CircRNA Identification and CircRNA–miRNA–mRNA Network in Cynoglossus semilaevis Sexual Size Dimorphism
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Fish Treatment, Samples Collection, and Ethics Statement
2.2. RNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. circRNA–miRNA–mRNA Association Analysis
2.4. Function Enrichment Analysis
2.5. RT-PCR and qRT-PCR
3. Result
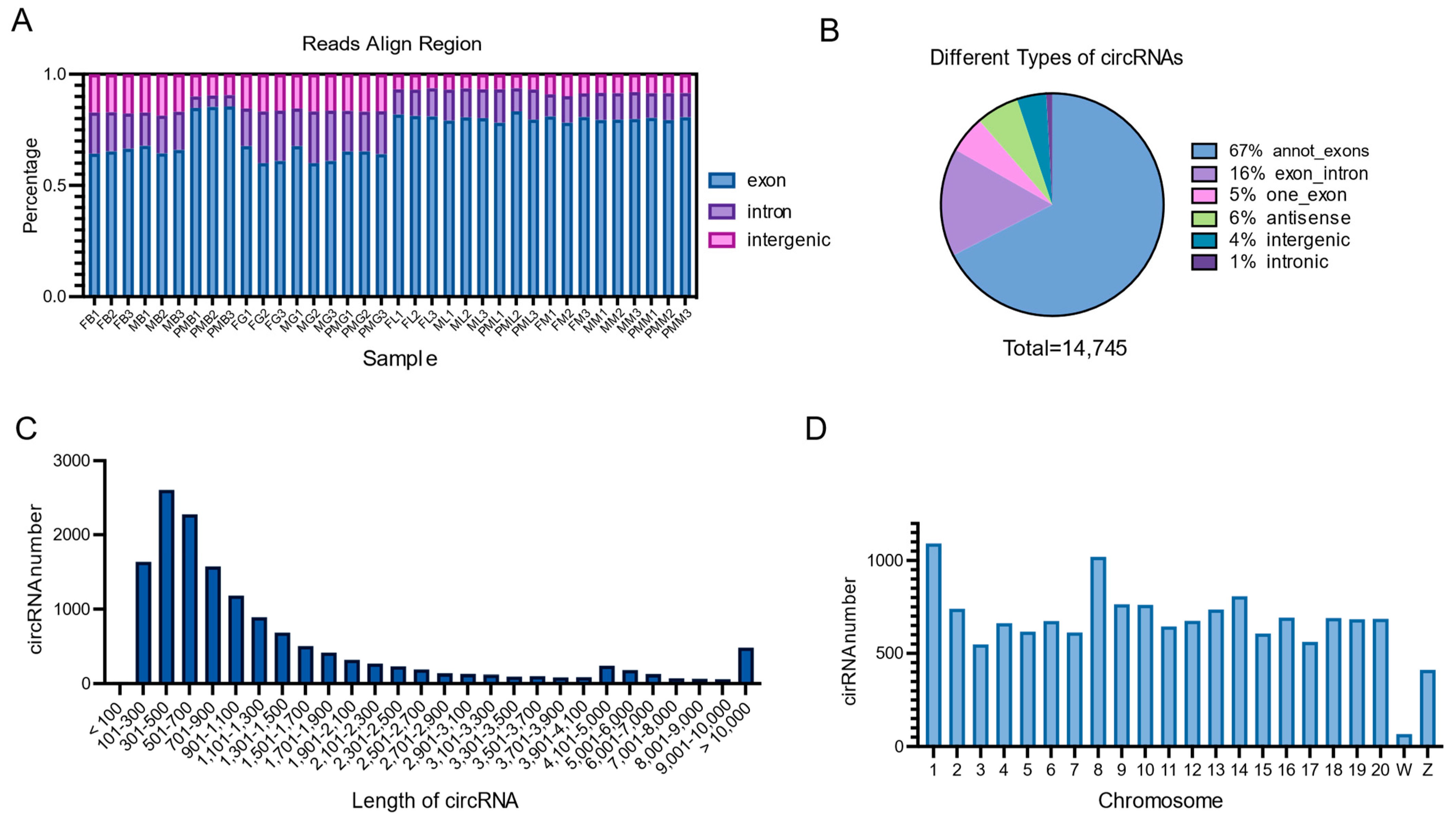
3.1. Overview of circRNA Identification in Chinese Tongue Sole
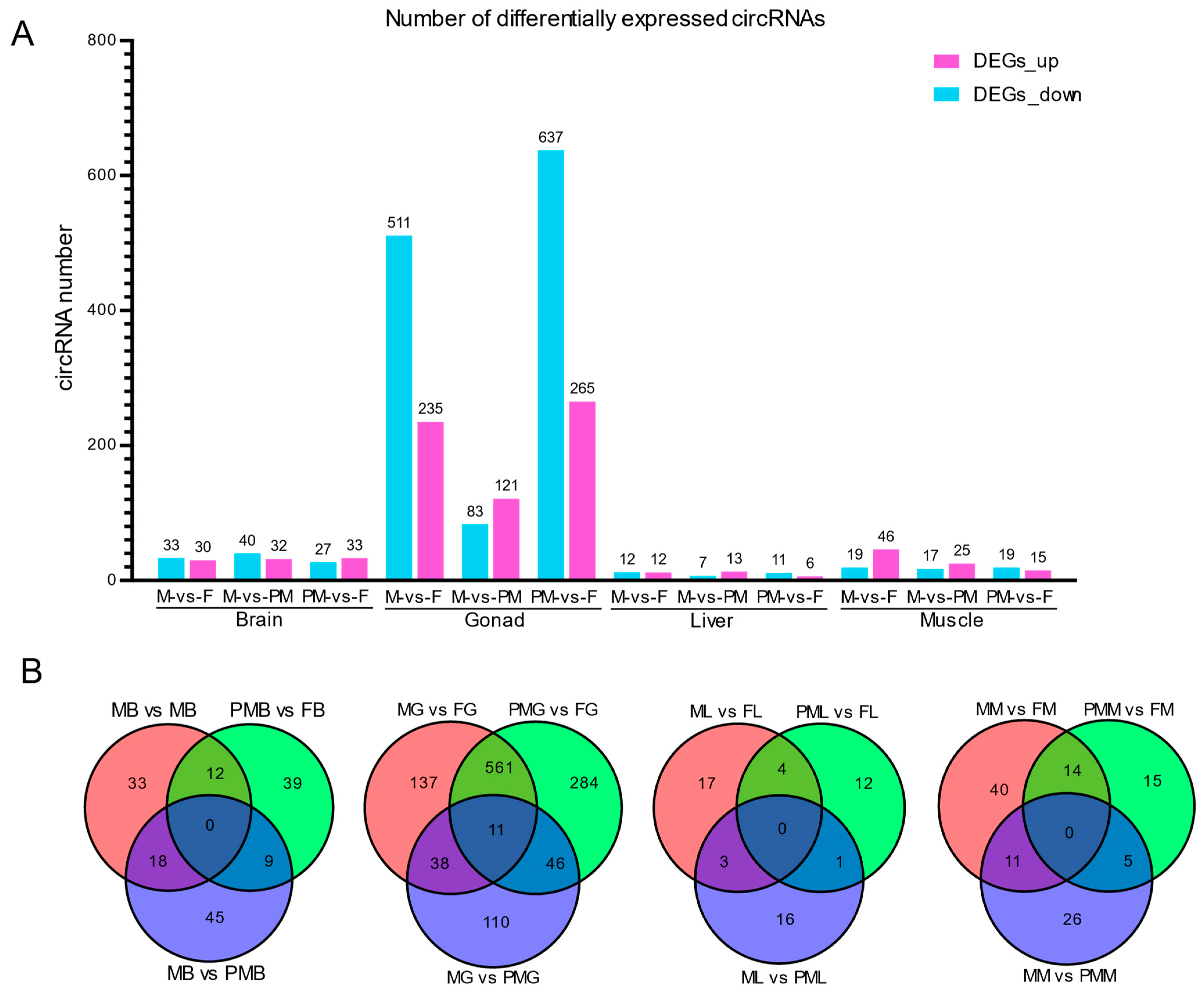
3.2. Differentially Expressed circRNAs
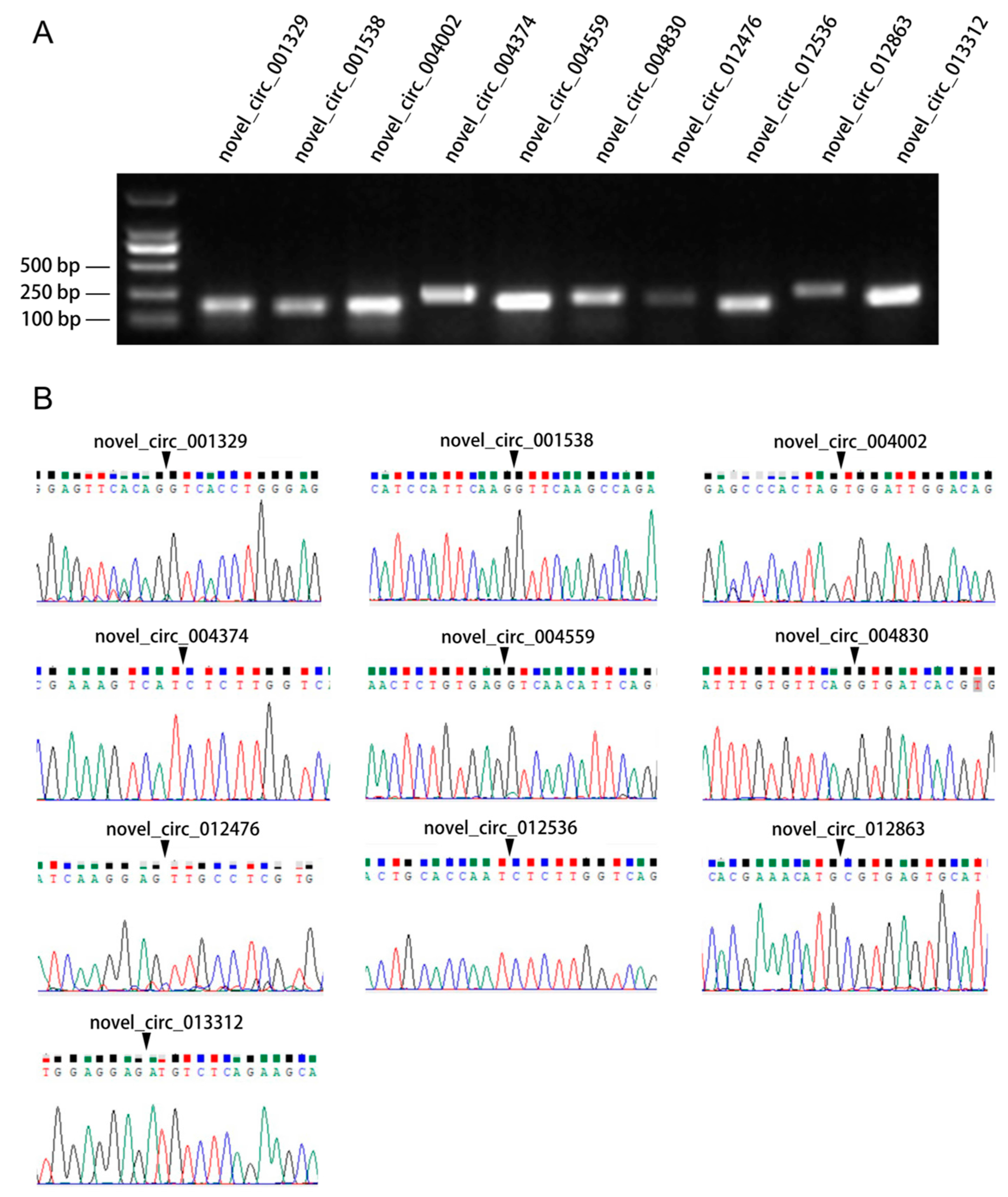
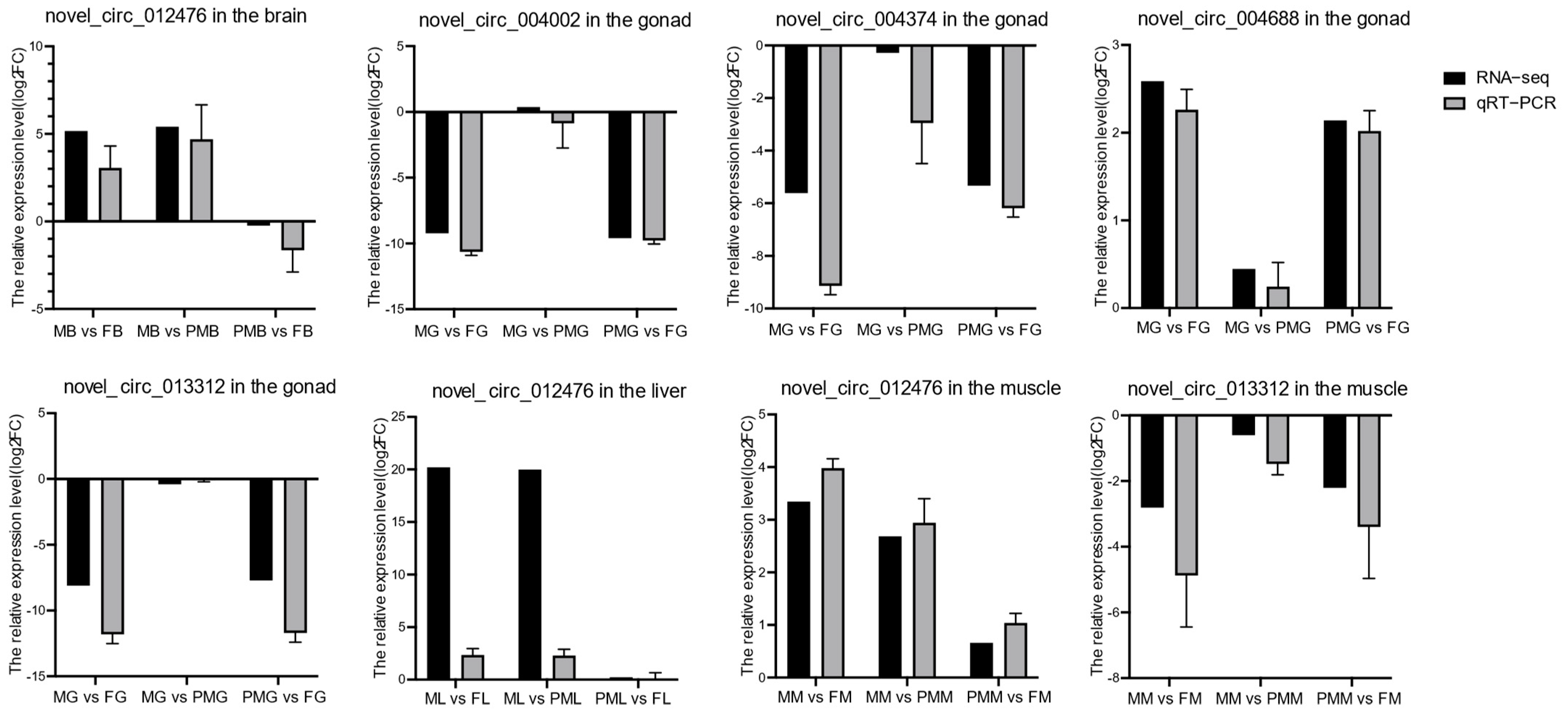
3.3. Verification of Differentially Expressed circRNAs
3.4. Differentially Expressed circRNAs ceRNA Network
3.5. Biological Functions of ceRNAs-Relevant mRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kissner, K.; Weatherhead, P.; Francis, C. Sexual size dimorphism and timing of spring migration in birds. J. Evol. Biol. 2003, 16, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskins, T.D.; Boone, M.D. Atrazine feminizes sex ratio in Blanchard’s cricket frogs (Acris blanchardi) at concentrations as low as 0.1 μg/L. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Jiang, T.; Huang, X.; Lin, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Niu, H.; Feng, J. A test of Rensch’s rule in greater horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus ferrumequinum) with female-biased sexual size dimorphism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Meiri, S.; Shi, L. Sexual size dimorphism in lizards: Rensch’s rule, reproductive mode, clutch size, and line fitting method effects. Integr. Zool. 2021, 17, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, C.R.; Hirst, A.G.; Atkinson, D. Selection for increased male size predicts variation in sexual size dimorphism among fish species. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20192640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Gui, J.-F. Genetic basis and biotechnological manipulation of sexual dimorphism and sex determination in fish. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, N.; Xie, M.S.; Sha, Z.X.; Chen, S.L. Establishment and characterization of a new fish cell line from head kidney of half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.-S.; Chen, S.-L.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Xu, T.-J.; Yang, J.-F.; Tian, Y.