Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals That PvGUX1_1 Is Associated with Pod Stringlessness in Snap Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Resequencing
2.2. Measurement of Pod Sutures
2.3. Expression Analysis of PvGUX1_1
2.4. Variant Calling and Annotation
2.5. Population Genetics Analyses
2.6. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
2.7. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
2.8. Analyses of Collinearity and Synteny
3. Results
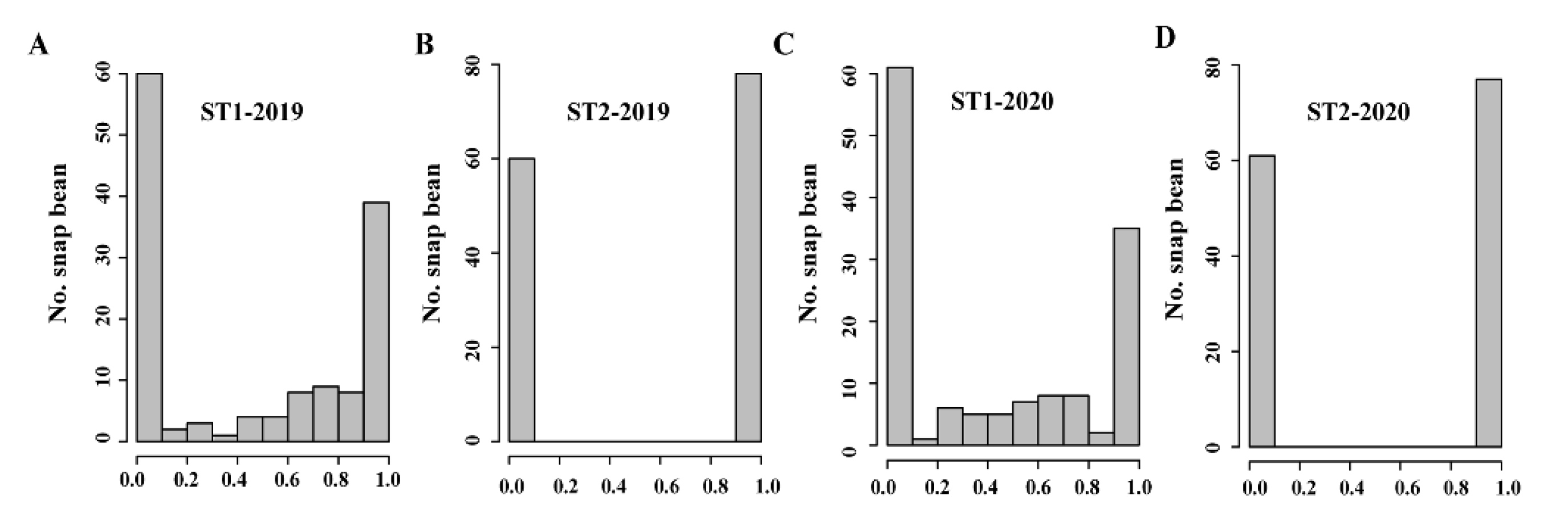
3.1. Pod Suture String Phenotyping
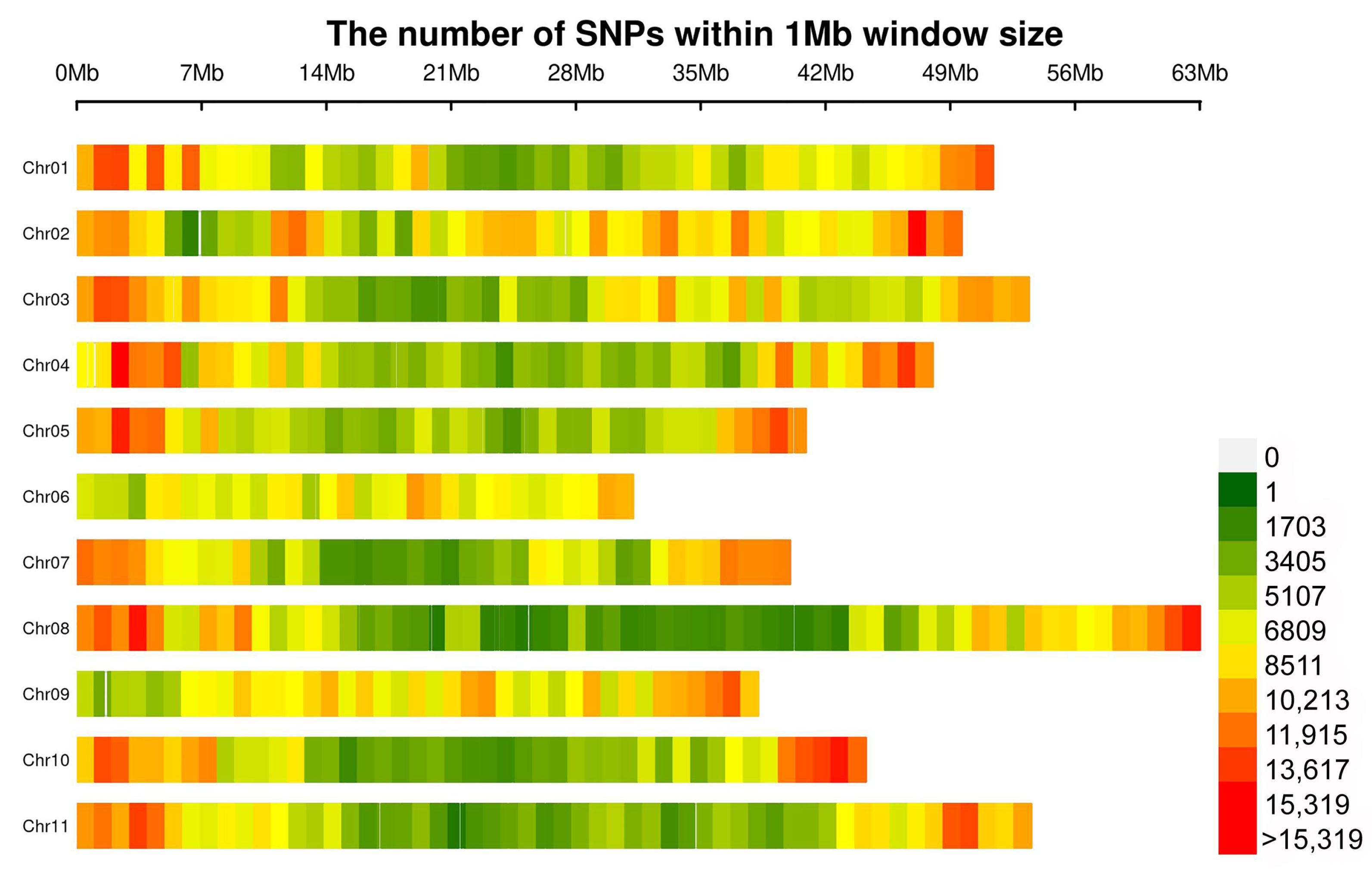
3.2. Resequencing of Snap Bean Accessions
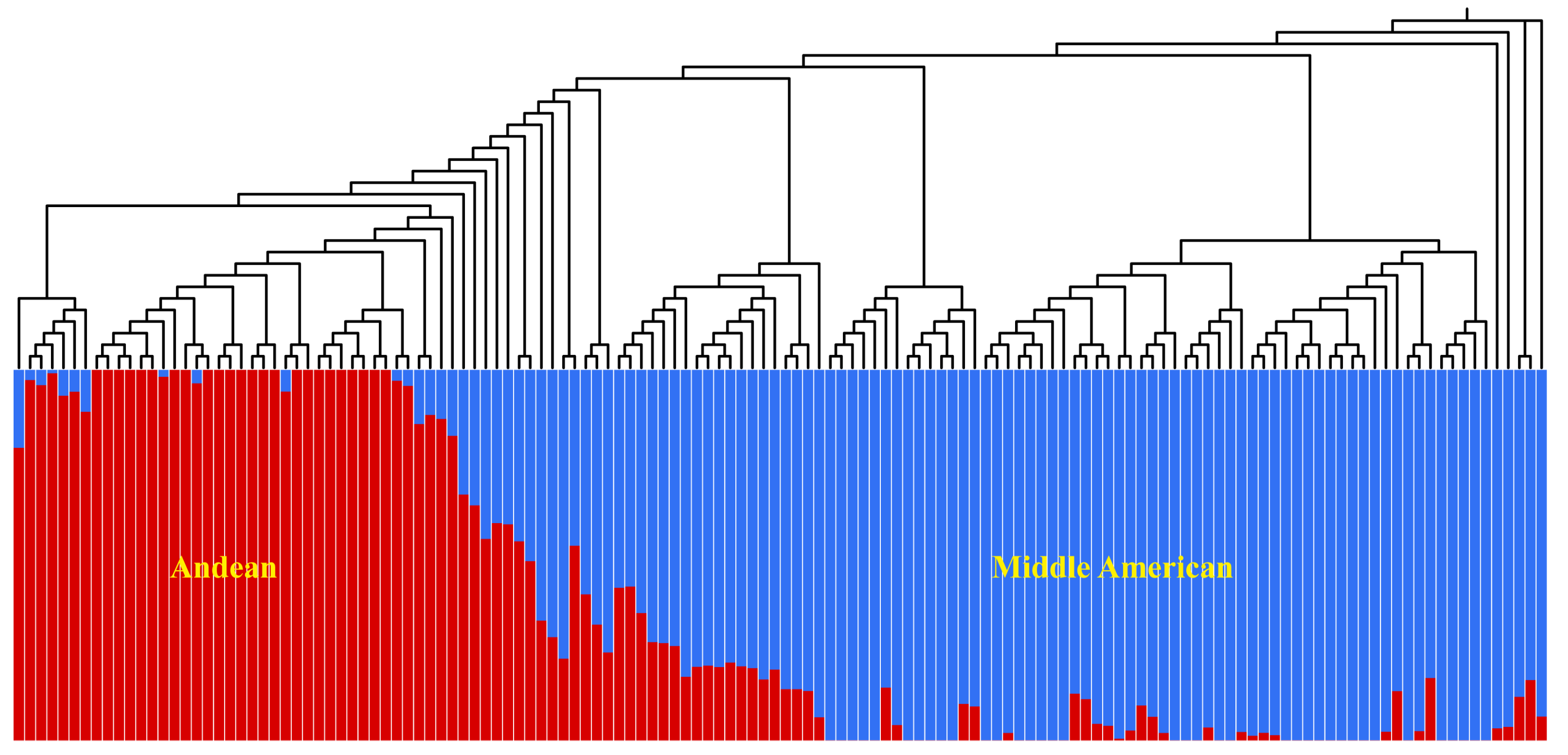
3.3. Population Structure and LD Analysis
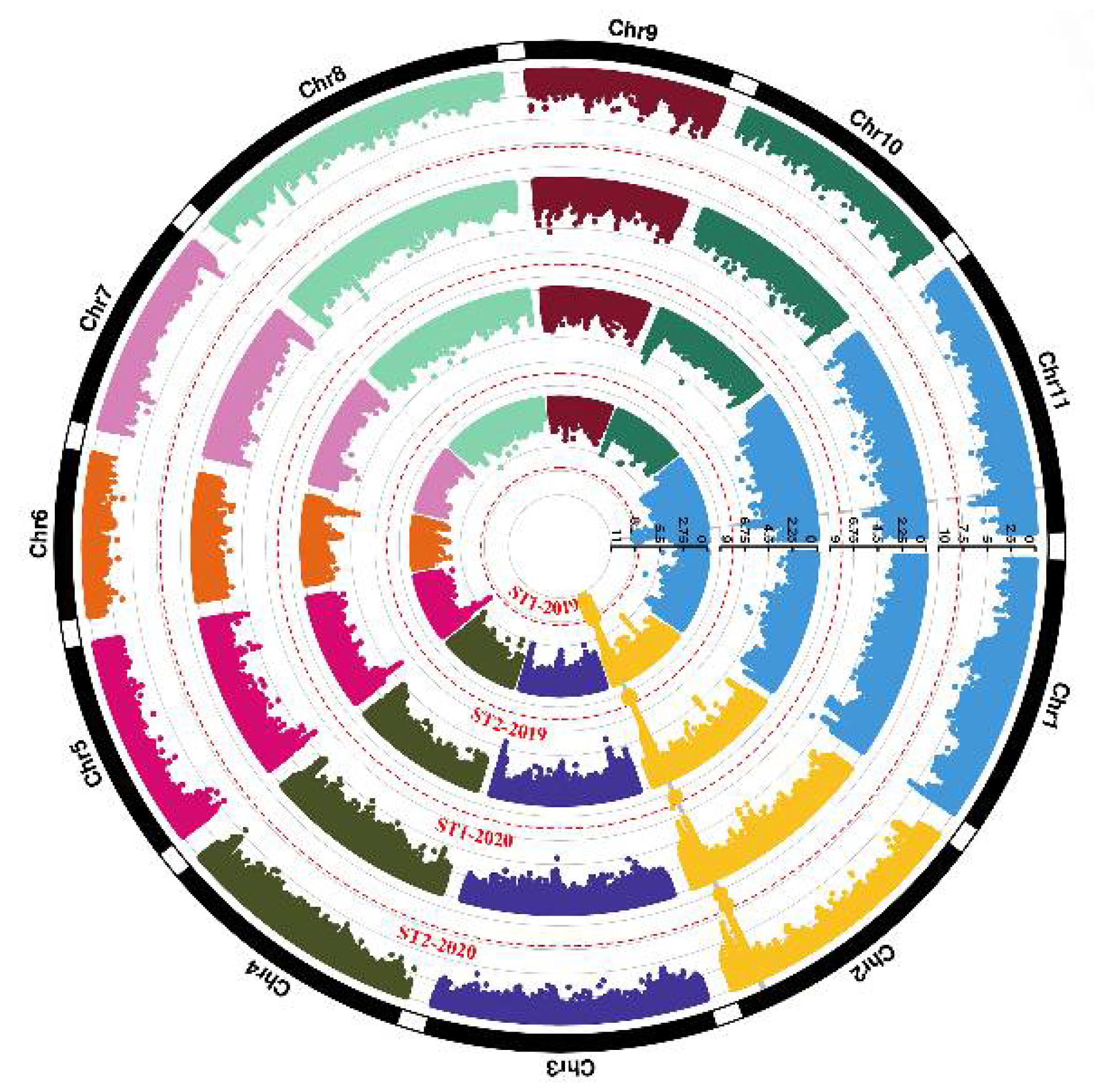
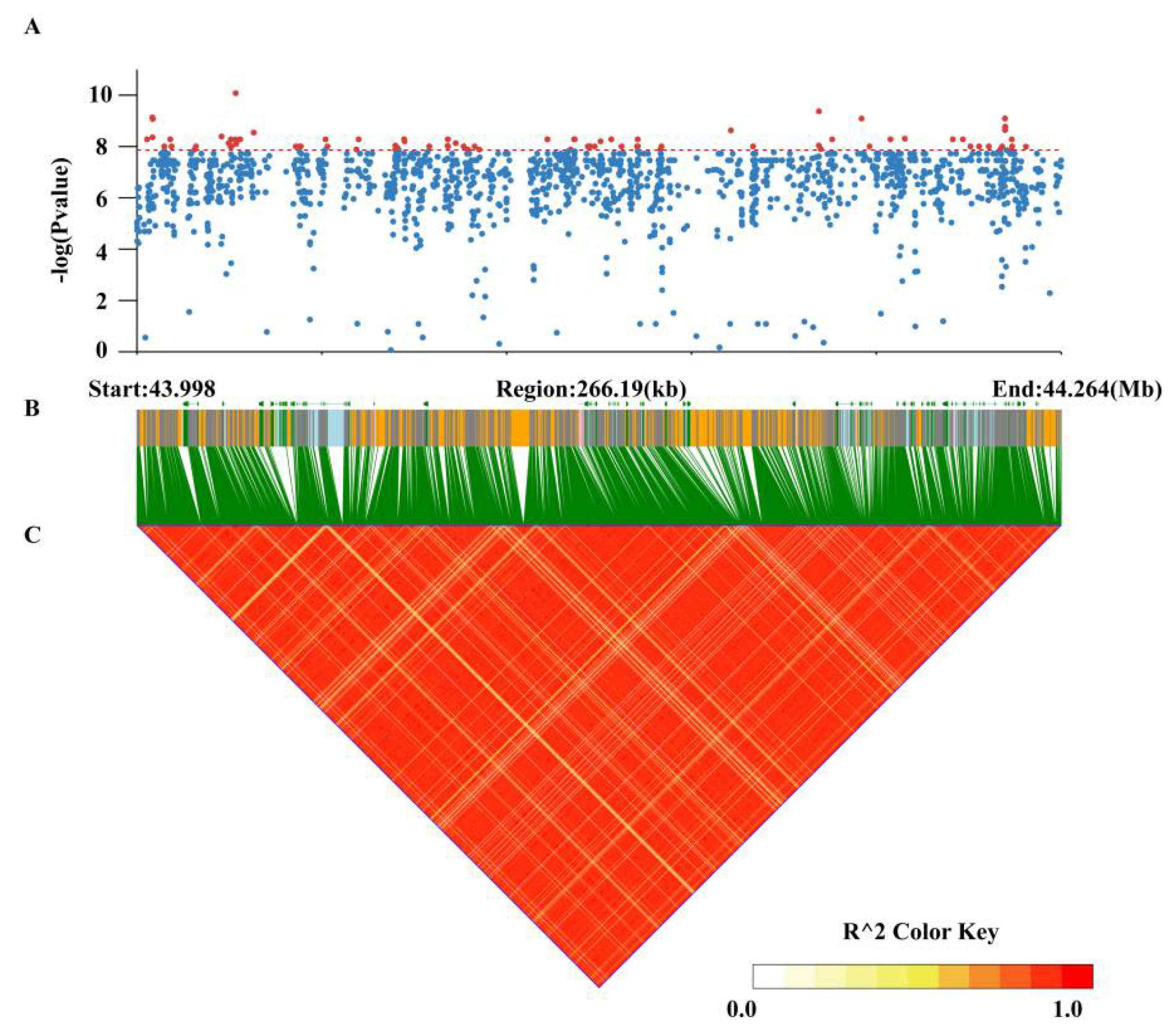
3.4. Genome-Wide Association Study for Pod Stringlessness
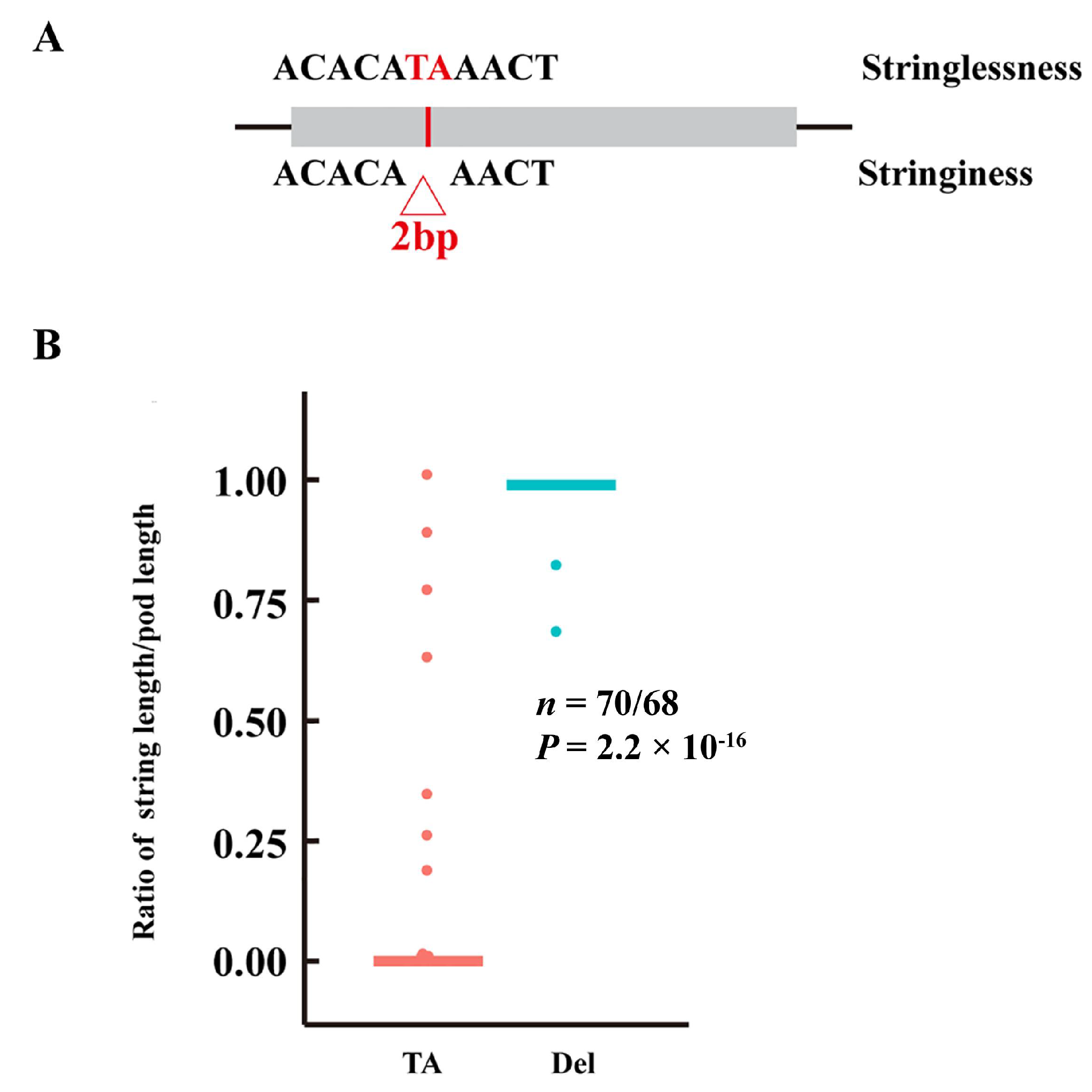
3.5. Identification of Candidate Genes for Pod Stringlessness
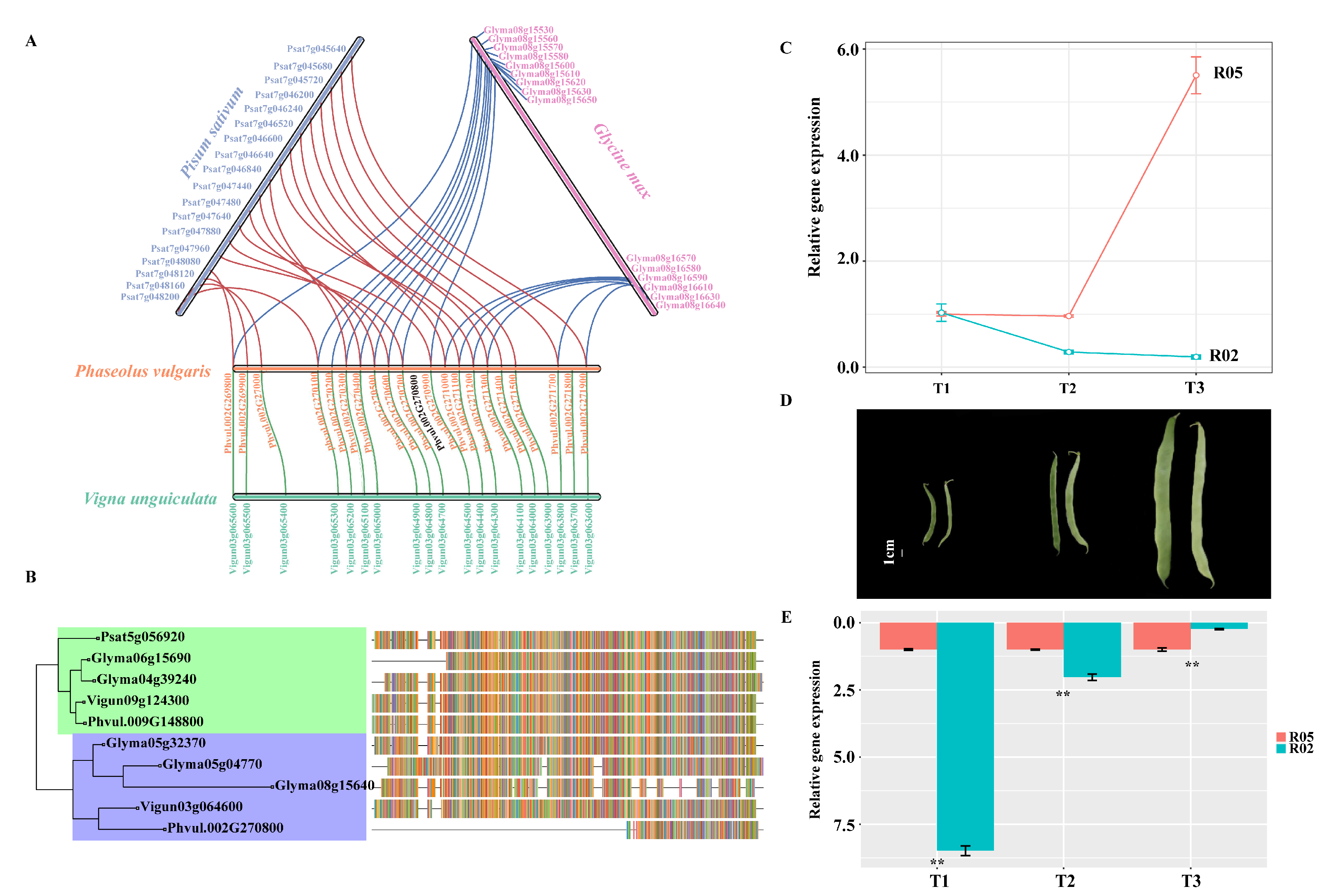
3.6. Syntenic Analysis of the Candidate Region of the Common Bean and Other Legumes
3.7. Gene Expression Patterns of PvGUX1_1
