Towards a More Comprehensive Picture of the MicroRNA-23a/b-3p Impact on Impaired Male Fertility
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. In-Silico Prediction of MicroRNA-23a/b-3p Target Genes
2.3. Cloning of MiRNA Expression and 3’UTR Reporter Vector Constructs
2.4. Cell Line and Cell Culture
2.5. Automated Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.6. RNAs Collection and Prepaartion
2.7. cDNA Conversion, and qPCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
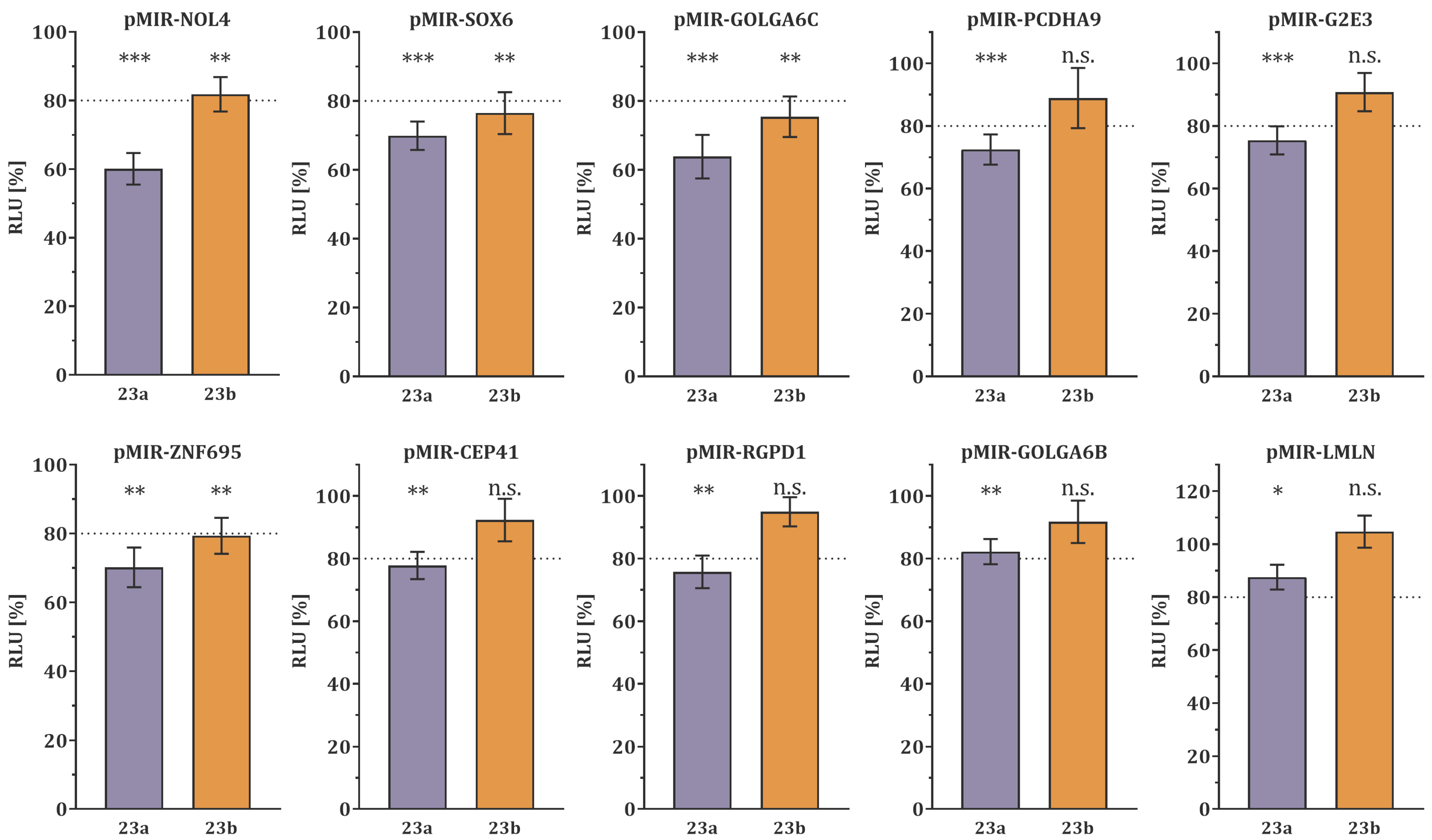
3.1. Target Gene Validation by Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
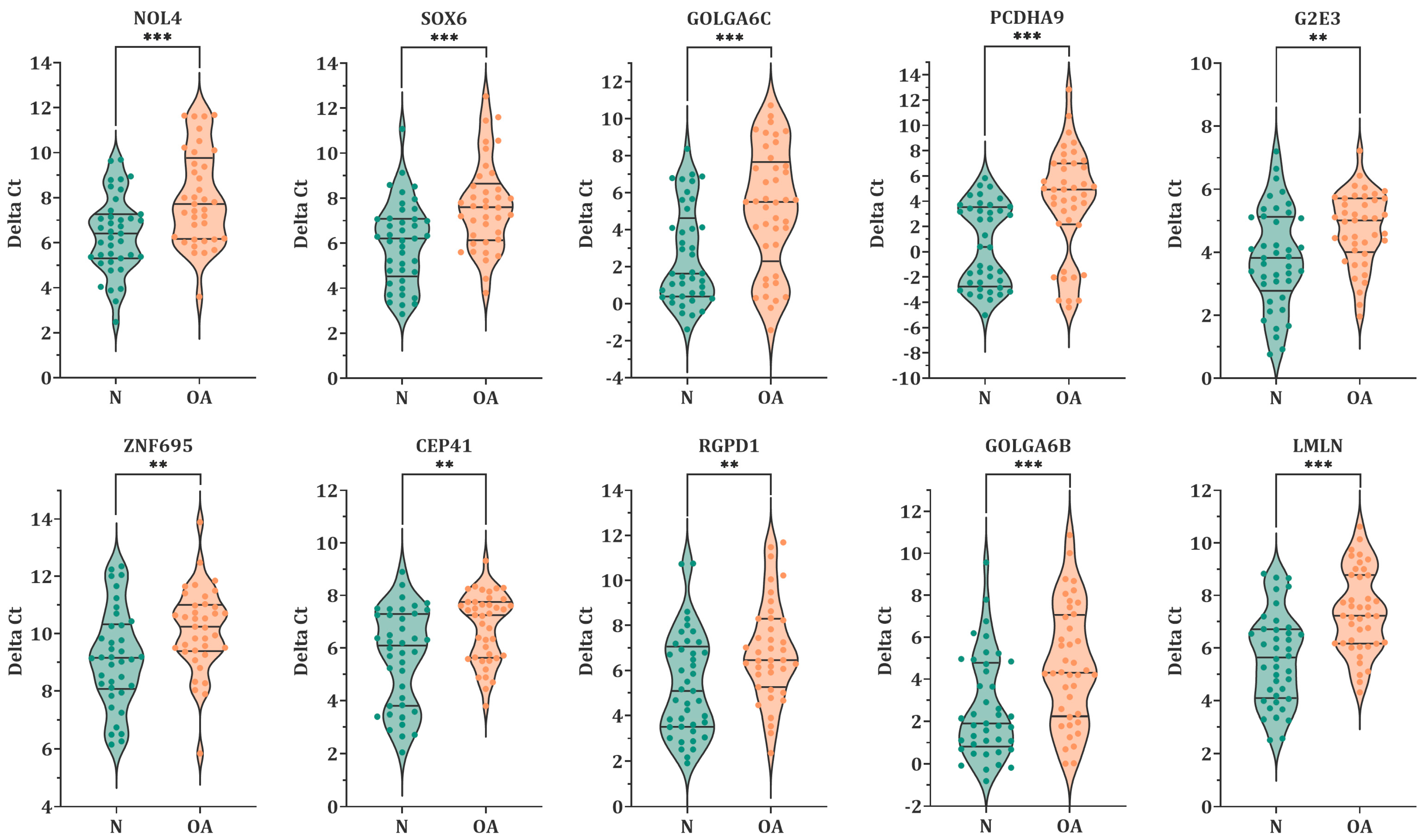
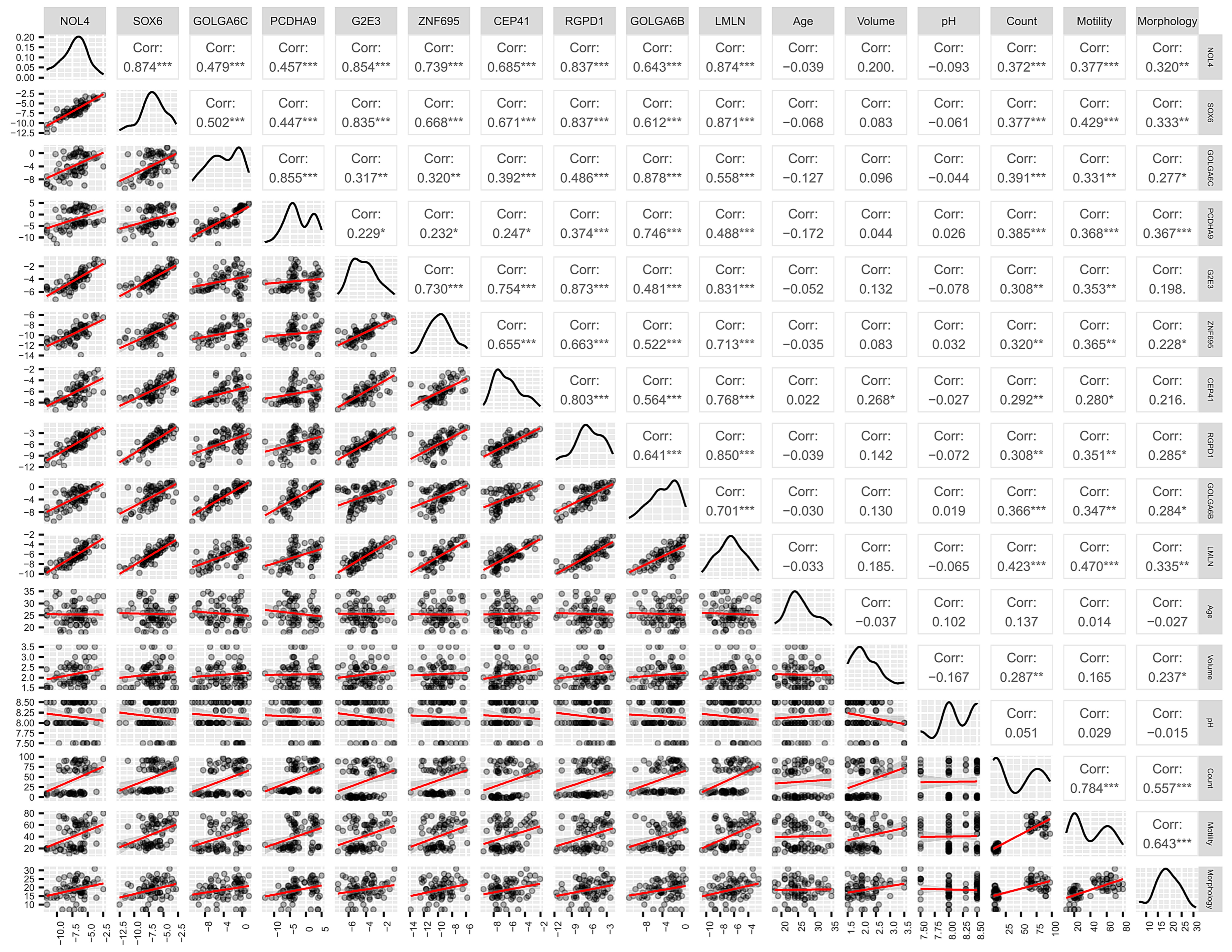
3.2. Expression Level of MiR-23a/23b Target Genes in Spermatozoa by RT-qPCR
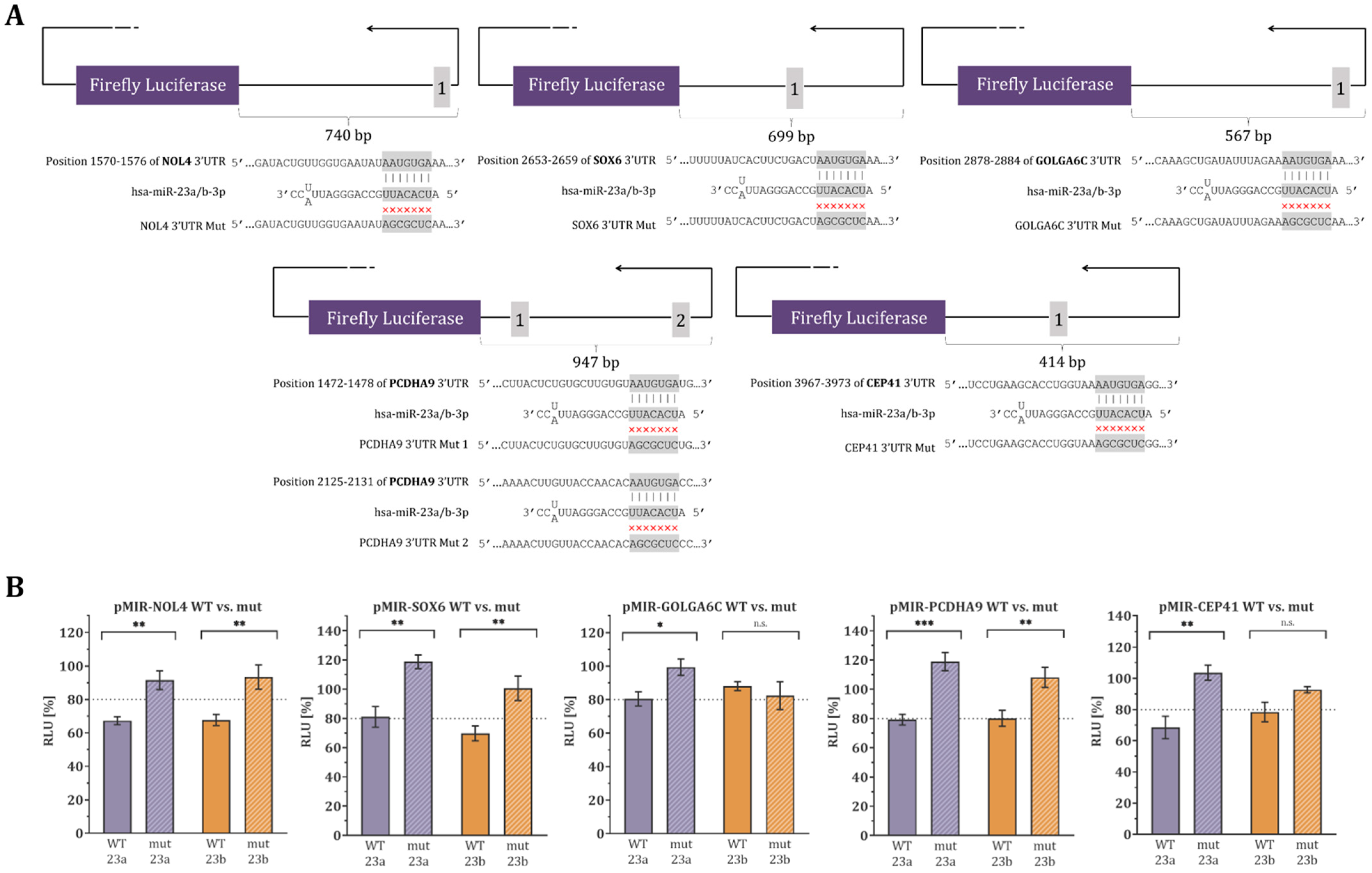
3.3. Validation of Binding-Site Specificity by Mutagenesis Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebert, L.F.R.; MacRae, I.J. Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 20, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kowdley, K.V. MicroRNAs in common human diseases. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2012, 10, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. MiRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alles, J.; Fehlmann, T.; Fischer, U.; Backes, C.; Galata, V.; Minet, M.; Hart, M.; Abu-Halima, M.; Grasser, F.A.; Lenhof, H.P.; et al. An estimate of the total number of true human miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3353–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Cui, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.; et al. MiRTarBase update 2022: An informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Huetos, A.; James, E.R.; Aston, K.I.; Carrell, D.T.; Jenkins, T.G.; Yeste, M. The role of miRNAs in male human reproduction: A systematic review. Andrology 2020, 8, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Halima, M.; Becker, L.S.; Al Smadi, M.A.; Abdul-Khaliq, H.; Raeschle, M.; Meese, E. Sperm Motility Annotated Genes: Are They Associated with Impaired Fecundity? Cells 2023, 12, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Halima, M.; Becker, L.S.; Al Smadi, M.A.; Kunz, L.S.; Groger, L.; Meese, E. Expression of SPAG7 and its regulatory microRNAs in seminal plasma and seminal plasma-derived extracellular vesicles of patients with subfertility. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Halima, M.; Ayesh, B.M.; Hart, M.; Alles, J.; Fischer, U.; Hammadeh, M.; Keller, A.; Huleihel, M.; Meese, E. Differential expression of miR-23a/b-3p and its target genes in male patients with subfertility. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 112, 323–335.e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Halima, M.; Belkacemi, A.; Ayesh, B.M.; Simone Becker, L.; Sindiani, A.M.; Fischer, U.; Hammadeh, M.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. MicroRNA-targeting in spermatogenesis: Over-expressions of microRNA-23a/b-3p and its affected targeting of the genes ODF2 and UBQLN3 in spermatozoa of patients with oligoasthenozoospermia. Andrology 2021, 9, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweep, H.; Gretz, N. MiRWalk2.0: A comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlen, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallstrom, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, A.; Kampf, C.; Sjostedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Halima, M.; Becker, L.S.; Ayesh, B.M.; Meese, E. MicroRNA-targeting in male infertility: Sperm microRNA-19a/b-3p and its spermatogenesis related transcripts content in men with oligoasthenozoospermia. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 973849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M.; Zhang, C.; Mear, L.; Zhong, W.; Digre, A.; Katona, B.; Sjostedt, E.; Butler, L.; Odeberg, J.; Dusart, P.; et al. A single-cell type transcriptomics map of human tissues. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallstrom, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamachi, Y.; Kondoh, H. Sox proteins: Regulators of cell fate specification and differentiation. Development 2013, 140, 4129–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Son, E.I.; Kim, E.; Kim, I.S.; Yim, M.B.; Kim, S.P. Expression of cancer-testis genes in brain tumors. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2008, 43, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohe, K.; Lalli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P. A direct role of SRY and SOX proteins in pre-mRNA splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.; Barturen-Larrea, P.; Gomez, J.A. Emerging roles of Sox6 in the renal and cardiovascular system. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, N. Sox6, jack of all trades: A versatile regulatory protein in vertebrate development. Dev. Dyn. 2011, 240, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Cheeseman, I.M.; Hori, T.; Okawa, K.; McLeod, I.X.