Optimization of Propagation of the Polish Strain of Aldrovanda vesiculosa in Tissue Culture
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Disinfection of Plant Material
2.2. Influence of the Media Type on the Growth of A. vesiculosa Shoots
2.3. Influence of the Media and Nitrogen Concentration on the Growth of A. vesiculosa Shoots
2.4. Content of Photosynthetic Pigments in A. vesiculosa Leaves
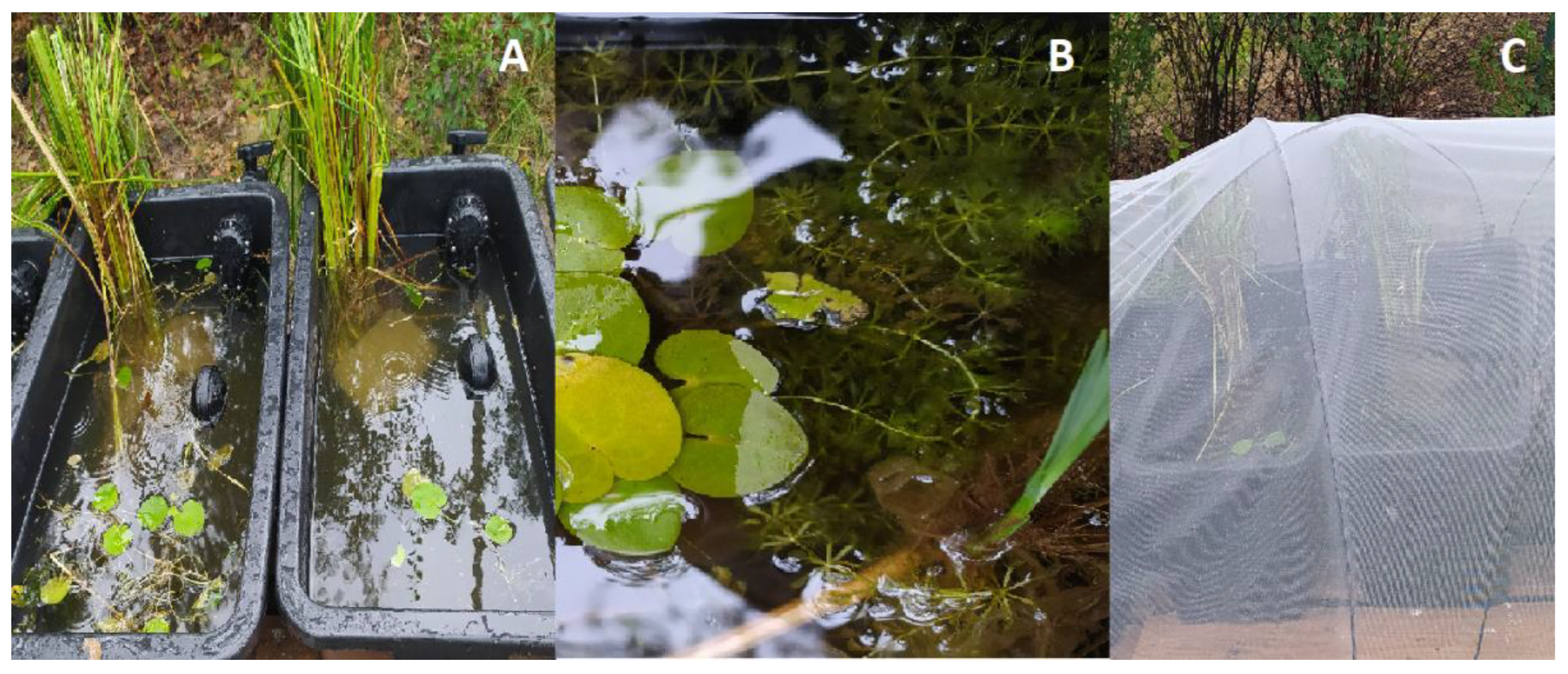
2.5. Acclimatization and Reintroduction Process
