An Emerging Role for OGDHL: From Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism to Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discovery and Structural Characteristics of the OGDHL Protein
3. Mutations in the Human OGDHL Gene and Associated Clinical Syndromes
4. The Functions of OGDHL in the Nervous System
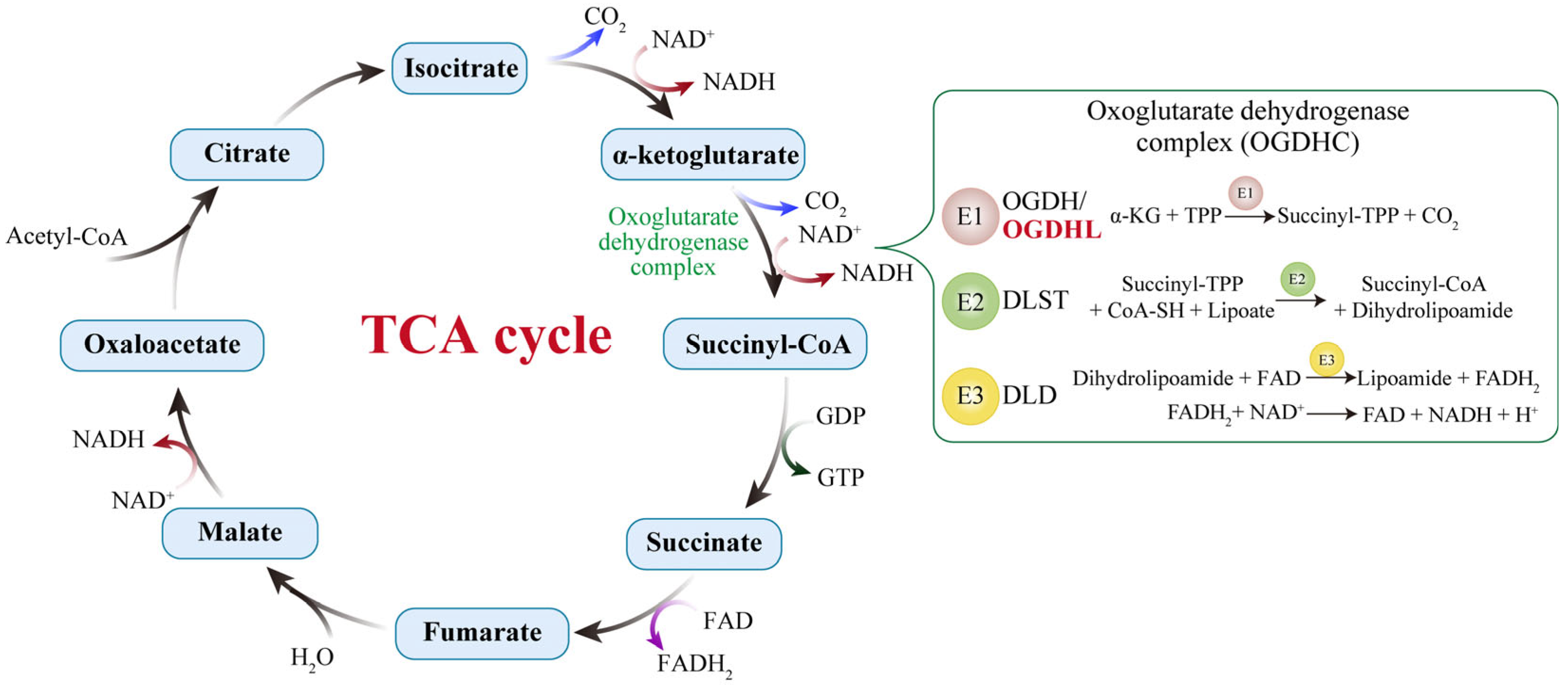
4.1. Central Role in Energy Metabolism
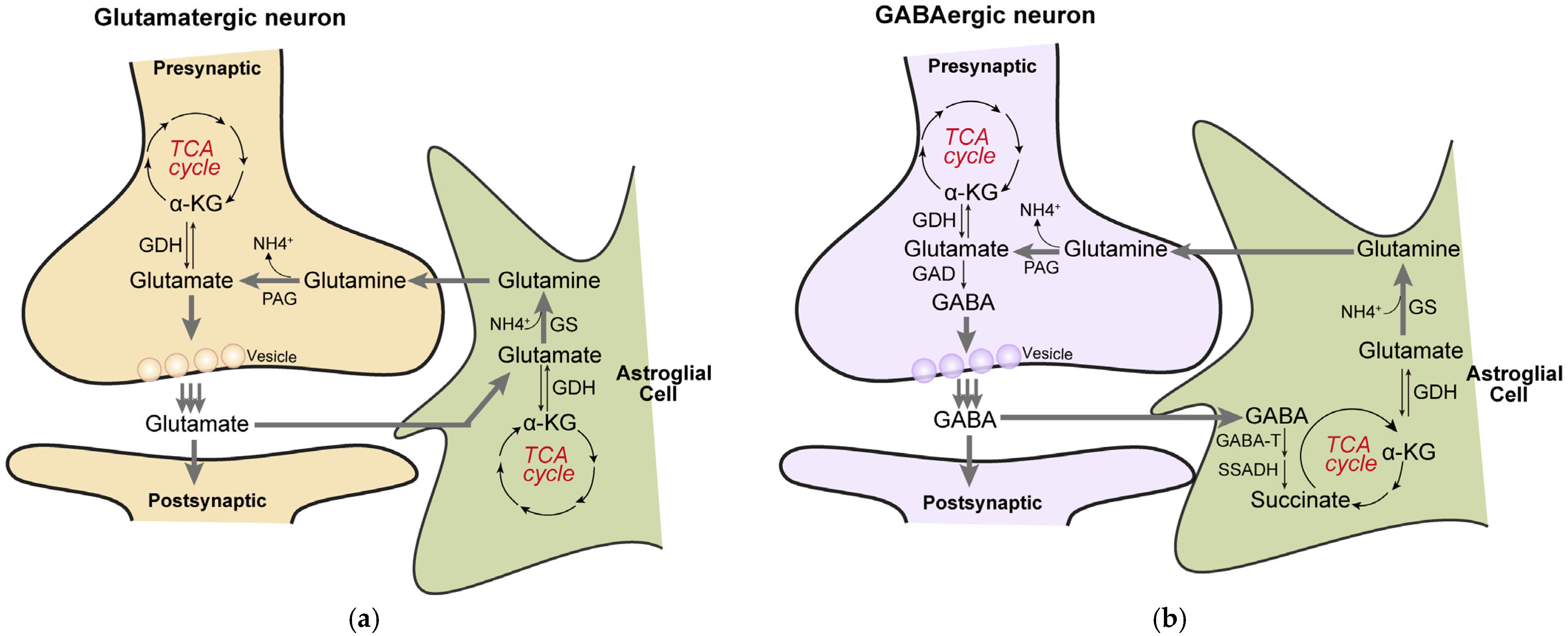
4.2. Biosynthesis of Neurotransmitters: Glutamate/GABA Cycle
5. The Roles of OGDHL in Other Systems
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-KG | Alpha-ketoglutarate |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ADHD | Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| ALS | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
| ASD | Autism Spectrum Disorder |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| ccRCC | Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| dNTP | Deoxyribonucleotide Triphosphate |
| DCM | Dilated Cardiomyopathy |
| DD | Developmental Delay |
| DLST | Dihydrolipoamide Succinyltransferase |
| DLD | Dihydrolipoamide Dehydrogenase |
| E1o | 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase |
| E2o | Dihydrolipoamide Succinyltransferase |
| E3 | Dihydrolipoamide Dehydrogenase |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| FASN | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| FTT | Failure to Thrive |
| GA | Gait Ataxia |
| GABA | Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid |
| GDH | Glutamate Dehydrogenase |
| HFpEF | Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| ID | Intellectual Disability |
| I/R | Ischemia–Reperfusion |
| miR-214 | MicroRNA-214 |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| mTORC1 | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 |
| mVNS | Magnetic Vagus Nerve Stimulation |
| NADH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (reduced form) |
| NDD | Neurodevelopmental Disorder |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa B |
| OGDHC | 2-Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex |
| OGDH | 2-Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase |
| OGDHL | Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase-Like |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| REST | RE1-Silencing Transcription Factor |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle |
| TFAP2A | Transcription Factor AP-2 Alpha |
| ThDP | Thiamine Diphosphate |
| TPP | Thiamine Pyrophosphate |
| TWIST1 | Twist Family BHLH Transcription Factor 1 |
| Wnt7B | Wingless-type MMTV Integration Site Family, Member 7B |
| ZBTB20 | Zinc Finger and BTB Domain Containing 20 |
References
- Rumpf, S.; Sanal, N.; Marzano, M. Energy metabolic pathways in neuronal development and function. Oxf. Open Neurosci. 2023, 2, kvad004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.J.; Jolivet, R.; Attwell, D. Synaptic energy use and supply. Neuron 2012, 75, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellen, G. Fueling thought: Management of glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation in neuronal metabolism. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnane, S.C.; Trushina, E.; Morland, C.; Prigione, A.; Casadesus, G.; Andrews, Z.B.; Beal, M.F.; Bergersen, L.H.; Brinton, R.D.; de la Monte, S.; et al. Brain energy rescue: An emerging therapeutic concept for neurodegenerative disorders of ageing. