Measurement of Salivary Cortisol in Two New World Primate Species
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
2.2. Saliva Collection
2.3. Salivary Cortisol Analyses
2.4. Biochemical Validation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
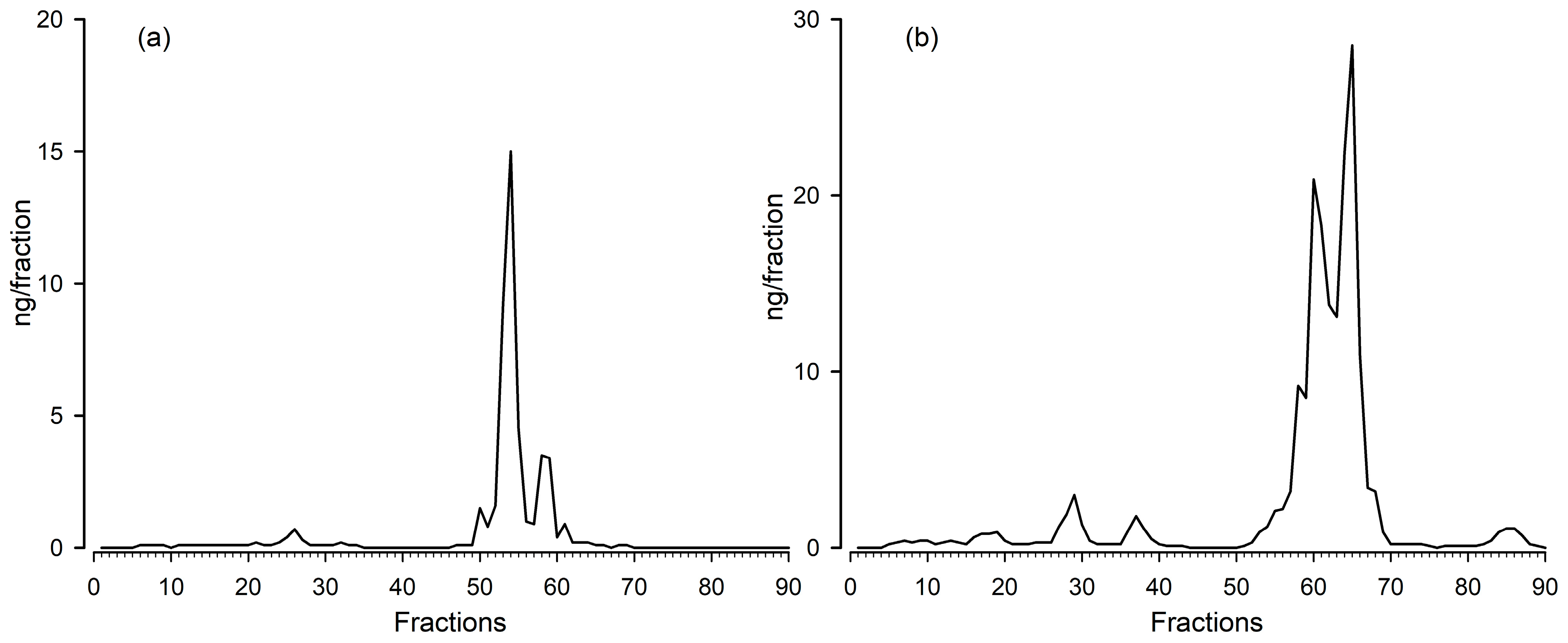
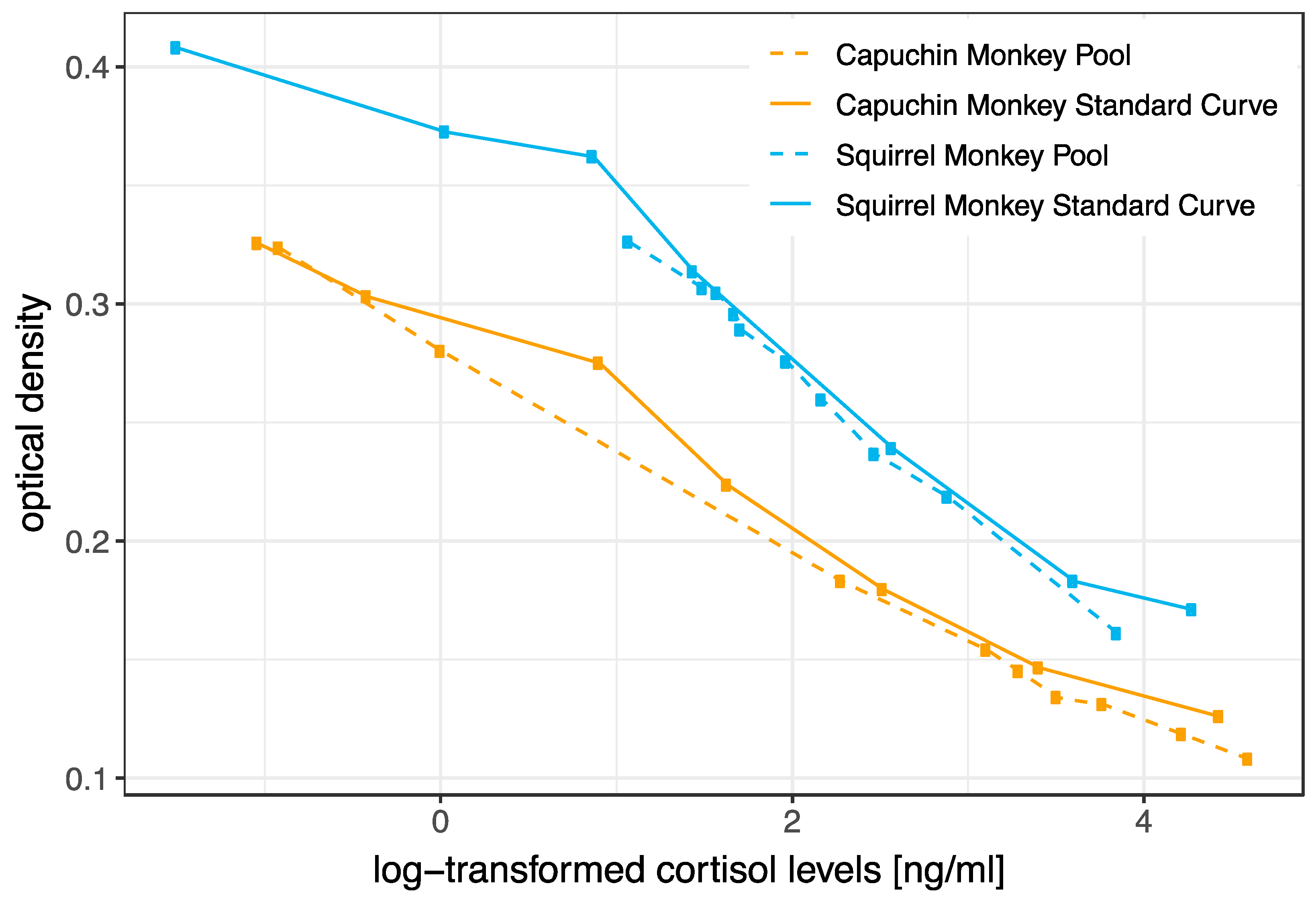
3.1. Biochemical Validation (HPLC and Parallelism)
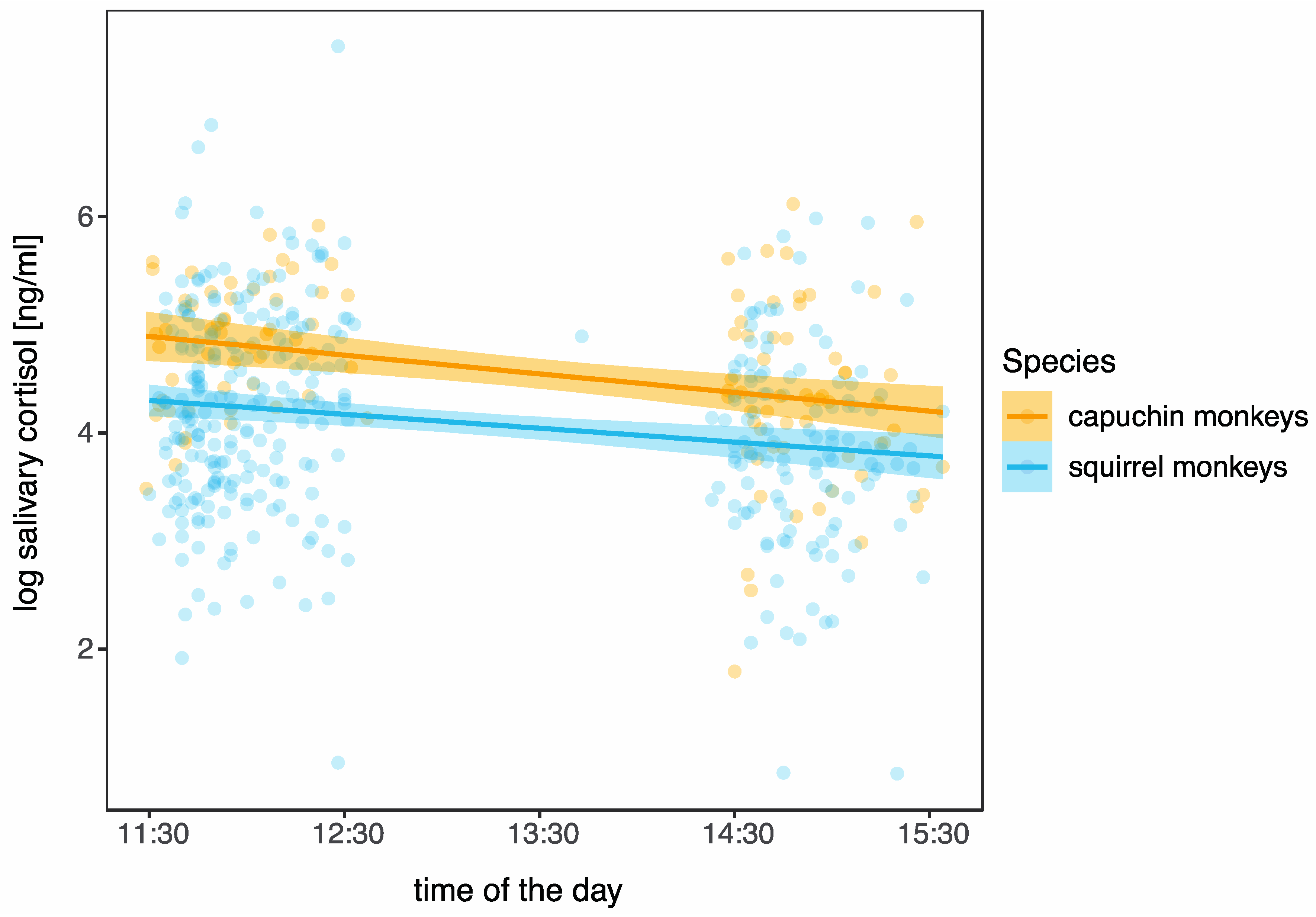
3.2. Daily Pattern in Cortisol
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hadley, M.E. Endocrinology; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-13-080356-6. [Google Scholar]
- Angelier, F.; Wingfield, J.C. Importance of the Glucocorticoid Stress Response in a Changing World: Theory, Hypotheses and Perspectives. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 190, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M.; Romero, L.M.; Munck, A.U. How Do Glucocorticoids Influence Stress Responses? Integrating Permissive, Suppressive, Stimulatory, and Preparative Actions. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 55–89. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, K.; Drevets, W.; Schulkin, J. Glucocorticoid Regulation of Diverse Cognitive Functions in Normal and Pathological Emotional States. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2003, 27, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatsoreos, I.N.; McEwen, B.S. Stress and Allostasis. In Handbook of Behavioral Medicine: Methods and Applications; Steptoe, A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 649–658. ISBN 978-0-387-09488-5. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, L.M.; Beattie, U.K. Common Myths of Glucocorticoid Function in Ecology and Conservation. J. Exp. Zool. Part. A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 337, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, L.M.; Wingfield, J.C. Tempests, Poxes, Predators, and People: Stress in Wild Animals and How They Cope; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. vii, 614. ISBN 978-0-19-536669-3. [Google Scholar]
- Behringer, V.; Berghänel, A.; Deschner, T.; Lee, S.M.; Fruth, B.; Hohmann, G. Transition to Siblinghood Causes a Substantial and Long-Lasting Increase in Urinary Cortisol Levels in Wild Bonobos. eLife 2022, 11, e77227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespi, E.J.; Williams, T.D.; Jessop, T.S.; Delehanty, B. Life History and the Ecology of Stress: How Do Glucocorticoid Hormones Influence Life-History Variation in Animals? Funct. Ecol. 2013, 27, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landys, M.M.; Ramenofsky, M.; Wingfield, J.C. Actions of Glucocorticoids at a Seasonal Baseline as Compared to Stress-Related Levels in the Regulation of Periodic Life Processes. General. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 148, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.; Stalder, T.; Jarczok, M.; Almeida, D.M.; Badrick, E.; Bartels, M.; Boomsma, D.I.; Coe, C.L.; Dekker, M.C.J.; Donzella, B.; et al. The CIRCORT Database: Reference Ranges and Seasonal Changes in Diurnal Salivary Cortisol Derived from a Meta-Dataset Comprised of 15 Field Studies. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 73, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, C.R.; Tilbrook, A.J. INVITED REVIEW: The Usefulness of Measuring Glucocorticoids for Assessing Animal Welfare. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, C.; Hellhammer, D.H. Salivary Cortisol in Psychobiological Research: An Overview. Neuropsychobiology 2008, 22, 150–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruessner, J.C.; Wolf, O.T.; Hellhammer, D.H.; Buske-Kirschbaum, A.; von Auer, K.; Jobst, S.; Kaspers, F.; Kirschbaum, C. Free Cortisol Levels after Awakening: A Reliable Biological Marker for the Assessment of Adrenocortical Activity. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.M.; Murphy, M.L.M.; Adam, E.K.; Chen, E.; Miller, G.E. How Stable Are Diurnal Cortisol Activity Indices in Healthy Individuals? Evidence from Three Multi-Wave Studies. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 39, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzman, E.D.; Fukushima, D.; Nogeire, C.; Roffwarg, H.; Gallagher, T.F.; Hellman, L. Twenty-Four Hour Pattern of the Episodic Secretion of Cortisol in Normal Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1971, 33, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohák, Z.; Szabó, F.; Beckers, J.-F.; Melo de Sousa, N.; Kutasi, O.; Nagy, K.; Szenci, O. Monitoring the Circadian Rhythm of Serum and Salivary Cortisol Concentrations in the Horse. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2013, 45, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Uchida, S.; Ueda, K.; Tobayama, T.; Katsumata, E.; Yoshioka, M.; Aida, K. Diurnal and Annual Changes in Serum Cortisol Concentrations in Indo-Pacific Bottlenose Dolphins Tursiops Aduncus and Killer Whales Orcinus Orca. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2003, 132, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.L.; Kersey, D.C.; Freeman, E.W.; Wagener, T. Assessment of Diurnal Urinary Cortisol Excretion in Asian and African Elephants Using Different Endocrine Methods. Zoo. Biol. 2010, 29, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verspeek, J.; Behringer, V.; Laméris, D.W.; Murtagh, R.; Salas, M.; Staes, N.; Deschner, T.; Stevens, J.M.G. Time-Lag of Urinary and Salivary Cortisol Response after a Psychological Stressor in Bonobos (Pan paniscus). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menargues, A.; Urios, V.; Limiñana, R.; Mauri, M. Circadian Rhythm of Salivary Cortisol in Asian Elephants (Elephas maximus): A Factor to Consider during Welfare Assessment. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2012, 15, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Werken, M.; Booij, S.H.; van der Zwan, J.E.; Simons, M.J.P.; Gordijn, M.C.M.; Beersma, D.G.M. The Biological Clock Modulates the Human Cortisol Response in a Multiplicative Fashion. Chronobiol. Int. 2014, 31, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, R.; Clow, A. Stress, the Cortisol Awakening Response and Cognitive Function. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2020, 150, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hucklebridge, F.; Hussain, T.; Evans, P.; Clow, A. The Diurnal Patterns of the Adrenal Steroids Cortisol and Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in Relation to Awakening. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2005, 30, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madliger, C.L.; Love, O.P.; Hultine, K.R.; Cooke, S.J. The Conservation Physiology Toolbox: Status and Opportunities. Conserv. Physiol. 2018, 6, coy029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, M.J.; Dantzer, B.; Delehanty, B.; Palme, R.; Boonstra, R. Measuring Stress in Wildlife: Techniques for Quantifying Glucocorticoids. Oecologia 2011, 166, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behringer, V.; Stevens, J.M.G.; Sonnweber, R. Salivary Cortisol Reaction Norms in Zoo-Housed Great Apes: Diurnal Slopes and Intercepts as Indicators of Stress Response Quality. Animals 2022, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, M.; Loretto, M.-C.; Sterck, E.H.M.; Bugnyar, T.; Massen, J.J.M. Cooperation with Closely Bonded Individuals Reduces Cortisol Levels in Long-Tailed Macaques. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 191056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.-P.; Rubinow, D.R.; Davis, C.L.; Kling, M.; Post, R.M. Salivary Cortisol: A Practical Method for Evaluation of Adrenal Function. Biol. Psychiatry 1988, 23, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, I.C.; Michell, A.R. Comparison of Cortisol Concentrations in Saliva and Plasma of Dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 1992, 53, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.E.; Keevil, B.; Huhtaniemi, I.T. Mass Spectrometry and Immunoassay: How to Measure Steroid Hormones Today and Tomorrow. