Identifying Whitemouth Croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) Populations along the Rio de Janeiro Coast, Brazil, through Microsatellite and Otolith Analyses
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
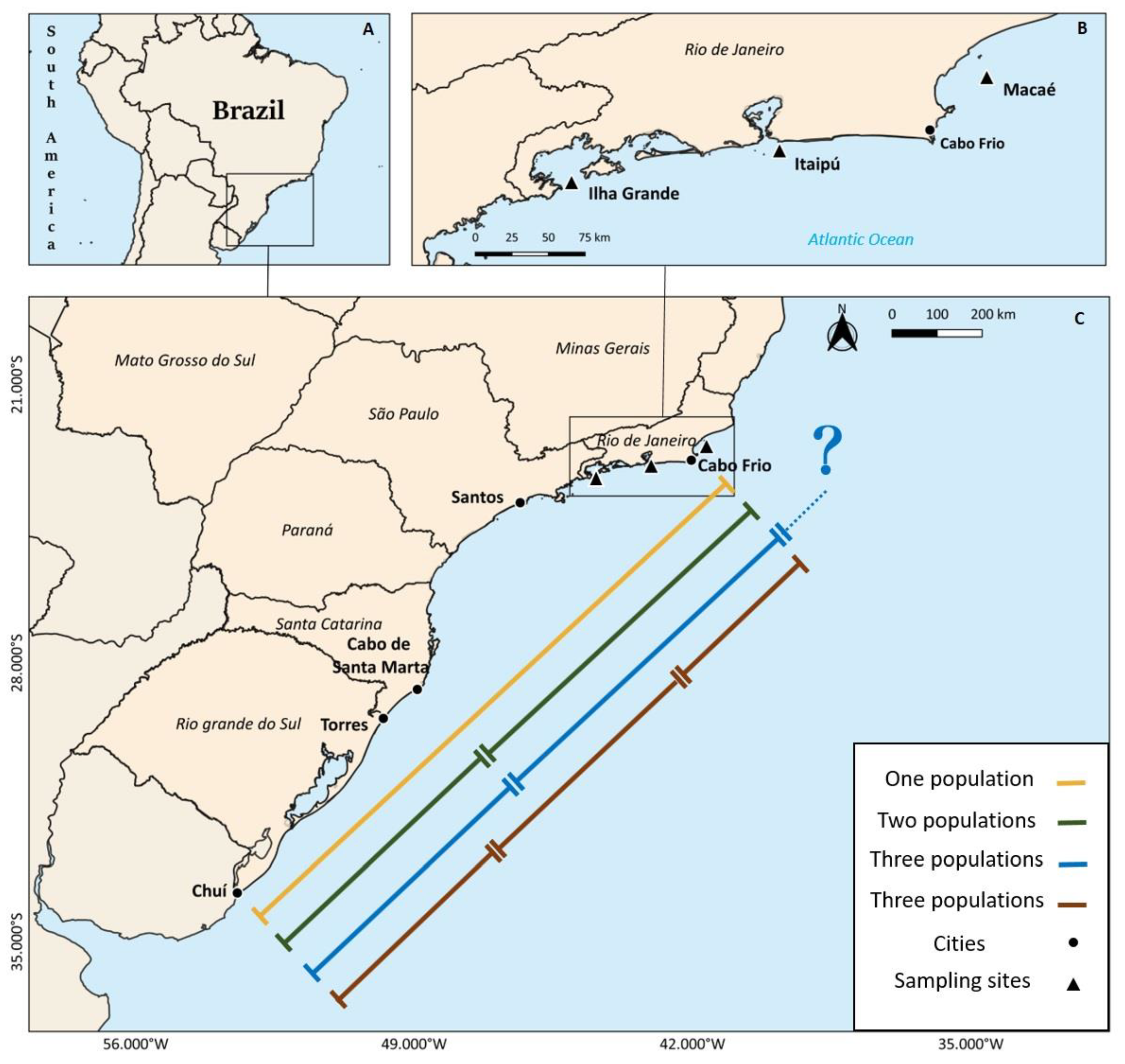
2.1. Study Area and Fish Sampling
2.2. Microsatellite Analysis
2.3. Otolith Analysis
3. Results
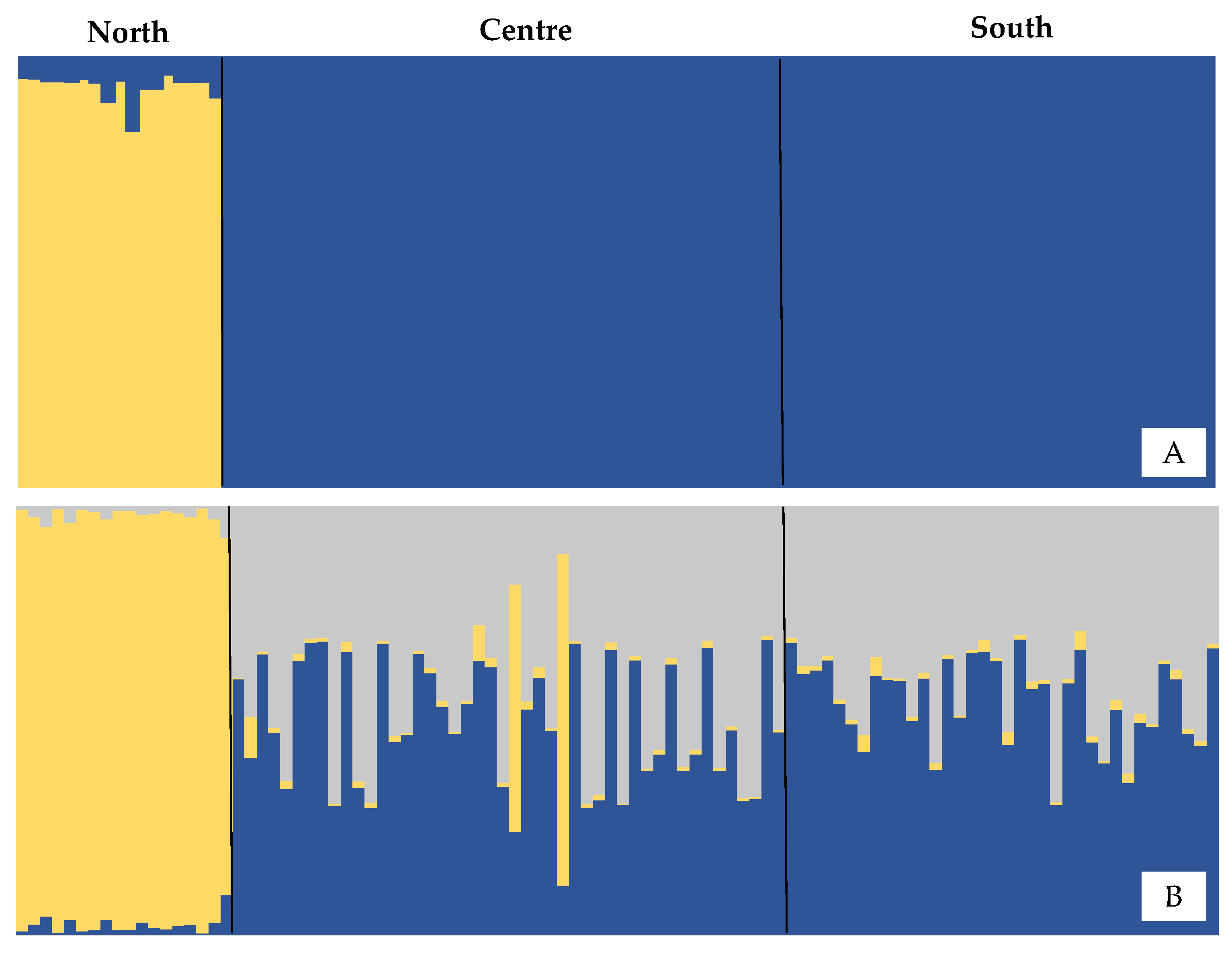
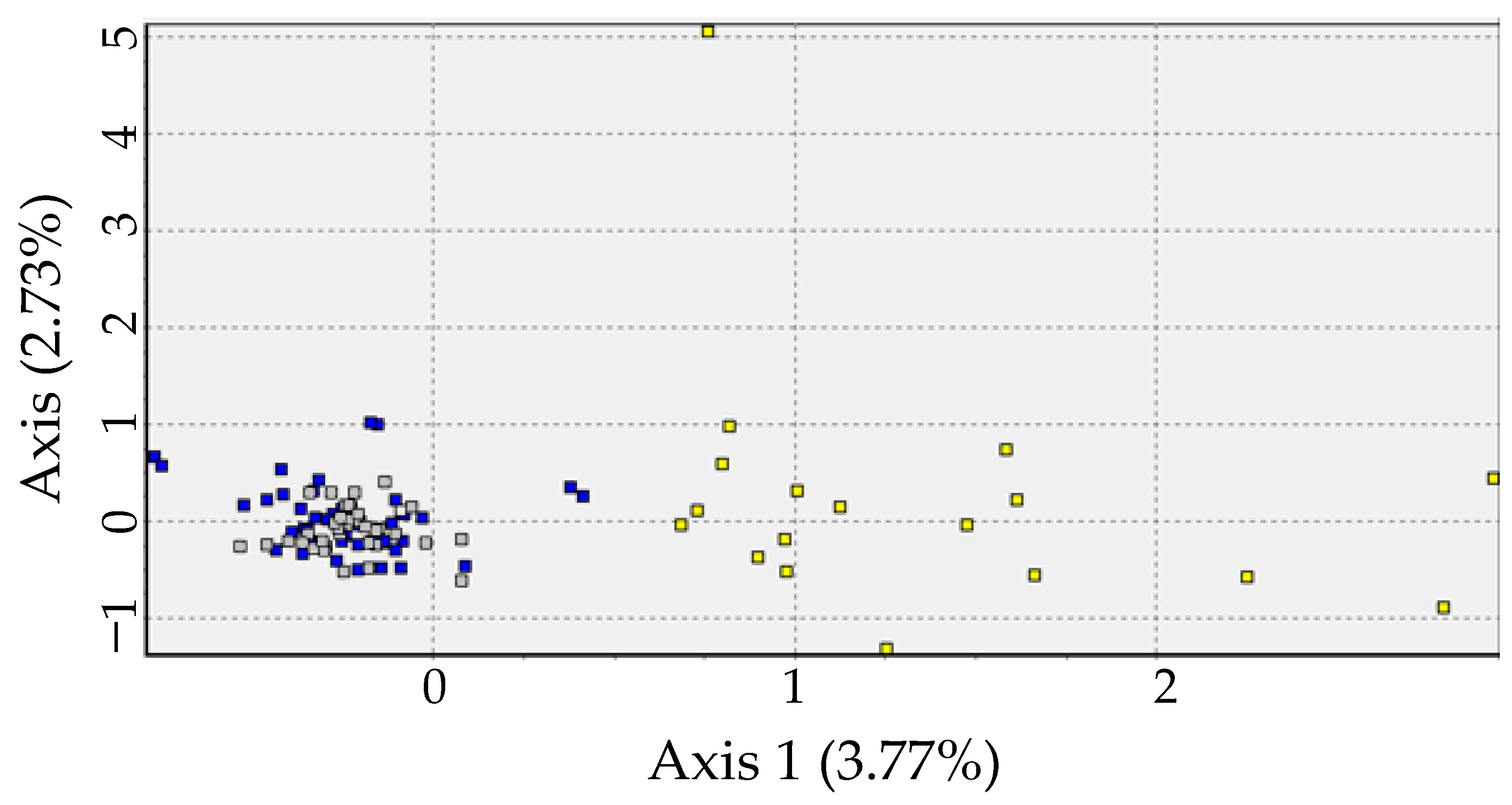
3.1. Microsatellites
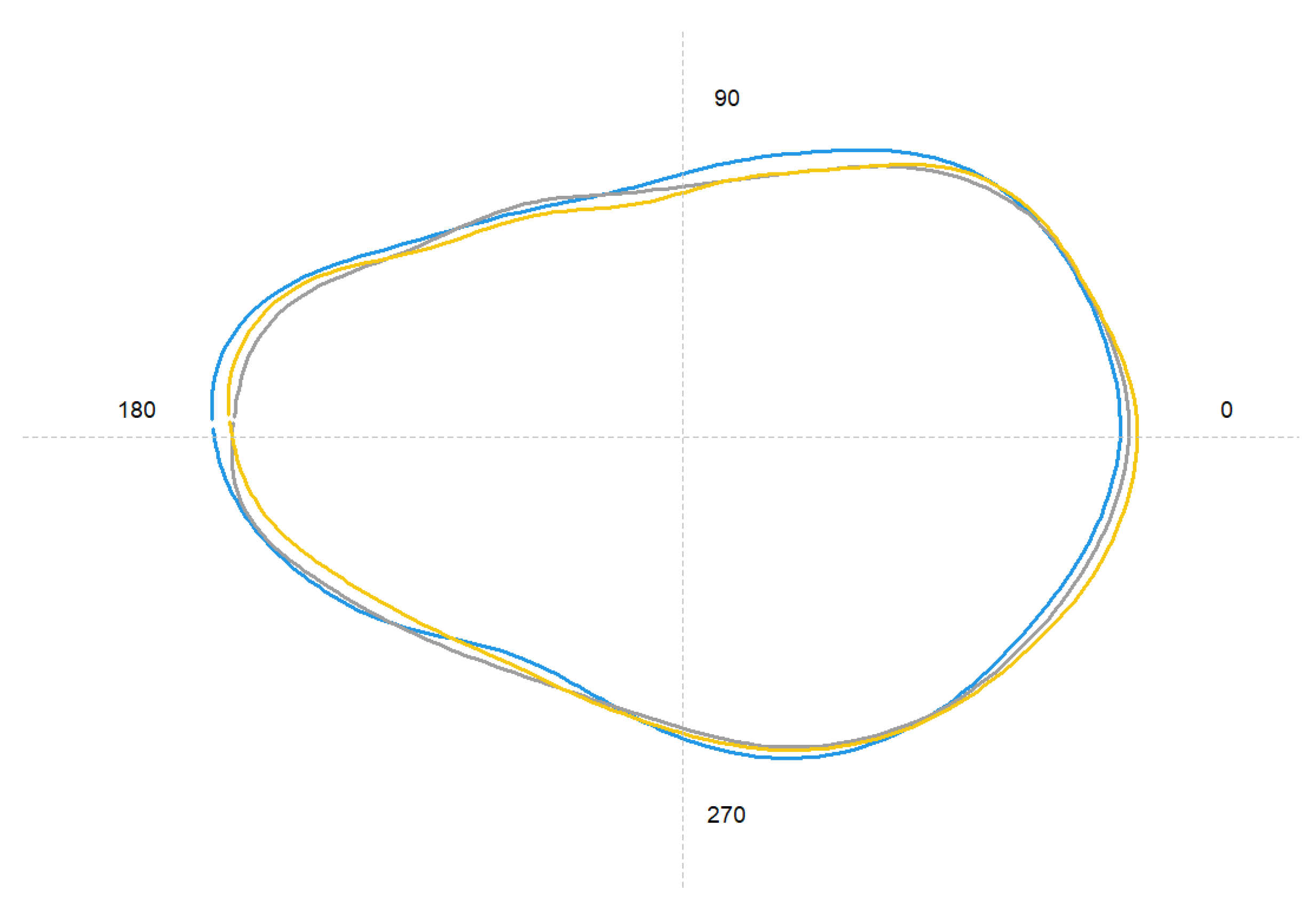
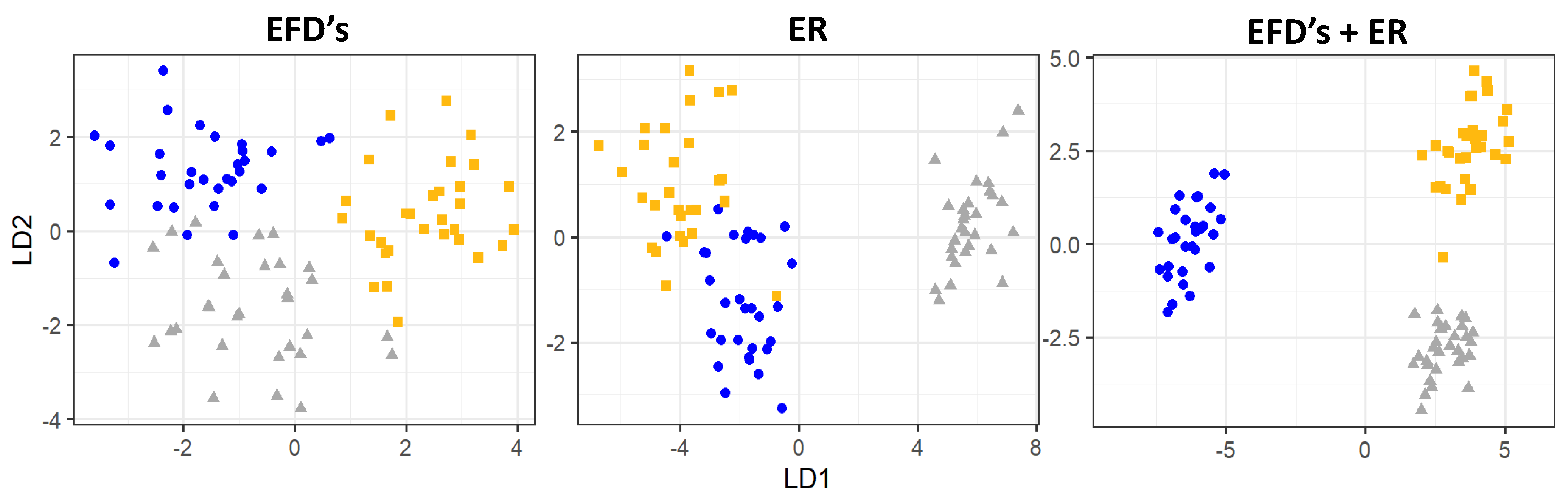
3.2. Otoliths
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haimovici, M.; Ignacio, J.M. Micropogonias furnieri (Desmarest, 1823). In Análise das Principais Pescarias Comerciais da Região Sudesde-Sul do Brasil: Dinâmica Populacional das Espécies em Exploração, 1st ed.; Cergole, M.C., Ávila-da-Silva, A.O., Rossi- Wongtschowski, C.L.D.B., Eds.; Sér. Doc. Revizee-Score Sul: São Paulo, Brazil, 2005; pp. 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, M.; Haimovici, M. Status of white croaker Micropogonias furnieri exploited in southern Brazil according to alternative hypotheses of stock discreetness. Fish. Res. 2006, 80, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimovici, M.; Cardoso, L.G.; Unpierre, R.G. Stocks and management units of Micropogonias furnieri (Desmarest, 1823) in southwestern Atlantic. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 44, 1080–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazzoler, A.E.A.D.M. Diversificação fisiológica e morfológica de Micropogonias furnieri (Desmarest, 1823) ao sul de Cabo Frio, Brasil. Bol. Do Inst. Ocean. 1971, 20, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, V.J. Synopsis of biological data on the whitemouth croaker Micropogonias furnieri (Desmarest, l823). FAO Fish. Synop. 1988, 150, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Puchnick-Legat, A.; Levy, J.A. Genetic structure of Brazilian populations of white mouth croaker Micropogronias furnieri (Perciformes: Sciaenidae). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2006, 49, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vasconcellos, A.V.; Lima, D.; Bonhomme, F.; Vianna, M.; Solé-Cava, A.M. Genetic population structure of the commercially most important demersal fish in the Southwest Atlantic: The whitemouth croaker (Micropogonias furnieri). Fish. Res. 2015, 167, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Vazzoler, A.E.A.D.M.; Phan, V.N. Estudo electroforético de proteínas de músculo esquelético de Micropogonias furnieri (Desmarest, 1823) da costa SE-S do Brasil. 1, Considerações técnicas. Bol. Inst. Oceanoqr. 1983, 32, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, R.; Pereira, A.; Jerez, B.; Marins, L.; Conceição, M.; Levy, J.A. Estudio preliminar de la estructura genética de la corvina Micropogonias furnieri, entre Rio Grande (Brasil) y el Rincon (Argentina). Frente Maritmo 1994, 15, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J.A.; Maggioni, R.; Conceição, M.B. Close genetic similarity among populations of the white croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) in the south and south-eastern Brazilian Coast. I. Allozyme studies. Fish. Res. 1998, 39, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazzoler, A.E.A.D.M.; Ngan, P.V. Padrões electroforéticos de proteínas gerais de cristalino de Micropogonias furnieri (Demarest, 1823), da costa sudeste-sul do Brasil: Estudo populacional. Bolm. Inst. Oceanogr. 