Complications of Severe Odontogenic Infections: A Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Pathophysiology, Patient Factors, and Microbiology
1.2. Airway Obstruction
1.3. Descending Necrotizing Mediastinitis
1.4. Orbital Cellulitis, Abscess, and Septic Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
1.5. Cerebral Abscess
1.6. Sepsis
1.7. Necrotizing Fasciitis
1.8. Lemierre’s Syndrome
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCormick, A.P.; Abubaker, A.O.; Laskin, D.M.; Gonzales, M.S.; Garland, S. Reducing the burden of dental patients on the busy hospital emergency department. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allareddy, V.; Rampa, S.; Lee, M.K.; Allareddy, V.; Nalliah, R.P. Hospital-based emergency department visits involving dental conditions: Profile and predictors of poor outcomes and resource utilization. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2014, 145, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalliah, R.P.; Allareddy, V.; Elangovan, S.; Karimbux, N.; Allareddy, V. Hospital based emergency department visits attributed to dental caries in the United States in 2006. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2010, 10, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opitz, D.; Camerer, C.; Camerer, D.M.; Raguse, J.D.; Menneking, H.; Hoffmeister, B.; Adolphs, N. Incidence and management of severe odontogenic infections-a retrospective analysis from 2004 to 2011. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmahan, S.; Tuopar, D.; Ameerally, P.J.; Kotecha, R.; Sisodia, B. Microbiological examination and antibiotic sensitivity of infections in the head and neck. Has anything changed? Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 52, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Stellin, M.; Muzzi, E.; Mantovani, M.; Fuson, R.; Lupato, V.; Trabalzini, F.; Da Mosto, M.C. Deep neck infections: A study of 365 cases highlighting recommendations for management and treatment. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 269, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.R.; Shanti, R.M.; Levi, M.H.; Adamo, A.K.; Kraut, R.A.; Trieger, N. Severe odontogenic infections, part 1: Prospective report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, T.R.; Shanti, R.M.; Hayes, C. Severe odontogenic infections, part 2: Prospective outcomes study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, T.W.; Hammad, Y.; Carr, B.R.; Wahidi, J.; Cannon, S.; Schlieve, T. Assessment of pro re nata inpatient opioid consumption following surgical treatment of severe odontogenic infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2022, 134, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, T.W.; Hammad, Y.; Carr, B.R.; Schlieve, T. The Cost of Surgically Treated Severe Odontogenic Infections: A Retrospective Study Using Severity Scores. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Mooradian, A.D.; Reed, R.L.; Meredith, K.E.; Scuderi, P. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor and IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1991, 14, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Roe, K.; Nerurkar, P.V.; Orillo, B.; Thompson, K.S.; Verma, S.; Nerurkar, V.R. Reduced immune cell infiltration and increased pro-inflammatory mediators in the brain of Type 2 diabetic mouse model infected with West Nile virus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, N.; Ketheesan, N.; Martens, G.W.; West, K.; Lien, E.; Kornfeld, H. Defects in early cell recruitment contribute to the increased susceptibility to respiratory Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in diabetic mice. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perner, A.; Nielsen, S.E.; Rask-Madsen, J. High glucose impairs superoxide production from isolated blood neutrophils. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, G.A.; Schultz, T.A.; Schaberg, S.J. Deep neck infection complicated by diabetes mellitus Report of a case. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1983, 55, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugata, T.; Fujita, Y.; Myoken, Y.; Fujioka, Y. Cervical cellulitis with mediastinitis from an odontogenic infection complicated by diabetes mellitus: Report of a case. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 55, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, Y.; Neal, T.W.; Schlieve, T. Admission C-reactive protein, WBC count, glucose, and body temperature in severe odontogenic infections: A retrospective study using severity scores. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2022, 133, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, X.; He, Y. Risk Factors for Life-Threatening Complications of Maxillofacial Space Infection. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, H.; Naros, A.; Weise, C.; Reinert, S.; Hoefert, S. Severe odontogenic infections with septic progress—A constant and increasing challenge: A retrospective analysis. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L.L., Jr.; Madsen, M.J.; Van Sickels, J.E. Using prealbumin as an inflammatory marker for patients with deep space infections of odontogenic origin. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rôças, I.N. Diversity of endodontic microbiota revisited. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemaleelakul, S.; Baumgartner, J.C.; Pruksakorn, S. Identification of bacteria in acute endodontic infections and their antimicrobial susceptibility. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2002, 94, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, E.L.; Ferraz, C.C.; Gomes, B.P.; Pinheiro, E.T.; Teixeira, F.B.; de Souza-Filho, F.J. Bacteriological study of root canals associated with periapical abscesses. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2003, 96, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, T.R.; Paster, B.J.; Stokes, L.N.; Susarla, S.M.; Shanti, R.M. Molecular methods for diagnosis of odontogenic infections. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 1854–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, A.; Miskoff, J.; Lis, R.J. Otolaryngologic critical care. Crit. Care Clin. 2003, 19, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saifeldeen, K.; Evans, R. Ludwig’s angina. Emerg. Med. J. 2004, 21, 242–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.C.; Guralnick, W.C. The diagnosis and treatment of Ludwig’s angina: A report of twenty cases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1943, 228, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hought, R.T.; Fitzgerald, B.E.; Latta, J.E.; Zallen, R.D. Ludwig’s angina: Report of two cases and review of the literature from 1945 to January 1979. J. Oral Surg. 1980, 38, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riekert, M.; Kreppel, M.; Zöller, J.E.; Zirk, M.; Annecke, T.; Schick, V.C. Severe odontogenic deep neck space infections: Risk factors for difficult airways and ICU admissions. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 23, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, M.; Biesler, I.; Börgers, A.; Pförtner, R.; Mohr, C.; Groeben, H. Tracheal intubation in patients with odentogenous abscesses and reduced mouth opening. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 112, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouruzi-Sedeh, P.; Schumann, M.; Groeben, H. Laryngoscopy via Macintosh blade versus GlideScope: Success rate and time for endotracheal intubation in untrained medical personnel. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, C.V.; Thøgersen, B.; Afshari, A.; Christensen, A.L.; Eriksen, C.; Gätke, M.R. Awake fiberoptic or awake video laryngoscopic tracheal intubation in patients with anticipated difficult airway management: A randomized clinical trial. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, H.; Aoki, T.; Kise, Y.; Watanabe, D.; Sasaki, J. Descending necrotizing mediastinitis due to odontogenic infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2000, 89, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrera, A.S.; Landay, M.J.; Grisham, J.M.; Sinn, D.P.; Platt, M.R. Descending necrotizing mediastinitis. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1983, 157, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biasotto, M.; Pellis, T.; Cadenaro, M.; Bevilacqua, L.; Berlot, G.; Di Lenarda, R. Odontogenic infections and descending necrotising mediastinitis: Case report and review of the literature. Int. Dent. J. 2004, 54, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takao, M.; Ido, M.; Hamaguchi, K.; Chikusa, H.; Namikawa, S.; Kusagawa, M. Descending necrotizing mediastinitis secondary to a retropharyngeal abscess. Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 1716–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, S.; Murayama, F.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sohara, Y.; Fuse, K.; Miyata, M.; Nishino, H. Guideline of surgical management based on diffusion of descending necrotizing mediastinitis. Jpn. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1999, 47, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahbar, R.; Robson, C.D.; Petersen, R.A.; DiCanzio, J.; Rosbe, K.W.; McGill, T.J.; Healy, G.B. Management of orbital subperiosteal abscess in children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2001, 127, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, B.P.; Lee, W.W. Orbital Cellulitis and Subperiosteal Abscess: A 5-year Outcomes Analysis. Orbit 2015, 34, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, V.; Mohamad Ikbal, M.F.; Min, N.C.; Chan, Y.H.; Ganapathy, S. Periorbital Cellulitis in Paediatric Emergency Medicine Department Patients. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2018, 47, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovilla-Canales, J.L.; Nava, A.; Tovilla y Pomar, J.L. Orbital and periorbital infections. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2001, 12, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, M.I.; Pinheiro-Neto, C.D.; Rubinstein, T.J. Odontogenic Abscess with Orbital Extension Through the Inferior Orbital Fissure Treated with Bony Decompression. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 36, e131–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.R.; Langenbrunner, D.J.; Stevens, E.R. The pathogenesis of orbital complications in acute sinusitis. Laryngoscope 1970, 80, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- René, C. Update on orbital anatomy. Eye 2006, 20, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, A.; Campero, A.; Martins, C.; Rhoton, A.L., Jr.; de Oliveira, E.; Ribas, G.C. Microsurgical anatomy and approaches to the cavernous sinus. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwick, F.S.; Richardson, E.P., Jr.; Swartz, M.N. Septic thrombosis of the dural venous sinuses. Medicine 1986, 65, 82–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, K.; Jones, N.S. Septic cavernous sinus thrombosis secondary to sinusitis: Are anticoagulants indicated? A review of the literature. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2002, 116, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geggel, H.S.; Isenberg, S.J. Cavernous sinus thrombosis as a cause of unilateral blindness. Ann. Ophthalmol. 1982, 14, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khatri, I.A.; Wasay, M. Septic cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 362, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.F.; Cusimano, M.D. The spectrum of cavernous sinus and orbital venous thrombosis: A case and a review. Skull Base Surg. 1996, 6, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Poel, N.A.; Mourits, M.P.; de Win, M.M.L.; Coutinho, J.M.; Dikkers, F.G. Prognosis of septic cavernous sinus thrombosis remarkably improved: A case series of 12 patients and literature review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarington, C.T., Jr. The prognosis and treatment of cavernous sinus thrombosis Review of 878 cases in the literature. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1961, 70, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasagayam, S.; Wyatt, B.; Leyden, J.; Kleinig, T. Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Incidence Is Higher Than Previously Thought: A Retrospective Population-Based Study. Stroke 2016, 47, 2180–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzam, A.A.; Rajagopal, S.M.; Sedghizadeh, P.P.; Zada, G.; Habibian, M. Intracranial bacterial infections of oral origin. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisboa, E.C.C.; Silva, W.O.; Rodrigues, R.C.V.; Brum, S.C.; Alves, F.R.F. The connection between brain abscess and odontogenic infections: A systematic review. Arch. Oral Biol. 2022, 135, 105360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, H.; Karakida, K.; Otsuru, M.; Arai, M.; Shimoda, M. A case of brain abscess extended from deep fascial space infection. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 108, e21–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T.C.; Kalamchi, S. A case of odontogenic brain abscess arising from covert dental sepsis. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2012, 94, e41–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Larraín, L.F.; Vázquez-Portela, Á.; Cobo-Vázquez, C.M.; Sáez-Alcaide, L.M.; Sánchez-Labrador, L.; Meniz-García, C. Brain complications from odontogenic infections: A systematic review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 123, e794–e800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, C.; Kuhn, S.; Kalff, R. Pyogenic infections of the central nervous system secondary to dental affections—A report of six cases. Neurosurg. Rev. 2006, 29, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, M.C.; Coutinho, J.M.; van de Beek, D. Clinical characteristics and outcome of brain abscess: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2014, 82, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; de Mendonça, A.; Cantraine, F.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Suter, P.M.; Sprung, C.L.; Colardyn, F.; Blecher, S. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: Results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working group on “sepsis-related problems” of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 26, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevon, P.; Abdelrahman, A.; Pigadas, N. Management of odontogenic infections and sepsis: An update. Br. Dent. J. 2020, 229, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.I.; Park, S. Sepsis: Early Recognition and Optimized Treatment. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2019, 82, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawijn, F.; Smeeing, D.P.J.; Houwert, R.M.; Leenen, L.P.H.; Hietbrink, F. Time is of the essence when treating necrotizing soft tissue infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHenry, C.R.; Piotrowski, J.J.; Petrinic, D.; Malangoni, M.A. Determinants of mortality for necrotizing soft-tissue infections. Ann. Surg. 1995, 221, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, T.; Goh, L.G.; Ang, C.H.; Wong, C.H. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, e119–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Wong, C.H.; Tay, Y.K. Staging of necrotizing fasciitis based on the evolving cutaneous features. Int. J. Dermatol. 