-S. Growth differences and differential expression analysis of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) and growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) between the sexes in half-smooth tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 170, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Shao, C.; Huang, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, P.; Song, W.; An, N.; Chalopin, D.; Volff, J.-N. Whole-genome sequence of a flatfish provides insights into ZW sex chromosome evolution and adaptation to a benthic lifestyle. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, P.; Lian, J.; Hu, Q.; Sun, B.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. Epigenetic modification and inheritance in sexual reversal of fish. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 604–615. Available online: https://www.genome.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/gr.162172.113 (accessed on 10 May 2022). [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, H. Single locus maintains large variation of sex reversal in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Chen, S. Transcriptomics analysis revealing candidate networks and genes for the body size sexual dimorphism of Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2018, 18, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Lin, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Su, Y.; Tang, Q. Genomic structure, polymorphism and expression analysis of the growth hormone (GH) gene in female and male Half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Gene 2012, 493, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Liu, S.-F.; Zhuang, Z.-M.; Sun, Z.-Z.; Liu, C.-L.; Tang, Q.-S. The co-existence of two growth hormone receptors and their differential expression profiles between female and male tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Gene 2012, 511, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Shi, R.; Li, M.; Gao, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S. Integration of transcriptome and methylome highlights the roles of cell cycle and hippo signaling pathway in flatfish sexual size dimorphism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 743722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, N. Identification of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Involved in Sexual Size Dimorphism of Chinese Tongue Sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 795525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.