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.H.; Cai, Q. Mitochondrial transport in neurons: Impact on synaptic homeostasis and neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sade, A.N.; Wiener, G.; Barak, B. Intersection of mitochondrial dysfunction and myelination: An overlooked aspect in neurodevelopmental disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 2026, 21, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorente-Folch, I.; Rueda, C.B.; Pardo, B.; Szabadkai, G.; Duchen, M.R.; Satrustegui, J. The regulation of neuronal mitochondrial metabolism by calcium. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 3447–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Reddy, P.H. Defective mitophagy in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Boveris, A.; Cadenas, E. Mitochondrial energy metabolism and redox signaling in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, D.; Avelar, C.; Fernandes, M.; Sá, J.; da Cruz, E.S.O. Mitochondria, energy, and metabolism in neuronal health and disease. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.E.; Blass, J.P.; Beal, M.F.; Bunik, V. The alpha-ketoglutarate-dehydrogenase complex: A mediator between mitochondria and oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 31, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretter, L.; Adam-Vizi, V. Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase: A target and generator of oxidative stress. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailloux, R.J. Targeted Redox Regulation α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex for the Treatment of Human Diseases. Cells 2025, 14, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Yin, J.; Yang, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M. Molecular architecture of the mammalian 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunik, V.I.; Degtyarev, D. Structure-function relationships in the 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase family: Substrate-specific signatures and functional predictions for the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like proteins. Proteins 2008, 71, 874–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunik, V.; Kaehne, T.; Degtyarev, D.; Shcherbakova, T.; Reiser, G. Novel isoenzyme of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase is identified in brain, but not in heart. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 4990–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, Z.Y.; Efthymiou, S.; Seiffert, S.; Vargas Parra, K.; Lee, S.; Nasca, A.; Maroofian, R.; Schrauwen, I.; Pendziwiat, M.; Jung, S.; et al. Bi-allelic variants in OGDHL cause a neurodevelopmental spectrum disease featuring epilepsy, hearing loss, visual impairment, and ataxia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 2368–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Brophy, C.; Hickling, M.; Neve, J.; Furger, A. Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation of genes associated with protein turnover and mitochondrial function are deregulated in Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s and ALS disease. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Kikuno, R.; Hirosawa, M.; Nomura, N.; Ohara, O. Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XV. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro. DNA Res. 1999, 6, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Nishikawa, T.; Otsuki, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Irie, R.; Wakamatsu, A.; Hayashi, K.; Sato, H.; Nagai, K.; et al. Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strausberg, R.L.; Feingold, E.A.; Grouse, L.H.; Derge, J.G.; Klausner, R.D.; Collins, F.S.; Wagner, L.; Shenmen, C.M.; Schuler, G.D.; Altschul, S.F.; et al. Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16899–16903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, R.G.; Rice, J.E.; Sanderson, S.J.; Bunik, V.; Lindsay, H.; Lindsay, J.G. Subunit interactions in the mammalian alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Evidence for direct association of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase components. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24158–24164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengeveld, A.F.; de Kok, A. Identification of the E2-binding residues in the N-terminal domain of E1 of a prokaryotic pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. FEBS Lett. 2002, 522, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ævarsson, A.; Chuang, J.L.; Wynn, R.M.; Turley, S.; Chuang, D.T.; Hol, W.G. Crystal structure of human branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase and the molecular basis of multienzyme complex deficiency in maple syrup urine disease. Structure 2000, 8, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Wei, W.; Zhou, L.; Nemeria, N.; Jordan, F. Amino-terminal residues 1-45 of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E1 subunit interact with the E2 subunit and are required for activity of the complex but not for reductive acetylation of the E2 subunit. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 14037–14046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Koike, K.; Hamada, M.; Otsuka, K.I.; Suematsu, T.; Koike, M. Mammalian α-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. VII. Resolution and reconstitution of the pig heart 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 4043–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.J.; Vona, B.; Lau, T.; Huang, K.; Zaki, M.S.; Aldeen, H.S.; Karimiani, E.G.; Rocca, C.; Noureldeen, M.M.; Saad, A.K.; et al. Evaluating the association of biallelic OGDHL variants with significant phenotypic heterogeneity. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Tian, H.; Fang, T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Dou, G.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.; et al. OGDHL Variant rs2293239: A Potential Genetic Driver of Chinese Familial Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 771950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, R.; Liao, W.; Xie, P.; Zhou, J. Hippocampal proteomic changes of susceptibility and resilience to depression or anxiety in a rat model of chronic mild stress. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugani, H.T.; Phelps, M.E.; Mazziotta, J.C. Positron emission tomography study of human brain functional development. Ann. Neurol. 1987, 22, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D. A neuronal subcompartment view of ATP production. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2024, 25, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, S.; Li, M.; Xu, X.; Xia, X.; Wei, K.