transformational Leadership (GTL) | GTL1 | 0.880 | 0.000 | 0.925 | 0.927 | 0.944 | 0.770 |
| GTL2 | 0.871 | 0.000 | |||||
| GTL3 | 0.864 | 0.000 | |||||
| GTL5 | 0.870 | 0.000 | |||||
| GTL6 | 0.901 | 0.000 | |||||
| Green Absorptive Capacity (GAC) | GAC1 | 0.890 | 0.000 | 0.910 | 0.910 | 0.936 | 0.787 |
| GAC2 | 0.886 | 0.000 | |||||
| GAC3 | 0.884 | 0.000 | |||||
| GAC4 | 0.888 | 0.000 | |||||
| Internal Environmental Orientation (IEO) | IEO1 | 0.903 | 0.000 | 0.912 | 0.915 | 0.938 | 0.792 |
| IEO2 | 0.902 | 0.000 | |||||
| IEO3 | 0.909 | 0.000 | |||||
| IEO4 | 0.843 | 0.000 | |||||
| External Environmental Orientation (EEO) | EEO1 | 0.870 | 0.000 | 0.915 | 0.918 | 0.940 | 0.796 |
| EEO2 | 0.897 | 0.000 | |||||
| EEO3 | 0.897 | 0.000 | |||||
| EEO4 | 0.906 | 0.000 |
| Constructs | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| External Environmental Orientation | 0.892 | |||
| Green Absorptive Capacity | 0.537 | 0.887 | ||
| Green Transformational Leadership | 0.491 | 0.754 | 0.877 | |
| Internal Environmental Orientation | 0.509 | 0.763 | 0.763 | 0.890 |
| Constructs | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| External Environmental Orientation | ||||
| Green Absorptive Capacity | 0.585 | |||
| Green Transformational Leadership | 0.530 | 0.819 | ||
| Internal Environmental Orientation | 0.554 | 0.836 | 0.829 |
| Structural Path | Coef (β) | S.D. | T-Values | p-Values | Adj. R2 | f2 | Q2 | VIF | Confidence Interval (BC) | Conclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL | UL | ||||||||||
| GTL→IEO | 0.763 *** | 0.052 | 14.626 | 0.000 | 0.583 | 1.396 | 0.455 | 1.000 | 0.621 | 0.836 | H2a Supported |
| GTL→EEO | 0.491 *** | 0.075 | 6.539 | 0.000 | 0.241 | 0.317 | 0.186 | 1.000 | 0.323 | 0.617 | H2b Supported |
| GTL→GAC | 0375 *** | 0.85 | 4.405 | 0.000 | 0.668 | 0.171 | 0.517 | 2.480 | 0.208 | 0.541 | H1 Supported |
| IEO→GAC | 0.401 ** | 0.113 | 3.533 | 0.000 | 0.190 | 2.541 | 0.203 | 0.631 | H3a Supported | ||
| EEO→GAC | 0.149 * | 0.070 | 2.120 | 0.035 | 0.048 | 1.397 | 0.029 | 0.294 | H3b Supported | ||
| Structural Path | Coef (β) | S.D. | T-Values | p-Values | Confidence Interval (BC) | Conclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL | UL | ||||||
| GTL → IEO → GAC | 0.306 * | 0.098 | 3.136 | 0.002 | 0.143 | 0497 | H4a Supported Complementary Partial Mediation |
| GTL → EEO → GAC | 0.073 * | 0.036 | 2.008 | 0.045 | 0.015 | 0161 | H4b Supported Complementary Partial Mediation |
| GTL → GAC | 0.375 ** | 0.085 | 4.405 | 0.000 | 0.208 | 0.541 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ozgul, B. Does Green Transformational Leadership Develop Green Absorptive Capacity? The Role of Internal and External Environmental Orientation. Systems 2022, 10, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10060224
Ozgul B. Does Green Transformational Leadership Develop Green Absorptive Capacity? The Role of Internal and External Environmental Orientation. Systems. 2022; 10(6):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10060224
Chicago/Turabian StyleOzgul, Burcu. 2022. "Does Green Transformational Leadership Develop Green Absorptive Capacity? The Role of Internal and External Environmental Orientation" Systems 10, no. 6: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10060224
APA StyleOzgul, B. (2022). Does Green Transformational Leadership Develop Green Absorptive Capacity? The Role of Internal and External Environmental Orientation. Systems, 10(6), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10060224










