Chrysanthemum: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Developments on In Vitro Regeneration
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
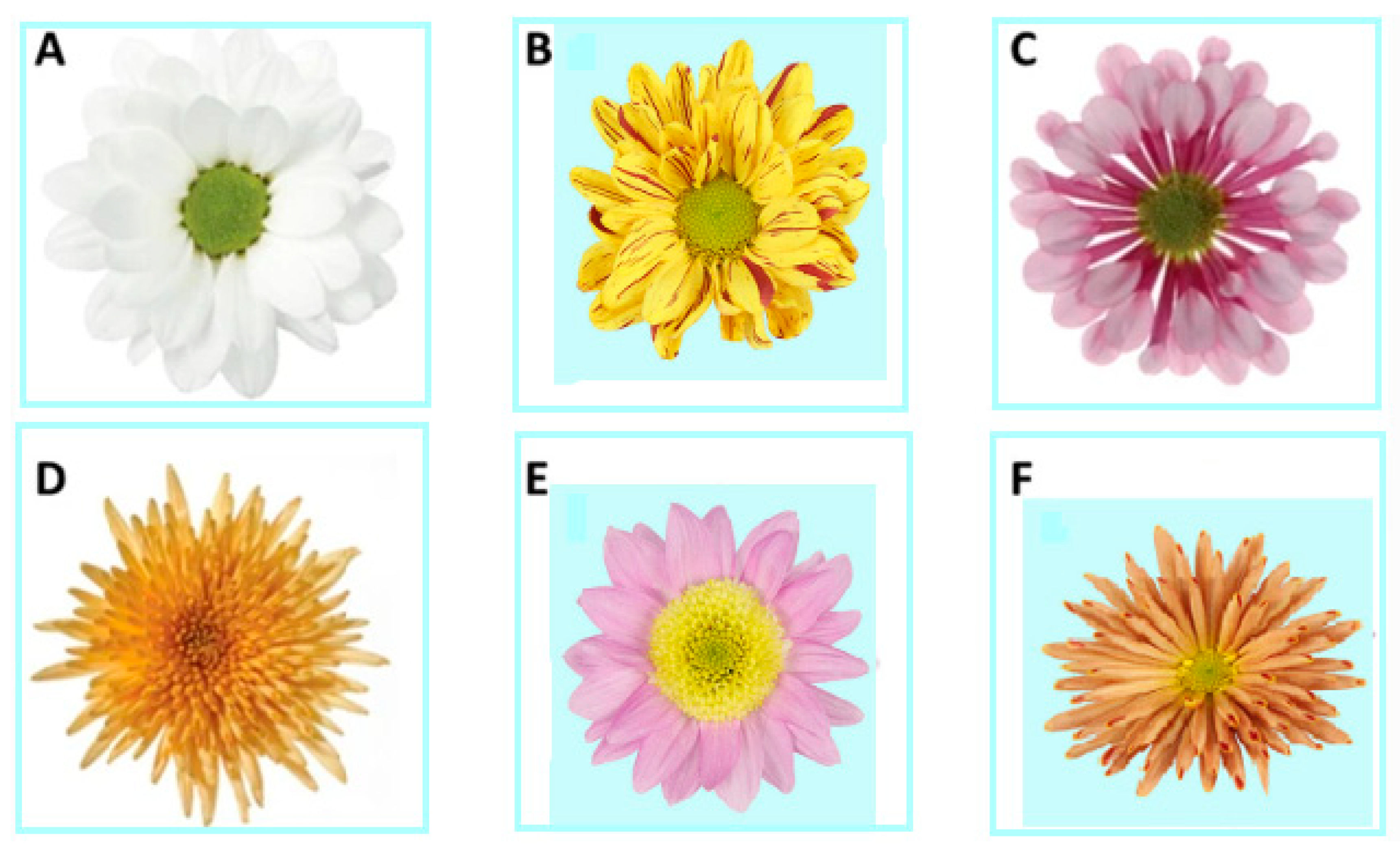
1. Introduction
2. In Vitro Plantlet Propagation
2.1. Propagation from Axillary Buds
2.2. Propagation from Adventitious Shoots or Embryos
Direct and Indirect Morphogenesis
3. Basal Medium for Regeneration
4. The Alternative Disinfection Methods of Culture Media
4.1. Microponic Systems
4.2. Essential Oils and Chemical Compounds in Tissue Culture Media
4.3. Nanomaterials in Tissue Culture Media
4.4. Reintroduction of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) in Tissue Culture Media
4.5. High-Energy Photons and Electrons
5. Protocols for Cloning and Large-Scale Plant Production of Chrysanthemum
5.1. Optimization of Phytohormones on the Shoot, Callus, Somatic Embryo, and Root Induction
5.1.1. Shoot Induction
5.1.2. Callus Induction
5.1.3. Somatic Embryogenesis Induction
5.1.4. Root Induction
5.2. Plant Growth Regulators in the Best Combination
5.3. Optimization of Light Conditions
6. Irradiation Treatment In Vitro
7. The Acclimatization Stage
8. Alternative Light Sources in the Greenhouse
9. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azadi, P.; Bagheri, H.; Nalousi, A.M.; Nazari, F.; Chandler, S. Current Status and Biotechnological Advances in Genetic Engineering of Ornamental Plants. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1073–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getu, M. Ethiopian Floriculture and Its Impact on the Environment. Mizan Law Rev. 2009, 3, 240–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, J.S. Introductory Ornamental Horticulture; Kalyani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 1990; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Spaargaren, J.; Geest, G.V. Chrysanthemum. In Ornamental Crops; Van Huylenbroeck, J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11, pp. 319–348. ISBN 9783319906973. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.; Nam, B.; Kim, B.R.; Kim, S.H.; Jo, Y.D.; Ahn, J.W.; Han, A.R.; Kim, J.B.; Jin, C.H.; Han, A.-R. Comparative Analysis of Phytochemical Composition of Gamma-Irradiated Mutant Cultivars of Chrysanthemum Morifolium. Molecules 2019, 24, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassi, A.B.; Harzallah-Skhiri, F.; Bourgougnon, N.; Aouni, M. Antimicrobial Activities of Four Tunisian Chrysanthemum Species. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 127, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marongiu, B.; Piras, A.; Porcedda, S.; Tuveri, E.; Laconi, S.; Deidda, D.; Maxia, A. Chemical and Biological Comparisons on Supercritical Extracts of Tanacetum cinerariifolium (Trevir) Sch. Bip. with Three Related Species of Chrysanthemums of Sardinia (Italy). Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.A.; Ng, T.B.; Fong, W.P.; Wan, C.C.; Yeung, H.W. A Comparison of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Inhibition by Partially Purified Aqueous Extracts of Chinese Medicinal Herbs. Life Sci. 1997, 60, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AIPH International Statistics Flowers International Statistics Flowers and Plants 2014; Union Fleurs: Reading, UK, 2014; Volume 63, pp. 15–22.
