Histology and Ultrastructure of the Nephron and Kidney Interstitial Cells in the Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar Linnaeus 1758) at Different Stages of Life Cycle
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
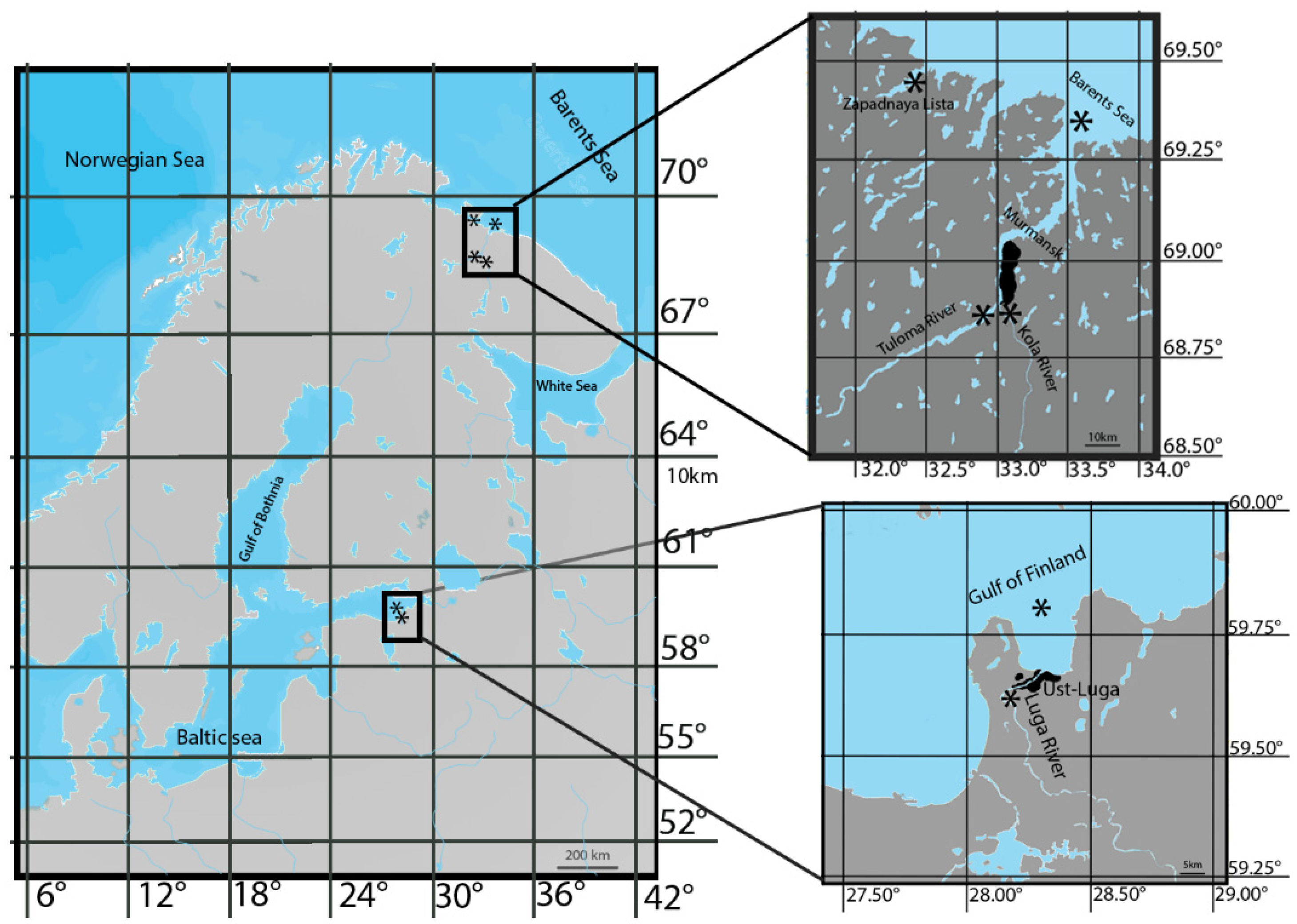
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Fish and Sampling
2.4. Trunk-Kidney Histology
2.5. Trunk-Kidney Ultrastructure
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
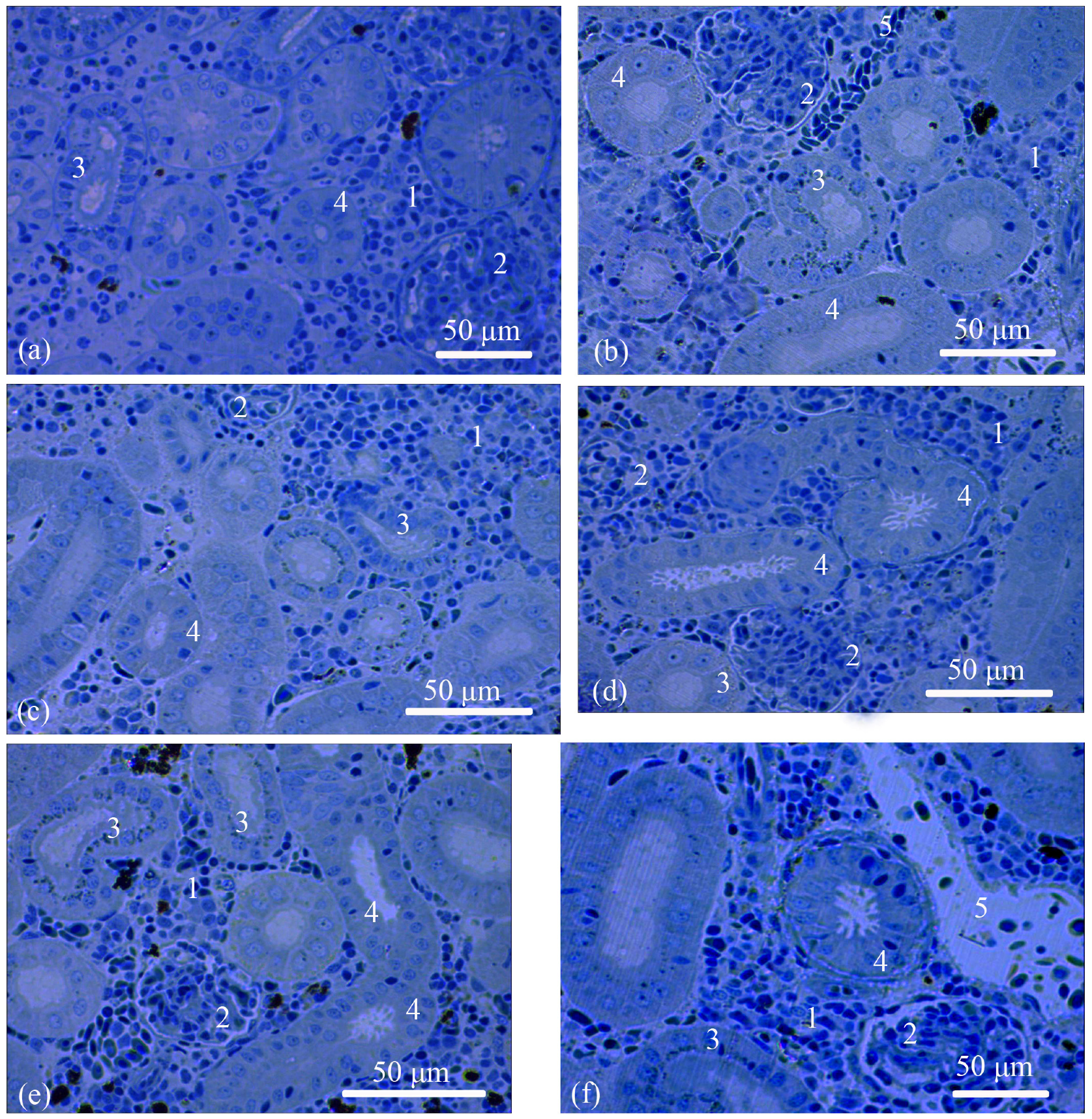
3.1. Trunk-Kidney Histology
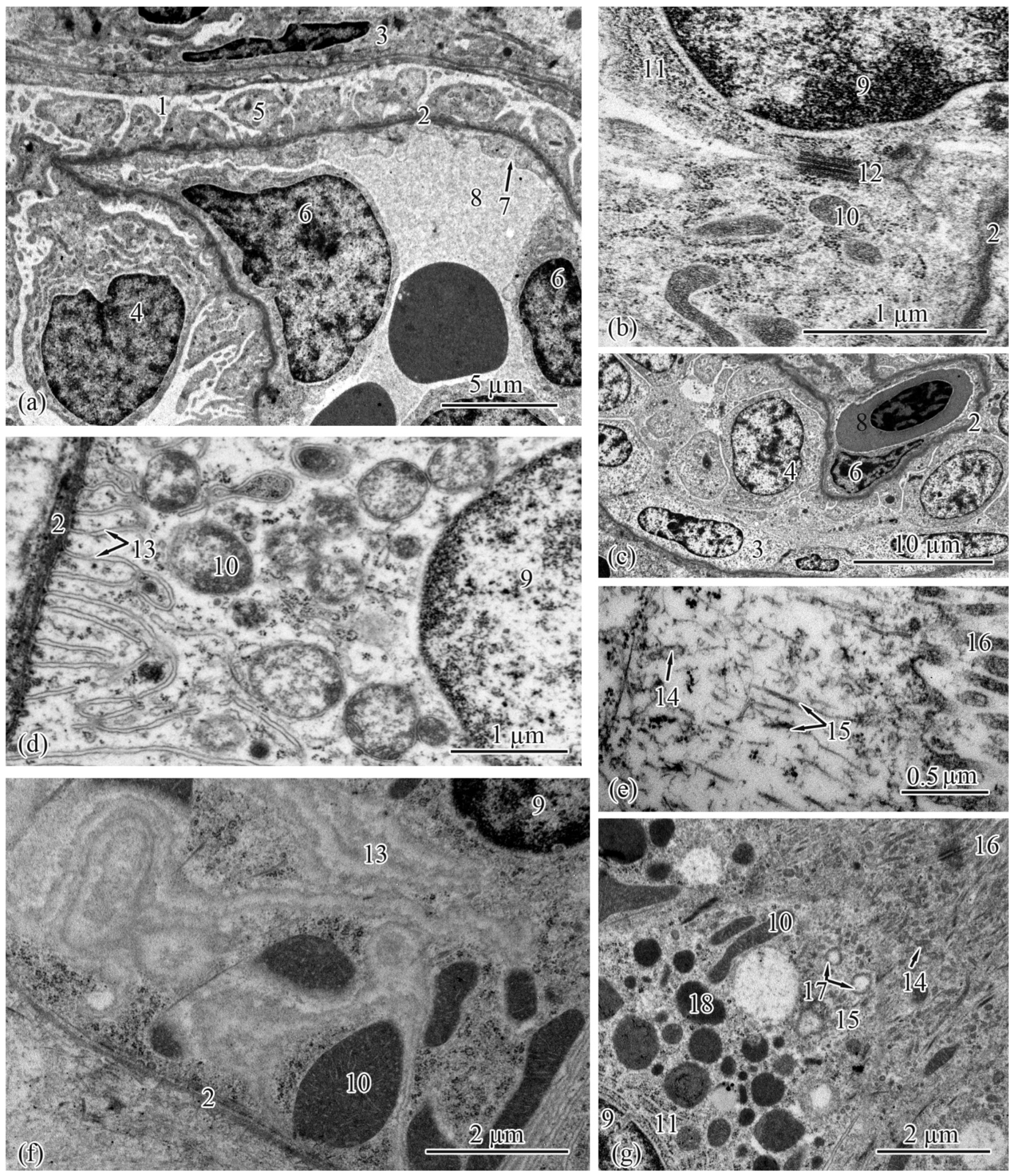
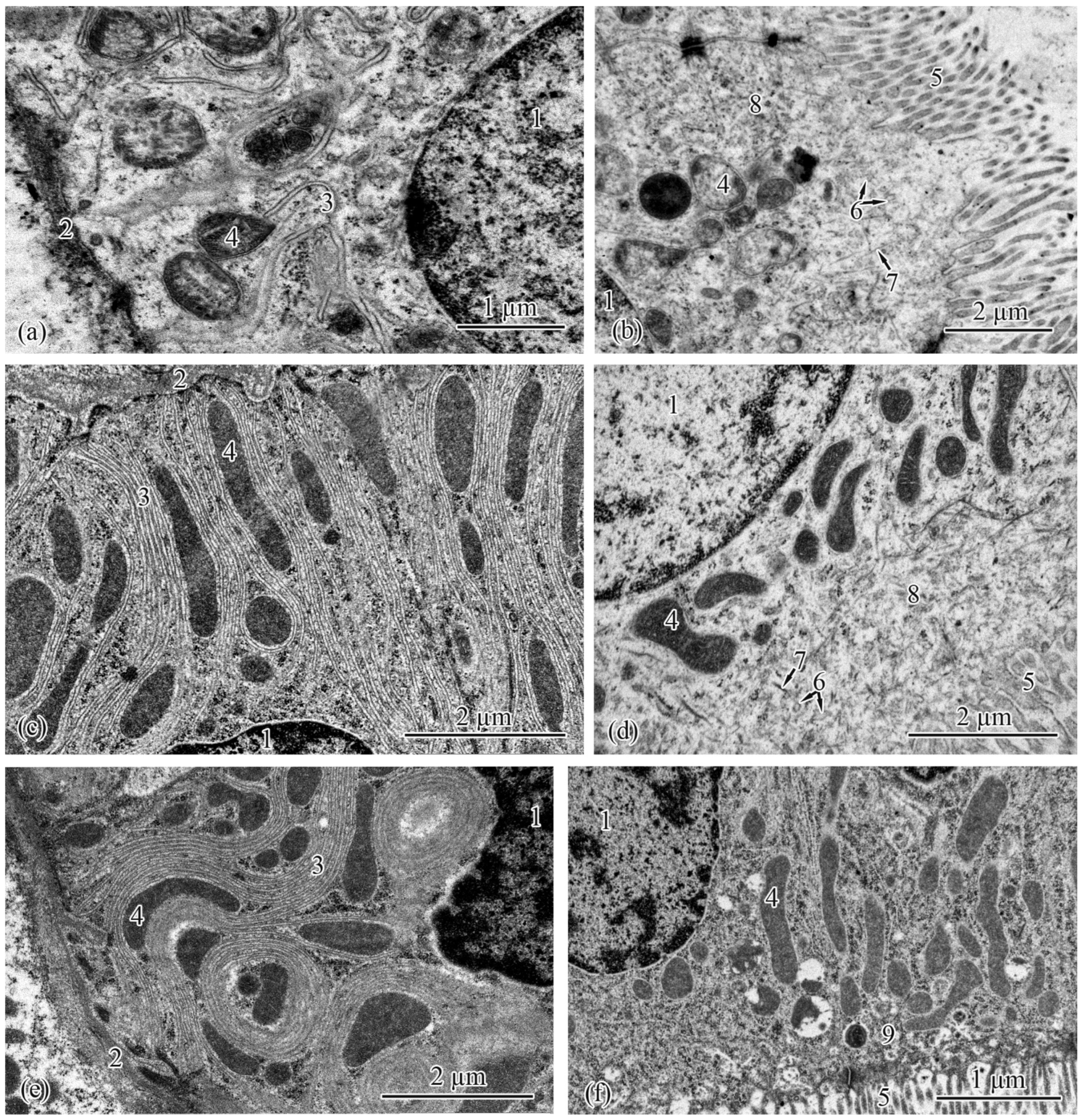
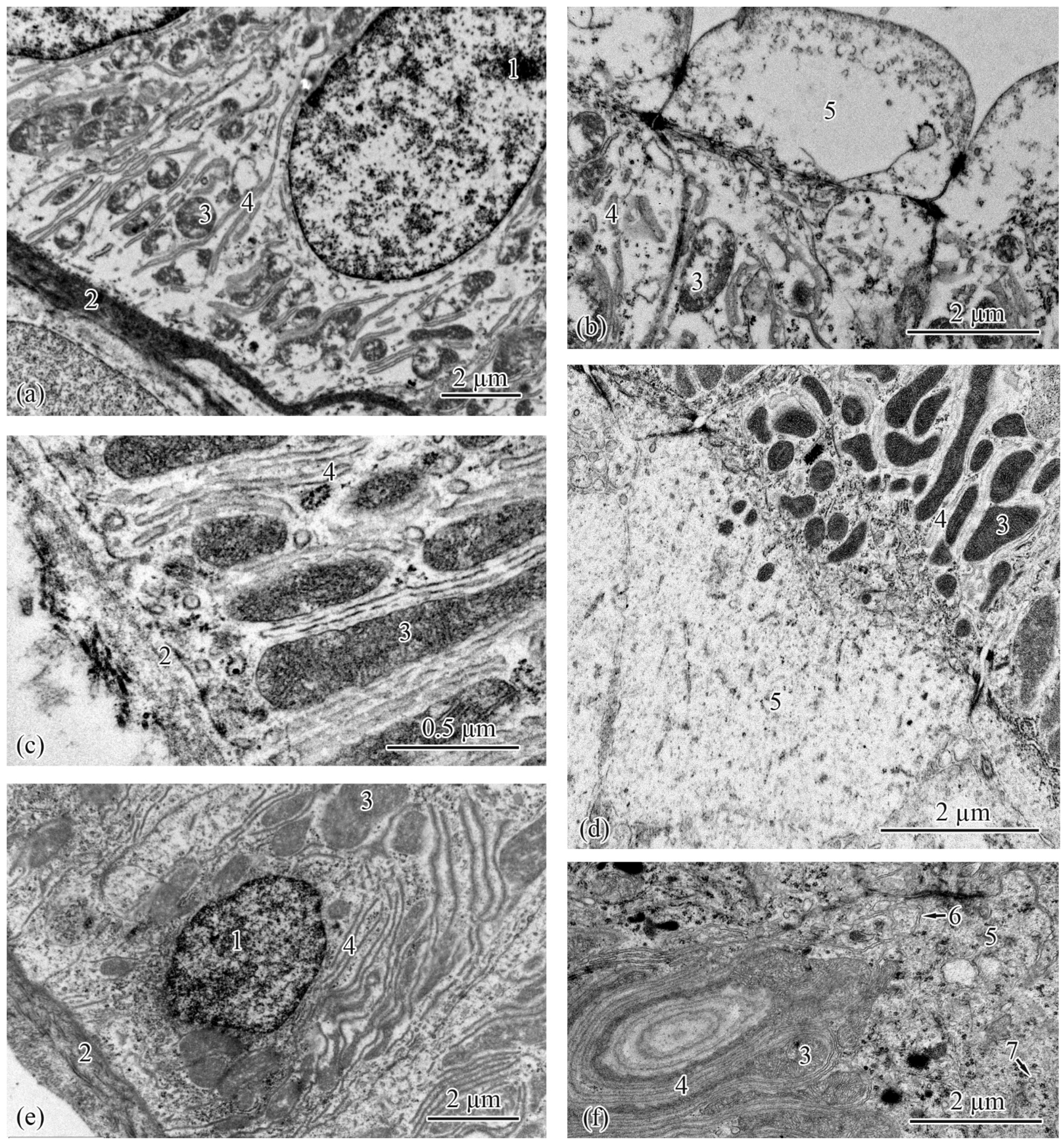
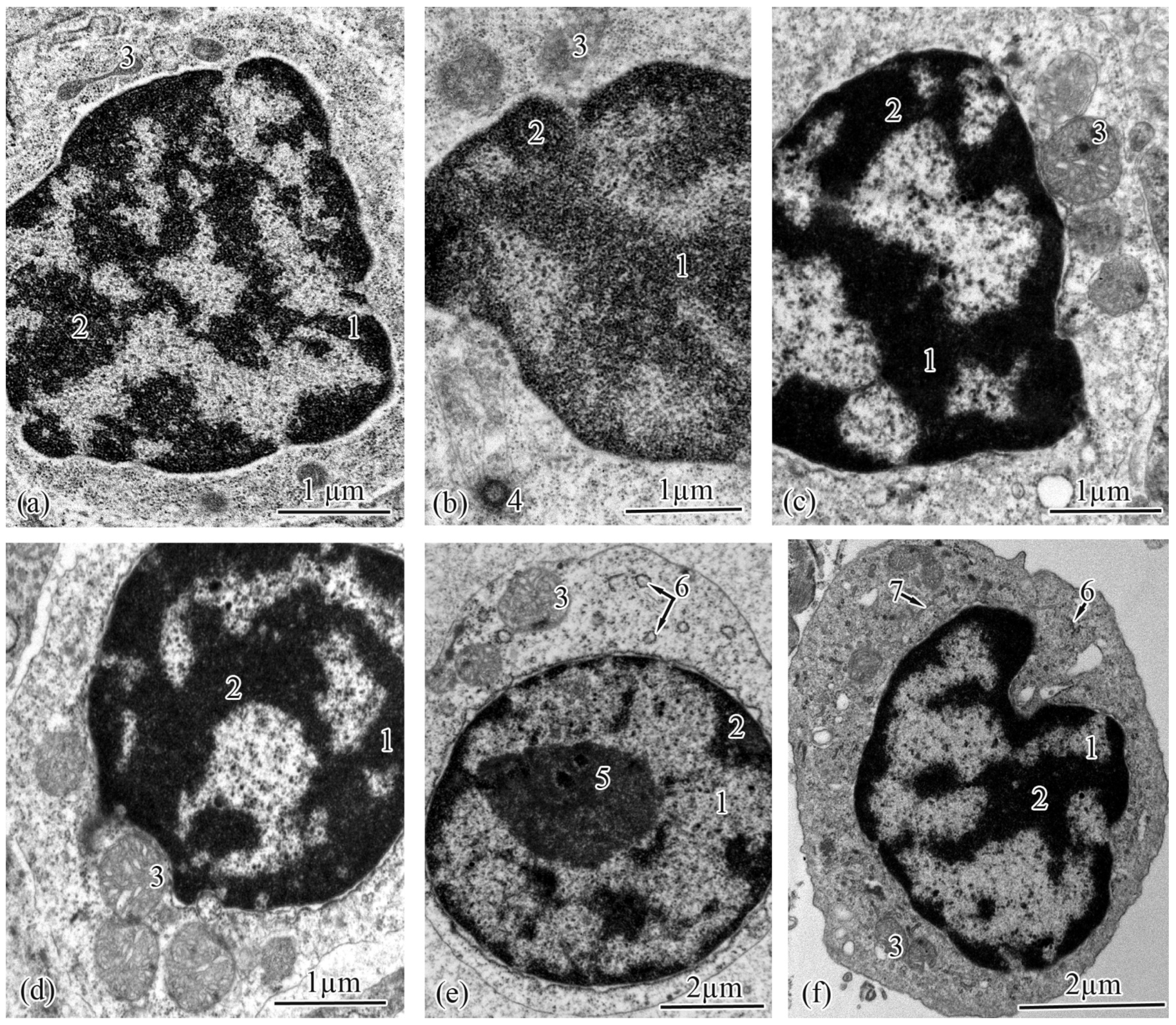
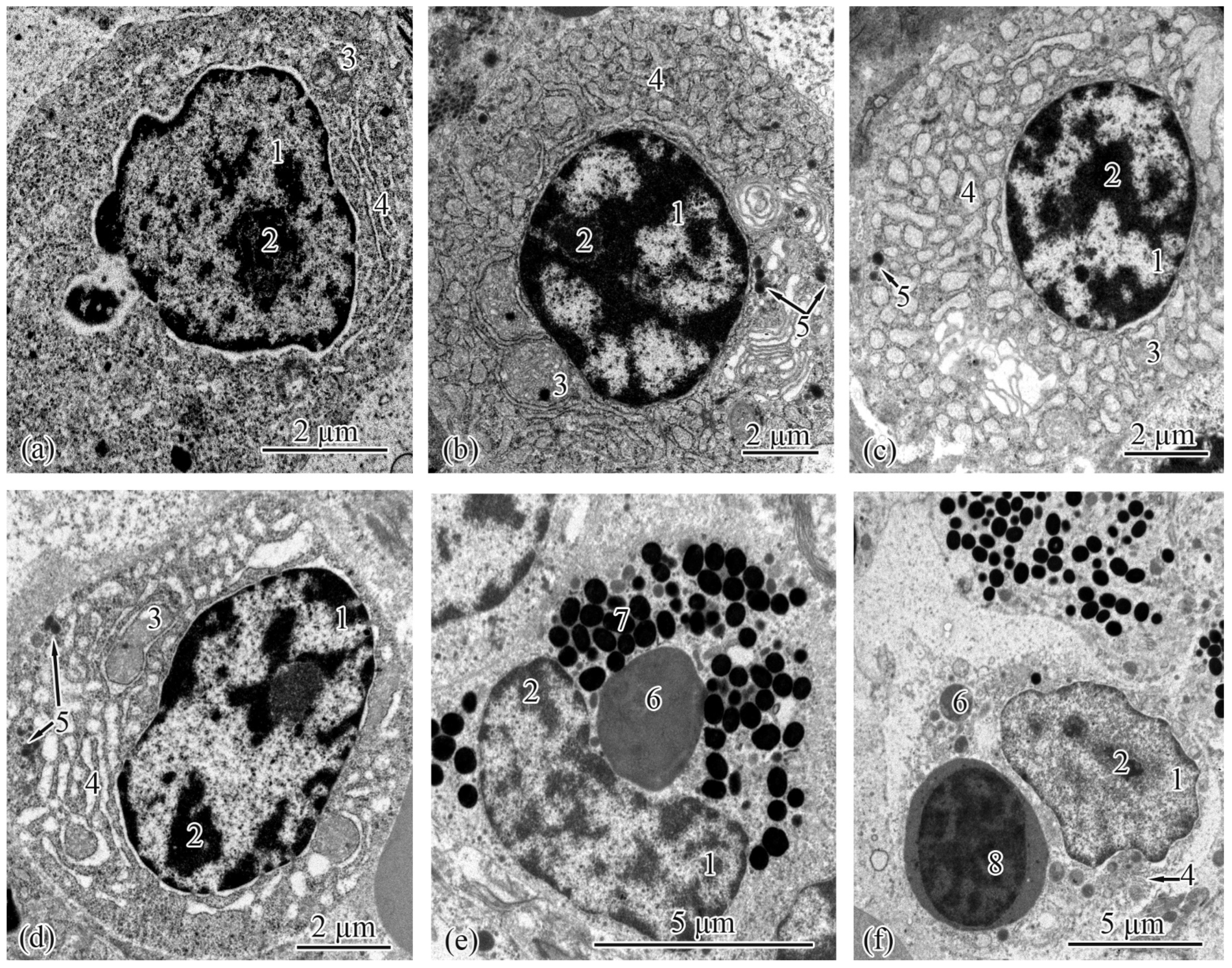
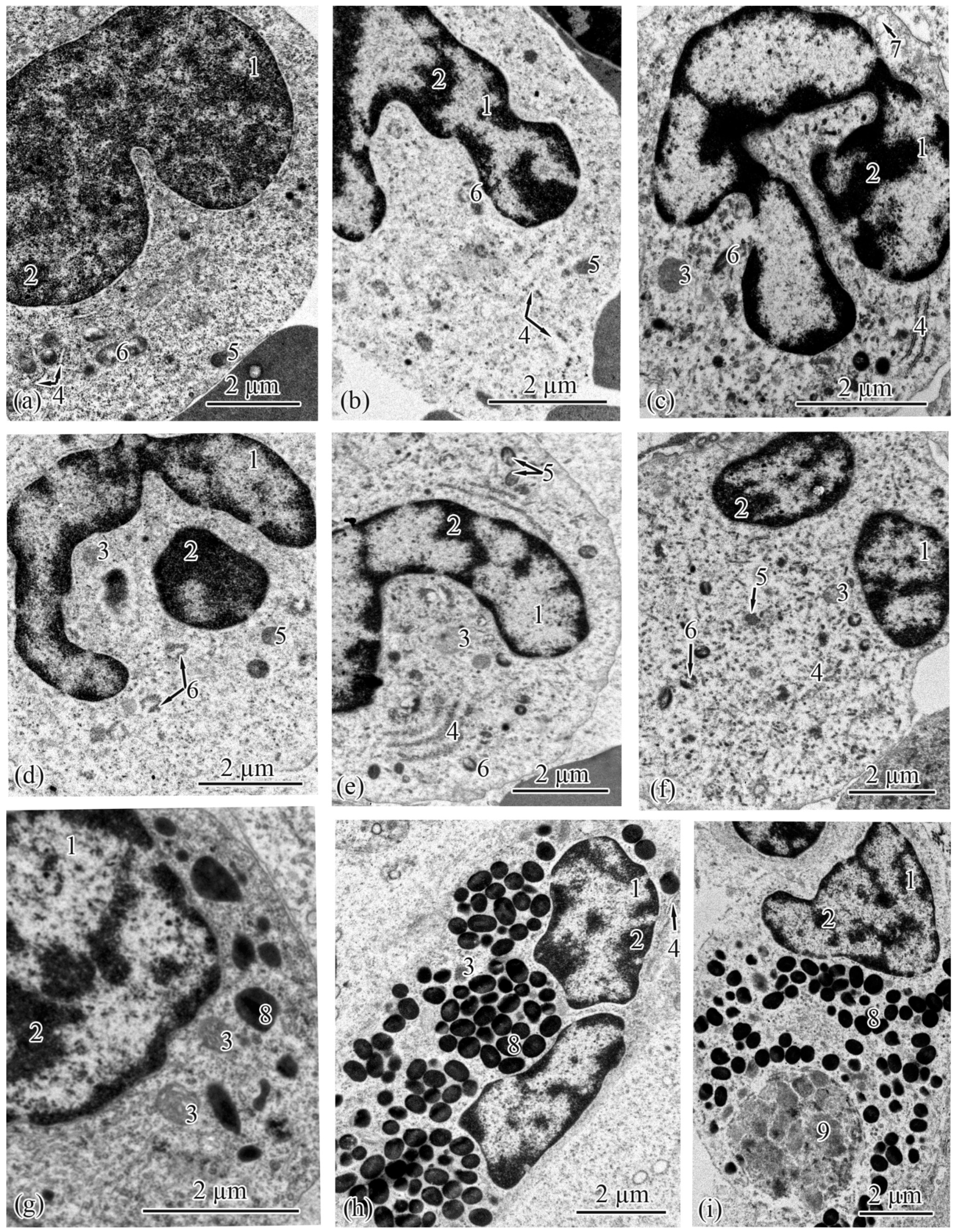
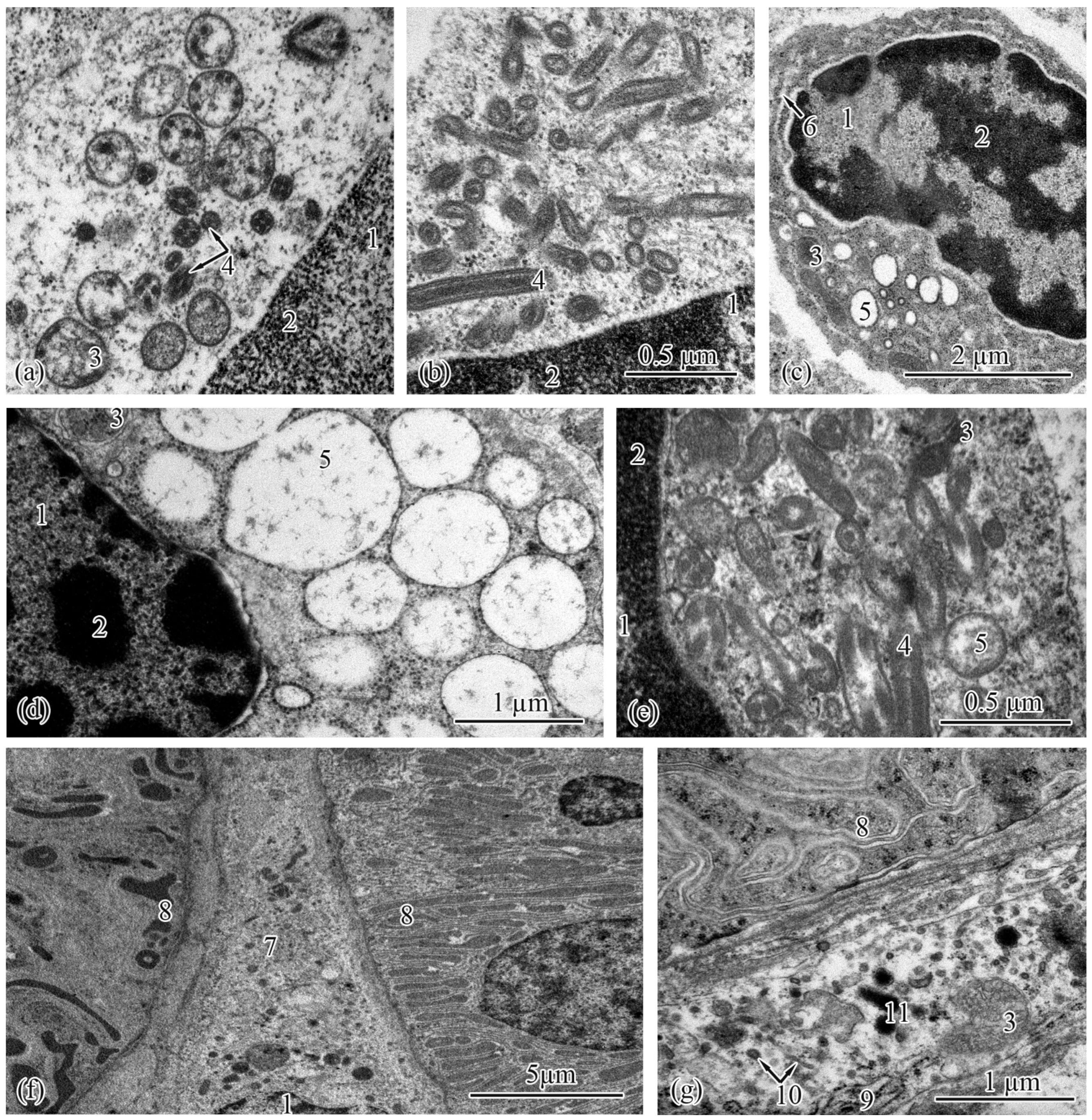
3.2. Trunk-Kidney Ultrastructure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thorstad, E.B.; Whoriskey, F.; Rikardsen, A.H.; Aarestrup, K. Aquatic nomads: The life and migrations of the Atlantic salmon. In Atlantic Salmon. Ecology, 1st ed.; Aas, Ø., Klemetsen, A., Einum, S., Skurdal, J., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Nisembaum, L.G.; Martin, P.; Lecomte, F.; Falcón, J. Melatonin and osmoregulation in fish: A focus on Atlantic salmon Salmo salar smoltification. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 33, e12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, O.M.; Gregory, S.D.; Gillingham, P.K.; Riley, W.D.; Scott, L.J.; Britton, J.R. Biological and environmental influences on the migration phenology of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar smolts in a chalk stream in southern England. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 1581–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmar, L.C.; Dickhoff, W.W. The parr–smalt transformation (smoltification) and seawater adaptation in salmonids: A review of selected literature. Aquaculture 1980, 21, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, J.M.; Ombredane, D.; Baglinière, J.L.; Prunet, P. Aspects of Parr-smolt transformation in anadromous and resident forms of brown trout (Salmo trutta) in comparison with Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 1994, 121, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønneseth, A.; Pettersen, A.F.; Wergeland, H.I. Leucocytes of anadromous and landlocked strains of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in the smolting period. Fish. Shellfish Immun. 2005, 19, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantserova, N.P.; Lysenko, L.A.; Veselov, A.E.; Nemova, N.N. Protein degradation systems in the skeletal muscles of parr and smolt Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. and brown trout Salmo trutta L. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinnichenko, L.N.; Natochin, Y.V.; Sabinin, G.V. Ultrastruktura i funktsii kletok proksimalnogo i distalnogo segmentov nefrona prokhodnykh i presnovodnykh ryb [Ultrastructure and functions of cells of proximal and distal segments of the nephron in anadromous and freshwater fishes]. Tsitologiya 1975, 17, 403–406. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Maksimovich, A.A.; Serkov, V.M.; Zagal’skaya, E.O.; Kudra, A.A. Ultrastructure and function of proximal tubular cells of nephrons of Pacific salmons adapted to environments with different salinity. J. Evol. Biochem. Phys. 2000, 36, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flerova, E.A.; Yurchenko, V.V.; Sapozhnikova, Y.P.; Sendek, D.S.; Titov, S.F.; Morozov, A.A. Microanatomy and ultrastructure of kidney interstitial cells and nephron in brown trout (Salmo trutta) at different stages of the life cycle. Can. J. Zool. 2022, 100, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Fishelson, L.; Amselgruber, W.M. Cytological ontogenesis and involution of the thymus and head-kidney in juvenile and old domestic carp: Is ageing in fish a chronological or growth-related phenomenon? J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2001, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.; Diez, B.; Cejalvo, T.; Gutiérrez-de Frías, C.; Cortés, A. Ontogeny of the immune system of fish. Fish. Shellfish Immun. 2006, 20, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, A.D.; Lobo-da-Cunha, A.; Malhao, F.; Franquinho, F. Histological and stereological characterisation of brown trout (Salmo trutta f. fario) trunk kidney. Microsc. Microanal. 2010, 16, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksimovich, A.A. Evolutionary physiological aspects of adaptation of the Pacific salmon fry of the Oncorhynchus genus to migration to the sea water. J. Evol. Biochem. Phys. 2008, 44, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Gross, R.; Asplund, T.; Dove, O.; Jansson, H.; Kelloniemi, J.; Kohlmann, K.; Löytynoja, A.; Nielsen, E.E.; Paaver, T.; et al. Matrilinear phylogeography of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in Europe and postglacial colonization of the Baltic Sea area. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyev, M.G. Baltiyskoye more [The Baltic Sea]. In Bolshaya Rossiyskaya Entsiklopediya [Great Russian Encyclopedia]; Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 2017; Available online: https://old.bigenc.ru/geography/text/4343809 (accessed on 27 March 2023). (In Russian)
- Trofimchuk, M.M. (Ed.) Kachestvo Poverkhnostnykh vod Rossiyskoy Federatsii Ezhegodnik 2017 [Surface Water Quality in the Russian Federation Annual 2017]; Agency on Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring: Rostov-on-Don, Russia, 2018; p. 555. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Deyev, M.G. Barentsevo more [The Barents Sea]. In Bolshaya Rossiyskaya Entsiklopediya [Great Russian Encyclopedia]; Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 2017; Available online: https://old.bigenc.ru/geography/text/862483 (accessed on 27 March 2023). (In Russian)
- Timakova, T.K.; Flerova, E.A.; Zabotkina, E.A. Metody Svetovoy i Elektronnoy Mikroskopii v Biologii i Veterenarii [Methods of Light and Electronic Microscopy for Biology and Veterinary Science]; FGBOU VPO “Yaroslavskaya GSHA” Publishing House: Yaroslavl, Russia, 2014. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Virabhadrachari, V. Structural changes in the gills, intestine, and kidney of Etroplus maculatus (Teleostei) adapted to different salinities. J. Cell. Sci. 1961, 3, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oğuz, A.R. A histological study of the kidney structure of Van fish (Alburnus tarichi) acclimated to highly alkaline water and freshwater. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Phy. 2015, 48, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natochin, Y.V. Ionoreguliruyushchaya Funktsiya Pochki [Ion Regulating Function of the Kidney]; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1976. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, C.; Eddy, F.; Potts, W.T.; Primmett, D.R. Renal function in migrating adult Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Comp. Biochem. Phys. A 1989, 92, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.H. Renal function in migrating adult Coho salmon. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1971, 38, 787–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoar, W.S. 4 The physiology of smolting salmonids. Fish. Physiol. 