-T.; Coca-Prados, M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature 1979, 280, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.; Memczak, S.; Wyler, E.; Torti, F.; Porath, H.T.; Orejuela, M.R.; Piechotta, M.; Levanon, E.Y.; Landthaler, M.; Dieterich, C. Analysis of intron sequences reveals hallmarks of circular RNA biogenesis in animals. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Q.H.; Fan, L. Widespread noncoding circular RNA s in plants. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danan, M.; Schwartz, S.; Edelheit, S.; Sorek, R. Transcriptome-wide discovery of circular RNAs in Archaea. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 3131–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-X.; Chen, L.-L. Circular RNAs: Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell 2022, 185, 2016–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zonneveld, A.J.; Kölling, M.; Bijkerk, R.; Lorenzen, J.M. Circular RNAs in kidney disease and cancer. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, V.M.; Hugouvieux, V.; Nayak, A.; Conos, S.A.; Capovilla, G.; Cildir, G.; Jourdain, A.; Tergaonkar, V.; Schmid, M.; Zubieta, C. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, G. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burd, C.E.; Jeck, W.R.; Liu, Y.; Sanoff, H.K.; Wang, Z.; Sharpless, N.E. Expression of linear and novel circular forms of an INK4/ARF-associated non-coding RNA correlates with atherosclerosis risk. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, L.M.; Stahringer, A.; Sass, K.; Pichler, G.; Kulak, N.A.; Wilfert, W.; Kohlmaier, A.; Herbst, A.; Northoff, B.H.; Nicolaou, A. Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Clark, N.E.; Freije, C.A.; Pauwels, E.; Taggart, A.J.; Okada, S.; Mandel, H.; Garcia, P.; Ciancanelli, M.J.; Biran, A. Inborn errors of RNA lariat metabolism in humans with brainstem viral infection. Cell 2018, 172, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legnini, I.; Di Timoteo, G.; Rossi, F.; Morlando, M.; Briganti, F.; Sthandier, O.; Fatica, A.; Santini, T.; Andronache, A.; Wade, M. Circ-ZNF609 is a circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 22–37.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamudurti, N.R.; Bartok, O.; Jens, M.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Stottmeister, C.; Ruhe, L.; Hanan, M.; Wyler, E.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Ramberger, E. Translation of circRNAs. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 9–21.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xiao, S.; Qiu, C.; Wang, Z. Transcriptome-wide identification and functional investigation of circular RNA in the teleost large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Mar. Genom. 