- Kulus, D. Selected Aspects of Ornamental Plants Micropropagation in Poland and Worldwide. Nauk. Przyr. 2015, 4, 10–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.K.; Singh, K.P.; Raju, D.V.S. Effect of Different Strains of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) on Macro and Micro Nutrient Uptake in Micropropagated Chrysanthemum Plantlets. Vegetos 2015, 28, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, G.R.; Das, P. Recent Trends in the Biotechnology of Chrysanthemum: A Critical Review. Sci. Hortic. 1997, 69, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.K. Induced Mutations: Technological Advancement for Development of New Ornamental Varieties. Nucleus 2020, 63, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miler, N.; Iwona, J.; Jakubowski, S.; Winiecki, J. Ovaries of Chrysanthemum Irradiated with High-Energy Photons and High-Energy Electrons Can Regenerate Plants with Novel Traits. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, C.; Carra, A.; Carimi, F.; Motisi, A.; Abbate, L.; Sarno, M.; Carrubba, A. Long-Term Field Evaluation of Conventional vs. Micropropagated Plants of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2756. [Google Scholar]
- Hesami, M.; Naderi, R.; Tohidfar, M.; Miler, N.; Iwona, J.; Jakubowski, S.; Winiecki, J.; Hesami, M.; Naderi, R.; Tohidfar, M.; et al. Effects of Growth Regulators and Genotypes on Pyrethrum in Vitro. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 8, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.B.; Kwon, S.J.; Lee, S.I.; Hwang, Y.J.; Naing, A.H. Influence of Genotype, Explant Source, and Gelling Agent on in Vitro Shoot Regeneration of Chrysanthemum. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2012, 53, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, A.H.; Jeon, S.M.; Han, J.S.; Lim, S.H.; Lim, K.B.; Kim, C.K. Factors Influencing in Vitro Shoot Regeneration from Leaf Segments of Chrysanthemum. Comptes Rendus-Biol. 2014, 337, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, S.C. Influence of Auxin Concentration on in Vitro Rooting of Chrysanthemum Morifolium Ramat. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2016, 13, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, H.T.; Nam, N.B.; Huy, N.P.; Luan, V.Q.; Hien, V.T.; Phuong, T.T.B.; Nhut, D.T. A System for Large Scale Production of Chrysanthemum Using Microponics with the Supplement of Silver Nanoparticles under Light-Emitting Diodes. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 232, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jo, Y.D.; Kang, S.Y.; Ahn, J.W.; Kang, B.C.; Kim, J.B. Sucrose and Methyl Jasmonate Modulate the Expression of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Genes and Increase the Frequency of Flower-Color Mutants in Chrysanthemum. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmy, N.; Thomy, Z.; Yunita; Harnelly, E. The Effect of Some of Coconut Water Concentration in Artificial Media to Chrysanthemum Growth (Dendranthema Grandiflora) by in Vitro. J. Nat. 2019, 19, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jahan, M.T.; Islam, M.R.; Islam, S.S.; Das, P.; Islam, M.M.; Kabir, M.H.; Mamun, A.N.K. Clonal Propagation of Chrysanthemum Morifolium Ramat Using Various Explants Obtained from Field Grown Plants. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 087–093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulus, D.; Zalewska, M. In Vitro Plant Recovery from Alginate-Encapsulated Chrysanthemum × Grandiflorum (Ramat.) Kitam. Shoot Tips. Propag. Ornam. Plants 2014, 14, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Deein, W.; Thepsithar, C.; Thongpukdee, A. In Vitro Culture Medium Sterilization by Chemicals and Essential Oils without Autoclaving and Growth of Chrysanthemum Nodes. World Acad. Sci. 2013, 7, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Zalewska, M.; Tymoszuk, A.; Miler, N. New Chrysanthemum Cultivars as a Result of in Vitro Mutagenesis with the Application of Different Explant Types. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2011, 10, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Dwimahyani, I.; Widiarsih, S. The Effects of Gamma Irradiation on the Growth and Propagation of In-Vitro Chrysanthemum Shoot Explants (Cv. Yellow Puma). At. Indones. 2010, 36, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.B.; Huy, N.P.; Luan, V.Q.; Tung, H.T.; Nhut, D.T. Application of Wireless Power Transmission Led Lighting System in Propagation of Chrysanthemum and Strawberry. Planta Daninha 2016, 34, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhut, D.T.; Nam, N.B.; Tung, H.T. Wireless Light-Emitting Diode System for Micropropagating Chrysanthemum and Strawberry. In Plant Tissue Culture: New Techniques and Application in Horticultural Species of Tropical Region; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 383–397. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, S.K. Need Based Tissue Culture in Floriculture: Asuccess Story. J. Plant Sci. Res. 2019, 35, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyte, L.; Kleyn, J.; Scoggins, H.; Bridgen, M. Plants from Test Tubes: An Introduction to Micropropogation, 4th ed.; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 2013; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, W.C. Mass Propogation by Tissue-Culture-Principles and Techniques. Sci. Educ. Adm. Publ. 1980, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Thrope, T.A. Organogenesis in Vitro: Structural, Physiological, and Biochemical Aspects. In Plant Aging. NATO ASI Series; Rodríguez, R., Tamés, R.S., Durzan, D.J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 186, pp. 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, A.H.; Il Park, K.; Chung, M.Y.; Lim, K.B.; Kim, C.K. Optimization of Factors Affecting Efficient Shoot Regeneration in Chrysanthemum Cv. Shinma. Rev. Bras. Bot. 2016, 39, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevremovic, S.; Subotic, A.; Miljkovic, D.; Trifunovic, M.; Petric, M.; Cingel, A. Clonal Fidelity of Chrysanthemum Cultivars after Long Term Micropropagation by Stem Segment Culture. Acta Hortic. 2011, 961, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, K.; Jilani, M.S.; Khan, M.S. Rapid Plant Regeneration of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum Morifolium L.) through Shoot Tip Culture. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhede, K.N.; Narkhede, M.N.; Shivankar, R.S.; Rathod, T.H. Callus Induction and Micropropagation Studies in Chrysanthemum. Ann. Plant Physiol. 2000, 14, 174–177. [Google Scholar]