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. Aerobic glycolysis is the predominant means of glucose metabolism in neuronal somata, which protects against oxidative damage. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, K.F.; Blass, J.P. The alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 893, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskiewicz, D.E.; Hammes, G.G. Elementary steps in the reaction mechanism of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Escherichia coli: Kinetics of succinylation and desuccinylation. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 3136–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.E.; Park, L.C.; Sheu, K.F.; Blass, J.P.; Calingasan, N.Y. The alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in neurodegeneration. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 36, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobolyi, A.; Bago, A.; Palkovits, M.; Nemeria, N.S.; Jordan, F.; Doczi, J.; Ambrus, A.; Adam-Vizi, V.; Chinopoulos, C. Exclusive neuronal detection of KGDHC-specific subunits in the adult human brain cortex despite pancellular protein lysine succinylation. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 639–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Xie, F.; Guo, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. OGDHL ameliorates cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 418, 113673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, Y.; Li, A.; Yan, J.; Li, P.; Qin, K.; Zhang, T.; Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated metabolic remodeling of TCA cycle promotes Parkinson’s disease through inhibition of H3K4me3 demethylation. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Petersen, K.F.; Behar, K.L.; Brown, P.; Nixon, T.W.; Mason, G.F.; Petroff, O.A.; Shulman, G.I.; Shulman, R.G.; Rothman, D.L. Determination of the rate of the glutamate/glutamine cycle in the human brain by in vivo 13C NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8235–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oz, G.; Berkich, D.A.; Henry, P.G.; Xu, Y.; LaNoue, K.; Hutson, S.M.; Gruetter, R. Neuroglial metabolism in the awake rat brain: CO2 fixation increases with brain activity. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 11273–11279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibson, N.R.; Dhankhar, A.; Mason, G.F.; Rothman, D.L.; Behar, K.L.; Shulman, R.G. Stoichiometric coupling of brain glucose metabolism and glutamatergic neuronal activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; de Graaf, R.A.; Mason, G.F.; Rothman, D.L.; Shulman, R.G.; Behar, K.L. The contribution of GABA to glutamate/glutamine cycling and energy metabolism in the rat cortex in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5588–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.V. The Glutamate/GABA-Glutamine Cycle: Insights, Updates, and Advances. J. Neurochem. 2025, 169, e70029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schousboe, A.; Bak, L.K.; Waagepetersen, H.S. Astrocytic Control of Biosynthesis and Turnover of the Neurotransmitters Glutamate and GABA. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, L. Functional interactions between neurons and astrocytes I. Turnover and metabolism of putative amino acid transmitters. Prog. Neurobiol. 