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Desai, A.; Fukagawa, T. The CENP-H-I complex is required for the efficient incorporation of newly synthesized CENP-A into centromeres. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2006, 8, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Ito, M.; Takamatsu, N.; Shiba, T. Characterization of Solt, a novel SoxLZ/Sox6 binding protein expressed in adult mouse testis. FEBS Lett. 2000, 481, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohe, K.; Tamai, K.T.; Parvinen, M.; Sassone-Corsi, P. DAX-1 and SOX6 molecular interplay results in an antagonistic effect in pre-mRNA splicing. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.J.; Silva, J.V.; Brothag, C.; Regadas-Correia, B.; Fardilha, M.; Vijayaraghavan, S. Isoform-specific GSK3A activity is negatively correlated with human sperm motility. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 25, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, P.; Livstone, M.S.; Lewis, S.E.; Thomas, P.D. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief. Bioinform. 2011, 12, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Silhavy, J.L.; Zaki, M.S.; Schroth, J.; Bielas, S.L.; Marsh, S.E.; Olvera, J.; Brancati, F.; Iannicelli, M.; Ikegami, K.; et al. CEP41 is mutated in Joubert syndrome and is required for tubulin glutamylation at the cilium. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.; Prozzillo, Y.; Monache, F.D.; Santopietro, M.V.; Dimitri, P. Evolutionary conserved relocation of chromatin remodeling complexes to the mitotic apparatus. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozzillo, Y.; Fattorini, G.; Ferreri, D.; Leo, M.; Dimitri, P.; Messina, G. Knockdown of DOM/Tip60 Complex Subunits Impairs Male Meiosis of Drosophila melanogaster. Cells 2023, 12, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancati, G.; Grosshans, H. An interplay of miRNA abundance and target site architecture determines miRNA activity and specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 3259–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeary, S.E.; Bisaria, N.; Pham, T.M.; Wang, P.Y.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA 3′-compensatory pairing occurs through two binding modes, with affinity shaped by nucleotide identity and position. Elife 2022, 11, e69803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imig, J.; Brunschweiger, A.; Brummer, A.; Guennewig, B.; Mittal, N.; Kishore, S.; Tsikrika, P.; Gerber, A.P.; Zavolan, M.; Hall, J. MiR-CLIP capture of a miRNA targetome uncovers a lincRNA H19-miR-106a interaction. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipman, L.B.; Pasquinelli, A.E. MiRNA Targeting: Growing beyond the Seed. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.S.; Al Smadi, M.A.; Raeschle, M.; Rishik, S.; Abdul-Khaliq, H.; Meese, E.; Abu-Halima, M. Proteomic Landscape of Human Sperm in Patients with Different Spermatogenic Impairments. Cells 2023, 12, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamatani, T. Human spermatozoal RNAs. Fertil. Steril. 2012, 97, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermeier, G.C.; Dix, D.J.; Miller, D.; Khatri, P.; Krawetz, S.A. Spermatozoal RNA profiles of normal fertile men. Lancet 2002, 360, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Vazquez, C.; Blanco, J.; Aiese Cigliano, R.; Sarrate, Z.; Rivera-Egea, R.; Vidal, F.; Garrido, N.; Daub, C.; Anton, E. The RNA content of human sperm reflects prior events in spermatogenesis and potential post-fertilization effects. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 27, gaab035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodar, M.; Sendler, E.; Krawetz, S.A. The protein and transcript profiles of human semen. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 363, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becker, L.S.; Al Smadi, M.A.; Koch, H.; Abdul-Khaliq, H.; Meese, E.; Abu-Halima, M. Towards a More Comprehensive Picture of the MicroRNA-23a/b-3p Impact on Impaired Male Fertility. Biology 2023, 12, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060800
Becker LS, Al Smadi MA, Koch H, Abdul-Khaliq H, Meese E, Abu-Halima M. Towards a More Comprehensive Picture of the MicroRNA-23a/b-3p Impact on Impaired Male Fertility. Biology. 2023; 12(6):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060800
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecker, Lea Simone, Mohammad A. Al Smadi, Hanna Koch, Hashim Abdul-Khaliq, Eckart Meese, and Masood Abu-Halima. 2023. "Towards a More Comprehensive Picture of the MicroRNA-23a/b-3p Impact on Impaired Male Fertility" Biology 12, no. 6: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060800
APA StyleBecker, L. S., Al Smadi, M. A., Koch, H., Abdul-Khaliq, H., Meese, E., & Abu-Halima, M. (2023). Towards a More Comprehensive Picture of the MicroRNA-23a/b-3p Impact on Impaired Male Fertility. Biology, 12(6), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060800






