The Isopropyl Gallate Counteracts Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Mice
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Isopropyl Gallate (IPG)
2.2. Experimental Animals and Euthanasia
2.3. Experimental Model of Induction of Hemorrhagic Cystitis with Ifosfamide
2.4. Evaluation of the Bladder Tissue Wet Weight
2.5. Evaluation of Macroscopic Parameters
2.6. Histopathological Analysis
2.7. Quantification of Bladder Hemoglobin by the Cyanmethemoglobin Method
2.8. Evaluation of Vascular Protein Leakage by Evans Blue Dye Technique
2.9. Determination of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity in Bladder Tissue
2.10. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels in Bladder Tissue
2.11. Ultra-Sensitive Quantitative Determination of C-Reactive Protein (CRP) in Serum Samples by Immunoturbidimetry
2.12. Tissue Levels of TNF-α and IL-1β by ELISA
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Chemical Parameters of Isopropyl Gallate (IPG)
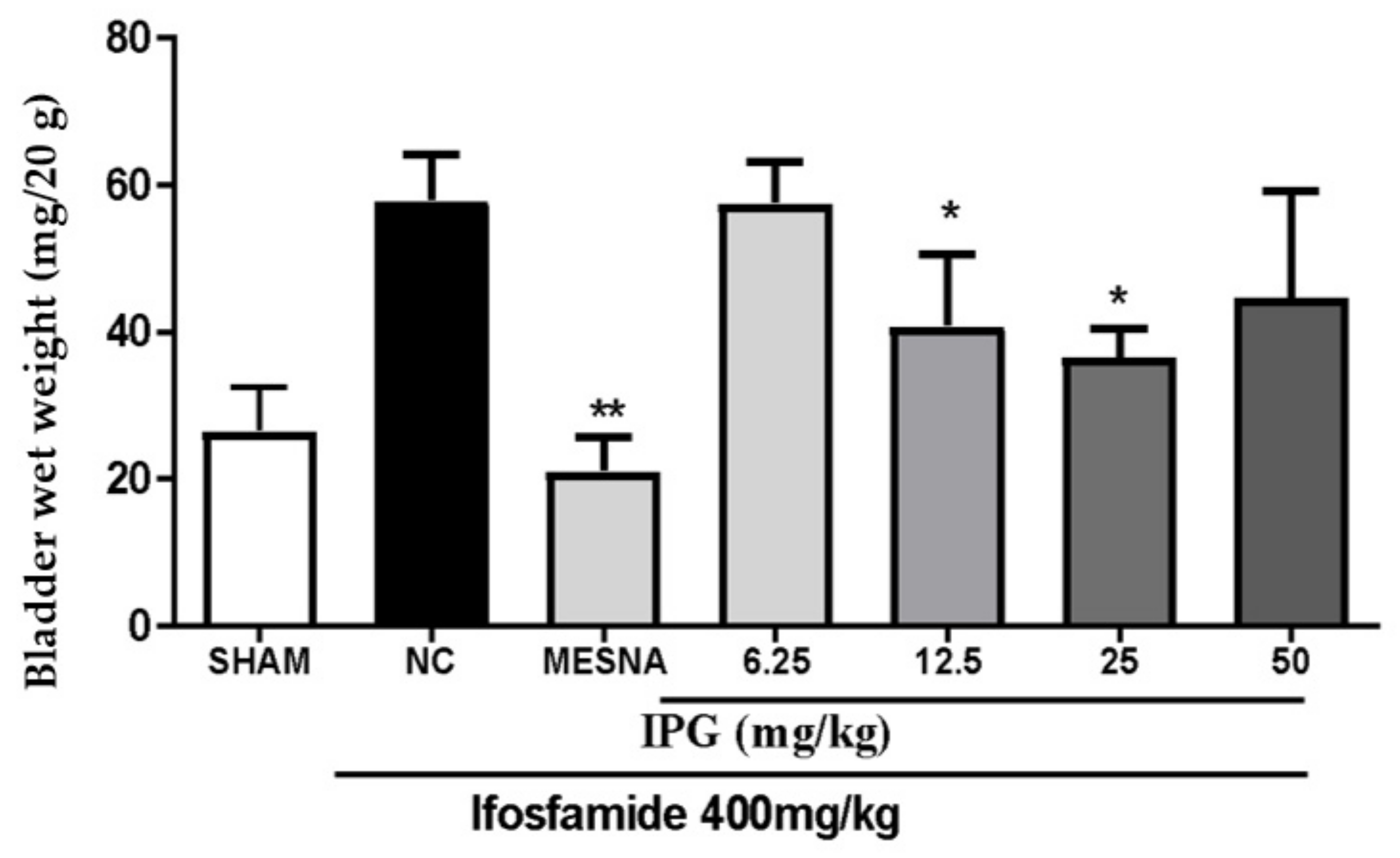
3.2. Effects of IPG on Wet Weight of the Bladder Tissue
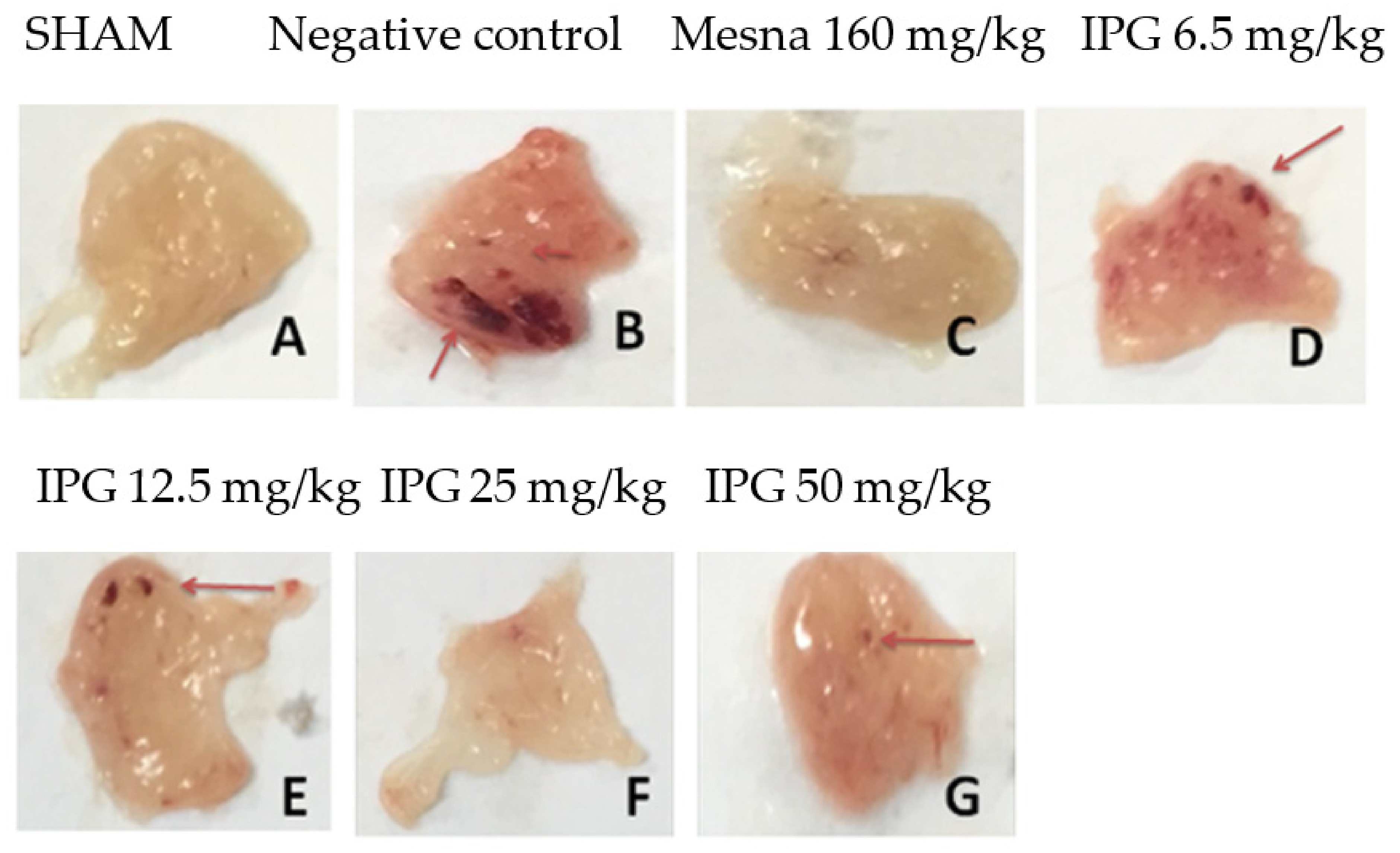
3.3. Effects of IPG on Macroscopic Parameters
3.4. Effects of IPG on Histopathological Changes
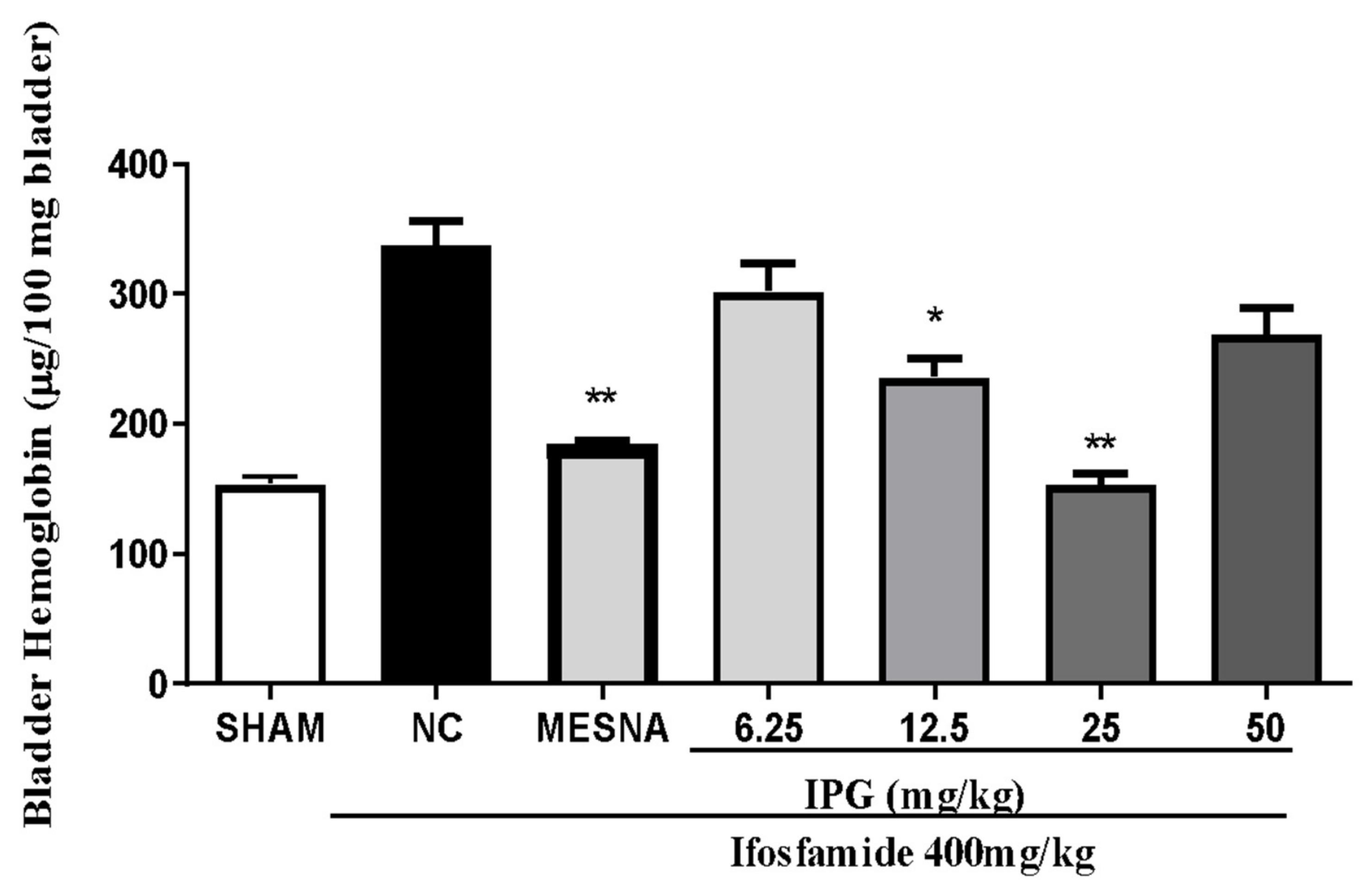
3.5. Effect of IPG on Bleeding Induced by Ifosfamide
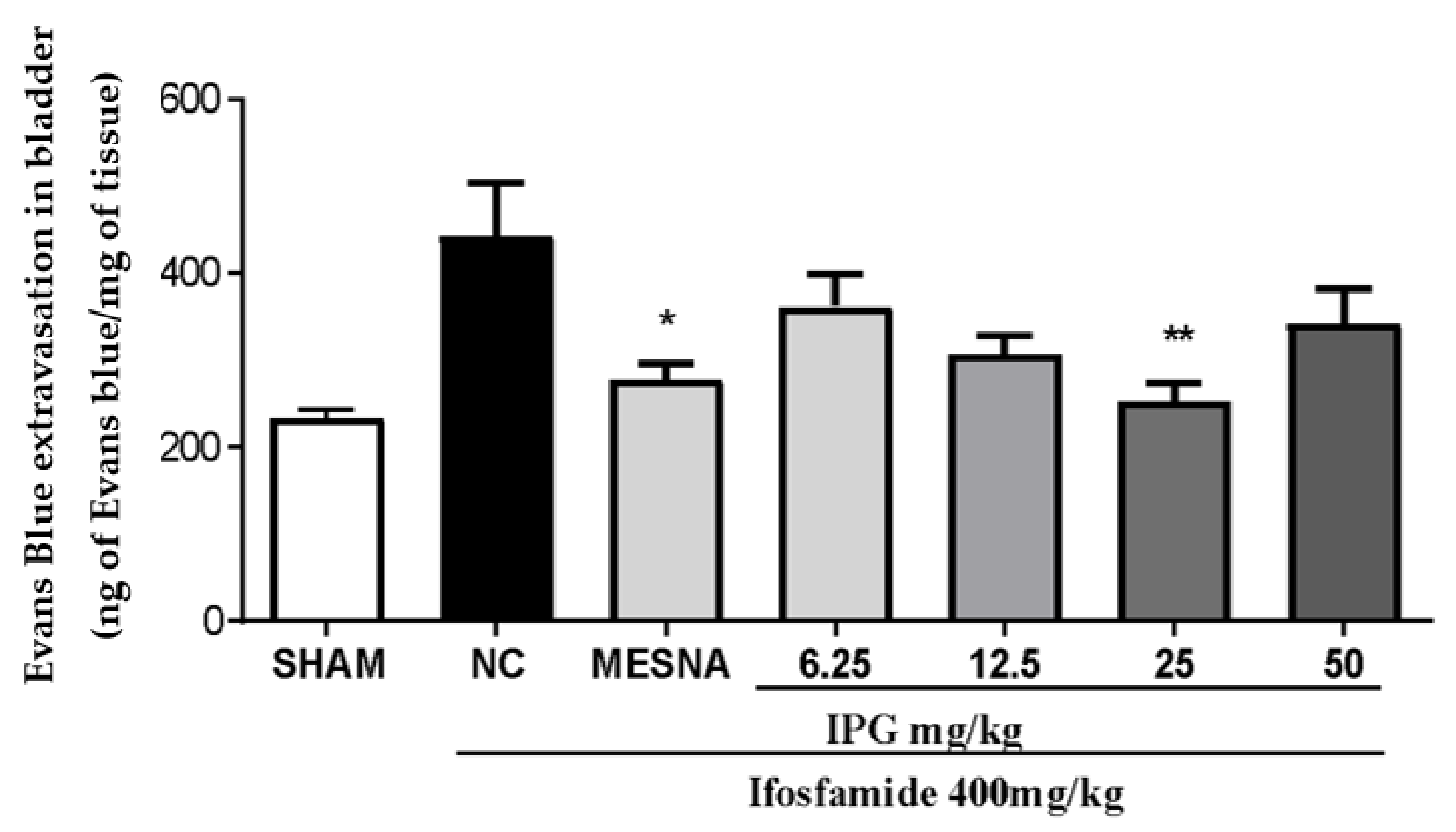
3.6. Effects of IPG on Vascular Protein Leakage
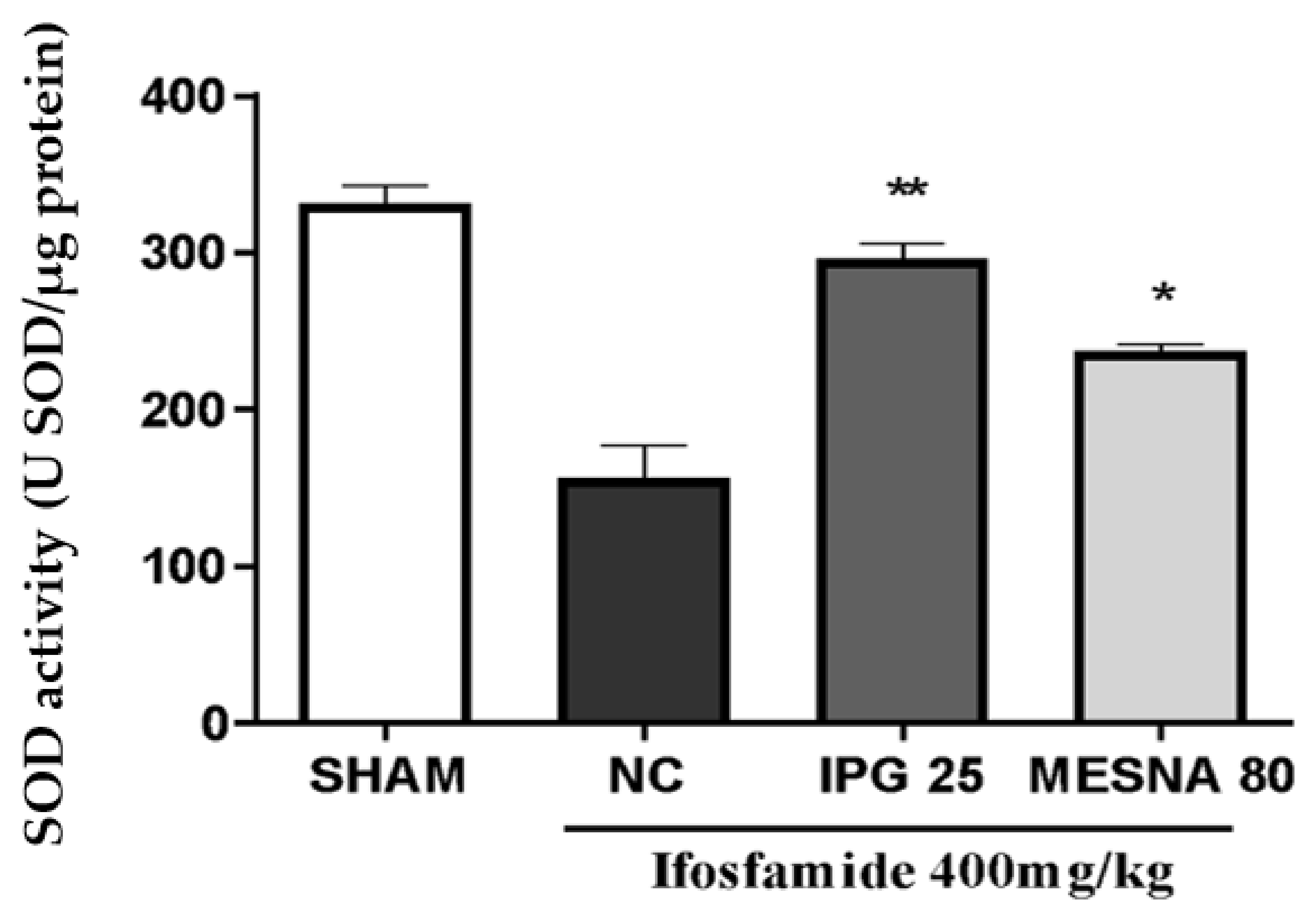
3.7. Effect of IPG on Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity
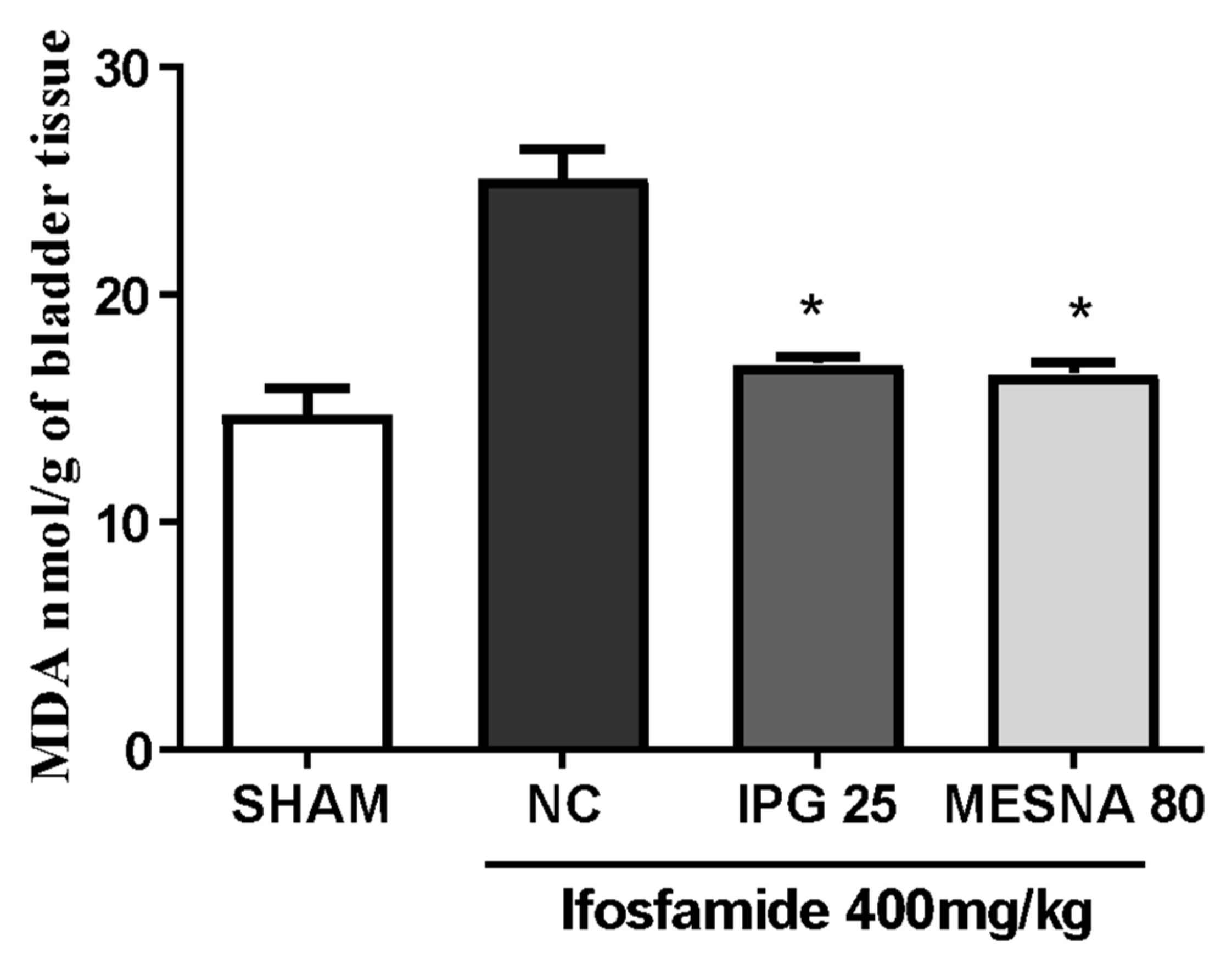
3.8. Effect of IPG on Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels
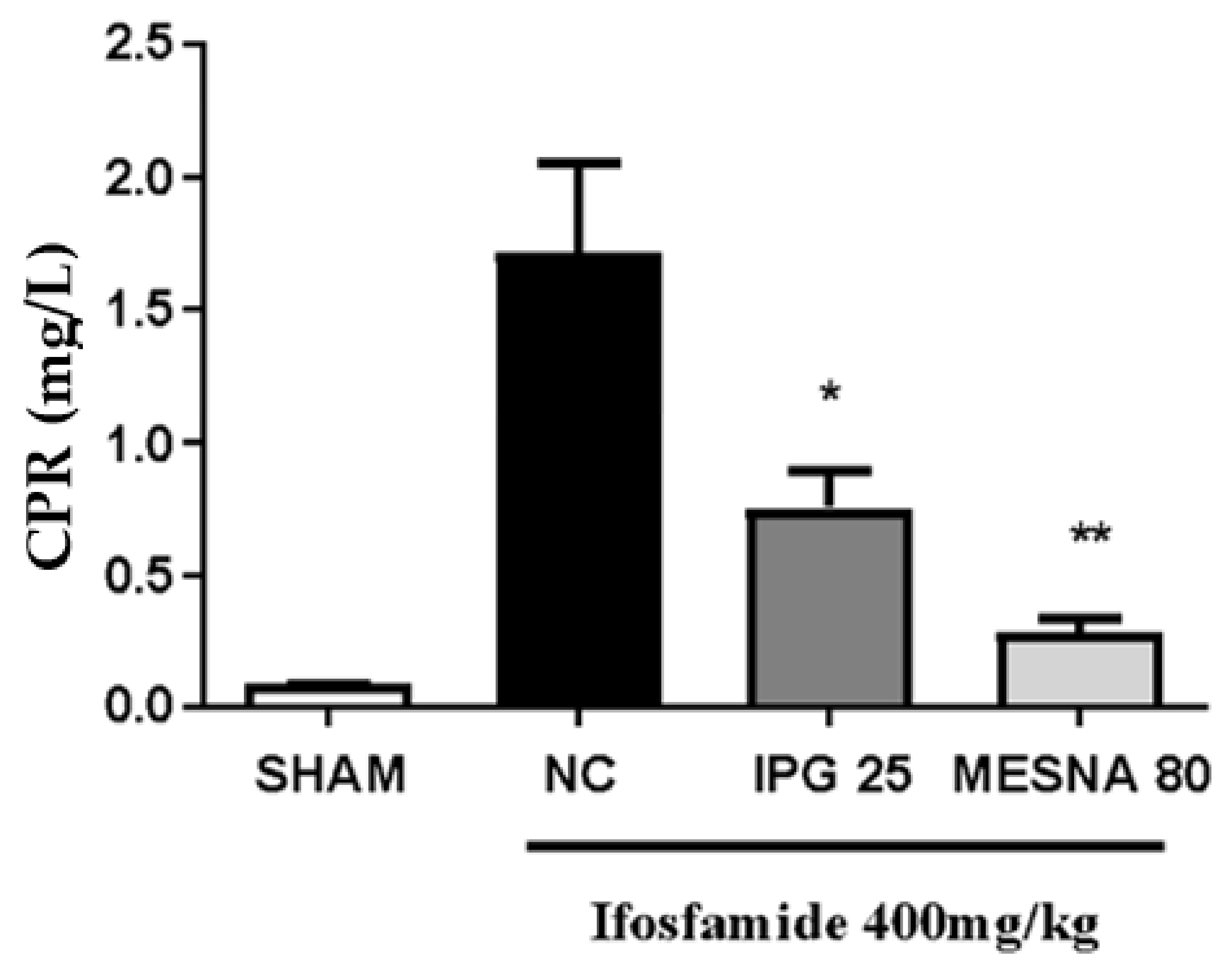
3.9. Effect of IPG on C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
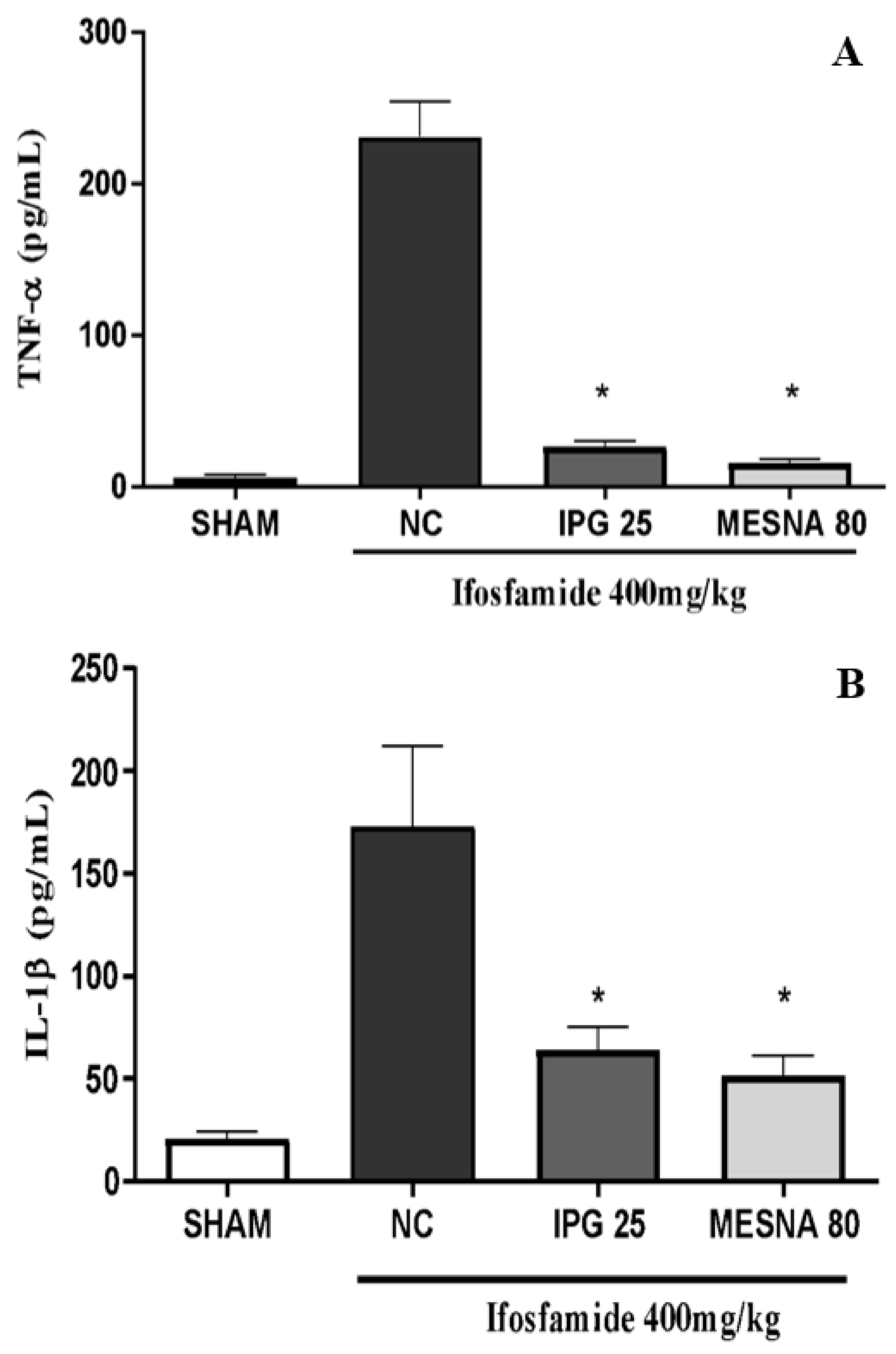
3.10. Effect of IPG on TNF-α and IL-1β Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sloderbach, A.; Górska, A.; Sikorska, M.; Misiura, K.; Hładoń, B. Klasyczne oksazafosforinany—Metabolizm i właściwości terapeutyczne--nowe implikacje [Classical oxazaphosphorines—metabolism and therapeutic properties—new implications]. Postepy