4. Discussion
4.1. GWAS Analysis for Pod Stringlessness
4.2. Pod Stringlessness Is Controlled by a Major Locus
4.3. Candidate Gene for Stringlessness in Snap Beans
4.4. Pod Stringlessness in Other Legumes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Myers, J.R.; Kmiecik, K. Economic importance and relevance to biological science research. In The Common Bean Genome; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerty, C.H.; Cuesta-Marcos, A.; Cregan, P.; Song, Q.; McClean, P.; Myers, J.R. Mapping snap bean pod and color traits, in a dry bean × snap bean recombinant inbred population. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 141, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Blair, M.W.; Wang, S. Genetic diversity of Chinese common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces assessed with simple sequence repeat markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.K.; Singh, B. Breeding perspectives of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Veg. Sci. 2015, 42, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yuste-Lisbona, F.J.; González, A.M.; Capel, C.; García-Alcázar, M.; Capel, J.; De Ron, A.M.; Santalla, M.; Lozano, R. Genetic variation underlying pod size and color traits of common bean depends on quantitative trait loci with epistatic effects. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakken, R. Inheritance of colours and pod characters in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Genetica 1934, 16, 177–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koinange, E.M.; Singh, S.P.; Gepts, P. Genetic control of the domestication syndrome in common bean. Crop Sci. 1996, 36, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gioia, T.; Logozzo, G.; Kami, J.; Zeuli, P.S.; Gepts, P. Identification and characterization of a homologue to the Arabidopsis INDEHISCENT gene in common bean. J. Hered. 2012, 104, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rau, D.; Murgia, M.L.; Rodriguez, M.; Bitocchi, E.; Bellucci, E.; Fois, D.; Albani, D.; Nanni, L.; Gioia, T.; Santo, D.; et al. Genomic dissection of pod shattering in common bean: Mutations at non-orthologous loci at the basis of convergent phenotypic evolution under domestication of leguminous species. Plant