1989, 37, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D. Genética de Populações da Corvina Micropogonias furnieri e Sistemática Molecular da Maria-da-Toca Bathygobius soporator. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Palacio, F.J. Revisión zoogeográfica marina del sur del Brasil. Bol. Inst. Oceanogr. 1980, 31, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floeter, S.R.; Soares-Gomes, A. Biogeographic and species richness patterns of Gastropoda on the southwestern Atlantic. Rev. Bras. Biol. 1999, 59, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, F.G.; Rodrigues, F.L.; Teixeira-Neves, T.P.; Vieira, J.P.; Azevedo, M.C.C.; Guedes, A.P.P.; Garcia, A.M.; Pessanha, A.L.M. Regional patterns in species richness and taxonomic diversity of the nearshore fish community in the Brazilian coast. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 208, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, S. Zoogeography of the Sea, 1st ed.; Sidgwick & Jackson: London, UK, 1953; 417p. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, J.C. Marine Zoogeography, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1974; 475p. [Google Scholar]
- Valentin, J.L.; Moreira, A.P. A matéria orgânica de origem zooplanctônica nas âguas de ressurgência de Cabo Frio (Brasil). Pascal Fr. Bibliogr. Databases 1978, 50, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Rodriguez, E.; Valentin, J.V.; Lacerda, D.; Jacob, S.A. Upwelling and downwelling at Cabo Frio (Brazil): Comparison of biomass and primary production responses. J. Plankton Res. 1992, 12, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzer, P.J.; Sale, P.F. (Eds.) Marine Metapopulations, 1st ed.; Elservier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; 577p. [Google Scholar]
- Shanks, A.L.; Largier, J.; Brink, L.; Brubaker, J.; Hoof, R. Demonstration of the onshore transport of larval invertebrates by the shoreward movement of an upwelling front. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahle, G.; Johansen, T.; Westgaardc, J.; Aglena, A.; Glover, K.A. Genetic management of mixed-stock fisheries “real-time”: The case of the largest remaining cod fishery operating in the Atlantic in 2007–2017. Fish. Res. 2018, 205, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Correia, A.T.; Vaz-Pires, P.; Froufe, E. Genetic diversity and population structure of the blue jack mackerel Trachurus picturatus across its western distribution. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Presa, P.; Correia, A.T.; Vaz-Pires, P.; Froufe, E. Spatio-temporal microsatellite data suggest a multidirectional connectivity pattern in Trachurus picturatus metapopulation from the NE Atlantic. Fish. Res. 2020, 225, 105499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, I.R.; Campana, S.E.; Bentzen, P. Estimating contemporary early life-history dispersal in an estuarine fish: Integrating molecular and otoliths elemental approaches. Mar. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.J.; Campana, S.E. Integrated stock mixture analysis for continuous and categorical data, with application to genetic–otolith combinations. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 67, 1533–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.T.; Ramos, A.A.; Barros, F.; Silva, G.; Hamer, P.; Morais, P.; Cunha, R.L.; Castilho, R. Population structure and connectivity of the European conger eel (Conger conger) across the Northeastern-Atlantic and Western- Mediterranean: Integrating molecular and otolith elemental approaches. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1509–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, A.N.; Coombs, S. Auditing mechanisms in teleost fishes: Significant variations in both hearing capabilities and auditory structures are found among species of bony fishes. Am. Sci. 1980, 68, 429–440. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S.E. Chemistry and composition of fish otoliths: Pathways, mechanisms and applications. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 188, 263–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Nin, B. Review of the growth regulation processes of otolith daily increment formation. Fish. Res. 2000, 46, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.M.; Thorrold, S.R.; David, O. Conover. Population differences in otolith chemistry have a genetic basis in Menidia menidia. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avigliano, E.; Velasco, G.; Volpedo, A.V. Use of lapillus otolith microchemistry as an indicator of the habitat of Genidens barbus from different estuarine environments in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2015, 98, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüssy, K.; Limburg, K.E.; Hélène, D.P.; Thomas, O.R.B.; Cook, K.; Heimbrand, Y.; Blass, M.; Sturrock, A.M. Trace element patterns in otoliths: The role of biomineralization. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 445–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, R.; Schwingel, P.R.; Pinto, E.; Almeida, A.; Correia, A.T. Stock structure of the Brazilian sardine Sardinella brasiliensis from Southwest Atlantic Ocean inferred from otolith elemental signatures. Fish. Res. 2022, 248, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anatro, A.; Pereira, A.N.; Lessa, E.P. Genetic structure of the white croaker, Micropogonias furnieri Desmarest 1823 (Perciformes: Sciaenidae) along Uruguayan coasts: Contrasting marine, estuarine, and lacustrine populations. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2011, 91, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, S.E.; Pérez, M.; Presa, P.; Thorrold, S.R.; Cabral, H.N. Integrating microsatellite DNA markers and otolith geochemistry to assess population struture ofEuropean hake (Merlucius merluccius). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 142, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, S.; Reis-Santos, P.; Cabral, H.N. Otolith chemistry in stock delineation: A brief overview, current challenges and future prospects. Fish. Res. 2016, 173, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Santos, P.; Vasconcelos, R.P.; Ruano, M.; Latkoczy, C.; Gunther, D.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H. Interspecific variations of otolith chemistry in estuarine fish nurseries. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 2595–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, T.R.; Avigliano, E.; Carvalho, B.M.; Miller, N.; Vianna, M. Population structure and habitat connectivity of Genidens genidens (Siluriformes) in tropical and subtropical coasts from Southwestern Atlantic. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 242, 106839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avigliano, E.; Pisonero, J.; Dománico, A.; Silva, N.; Sánches, S.; Volpedo, A.V. Spatial segregation and connectivity in young and adult stages of Megaleporinus obtusidens inferred from otolith elemental signatures: Implications for management. Fish. Res. 2018, 204, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, E.T.; Moraes, L.E.; Fernandes, F.C.; Fagundes Netto, E.B.; Gaelzer, L.R. Influência do fenômeno “El Niño” sobre as comunidades de peixes demersais da região de ressurgência de Arraial do Cabo Rio de Janeiro Brasil. In Proceedings of the VIII Colacmar: Congresso Latino-americano sobre Ciências do Mar, Trujillo, Peru, 17–21 October 1999; pp. 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcellos, A.V. Diferenciação molecular de estoques de corvinas (Micropogonias furnieri) na costa Atlântica da América do Sul. Ph.D. Thesis, UFRJ Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2012; 203p. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuelke, M. An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molecular Ecology Resources Primer Development Consortium; Arias, M.C.; Arnoux, E.; Bell, J.J.; Bernadou, A.; Bino, G.; Blatrix, R.; Bourgout, D.; Carrea, C.; Clamens, A.L.; et al. Permanent Genetic Resources added to Molecular Ecology Resources Databaser. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oosterhout, C.; Hutchinson, W.F.; Wills, D.P.M.; Shipley, P. Micro-checker: Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, J.A.; Letcher, B.H.; Nislow, K.H. CREATE: A software to create input files from diploid genotypic data for 52 genetic software programs. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, M.; Rousset, F. GENEPOP (version 1.2): Population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. J. Hered. 1995, 86, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Laval, G.; Schneider, S. Arlequin ver. 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform. 2005, 1, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; Von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conser. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, N.A. Distruct: A program for the graphical display of population structure. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhir, K.; Borsa, P.; Chikhi, L.; Raufaste, N.; Bonhomme, F. GENETIX 4.04, Logiciel sous Windows TM Pour la Génétique des Populations. Laboratoire Génome, Populations, Interactions; CNRS UMR 5000; Université de Montpellier II: Montpellier, France, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerli, P.; Felsenstein, J. Maximum likelihood estimation of a migration matrix and effective population sizes in n subpopulations by using a coalescent approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4563–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerli, P. Comparison of Bayesian and maximum likelihood inference of population genetic parameters. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Wagner, A.P.; Taper, M.L. ML-RELATE: A computer program for maximum likelihood estimation of relatedness and relationship. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libungan, L.A.; Pálsson, S. ShapeR: An R Package to Study Otolith Shape Variation among Fish Populations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, H.M.; Thorrold, S.R.; Shenker, J.M. Analysis of otolith chemistry in Nassau grouper (Epinephelus striatus) from the Bahamas and Belize using solution-based ICPMS. Coral Reefs 1999, 18, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpedo, A.V.; Cirelli, A.F. Otolith chemical composition as a useful tool for sciaenid stock discrimination in the south-western Atlantic. Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 25–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, R.E.; Willie, S.N.; Yang, L.; Greenberg, R.; Spatz, R.O.; Chen, Z.; Scriver, C.; Clancy, V.; Lam, J.W.; Thorrold, S. Certification of a fish otolith reference material in support of quality assurance for trace element analysis. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2005, 20, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, G.E.; Thorrold, S.R.; Jones, C.M.; Campana, S.E.; Mclaren, J.W.; Lam, J.W.H. Strontium and barium uptake in aragonitic otoliths of marine fish. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.J.; Campana, S.E.; Jones, C.M.; Thorrold, S.R. Experimental assessment of the effect of temperature and salinity on elemental composition of otoliths using laser ablation ICPMS. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.M.; Santos, P.; Correia, A.T. Discrimination of Trisopterus luscus stocks in the northern of Portugal using otolith elemental fingerprints. Aquat. Living Resour. 2011, 24, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, R.P.; Palma, E.D.; Piola, A.R. The influence of the Brazil and Malvinas Currents on the southwestern Atlantic Shelf circulation. Ocean. Sci. 2010, 6, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, A.C.G.; Miño, C.I.; Marins, L.F.F.; Monteiro-Neto, C.; Miranda, L.; Schwingel, P.R.; Lemos, V.M.; González-Castro, M.; Castello, J.P.; Vieira, J.P. Microsatellite variation and genetic structuring in Mugil liza (Teleostei: Mugilidae) populations from Argentina and Brazil. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 149, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Hrbek, T.; Farias, I.P.; Schneider, H.; Sampaio, I. Population genetic structuring of the king weakfish, Macrodon ancylodon (Sciaenidae), in Atlantic coastal waters of South America: Deep genetic divergence without morphological change. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 4361–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Filho, A.; Santos, S.; Sampaio, I. Macrodon atricauda (Günther, 1880) (Perciformes: Sciaenidae), a valid species from the southwestern Atlantic, with comments on its conservation. Zootaxa 2010, 2519, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, V.M.; Monteiro-Neto, C.; Cabral, H.; Vieira, J.P. Stock identification of tainha (Mugil liza) by analyzing stable carbon and oxygen isotopes in otoliths. Fish. Bull. 2017, 115, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, R.; Potts, W.M.; Santos, C.V.; Sauer, W.H.H.; Shaw, P.W. Population connectivity and phylogeography of a coastal fish, Atractoscion aequidens (Sciaenidae), across the Benguela Current region: Evidence of an ancient vicariant event. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, R.; Potts, W.M.; Sauer, W.H.H.; Shaw, P.W. Incipient genetic isolation of a temperate migratory coastal sciaenid fish (Argyrosomus inodorus) within the Benguela Cold Current system. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, R.; Potts, W.M.; Sauer, W.H.; Santos, C.V.; Kruger, J.; Thomas, J.A.; Shaw, P.W. Molecular genetic, life-history and morphological variation in a coastal warm-temperate sciaenid fish: Evidence for an upwelling-driven speciation event. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lett, C.; Veitch, J.; Van Der Lingen, C.D.; Hutchings, L. Assessment of an environmental barrier to transport of ichthyoplankton from the southern to the northern Benguela ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 347, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secor, D.H.; Dean, M. Somatic growth effects on the otolith -fish size relationship in young pondreared striped bass, Mosone saxatilis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedland, K.D.; Reddin, D. Use of otolith morphology in stock discriminations of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1994, 54, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmore, C.; Fogarty, K.; Neat, F.; Brophy, D.; Trueman, C.N.; Milton, A.; Mariani, S. A comparison of otolith microchemistry and otolith shape analysis for the study of spatial variation in a deep-sea teleost, Coryphaenoides rupestris. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2010, 89, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignon, M.; Morat., F. Environmental and genetic determinant of otolith shape revealed by non-indigenous tropical fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 411, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignon, M. Ontogenetic trajectories of otolith shape during shift in habitat use: Interaction between otolith growth and environment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 420–421, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsdon, T.S.; Wells, B.K.; Campana, S.E.; Gillanders, B.M.; Jones, C.M.; Limburg, K.E.; Secor, D.H.; Thorrold, S.R.; Walther, B.D. Otolith Chemistry to Describe Movements and Life-History Parameters of Fishes-Hypotheses, Assumptions, Limitations and Inferences, 1st ed.; CRC Press In Oceanography Marine Biology: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodson, L.E.; Wells, B.K.; Grimes, C.B.; Franks, R.P.; Santora, J.A.; Carr, M.H. Water and otolith chemistry identify exposure of juvenile rockfish to upwelled waters in an open coastal system. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 473, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.; Severin, K.P. Otolith chemistry analyses indicate that water Sr:Ca is the primary factor influencing otolith Sr:Ca for freshwater and diadromous fish but not for marine fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 1790–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limburg, K.E.; Olsonb, C.; Waltherc, Y.; Daled, D.; Slompe, C.P.; Høie, H. Tracking Baltic hypoxia and cod migration over millennia with natural tags. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2011, 108, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limburg, K.E.; Walther, B.D.; Lu, Z.; Jackman, G.; Mohan, J.; Walther, Y.; Nissling, A.; Weber, P.K.; Schmitt, A.K. In search of the dead zone: Use of otoliths for tracking fish exposure to hypoxia. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 141, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avigliano, E. Optimizing the methodological design in fish stock delineation from otolith chemistry: Review of spatio-temporal analysis scales. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 30, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daros, A.; Spach, H.L.; Correia, A.T. Habitat residency and movement patterns of Centropomus parallelus juveniles in a subtropical estuarine complex. J. Fish. Biol. 2016, 88, 1796–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Froufe, E.; Sial, A.N.; Caeiro, A.; Vaz-Pires, P.; Correia, A.T. Population structure of the blue jack mackerel (Trachurus picturatus) in the NE Atlantic inferred from otolith microchemistry. Fish. Res. 2018, 197, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.G.; Moreira, C.; Cardoso, J.F.M.F.; Brummer, G.J.A.; Van Gaever, P.; Van Der Veer, H.W.; Queiroga, H.; Santos, P.T.; Correia, A.T. Movement, connectivity and population structure of the intertidal fish Lipophrys pholis as revealed by otolith oxygen and carbon stable isotopes. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelir-Alves, J.; Daros, F.A.; Spach, H.L.; Soeth., M.; Correia, A.T. Otoliths as a tool to study reef fish population structure from coastal islands of south Brazil. Mar. Biol. Res. 2018, 14, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeth, M.; Spach, H.L.; Daros, F.A.; Adelir-Alvesa, J.; Almeida, A.C.O.; Correia, A.T. Stock structure of Atlantic spadefish Chaetodipterus faber from Southwest Atlantic Ocean inferred from otolith elemental and shape signatures. Fish. Res. 2019, 211, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.R.; Araújo, F.G. Use of a tropical bay in south eastern Brazil by juvenile and subadult Micropogonias furnieri (Perciformes.Sciaenidae). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, D.M.; Tanasichuk, R.W. Biological basis of maturation and spawning waves in pacific Herring (Clupea harengus pallasi). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasuka, A.; Oozeki, Y.; And Kubota, H. Multi-species regime shifts reflect in spawning temperature optima of small pelagic fish in the western North Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 360, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.M.; Roy, M.S. Phylogeography of a high-dispersal New Zealand sea-star: Does upwelling block geneflow? Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 2797–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, P.R.; Papadopoulos, I.; Mmonwa, K.L.; Matumba, T.G.; Mcquaid, C.D.; Barker, N.P.; Beheregaray, L.B. Climate-driven genetic divergence of limpets with different life histories across a southeast African marine biogeographic disjunction: Different processes, same outcome. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 5025–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
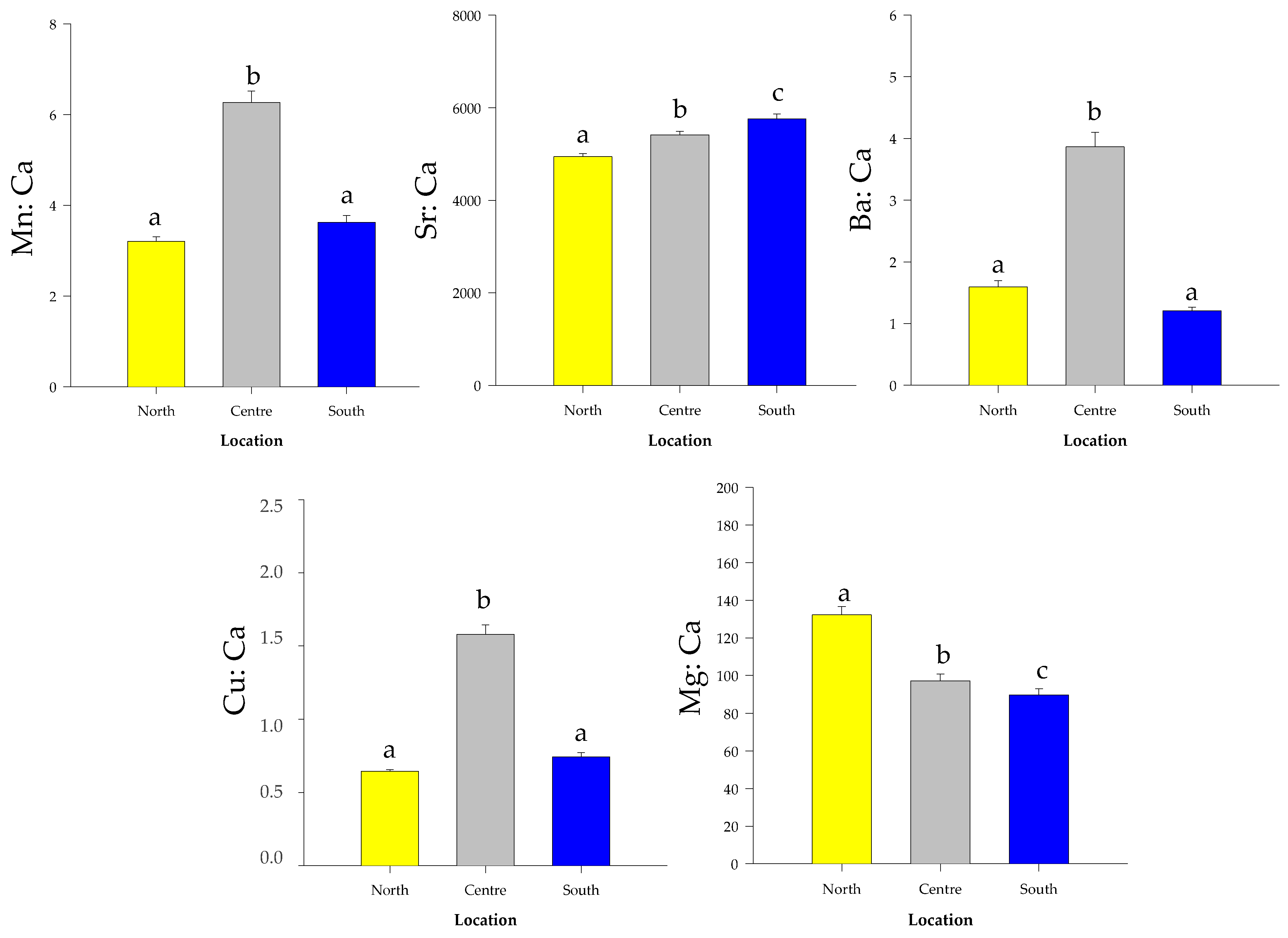
| Locus | Mfur02 | Mfur03 | Mfur04 | Mfur06 | Mfur07 | Mfur10 | Mfur12 | Mfur17 | Mfur20 | Mfur24 | Mfur25 | Mfur26 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNA | 31 | 33 | 15 | 10 | 19 | 28 | 9 | 10 | 6 | 18 | 26 | 18 |
| North | ||||||||||||
| N | 12 | 10 | 12 | 11 | 16 | 5 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 15 | 9 |
| NA | 9 | 14 | 9 | 4 | 9 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 12 | 8 |
| HO | 0.583 | 0.700 | 0.500 | 0.545 | 0.500 | 0.800 | 0.273 | 0.250 | 0.727 | 0.667 | 0.800 | 0.444 |
| HE | 0.809 | 0.910 | 0.854 | 0.566 | 0.727 | 0.860 | 0.483 | 0.569 | 0.587 | 0.875 | 0.887 | 0.747 |
| HWE | 0.170 | 0.097 | 0.013 | 0.934 | 0.976 | 0.363 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.795 | 0.631 | 0.051 | 0.107 |
| FIS | 0.319 | 0.280 | 0.450 | 0.084 | 0.341 | 0.179 | 0.474 | 0.590 | −0.194 | 0.279 | 0.132 | 0.453 |
| Center | ||||||||||||
| N | 35 | 34 | 33 | 37 | 36 | 37 | 35 | 31 | 36 | 32 | 27 | 34 |
| NA | 21 | 25 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 22 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| HO | 0.857 | 0.971 | 0.727 | 0.432 | 0.722 | 0.946 | 0.657 | 0.581 | 0.361 | 0.844 | 0.852 | 0.824 |