Hig. I Med. Dosw. 2013, 67, 1235–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matz, E.L.; Hsieh, M.H. Review of advances in uroprotective agents for cyclophosphamide-and ifosfamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. Urology 2017, 100, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vieira, M.M.; Macêdo, F.Y.B.; Belarmino Filho, J.N.; Costa, A.C.L.V.; Cunha, A.N.; Silveira, E.R.; Brito, G.A.C.; Ribeiro, R.A. Ternatin, a flavonoid, prevents cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in rats. Phytother. Res. 2004, 8, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voelcker, G. Oxazaphosphorine cytostatics: From serendipity to rational drug design. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2019, 30, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombel, M.; Wallet, H.L. Cistitis hemorrágica: Fisiopactología y conducta práctica. EMC-Urol. 2019, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, C.K.; Mota, J.M.; Souza, M.L.; Leitão, B.T.; Souza, M.H.; Brito, G.A.; Cunha, F.Q.; Ribeiro, R.A. Amifostine and glutathione prevent ifosfamide- nd acrolein-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, A.; Topal, T.; Oter, S. Pathophysiological aspects of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis; implication of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as well as PARP activation. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2007, 23, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, O.; Keles, H. Pathologic examination of the protective effect of glycyrrhizin on cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in rats. Kocatepe Vet. Derg. 2019, 12, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, S.; Dru, C.; Bhowmick, N.A. Mechanisms of hemorrhagic cystitis. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2014, 2, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, D.N.; Jena, G.B. Intervention of astaxanthin against cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage: A study in mice. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2009, 180, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Yang, D.; Wu, X.; Zhu, J.; Wei, W.; Yang, B. Cytoprotective effects of glycyrrhetinic acid liposome against cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis through inhibiting inflammatory stress. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, I. Uroprotective mechanisms of natural products against cyclophosphamide-induced urinary bladder toxicity: A comprehensive review. Acta. Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2020, 19, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.L.G.; Cunha, F.V.M.; Sousa-Neto, B.P.S.; Oliveira, L.S.A.; Lopes, M.E.; Rezende, D.C.; Sousa, I.J.O.; Nogueira, K.M.; Souza, L.K.M.; Medeiros, J.V.R.; et al. α-Phellandrene attenuates tissular damage, oxidative stress, and TNF-α levels on acute model ifosfamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.H.; Salgado, H.R. Gallic acid: Review of the methods of determination and quantification. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, L.B. Anti-inflammatory effect of methyl gallate on experimental arthritis: Inhibition of neutrophil recruitment, production of inflammatory mediators, and activation of macrophages. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hu, J.; Hu, D.; Yang, X. A role of gallic acid in oxidative damage diseases: A comprehensive review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19874174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Hou, Y.; Ai, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, X. Gallic acid: Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Shen, X.-J.; Xiao, C.-N.; Wang, S.-X.; Zheng, X.-H. Isopropyl-3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate. Acta Cryst. 2012, E68, o650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva Junior, R.N.C.; Fialho, S.E.M.; Assunção, A.K.M.; Machado, J.L.; Arruda, D.; Furtado, P.G.R.; Gonçalves, F.A.; Nascimento, F.R.F. Caracterização do modelo inflamatório de cistite induzida por ciclofosfamida em camundongos Swiss. Rev. De Ciências Da Saúde 2013, 15, 55–67. Available online: http://www.periodicoseletronicos.ufma.br/index.php/rcisaude/article/view/1922 (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Gray, K.J.; Engelmann, U.H.; Johnson, E.H.; Fishman, I.J. Evaluation of misoprostol cytoprotection of the bladder with cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) therapy. J. Urol. 1986, 136, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harold, J.; Drabkin, L. Spectrophotometric studies. J. Biol. Chem. 1935, 112, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, F.Y.; Mourão, L.T.; Freitas, H.C.; Lima-Junior, R.C.; Wong, D.A.; Oria, R.B.; Vale, M.L.; Brito, G.A.; Cunha, F.Q.; Ribeiro, R.A. Interleukin-4 modulates the inflammatory response in ifosfamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. Inflammation 2011, 35, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Samanta, L.; Chainy, G.B.D. A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase using nitrite formation by superoxide radicals. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 37, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Mihara, M.; Uchiyama, M. Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Sherif, I.O.; Nakshabandi, Z.M.; Mohamed, M.A.; Sarhan, O.M. Uroprotective effect of oleuropein in a rat model of hemorrhagic cystitis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 74, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theman, H.; Oberdorf, E.; Brock, N.; Pohl, J. Electron microscopic investigations of cyclophosphamide-induced lesions of the urinary bladder of the rat and their prevention by MESNA. Urol. Int. 1987, 42, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.R.; Fong, T.; Belmar, N.; Saban, M.; Felsen, D.; Te, A. Modulating bladder neuro-inflammation: RDP58, a novel anti-inflammatory peptide, decreases inflammation and nerve growth factor production in experimental cystitis. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, F.Y.; Baltazar, F.; Mourão, L.C.; Almeida, P.R.; Mota, J.M.; Schmitt, F.C.; Ribeiro, R.A. Induction of COX-2 expression by acrolein in the rat model of hemorrhagic cystitis. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 59, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börner, K.; Kisro, J.; Brüggemann, S.K.; Hagenah, W.; Peters, S.O.; Wagner, T. Metabolism of ifosfamide to chloroacetaldehyde contributes to antitumor activity in vivo. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2000, 28, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.A.; Chess-Williams, R.; McDermott, C. Novel insights into the mechanism of cyclophosphamide-induced bladder toxicity: Chloroacetaldehyde’s contribution to urothelial dysfunction in vitro. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monach, P.A.; Arnold, L.M.; Merkel, P.A. Incidence and prevention of bladder toxicity from cyclophosphamide in the treatment of rheumatic diseases: A data-driven review. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, S.L.; Downie, P.A.; Waters, K.D.; Ashley, D.M.; Heath, J.A. Adverse hypersensitivity reactions to Mesna as adjunctive therapy for cyclophosphamide. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 49, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeira, V.T.; Leite, C.E.; Santo, A.A., Jr.; Edelweiss, M.I.; Calixto, J.B.; Campos, M.M.; Morrone, F.B. Effects of the hydroalcoholic extract of Phyllanthus niruri and its isolated compounds on cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in mouse. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2011, 384, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis: A revolution in toxicology, risk assessment and medicine. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis and medicine. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 66, 594–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, T.G.; Camandola, S.; Mattson, M.P. Hormetic Dietary Phytochemicals. NeuroMolecular Med. 2008, 10, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campobasso, O.; Berrino, F. Early effects of cyclophosphamide on mouse bladder epithelium. Pathol. Microbiol. 1972, 38, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas-Filho, A.C.; Pereira, V.B.M.; Wong, D.V.T.; Nobre, L.M.S.; Melo, A.T.; Silva, C.M.S.; Wanderley, C.W.S.; Nour, M.L.; Araújo, L.C.N.C.; Silva, R.O.; et al. Neutrophils contribute to the pathogenesis of hemorrhagic cystitis induced by ifosfamide. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 62, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, K.; Ahmad, F.; Rashid, H.; Raisuddin, S. Protective effect of S-allylcysteine against cyclophosphamide-induced bladder hemorrhagic cystitis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3368–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozguven, A.; Yilmaz, O.; Taneli, F.; Ulman, C.; Vatansever, S.; Onag, A. Protective effect of ketamine against hemorrhagic cystitis in rats receiving ifosfamide. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2014, 46, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoosh, R.; Nystrom, L. Antioxidant potency of gallic acid, methyl gallate and their combinations in sunflower oil triacylglycerols at high temperature. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velderrain-Rodríguez, G.R.; Torres-Moreno, H.; Villegas-Ochoa, M.A.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Robles-Zepeda, R.E.; Wall-Medrano, A.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Gallic acid content and an antioxidant mechanism are responsible for the antiproliferative activity of ‘ataulfo’ mango peel on LS180 cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanyam, D.; Gurunathan, D.; Gaayathri, R.; Priya, V.V. Comparative evaluation of salivary malondialdehyde levels as a marker of lipidperoxidation in early childhood caries. Eur. J. Dent. 2018, 12, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mameria, A.; Bournine, L.; Mounia, L.; Bensalem, S.; Iguer-Ouada, S. Oxidative stress as an underlying mechanism of anticancer drugs cytotoxicity on human red blood cells’ membrane. Toxicol. Vitr. 2021, 72, 105106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.K.; Park, H.S.; Han, I.; Mihyun, O.; Namkoong, H.; Kim, H.K.; Hwanhg, D.W.; Hur, S.Y.; Kim, T.E.; Park, Y.G.; et al. Methyl gallate and chemicals structurally related to methyl gallate protect human umbilical vein endothelial cells from oxidative stress. Exp. Mol. Med. 2005, 37, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurutas, E.B. The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: Current state. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valle, L.G. Oxidative stress in aging: Theoretical outcomes and clinical evidences in humans. Biomed. Aging Pathol. 2011, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-reactive protein at sites of inflammation and infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, J.; Martínez, M.S.; Chávez-Castillo, M.; Núñez, V.; Añez, R.; Torres, Y.; Toledo, A.; Chacín, M.; Silva, C.; Pacheco, R.; et al. C-Reactive protein: An in-depth look into structure, function, and regulation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 653045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Lima-Junior, R.C.P.; Leite, C.A.V.G. Chemotherapy-induced hemorrhagic cystitis: Pathogenesis, pharmacological approaches and new insights. J. Exp. Integr. Med. 2012, 2, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Freitas, H.C.; Campos, M.C.; Santos, C.C.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Brito, G.A.C.; Cunha, F.Q. Tumor necrosis factor-alfa and interleukin-1beta mediate the production of nitric oxide involved in the pathogenesis of ifosfamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis in mice. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelles, F.N.; Andrade, E.L.; Campos, M.M.; Calixto, J.B. Role of CXCR2 and TRPV1 in functional, inflammatory and behavioral changes in the rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Yang, C.; Luo, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Song, B.; Zhao, J.; Li, L. Chlorogenic acid attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced rat interstitial cystitis. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, V.Y.; Malley, S.; Dattilio, A.; Folsom, J.B.; Zvara, P.; Vizzard, M.A. COX-2 and prostanoid expression in micturition pathways after cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R574–R585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

 ) and nucleated polymorphs (
) and nucleated polymorphs (  ) (Hematoxylin and Eosin staining, ×400 magnification).