J. 2019, 97, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vittori, V.; Bitocchi, E.; Rodriguez, M.; Alseekh, S.; Bellucci, E.; Nanni, L.; Papa, R. Pod indehiscence in common bean is associated to the fine regulation of PvMYB26 and a non-functional abscission layer. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 72, 1617–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, T.A.; Berny; Miery Teran, J.C.; Palkovic, A.; Jernstedt, J.; Gepts, P. Pod indehiscence is a domestication and aridity resilience trait in common bean. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmutz, J.; McClean, P.E.; Mamidi, S.; Wu, G.A.; Cannon, S.B.; Grimwood, J.; Jackson, S.A. A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamfwa, K.; Cichy, K.A.; Kelly, J.D. Genome-wide association study of agronomic traits in common bean. Plant Genome 2015, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, S.M.; Mamidi, S.; Osorno, J.M.; Lee, R.; Brick, M.; Kelly, J.; McClean, P.E. Genome-wide association study identifies candidate loci underlying agronomic traits in a Middle American diversity panel of common bean. Plant Genome 2016, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Fu, J.; Chen, J.; Wei, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S. Resequencing of 683 common bean genotypes identifies yield component trait associations across a north-south cline. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggi, L.; Caproni, L.; Carboni, A.; Negri, V. Genome-wide association study reveals candidate genes for flowering time variation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S. Genome-wide association study identifies NBS-LRR-encoding genes related with anthracnose and common bacterial blight in the common bean. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delfini, J.; Moda-Cirino, V.; dos Santos Neto, J.; Zeffa, D.M.; Nogueira, A.F.; Ribeiro, L.A.B.; Gonçalves, L.S.A. Genome-wide association study for grain mineral content in a Brazilian common bean diversity panel. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 2795–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, J. The aquaporin gene PvXIP1;2 conferring drought resistance identified by GWAS at seedling stage in common bean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; MafiMoghaddam, S.; Oladzad-Abbasabadi, A.; Walter, K.; Kearns, P.J.; Vasquez-Guzman, J.; Osorno, J.M. Genetic analysis of flooding tolerance in an Andean diversity panel of dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Myers, J.R.; Wallace, L.T.; Moghaddam, S.M.; Kleintop, A.E.; Echeverria, D.; Thompson, H.J.; Brick, M.A.; Lee, R.; McClean, P.E. Improving the Health Benefits of Snap Bean: Genome-Wide Association Studies of Total Phenolic Content. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; 1000 Genomes Project Analysis Group. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Sham, P.C. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKenna, A.; Hann, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; DePristo, M.A.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Lange, K. Enhancements to the admixture algorithm for individual ancestry estimation. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP–Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 1989, 5, 164–166. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2830216 (accessed on 5 October 2020).