2017, 32, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, S.; Diao, J.; Liu, H.; Su, B.; Li, C. Identification of Potential Immune-Related circRNA–miRNA–mRNA Regulatory Network in Intestine of Paralichthys olivaceus During Edwardsiella tarda Infection. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, B.; Dai, K.; Zhu, M.; Liang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z. Grass carp reovirus encoding circular RNAs with antiviral activity. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dai, K.; Liu, B.; Yuan, R.; Feng, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, M. Identification and characterization of novel type of RNAs, circRNAs in crucian carp Carassius auratus gibelio. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Yin, J.; Yan, X.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Jiang, C.Y.; Hu, X.S.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhu, J.G.; Yu, Z.B. Profiles analysis reveals circular RNAs involving zebrafish physiological development. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 15922–15933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rbbani, G.; Nedoluzhko, A.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Fernandes, J.M. Function of circular RNAs in fish and their potential application as biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, R.; Yu, Y.; Shan, C.; Bian, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y. Identification and characterization of a conservative W chromosome-linked circRNA in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis) reveal its female-biased expression in immune organs. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shi, B.; Wang, C.; Shao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D. Comprehensive CircRNA Profiling and Selection of Key CircRNAs Reveal the Potential Regulatory Roles of CircRNAs throughout Ovarian Development and Maturation in Cynoglossus semilaevis. Biology 2021, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Huang, F.; You, W.; Poetsch, A.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Power, D.M.; Zhu, T.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, Q. ceRNA crosstalk mediated by ncRNAs is a novel regulatory mechanism in fish sex determination and differentiation. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 1502–1515. Available online: https://www.genome.