Exploring the Causal Relationship between Ibuprofen Use and Osteoarthritis Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Selection of Genetic Variants
2.2. Statistical Analysis for MR
2.3. Estimation of the Causal Relationship between IBU and OA
2.4. Heterogeneity and Sensitivity Tests
3. Results
3.1. Instrumental Variables for MR
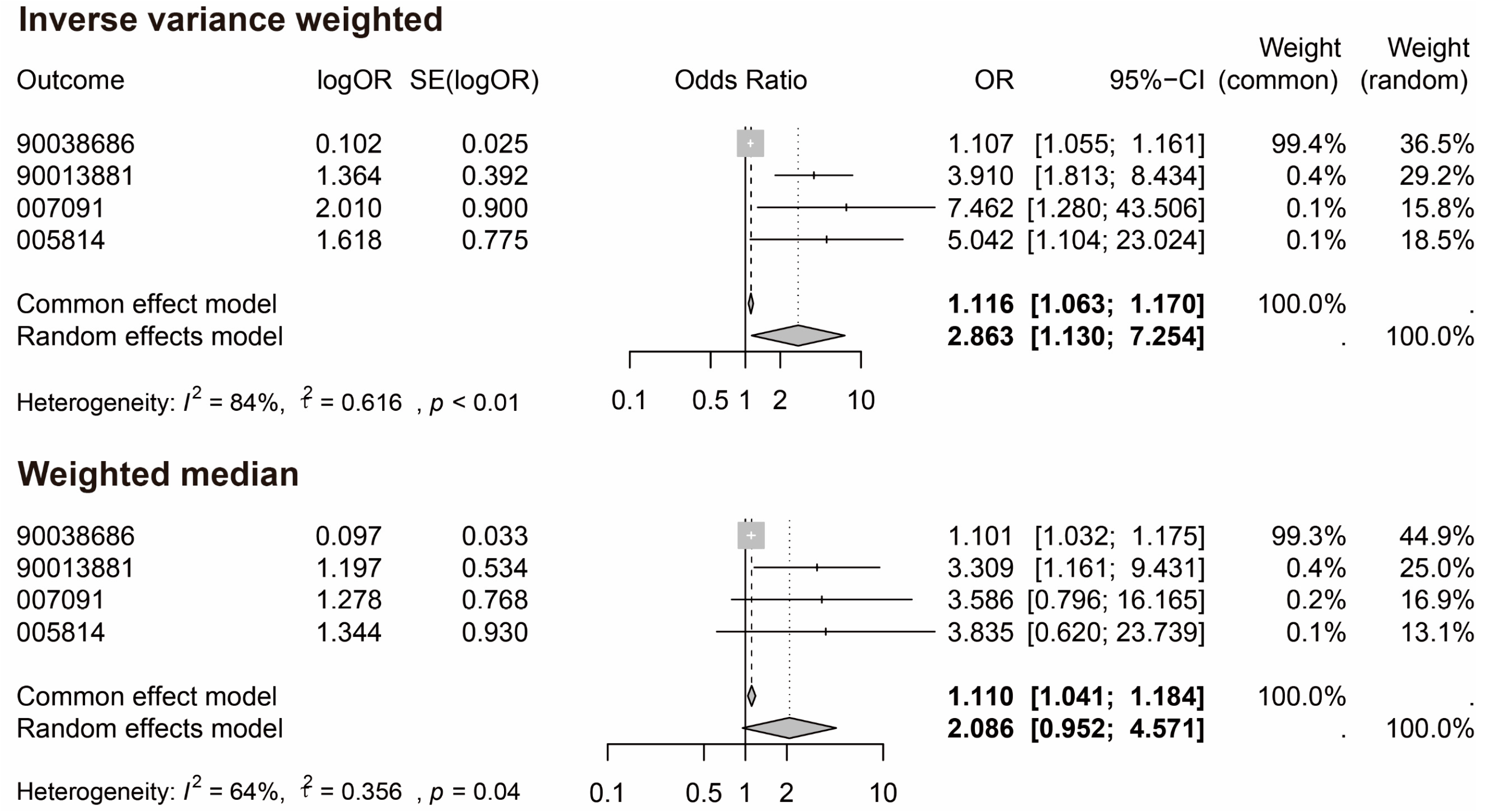
3.2. MR and Meta-Analysis Results
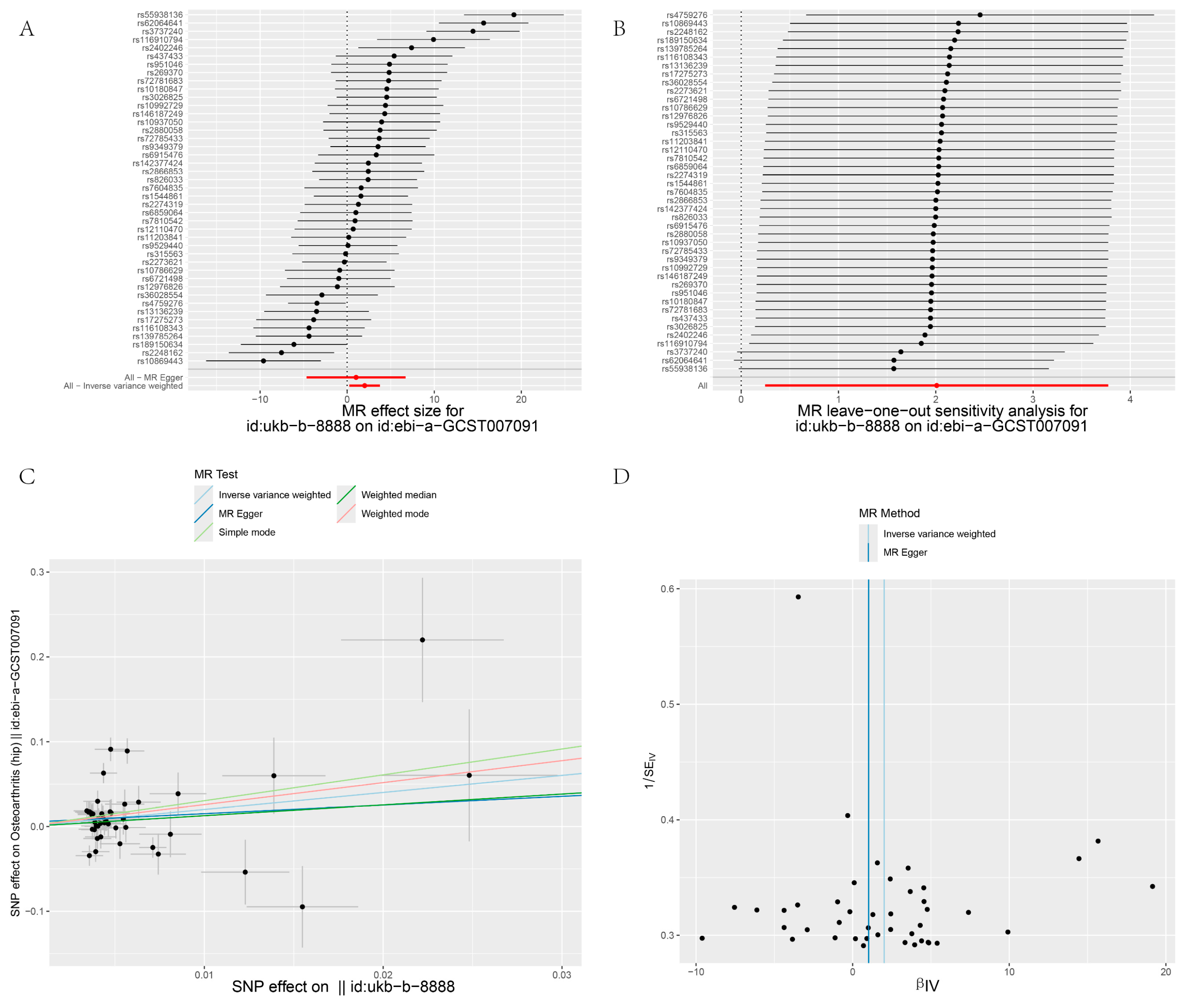
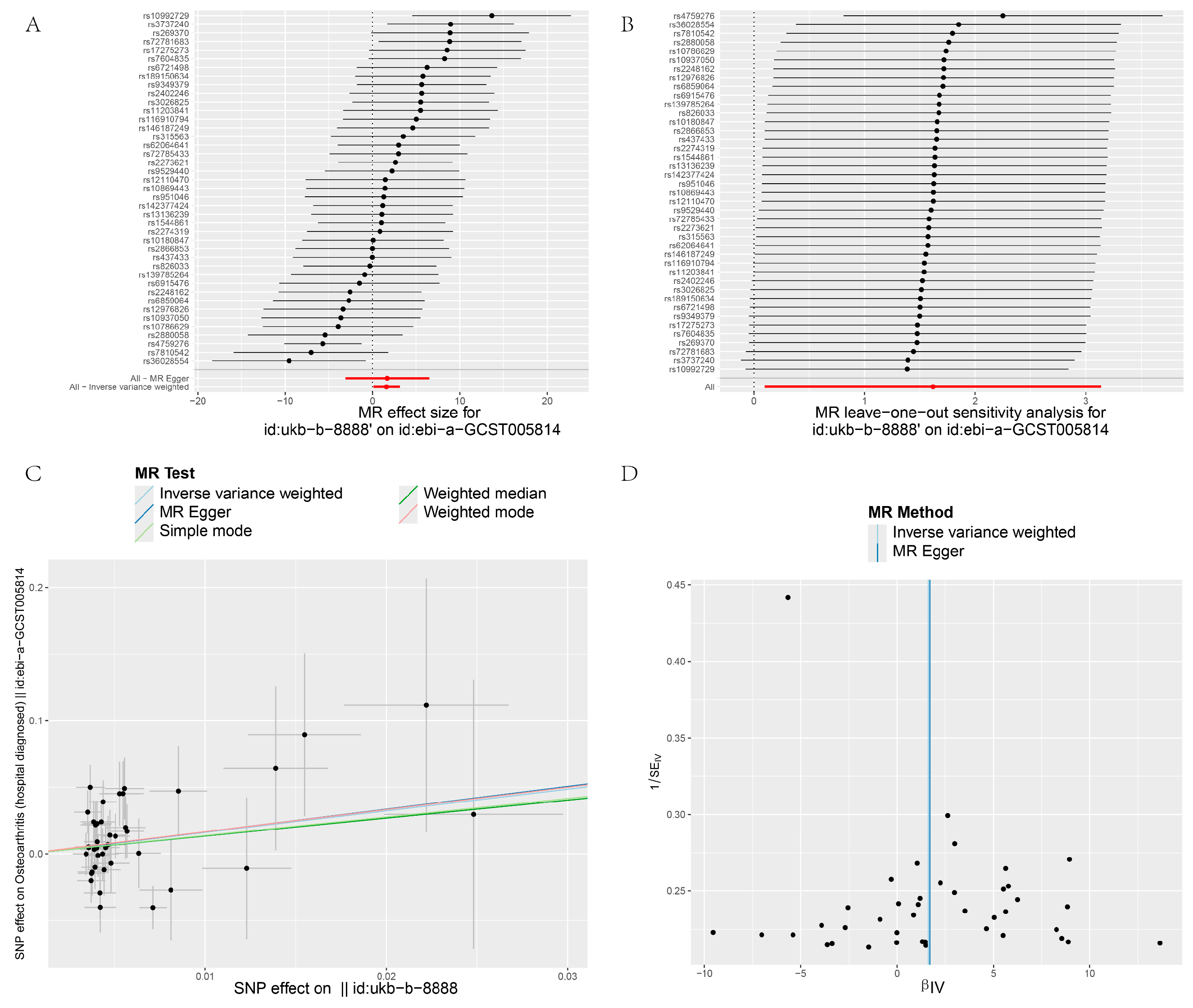
3.3. Pleiotropy
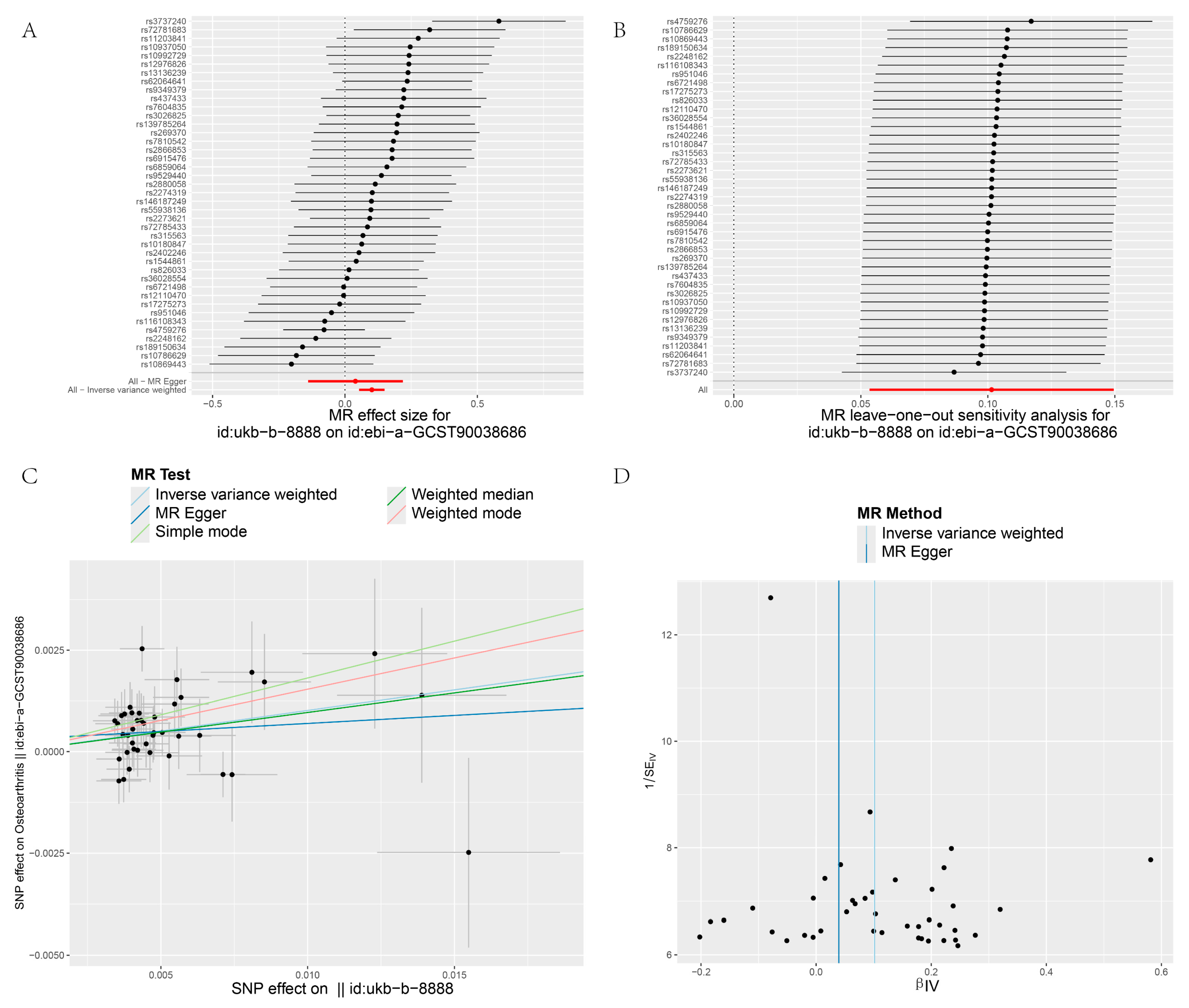
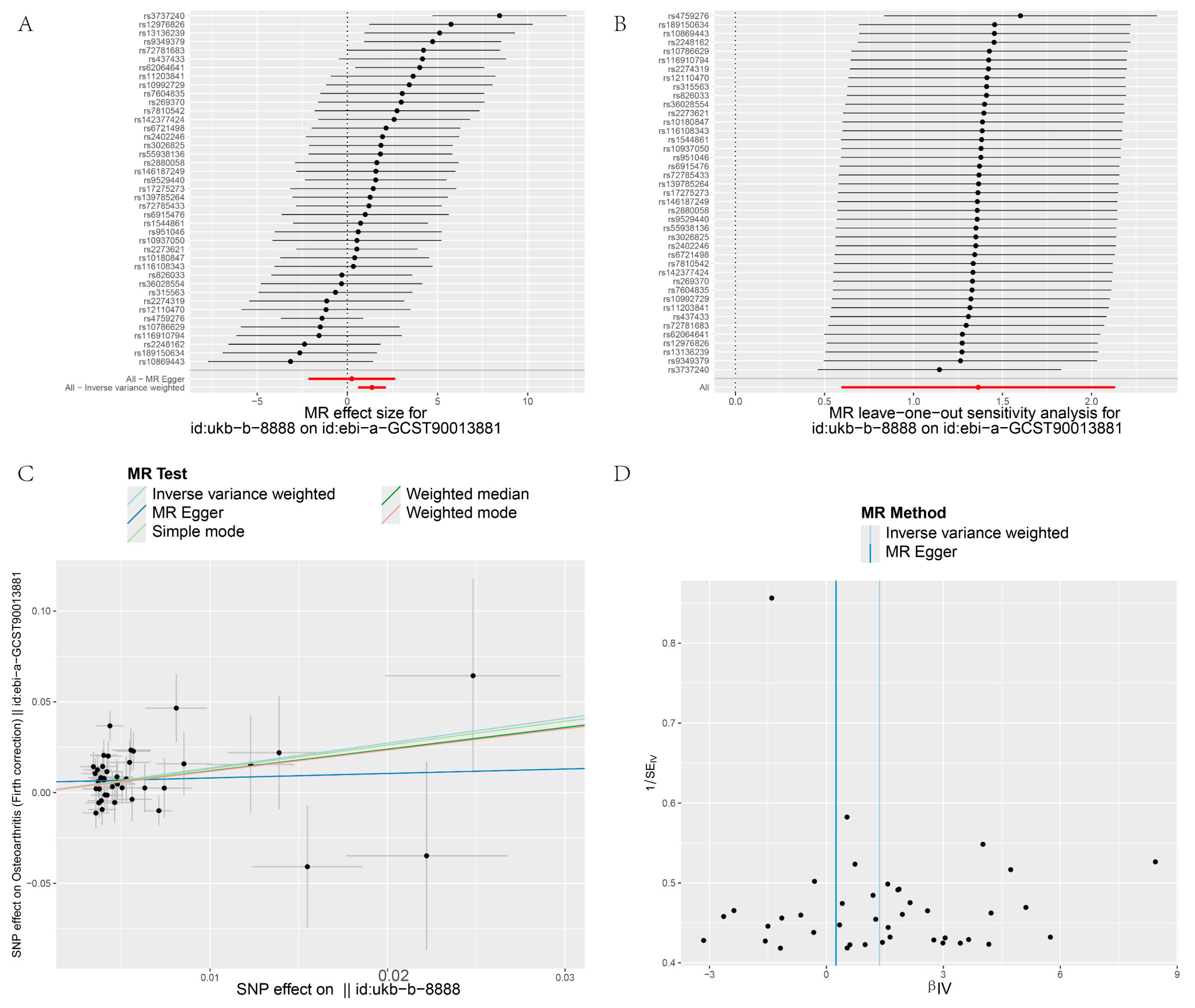
3.4. Heterogeneity and Sensitivity Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Felson, D.T. Osteoarthritis: New Insights. Part 1: The Disease and Its Risk Factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 133, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Barr, A.J.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Cooper, C.; Goldring, M.B.; Goldring, S.R.; Jones, G.; Teichtahl, A.J.; Pelletier, J.-P. Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zheng, C.; He, M.-H.; Huang, J.