1988, 11, 275–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, C.; Stagg, R.M.; Eddy, F.B. Renal, respiratory and ionic regulation in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) kelts following transfer from fresh water to seawater. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1992, 162, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyenbach, K.W. Secretory electrolyte transport in renal proximal tubules of fish. Fish. Physiol. 1995, 14, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, F.; Cozzi, R.R.F.; Marshall, W.S.; Goss, G.G. Distinct Na+/K+/2Cl– cotransporter localization in kidneys and gills of two euryhaline species, rainbow trout and killifish. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 334, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, S. Ontogeny of the osmoregulatory capacity of teleosts and the role of ionocytes. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogliati, S.; Frezza, C.; Soriano, M.E.; Varanita, T.; Quintana-Cabrera, R.; Corrado, M.; Cipolat, S.; Costa, V.; Casarin, A.; Gomes, L.C.; et al. Mitochondrial cristae shape determines respiratory chain supercomplexes assembly and respiratory efficiency. Cell 2013, 155, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, S.; Nowikovsky, K. Mitochondrial osmoregulation in evolution, cation transport and metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2021, 1862, 148368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaasik, A.; Safiulina, D.; Zharkovsky, A.; Veksler, V. Regulation of mitochondrial matrix volume. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C157–C163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Neto, W.; Cabrera-Orefice, A.; Uribe-Carvajal, S.; Kowaltowski, A.J.; Alberto Luévano-Martínez, L. High osmolarity environments activate the mitochondrial alternative oxidase in Debaryomyces hansenii . PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balabanova, L.V.; Zabotkina, E.A. Ultrastruktura kletok immunnoy sistemy karpa Cyprinus carpio L.v norme I pri immunizatsii [The ultrastructure of the immune system cells of the carp Cyprinus carpio in normal state and after immunization]. Tsitologiya 1988, 30, 657–661. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A.; Lopez-Ruiz, A.; Bielek, E. Ultrastructure of nonspecific cytotoxic cells in teleosts. I. Effector-target cell binding in a marine and a freshwater species (Seabream: Sparus aurata L., and Carp: Cyprinus carpio L.). Anat. Rec. 1994, 239, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, D.M.; Zaccone, G.; Alesci, A.; Kuciel, M.; Hussein, M.T.; Sayed, R.K. Main components of fish immunity: An overview of the fish immune system. Fishes 2023, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ontogenetic Stage | n | Interstitium Proportion, % | Renal Corpuscle, μm | Proximal Tubule, μm | Distal Tubule, μm | Blood Vessel, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parr | 15 | 49.7 ± 3.08 | 81.7 ± 3.13 b | 60.7 ± 1.94 b | 58.5 ± 2.41 b | 20.5 ± 3.50 |
| Smolts | 12 | 51.2 ± 2.89 | 62.1 ± 4.47 a | 43.8 ± 1.22 a | 52.8 ± 2.51 a | 24.5 ± 2.45 |
| Adults | 6 | 48.2 ± 1.78 | 74.4 ± 3.32 a | 61.4 ± 2.99 b | 53.5 ± 1.95 a,b | 23.3 ± 2.83 |
| Spawners | 5 | 48.6 ± 1.55 | 82.1 ± 2.27 b | 61.6 ± 2.73 b | 57.3 ± 2.49 b | 23.9 ± 2.32 |
| Ontogenetic Stage | n | Interstitium Proportion, % | Renal Corpuscle, μm | Proximal Tubule, μm | Distal Tubule, μm | Blood Vessel, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parr | 21 | 50.4 ± 2.25 a | 81.7 ± 3.13 b | 63.9 ± 1.55 b | 63.5 ± 1.67 c | 22.5 ± 1.70 |
