MeHA: A Computational Framework in Revealing the Genetic Basis of Animal Mental Health Traits Under an Intensive Farming System—A Case Study in Pigs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
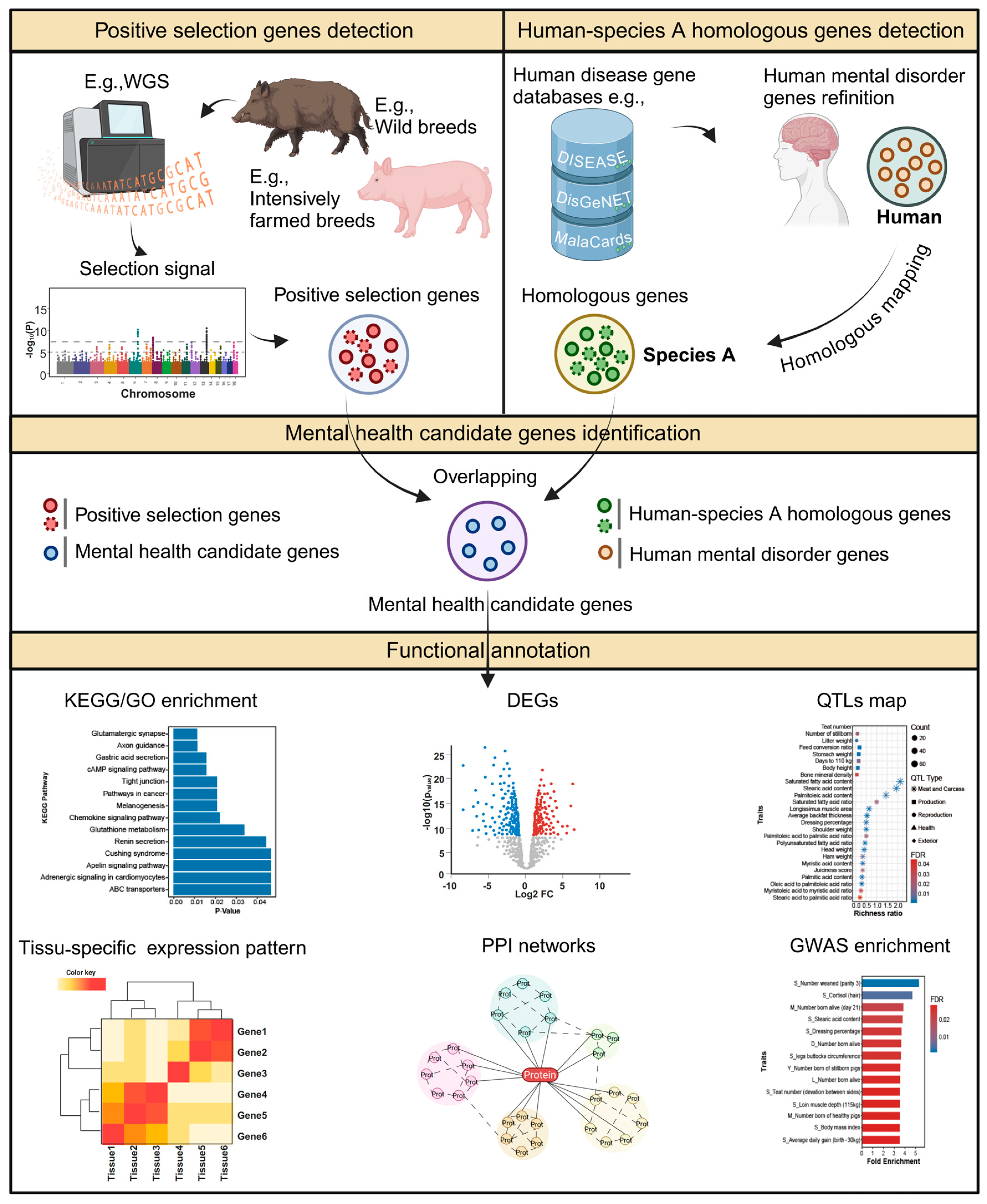
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Genotypes
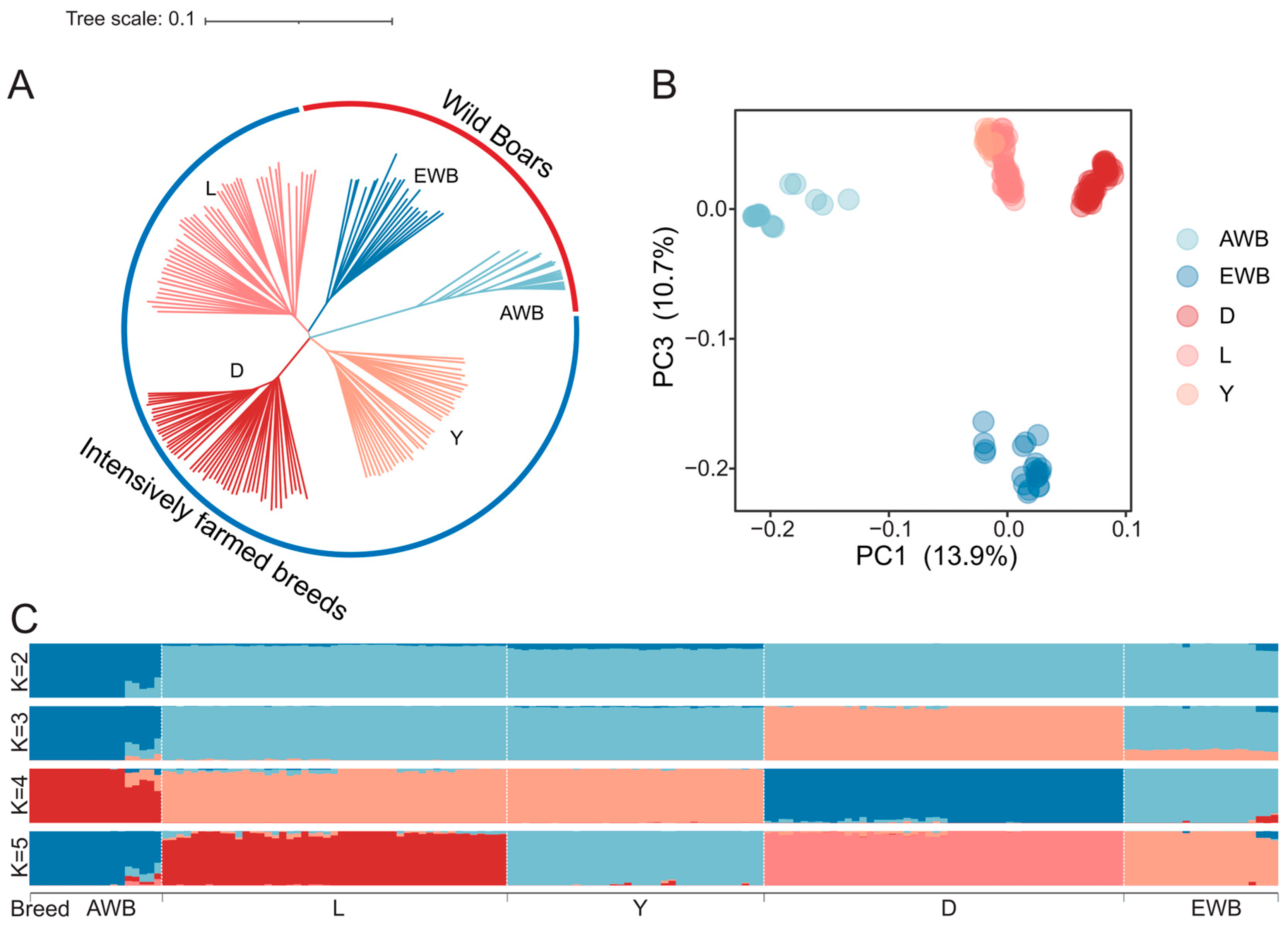
2.2. Population Genetic Structure Analysis
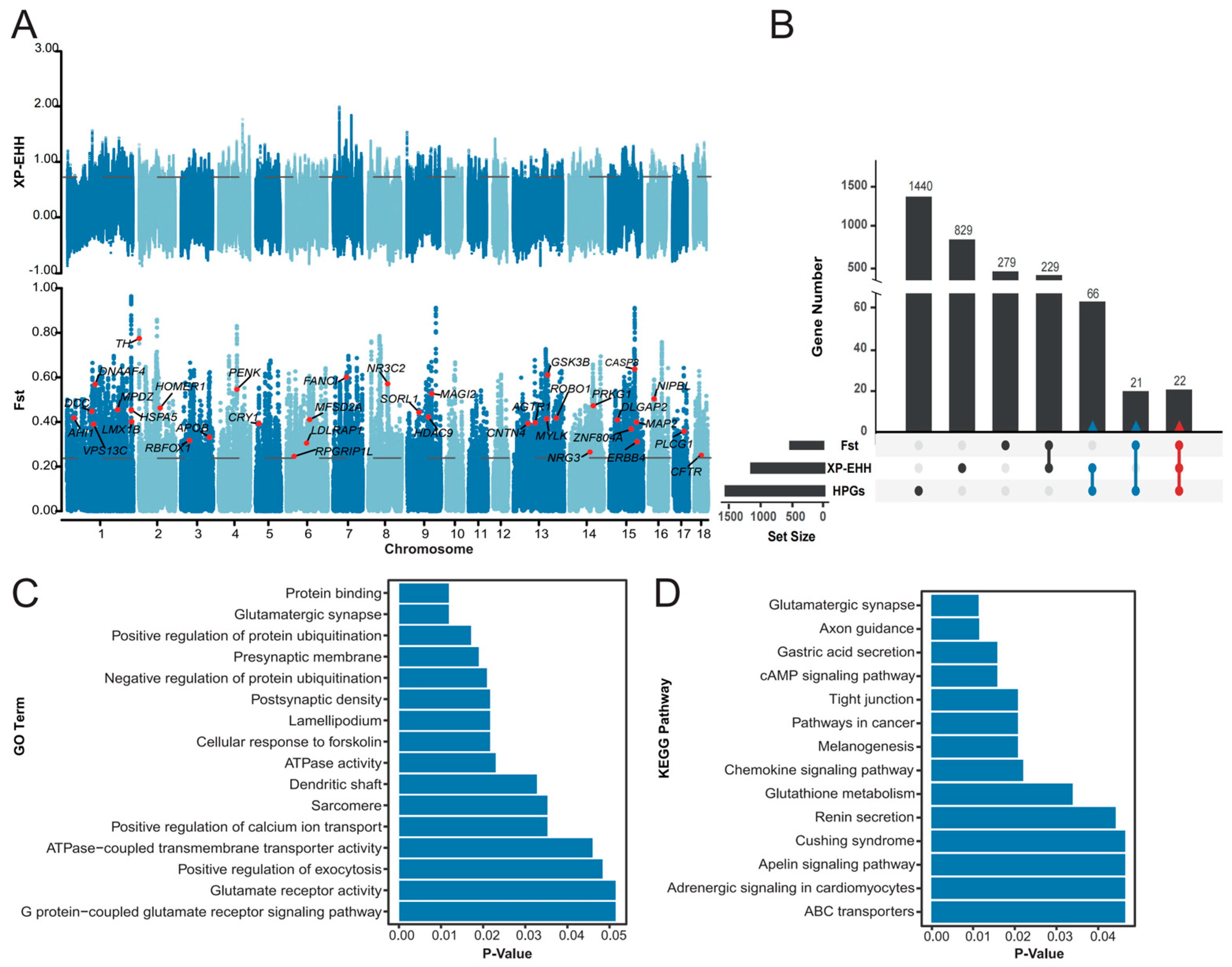
2.3. Signal Detection
2.3.1. Fst Test
2.3.2. XP-EHH Test
2.4. Putative Candidate Genes Under Selection
2.5. PMH Candidate Gene Identification
2.6. Characterization of PMH Candidate Genes
2.6.1. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.6.2. Tissue-Specific Gene Expression Analysis
2.6.3. QTL Mapping Analysis
2.6.4. GWAS Signal Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Genetic Structure
3.2. Candidate Genes Under Selection
3.3. PMH Candidate Genes
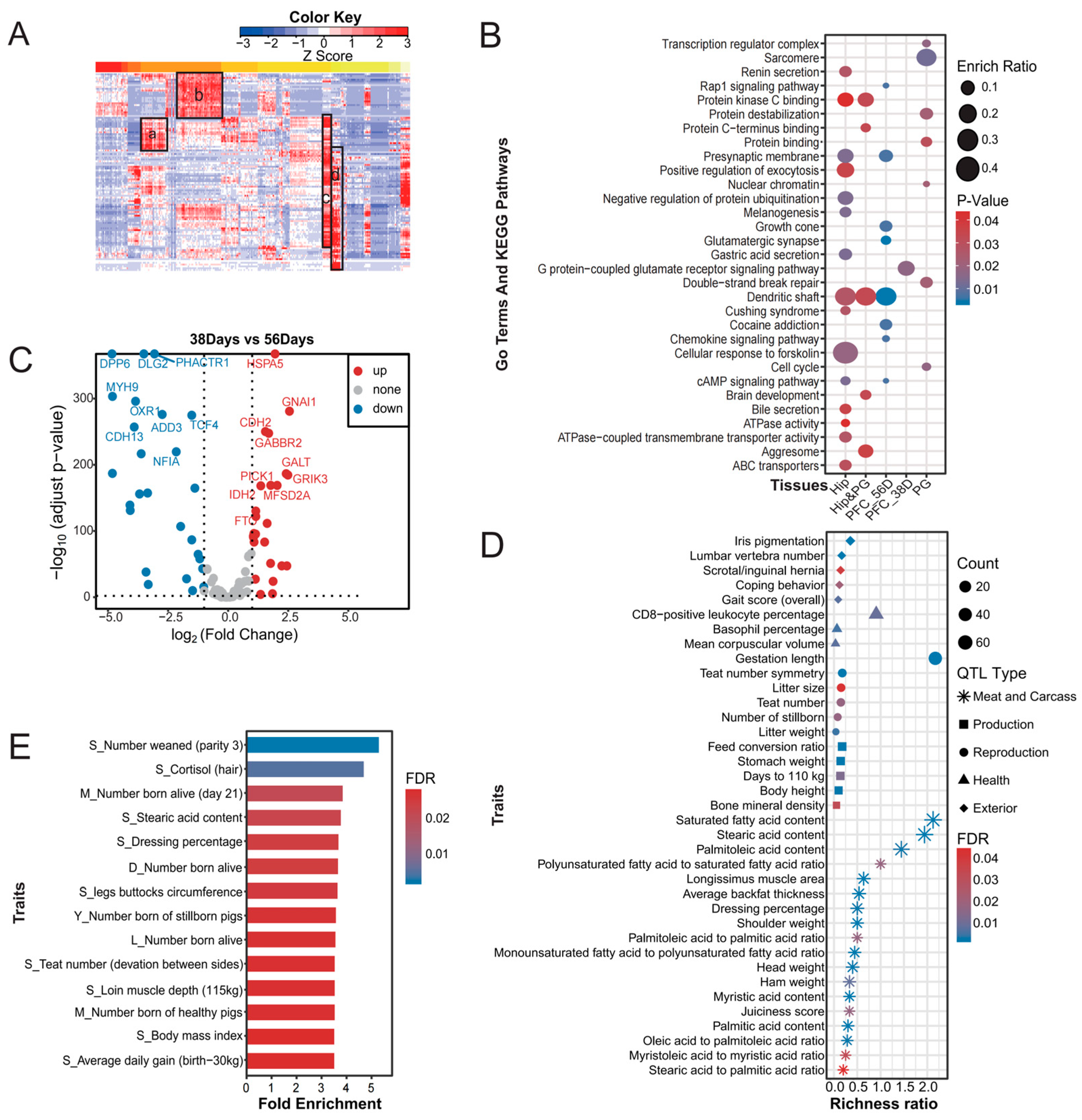
3.4. KEGG Pathways and GO Biological Processes Enriched with PMH Candidate Genes
