Shape and Size Variability of the Gynostemium in Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz (Orchidaceae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
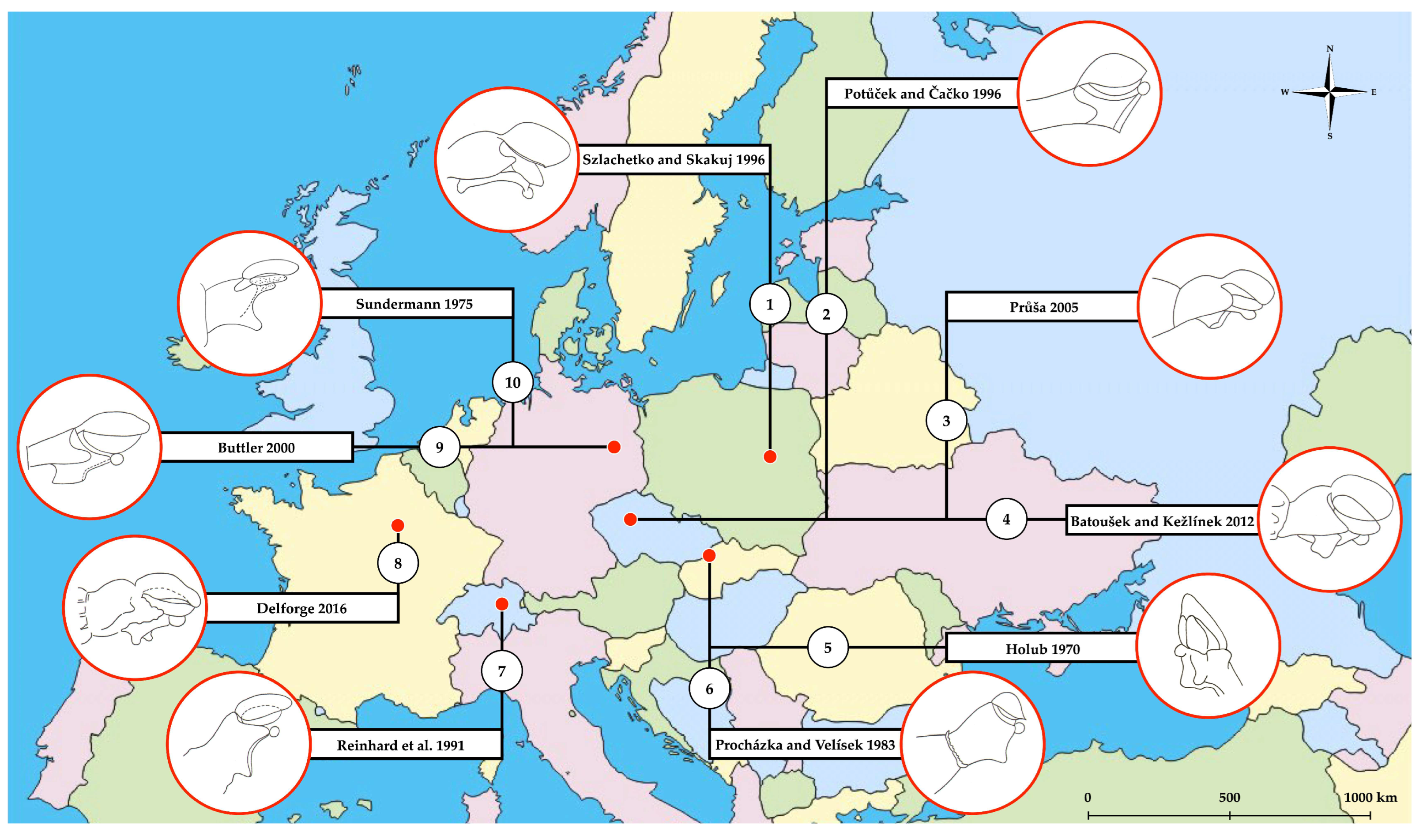
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Procedure
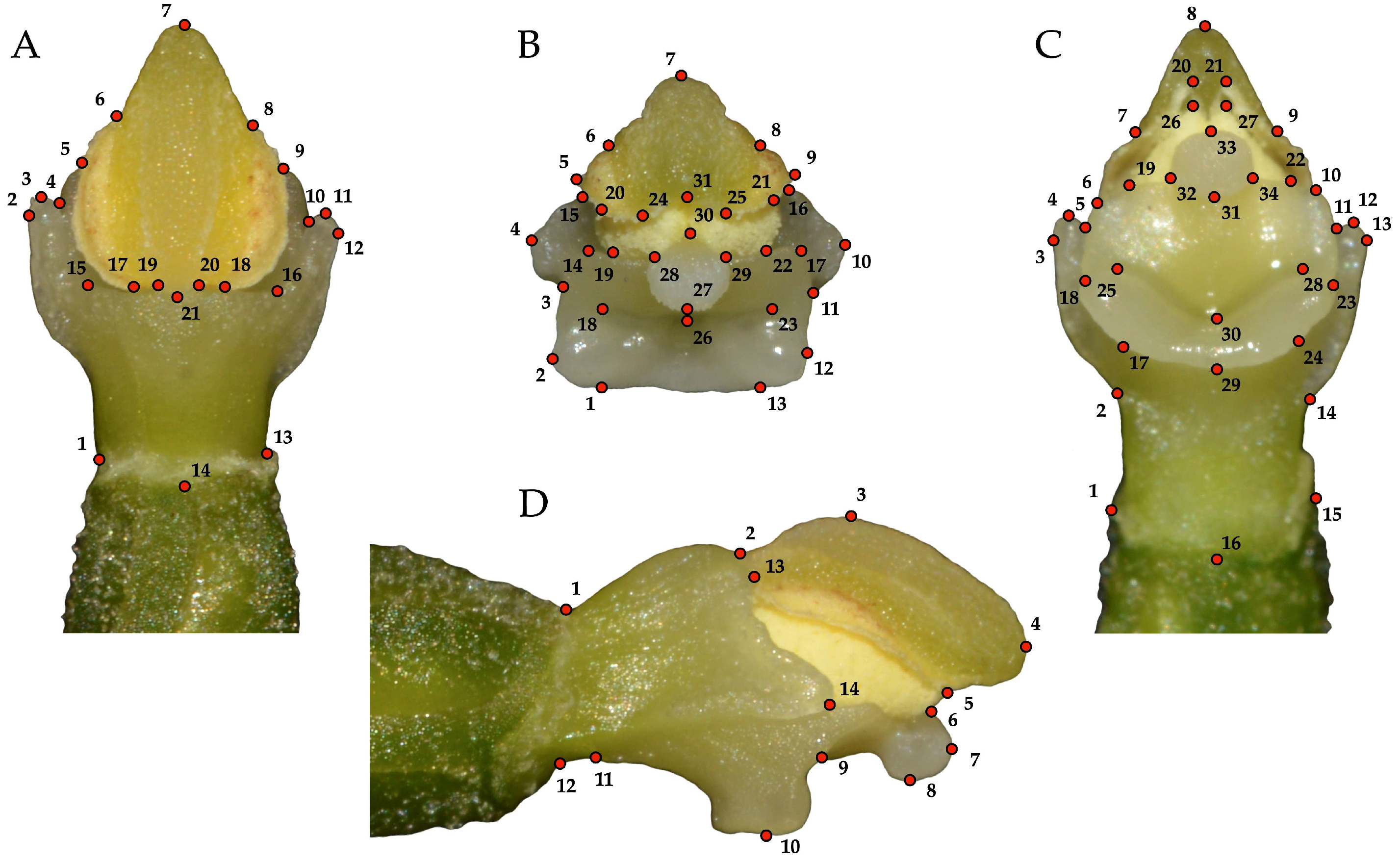
2.2. Geometric Morphometric Analyses of Gynostemium Shape Variation
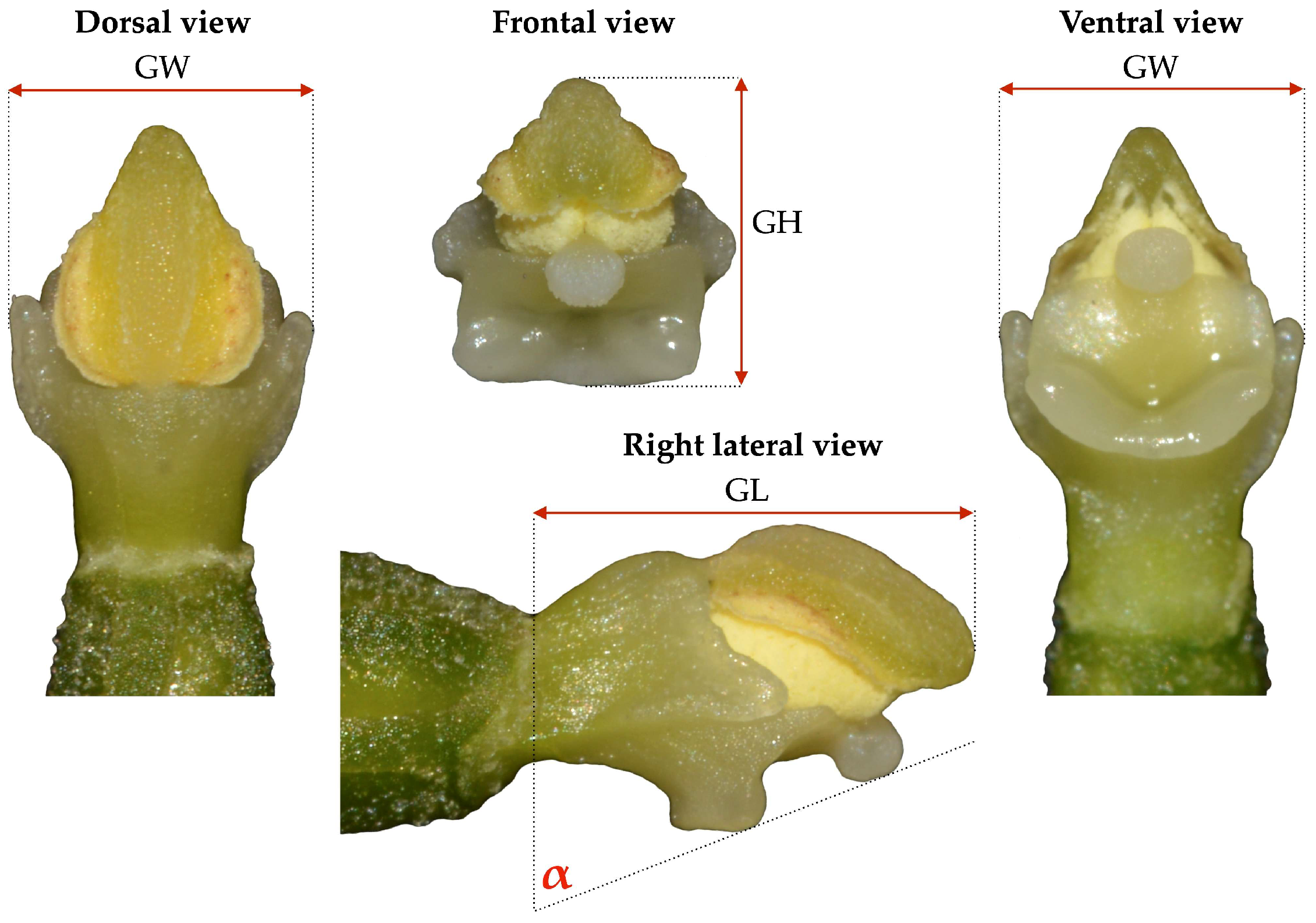
2.3. Statistical Analysis of Gynostemium Size and Angle of Stigma Inclination
3. Results
3.1. Variations of Gynostemium Shape
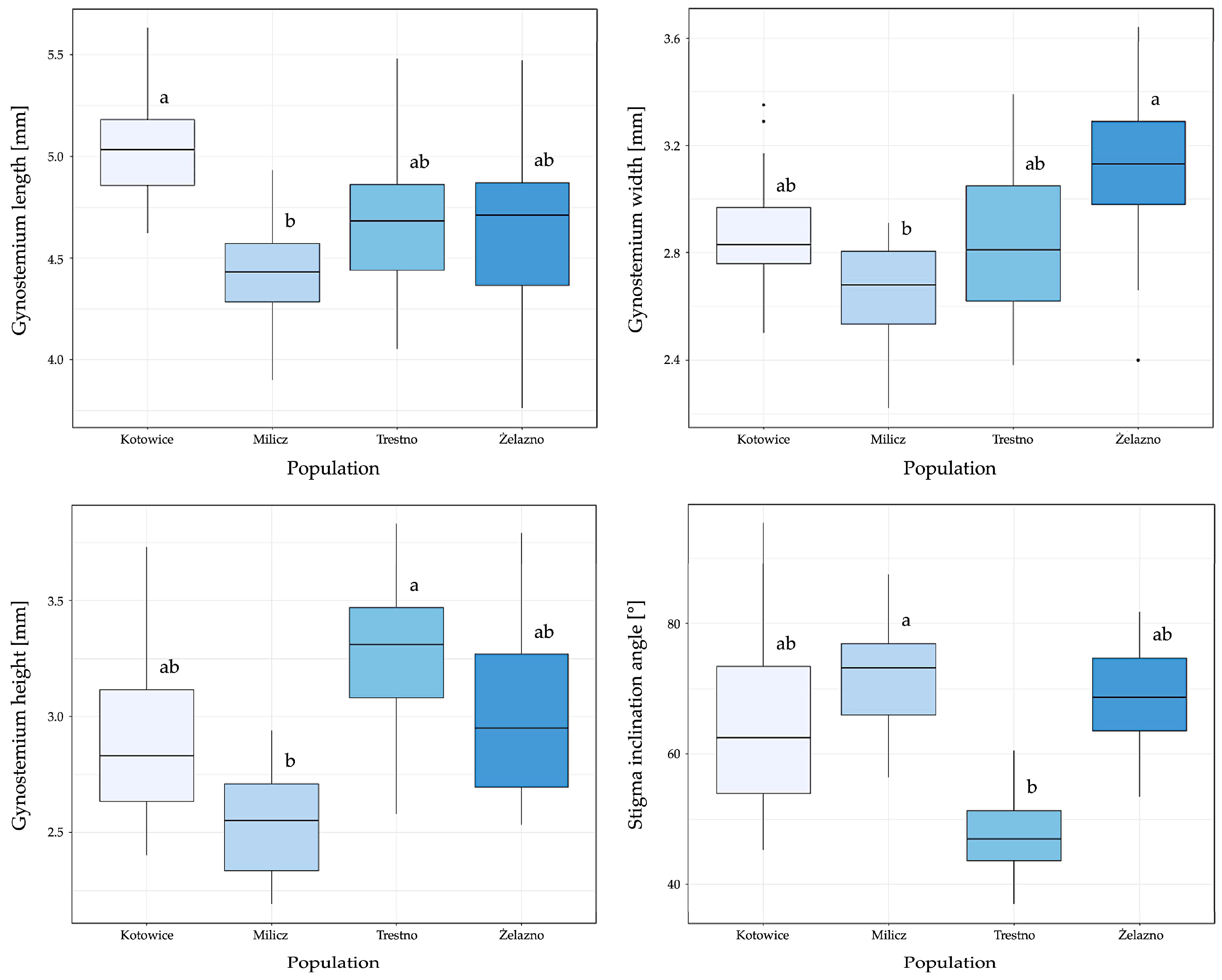
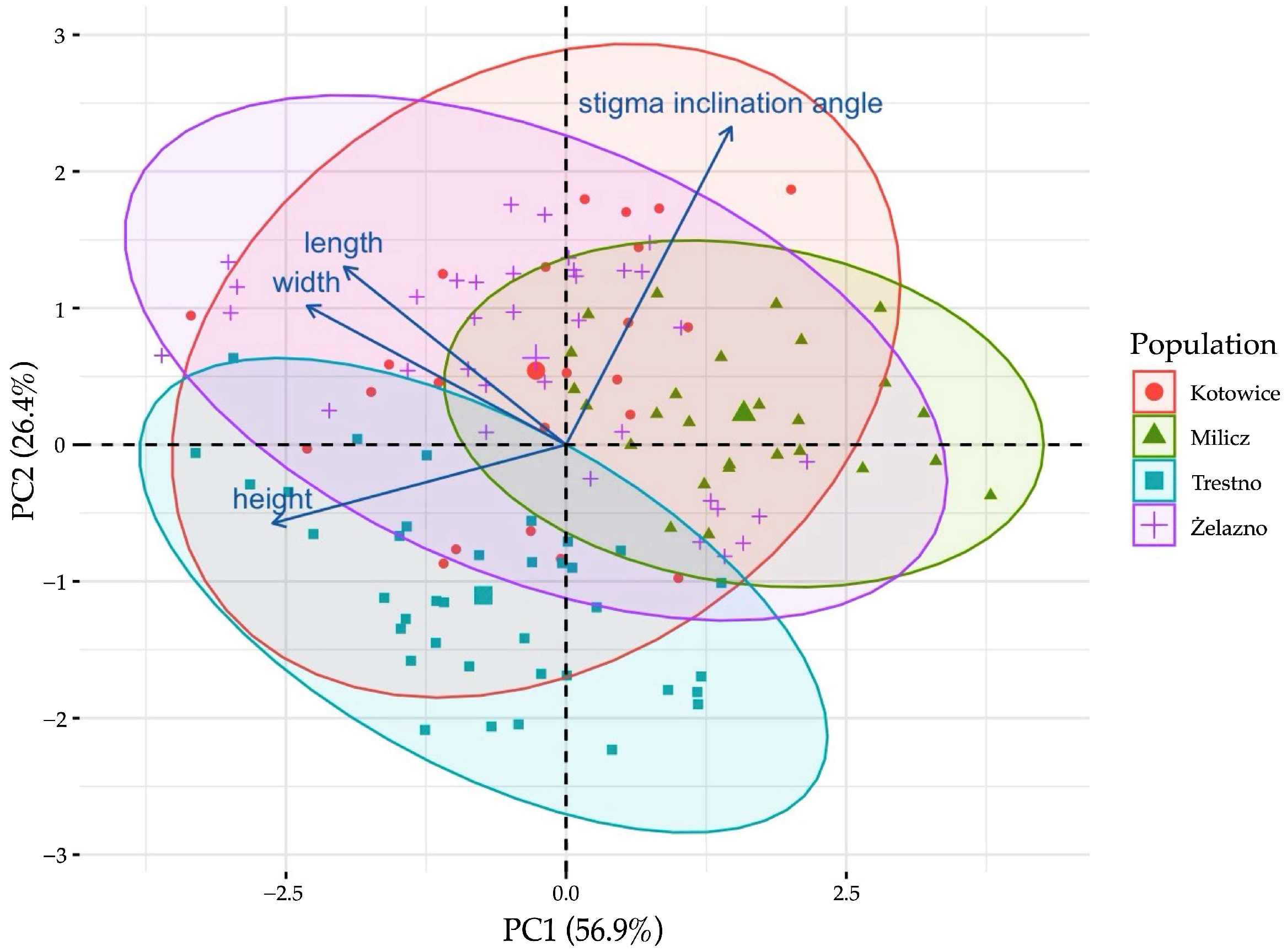
3.2. Variations of the Gynostemium Size and Angle of Stigma Inclination
3.3. General Structural Pattern of Gynostemium Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simpson, M.G. Plant Systematics; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Łobas, Z.; Khapugin, A.; Żołubak, E.; Jakubska-Busse, A. The Epipactis helleborine Group (Orchidaceae): An Overview of Recent Taxonomic Changes, with an Updated List of Currently Accepted Taxa. Plants 2021, 10, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holub, J. Epipactis leptochila (Godf.) Godf., a Epipactis muelleri Godf.—Nové druhy československé flóry. Preslia 1970, 42, 330–349. [Google Scholar]
- Procházka, F.; Velísek, V. Orchideje Naší Přírody; Academia Ved: Praha, Czech Republic, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard, H.R.; Gölz, P.; Peter, R.; Wildermuth, H. Die Orchideen de Schweiz und Angrenzender Gebiete; Fotorotar AG: Egg, Switzerland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Delforge, P. Orchidées d’Europe, d’Afrique du Nord et du Proche-Orient, 4th ed.; Delachaux et Niestlé: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tyteca, D.; Dufrêne, M. Biostatistical studies of western European allogamous populations of the Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz species group (Orchidaceae). Syst. Bot. 1994, 19, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potůček, O.; Čačko, Ľ. Všechno o Orchidejích; Slovart: Praha, Czech Republik, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Szlachetko, D.L.; Skakuj, M. Storczyki Polski; Wydawnictwo Sorus: Poznań, Poland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mereďa, P. Kl’úč na určovanie druhov rodu Epipactis Zinn publikovaných z územia Slovenska. Bull. Slov. Bot. Soc. 1999, 21, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Buttler, K.P. Storczyki. Dziko Rosnące Gatunki i Podgatunki Europy, Północnej Afryki i Bliskiego Wschodu; Świat Książki: Warszawa, Poland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Průša, D. Orchideje České Republiky; Computer Press: Brno, Czech Republik, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, H.; Künkele, S.; Lorenz, R. Ulmer Naturführer Orchideen Europas Mit Angrenzenden Gebieten; Ulmer Eugen Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Harrap, A.; Harrap, S. Orchids of Britain and Ireland. A field and Site Guide; A&C Black Publishers Ltd.: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Batoušek, P.; Kežlínek, Z. Kruštíky České Republiky; Český svaz ochránců přírody ZO Hořepník: Prostějov, Czech Republik, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brullo, C.; D’Emerico, S.; Pulvirenti, S. Karyological and taxonomical considerations on Epipactis cupaniana sp. nov. (Orchidaceae) from Sicily. Nord. J. Bot. 2013, 31, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanuš, A. Morphological and Molecular Analyses of Individual Genotypes from the Group of Epipactis helleborine s.l. in the Region of Goričko. Master’s Thesis, University of Maribor, Maribor, Slovenia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Krajnc, A.U.; Ivanuš, A.; Luthar, Z.; Lipovšek, M. Morphological variability and taxonomic concepts of Broad-leaved Helleborine ingroup Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz. Folia Biol. Geol. 2020, 61, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squirrell, J.; Hollingsworth, P.M.; Bateman, R.M.; Dickson, J.H.; Light, M.H.S.; MacConaill, M.; Tebbitt, M.C. Partitioning and diversity of nuclear and organelle markers in native and introduced populations of Epipactis helleborine (Orchidaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2001, 88, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, B.K.; Olesen, J.M.; Ågren, J. Floral morphology and reproductive success in the orchid Epipactis helleborine: Regional and