- Zhang, C.; Dong, S.; Xu, J.; He, W.; Yang, T. PopLDdecay: A fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Tian, F.; Su, Z.; Pan, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. GAPIT version 2: An enhanced integrated tool for genomic association and prediction. Plant Genome 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gou, Z.; Lyu, J.; Li, W. Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Sang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Lu, T.; Li, D.; Han, B.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.-H.; Liu, B.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. Pod shattering resistance associated with domestication is mediated by a NAC gene in soybean. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrell, P.L.; Buckler, E.S.; Ross-Ibarra, J. Crop genomics: Advances and applications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, M.W.; Astudillo, C.; Grusak, M.A.; Graham, R.; Beebe, S.E. Inheritance of seed iron and zinc concentrations in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol. Breed. 2009, 23, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hu, J.; Myers, J.R.; Mazourek, M.; Coyne, C.J.; Main, D.; McGee, R.J. Development of SCAR markers linked to sin-2, the stringless pod trait in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currence, T.M. Inheritance studies in Phaseolus vulgaris. Tech. Bull. Minn. Agric. Exp. Stn. 1930, 68, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.W.; Kean, D.; Yorgey, B.; Fourie, D.; Miklas, P.N.; Myers, J.R. A molecular marker linkage map of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Annu. Rep.-Bean Improv. Coop. 2006, 49, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Drijfhout, E. Inheritance of temperature-dependent string formation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 1978, 26, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Hahn, M.G.; Mohnen, D.; Xu, Y. Evolution and function of the plant cell wall synthesis-related glycosyltransferase family 8. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1729–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.; Teng, Q.; Zhong, R.; Ye, Z.H. Arabidopsis GUX proteins are glucuronyltransferases responsible for the addition of glucuronic acid side chains onto xylan. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oikawa, A.; Joshi, H.J.; Rennie, E.A.; Ebert, B.; Manisseri, C.; Heazlewood, J.L.; Scheller, H.V. An integrative approach to the identification of Arabidopsis and rice genes involved in xylan and secondary wall development. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girin, T.; Stephenson, P.; Goldsack, C.M.; Kempin, S.A.; Perez, A.; Pires, N.; Sparrow, P.A.; Wood, T.A.; Yanofsky, M.F.; Østergaard, L. Brassicaceae INDEHISCENT genes specify valve margin cell fate and repress replum formation. Plant J. 2010, 63, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, P.; Groszmann, M.; Ross, J.J.; Parish, R.W.; Swain, S.M. Modifications of a conserved regulatory network involving INDEHISCENT controls multiple aspects of reproductive tissue development in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.Z. Seed shattering: From models to crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, S.G.; Mizrachi, E.; Spokevicius, A.V.; Bossinger, G.; Berger, D.K.; Myburg, A.A. SND2, a NAC transcription factor gene, regulates genes involved in secondary cell wall development in Arabidopsis fibres and increases fibre cell area in Eucalyptus. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Goué, N.; Igarashi, H.; Ohtani, M.; Nakano, Y.; Mortimer, J.C. VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN6 and VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7 effectively induce transdifferentiation into xylem vessel elements under control of an induction system. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reusche, M.; Thole, K.; Janz, D.; Truskina, J.; Rindfleisch, S.; Drübert, C.; Teichmann, T. Verticillium infection triggers VASCULAR-RELATED NAC DOMAIN7-dependent de novo xylem formation and enhances drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3823–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, Z.A.; Song, J.; Taylor, B.; Yang, C. The final split: The regulation of anther dehiscence. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1633–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.C.; Ko, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Bae, H.J.; Han, K.H. MYB 46 directly regulates the gene expression of secondary wall-associated cellulose synthases in A rabidopsis. Plant J. 2013, 73, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Ko, J.H.; Kang, H.; Han, K.H. Identification of direct targets of transcription factor MYB46 provides insights into the transcriptional regulation of secondary wall biosynthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 85, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lee, C.; Zhong, R.; Ye, Z.-H. MYB58 and MYB63 are transcriptional activators of the lignin biosynthetic pathway during secondary cell wall formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakano, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Endo, H.; Rejab, N.A.; Ohtani, M. NAC-MYB-based transcriptional regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis in land plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wellensiek, S.J. Lamprecht’s gene sin for stringless. Pisum Newsl. 1971, 3, 48. [Google Scholar]