2007, 46, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.H.; Khin, L.W.; Heng, K.S.; Tan, K.C.; Low, C.O. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: A tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.M.; Tran, A.; Cheng, W.; Rochwerg, B.; Kyeremanteng, K.; Seely, A.J.E.; Inaba, K.; Perry, J.J. Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection: Diagnostic Accuracy of Physical Examination, Imaging, and LRINEC Score: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarricone, A.; Mata, K.; Gee, A.; Axman, W.; Buricea, C.; Mandato, M.G.; Trepal, M.; Krishnan, P. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of LRINEC Score for Predicting Upper and Lower Extremity Necrotizing Fasciitis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022, 61, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysoki, M.G.; Santora, T.A.; Shah, R.M.; Friedman, A.C. Necrotizing fasciitis: CT characteristics. Radiology 1997, 203, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, N.; Yousfi, S.; Vinnard, C. Deaths from necrotizing fasciitis in the United States, 2003-2013. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.M.; Lim, H.K. Necrotizing fasciitis: Eight-year experience and literature review. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 18, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttger, S.; Zechel-Gran, S.; Schmermund, D.; Streckbein, P.; Wilbrand, J.F.; Knitschke, M.; Pons-Kühnemann, J.; Hain, T.; Weigel, M.; Imirzalioglu, C.; et al. Odontogenic Cervicofacial Necrotizing Fasciitis: Microbiological Characterization and Management of Four Clinical Cases. Pathogens 2022, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemplenyi, K.; Lopez, B.; Sardesai, M.; Dillon, J.K. Can progression of odontogenic infections to cervical necrotizing soft tissue infections be predicted? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, M.R. Odontogenic necrotizing fasciitis: A systematic review of the literature. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2018, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandner, A.; Moritz, S.; Unverzagt, S.; Plontke, S.K.; Metz, D. Cervical Necrotizing Fasciitis--The Value of the Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis Score as an Indicative Parameter. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 2319–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.J.; Meyer, T.K. Retrospective evaluation of laboratory-based diagnostic tools for cervical necrotizing fasciitis. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 2683–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, T. Human infection with Fusobacterium necrophorum (Necrobacillosis), with a focus on Lemierre’s syndrome. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 622–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemierre, A. On Certain Septicaemias Due to Anaerobic Organisms. Lancet 1936, 227, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkos, P.D.; Asrani, S.; Karkos, C.D.; Leong, S.C.; Theochari, E.G.; Alexopoulou, T.D.; Assimakopoulos, A.D. Lemierre’s syndrome: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, L.; Corsi, G.; Sebastian, T.; Barco, S. Lemierre syndrome: Current evidence and rationale of the Bacteria-Associated Thrombosis, Thrombophlebitis and LEmierre syndrome (BATTLE) registry. Thromb. Res. 2020, 196, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.I.; Baring, D.; Addidle, M.; Murray, C.; Adams, C. Lemierre syndrome: Two cases and a review. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
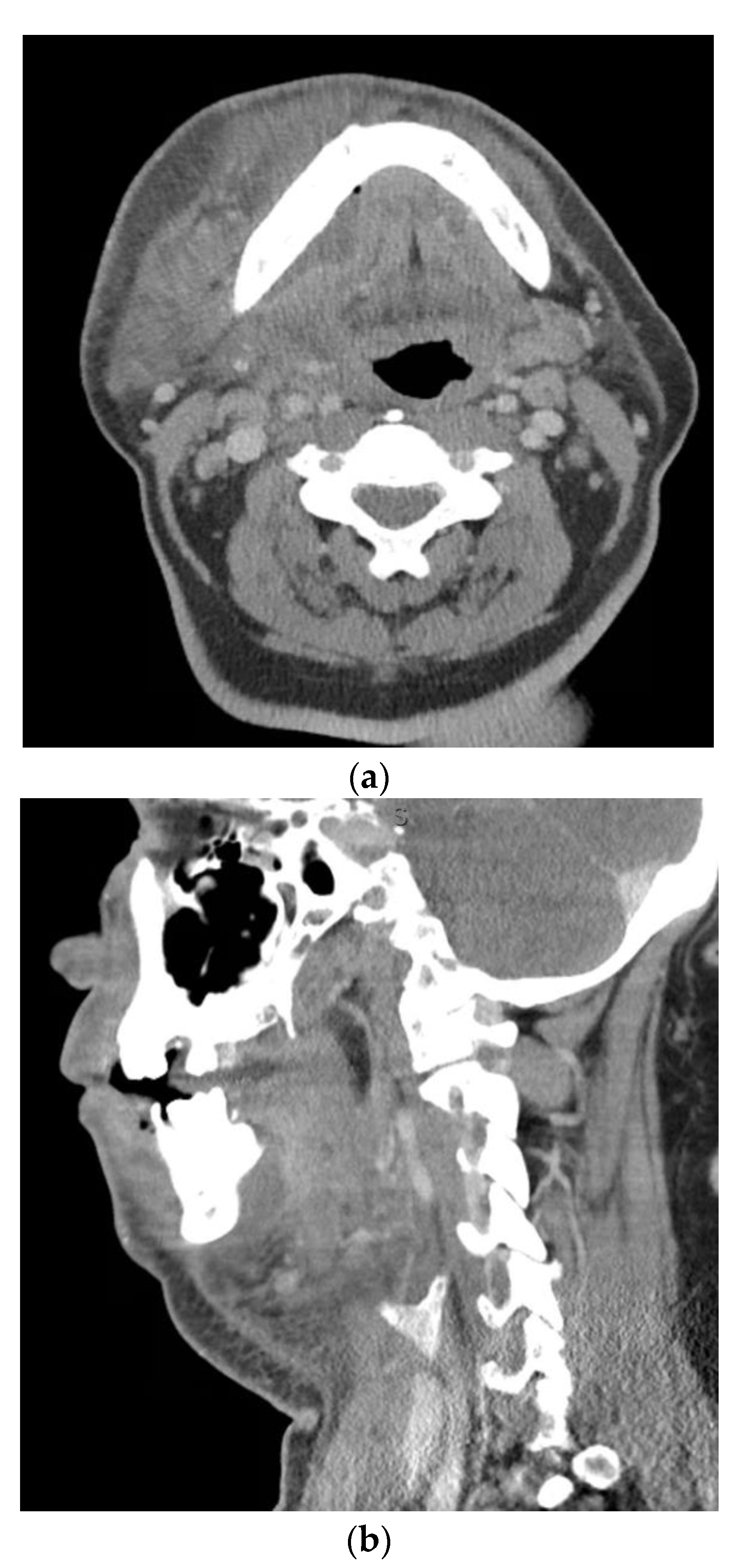
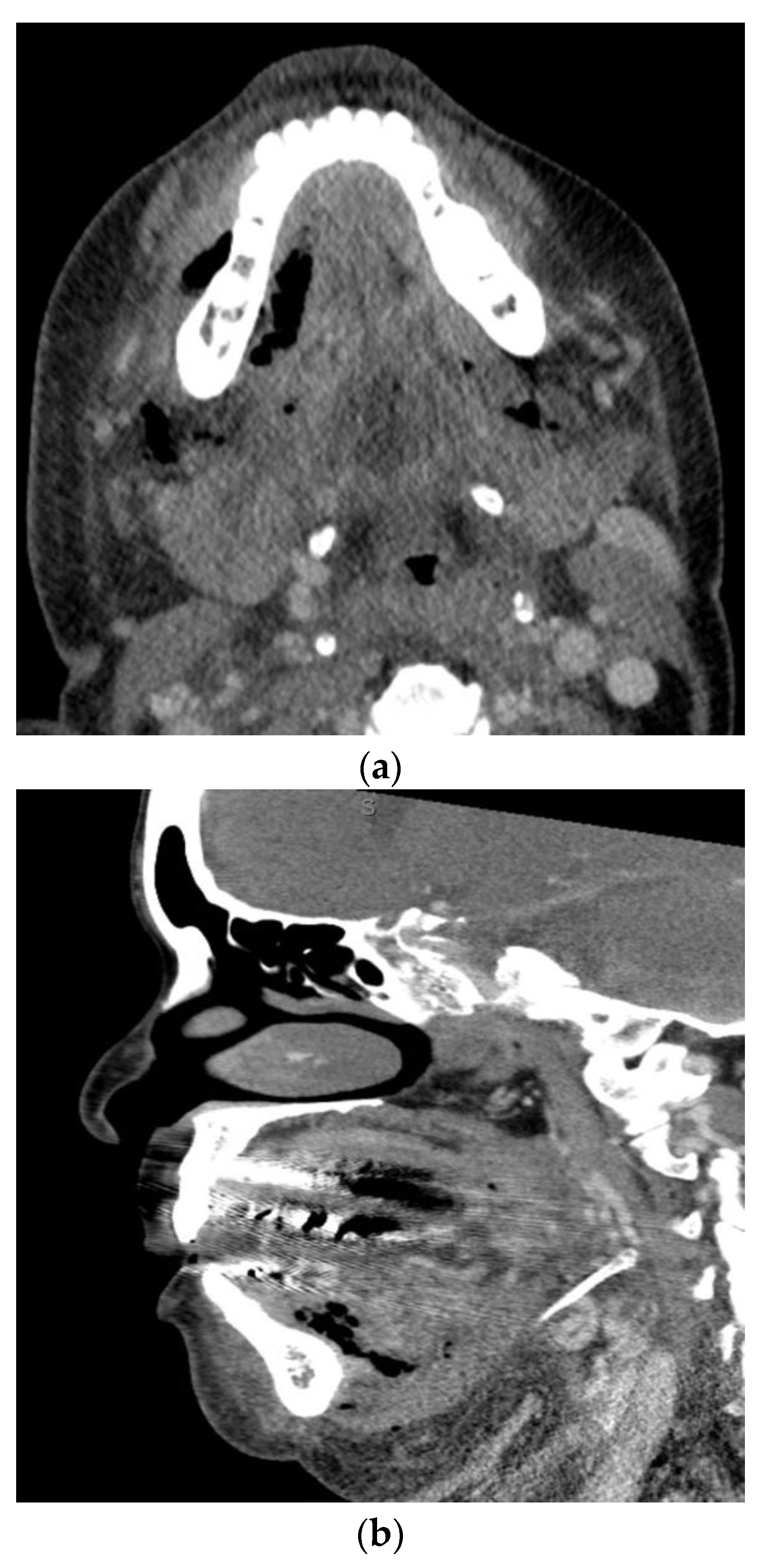
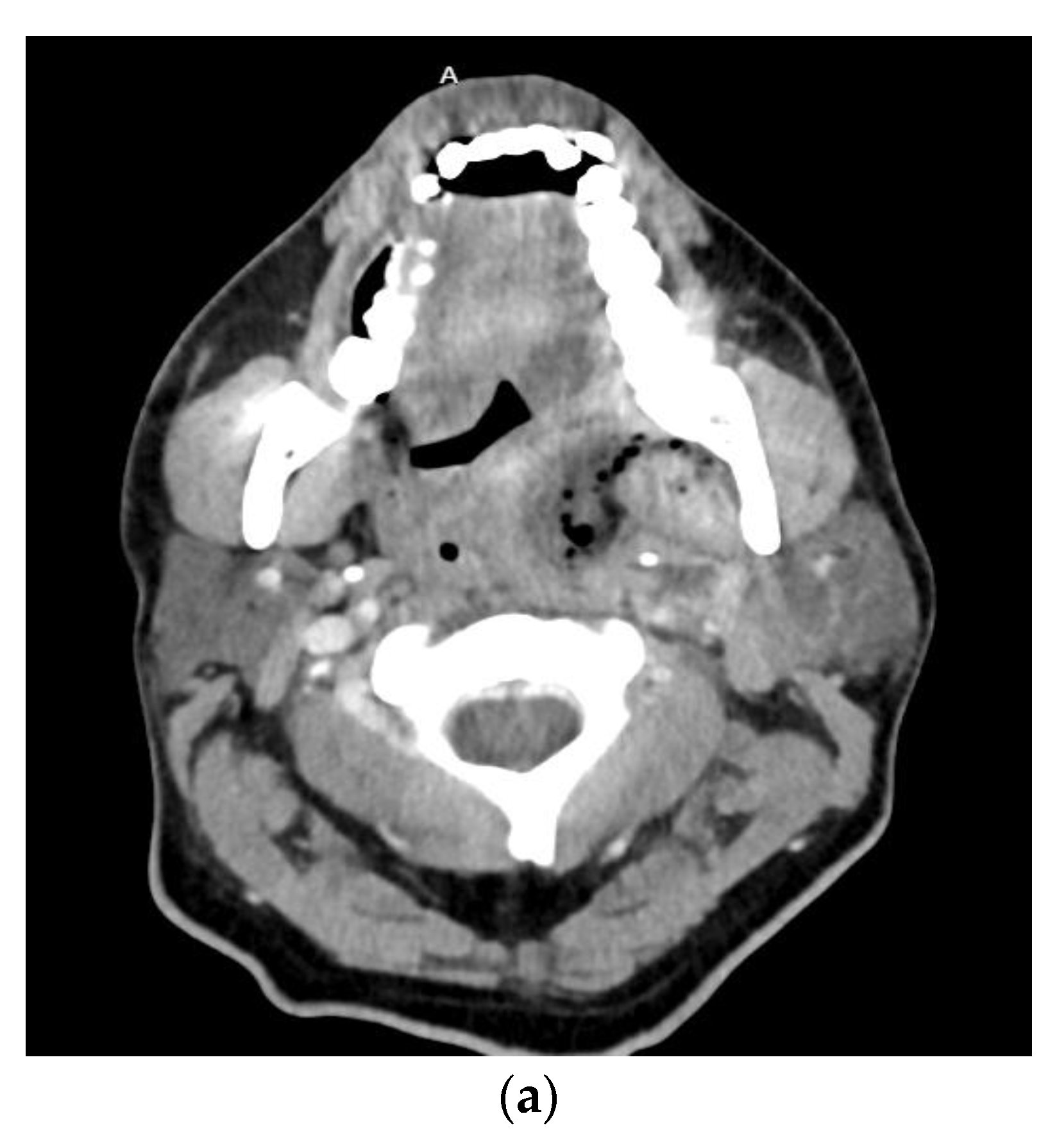
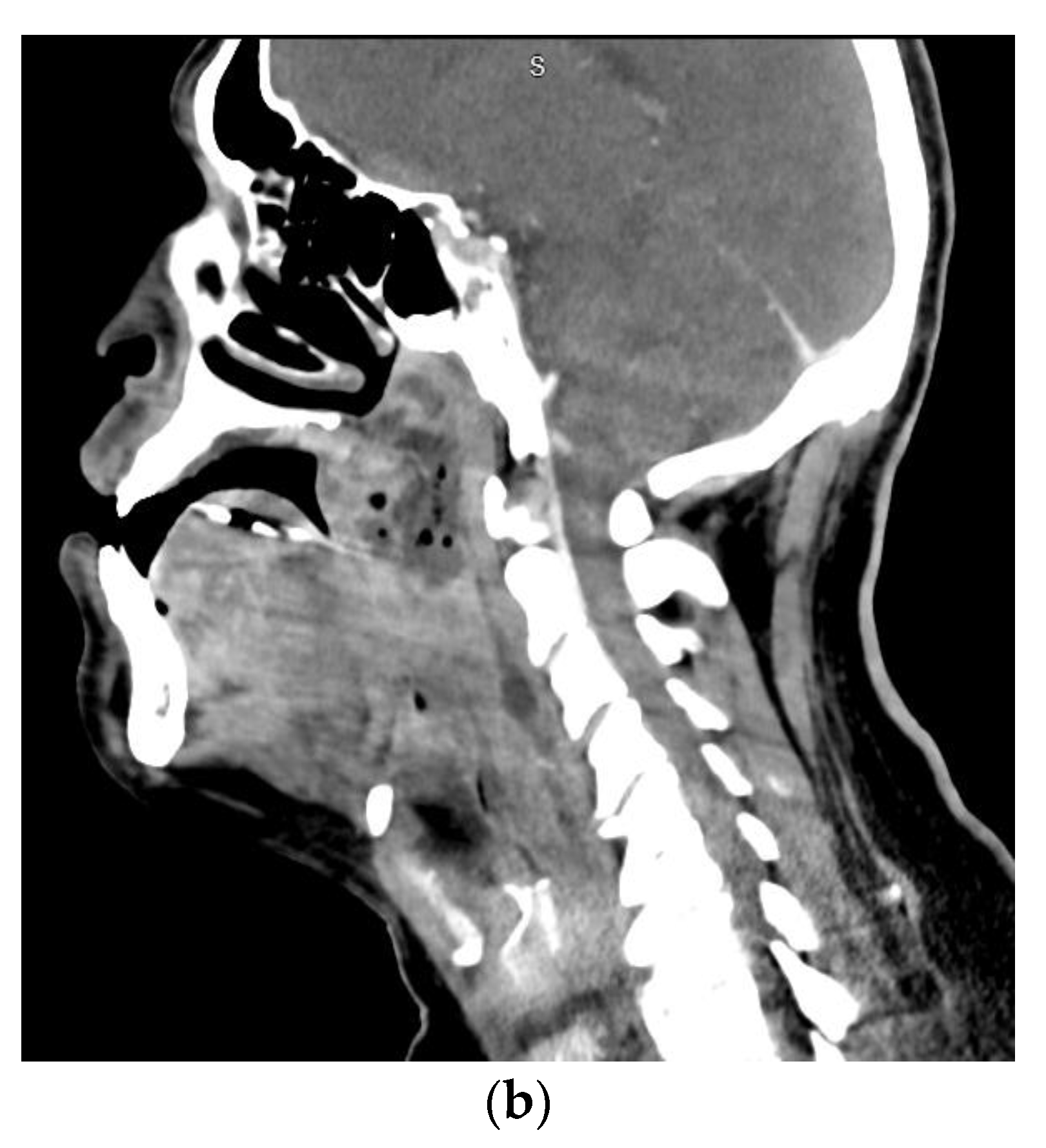
| Anatomic Location | Fascial Spaces Involved | Severity Score |
|---|---|---|
| Maxillary Teeth | Vestibular | 1 |
| Infraorbital | 1 | |
| Buccal | 1 | |
| Infratemporal | 2 | |
| Mandibular Teeth | Vestibular | 1 |
| Buccal | 1 | |
| Submandibular | 2 | |
| Sublingual | 2 | |
| Submental | 2 | |
| Pterygomandibular | 2 | |
| Submasseteric | 2 | |
| Superficial temporal | 2 | |
| Neck and Chest | Lateral pharyngeal | 3 |
| Retropharyngeal | 3 | |
| Pretracheal | 3 | |
| Danger space | 3 | |
| Mediastinum | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neal, T.W.; Schlieve, T. Complications of Severe Odontogenic Infections: A Review. Biology 2022, 11, 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121784
Neal TW, Schlieve T. Complications of Severe Odontogenic Infections: A Review. Biology. 2022; 11(12):1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121784
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeal, Timothy W., and Thomas Schlieve. 2022. "Complications of Severe Odontogenic Infections: A Review" Biology 11, no. 12: 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121784
APA StyleNeal, T. W., & Schlieve, T. (2022). Complications of Severe Odontogenic Infections: A Review. Biology, 11(12), 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121784