| Smolts | 5 | 51.1 ± 2.23 a,b | 54.7 ± 2.69 a | 44.7 ± 1.14 a | 50.7 ± 1.71 b | 21.1 ± 1.40 |
| Adults S | 7 | 68.0 ± 1.45 c | 53.8 ± 2.69 a | 37.0 ± 1.07 a | 39.0 ± 0.98 a | 19.6 ± 2.02 |
| Adults M | 5 | 56.2 ± 2.16 b | 61.3 ± 2.92 a | 40.5 ± 1.79 a | 54.3 ± 2.82 b | 25.2 ± 5.75 |
| Spawners | 5 | 51.3 ± 1.83 a,b | 82.1 ± 2.62 b | 63.8 ± 1.45 b | 63.5 ± 1.51 c | 22.4 ± 0.93 |
| Parameter | Parr (n = 15) | Smolts (n = 12) | Adults (n = 6) | Spawners (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Podocyte area, μm2 | 46.0 ± 13.8 | 39.0 ± 4.00 | 48.0 ± 12.1 | 48.7 ± 4.44 |
| Nucleus area, μm2 | 21.2 ± 13.5 | 11.2 ± 1.92 | 26.5 ± 7.01 | 27.2 ± 2.58 |
| Urinary-space width, μm | 5.69 ± 0.88 b | 1.15 ± 0.06 a | 1.04 ± 0.17 a | 3.29 ± 0.58 b |
| Basement-membrane width, μm | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.43 ± 0.05 b | 0.40 ± 0.13 b | 0.18 ± 0.06 a |
| Capillary diameter, μm | 30.1 ± 4.43 b | 12.1 ± 1.61 a | 26.8 ± 2.03 b | 33.8 ± 0.40 b |
| Parameter | Parr (n = 21) | Smolts (n = 5) | Adults S (n = 7) | Adults M (n = 5) | Spawners (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Podocyte area, μm2 | 44.7 ± 11.5 | 38.1 ± 2.36 | 29.7 ± 4.41 | 48.8 ± 10.8 | 48.7 ± 8.38 |
| Nucleus area, μm2 | 16.7 ± 5.85 | 10.7 ± 1.12 | 17.8 ± 2.31 | 20.5 ± 2.81 | 19.7 ± 2.46 |
| Urinary-space width, μm | 5.22 ± 0.47 b | 1.58± 0.07 a | 1.00 ± 0.12 a | 3.84 ± 0.29 b | 4.38 ± 0.38 b |
| Basement-membrane width, μm | 0.18 ± 0.03 a | 0.38 ± 0.06 b | 0.52 ± 0.09 c | 0.44 ± 0.11 b,c | 0.27 ± 0.02 b |
| Capillary diameter, μm | 27.9 ± 3.02 b | 11.9 ± 0.61 a | 15.5 ± 0.66 a | 29.0 ± 0.74 b | 29.0 ± 0.82 b |
| Parameter | Parr (n = 15) | Smolts (n = 12) | Adults (n = 6) | Spawners (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell area, μm2 | 94.4 ± 11.3 b | 60.3 ± 5.99 a | 67.6 ± 3.57 a | 116 ± 4.80 b |
| Cell height, μm | 17.4 ± 1.08 b | 14.0 ± 0.81 a | 14.8 ± 0.17 a | 18.8 ± 0.43 b |
| Nucleus area, μm2 | 38.4 ± 6.38 | 27.1 ± 5.78 | 25.4 ± 8.23 | 31.5 ± 1.29 |
| Mitochondrion area, μm2 | 0.30 ± 0.14 a | 0.77 ± 0.07 c | 0.76 ± 0.09 c | 0.58 ± 0.07 b |
| Number of mitochondria; (min–max) | 24.0 ± 0.35 a (22–26) | 35.8 ± 2.20 b (31–43) | 36.5 ± 2.13 b (31–41) | 27.5 ± 1.36 a (19–39) |
| Secretory granule area, μm2 | 1.45 ± 0.04 b | 1.58 ± 0.27 b | 1.73 ± 0.35 b | 0.52 ± 0.02 a |
| Number of secretory granules; (min–max) | 3.17 ± 0.09 a (3–4) | 9.50 ± 1.12 a (6–12) | 22.7 ± 3.57 b (17–33) | 19.9 ± 1.03 b (12–26) |
| Cisterna width of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, μm | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 b | 0.11 ± 0.02 b |
| Endocytosis-zone length, μm | 2.98 ± 0.12 | 3.38 ± 0.15 | 4.15 ± 0.21 | 3.97 ± 0.18 |
| Brush-border length, μm | 2.44 ± 0.08 | 2.41 ± 0.17 | 2.49 ± 0.16 | 2.75 ± 0.07 |
| Microvillus diameter, μm | 0.08 ± 0.00 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 b |
| Cilium diameter, μm | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.00 |
| Parameter | Parr (n = 21) | Smolts (n = 5) | Adults S (n = 7) | Adults M (n = 5) | Spawners (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell area, μm2 | 105 ± 12.5 b | 60.3 ± 5.99 a | 66.9 ± 3.30 a | 74.5 ± 2.12 b | 73.0 ± 7.48 b |
| Cell height, μm | 18.5 ± 1.20 b | 14.9 ± 0.22 a | 14.7 ± 0.32 a | 15.2 ± 0.18 a | 18.3 ± 1.63 b |
| Nucleus area, μm2 | 38.4 ± 7.50 | 26.6 ± 2.18 | 28.9 ± 7.39 | 31.1 ± 3.53 | 29.01 ± 4.09 |
| Mitochondrion area, μm2 | 0.34 ± 0.14 a | 0.82 ± 0.05 b | 1.34 ± 0.13 c | 0.71 ± 0.05 b | 0.56 ± 0.07 a |
| Number of mitochondria; (min–max) | 25.5 ± 2.08 a (23–28) | 36.2 ± 1.08 b (33–43) | 39.4 ± 1.60 b (36–42) | 35.0 ± 3.62 b (30–40) | 27.5 ± 3.92 a (19–34) |