- McGee, R.J.; Baggett, J.R. Inheritance of Stringless Pod in Pisum sativum L. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1992, 117, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weeden, N.F. Genetic changes accompanying the domestication of Pisum sativum: Is there a common genetic basis to the ‘domestication syndrome’ for legumes? Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Song, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Tang, B.; Dong, L.; Ding, N.; Zhao, W.; et al. GSA: Genome sequence archive. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Position | Homologs of Arabidopsis | Functional Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phvul.002G269700 | Chr02:44022772_44024106 | Unknown | |
| Phvul.002G269800 | Chr02:44033313_44034850 | AT4G08250 | GRAS family transcription factor |
| Phvul.002G269900 | Chr02:44036772_44037686 | AT5G45420 | MYB transcription factor |
| Phvul.002G270000 | Chr02:44037878_44041667 | AT3G18750 | WNK family of protein kinases |
| Phvul.002G270100 | Chr02:44042454_44059878 | AT3G18730 | Involved in cell division control and plant morphogenesis |
| Phvul.002G270200 | Chr02:44066265_44067018 | AT5G64667 | Involved in floral organ abscission |
| Phvul.002G270300 | Chr02:44080456_44082336 | AT5G64660 | CYS, MET, PRO, and GLY protein |
| Phvul.002G270400 | Chr02:44125511_44131328 | AT5G24320 | Transducin/WD40 repeat-like superfamily protein |
| Phvul.002G270500 | Chr02:44133980_44137288 | AT3G18680 | UMP Kinase |
| Phvul.002G270600 | Chr02:44139105_44139713 | AT3G18690 | Involved in mediating responses to pathogens |
| Phvul.002G270700 | Chr02:44142989_44144630 | AT4G14620 | Unknown |
| Phvul.002G270800 | Chr02:44150261_44150926 | AT3G18660 | Encodes a glucuronyltransferase responsible for the addition of GlcA residues onto xylan and for secondary wall deposition |
| Phvul.002G270900 | Chr02:44155318_44157803 | AT5G09760 | Plant invertase/pectin methylesterase inhibitor |
| Phvul.002G271000 | Chr02:44186987_44188326 | AT4G00120 | IND(basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) DNA-binding superfamily protein) |
| Phvul.002G271100 | Chr02:44199222_44205529 | AT1G48880 | Encodes a member of the TBL |
| Phvul.002G271200 | Chr02:44205946_44210215 | AT5G64630 | Involved in organization of the shoot and root apical meristems |
| Phvul.002G271300 | Chr02:44216969_44222195 | Unknown | |
| Phvul.002G271400 | Chr02:44224184_44228271 | AT1G08490 | Chloroplastic NifS-like protein |
| Phvul.002G271500 | Chr02:44229799_44246330 | AT5G64070 | Encodes a phosphatidylinositol 4-OH kinase |
| Phvul.002G271600 | Chr02:44232557_44233756 | Unknown | |
| Phvul.002G271700 | Chr02:44247536_44251023 | AT5G09330 | NAC domain containing protein |
| Phvul.002G271800 | Chr02:44251436_44254178 | AT2G13690 | PRLI-interacting factor |
| Phvul.002G271900 | Chr02:44257054_44258132 | Unknown |
| Gene | Variant Type | Base Change | Amino Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phvul.002G269700 | Nonsynonymous | A491G | E164G |
| Phvul.002G270100 | Nonsynonymous | T1617A | D539E |
| Nonsynonymous | A1899T | R633S | |
| Nonsynonymous | G2092A | D698N | |
| Nonsynonymous | C3050T | S1017L | |
| Phvul.002G270300 | Nonsynonymous | C257T | S86L |
| Nonsynonymous | T382C | F128L | |
| Phvul.002G270400 | Nonsynonymous | G563A | R188K |
| Nonsynonymous | C833A | T278N | |
| Phvul.002G270800 | Nonsynonymous | A92G | D31G |
| Frameshift deletion | AT163_ | ||
| Phvul.002G270900 | Nonsynonymous | G1374C | E458D |
| Phvul.002G271000 | Nonsynonymous | T32C | V11A |
| Nonsynonymous | C604T | P202S | |
| Nonsynonymous | C737T | T246M | |
| Phvul.002G271100 | Nonsynonymous | A257G | N86S |
| Phvul.002G271200 | Nonsynonymous | G870A | M290I |
| Phvul.002G271300 | Nonsynonymous | G241T | G81C |
| Nonsynonymous | A638C | E213A | |
| Nonsynonymous | A781G | T261A | |
| Nonsynonymous | T1945G | S649A | |
| Nonsynonymous | A2008G | N670D | |
| Phvul.002G271400 | Nonsynonymous | G234A | M78I |
| Nonsynonymous | A335C | K112T | |
| Nonsynonymous | C902T | A301V | |
| Nonsynonymous | A1099G | T367A | |
| Phvul.002G271600 | Nonsynonymous | T17C | L6S |
| Nonsynonymous | A24C | L8F | |
| Frameshift deletion | GT57_ | ||
| Phvul.002G271700 | Nonsynonymous | A77G | N26S |
| Nonsynonymous | C78G | N26K | |
| Nonsynonymous | T100G | F34V | |
| Nonsynonymous | T154C | S52P | |
| Nonsynonymous | G162C | K54N | |
| Nonsynonymous | A359T | K120I | |
| Nonsynonymous | T476C | V159A | |
| Nonsynonymous | A785C | D262A | |
| Phvul.002G271800 | Nonsynonymous | A1346C | Y449S |
| Nonsynonymous | A1138C | K380Q | |
| Nonsynonymous | A772C | N258H | |
| Nonsynonymous | T563A | F188Y | |
| Nonsynonymous | A385G | N129D | |
| Nonsynonymous | C328A | L110M | |
| Phvul.002G271900 | Nonsynonymous | T5G | F2C |
| Nonsynonymous | T377C | V126A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Qian, W. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals That PvGUX1_1 Is Associated with Pod Stringlessness in Snap Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Biology 2022, 11, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040611
Liu Z, Gao S, Zhang H, Xu Z, Qian W. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals That PvGUX1_1 Is Associated with Pod Stringlessness in Snap Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Biology. 2022; 11(4):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040611
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhiyuan, Shuo Gao, Helong Zhang, Zhaosheng Xu, and Wei Qian. 2022. "Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals That PvGUX1_1 Is Associated with Pod Stringlessness in Snap Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)" Biology 11, no. 4: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040611
APA StyleLiu, Z., Gao, S., Zhang, H., Xu, Z., & Qian, W. (2022). Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals That PvGUX1_1 Is Associated with Pod Stringlessness in Snap Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Biology, 11(4), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040611





