Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems
Simple Summary
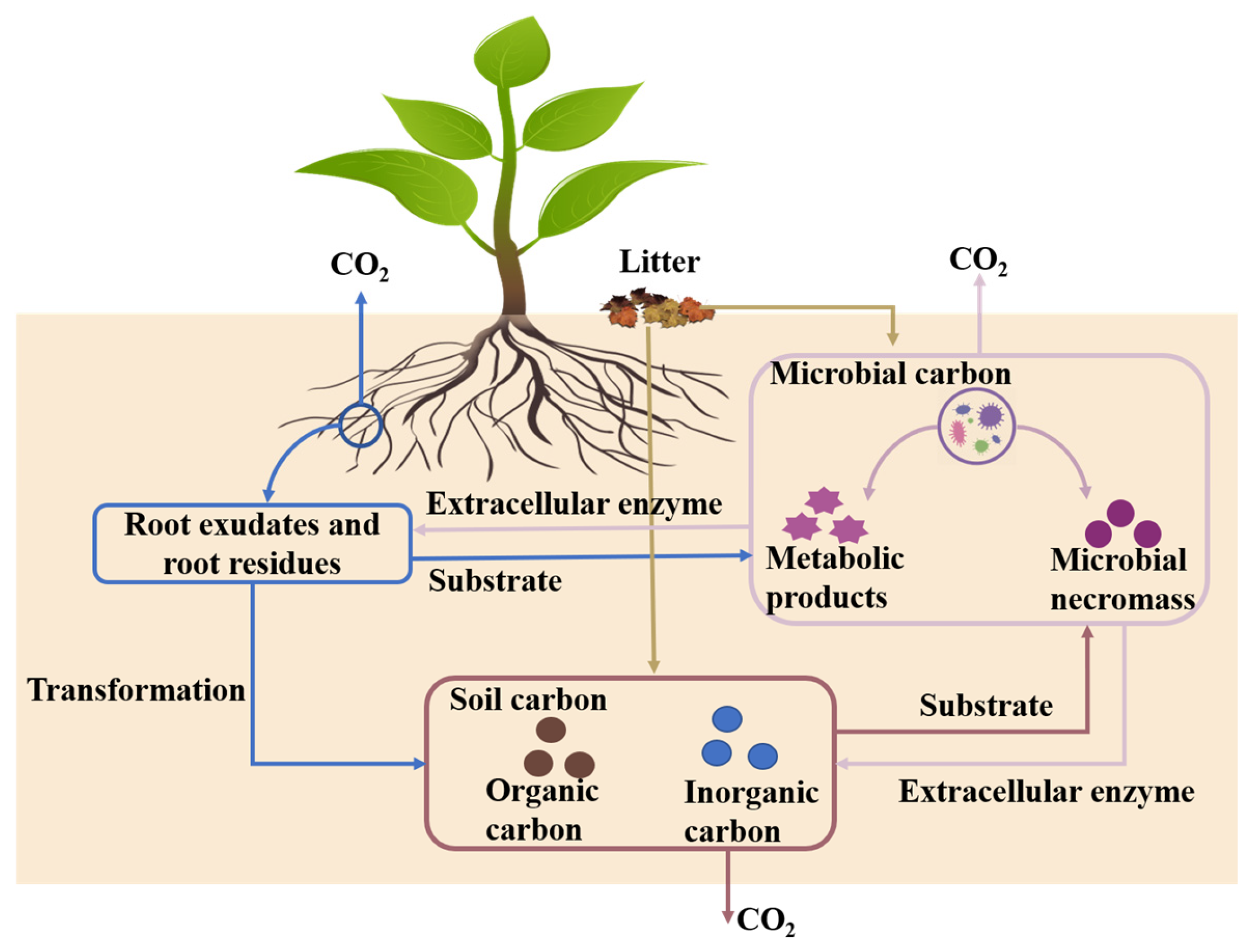
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Variations in Various Methods
2.1. Stoichiometric Modeling
2.2. 13C Glucose Tracing
2.3. 18O Water Tracing
3. Terrestrial Ecosystems
3.1. Grassland Ecosystems
3.2. Forest Ecosystems
3.3. Wetland Ecosystems
4. Future Research
4.1. Management Patterns
4.2. Strategies of Microorganisms for Adapting to Environmental Change
4.3. Anaerobic Metabolic Pathways
4.4. Microbial Taxonomic Level
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CUE | microbial carbon use efficiency |
| BG | β-1,4-glucosidase |
| LAP | leucine aminopeptidase |
| NAG | β-1,4-N-acetylaminoglucosidase |
| AP | acid phosphatase |
| MBC | microbial biomass carbon |
| R | respiration |
| C | carbon |
| N | nitrogen |
| P | phosphorus |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| CH4 | methane |
References
- Wieder, W.R.; Bonan, G.B.; Allison, S.D. Global soil carbon projections are improved by modelling microbial processes. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Luo, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, J. Trade-off between microbial carbon use efficiency and microbial phosphorus limitation under salinization in a tidal wetland. Catena 2022, 209, 105809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X. Redox potential and microbial functional gene diversity in wetland sediments under simulated warming conditions: Implications for phosphorus mobilization. Hydrobiologia 2015, 743, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Trumbore, S.E.; Amundson, R. Soil warming and organic carbon content. Nature 2000, 408, 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Manzoni, S.; Moorhead, D.L.; Richter, A. Carbon use efficiency of microbial communities: Stoichiometry, methodology and modelling. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Noll, L.; Bockle, T.; Richter, A.; Wanek, W. Growth explains microbial carbon use efficiency across soils differing in land use and geology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Taylor, P.; Richter, A.; Porporato, A.; Agren, G.I. Environmental and stoichiometric controls on microbial carbon-use efficiency in soils. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Pötsch, E.M.; Eichorst, S.A.; Woebken, D.; Wanek, W.; Richter, A. Soil microbial carbon use efficiency and biomass turnover in a long-term fertilization experiment in a temperate grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Huang, Y.; Hungate, B.A.; Manzoni, S.; Frey, S.D.; Schmidt, M.W.I.; Reichstein, M.; Carvalhais, N.; Ciais, P.; Jiang, L.; et al. Microbial carbon use efficiency promotes global soil carbon storage. Nature 2023, 618, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.; Jensen, H.E.; Nielsen, N.E.; Svendsen, H. Simulation of nitrogen dynamics and biomass production in winter wheat using the Danish simulation model DAISY. Fertil. Res. 1991, 27, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kätterer, T.; Andrén, O. The ICBM family of analytically solved models of soil carbon, nitrogen and microbial biomass dynamics —Descriptions and application examples. Ecol. Model. 2001, 136, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, W.J.; Schimel, D.S.; Cole, C.V.; Ojima, D.S. Analysis of Factors Controlling Soil Organic Matter Levels in Great Plains Grasslands. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeignoz-Horta, L.A.; Pold, G.; Liu, X.A.; Frey, S.D.; Melillo, J.M.; DeAngelis, K.M. Microbial diversity drives carbon use efficiency in a model soil. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeplau, C.; Helfrich, M.; Dechow, R.; Szoboszlay, M.; Tebbe, C.C.; Don, A.; Greiner, B.; Zopf, D.; Thumm, U.; Korevaar, H.; et al. Increased microbial anabolism contributes to soil carbon sequestration by mineral fertilization in temperate grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 130, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Martínez, M.; Vicca, S.; Janssens, I.A.; Sardans, J.; Luyssaert, S.; Campioli, M.; Chapin Iii, F.S.; Ciais, P.; Malhi, Y.; Obersteiner, M.; et al. Nutrient availability as the key regulator of global forest carbon balance. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiblinger, K.M.; Hall, E.K.; Wanek, W.; Szukics, U.; Hammerle, I.; Ellersdorfer, G.; Bock, S.; Strauss, J.; Sterflinger, K.; Richter, A.; et al. The effect of resource quantity and resource stoichiometry on microbial carbon-use-efficiency. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 73, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Duan, C.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L. Soil moisture mediates microbial carbon and phosphorus metabolism during vegetation succession in a semiarid region. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 147, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Mudrák, O.; Ardestani, M.M.; Frouz, J. Unravelling the role of soil microflora from micro and macro aggregates in plant growth during primary and secondary successions. Catena 2023, 220, 106655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, L.K.; Billings, S.A. Changes in variability of soil moisture alter microbial community C and N resource use. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tian, J.; Chen, H.; Ho, M.; Vilgalys, R.; Bu, Z.-J.; Liu, X.; Richardson, C.J. Vegetation and microbes interact to preserve carbon in many wooded peatlands. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Shah, J.J.F.; Findlay, S.G.; Kuehn, K.A.; Moorhead, D.L. Scaling microbial biomass, metabolism and resource supply. Biogeochemistry 2014, 122, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takriti, M.; Wild, B.; Schnecker, J.; Mooshammer, M.; Knoltsch, A.; Lashchinskiy, N.; Eloy Alves, R.J.; Gentsch, N.; Gittel, A.; Mikutta, R.; et al. Soil organic matter quality exerts a stronger control than stoichiometry on microbial substrate use efficiency along a latitudinal transect. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.; Rousk, J. Microbial growth and carbon use efficiency in soil: Links to fungal-bacterial dominance, SOC-quality and stoichiometry. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 131, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinweg, J.M.; Plante, A.F.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Tanaka, D.L. Patterns of substrate utilization during long-term incubations at different temperatures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2722–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiong, X.; Hui, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Su, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. Soil aggregate size distribution mediates microbial responses to prolonged acid deposition in a subtropical forest in south China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 198, 109544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, G.R. Advances in the soil microbial carbon use efficiency. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 756–767. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, P.; Fu, R.; Nottingham, A.T.; Domeignoz-Horta, L.A.; Yang, X.; Du, H.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Tree species diversity increases soil microbial carbon use efficiency in a subtropical forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 7131–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Lee, J.; Melillo, J.M.; Six, J. The temperature response of soil microbial efficiency and its feedback to climate. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Ao, G.; Han, M.; Liu, M.; Yin, R.; Feng, J.; Zhu, B. Minor Effects of Warming on Soil Microbial Diversity, Richness and Community Structure. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, W.; Nottingham, A.T.; Xiao, D.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Xiao, J.; Duan, P.; Tang, T.; et al. Lithological Controls on Soil Aggregates and Minerals Regulate Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency and Necromass Stability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 21186–21199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Turner, B.L.; Talbot, J.M.; Waring, B.G.; Powers, J.S.; Kuske, C.R.; Moorhead, D.L.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Stoichiometry of microbial carbon use efficiency in soils. Ecol. Monogr. 2016, 86, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, K.M.; Dijkstra, P.; Sinsabaugh, R.; Frey, S.D. Clarifying the interpretation of carbon use efficiency in soil through methods comparison. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamer, C.A.; Jones, D.L.; Baldock, J.A.; Rui, Y.; Murphy, D.V.; Hoyle, F.C.; Farrell, M. Is the fate of glucose-derived carbon more strongly driven by nutrient availability, soil texture, or microbial biomass size? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, P.M.; Stark, J.M.; Holt, C.; Hooker, T.; Cardon, Z.G. Microbial growth efficiencies across a soil moisture gradient assessed using 13C-acetic acid vapor and 15N-ammonia gas. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungate Bruce, A.; Mau Rebecca, L.; Schwartz, E.; Caporaso, J.G.; Dijkstra, P.; van Gestel, N.; Koch Benjamin, J.; Liu Cindy, M.; McHugh Theresa, A.; Marks Jane, C.; et al. Quantitative Microbial Ecology through Stable Isotope Probing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7570–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Protozoan grazing affects estimates of carbon utilization efficiency of the soil microbial community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.; Ji, C.; Shen, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, B. Soil microbial carbon and nutrient constraints are driven more by climate and soil physicochemical properties than by nutrient addition in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosinger, C.; Rousk, J.; Sandén, H. Can enzymatic stoichiometry be used to determine growth-limiting nutrients for microorganisms?