| HE | 0.920 | 0.939 | 0.770 | 0.469 | 0.711 | 0.925 | 0.689 | 0.539 | 0.472 | 0.881 | 0.878 | 0.872 |
| HWE | 0.485 | 0.185 | 0.957 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.247 | 0.775 | 0.997 | 0.386 | 0.983 | 0.054 | 0.380 |
| FIS | 0.082 | −0.019 | 0.071 | 0.091 | −0.002 | −0.008 | 0.060 | −0.061 | 0.249 | 0.058 | 0.049 | 0.070 |
| South | ||||||||||||
| N | 40 | 41 | 44 | 43 | 39 | 40 | 32 | 45 | 45 | 35 | 44 | 42 |
| NA | 24 | 26 | 11 | 8 | 10 | 22 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 13 | 18 | 16 |
| HO | 0.875 | 0.902 | 0.705 | 0.395 | 0.795 | 0.800 | 0.750 | 0.600 | 0.422 | 0.829 | 0.932 | 0.929 |
| HE | 0.904 | 0.936 | 0.755 | 0.384 | 0.733 | 0.922 | 0.723 | 0.572 | 0.499 | 0.855 | 0.890 | 0.898 |
| HWE | 0.000 | 0.069 | 0.000 | 0.999 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.411 | 0.683 | 0.122 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| FIS | 0.044 | 0.048 | 0.078 | −0.017 | −0.071 | 0.144 | −0.022 | −0.037 | 0.165 | 0.045 | −0.036 | −0.022 |
| Location | North | Center | South |
|---|---|---|---|
| North | 0.000 | - | - |
| Center | 0.092 | 0.000 | - |
| South | 0.101 | 0.012 | 0.000 |
| To North | To Center | To South | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | (CI 95%) | M | (CI 95%) | M | (CI 95%) | |
| From North | - | - | 0.867 | (0.573–1160) | 1.081 | (0.480–1233) |
| From Center | 0.667 | (0.393–0.933) | - | - | 0.602 | (0.573–1160) |
| From South | 0.834 | (0.480–1233) | 0.789 | (0.367–1.360) | - | - |
| ER | Predicted Site | % Overall Reallocation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Site | North | Center | South | |
| North | 100% | 97% | ||
| Center | 90% | 10% | ||
| South | 100% | |||
| EFDs | ||||
| Original Site | North | Center | South | |
| North | 100% | |||
| Center | 90% | 10% | 97% | |
| South | 100% | |||
| ER + EFDs | ||||
| Original Site | North | Center | South | |
| North | 100% | |||
| Center | 100% | 100% | ||
| South | 100% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, T.P.; Vilasboa, A.; Araújo, F.G.; de Moura Gama, J.; Correia, A.T. Identifying Whitemouth Croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) Populations along the Rio de Janeiro Coast, Brazil, through Microsatellite and Otolith Analyses. Biology 2023, 12, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030360
Franco TP, Vilasboa A, Araújo FG, de Moura Gama J, Correia AT. Identifying Whitemouth Croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) Populations along the Rio de Janeiro Coast, Brazil, through Microsatellite and Otolith Analyses. Biology. 2023; 12(3):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030360
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, Taynara Pontes, Anderson Vilasboa, Francisco Gerson Araújo, Joana de Moura Gama, and Alberto Teodorico Correia. 2023. "Identifying Whitemouth Croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) Populations along the Rio de Janeiro Coast, Brazil, through Microsatellite and Otolith Analyses" Biology 12, no. 3: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030360
APA StyleFranco, T. P., Vilasboa, A., Araújo, F. G., de Moura Gama, J., & Correia, A. T. (2023). Identifying Whitemouth Croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) Populations along the Rio de Janeiro Coast, Brazil, through Microsatellite and Otolith Analyses. Biology, 12(3), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030360