3.5. Disease Enrichment Analysis of PMH Candidate Genes and Eliminated Genes
3.6. Clustered Expression of PMH Candidate Genes in Different Pig Brain Tissues
3.7. Correlations Between the PMH Candidate Genes and Economic Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AWB | Asian wild boars |
| D | Duroc |
| EWB | European wild boar |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| IBS | Identical-by-state |
| IFBs | Intensively farmed breeds |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| L | Landrace |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| MAF | Minor allele frequency |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PMH | Pig mental health |
| PPI | Protein‒protein interaction |
| PSD | Postsynaptic density |
| QTL | Quantitative Trait Locus |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| Y | Yorkshire |
References
- Zhang, G. Feeding and management strategies for sire pigs in intensive pig farms. Anim. Husb. Vet. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2023, 6, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Roche, J.; Berry, D.; Bryant, A.; Burke, C.; Butler, S.; Dillon, P.; Donaghy, D.; Horan, B.; Macdonald, K.; Macmillan, K. A 100-year review: A century of change in temperate grazing dairy systems. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10189–10233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, B.; Li, K. Analysis of genome-wide copy number variations in Chinese indigenous and western pig breeds by 60 K SNP genotyping arrays. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, M. Transforming Intensive Animal Production: Challenges and Opportunities for Farm Animal Welfare in the European Union. Animals 2022, 12, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornale, P.; Macchi, E.; Miretti, S.; Renna, M.; Lussiana, C.; Perona, G.; Mimosi, A. Effects of stocking density and environmental enrichment on behavior and fecal corticosteroid levels of pigs under commercial farm conditions. J. Vet. Behav. 2015, 10, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.; Nienaber, J.; Christenson, R.; Manak, R.; DeShazer, J.; Hahn, G. Peripheral concentrations of cortisol as an indicator of stress in the pig. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1985, 46, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Z. Porcine Stress Syndrome (PSS). Anim. Husb. Vet. Sci. 1988, 4, 181–182. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteford, H.A.; Degenhardt, L.; Rehm, J.; Baxter, A.J.; Ferrari, A.J.; Erskine, H.E.; Charlson, F.J.; Norman, R.E.; Flaxman, A.D.; Johns, N. Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2013, 382, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Belkin, G.S.; Chockalingam, A.; Cooper, J.; Saxena, S.; Unützer, J. Grand challenges: Integrating mental health services into priority health care platforms. PloS Med. 2013, 10, e1001448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Europe, W. Policies and Practices for Mental Health in Europe–Meeting the Challenges. 2008. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0018/103536/fs_mh_10oct2008e.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2024).