- Himstedt, J.P.; Jacobsen, H.J.; Fischer, K. Shoot regeneration from stem and leaf explants of Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema × grandiflorum). Acta Hortic. 2000, 560, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Ma, X.; Dong, F.L.; Zhou, Y.W. Establishment of Regeneration System of Chrysanthemum Morifolium ‘ziyan’ and ‘niu 9722’. Pratacultural Sci. 2015, 32, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Petty, L.M.; Harberd, N.P.; Carré, I.A.; Thomas, B.; Jackson, S.D. Expression of the Arabidopsis Gai Gene under Its Own Promoter Causes a Reduction in Plant Height in Chrysanthemum by Attenuation of the Gibberellin Response. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvadet, M.-A.; Brochard, P.; Boccon-Gibod, J. A Protoplast-to-Plant System in Chrysanthemum: Differential Responses among Several Commercial Clones. Plant Cell Rep. 1990, 8, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu-Yun, L. Tissue Culture and Rapid Propagation of Chrysanthemum Morifolium. Plant Phisiol. Commun. 2010, 12, 314–316. [Google Scholar]
- Jevremovic, S.; Radojevic, L.J. Mass Production of Different Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum Morifolium) Cultivars by Culture in Vitro. J. Sci. Agric. Res. 2004, 65, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, L.; Peng, Y.; Xi, C.; Lin, D. Studies on Rapid-Micropropagation Technology of Different Chrysanthemum Cultivars. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. Sci. 2013, 31, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.I. In Vitro Planet Regeneration of Chrtsanthemum (Chrysanthemum Morifolium). Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Biotechnology, ShereBangla Agricultural University, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2017; pp. 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, M.; Lal, A.; Jain, R. A Simple Cost Effective Method for Mass Propagation of Chrysanthemum Morifoliumi and Antibacterial Activity Assessment of in Vitro Raised Plantlets. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Waseem, K.; Jilani, M.; Jaskani, M.; Khan, M.; Kiran, M.; Khan, G. Significance of Different Plant Growth Regulators on the Regeneration of Chrysanthemum Plantlets (Dendranthema Morifolium L.) through Shoot Tip Culture. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Lacostales, L.E.; Acedo, V.Z. Single Nodal Cutting Propagation of Tissue Culture-Derived Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum Morifolium Ramat.). Philipp. J. Crop Sci. (Philipp.) 2015, 40, 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zalewska, M.; Miler, N.; Wenda-Piesik, A. Effect of in Vitro Topophysis on the Growth, Development, and Rooting of Chrysanthemum Explants (Chrysanthemum Grandiflorum/Ramat./Kitam). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 4, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.N.; AbdelFattah, R.S.; Badr, M.; El-Torky, M.G. In Vitro Culture and Plant Regeneration Derived from Ray Florets of Chrysanthemum Morifolium. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TeixeiradaSilva, J.A.; Kulus, D. Chrysanthemum Biotechnology: Discoveries from the Recent Literature. Folia Hortic. 2014, 26, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.K. Indian Floriculture: Role of CSIR; Regency Publications, A Division of Astral International (P) Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2015; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
- Miler, N.; Zalewska, M. Somaclonal Variation of Chrysanthemum Propagated in Vitro from Different Explants Types. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2014, 13, 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kengkarj, P.; Smitamana, P.; Fujime, Y. Assessment of Somaclonal Variation in Chrysan-Themum (Dendranthema Grandiflora Kitam.) Using RAPD and Morphological Analysis. Plant Tissue Cult. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bio Assays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Huang, M.E.E.; Pua, E.-C.C. High Frequency Shoot Regeneration from Leaf Disc Explants of Garland Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum Coronarium L.) in vitro. Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, R.K.; Agrawal, A.; Mahalakshmi, C.; Hussain, Z.; Tyagi, H. Low-Cost Media for in Vitro Conservation of Turmeric (Curcuma Longa L.) and Genetic Stability Assessment Using RAPD Markers. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2007, 43, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atici, T.; Khawar, K.M.; Ozel, C.A.; Katircioglu, H.; Ates, M.A. Use of Psyllium (Isubgol) Husk as an Alternative Gelling Agent for the Culture of Prokaryotic Microalgae (Cyanobacteria) Chroococcus Limneticus Lemmermann and Eukaryotic Green Microalgae (Chlorophyta) Scenedesmus Quadricauda (Turpin) Brebisson. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.N.P.; Kumar, A.Y.R. Effects of Antioxidants and Gelling Agents on Regeneration, in Vitro Conservation and Genetic Stability of Bacopa Monnieri (L.) Pennell. Int. J. Ayurvedic Herb. Med. 2011, 1, 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- George, E.F.; Hall, M.A.; Klerk, G.-J. De The Components of Plant Tissue Culture Media II: Organic Additions, Osmotic and PH Effects, and Support Systems. In Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture; George, E.F., Hall, M.A., Klerk, G.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 115–173. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, J.; Sahu, R.K. A Review on Low Cost Methods for in Vitro Micropropagation of Plant through Tissue Culture Technique. Pharm. Biosci. J. 2013, 1, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, H.T.; Bao, H.G.; Cuong, D.M.; Ngan, H.T.M.; Hien, V.T.; Luan, V.Q.; Nhut, D.T. Silver Nanoparticles as the Sterilant in Large-Scale Micropropagation of Chrysanthemum. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2021, 57, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Cost Analysis of Plant Micropropagation of Phalaenopsis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2016, 126, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Hsiao, K.-C. Sugar Degradation during Autoclaving: Effects of Duration and Solution Volume on Breakdown of Glucose. Physiol. Plant. 1995, 94, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brondani, G.E.; de Oliveira, L.S.; Bergonci, T.; Brondani, A.E.; França, F.A.M.; da Silva, A.L.L.; Goncalves, A.N. Chemical Sterilization of Culture Medium: A Low Cost Alternative to in Vitro Establishment of Plants. Sci. For. 2013, 41, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Pais, A.K.; da Silva, A.P.; de Souza, J.C.; Teixeira, S.L.