| Secretory granule area, μm2 | 1.47 ± 0.27 b | 1.61 ± 0.17 b | 1.90 ± 0.44 b | 0.44 ± 0.17 a | 0.50 ± 0.03 a |
| Number of secretory granules; (min–max) | 3.25 ± 0.50 a (3–4) | 9.29 ± 0.59 a (6–12) | 34.8 ± 1.24 c (32–38) | 18.0 ± 1.74 b (11–22) | 9.0 ± 1.41 a (6–12) |
| Cisterna width of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, μm | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.01 c | 0.11 ± 0.02 b | 0.11 ± 0.02 b |
| Endocytosis-zone length, μm | 3.09 ± 0.75 | 3.75 ± 0.18 | 4.11 ± 0.41 | 3.13 ± 0.38 | 2.25 ± 0.37 |
| Brush-border length, μm | 3.39 ± 0.45 b | 3.31 ± 0.17 b | 1.91 ± 0.33 a | 2.91 ± 0.17 b | 3.47 ± 0.30 b |
| Microvillus diameter, μm | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 |
| Cilium diameter, μm | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.00 |
| Parameter | Parr (n = 15) | Smolts (n = 12) | Adults (n = 6) | Spawners (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell area, μm2 | 75.4 ± 1.79 a,b | 59.2 ± 5.68 a | 66.8 ± 5.16 a,b | 77.7 ± 3.91 b |
| Cell height, μm | 15.2 ± 0.15 a,b | 13.9 ± 0.71 a | 14.6 ± 0.42 a,b | 15.4 ± 0.12 b |
| Nucleus area, μm2 | 29.3 ± 2.25 | 28.9 ± 8.10 | 25.2 ± 3.51 | 27.4 ± 2.12 |
| Mitochondrion area, μm2 | 0.29 ± 0.03 a | 0.63 ± 0.06 b | 0.88 ± 0.06 c | 0.46 ± 0.06 a |
| Number of mitochondria; (min–max) | 25.0 ± 0.47 a (23–27) | 49.0 ± 8.15 c (37–60) | 31.6 ± 1.24 b (26–35) | 21.8 ± 1.06 a (14–29) |
| Endocytosis-zone length, μm | 1.35 ± 0.07 | 1.46 ± 0.09 | 1.52 ± 0.29 | 1.29 ± 0.02 |
| Brush-border length, μm | 2.68 ± 0.09 | 2.21 ± 0.33 | 2.30 ± 0.25 | 2.41 ± 0.15 |
| Cilium diameter, μm | 0.21± 0.00 | 0.21± 0.00 | 0.21± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.00 |
| Microvillus diameter, μm | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.00 b | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.00 |
| Parameter | Parr (n = 21) | Smolts (n = 5) | Adults S (n = 7) | Adults M (n = 5) | Spawners (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell area, μm2 | 73.5 ± 7.03 b | 60.3 ± 6.32 a,b | 54.9 ± 2.38 a | 69.9 ± 2.87 a,b | 73.9 ± 8.63 b |
| Cell height, μm | 14.8 ± 0.34 b | 14.3 ± 0.26 b | 12.9 ± 0.26 a | 14.5 ± 0.27 b | 14.8 ± 0.41 b |
| Nucleus area, μm2 | 30.0 ± 8.97 | 26.9 ± 1.92 | 24.3 ± 2.52 | 27.9 ± 1.59 | 26.8 ± 5.24 |
| Mitochondrion area, μm2 | 0.30 ± 0.04 a | 0.54 ± 0.05 b | 1.34 ± 0.13 c | 1.28 ± 0.06 c | 0.50 ± 0.14 a,b |
| Number of mitochondria; (min–max) | 26.0 ± 1.03 a (23–28) | 57.2 ± 8.15 b (50–67) | 58.4 ± 2.14 b (49–68) | 26.6 ± 1.01 a (25–32) | 22.3 ± 2.21 a (19–29) |
| Endocytosis-zone length, μm | 1.31 ± 0.05 a | 1.38 ± 0.14 a | 1.88 ± 0.21 b | 1.31 ± 0.07 a | 1.23 ± 0.05 a |
| Brush-border length, μm | 2.33 ± 0.46 | 2.21 ± 0.33 | 1.93 ± 0.09 | 2.31 ± 0.14 | 2.43 ± 0.14 |
| Cilium diameter, μm | 0.21± 0.01 | 0.21± 0.00 | 0.21± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.00 |
| Microvillus diameter, μm | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 b |
| Parameter | Parr (n = 15) | Smolts (n = 12) | Adults (n = 6) | Spawners (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell area, μm2 | 137 ± 2.85 b | 69.9 ± 6.35 a | 114 ± 14.6 b | 124 ± 8.10 b |
| Cell height, μm | 25.1 ± 0.30 b | 17.1 ± 0.55 a | 22.3 ± 0.13 b | 21.1 ± 0.34 b |
| Nucleus area, μm2 | 44.1 ± 1.73 b | 18.9 ± 3.55 a | 21.4 ± 2.27 a | 20.9 ± 1.21 a |
| Mitochondrion area, μm2 | 0.95 ± 0.07 b | 1.42 ± 0.30 c | 1.30 ± 0.25 b | 0.45 ± 0.03 a |
| Number of mitochondria; (min–max) | 31.5 ± 1.28 a (22–41) | 62.2 ± 2.84 b (56–68) | 42.2 ± 3.93 a (27–59) | 33.3 ± 1.75 a (24–49) |