- Carter, J.; Hidreth, H.; Knutson, A. Mental health and the American Psychological Association. Ad hoc Planning Group on the Role of the APA in Mental Health Programs and Research. Am. Psychol. 1959, 14, 820–825. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, M. Mental Health Promotion: A Lifespan Approach. Ment. Health Pract. 2007, 11, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.M. What is mental health? Who are mentally healthy? Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 1960, 6, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sells, S.B. The Definition and Measurement of Mental Health: SB Sells; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, R.M.; Lau-Zhu, A.; Henson, R.N.; Holmes, E.A. Multiple memory systems, multiple time points: How science can inform treatment to control the expression of unwanted emotional memories. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumake, J.; Jones, C.; Auchter, A.; Monfils, M.-H. Data-driven criteria to assess fear remission and phenotypic variability of extinction in rats. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheulin, K.M.; Jurgielewicz, B.J.; Spellicy, S.E.; Waters, E.S.; Baker, E.W.; Kinder, H.A.; Simchick, G.A.; Sneed, S.E.; Grimes, J.A.; Zhao, Q. Exploring the predictive value of lesion topology on motor function outcomes in a porcine ischemic stroke model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, X.; Ming, X. Habits, hazards, and control strategies of wild boars. Agric. Technol. Equip. 2019, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Sampels, S.; Jonsson, M.; Sandgren, M.; Karlsson, A.; Segerkvist, K.A. Sustainable Delicacy: Variation in Quality and Sensory Aspects in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Meat and Comparison to Pork Meat—A Case Study. Foods 2023, 12, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Burgos-Paz, W.; Manunza, A.; Amills, M. Mining the pig genome to investigate the domestication process. Heredity 2014, 113, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, S.; Buglione, M.; Maselli, V.; Troiano, C.; Larson, G.; Frantz, L.; Manin, A.; Ricca, E.; Baccigalupi, L.; Wright, D. Population genomic, olfactory, dietary, and gut microbiota analyses demonstrate the unique evolutionary trajectory of feral pigs. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 220–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, L.A.; Haile, J.; Lin, A.T.; Scheu, A.; Geörg, C.; Benecke, N.; Alexander, M.; Linderholm, A.; Mullin, V.E.; Daly, K.G. Ancient pigs reveal a near-complete genomic turnover following their introduction to Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17231–17238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovo, S.; Ribani, A.; Muñoz, M.; Alves, E.; Araujo, J.P.; Bozzi, R.; Čandek-Potokar, M.; Charneca, R.; Di Palma, F.; Etherington, G. Whole-genome sequencing of European autochthonous and commercial pig breeds allows the detection of signatures of selection for adaptation of genetic resources to different breeding and production systems. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2020, 52, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.-F. Genome-wide detection of selection signatures in Duroc revealed candidate genes relating to growth and meat quality. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020, 10, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupová, Z.; Krupa, E.; Michaličková, M.; Wolfová, M.; Kasarda, R. Economic values for health and feed efficiency traits of dual-purpose cattle in marginal areas. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sun, J.; Cao, C.; Wu, F.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Sun, H.; Guo, L. PHARP: A pig haplotype reference panel for genotype imputation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Lange, K. Enhancements to the ADMIXTURE algorithm for individual ancestry estimation. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, B.S.; Hill, W.G. Estimating F-statistics. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2002, 36, 721–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, P.C.; Varilly, P.; Fry, B.; Lohmueller, J.; Hostetter, E.; Cotsapas, C.; Xie, X.; Byrne, E.H.; McCarroll, S.A.; Gaudet, R. Genome-wide detection and characterization of positive selection in human populations. Nature 2007, 449, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Coop, G.; Novembre, J.; Kudaravalli, S.; Li, J.Z.; Absher, D.; Srinivasan, B.S.; Barsh, G.S.; Myers, R.M.; Feldman, M.W. Signals of recent positive selection in a worldwide sample of human populations. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpiech, Z.A.; Hernandez, R.D. selscan: An efficient multithreaded program to perform EHH-based scans for positive selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2824–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Gao, Y.; Yin, H.; Bai, Z.; Liu, S.; Zeng, H.; Consortium, P.; Bai, L.