-R. The Causal Relationship Between Body Mass Index and the Risk of Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 2227–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, J.L.; Losciale, J.M.; Juhl, C.B.; Thorlund, J.B.; Lundberg, M.; Truong, L.K.; Miciak, M.; van Meer, B.L.; Culvenor, A.G.; Crossley, K.M.; et al. Risk Factors for Knee Osteoarthritis after Traumatic Knee Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials and Cohort Studies for the OPTIKNEE Consensus. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 1406–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glyn-Jones, S.; Palmer, A.J.R.; Agricola, R.; Price, A.J.; Vincent, T.L.; Weinans, H.; Carr, A.J. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2015, 386, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, M.C.; Altman, R.D.; April, K.T.; Benkhalti, M.; Guyatt, G.; McGowan, J.; Towheed, T.; Welch, V.; Wells, G.; Tugwell, P. American College of Rheumatology 2012 Recommendations for the Use of Nonpharmacologic and Pharmacologic Therapies in Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosser, T.; Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. The Cardiovascular Pharmacology of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvernstein, F.; Faich, G.; Goldstein, J.L.; Simon, L.S.; Pincus, T.; Whelton, A.; Stenson, W.F.; Burr, A.M.; Zhao, W.W.; Kent, J.D.; et al. Gastrointestinal Toxicity With Celecoxib Vs. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2000, 284, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Baigent, C.; Bhala, N.; Emberson, J.; Merhi, A.; Abramson, S.; Arber, N.; Baron, J.A.; Bombardier, C.; Cannon, C.; Farkouh, M.E.; et al. Vascular and Upper Gastrointestinal Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Meta-Analyses of Individual Participant Data from Randomised Trials. Lancet 2013, 382, 769–779. [Google Scholar]
- Bally, M.; Dendukuri, N.; Rich, B.; Nadeau, L.; Helin-Salmivaara, A.; Garbe, E.; Brophy, J.M. Risk of Acute Myocardial Infarction with NSAIDs in Real World Use: Bayesian Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. Br. Med. J. 2017, 357, j1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Berenbaum, F.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G. Osteoarthritis: An Update with Relevance for Clinical Practice. Lancet 2011, 377, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey Smith, G.; Ebrahim, S. ‘Mendelian Randomization’: Can Genetic Epidemiology Contribute to Understanding Environmental Determinants of Disease?*. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davies, N.M.; Hemani, G.; Davey Smith, G. Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization: Avoiding the Downsides of a Powerful, Widely Applicable but Potentially Fallible Technique. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, B.L.; Burgess, S. Efficient Design for Mendelian Randomization Studies: Subsample and 2-Sample Instrumental Variable Estimators. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian Randomization Analysis With Multiple Genetic Variants Using Summarized Data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Avoiding Bias from Weak Instruments in Mendelian Randomization Studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian Randomization with Invalid Instruments: Effect Estimation and Bias Detection through Egger Regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davey Smith, G.; Bowden, J. Robust Inference in Summary Data Mendelian Randomization via the Zero Modal Pleiotropy Assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Davey Smith, G.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Assessing the Suitability of Summary Data for Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analyses Using MR-Egger Regression: The Role of the I2 Statistic. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying Heterogeneity in a Meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring Inconsistency in Meta-Analyses. Br. Med. J. 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C. Do NSAIDs Affect the Progression of Osteoarthritis? Inflammation 2002, 26, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driban, J.B.; Lo, G.H.; Eaton, C.B.; Lapane, K.L.; Nevitt, M.; Harvey, W.F.; McCulloch, C.E.; McAlindon, T.E. Exploratory Analysis of Osteoarthritis Progression among Medication Users: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2016, 8, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, T.A.; Wang, X.; Nevitt, M.; Abdelshaheed, C.; Arden, N.; Hunter, D.J. Association between Current Medication Use and Progression of Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 4624–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey Smith, G.; Hemani, G. Mendelian Randomization: Genetic Anchors for Causal Inference in Epidemiological Studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R89–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Fort, J.G.; Goldstein, J.L.; Levy, R.A.; Hanrahan, P.S.; Bello, A.E.; Andrade-Ortega, L.; Wallemark, C.; Agrawal, N.M.; Eisen, G.M.; et al. Celecoxib Versus Naproxen and Diclofenac in Osteoarthritis Patients: SUCCESS-I Study. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainsford, K.D. Ibuprofen: Pharmacology, Efficacy and Safety. Inflammopharmacology 2009, 17, 275–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Cicuttini, F.; Jones, G. Do NSAIDs Affect Longitudinal Changes in Knee Cartilage Volume and Knee Cartilage Defects in Older Adults? Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijman, M.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Pols, H.A.P.; Koes, B.W.; Stricker, B.H.C.; Hazes, J.M.W. Is There an Association between the Use of Different Types of Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs and Radiologic Progression of Osteoarthritis?: The Rotterdam Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3137–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, C.J. New Drug Classes COX-2 Inhibitors. Lancet 1999, 353, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, B.; Tjoumakaris, F.P.; Harwood, M.I.; Good, R.P.; Ciccotti, M.G.; Freedman, K.B. Chondroprotection and the Prevention of Osteoarthritis Progression of the Knee. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
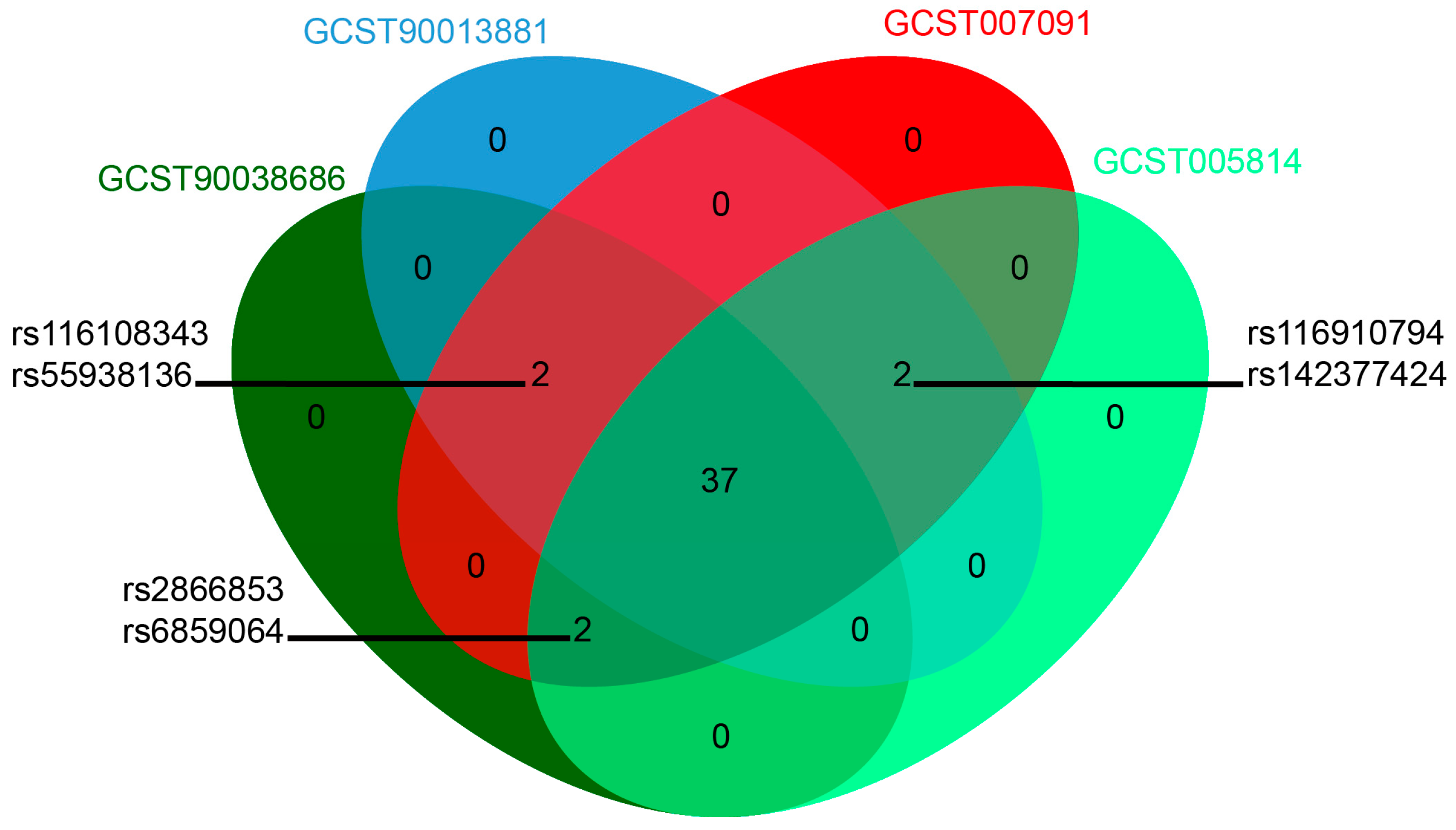