| Parameter | Parr (n = 21) | Smolts (n = 5) | Adults S (n = 7) | Adults M (n = 5) | Spawners (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell area, μm2 | 126 ± 4.88 b | 68.9 ± 2.90 a | 82.2 ± 8.44 a | 115 ± 7.95 b | 125 ± 2.45 b |
| Cell height, μm | 24.3 ± 0.36 c | 16.6 ± 0.15 a | 16.5 ± 0.54 a,b | 22.0 ± 0.94 b | 21.1 ± 0.74 b |
| Nucleus area, μm2 | 44.3 ± 5.21 b | 18.0 ± 1.44 a | 17.0 ± 2.59 a | 28.9 ± 2.65 a | 26.9 ± 4.62 a |
| Mitochondrion area, μm2 | 0.96 ± 0.11 b | 1.57 ± 0.20 c | 1.70 ± 0.20 c | 0.90 ± 0.33 b | 0.44 ± 0.07 a |
| Number of mitochondria; (min–max) | 32.1 ± 2.18 a (22–41) | 62.3 ± 0.80 b (58–68) | 63.0 ± 1.45 b (59–71) | 33.2 ± 4.60 a (29–56) | 34.1 ± 4.32 a (24–49) |
| Leukocyte Type | Ontogenetic Stage | n | Cell Area, μm2 | Nucleus Area, μm2 | Mitochondrion Area, μm2 | Number of Mitochondria (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphocyte | Parr | 15 | 18.5 ± 4.22 a | 15.8 ± 2.49 | 0.14 ± 0.08 a | 1.40 ± 0.32 a; (1–2) |
| Smolts | 12 | 27.1 ± 3.86 a,b | 16.0 ± 0.68 | 0.26 ± 0.04 a,b | 4.20 ± 0.75 b; (2–5) | |
| Adults | 6 | 32.5 ± 3.34 b | 16.3 ± 2.00 | 0.39 ± 0.10 b | 3.80 ± 0.26 b; (3–4) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 17.9 ± 1.07 a | 10.4 ± 0.67 | 0.16 ± 0.02 a | 2.50 ± 0.24 a,b; (2–3) | |
| Plasma cell | Parr | 15 | 62.8 ± 5.63 a | 30.2 ± 4.19 | 0.26 ± 0.03 a | 1.17 ± 0.24 a; (1–2) |
| Smolts | 12 | 73.5 ± 5.20 a,b | 20.3 ± 3.59 | 0.36 ± 0.04 a | 6.80 ± 0.63 b; (5–7) | |
| Adults | 6 | 85.5 ± 3.43 b | 24.5 ± 1.94 | 1.10 ± 0.12 b | 6.00 ± 0.28 b; (5–7) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 59.0 ± 6.00 a | 25.2 ± 3.12 | 0.17 ± 0.03 a | 1.38 ± 0.23 a; (1–2) | |
| Macrophage | Parr | 15 | 113 ± 8.69 a,b | 22.2 ± 5.72 b | 0.36 ± 0.12 a | 1.33 ± 0.30 a; (1–2) |
| Smolts | 12 | 101 ± 13.8 a,b | 16.0 ± 2.05 a,b | 1.02 ± 0.12 b | 6.25 ± 0.55 b; (5–7) | |
| Adults | 6 | 130 ± 7.60 b | 9.39 ± 0.58 a | 0.85 ± 0.14 b | 5.17 ± 0.58 b; (4–7) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 92.1 ± 8.81 a | 14.0 ± 4.56 a,b | 0.27 ± 0.09 a | 2.29 ± 0.44 a; (1–3) |
| Leukocyte Type | Ontogenetic Stage | n | Cell Area, μm2 | Nucleus Area, μm2 | Mitochondrion Area, μm2 | Number of Mitochondria (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphocyte | Parr | 21 | 19.1 ± 5.15 a | 14.0 ± 3.81 | 0.18 ± 0.08 a | 2.00 ± 0.58 a; (1–3) |
| Smolts | 5 | 29.2 ± 2.16 a | 15.3 ± 1.06 | 0.25 ± 0.05 a,b | 4.29 ± 0.80 b; (2–6) | |
| Adults S | 7 | 32.4 ± 2.85 b | 13.1 ± 1.80 | 0.49 ± 0.11 b | 4.00 ± 0.58 b; (3–5) | |
| Adults M | 5 | 22.7 ± 4.54 a | 12.2 ± 2.99 | 0.30 ± 0.05 b | 2.75 ± 0.35 a,b; (2–3) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 18.6 ± 1.03 a | 10.4 ± 0.78 | 0.15 ± 0.02 a | 2.83 ± 0.34 a,b; (2–4) | |
| Plasma cell | Parr | 21 | 65.5 ± 7.32 | 27.2 ± 5.76 | 0.26 ± 0.04 a | 1.25 ± 0.29 a; (1–2) |
| Smolts | 5 | 72.7 ± 4.64 | 20.0 ± 3.12 | 0.34 ± 0.04 a | 7.40 ± 1.05 b; (5–9) | |
| Adults S | 7 | 87.4 ± 5.18 | 23.4 ± 1.01 | 1.03 ± 0.25 b | 6.00 ± 0.87 b; (5–8) | |
| Adults M | 5 | 80.7 ± 1.77 | 22.9 ± 4.37 | 0.64 ± 0.17 a,b | 4.80 ± 0.17 a,b; (2–6) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 60.6 ± 6.92 | 26.8 ± 3.48 | 0.18 ± 0.04 a | 1.33 ± 0.23 a,b; (1–2) | |
| Macrophage | Parr | 21 | 107 ± 9.05 a,b | 24.5 ± 9.10 | 0.33 ± 0.15 a | 1.33 ± 0.33 a; (1–2) |
| Smolts | 5 | 115 ± 13.0 b | 15.5 ± 1.87 | 1.01 ± 0.10 b | 7.17 ± 0.77 b; (5–9) | |
| Adults S | 7 | 132 ± 22.7 b | 11.8 ± 6.77 | 0.92 ± 0.14 b | 5.40 ± 0.63 b; (4–6) | |
| Adults M | 5 | 117 ± 11.8 b | 24.5 ± 11.1 | 0.73 ± 0.17 b | 4.40 ± 0.81 b; (3–6) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 77.2 ± 10.4 a | 15.3 ± 5.25 | 0.27 ± 0.10 a | 2.40 ± 0.51 a; (1–4) |