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/gr.275962.121 (accessed on 20 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Gao, F.; Meng, L.; Hu, Q.; Song, W.; Shao, C.; Lv, W. SCAR-transformation of sex-specific SSR marker and its application in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semiliaevis). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2014, 22, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, C.; Chen, C.; Lu, Q.; Shi, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, H. Integration of lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA reveals novel insights into oviposition regulation in honey bees. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; Gorospe, M. Detection and analysis of circular RNAs by RT-PCR. Bio-protocol 2018, 8, e2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Lin, Z.; Xie, F.; Luo, J.; Chen, T.; Xi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Identification of circRNA-associated ceRNA networks using longissimus thoracis of pigs of different breeds and growth stages. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, J.; He, J.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, K.; Duan, Y.; He, J.; Ma, H. Spatiotemporal regulation and functional analysis of circular RNAs in skeletal muscle and subcutaneous fat during pig growth. Biology 2021, 10, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Xiong, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Suo, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, M. Circular RNA profiling reveals chi_circ_0008219 function as microRNA sponges in pre-ovulatory ovarian follicles of goats (Capra hircus). Genomics 2018, 110, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gòdia, M.; Castelló, A.; Rocco, M.; Cabrera, B.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E.; Balasch, S.; Lewis, C.; Sánchez, A.; Clop, A. Identification of circular RNAs in porcine sperm and evaluation of their relation to sperm motility. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Xie, X.; Li, M.; Shi, J.; Zhou, J.J.; Knox, K.S.; Wang, T.; Chen, Q.; Gu, W. Rat BodyMap transcriptomes reveal unique circular RNA features across tissue types and developmental stages. Rna 2018, 24, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, P.; Pierotti, C.; Lozano, E.; Amoah, S.K.; Gardiner, A.S.; Caldwell, K.K.; Allan, A.M.; Mellios, N. Prenatal alcohol exposure results in sex-specific alterations in circular RNA expression in the developing mouse brain. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 581895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, A.; Xiong, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Deep circular RNA sequencing provides insights into the mechanism underlying grass carp reovirus infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliseno, L.; Salmena, L.; Zhang, J.; Carver, B.; Haveman, W.J.; Pandolfi, P.P. A coding-independent function of gene and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature 2010, 465, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, A.; Sirma, H.; Hofmann, T.G.; Rueffer, S.; Klimczak, E.; Dröge, W.; Will, H.; Schmitz, M.L. PML is required for homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2)-mediated p53 phosphorylation and cell cycle arrest but is dispensable for the formation of HIPK domains. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 4310–4314. Available online: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/63/15/4310/510200/PML-Is-Required-for-Homeodomain-interacting (accessed on 5 April 2022). [PubMed]
- Hofmann, T.G.; Möller, A.; Sirma, H.; Zentgraf, H.; Taya, Y.; Dröge, W.; Will, H.; Schmitz, M.L. Regulation of p53 activity by its interaction with homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierantoni, G.M.; Fedele, M.; Pentimalli, F.; Benvenuto, G.; Pero, R.; Viglietto, G.; Santoro, M.; Chiariotti, L.; Fusco, A. High mobility group I (Y) proteins bind HIPK2, a serine-threonine kinase protein which inhibits cell growth. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6132–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.J.; Wei, J.; Wu, X.Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.H.; Zhang, Q.H.; Chen, S.J.; Huang, Q.H.; Chen, Z. Identification and characterization of a novel human histone H3 lysine 36-specific methyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35261–35271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, J.D. SETD2: A complex role in blood malignancy. Blood 2017, 130, 2576–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; He, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, F.; Xiao, J. Histone methyltransferase SETD2 regulates osteosarcoma cell growth and chemosensitivity by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Hao, D.; Dong, D.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Plath, M.; Lei, C.; Lin, F. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circLMO7 that regulates myoblasts differentiation and survival by sponging miR-378a-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, Z.; Cao, X.; He, H.; Han, S.; Chen, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Circular RNA profiling identified an abundant circular RNA circTMTC1 that inhibits chicken skeletal muscle satellite cell differentiation by sponging miR-128-3p. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedoluzhko, A.; Sharko, F.; Rbbani, M.G.; Teslyuk, A.; Konstantinidis, I.; Fernandes, J.M. CircParser: A novel streamlined pipeline for circular RNA structure and host gene prediction in non-model organisms. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wu, P.; Li, T.; Wu, P.; Chen, F.; Chen, L.; Xie, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G. Transcriptome analysis of circRNA and mRNA in Theca cells during follicular development in chickens. Genes 2020, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| sex-F | CCTAAATGATGGATGTAGATTCTGTC |
| sex-R | GATCCAGAGAAAATAAACCCAGG |
| β-actin-F | GCTGTGCTGTCCCTGTA |
| β-actin-R | GAGTAGCCACGCTCTGTC |
| nc1329-F | GGACATCGTTTCCTCCATC |
| nc1329-R | TGCTTCCTCTTCTGTAGCCC |
| nc1538-F | TGTGTCTTGGAGAAGGACTG |
| nc1538-R | TTTCAGCGAACTCTGGCT |
| nc4002-F | CTTGTGGATGAGATTCTGACTG |
| nc4002-R | ACTTGGAAACAGGCAGCAC |
| nc4374-F | GCTATTGATGACCCAGTGAA |
| nc4374-R | CACCACCAAACGGAACTT |
| nc4559-F | GCAGGCATTTGTGATGTCA |
| nc4559-R | GGCTTATTGGTCAGATTGTGTC |
| nc4830-F | GCCGCTGTTCGGATTATT |
| nc4830-R | ACAACGACAGGACAATGGG |
| nc12476-F | GCGTCTTTGACCACCGTAT |
| nc12476-R | TGTTGACCATTCGGAGGA |
| nc12863-F | CACATACTTCTTACGCACGAC |
| nc12863-R | GAATCATCTCCTCCTCCAAG |
| nc13312-F | CATCCAGAAGTAATGACCATCC |
| nc13312-R | AGAAGTCCTCCTATGACCTGC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Z.; Shi, R.; Chen, S.; Wang, N. CircRNA Identification and CircRNA–miRNA–mRNA Network in Cynoglossus semilaevis Sexual Size Dimorphism. Biology 2022, 11, 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101451
Gong Z, Shi R, Chen S, Wang N. CircRNA Identification and CircRNA–miRNA–mRNA Network in Cynoglossus semilaevis Sexual Size Dimorphism. Biology. 2022; 11(10):1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101451
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Zhihong, Rui Shi, Songlin Chen, and Na Wang. 2022. "CircRNA Identification and CircRNA–miRNA–mRNA Network in Cynoglossus semilaevis Sexual Size Dimorphism" Biology 11, no. 10: 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101451
APA StyleGong, Z., Shi, R., Chen, S., & Wang, N. (2022). CircRNA Identification and CircRNA–miRNA–mRNA Network in Cynoglossus semilaevis Sexual Size Dimorphism. Biology, 11(10), 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101451