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Peixoto, A.R.; da Paz, C.D. Sodium Hypochlorite Sterilization of Culture Medium in Micropropagation of Gerbera Hybrida Cv. Essandre. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 1995–1998. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, D.P.; Formoso, R.S.; Dutra, L.F.; Mayer, N.A.; Santos, J.D.; Ueno, B. Chemical Sterilization of in vitro Culture for Peach Rootstock. In Proceedings of the Colloquium Agrariae; Universidade do Oeste Paulista (UNOESTE): Presidente Prudente, Brazil, 2016; Volume 12, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, J.C.; Gerald, L.T.S.; da Silva, J.A.T. Micropropagation in the Twenty-First Century. In Micropropagation in the Twenty-First Century, in Plant Cell Culture Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 17–46. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, T.; Sheng, W.; Zhao, F.; Duan, Y. Microgram-Grade Concentration of Chlorine Dioxide Induces One-Step Plant Regeneration in Chrysanthemum. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymoszuk, A. Application of Silver and Copper Nanocolloids in Disinfection of Explants in Chrysanthemum In Vitro Cultures. In Book of Abstracts, Proceedings of the NanoPL; Nano PL on-line journal, 2014; Volume 10, Available online: http://science24.com/paper/31231 (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Sarmast, M.; Salehi, H.; Khosh-Khui, M. Nano Silver Treatment Is Effective in Reducing Bacterial Contaminations of Araucaria Excelsa R. Br. Var. Glauca Explants. Acta Biol. Hung. 2011, 62, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmast, M.K.; Salehi, H. Silver Nanoparticles: An Influential Element in Plant Nanobiotechnology. Mol. Biotechnol. 2016, 58, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fan, L.; Hu, Q.; Gao, S. Stem Apex Detoxification Culture Markedly Improved Several Physiological Characters of Chrysanthemum ‘YUTAI. ’ Plant Cell. Tissue Organ Cult. 2014, 119, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, E.J.; Lee, Y.B.; Ahn, C.H. A New Method on Mass-Production of Micropropagated Chrysanthemum Plants Using Microponic System in Plant Factory. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Plant Production in Closed Ecosystems, 26–29 August 1996; Kozai, T., Ed.; Acta Horticulture: Narita, Japan; 440, pp. 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, E.J.; Bae, J.H.; Lee, Y.B. Growth and Leaf-Surface Characteristics of Chrysanthemum Plantlets between Micropropagation and Microponic System. J. Korean Soc. Hortic. Sci. (Korea Repub.) 1998, 39, 838–842. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, E.-J.; Bae, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Chrysanthemum Plantlets as Affected by PH and EC of the Nutrient Solution in Microponic Culture. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2000, 41, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, H.T.; Ngan, H.T.M.; Phuong, T.T.B.; Nhut, D.T. Microponic Culture System in the Propagation of Some Plants. In Plant Tissue Culture: New Techniques and Application in Horticultural Species of Tropical Region; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 207–229. [Google Scholar]
- Thepsithar, C.; Thongpukdee, A.; Daorat, A. Sterilisation of in Vitro Culture Medium of Chrysanthemum by Plant Essential Oils without Autoclaving. Int. J. Bioeng. Life Sci. 2013, 7, 802–805. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, A.D. Similarities and Differences in the Responses of Microorganisms to Biocides. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.K.; Misra, P.; Kole, C. Plant Nanotechnology: Principles and Practices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 219–256. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, N.; Soni, D.; Chandrashekhar, B.; Sarangi, B.K.; Satpute, D.; Pandey, R.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Cynodon Dactylon Leaves and Assessment of Their Antibacterial Activity. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 36, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savithramma, N.; Ankanna, S.; Bhumi, G. Effect of Nanoparticles on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Boswellia Ovalifoliolata an Endemic and Endangered Medicinal Tree Taxon. Nano Vis. 2012, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Tymoszuk, A.; Miler, N. Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Impact on in Vitro Adventitious Organogenesis in Chrysanthemum, Gerbera and Cape Primrose. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; McLean, J.E.; Britt, D.W.; Anderson, A.J. Bioactivity and Biomodification of Ag, ZnO, and CuO Nanoparticles with Relevance to Plant Performance in Agriculture. Ind. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, H.T.; Bao, H.G.; Buu, N.Q.; Chau, N.H.; Nhut, D.T. The Use of Silver Nanoparticles as a Disinfectant and Media Additive in Plant Micropropagation. In Plant Tissue Culture: New Techniques and Application in Horticultural Species of Tropical Region; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 287–302. [Google Scholar]
- Azcón-Aguilar, C.; Barea, J.M. Arbuscular Mycorrhizas and Biological Control of Soil-Borne Plant Pathogens—An Overview of the Mechanisms Involved. Mycorrhiza 1997, 6, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandavalli, R.B.; Dillenburg, L.R.; de Souza, P.V.D. Growth Responses of Araucaria Angustifolia (Araucariaceae) to Inoculation with the Mycorrhizal Fungus Glomus Clarum. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 25, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, B.K.; Kim, K.Y.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, W.S.; Park, S.M.; Kang, J.G.; Rim, Y.S.; Cho, J.S.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, J.H. Effect of the Different Timing of AMF Inoculation on Plant Growth and Flower Quality of Chrysanthemum. Sci. Hortic. 2003, 98, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.E.; Abdel-Fattah, G.M. Influence of the Endomycorrhizal Fungus Glomus Mosseae on the Development of Peanut Pod Rot Disease in Egypt. Mycorrhiza 2000, 10, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Lozano, J.M.; Azcón, R. Hyphal Contribution to Water Uptake in Mycorrhizal Plants as Affected by the Fungal Species and Water Status. Physiol. Plant. 1995, 95, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.F.; Paul, L.R.; Finlay, R.D. Microbial Interactions in the Mycorrhizosphere and Their Significance for Sustainable Agriculture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, B.J. Sterilisation Procedures for Tissue Allografts. Stand. Cell Tissue Eng. 2013, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, J.S.; Shyamali, S.; Kazumi, H. High Frequency Shoot Regeneration from Petal Explants of Chrysanthemum Morifolium Ramat. in Vitro. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 3356–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Jerzy, M.; Zalewska, M.; Tymoszuk, A. Effect of Kinetin on the Elongation of Adventitious Shoots Regenerated in vitro from Ligulate Florets in Chrysanth. × Grandiflorum Ramat. Kitam. Acta Hortic. 2015, 1083, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjahril, R.; Haring, F.; Riadi, M.; Rahim, M.D.; Khan, R.S.; Amir, A.; Trisnawaty, A.R. Performance of NAA, 2iP, BAP and TDZ on Callus Multiplication, Shoots Initiation and Growth for Efficient Plant Regeneration System in Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum Morifolium Ramat). Int. J. Agric. Syst. Perform. 2015, 4, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Labade, G.B.; Dale, N.S.; Umbarkar, R.B.; Gadhe, S.K.; Rote, Y.N. In Vitro Regeneration of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum Morifolium L.). Int. J. Inf. Res. Rev. 2016, 3, 3043–3045. [Google Scholar]
- Miler, N.; Kulus, D. Microwave Treatment Can Induce Chrysanthemum Phenotypic and Genetic Changes. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 227, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, M.; Naderi, R.; Tohidfar, M. Introducing a Hybrid Artificial Intelligence Method for High-Throughput Modeling and Optimizing Plant Tissue Culture Processes: The Establishment of a New Embryogenesis Medium for Chrysanthemum, as a Case Study. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10249–10263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesami, M.; Naderi, R.; Tohidfar, M.; Yoosefzadeh-Najafabadi, M.; Hesami, M.; Naderi, R.; Tohidfar, M.; Yoosefzadeh-Najafabadi, M. Development of Support Vector Machine-Based Model and Comparative Analysis with Artificial Neural Network for Modeling the Plant Tissue Culture Procedures: Effect of Plant Growth Regulators on Somatic Embryogenesis of Chrysanthemum, as a Case Study. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsoufi, A.S.M.M.; Ahmed, Z.S.; Salim, A.M. The Efficiency of Interaction between Cytokines and Auxins in Micropropagation of Chrysanthemum Plant (Chrysanthemum Indicum L.). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 735, 12048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, M.; Khattak, A.M.; Ara, N.; Iqbal, A.; Rahman, H.U. Micropropagation of Jartorpha Curcas L. through Shoot Tip Explants Using Different Concentrations of Phytohormones. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2014, 24, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, G.H.; Jeong, B.R. Adventitious Shoot Regeneration from Cultured Petal Explants of Chrysanthemum. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2007, 48, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Janarthanam, B.; Seshadri, S. Plantlet Regeneration from Leaf Derived Callus of Vanilla Planifolia Andr. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2008, 44, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigiano, R.N.; Gray, D.J. Plant Development and Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; p. 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Q. Shoot Regeneration from Stem and Leaf Explants of Dendrathema Grandiflorum. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2001, 23, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kashif, W.; Khan, M.Q.; Jaffar, J.; Khan, M.S. Impact of Different Auxins on the Regeneration of Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema Morifolium) through in Vitro Shoot Tip Culture. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 20, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.I.; Fatema, M. In Vitro Multiple Shoot Regeneration in Chrysanthemum Morifolium Ramat. Plant Tissue Cult 1995, 5, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.N.; Hakim, L.; Islam, M.R.; Munshi, M.K.; Hossain, M. In Vitro Plant Regeneration of Apple (Malus Domestica Borkh). Bangladesh J. Bot. 2002, 31, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, M.T.; Islam, M.R.; Khan, R.; Mamun, A.N.K.; Ahmed, G.; Hakim, L. In Vitro Clonal Propagation of Anthurium (Anthurium Andraeanum L.) Using Callus Culture. Plant Tissue Cult. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindiro, C.; Kahia, J.; Asiimwe, T.; Mushimiyimana, I.; Waweru, B.; Kouassi, M.; Koffi, E.; Kone, S.; Sallah, P.Y. In Vitro Regeneration of Pyrethrum (Chrysanthemum Cinerariaefolium) Plantlets from Nodal Explants of in Vitro Raised Plantlets. Int. J. Appl. Or Innov. Eng. Manag. 2013, 2, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Haberer, G.; Kieber, J.J. Cytokinins. New Insights into a Classic Phytohormone. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jobouri, A.H. Studying Some The Functional Properties of Tamarind Tamarindus Indica L. Mucilage. Al-Qadisiyah J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 10, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XiaoHan, Y.; Bo, J.; Yan, Z.; Ding, M.; XueMei, T. Inhancement of Direct Shoot Regeneration from Internode Segments of Chrysanthemum by Silver Nitrate. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Cultivar Improvement of Horticultural Crops; Part 3: Flowers 404; Dewei, Z., Ed.; Acta Horticulture: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, U.-H.; Kasha, K.J. Ethylene Production and Embyogenesis from Anther Cultures of Barley (Hordeum Vulgare). Plant Cell Rep. 1989, 8, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierik, R.L.M. In Vitro Culture of Higher Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; p. 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Sorrell, D.A. The Interface between the Cell Cycle and Plant Growth Regulators: A Mini Review. Plant Growth Regul. 2001, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.D.; Maseena, E.A. Callus Induction and Plant Regeneration in Cardiospermum Halicacabum Linn. an Important Medicinal Plant. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 108, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukosia, S.D.; Kimani, E.; Waithaka, K.; Mutitu, E.; Kimani, P.M. Effects of Growth Regulators and Genotypes on Pyrethrum in Vitro. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2005, 41, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwin; Slregar, I.Z.; Supriyanto, D. The Use of BAP and TDZ for Propagation of Agarwood (Aquilaria Malaccensis Lamk.). Media. Media Konserv. 