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, B. A compendium of genetic regulatory effects across pig tissues. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warr, A.; Affara, N.; Aken, B.; Beiki, H.; Bickhart, D.M.; Billis, K.; Chow, W.; Eory, L.; Finlayson, H.A.; Flicek, P. An improved pig reference genome sequence to enable pig genetics and genomics research. Gigascience 2020, 9, giaa051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordovez, F.J.A.; McMahon, F.J. The genetics of bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Parker, N.; Karadag, N.; Koch, E.; Hindley, G.; Icick, R.; Shadrin, A.; O’Connell, K.S.; Bjella, T.; Bahrami, S. The relationship between cannabis use, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder: A genetically informed study. Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, J.B.; Genro, J.P.; Bastos, C.R.; Ghisleni, G.; Tovo-Rodrigues, L. The role of CLOCK gene in psychiatric disorders: Evidence from human and animal research. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2018, 177, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Luo, H.; Huo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, J. KOBAS-i: Intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W317–W325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; Schiettecatte, F.; Scott, A.F.; Hamosh, A. OMIM. org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D789–D798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollis, E.; Mosaku, A.; Abid, A.; Buniello, A.; Cerezo, M.; Gil, L.; Groza, T.; Güneş, O.; Hall, P.; Hayhurst, J. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog: Knowledgebase and deposition resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D977–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The ensembl variant effect predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-L.; Dracheva, S.; Jang, W.; Maglott, D.; Bastiaansen, J.; Rothschild, M.F.; Reecy, J.M. A QTL resource and comparison tool for pigs: PigQTLDB. Mamm. Genome 2005, 16, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.; Teng, J.; Xu, Z.; Cai, X.; Zhong, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y. PigBiobank: A valuable resource for understanding genetic and biological mechanisms of diverse complex traits in pigs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D980–D989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Han, H.; Wei, R.; Zhao, W.; Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Hou, X.; Wang, J.; He, Y. Cross-ancestry meta-genome-wide association studies provide insights to the understanding of semen traits in pigs. Animal 2024, 18, 101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.M.; Bush, S.J.; Summers, K.M.; Hume, D.A.; Lawrence, A.B. Environmentally enriched pigs have transcriptional profiles consistent with neuroprotective effects and reduced microglial activity. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 350, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, A.; Dai, D.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.-F.; Xiong, L. Role of the GRP/GRPR system in regulating brain functions. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 3588–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetre, P.; Lindberg, J.; Leonard, J.A.; Olsson, K.; Pettersson, U.; Ellegren, H.; Bergström, T.F.; Vila, C.; Jazin, E. From wild wolf to domestic dog: Gene expression changes in the brain. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 126, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peremans, K.; Audenaert, K.; Hoybergs, Y.; Otte, A.; Goethals, I.; Gielen, I.; Blankaert, P.; Vervaet, M.; Van Heeringen, C.; Dierckx, R. The effect of citalopram hydrobromide on 5-HT 2A receptors in the impulsive–aggressive dog, as measured with 123 I-5-I-R91150 SPECT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2005, 32, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, E.; Ratnakumar, A.; Arendt, M.-L.; Maqbool, K.; Webster, M.T.; Perloski, M.; Liberg, O.; Arnemo, J.M.; Hedhammar, Å.; Lindblad-Toh, K. The genomic signature of dog domestication reveals adaptation to a starch-rich diet. Nature 2013, 495, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ZHANG, T.; Qing-Min, R.; Yong-Yin, H.; Jin-Tai, C.; Hai-Ying, L.; Yu-Long, L. Association of SCN2A, ABCB1 and CYP2C19* 3 with genetic susceptibility to major depressive disorder. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 56, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Khan, R.A.W.; He, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Shen, J.; Song, Z.; Li, W.; Wen, Z. The GSK3B gene confers risk for both major depressive disorder and schizophrenia in the Han Chinese population. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 185, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xiu, J.; Zhu, C.; Meng, K.; Li, C.; Han, R.; Du, T.