—A critical assessment in two subtropical soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.; Weintraub, M.N.; Moorhead, D. Estimating microbial carbon use efficiency in soil: Isotope-based and enzyme-based methods measure fundamentally different aspects of microbial resource use. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 169, 108677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry and Ecological Theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roels, J.A. Application of macroscopic principles to microbial metabolism. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1980, 22, 2457–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.H.; Elonen, C.M.; Herlihy, A.T.; Jicha, T.M.; Serenbetz, G. Microbial ecoenzyme stoichiometry, nutrient limitation, and organic matter decomposition in wetlands of the conterminous United States. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 26, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Active microorganisms in soil: Critical review of estimation criteria and approaches. Soil Boil. Biochem. 2013, 67, 192–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öquist, M.G.; Erhagen, B.; Haei, M.; Sparrman, T.; Ilstedt, U.; Schleucher, J.; Nilsson, M.B. The effect of temperature and substrate quality on the carbon use efficiency of saprotrophic decomposition. Plant Soil 2017, 414, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosatta, E.; Ågren, G.I. Soil organic matter quality interpreted thermodynamically. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 1889–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazewicz, S.J.; Schwartz, E. Dynamics of 18O incorporation from H2 18O into soil microbial DNA. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazzola, A.; Brown, C.; Dettlaff, M.A.; Batbaatar, A.; Grenke, J.; Bao, T.; Peetoom Heida, I.; Cahill, J.F., Jr. The effects of livestock grazing on biodiversity are multi-trophic: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, S.E.; Smith, M.D.; Burkepile, D.E.; Hanan, N.P.; Avolio, M.L.; Collins, S.L.; Knapp, A.K.; Lemoine, N.P.; Forrestel, E.J.; Eby, S.; et al. Change in dominance determines herbivore effects on plant biodiversity. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Wang, D.; Isbell, F.; Liu, J.; Feng, C.; Liu, J.; Zhong, Z.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, X.; et al. Diversifying livestock promotes multidiversity and multifunctionality in managed grasslands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6187–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurlock, J.M.O.; Hall, D.O. The global carbon sink: A grassland perspective. Glob. Change Biol. 2002, 4, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchslueger, L.; Wild, B.; Mooshammer, M.; Takriti, M.; Kienzl, S.; Knoltsch, A.; Hofhansl, F.; Bahn, M.; Richter, A. Microbial carbon and nitrogen cycling responses to drought and temperature in differently managed mountain grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, I.A.; Dieleman, W.; Luyssaert, S.; Subke, J.A.; Reichstein, M.; Ceulemans, R.; Ciais, P.; Dolman, A.J.; Grace, J.; Matteucci, G.; et al. Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Moorhead, D.L.; Shen, G.; Cui, Y.; Fang, L. Soil aggregate development and associated microbial metabolic limitations alter grassland carbon storage following livestock removal. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Liang, C.; Hautier, Y.; Wilcox, K.R.; Wang, S. Grazing-induced biodiversity loss impairs grassland ecosystem stability at multiple scales. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W. Advances in the carbon use efficiency of forest. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 37, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Ling, N.; Nan, Z. Microbial carbon use efficiency in different ecosystems: A meta-analysis based on a biogeochemical equilibrium model. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 4758–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdig, M.; Schleuss, P.-M.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Crawley, M.J.; Kirkman, K.P.; Seabloom, E.W.; Wragg, P.D.; Spohn, M. Microbial carbon use efficiency in grassland soils subjected to nitrogen and phosphorus additions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 146, 107815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Cao, Z.; Jia, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, G.; He, J.S.; Feng, X. Inactive and inefficient: Warming and drought effect on microbial carbon processing in alpine grassland at depth. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2241–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Gao, W.; Shi, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, J.-S. Effects of short- and long-term nutrient addition on microbial carbon use efficiency and carbon accumulation efficiency in the Tibetan alpine grassland. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 229, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnaz, K.R.; Corneo, P.E.; Keitel, C.; Dijkstra, F.A. Carbon and phosphorus addition effects on microbial carbon use efficiency, soil organic matter priming, gross nitrogen mineralization and nitrous oxide emission from soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, C.E.; Hobbie, S.E. Mechanisms driving the soil organic matter decomposition response to nitrogen enrichment in grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutknecht, J.L.M.; Field, C.B.; Balser, T.C. Microbial communities and their responses to simulated global change fluctuate greatly over multiple years. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 2256–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; He, Z. Effects of grazing patterns on grassland biomass and soil environments in China: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, F. Effects of different grazing intensities on grassland production in China: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 8, e81466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.; Wardle, D. Herbivore-mediated linkages between aboveground and belowground communities. Ecology 2003, 84, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltbrunner, D.; Schulze, S.; Hagedorn, F.; Schmidt, M.W.I.; Zimmmermann, S. Cattle trampling alters soil properties and changes soil microbial communities in a Swiss sub-alpine pasture. Geoderma 2012, 170, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Yan, R.; Ren, Y.; Jin, D.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, G.; Cui, Z.; Xin, X.; Zhang, R. Grazing-induced microbiome alterations drive soil organic carbon turnover and productivity in meadow steppe. Microbiome 2018, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzé, E.; Sandhage-Hofmann, A.; Meinel, J.A.; du Preez, C.C.; Amelung, W. Rangeland management impacts on the properties of clayey soils along grazing gradients in the semi-arid grassland biome of South Africa. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 97, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Bradford, M.A. Soil-carbon response to warming dependent on microbial physiology. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, P.; Thomas, S.C.; Heinrich, P.L.; Koch, G.W.; Schwartz, E.; Hungate, B.A. Effect of temperature on metabolic activity of intact microbial communities: Evidence for altered metabolic pathway activity but not for increased maintenance respiration and reduced carbon use efficiency. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, J.T.; Jones, S.E. Microbial seed banks: The ecological and evolutionary implications of dormancy. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyano, F.E.; Manzoni, S.; Chenu, C. Responses of soil heterotrophic respiration to moisture availability: An exploration of processes and models. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 59, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillaway, D.N.; Kruger, E.L. Trends in seedling growth and carbon-use efficiency vary among broadleaf tree species along a latitudinal transect in eastern North America. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zeng, X.M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, X.Q.; Liu, Y.R.; Huang, Q. Soil microbial trait-based strategies drive metabolic efficiency along an altitude gradient. ISME Commun. 2021, 1, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qu, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Morrissey, E.; Miao, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Bai, E. Large-scale importance of microbial carbon use efficiency and necromass to soil organic carbon. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigyo, N.; Umeki, K.; Hirao, T. Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Fungal and Bacterial Communities in Cool-Temperate Montane Forests. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Z.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Differential responses of soil microbial biomass, diversity, and compositions to altitudinal gradients depend on plant and soil characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.A.-O.; Suyal, D.C.; Yadav, A.; Shouche, Y.; Goel, R. Microbial diversity and soil physiochemical characteristic of higher altitude. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213844. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, B.; Cheng, S. Soil hydraulic conductivity as affected by vegetation restoration age on the Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Wassmann, R.; Vlek, P. An Appraisal of Global Wetland Area and Its Organic Carbon Stock. Curr. Sci. 2005, 88, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Woodwell, G.M.; Mackenzie, F.T.; Houghton, R.A.; Apps, M.; Gorham, E. Biotic feedbacks in the warming of the earth. Clim. Change 1998, 40, 495–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.E.; Baird, A.J. Peatlands and Global Change: Response and Resilience. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Distribution and accumulation of soil carbon in temperate wetland, northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amstrong, W.; Drew, M.C. Root growth and metabolism under deficiency. In Plant and Roots: The Hidden Half; Waisel, Y., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 729–761. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pei, J.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Nie, M.; Pendall, E. Microbial carbon use efficiency, biomass residence time and temperature sensitivity across ecosystems and soil depths. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 154, 108117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastviken, D.; Olsson, M.; Tranvik, L. Simultaneous measurements of organic carbon mineralization and bacterial production in oxic and anoxic lake sediments. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 46, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picek, T.; Šimek, M.; Šantrůčková, H. Microbial responses to fluctuation of soil aeration status and redox conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.F. Effect of Water Potential on Microbial Growth and Activity. In Water Potential Relations in Soil Microbiology; Parr, J.F., Gardner, W.R., Elliott, L.F., Eds.; SSSA Special Publications: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981; pp. 23–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.M.; Firestone, M.K. Mechanisms for soil moisture effects on activity of nitrifying bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Deng, L.; Kim, D.-G.; Huang, C.; Tian, K. Carbon budgets of wetland ecosystems in China. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2061–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Peterson, M.P.; Zhang, L.; Hurynovich, V.; He, Y. Greenhouse gases emissions and global climate change: Examining the influence of CO2, CH4, and N2O. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devêvre, O.C.; Horwáth, W.R. Decomposition of rice straw and microbial carbon use efficiency under different soil temperatures and moistures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | Stoichiometric Modeling | 13C Glucose Tracing | 18O Water Tracing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Principle | Based on stoichiometric ratios | Based on biomass variation | Based on growth rate variation |
| Formula | |||
| Substrate | —— | 13C-Glucose | 18O-H2O |
| Labeled | No | Yes | Yes |
| Incubation time | —— | Short-term | Short-term |
| Advantages | No cultivation is required and it can be measured directly | Simple and easy to use | Measures the rate of microbial growth directly |
| Disadvantages | Model assumptions, obtained from empirical coefficients | Microbial biomass needs to be measured and is sensitive to changes over time | Only suitable for short-term experiments, stable over time |
| Carbon use efficiency (CUE) | The maximum value of the CUE is 0.6, with a small fluctuation range [31] | (1) CUE may be underestimated [28,32] (2) CUE may be overestimated [33,34] | CUE may be underestimated [35,36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.; Sheng, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Yuan, J.; Luo, W. Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems. Biology 2025, 14, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040348
Yu W, Sheng L, Wang X, Tang X, Yuan J, Luo W. Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems. Biology. 2025; 14(4):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040348
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Weirui, Lianxi Sheng, Xue Wang, Xinyu Tang, Jihong Yuan, and Wenbo Luo. 2025. "Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems" Biology 14, no. 4: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040348
APA StyleYu, W., Sheng, L., Wang, X., Tang, X., Yuan, J., & Luo, W. (2025). Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency in Natural Terrestrial Ecosystems. Biology, 14(4), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040348