2006, 11, 98–104. Available online: http://repository.ipb.ac.id/handle/123456789/43541 (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Murgayanti, S.E.; Wieny, R.H.; Rustiani, S. Callus Formation and Plant Regeneration of Chrysanthemum Leaf Disks Explants through in Vitro. International. Int. Semin. Hortic. Support Food Secur. 2010, 4, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.H. Plant Tissue Culture: Techniques and Experiments; Elseivier, Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- Rivai, R.R.; Helmanto, H. Callus Induction of Chrysanthemum Indicum for Increasing Genetic Diversity from Somatic Cell. Pros. Semin. Nas. Masy. Biodiversitas Indones. 2015, 1, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Nasri, F.; Zakizadeh, H.; Vafaee, Y.; Mozafari, A. In Vitro Propagation of Chrysanthemum: An Overview on Its Utility in Mutagenesis and Genetic Transformation Techniques. Agric. Res. Technol. Open Access J. 2018, 15, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenway, M.B.; Phillips, I.C.; Lloyd, M.N.; Hubstenberger, J.F.; Phillips, G.C. A Nutrient Medium for Diverse Applications and Tissue Growth of Plant Species in Vitro. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2012, 48, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoyama, H.; Nomura, Y.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kazuma, T. A Simple and Efficient Method for Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Leaves of Chrysanthemum [Dendranthema × Grandiflorum (Ramat.) Kitamura]. Plant Biotechnol. 2004, 21, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kereša, S.; Mihovilović, A.; Barić, M.; Židovec, V.; Skelin, M. The Micropropagation of Chrysanthemums via Axillary Shoot Proliferation and Highly Efficient Plant Regeneration by Somatic Embryogenesis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Senthil, K. Multiplication of Chrysanthemum through Somatic Embryogenesis. Asian J. Pharma Tech. 2011, 1, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Naing, A.H.; Kim, C.K.; Yun, B.J.; Jin, J.Y.; Lim, K.B. Primary and Secondary Somatic Embryogenesis in Chrysanthemum Cv. Euro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2013, 112, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymoszuk, A.; Zalewska, M.; Lema-Rumińska, J. Regeneration of Somatic Embryos from in Vitro Isolated Ligulate Florets of Chrysanthemum. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2014, 13, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cline, M.G. Apical Dominance. Bot. Rev. 1991, 57, 318–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roest, S.; Bokelmann, G.S. Vegetative Propagation of Chrysanthemum Cinerariaefolium in Vitro. Sci. Hortic. 1973, 1, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeroonian, N.; Power, J.B.; Davey, M.R. An Assessment of Somaclonal Variation on Chrysanth. Cv. “Rosomee Splendid”. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 38, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Schenk, R.U.; Hildebrandt, A.C. Medium and Techniques for Induction and Growth of Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous Plant Cell Cultures. Can. J. Bot. 1972, 50, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, M.; Khattak, A.M.; Khan, M.A.; Jalal, F.; Hussain, S.; Said, F.; Bo, H. Rapid in-Vitro Propagation of Chrysanthemum Morifolium through Shoot Bud Explants. Pak. J. Bot. 2019, 51, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, O.P. Standardization of Auxin Concentration for Root Induction in Chrysanthemum Morifolium. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res 2012, 3, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan, B.; Braun, S.; Cortés, M.J.; Bergmann, F.; Karl, C.; Füzesi, L. Characterization of a Newly Established Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma Cell Line. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, Z. Multiplikasi Empat Varietas Krisan Melalui Teknik Kultur Jaringan. J. Agroland. 2008, 15, 271–277. (In Indonesian) [Google Scholar]
- Malik, S.; Chadhury, R.; Kalia, R. Rapid in Vitro Multiplication and Conservation of Garcinia Indica: A Tropical Medicinal Tree Species. Sci. Hortic. 2005, 106, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilahi, I.; Jabeen, M.; Nazneen Sadaf, S. Rapid Clonal Propagation of Chrysanthemum through Embryogenic Callus Formation. Pak. J. Bot. 2007, 39, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Tymoszuk, A.; Zalewska, M. In Vitro Adventitious Shoots Regeneration from Ligulate Florets in the Aspect of Application in Chrysanthemum Breeding. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2014, 13, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, M.K.; Patil, S.R.; Chakrapani, K.; Kalamkar, V.B.; Lende, S.R. Studies on Callus Induction and Differentiation in Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema Grandiflora). J. Soils Crop. 2006, 16, 324–330. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, A.; Nomizu, T.; Furutani, N.; Hayashi, K.; Minamiyama, Y.; Hase, Y. Ray Florets Color and Shape Mutants Induced by 12C5+ Ion Beam Irradiation in Chrysanthemum. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 123, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalini, R.; Anjana, M.J.; Arathi, C.S.; Aswathy, M.; Ayana, B.; Bhuvaneswari, R. Effect of Growth Regulators on Micropropagation of Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema Grandiflora Ramat.) Scru. IRJ Agric 2016, 3, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zafarullah, A.; Ilyas, S.; Naz, S.; Aslam, F.; Manzoor, F. Effect of Culture Media and Growth Regulators on In Vitro Propogation of Chrysanthemum Indicum L. Pak. J. Sci. 2013, 65, 462. [Google Scholar]
- Hitmi, A.; Barthomeuf, C.; Sallanon, H. Rapid Mass Propagation of Chrysanthemum Cinerariaefolium Vis. by Callus Culture and Ability to Synthesise Pyrethrins. Plant Cell Rep. 1999, 19, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelake, R.M.; Pramanik, D.; Kim, J.-Y. Evolution of Plant Mutagenesis Tools: A Shifting Paradigm from Random to Targeted Genome Editing. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 13, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPVO Varieties Database. Available online: http://Cpvo.Europa.Eu (accessed on 12 April 2017).
- Protocol for Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability Test for Chrysanthemum × Morifolium (Ramat.), Community Plant Variety Office (CPVO). 2008. Available online: https://cpvo.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/chrysanthemum_2.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2021).