| Leukocyte Type | Ontogenetic Stage | n | Cell Area, μm2 | Nucleus Area, μm2 | Mitochondrion Area, μm2 | Number of Mitochondria (Min–Max) | Granule Area, μm2 | Number of Granules (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil | Parr | 15 | 53.9 ± 1.40 a | 11.1 ± 3.78 | 0.07± 0.01 a | 3.00 ± 0.24 a (2–4) | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 4.14 ± 0.70 a (3–6) |
| Smolts | 12 | 57.1 ± 6.62 a | 13.6 ± 2.18 | 0.20 ± 0.03 b | 6.00 ± 0.41 b (5–7) | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 6.50 ± 0.71 b (5–8) | |
| Adults | 6 | 62.7 ± 8.65 a,b | 13.0 ± 0.81 | 3.82 ± 1.47 c | 5.43 ± 0.57 b (4–7) | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 6.71 ± 0.31 b (6–8) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 76.1 ± 5.19 b | 15.0 ± 4.72 | 5.13 ± 1.61 c | 5.60 ± 0.41 b (4–7) | 0.14 ± 0.08 | 10.4 ±1.38 c (8–13) | |
| Eosinophil | Parr | 15 | 64.9 ± 10.5 a | 15.6 ± 1.93a | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 a (1) | 0.22 ± 0.02 b | 29.6 ± 2.76 a (22–35) |
| Smolts | 12 | 86.7 ± 10.7 b | 14.2 ± 1.50a | 0.69 ± 0.06 b | 5.20 ±0.75 b (4–7) | 0.18 ± 0.03 b | 86.0 ± 10.5 b (64–108) | |
| Adults | 6 | 94.0 ± 7.63 b | 12.2 ± 2.06a | 1.08 ± 0.11 b | 6.00 ± 1.18 b (4–8) | 0.20 ± 0.03 b | 73.7 ± 8.09 b (60–101) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 93.8 ± 6.25 b | 8.18 ± 1.03b | 0.78 ± 0.19 b | 2.67 ± 0.47 a (2–4) | 0.15 ± 0.02 a | 85.2 ± 12.1 b (64–102) |
| Leukocyte Type | Ontogenetic Stage | n | Cell Area, μm2 | Nucleus Area, μm2 | Mitochondrion Area, μm2 | Number of Mitochondria (Min–Max) | Granule Area, μm2 | Number of Granules (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil | Parr | 21 | 53.1 ± 1.75 a | 12.4 ± 4.63 | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 3.33 ± 0.33 a (3–4) | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 4.20 ± 0.75 a (3–6) |
| Smolts | 5 | 67.4 ± 6.86 b | 13.3 ± 1.73 | 0.22 ± 0.04 b | 5.71 ± 0.55 b (4–7) | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 6.80 ± 0.71 b (5–9) | |
| Adults S | 7 | 76.1 ± 5.19 b | 15.0 ± 4.72 | 5.13 ± 1.61 c | 5.60 ± 0.95 b (4–7) | 0.14 ± 0.08 | 10.4 ±1.38 b (8–13) | |
| Adults M | 5 | 48.8 ± 2.38 a,b | 10.9 ± 1.62 | 0.17 ± 0.03 b | 4.80 ± 0.77 b (4–6) | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 10.4 ± 2.19 b (7–16) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 47.5 ± 1.27 a | 11.0 ± 1.83 | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 3.60 ± 0.24 a (3–4) | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 11.8 ± 1.53 b (7–15) | |
| Eosinophil | Parr | 21 | 63.5 ± 13.4 a | 16.9 ± 2.89 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 a (1) | 0.24 ± 0.03 a | 16.0 ± 9.85 a (12–35) |
| Smolts | 5 | 86.7 ± 11.4 b | 13.5 ± 1.68 | 0.67 ± 0.05 b | 2.75 ± 0.51 b (2–4) | 0.18 ± 0.02 a | 83.8 ± 8.67 b (64–108) | |
| Adults S | 7 | 93.8 ± 6.51 b | 8.18 ± 1.03 b | 1.08 ± 0.11 c | 6.00 ± 1.18 c (4–8) | 0.15 ± 0.02 a | 85.2 ± 12.1 b (64–102) | |
| Adults M | 5 | 74.3 ± 12.8 a | 12.5 ± 2.77 | 0.17 ± 0.03 a | 4.20 ± 0.59 b (3–5) | 0.20 ± 0.03 a | 88.7 ± 8.41 b (71–103) | |
| Spawners | 5 | 55.6 ± 6.78 a | 13.1 ± 2.17 | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 2.67 ± 0.23 b (2–3) | 0.83 ± 0.05 b | 96.0 ± 4.25 b (84–112) |
| Cell Type | Ontogenetic Stage | n | Cell Area, μm2 | Nucleus Area, μm2 | Mitochondrion Area, μm2 | Number of Mitochondria (Min–Max) | Vesicle Area, μm2 | Number of Granules (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell with radially arranged vesicles | Parr | 15 | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. |
| Smolts | 12 | 28.8 ± 3.71 | 10.4 ± 0.79 | 0.49 ± 0.05 a | 6.40 ± 0.52 a (5–7) | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 6.40 ± 0.52 (5–7) | |