1979, 13, 277–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, L.K.; Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S. The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnewald, U.; Schousboe, A. Introduction to the Glutamate-Glutamine Cycle. In The Glutamate/GABA-Glutamine Cycle: Amino Acid Neurotransmitter Homeostasis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 13, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.V.; Markussen, K.H.; Jakobsen, E.; Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Aldana, B.I. Glutamate metabolism and recycling at the excitatory synapse in health and neurodegeneration. Neuropharmacology 2021, 196, 108719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norenberg, M.D.; Martinez-Hernandez, A. Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res. 1979, 161, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvamme, E.; Torgner, I.A.; Roberg, B. Kinetics and localization of brain phosphate activated glutaminase. J. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 66, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzsáki, G.; Wang, X.J. Mechanisms of gamma oscillations. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ruiz, A.; Sirota, A.; Lopes-Dos-Santos, V.; Dupret, D. Over and above frequency: Gamma oscillations as units of neural circuit operations. Neuron 2023, 111, 936–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Xu, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, G.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Song, G.; Weng, S.; Dong, L.; Zhu, J.; et al. OGDHL silencing promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by reprogramming glutamine metabolism. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, Z.; Hou, L.; Chen, Q.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, P.; He, M.; Yang, Z. OGDHL Expression as a Prognostic Biomarker for Liver Cancer Patients. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 9037131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Peng, J.; Xie, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, C.; Yan, P.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing DNA damage through non-canonical function. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, W.; Song, S.; Bai, L.; Nie, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, G. Proteogenomics Integrating Reveal a Complex Network, Alternative Splicing, Hub Genes Regulating Heart Maturation. Genes 2022, 13, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, A.J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Wei, C.; Wang, K.; Ma, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; et al. Zbtb20 deficiency causes cardiac contractile dysfunction in mice. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 13862–13876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.N.; Zhang, M.; Tian, W.; Quan, W.; Song, F.; Liu, S.Y.; Liu, X.X.; Mo, D.; Sun, Y.; Gao, Y.Y.; et al. Canonical transient receptor potential channel 1 aggravates myocardial ischemia-and-reperfusion injury by upregulating reactive oxygen species. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 1309–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhao, W.; Hua, Y.; Bao, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Ge, G.; Yu, Y.; Sun, J.; et al. Magnetic vagus nerve stimulation alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by the inhibition of pyroptosis through the M(2)AChR/OGDHL/ROS axis in rats. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, K.; Irion, C.I.; Takeuchi, L.M.; Ding, W.; Lambert, G.; Eisenberg, T.; Sukkar, S.; Granzier, H.L.; Methawasin, M.; Lee, D.I.; et al. Osteopontin Promotes Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction Through a Mitochondrial Pathway. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2705–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Du, Y.; Yuan, J. The Potential of Metabolism-Related Gene OGDHL as a Biomarker for Myocardial Remodeling in Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 741920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gong, S.; Zhou, C.; Xin, W.; Qin, S.; Yao, M.; Lan, Q.; Liao, W.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Y. REST contributes to renal fibrosis through inducing mitochondrial energy metabolism imbalance in tubular epithelial cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2025, 23, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj-Kondori, M.; Hosseinnejad, M.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Behroz Sharif, S.; Hashemzadeh, S. Aberrant hypermethylation of OGDHL gene promoter in sporadic colorectal cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2020, 44, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, M.; Huang, R.Z.; Zheng, J.; Liang, H.Q.; Huang, W.H.; Liu, J.; Li, J.H. OGDHL closely associates with tumor microenvironment and can serve as a prognostic biomarker for papillary thyroid cancer. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Long, J.; Chen, Z.; Shu, X.O.; Xiang, Y.B.; Wen, W.; Zeng, C.; Gao, Y.T.; Cai, Q.; Zheng, W. Discovery of rare coding variants in OGDHL and BRCA2 in relation to breast cancer risk in Chinese women. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, T.; Sen, N.; Noordhuis, M.G.; Ravi, R.; Wu, T.C.; Ha, P.K.; Sidransky, D.; Hoque, M.O. OGDHL is a modifier of AKT-dependent signaling and NF-κB function. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Miao, D.; Lv, Q.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q.; Liang, H.; Yang, H.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, X. The m6A modification-mediated OGDHL exerts a tumor suppressor role in ccRCC by downregulating FASN to inhibit lipid synthesis and ERK signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, G.; Song, R.; Zheng, T.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yin, D.; et al. A Novel Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase-Like Mediated miR-214/TWIST1 Negative Feedback Loop Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5407–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, G.; Tsai, L.H. Mechanisms of DNA damage-mediated neurotoxicity in neurodegenerative disease. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.Q. DNA damage response in neurodevelopment and neuromaintenance. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 3300–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Herrup, K. Context-Dependent Functions of E2F1: Cell Cycle, Cell Death, and DNA Damage Repair in Cortical Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, E.I.; Smilenov, L.B.; Price, M.A.; Osredkar, T.; Baker, R.A.; Ghosh, S.; Shi, F.D.; Vollmer, T.L.; Lencinas, A.; Stearns, D.M.; et al. Cell cycle activation in postmitotic neurons is essential for DNA repair. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koblan, L.W.; Erdos, M.R.; Wilson, C.; Cabral, W.A.; Levy, J.M.; Xiong, Z.M.; Tavarez, U.L.; Davison, L.M.; Gete, Y.G.; Mao, X.; et al. In vivo base editing rescues Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome in mice. Nature 2021, 589, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newby, G.A.; Liu, D.R. In vivo somatic cell base editing and prime editing. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 3107–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbab, M.; Matuszek, Z.; Kray, K.M.; Du, A.; Newby, G.A.; Blatnik, A.J.; Raguram, A.; Richter, M.F.; Zhao, K.T.; Levy, J.M.; et al. Base editing rescue of spinal muscular atrophy in cells and in mice. Science 2023, 380, eadg6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.K.; Zhang, S.Q.; Peng, W.L.; Shi, Y.H.; Yuan, B.; Yuan, Y.T.; Xue, Z.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Han, W.J.; Chen, Z.F.; et al. Whole-brain in vivo base editing reverses behavioral changes in Mef2c-mutant mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, R.; Casimir, P.; Erkol, E.; Boubakar, L.; Planque, M.; Gallego López, I.M.; Ditkowska, M.; Gaspariunaite, V.; Beckers, S.; Remans, D.; et al. Mitochondria metabolism sets the species-specific tempo of neuronal development. Science 2023, 379, eabn4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujovic, F.; Simonian, M.; Hughes, W.E.; Shepherd, C.E.; Hunter, N.; Farahani, R.M. Mitochondria facilitate neuronal differentiation by metabolising nuclear-encoded RNA. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Okamoto, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Sheng, M. The importance of dendritic mitochondria in the morphogenesis and plasticity of spines and synapses. Cell 2004, 119, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Sirois, C.L.; Guo, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, Q.; Méndez-Albelo, N.M.; Gao, Y.; Khullar, S.; Kissel, L.; Sandoval, S.O.; et al. Species-specific FMRP regulation of RACK1 is critical for prenatal cortical development. Neuron 2023, 111, 3988–4005.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.C. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in diseases of energy metabolism. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1994, 26, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S. Leigh syndrome. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 194, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
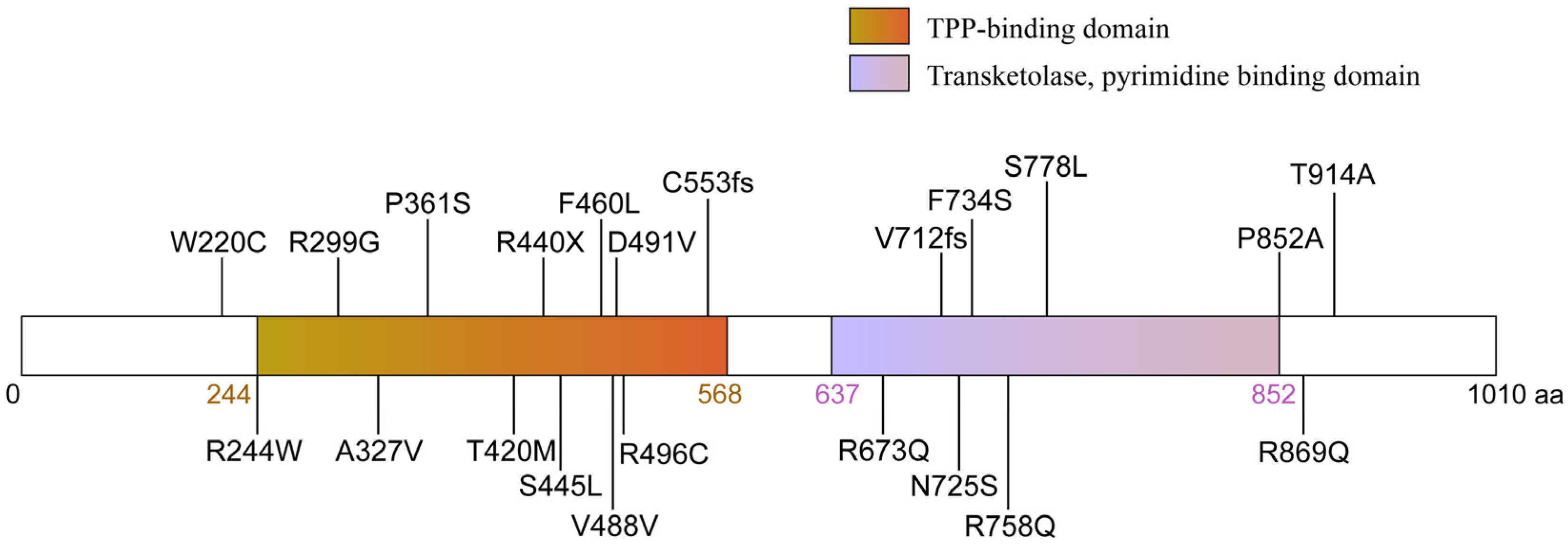
| Domain | Mutation | Amino Acid | Family | Clinical Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPP-binding domain | c.730 A>T | Missense mutation, p.R244W | Family5 | global DD and ID, spastic, optic atrophy, quadriplegic, microcephaly, corpus callosum hypoplasia |
| TPP-binding domain | c.895 A>T | Missense mutation, p.R299G | Family7 | moderate to severe ID, mild nystagmus |
| TPP-binding domain | c.980 C>T | Missense mutation, p.A327V | Family11 | motor delay and borderline ID, hyporeflexia, FTT |
| TPP-binding domain | c.1081 C>T | Missense mutation, p.P361S | Family6 | Moderate ID, focal tonic seizures, hypertonia, ataxia, NDD, corpus callosum hypoplasia |
| TPP-binding domain | c.1259 C>T | Missense mutation, p.T420M | Family1,2,3 | Microcephaly, short stature, FTT, DD and ID, Hypotonia, Sensorineural hearing loss (family1), NDD |
| TPP-binding domain | c.1318 C>T | Non-sense mutation, p.R440X | Family8 | global DD and ID, hypotonia, GA, hearing and vision deficit, developmental and epileptic encephalopathy |