- Zhao, M.-X.; Sun, H.-Y.; Ji, R.-R.; Hu, X.-H.; Sui, J.-M.; Qiao, L.-X.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.-S. In Vitro Mutagenesis and Directed Screening for Salt-Tolerant Mutants in Peanut. Euphytica 2013, 193, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretescu, I.; Rodica, C.; Velicevici, G.; Ropciuc, S.; Buzamat, G. Response of Barley Seedlings to Microwaves at 2.45 GHz. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 46, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Halmagyi, A.; Surducan, E.; Surducan, V. The Effect of Low- and High-Power Microwave Irradiation on in Vitro Grown Sequoia Plants and Their Recovery after Cryostorage. J. Biol. Phys. Vol. 2017, 43, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Datta, S.K.; Chakrabarty, D. Mutation in Flower Colour and Shape of Chrysanthemum Morifolium Induced by-γ-Radiation. Biol. Plant. 2003, 47, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Shimizu, A.; Hase, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Shikazono, N.; Degi, K.; Morishita, T. Effects of Ion Beam Irradiation on Mutation Induction and Nuclear DNA Content in Chrysanthemum. Breed. Sci. 2010, 60, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.D.; Kim, J.-B. Frequency and Spectrum of Radiation-Induced Mutations Revealed by Whole-Genome Sequencing Analyses of Plants. Quantum Beam Sci. 2019, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miler, N.; Muszczyk, P. Regeneration of Callus and Shoots from the Ovules and Ovaries of Chrysanthemum in Vitro. Acta Hortic. 2015, 1083, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, B.; Jiang, J.; Fang, W.; Guan, Z.; Liao, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, F. Characterization of in Vitro Haploid and Doubled Haploid Chrysanthemum Morifolium Plants via Unfertilized Ovule Culture for Phenotypical Traits and DNA Methylation Pattern. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Dobránszki, J. Dissecting the Concept of the Thin Cell Layer: Theoretical Basis and Practical Application of the Plant Growth Correction Factor to Apple, Cymbidium and Chrysanthemum. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 33, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero-Aracama, C.; Kane, M.E.; Wilson, S.B.; Vu, J.C.; Anderson, J.; Philman, N.L. Photosynthetic and Carbohydrate Status of Easy-and Difficult-to-Acclimatize Sea Oats (Uniola Paniculata L.) Genotypes during in Vitro Culture and Ex Vitro Acclimatization. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2006, 42, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Mathur, A.K.; Verma, P.; Yadav, S.; Gupta, M.L.; Darokar, M.P. Biological Hardening and Genetic Fidelity Testing of Micro-Cloned Progeny of Chlorophytum Borivilianum Sant. et Fernand. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.D.; Jatothu, B. Fundamentals and Applications of Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) in in Vitro Plant Growth and Morphogenesis. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2013, 7, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.C.; Brown, C.S. Root-Shoot Interaction in the Greening of Wheat Seedlings Grown under Red Light. Plant Physiol. 1995, 107, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennessen, D.J.; Singsaas, E.L.; Sharkey, T.D. Light-Emitting Diodes as a Light Source for Photosynthesis Research. Photosynth. Res. 1994, 39, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenecke, M.E.; Bula, R.J.; Tibbitts, T.W. Importance of Blue’Photon Levels for Lettuce Seedlings Grown under Red-Light-Emitting Diodes. HortScience 1992, 27, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E. Plant Physiology; Benjamin/Cummings Pub Co: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 115–575. [Google Scholar]
- Steigerwald, D.A.; Bhat, J.C.; Collins, D.; Fletcher, R.M.; Holcomb, M.O.; Ludowise, M.J.; Martin, P.S.; Rudaz, S.L. Illumination with Solid State Lighting Technology. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2002, 8, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bula, R.J.; Morrow, R.C.; Tibbitts, T.W.; Barta, D.J.; Ignatius, R.W.; Martin, T.S. Light-Emitting Diodes as a Radiation Source for Plants. HortScience 1991, 26, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Doi, M.; Suetsugu, N.; Kagawa, T.; Wada, M.; Shimazaki, K. Phot1 and Phot2 Mediate Blue Light Regulation of Stomatal Opening. Nature 2001, 414, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoyunoglou, G.; Anni, H. Blue Light Effect on Chloroplast Development in Higher Plants. In Blue Light Effects in Biological Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 397–406. [Google Scholar]
- Ouzounis, T.; Fretté, X.; Rosenqvist, E.; Ottosen, C.-O. Spectral Effects of Supplementary Lighting on the Secondary Metabolites in Roses, Chrysanthemums, and Campanulas. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtentaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determination of Total Carotenoids, Chlorophyll a and b of Leaf in Different Solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurs, A.; Karalis, A.; Moffatt, R.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fisher, P.; Soljacic, M. Wireless Power Transfer via Strongly Coupled Magnetic Resonances. Science. Science 2007, 317, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Plant Sp. | Explant Type | Medium Content | Responding | Survival Response | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chrysanthemum morifolium | Segments of nodal nodules with a single axillary bud | Full strength MS basal medium + BAP (0.1 mg/L) + sucrose (30 g/L) + agar (7 g/L w/v). | Bud induction | 96% | [46] |
| -MS medium + BAP (0.5 mg/L) | Shoot multipication | ||||
| -MS medium + 25 g/L psyllium husk + 20 g/L market sugar + RO | Shoot multiplication | ||||
| 1/2 strength MS medium + 0.6% agar + 20 g/L market sugar + 0.50 mg/L IBA | Root formation | ||||
| Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Ramat. Kitam. cv. Capitola | Ligulate florets | -MS (Medium) + calcium and iron by half + 0.4 mg/L thiamine + 10 g/L sucrose, (6 weeks) 3 mg/L KIN + 0.5 mg/L (IAA) + 0.8% (w/v) agar Then (6 weeks) 1 mg/L KIN + 0.5 mg/L (IAA) + 0.8% (w/v) agar. | Shoot multiplication 51.26% | N/A | [94] |