| Adults | 6 | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | |
| Spawners | 5 | 20.4 ± 1.82 | 11.1 ± 1.71 | 0.19 ± 0.01 b | 3.20 ± 0.22 b (3–4) | 0.30 ± 0.04 b | 5.75 ± 0.73 (4–7) | |
| Chloride cell | Parr | 15 | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. |
| Smolts | 12 | 61.3 ± 10.2 a | 14.2 ± 1.50 a | 0.26 ± 0.04 b | 20.9 ± 1.23 b (17–24) | n.a. | n.a. | |
| Adults | 6 | 120 ± 0.00 b | 22.3 ± 1.16 b | 1.25 ± 0.34 c | 38.7 ±1.45 c (36–41) | n.a. | n.a. | |
| Spawners | 5 | 55.4 ± 2.80 a | 12.1 ± 0.30 a | 0.13 ± 0.02 a | 7.25 ± 0.47 a (5–9) | n.a. | n.a. |
| Cell Type | Ontogenetic Stage | n | Cell Area, μm2 | Nucleus Area, μm2 | Mitochondrion Area, μm2 | Number of Mitochondria (Min–Max) | Vesicle Area, μm2 | Number of Granules (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell with radially arranged vesicles | Parr | 21 | 26.6 ± 4.23 | 13.6 ± 2.26 | 0.14 ± 0.00 a | 2.80 ± 0.48 a (2–4) | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 6.00 ± 1.56 a (4–10) |
| Smolts | 5 | 28.8 ± 3.32 | 10.4 ± 0.65 | 0.52 ± 0.06 b | 6.17 ± 0.57 b (5–7) | 0.23 ± 0.09 b | 39.6 ± 0.99 b (38–42) | |
| Adults S | 7 | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | |
| Adults M | 5 | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | |
| Spawners | 5 | 20.4 ± 1.82 | 11.1 ± 1.71 | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 3.20 ± 0.22 a (3–4) | 0.30 ± 0.04 b | 5.75 ± 0.73 a (4–7) | |
| Chloride cell | Parr | 21 | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. |
| Smolts | 5 | 62.0 ± 1.66 a | 14.3 ± 1.72 a | 0.25 ± 0.04 b | 22.0 ± 1.85 b (17–26) | n.a. | n.a. | |
| Adults S | 7 | 125 ± 3.41 b | 23.0 ± 0.49 b | 1.07 ± 0.53 c | 40.7 ± 1.78 c (38–43) | n.a. | n.a. | |
| Adults M | 5 | 57.7 ± 8.12 a | 13.2 ± 2.11 a | 0.29 ± 0.14 b | 14.7 ± 2.67 b (9–18) | n.a. | n.a. | |
| Spawners | 5 | 53.7 ± 5.26 a | 13.2 ± 1.44 a | 0.16 ± 0.05 a | 8.17 ± 1.32 a (6–13) | n.a. | n.a. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flerova, E.A.; Yurchenko, V.V.; Morozov, A.A.; Evdokimov, E.G.; Bogdanova, A.A.; Alekseev, M.Y.; Sendek, D.S.; Titov, S.F. Histology and Ultrastructure of the Nephron and Kidney Interstitial Cells in the Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar Linnaeus 1758) at Different Stages of Life Cycle. Biology 2023, 12, 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050750
Flerova EA, Yurchenko VV, Morozov AA, Evdokimov EG, Bogdanova AA, Alekseev MY, Sendek DS, Titov SF. Histology and Ultrastructure of the Nephron and Kidney Interstitial Cells in the Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar Linnaeus 1758) at Different Stages of Life Cycle. Biology. 2023; 12(5):750. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050750
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlerova, Ekaterina A., Victoria V. Yurchenko, Alexey A. Morozov, Evgeniy G. Evdokimov, Alena A. Bogdanova, Maksim Yu. Alekseev, Dmitry S. Sendek, and Sergey F. Titov. 2023. "Histology and Ultrastructure of the Nephron and Kidney Interstitial Cells in the Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar Linnaeus 1758) at Different Stages of Life Cycle" Biology 12, no. 5: 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050750
APA StyleFlerova, E. A., Yurchenko, V. V., Morozov, A. A., Evdokimov, E. G., Bogdanova, A. A., Alekseev, M. Y., Sendek, D. S., & Titov, S. F. (2023). Histology and Ultrastructure of the Nephron and Kidney Interstitial Cells in the Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar Linnaeus 1758) at Different Stages of Life Cycle. Biology, 12(5), 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050750