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
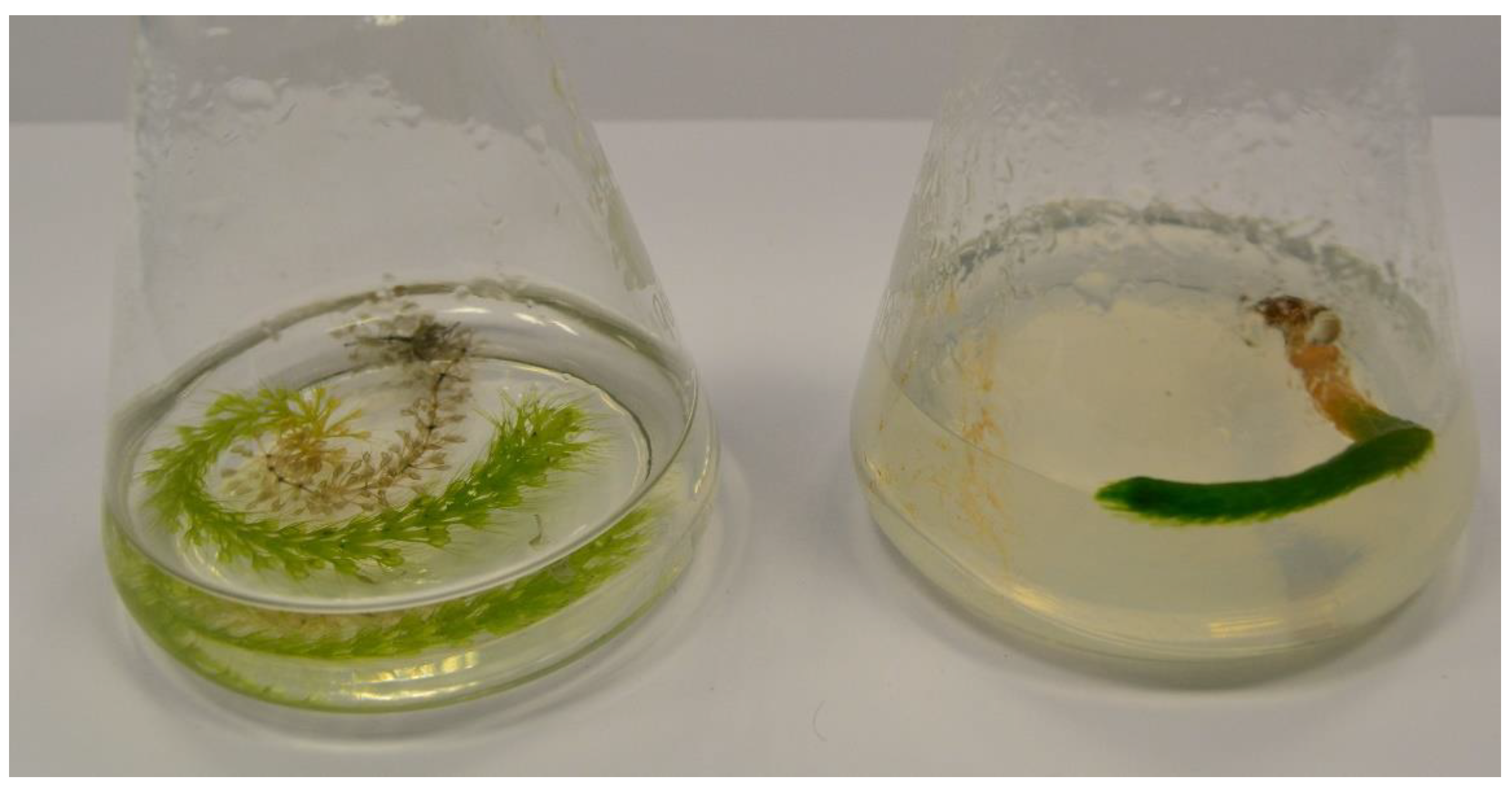
3.1. Disinfection of Plant Material
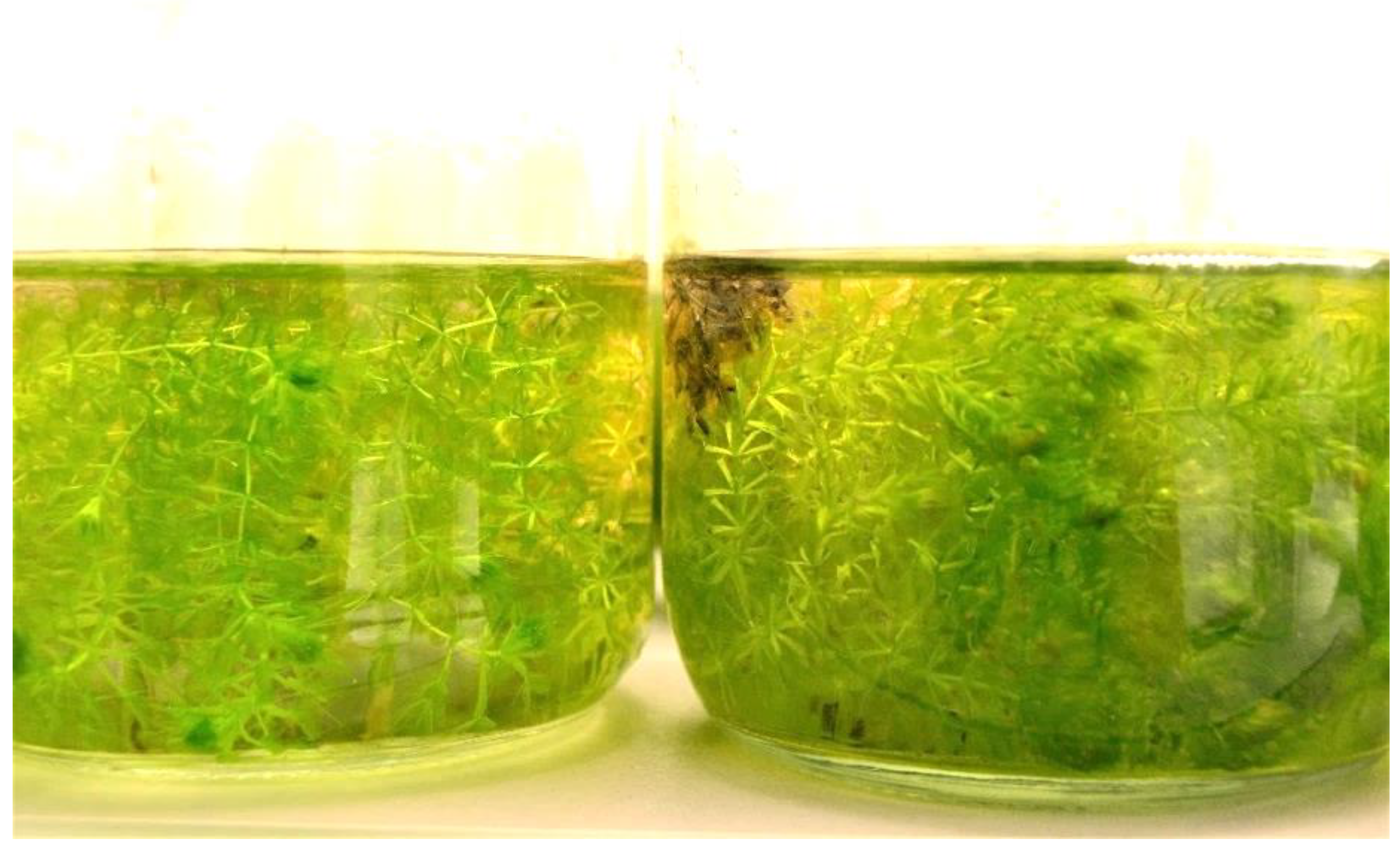
3.2. Influence of the Media Type on Growth of A. vesiculosa Shoots
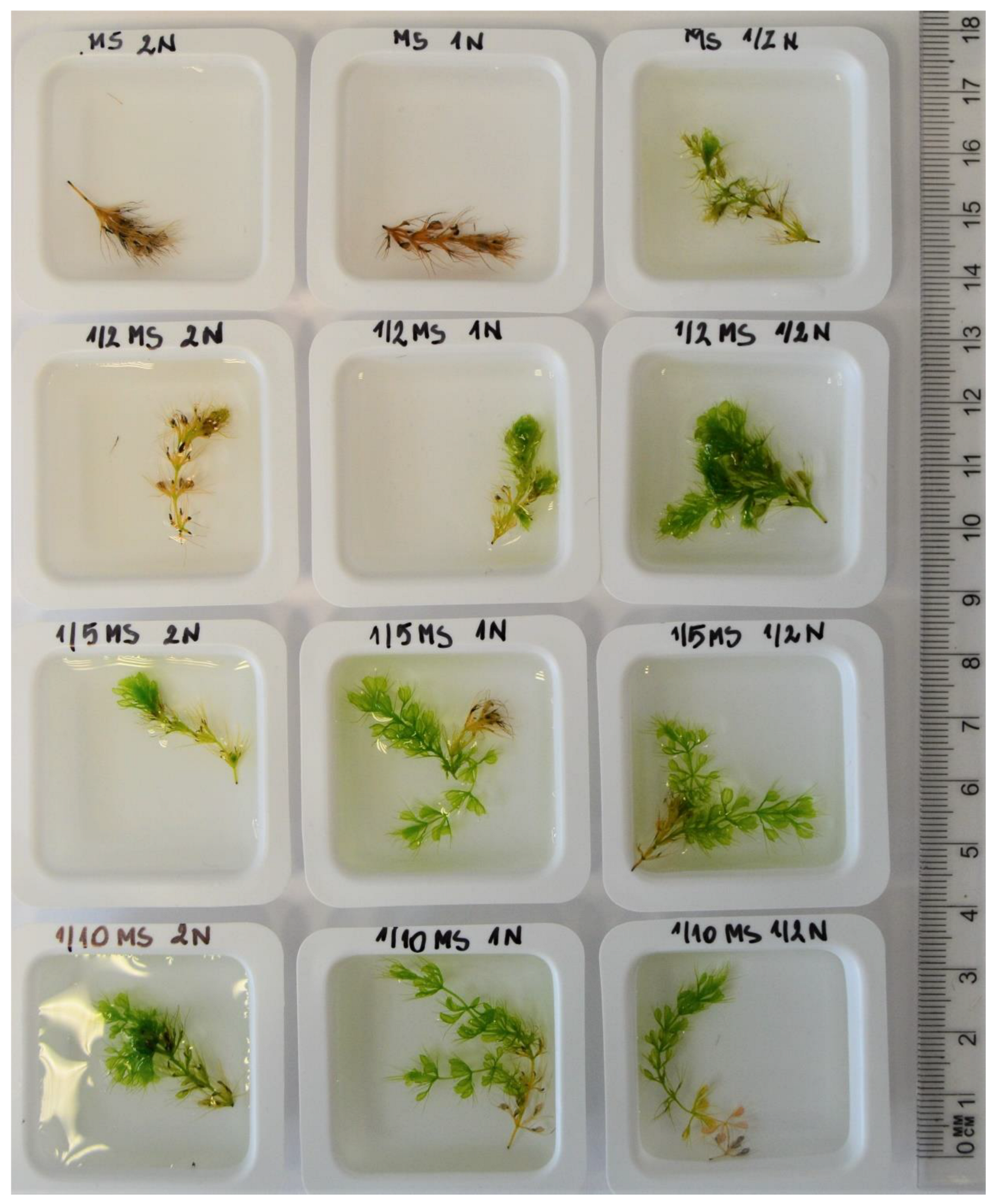