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, D1–D12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, V.; Deschner, T. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Physiological Markers in Primates. Horm. Behav. 2017, 91, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heistermann, M. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Endocrine Status in Laboratory Primates: Methods, Guidelines and Applications. Adv. Sci. Res. 2010, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palme, R. Non-Invasive Measurement of Glucocorticoids: Advances and Problems. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 199, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, K.L.; Goldsmith, A.R. Noninvasive Endocrine Data for Behavioural Studies: The Importance of Validation. Anim. Behav. 2004, 67, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palme, R. Measuring Fecal Steroids: Guidelines for Practical Application. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1046, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botía, M.; Escribano, D.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Tecles, F.; López-Arjona, M.; Cerón, J.J. Different Types of Glucocorticoids to Evaluate Stress and Welfare in Animals and Humans: General Concepts and Examples of Combined Use. Metabolites 2023, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palme, R.; Rettenbacher, S.; Touma, C.; El-Bahr, S.M.; Möstl, E. Stress Hormones in Mammals and Birds: Comparative Aspects Regarding Metabolism, Excretion, and Noninvasive Measurement in Fecal Samples. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1040, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, J.P. Field Endocrinology of Nonhuman Primates: Past, Present, and Future. Horm. Behav. 2016, 84, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touma, C.; Palme, R. Measuring Fecal Glucocorticoid Metabolites in Mammals and Birds: The Importance of Validation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1046, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abee, C.R. Squirrel Monkey (Saimiri spp.) Research and Resources. ILAR J. 2000, 41, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragaszy, D.M. Cognition in Squirrel Monkeys A Contemporary Perspective. In Handbook of Squirrel Monkey Research; Rosenblum, L.A., Coe, C.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 55–98. ISBN 978-1-4757-0812-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fragaszy, D.M.; Visalberghi, E.; Fedigan, L.M. The Complete Capuchin: The Biology of the Genus Cebus; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004; ISBN 978-0-521-66768-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lankau, E.W.; Turner, P.V.; Mullan, R.J.; Galland, G.G. Use of Nonhuman Primates in Research in North America. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2014, 53, 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, K.A.; Tukan, A.N.; Rigodanzo, A.D.; Reusch, R.T.; Brasky, K.M.; Meyer, J.S. Quantification of Hair Cortisol Concentration in Common Marmosets (Callithrix Jacchus) and Tufted Capuchins (Cebus Apella). Am. J. Primatol. 2018, 80, e22879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça-Furtado, O.; Izar, P.; Palme, R. Validation of an Enzyme Immunoassay for Measuring Fecal Cortisol Metabolites of Bearded (Sapajus libidinosus) and Black (Sapajus nigritus) Capuchins. Int. J. Primatol. 2017, 38, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, B.C.; Tiddi, B.; Kalbitzer, U.; Visalberghi, E.; Heistermann, M. Methodological Considerations in the Analysis of Fecal Glucocorticoid Metabolites in Tufted Capuchins (Cebus apella). Int. J. Primatol. 2013, 34, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, E.; Kirschbaum, C.; Benisch, D.; Bieser, A. Salivary Cortisol: A Non-Invasive Measure of Hypothalamo-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Activity in the Squirrel Monkey, Saimiri Sciureus. Lab. Anim. 1997, 31, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Tiefenbacher, S.; Platt, D.M.; Spealman, R.D. Role of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis in Reinstatement of Cocaine-Seeking Behavior in Squirrel Monkeys. Psychopharmacology 2003, 168, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Tiefenbacher, S.; Platt, D.M.; Spealman, R.D. Pharmacological Blockade of A2-Adrenoceptors Induces Reinstatement of Cocaine-Seeking Behavior in Squirrel Monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 29, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie-Quirk, S.D.; Miczek, K.A. Social Rank and Social Separation as Determinants of Alcohol Drinking in Squirrel Monkeys. Psychopharmacology 2008, 201, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, D.M.; Rowlett, J.K.; Spealman, R.D. Noradrenergic Mechanisms in Cocaine-Induced Reinstatement of Drug Seeking in Squirrel Monkeys. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiefenbacher, S.; Lee, B.; Meyer, J.S.; Spealman, R.D. Noninvasive Technique for the Repeated Sampling of Salivary Free Cortisol in Awake, Unrestrained Squirrel Monkeys. Am. J. Primatol. 2003, 60, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palme, R.; Möstl, E. Measurement of Cortisol Metabolites in Faeces of Sheep as a Parameter of Cortisol Concentration in Blood. Int. J. Mamm. Biol. 1997, 62, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Farfan, C.; Valenzuela, F.J.; Ebensperger, R.; Méndez, N.; Campino, C.; Richter, H.G.; Valenzuela, G.J.; Serón-Ferré, M. Circadian Cortisol Secretion and Circadian Adrenal Responses to ACTH Are Maintained in Dexamethasone Suppressed Capuchin Monkeys (Cebus apella). Am. J. Primatol. 