| GWAS ID | Year | First Author | Population | Sample Size | SNP Size | Trait |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ukb-b-8888 | 2018 | Ben Elsworth | European | 457,547 | 9,851,867 | Medication for pain relief, constipation, heartburn: IBU |
| ebi-a-GCST90038686 | 2021 | Dönertaş HM | European | 484,598 | 9,587,836 | OA |
| ebi-a-GCST90013881 | 2021 | Mbatchou J | European | 407,746 | 11,039,204 | OA (Firth correction) |
| ebi-a-GCST007091 | 2019 | Tachmazidou I | European | 393,873 | 29,771,219 | OA (hip) |
| ebi-a-GCST005814 | 2018 | Zengini E | European | 50,508 | 15,845,511 | OA (hospital diagnosed) |
| Outcomes | MR Method | SNPs | Beta | OR | Association | Cochran’s Q Statistic | I2 | Heterogeneity | Pleiotropy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | |||||||
| GCST90038686 | IVW | 41 | 0.101 | 1.107 | 0 | 48.75 | 0.179 | 0.162 | |
| MR–Egger | 41 | 0.04 | 1.04 | 0.667 | 48.137 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.485 | |
| GCST90013881 | IVW | 41 | 1.364 | 3.91 | 0.001 | 57.139 | 0.3 | 0.039 | |
| MR–Egger | 41 | 0.246 | 1.279 | 0.842 | 55.822 | 0.301 | 0.039 | 0.343 | |
| GCST007091 | IVW | 43 | 2.01 | 7.462 | 0.025 | 158.762 | 0.735 | 0 | |
| MR–Egger | 43 | 1.022 | 2.778 | 0.726 | 158.265 | 0.741 | 0 | 0.721 | |
| GCST005814 | IVW | 41 | 1.618 | 5.042 | 0.037 | 58.671 | 0.318 | 0.029 | |
| MR–Egger | 41 | 1.699 | 5.47 | 0.492 | 58.669 | 0.335 | 0.022 | 0.972 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jian, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Hashemolhosseini, S. Exploring the Causal Relationship between Ibuprofen Use and Osteoarthritis Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Biology 2024, 13, 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090748
Jian Y, Lyu Y, Hashemolhosseini S. Exploring the Causal Relationship between Ibuprofen Use and Osteoarthritis Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Biology. 2024; 13(9):748. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090748
Chicago/Turabian StyleJian, Yongzhi, Yanmin Lyu, and Said Hashemolhosseini. 2024. "Exploring the Causal Relationship between Ibuprofen Use and Osteoarthritis Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study" Biology 13, no. 9: 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090748
APA StyleJian, Y., Lyu, Y., & Hashemolhosseini, S. (2024). Exploring the Causal Relationship between Ibuprofen Use and Osteoarthritis Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Biology, 13(9), 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090748