| Chrysanthemum morifolium cv.ziyan | Stems with axillary bud | -MS + 6-BA 2.0 mg·L−1 + NAA 1.0 mg·L−1. | Callus induction 100% and bud differentiation 92.22%. | N/A Survival 100% | [39] |
| -1/2 MS + NAA 0.2 mg·L−1 | Rooting 100% and average root number of 15.50 | ||||
| C.morifolium cv.niu9722 | Stems with axillary bud | -MS + 6-BA 2.0 mg·L−1 + NAA 0.5 mg·L−1 | Callus induction 100%+ bud differentiation 45.59% | ||
| MS + 6-BA 2.0 mg·L−1 + NAA 0.5 mg·L−1 | Stem proliferation | ||||
| 1/2 MS + NAA 0.3 mg·L−1 | Rooting 100% + average root number of 14.87 | ||||
| Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat cv., “Pasopati” | Leaf explants | MS + 1.0 mg L−1 + 0.5 mg L−1 BAP | Callus induction (1.55 g biomass weight) | N/A | [95] |
| MS + NAA (0.5 mg L−1) + BAP (0.5 mg L−1) | Shoot initiation (30 days after planting) + N. of shoots (5) + shoot length (2.9 cm) | ||||
| MS + 2iP (0.5 mg L−1) and BAP (2.0 mg L−1) | Shoot imitation after after 30 days + shoot length (1.88 cm) + shoot Num. (1) | ||||
| MS + BAP 0.5 mg L−1 | Num.shoot (3) | ||||
| Chrysanthemum cv. Shinma | Leaf explant | MS + 0.5 BA mg/L + 0.5 NAA mg/L + 3 g L−1 of Gelrite under the 16 h photoperiod (37 L mol m−2 s−1) for 45 days | Shoot regeneration 60% | 95% | [34] |
| MS + 0.2 mg L−1 IBA under the 16 h photoperiod (37 L mol m−2 s−1) for 45 days | No. of roots/explant (12) + root length (10.7) | ||||
| Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat | Stem explant | SH basal medium + 1 mg/L IBA + 30 g/L sucrose + 3 g/L gelrite | The highest root no. (5.7) | 100% survival | [19] |
| SH basal medium + 1 mg/L IAA + 30 g/L sucrose + 3 g/L gelrite | The highest root length (36.2) | ||||
| Chrysanthemum morifolium | Nodal segments | MS medium + 1.0 mg/L BAP + 0.1 mg/L IAA | 90% shoot initiation and 5.5 cm average length of shoot per explant | N/A | [96] |
| MS medium + 1.0 mg/L BAP | 93% shoot proliferation, 5.7 cm average lengths of shoot per explant and 4.4 nodes per explant | ||||
| ½ MS medium + 0.2 mg/L IBA | 90% rooted micro cuttings; 9 cm length of root/explant + 11.8 no./explant | ||||
| Chrysanthemum morifolium | Nodal segment | MS + BA 2.0 mg/L | Shoot induction (80.00%) + shoot no. 3.00 at 28 DAI (days after induction) | 80% in shade condition and 75% in open atmospheric condition. | [45] |
| MS medium + BA 2.0 mg/L + 2,4-D 1.0 mg/L | Callus induction (76.00%) + shoot no. (3.20) at 40 DAI | ||||
| MS medium + BA 2.0 mg/L + IAA 1.0 mg/L | Shoot length 3.66 cm at 28 DAI | ||||
| 1/2MS + IAA 0.5 mg/L | Root induction (80.00%) within 13 days | ||||
| 1/2MS medium + BA 3.0 mg/L + IAA 1.5 mg/L | Root induction (76%) within 12.20 days | ||||
| 1/2MS medium + BA 2.0 mg/L + IAA 1.0 mg/L | Root no 4.20 at 28 DAI | ||||
| 1/2MS medium + 1.5 mg/L IAA | Root No. (5.40) at 28 DAI | ||||
| (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum/ Ramat./Kitam.) ‘Alchimist’ | Leaf explants with or without callus | MS medium + 11.42 μM IAA + 2.66 μM BA + Irradiation conditions (MW = power of 800 W·cm−2 and the frequency of 2.45 GHz) | 40% adventitious shoot | Acclimization 100% | [97] |
| ½MS medium + half-strength macronutrients + (11.42 μM) of IAA for 10 days | Rooting 100% | ||||
| Chrysanthemum moliforium | Shoots (3 cm in length) | MR: ½ MS, 30 g L−1 sucrose, pH 5.8 8 g L−1 agar + 7.5 ppm AgNP | MO: After 15 weeks in the greenhouse, flowering 100% | After 4 weeks well adapted and rapidly grown | [20] |
| MO: ½ MS, without sugar, pH 5.8 ½, nylon fill | |||||
| Chrysanthemum morifolium CV. (Delistar White) | Ray florets | MS medium + BAP 1.0 mg/L + NAA 0.5 mg/L + sucrose 30 g/L + agar 5.5 g/L | -Callus induction -Shoot formation | N/A | [30] |
| 1/2 strength (MS medium) + NAA 0.1 mg/L + sucrose 15 g/L + agar 5.5 g/L | Root induction | ||||
| Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema × grandiflorum) “Hornbill Dark” | Leaf segments | MS medium + 2 mg·L−1 2,4-D + 2 mg·L−1 BAP | 100% callogenesis rate + 95.56% callogenesis rate + (9.73) somatic embryo number | N/A | [98] |
| Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema × grandiflorum) “Hornbill Dark” | Leaf explant | (MS) medium consisted of (3% sucrose, 0.7% agar, and 100 mg/L Myo-inositol.) + 9.09 μM 2,4-D + 4.65 μM BAP + 20 μM SNP | Callogenesis rate (100%), embryogenes rate (100%), and the number of somatic embryos per explant (57.8) | N/A | [99] |
| (Chrysanthemum × morifolium/Ramat.) CV. Profesor Jerzy/ ‘Karolina | Ovaries from Irradiated inflorescence | Induction medium for 12 weeks: 1.0 mg dm−3 (BAP) + 1.0 mg dm−3 (2,4-D) | 33.3% (‘Karolina) induction callus | 89.18% survival for Profesor Jerzy | [14] |
| Regeneration medium for 18 weeks: 2.0 mg dm−3 kinetin + 1.0 mg dm−3 + (IAA) and 4.0 mg dm−3 glycine + pH 5.8 | Shoot induction (66.6% shoots for (Profesor Jerzy) | ||||
| Rooting medium: (MS based, supplemented with 2.0 mg dm−3 IAA, pH 5.8 | |||||
| Chrysanthemum indicum L. | Single nodes from shoots | 4 mg·L−1 Kin + 0.6 mg·L−1 IBA + (MS) | Shoot induction | N/A | [100] |
| 1/2 strength MS + 0.1 IBA | Root induction | ||||
| Ch. moliforium | Leaves (Four-week-old) | MS medium + AgNP(4 PPM), 30 g L−1 sucrose + 8 g L−1 agar. + 0.2 mg L−1 (BA) | Shoot regeneration 100% after 4 week of culture | 100% | [62] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eisa, E.A.; Tilly-Mándy, A.; Honfi, P.; Shala, A.Y.; Gururani, M.A. Chrysanthemum: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Developments on In Vitro Regeneration. Biology 2022, 11, 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121774
Eisa EA, Tilly-Mándy A, Honfi P, Shala AY, Gururani MA. Chrysanthemum: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Developments on In Vitro Regeneration. Biology. 2022; 11(12):1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121774
Chicago/Turabian StyleEisa, Eman Abdelhakim, Andrea Tilly-Mándy, Péter Honfi, Awad Yousef Shala, and Mayank Anand Gururani. 2022. "Chrysanthemum: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Developments on In Vitro Regeneration" Biology 11, no. 12: 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121774
APA StyleEisa, E. A., Tilly-Mándy, A., Honfi, P., Shala, A. Y., & Gururani, M. A. (2022). Chrysanthemum: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Developments on In Vitro Regeneration. Biology, 11(12), 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121774