2008, 70, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, C.L.; Levine, S. Diurnal and Annual Variation of Adrenocortical Activity in the Squirrel Monkey. Am. J. Primatol. 1995, 35, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, R.; Buchanan-Smith, H.M.; Dufour, V.; MacDonald, C.; Whiten, A. Living Together: Behavior and Welfare in Single and Mixed Species Groups of Capuchin (Cebus apella) and Squirrel Monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). Am. J. Primatol. 2010, 72, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keckeis, K.; Lepschy, M.; Schöpper, H.; Moser, L.; Troxler, J.; Palme, R. Hair Cortisol: A Parameter of Chronic Stress? Insights from a Radiometabolism Study in Guinea Pigs. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2012, 182, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. LmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An {R} Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks CA, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781544336473. [Google Scholar]
- Pryce, C.R.; Palme, R.; Feldon, J. Development of Pituitary-Adrenal Endocrine Function in the Marmoset Monkey: Infant Hypercortisolism Is the Norm. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.H.; Squires, W.L. The influence of cortisone on primate malaria. J. Exp. Med. 1951, 94, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, B.J.; Albrecht, E.D.; Pepe, G.J. Effect of Estrogen on the Metabolism of Cortisol and Cortisone in the Baboon Fetus at Midgestation. Biol. Reprod. 1988, 38, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, F.H.; Shannon, I.L. Identification and Significance of Parotid Fluid Corticosteroids. Acta Endocrinol. 1964, 46, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulenberg, P.M.M.; Ross, H.A.; Swinkels, L.M.J.W.; Benraad, T.J. The Effect of Oral Contraceptives on Plasma-Free and Salivary Cortisol and Cortisone. Clin. Chim. Acta 1987, 165, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morineau, G.; Boudi, A.; Barka, A.; Gourmelen, M.; Degeilh, F.; Hardy, N.; Al-Halnak, A.; Soliman, H.; Gosling, J.P.; Julien, R.; et al. Radioimmunoassay of Cortisone in Serum, Urine, and Saliva to Assess the Status of the Cortisol–Cortisone Shuttle. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, S.; Fujitaka, M.; Sakura, N.; Ueda, K. Circadian Rhythms in Plasma Cortisone and Cortisol and the Cortisone/Cortisol Ratio. Clin. Chim. Acta 1997, 266, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrousos, G.P.; Loriaux, D.L.; Tomita, M.; Brandon, D.D.; Renquist, D.; Albertson, B.; Lipsett, M.B. The New World Primates as Animal Models of Glucocorticoid Resistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1986, 196, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, P.J.; Smith, B.J.; Rogerson, F.M. Cortisol Resistance in the New World Revisited. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 15, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.M.; Martínez, M.; Leverett, K.L.; Rossettie, M.S.; Wilson, B.J.; Brosnan, S.F. Anything for a Cheerio: Brown Capuchins (Sapajus [Cebus] Apella) Consistently Coordinate in an Assurance Game for Unequal Payoffs. Am. J. Primatol. 2021, 83, e23321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Salivary Cortisol [ng/mL] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Individuals | Samples | Min. | 1st Qu. | Median | Mean | 3rd Qu. | Max. | |
| Squirrel monkeys | females | 17 | 341 | 2.33 | 33.38 | 61.35 | 96.13 | 119.08 | 1957.52 |
| Capuchin monkeys | males | 8 | 114 | 3.00 | 60.38 | 95.25 | 123.77 | 179.18 | 454.80 |
| Parameter | Estimate | SE | CI | df | t | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Squirrel monkeys | (Intercept) | 5.996 | 0.516 | (4.980, 7.041) | 158.700 | 11.621 | <0.001 | *** |
| time of day | −0.002 | 0.001 | (−0.003, −0.001) | 328.000 | −3.600 | <0.001 | *** | |
| age (in days) | 0.000 | 0.000 | (0.000, 0.000) | 13.140 | −0.739 | |||
| Capuchin monkeys | (Intercept) | 7.313 | 0.666 | (5.978, 8.631) | 68.700 | 10.987 | <0.001 | *** |
| time of day | −0.003 | 0.001 | (−0.004, −0.002) | 104.700 | −4.488 | <0.001 | *** | |
| age (in days) | 0.000 | 0.000 | (−0.001, 0.000) | 7.999 | −0.836 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stocker, M.; O’Sullivan, E.P.; Palme, R.; Millesi, E.; Sonnweber, R. Measurement of Salivary Cortisol in Two New World Primate Species. Biology 2023, 12, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091181
Stocker M, O’Sullivan EP, Palme R, Millesi E, Sonnweber R. Measurement of Salivary Cortisol in Two New World Primate Species. Biology. 2023; 12(9):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091181
Chicago/Turabian StyleStocker, Martina, Eoin P. O’Sullivan, Rupert Palme, Eva Millesi, and Ruth Sonnweber. 2023. "Measurement of Salivary Cortisol in Two New World Primate Species" Biology 12, no. 9: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091181
APA StyleStocker, M., O’Sullivan, E. P., Palme, R., Millesi, E., & Sonnweber, R. (2023). Measurement of Salivary Cortisol in Two New World Primate Species. Biology, 12(9), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091181