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, R. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein regulates RNA methylation associated with depression-like behavior in mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Dong, Z.; Xing, G.; Luo, B.; Gao, N.; Zou, W.-J.; Zhao, K. The laterodorsal tegmentum-ventral tegmental area circuit controls depression-like behaviors by activating ErbB4 in DA neurons. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1027–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Anttila, V.; Won, H.; Feng, Y.-C.A.; Rosenthal, J.; Zhu, Z.; Tucker-Drob, E.M.; Nivard, M.G.; Grotzinger, A.D.; Posthuma, D. Genomic relationships, novel loci, and pleiotropic mechanisms across eight psychiatric disorders. Cell 2019, 179, 1469–1482.e1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombieri, C.; Corsi, A.; Trabetti, E.; Ruggiero, A.; Marchetto, G.; Vattemi, G.; Valenti, M.T.; Zipeto, D.; Romanelli, M.G. Advanced Cellular Models for Rare Disease Study: Exploring Neural, Muscle and Skeletal Organoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupin, L.; Psilodimitrakopoulos, S.; Celsi, F.; Papadimitriou, L.; Ranella, A.; Crovella, S.; Ricci, G.; Stratakis, E.; Pascolo, L. Upside-down preference in the forskolin-induced in vitro differentiation of 50B11 sensory neurons: A morphological investigation by label-free non-linear microscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Ren, B. Glutamate receptors and signal transduction in learning and memory. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliss, T.V.; Lømo, T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. 1973, 232, 331–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. The molecular basis of G protein–coupled receptor activation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.A. Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 87–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Südhof, T.C. Towards an understanding of synapse formation. Neuron 2018, 100, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telias, M.; Kuznitsov-Yanovsky, L.; Segal, M.; Ben-Yosef, D. Functional deficiencies in fragile X neurons derived from human embryonic stem cells. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 15295–15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, M.J.; Rivet, J.-M.; Gobert, A. The frontal cortex as a network hub controlling mood and cognition: Probing its neurochemical substrates for improved therapy of psychiatric and neurological disorders. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 1099–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Kong, Z.; Deng, H.; Lai, W.; Ye, C.; Guan, F.; Li, P.; Zhao, M. Common gray matter loss in the frontal cortex in patients with methamphetamine-associated psychosis and schizophrenia. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 36, 103259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, M.; Yildirim, H.; Yilmaz, S.; Caglar, N.; Mermi, O.; Korkmaz, S.; Akaslan, U.; Gurok, M.G.; Kekilli, Y.; Turkcapar, H. Orbito-frontal cortex and thalamus volumes in the patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder before and after cognitive behavioral therapy. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 2018, 53, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrila, A.S.; Hakkarainen, A.; Castaneda, A.; Paunio, T.; Marttunen, M.; Lundbom, N. Frontal cortex Myo-inositol is associated with sleep and depression in adolescents: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Neuropsychobiology 2017, 75, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labonne, J.D.; Shen, Y.; Kong, I.-K.; Diamond, M.P.; Layman, L.C.; Kim, H.-G. Comparative deletion mapping at 1p31. 3-p32. 2 implies NFIA responsible for intellectual disability coupled with macrocephaly and the presence of several other genes for syndromic intellectual disability. Mol. Cytogenet. 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhail, F.M.; Lose, E.J.; Robin, N.H.; Descartes, M.D.; Rutledge, K.D.; Rutledge, S.L.; Korf, B.R.; Carroll, A.J. Clinically relevant single gene or intragenic deletions encompassing critical neurodevelopmental genes in patients with developmental delay, mental retardation, and/or autism spectrum disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2011, 155, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, O.; Selten, M.M.; Sich, S.; Popp, S.; Bacmeister, L.; Amendola, E.; Negwer, M.; Schubert, D.; Proft, F.; Kiser, D. Cadherin-13, a risk gene for ADHD and comorbid disorders, impacts GABAergic function in hippocampus and cognition. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, J.R.; Szeto, R.A.; Carvalho, V.M.; Muotri, A.R.; Papes, F. Transcription factor 4 and its association with psychiatric disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesius, S.; O’Donnell, C.; Waldron, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Dwyer, D.M.; Wilkinson, L.S.; Hall, J.; Robinson, E.S.; Mellor, J.R. Reduced expression of the psychiatric risk gene DLG2 (PSD93) impairs hippocampal synaptic integration and plasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, L.; Kim, C.-H.; Takamiya, K.; Yu, Y.; Huganir, R.L. Developmental regulation of protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) function in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21784–21789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barki, M.; Xue, H. GABRB2, a key player in neuropsychiatric disorders and beyond. Gene 2022, 809, 146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.M.; Gardner, J.F.; van Jaarsveld, R.H.; de Lange, I.M.; van der Smagt, J.J.; Wilson, G.N.; Dubbs, H.; Goldberg, E.M.; Zitano, L.; Bupp, C. Variants in GNAI1 cause a syndrome associated with variable features including developmental delay, seizures, and hypotonia. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Chao, M.; Cao, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Wnt signaling regulates MFSD2A-dependent drug delivery through endothelial transcytosis in glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 25, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, M.; Lau, B.W.-M.; Li, Y. SHANK family on stem cell fate and development. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltokhi, A.; Gonzalez-Lozano, M.A.; Oettl, L.-L.; Rozov, A.; Pitzer, C.; Röth, R.; Berkel, S.; Hüser, M.; Harten, A.; Kelsch, W. Imbalanced post-and extrasynaptic SHANK2A functions during development affect social behavior in SHANK2-mediated neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6482–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsicker, C.; Cristian, F.-B.; von Hahn, M.; Eckstein, V.; Rappold, G.A.; Berkel, S. SHANK2 mutations impair apoptosis, proliferation and neurite outgrowth during early neuronal differentiation in SH-SY5Y cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Hernan, R.; Marcogliese, P.C.; Huang, Y.; Gertler, T.S.; Akcaboy, M.; Liu, S.; Chung, H.-l.; Pan, X.; Sun, X. Loss-of-function variants in TIAM1 are associated with developmental delay, intellectual disability, and seizures. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianferrara, T.; Cescon, E.; Grieco, I.; Spalluto, G.; Federico, S. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β involvement in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 4631–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameister, T.; Puppe, B.; Tuchscherer, M.; Kanitz, E. Einfluss des Absetzalters von Ferkeln auf verhaltensbiologische und physiologische Reaktionen—Eine Literaturübersicht. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2010, 123, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Dziurkowska, E.; Wesolowski, M. Cortisol as a biomarker of mental disorder severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, E.K.; Quinn, M.E.; Tavernier, R.; McQuillan, M.T.; Dahlke, K.A.; Gilbert, K.E. Diurnal cortisol slopes and mental and physical health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 83, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Marle-Köster, E.; Visser, C. Unintended consequences of selection for increased production on the health and welfare of livestock. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2021, 64, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Q.; Ye, X.; Gu, J.; Cao, C.; et al. MeHA: A Computational Framework in Revealing the Genetic Basis of Animal Mental Health Traits Under an Intensive Farming System—A Case Study in Pigs. Biology 2024, 13, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100843
Jiang J, Xu L, Zhuang Y, Wei X, Zhang Z, Zhao W, Wang Q, Ye X, Gu J, Cao C, et al. MeHA: A Computational Framework in Revealing the Genetic Basis of Animal Mental Health Traits Under an Intensive Farming System—A Case Study in Pigs. Biology. 2024; 13(10):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100843
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Jinyun, Lingyao Xu, Yizheng Zhuang, Xingyu Wei, Zhenyang Zhang, Wei Zhao, Qingyu Wang, Xiaowei Ye, Jiamin Gu, Caiyun Cao, and et al. 2024. "MeHA: A Computational Framework in Revealing the Genetic Basis of Animal Mental Health Traits Under an Intensive Farming System—A Case Study in Pigs" Biology 13, no. 10: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100843
APA StyleJiang, J., Xu, L., Zhuang, Y., Wei, X., Zhang, Z., Zhao, W., Wang, Q., Ye, X., Gu, J., Cao, C., Sun, J., He, K., Zhang, Z., Wang, Q., Pan, Y., & Wang, Z. (2024). MeHA: A Computational Framework in Revealing the Genetic Basis of Animal Mental Health Traits Under an Intensive Farming System—A Case Study in Pigs. Biology, 13(10), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100843