| TPP-binding domain | c.1334 C>T | Missense mutation, p.S445L | Family5 | Severe DD, severe to profound ID, Short stature, FTT, seizures, NDD, corpus callosum hypoplasia |
| TPP-binding domain | c.1380 C>G | Missense mutation, p.F460L | Family10 | Severe DD, Generalized tonic–clonic seizures, spastic quadriplegia, Thin corpus callosum, NDD |
| TPP-binding domain | c.1658 delG | Frameshift mutation from C553, p. C553L fs * 16 | Family6 | mild ID, glioma, scaphocephaly |
| transketolase domain | c.2133 delA | Frameshift mutation from V712, p. V712S fs * 77 | Family9 | severe to profound Non- syndromic hearing loss |
| transketolase domain | c.2174 A>G | Missense mutation, p.725N>S | Family1 | Depressive Disorder |
| transketolase domain | c.2273 G>A | Missense mutation, p.758R>Q | Family12 | Congenital heart defects |
| transketolase domain | c.2333 C>T | Missense mutation, p.778S>L | Family9 | severe DD and ID, microcephaly, corpus callosum hypoplasia |
| transketolase domain | c.2554 C>G | Missense mutation, p.852P>A | Family1 | mild DD, mild GA, hearing deficit |
| C-terminal | c.2606 G>A | Missense mutation, p.869R>Q | Family4 | short stature, FTT, Hypotonia, Moderate ID, NDD |
| C-terminal | c.2740 A>G | Missense mutation, p.914T>A | Family7 | short stature, FTT, mild DD, Right eye esotropia, suspected hearing difficulty |
| N-terminal TPP-binding domain | c.660 G>C/ c.1472 A>T | Compound heterozygous single-nucleotide variants, p.220W>C/p.491D>V | Family4 | global DD, tonic–clonic, nystagmus, hypotonia, developmental and epileptic encephalopathy |
| N-terminal TPP-binding domain | c.660 G>C/ c.1486 C>T | Compound heterozygous single-nucleotide variants, p.220W>C/p.496R>C | Family8 | Mild motor delay, ADHD, Myoclonic-astatic epilepsy, hypotonia, DD |
| TPP-binding domain transketolase domain | c.980 C>T/ c.2201 T>C | Compound heterozygous single-nucleotide variants, p.327A>V/p.734F>S | Family3 | myoclonic-atonic, tonic–clonic, status epilepticus, developmental and epileptic encephalopathy |
| TPP-binding domain transketolase domain | c.1464 T>C/ c.2018 G>A | Compound heterozygous single-nucleotide variants, p.488V>V/p.673R>Q | Family2 | mild DD, GA, spasticity, retinopathy, dysmorphic features |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Yu, D.; Han, J. An Emerging Role for OGDHL: From Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism to Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Biology 2025, 14, 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121777
Liu X, Zhang G, Yu D, Han J. An Emerging Role for OGDHL: From Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism to Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Biology. 2025; 14(12):1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121777
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xian, Guicheng Zhang, Decai Yu, and Junhai Han. 2025. "An Emerging Role for OGDHL: From Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism to Neurodevelopmental Disorders" Biology 14, no. 12: 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121777
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, G., Yu, D., & Han, J. (2025). An Emerging Role for OGDHL: From Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism to Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Biology, 14(12), 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121777