) (Hematoxylin and Eosin staining, ×400 magnification).
 ) and nucleated polymorphs (
) and nucleated polymorphs (  ) (Hematoxylin and Eosin staining, ×400 magnification).
) (Hematoxylin and Eosin staining, ×400 magnification).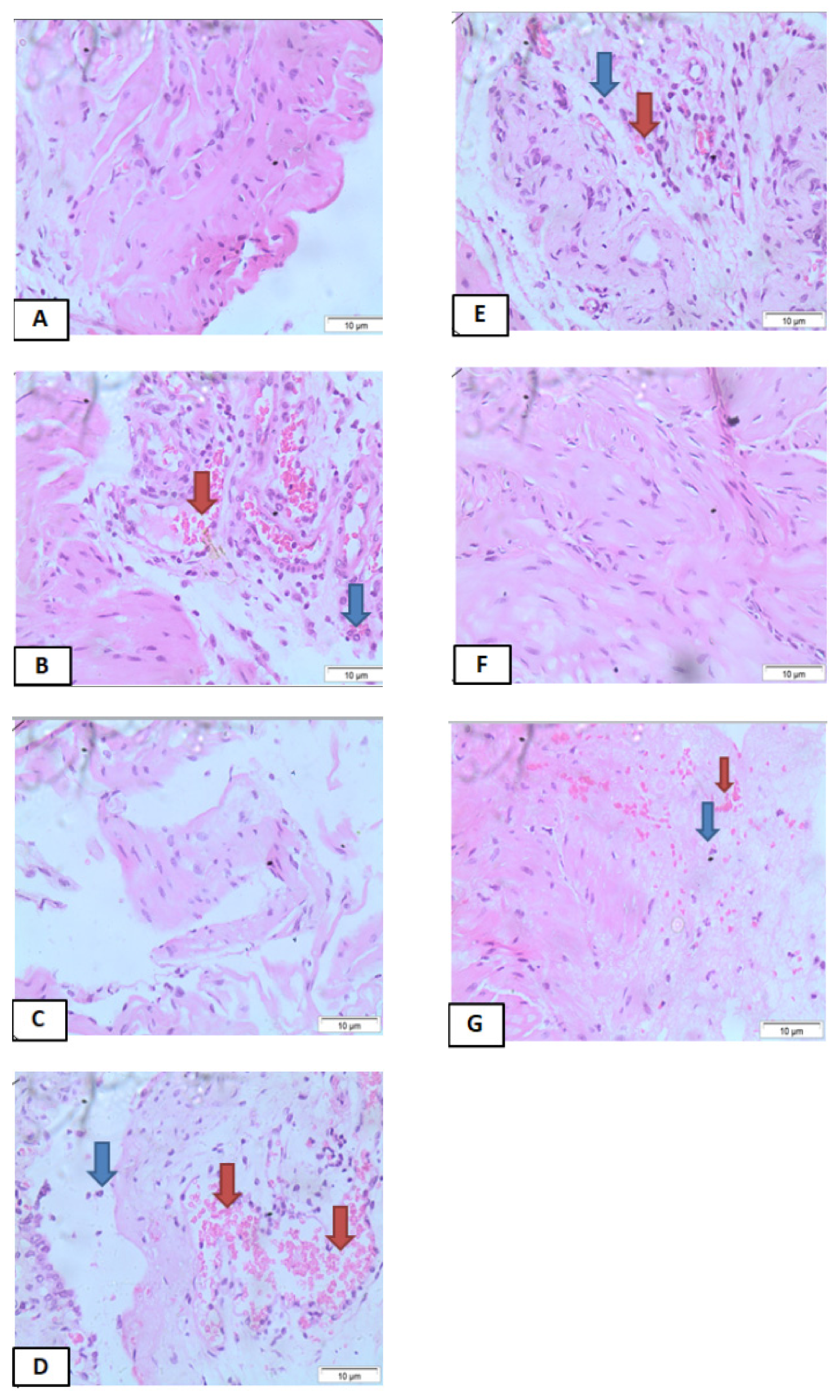
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida de Oliveira, L.S.; de Moura Bandeira, S.R.; Gomes Gonçalves, R.L.; Pereira de Sousa Neto, B.; Carvalho de Rezende, D.; dos Reis-Filho, A.C.; Sousa, I.J.O.; Pinheiro-Neto, F.R.; Timah Acha, B.; do Nascimento Caldas Trindade, G.; et al. The Isopropyl Gallate Counteracts Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Mice. Biology 2022, 11, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050728
Almeida de Oliveira LS, de Moura Bandeira SR, Gomes Gonçalves RL, Pereira de Sousa Neto B, Carvalho de Rezende D, dos Reis-Filho AC, Sousa IJO, Pinheiro-Neto FR, Timah Acha B, do Nascimento Caldas Trindade G, et al. The Isopropyl Gallate Counteracts Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Mice. Biology. 2022; 11(5):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050728
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida de Oliveira, Lucas Solyano, Sara Raquel de Moura Bandeira, Rodrigo Lopes Gomes Gonçalves, Benedito Pereira de Sousa Neto, Diana Carvalho de Rezende, Antonio Carlos dos Reis-Filho, Ian Jhemes Oliveira Sousa, Flaviano Ribeiro Pinheiro-Neto, Boris Timah Acha, Gabriela do Nascimento Caldas Trindade, and et al. 2022. "The Isopropyl Gallate Counteracts Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Mice" Biology 11, no. 5: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050728
APA StyleAlmeida de Oliveira, L. S., de Moura Bandeira, S. R., Gomes Gonçalves, R. L., Pereira de Sousa Neto, B., Carvalho de Rezende, D., dos Reis-Filho, A. C., Sousa, I. J. O., Pinheiro-Neto, F. R., Timah Acha, B., do Nascimento Caldas Trindade, G., do Nascimento, L. G., de Sousa, D. P., de Castro Almeida, F. R., Lucarini, M., Durazzo, A., Arcanjo, D. D. R., & de Assis Oliveira, F. (2022). The Isopropyl Gallate Counteracts Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis in Mice. Biology, 11(5), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050728