local across-habitat variation. Plant Syst. Evol. 2002, 236, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, R.M. How many orchid species are currently native to the British Isles. In Current Taxonomic Research on the British and European Flora; Bailey, J.P., Ellis, R.G., Eds.; Botanical Society of the British Isles: London, UK, 2006; pp. 89–110. [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Squirrell, J.; Hollingsworth, M.L.; Richards, A.J.; Bateman, R.M. Taxonomic complexity, conservation and recurrent origins of self-pollination in Epipactis (Orchidaceae). In Current Taxonomic Research on the British and European Flora; Bailey, J.P., Ellis, R.G., Eds.; Botanical Society of the British Isles: London, UK, 2006; pp. 27–44. [Google Scholar]
- Tranchida-Lombardo, V.; Cafasso, D.; Cristaudo, A.; Cozzolino, S. Phylogeographic patterns, genetic affinities and morphological differentiation between Epipactis helleborine and related lineages in a Mediterranean glacial refugium. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, R.M. Implications of next-generation sequencing for the systematics and evolution of the terrestrial orchid genus Epipactis, with particular reference to the British Isles. Kew Bull. 2020, 75, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzweil, H. Developmental studies in orchid flowers III: Neottioid species. Nord. J. Bot. 1988, 8, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlachetko, D.L.; Rutkowski, P. Gynostemia orchidalium I. Apostasiaceae, Cypripediaceae, Orchidaceae (Thelymitroideae, Orchidoideae, Tropidioideae, Spiranthoideae, Neottioideae, Vanilloideae). Acta Bot. Fenn. 2000, 169, 1–379. [Google Scholar]
- Bonatti, P.M.; Sgarbi, E.; Del Prete, C. Gynostemium micromorphology and pollination in Epipactis microphylla (Orchidaceae). J. Plant Res. 2006, 119, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubska-Busse, A.; Proćków, J.; Górniak, M.; Gola, E.M. Is Epipactis pseudopurpurata distinct from E. purpurata (Orchidaceae)? Evidence from morphology, anatomy, DNA and pollination biology. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 2012, 170, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suetsugu, K. Delayed autonomous self-pollination in two Japanese varieties of Epipactis helleborine (Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 2013, 173, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalkowska, A.K.; Kostelecka, J.; Bohdanowicz, J.; Kapusta, M.; Rojek, J. Studies on floral nectary, tepals’ structure, and gynostemium morphology of Epipactis palustris (L.) Crantz (Orchidaceae). Protoplasma 2015, 252, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jakubska-Busse, A.; Żołubak, E.; Górniak, M.; Łobas, Z.; Tsiftsis, S.; Steiu, C. A revision of the taxonomy and identification of Epipactis greuteri (Orchidaceae, Neottieae). Plants 2020, 9, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabón-Mora, N.; González, F. The gynostemium: More than the sum of its parts with emerging floral complexities. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2024, 81, 102609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlachetko, D.L. Systema Orchidalium. Fragm. Florist. Geobot. Supp. 1995, 3, 1–152. [Google Scholar]
- Łobas, Z. Zmienność Morfologiczna Gynostemium Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz (Orchidaceae, Neottieae) i Jej Znaczenie Taksonomiczne. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Wroclaw, Wroclaw, Poland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sundermann, H. Europäische und Mediterrane Orchideen; Brücke Verlag Kurt Schmersow: Hildesheim, Germany, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Matuszkiewicz, W. Przewodnik do Oznaczania Zbiorowisk Roślinnych Polski; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. The Tps series of software. Hystrix 2015, 26, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg, C.P. MorphoJ: An integrated software package for geometric morphometrics. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, C.P.; Duttke, S.; Whelan, S.; Kim, M. Developmental plasticity, morphological variation and evolvability: A multilevel analysis of morphometric integration in the shape of compound leaves. J. Evol. Biol. 2012, 25, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscosi, V.; Cardini, A. Leaf morphology, taxonomy and geometric morphometrics: A simplified protocol for beginners. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilford, J.P. Fundamental Statistics in Psychology and Education; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. A: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R.V. Least-squares means: The R package Ismeans. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 69, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing-Chi, C. The column types of Neottia and Archineottia of the family Orchidaceae and their taxonomic and phylogenetic significance. J. Syst. Evol. 1979, 17, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Freudenstein, J.V. Gynostemium structure and relationships of the Corallorhizinae (Orchidaceae: Epidendroideae). Plant Syst. Evol. 1994, 193, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzweil, H. Floral morphology and ontogeny in subtribe Satyriinae (Fam. Orchidaceae). Flora 1996, 191, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimov, P.G. An intriguing morphological variability of Platanthera s.l. Eur. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 1, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dressler, R.L. The Orchids: Natural History and Classification; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Carnevali, G.; Cetzal-Ix, W.; Balam, R.; Leopardi, C.; Romero-González, G.A. A Combined Evidence Phylogenetic Re–circumscription and a Taxonomic Revision of Lophiarella (Orchidaceae: Oncidiinae). Syst. Bot. 2013, 38, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Arditti, J. Rostellum in orchids. Lankesteriana 2024, 24, 285–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns-Balogh, P.; Szlachetko, D.L.; Dafni, A. Evolution, pollination, and systematics of the tribe Neottieae (Orchidaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 1987, 156, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubska-Busse, A. The range and significance of phenotypic plasticity of Broad-leaved Helleborine Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz for taxonomy (Orchidaceae: Neottieae). In The Importance of Natural History Museums for Taxonomy; Borowiec, L., Tarnawski, D., Eds.; Polish Taxonomical Biographs: Wrocław, Poland, 2008; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.D.; Kurzweil, H. Systematics and phylogeny of the Satyrium erectum group (Orchidaceae), with descriptions of two new species from the Karoo region of South Africa. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 1998, 127, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Niet, T.; Liltved, W.R.; Johnson, S.D. More than meets the eye: A morphological and phylogenetic comparison of long-spurred, white-flowered Satyrium species (Orchidaceae) in South Africa. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 2011, 166, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botes, C.; van der Niet, T.; Cowling, R.M.; Johnson, S.D. Is biodiversity underestimated by classical herbarium-based taxonomy? A multi-disciplinary case study in Satyrium (Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 2020, 194, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubska-Busse, A.; Żołubak, E.; Jarzembowski, P.; Proćków, J. Morphological variability in Epipactis purpurata s. stricto (Orchidaceae)—An analysis based on herbarium material and field observations. Ann. Bot. Fenn. 2017, 54, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, A.V.; Averyanova, E.A.; Shagarov, L.M. Orchids of the Black Sea coast of Krasnodarsky Krai (Russia): Current state, new records, conservation. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2020, 5, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robatsch, K. Beitrage zur Bliitenbiologie und Autogamie der Gattung Epipactis; Jahresberichte Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereins Wuppertal e.V.: Wuppertal, Germany, 1983; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Claessens, J.; Kleynen, J. The Flower of the European Orchid: Form and Function; Jean Claessens and Jacques Kleynen: Geuelle, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, A. Traditional morphometrics in plant systematics and its role in palm systematics. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 2006, 151, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelditch, M.L.; Swiderski, D.L.; Sheets, H.D. Geometric Morphometrics for Biologists: A Primer; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D.C.; Rohlf, F.J.; Slice, D.E. A field comes of age: Geometric morphometrics in the 21st century. Hystrix 2013, 24, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, M.D.; Clark, J.Y.; Culham, A. The Cinderella discipline: Morphometrics and their use in botanical classification. Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 2020, 194, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.; Davies, J.; Huxley, A. Wild Orchids of Britain and Europe; The Hogarth Press: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Lipovsek, M.; Dolinar, B.; Kosec, J.; Pausic, I.; Klenovsek, D. Prispevek k pregledu taksonov iz oblikovnega kroga širokolistne močvirnice (Epipactis helleborine s.l.). Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2006, 16, 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Martinčič, A.; Wraber, T.; Jogan, N.; Podobnik, A.; Turk, B.; Vreš, B.; Ravnik, V.; Frajmar, B.; Strgulc Krajšek, S.; Trčak, B.; et al. Mala Flora Slovenije. Ključ za Določanje Praprotnic in Semenk; Tehniška založba Slovenije: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Szlachetko, D.L. Flora Polski: Storczyki; Multico: Warszawa, Poland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhelj, A. Morphometric Analysis of Helleborines (Epipactis) in Slovenia. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dolinar, B. Kukavičevke v Sloveniji; Pipinova knjiga: Podsmreka, Slovenia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, S.; Waller, M. Britain’s Orchids: A Field Guide to the Orchids of Great Britain and Ireland; Princeton University Press: Woodstock, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanek Krajnc, A.U.; Lipovšek, M.; Luthar, Z.; Ivanuš, A.; Miljuš, S.; Bohanec, B.; Šiško, M. Taxonomic analysis of certain taxa of Epipactis in Slovenia. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2022, 56, 125674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubska-Busse, A.; Żołubak, E.; Proćków, J. Epitypification of the name Epipactis purpurata Sm. (Orchidaceae, Neottieae). Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2017, 86, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żołubak, E. Problem Taksonów Zbiorczych (Agregatów) w Rodzaju Epipactis Zinn, 1757 (Orchidaceae, Neottieae) na Przykładzie E. purpurata Agg. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Wroclaw, Wroclaw, Poland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sramkó, G.; Paun, O.; Brandrud, M.K.; Laczkó, L.; Molnár, A.; Bateman, R.M. Iterative allogamy–autogamy transitions drive actual and incipient speciation during the ongoing evolutionary radiation within the orchid genus Epipactis (Orchidaceae). Ann. Bot. 2019, 124, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, R.M. Systematics and conservation of British and Irish orchids: A “state of the union” assessment to accompany Atlas. Kew Bull. 2022, 77, 355–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Population | Geographic Location | Number of Collected Flowers | Phytosociological Characteristics * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | |||
| Kotowice | 50°1′59′′ | 17°12′54′′ | 23 | Riparian forest Ficario-Ulmetum minoris Knapp 1942 em. J. Mat. 1976 |
| Milicz | 51°31′5′′ | 17°15′40′′ | 27 | Anthropogenically modified forests Quercetea robori-petraeae Br.-Bl. Et R. Tx. 1943 |
| Trestno | 51°4′47′′ | 17°8′5′′ | 37 | Regenerative community of riparian shrub-forest Salicitea purpureae Moor 1958 |
| Żelazno | 50°21′22′′ | 16°40′59′′ | 35 | Degenerated form of orchid beech forests Cephalanthero-Fagenion Tüxen et Oberdorfer 1958 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łobas, Z.; Jakubska-Busse, A. Shape and Size Variability of the Gynostemium in Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz (Orchidaceae). Biology 2025, 14, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030241
Łobas Z, Jakubska-Busse A. Shape and Size Variability of the Gynostemium in Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz (Orchidaceae). Biology. 2025; 14(3):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030241
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁobas, Zbigniew, and Anna Jakubska-Busse. 2025. "Shape and Size Variability of the Gynostemium in Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz (Orchidaceae)" Biology 14, no. 3: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030241
APA StyleŁobas, Z., & Jakubska-Busse, A. (2025). Shape and Size Variability of the Gynostemium in Epipactis helleborine (L.) Crantz (Orchidaceae). Biology, 14(3), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030241