3.3. Influence of the MS Media and Nitrogen Concentration on the Growth of Shoots
3.4. Content of Photosynthetic Pigments in A. vesiculosa Leaves Depending on the Media and Nitrogen Concentration
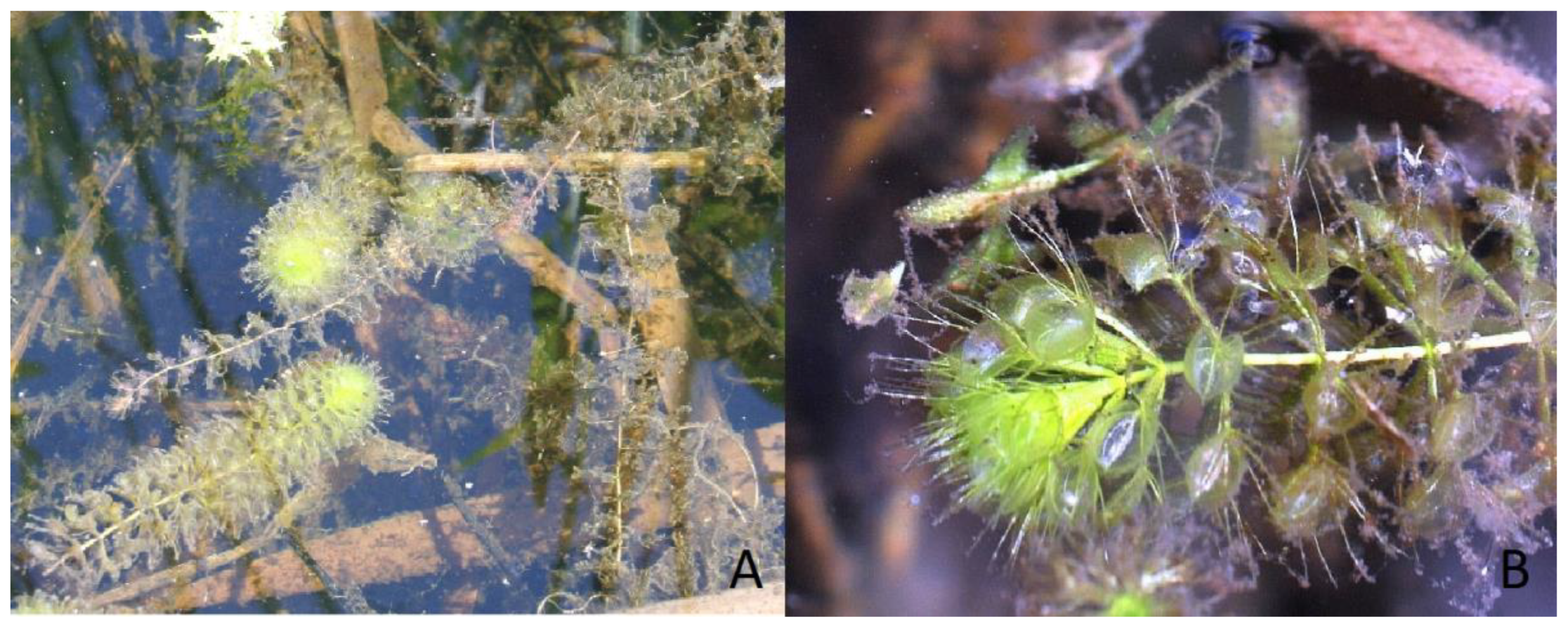
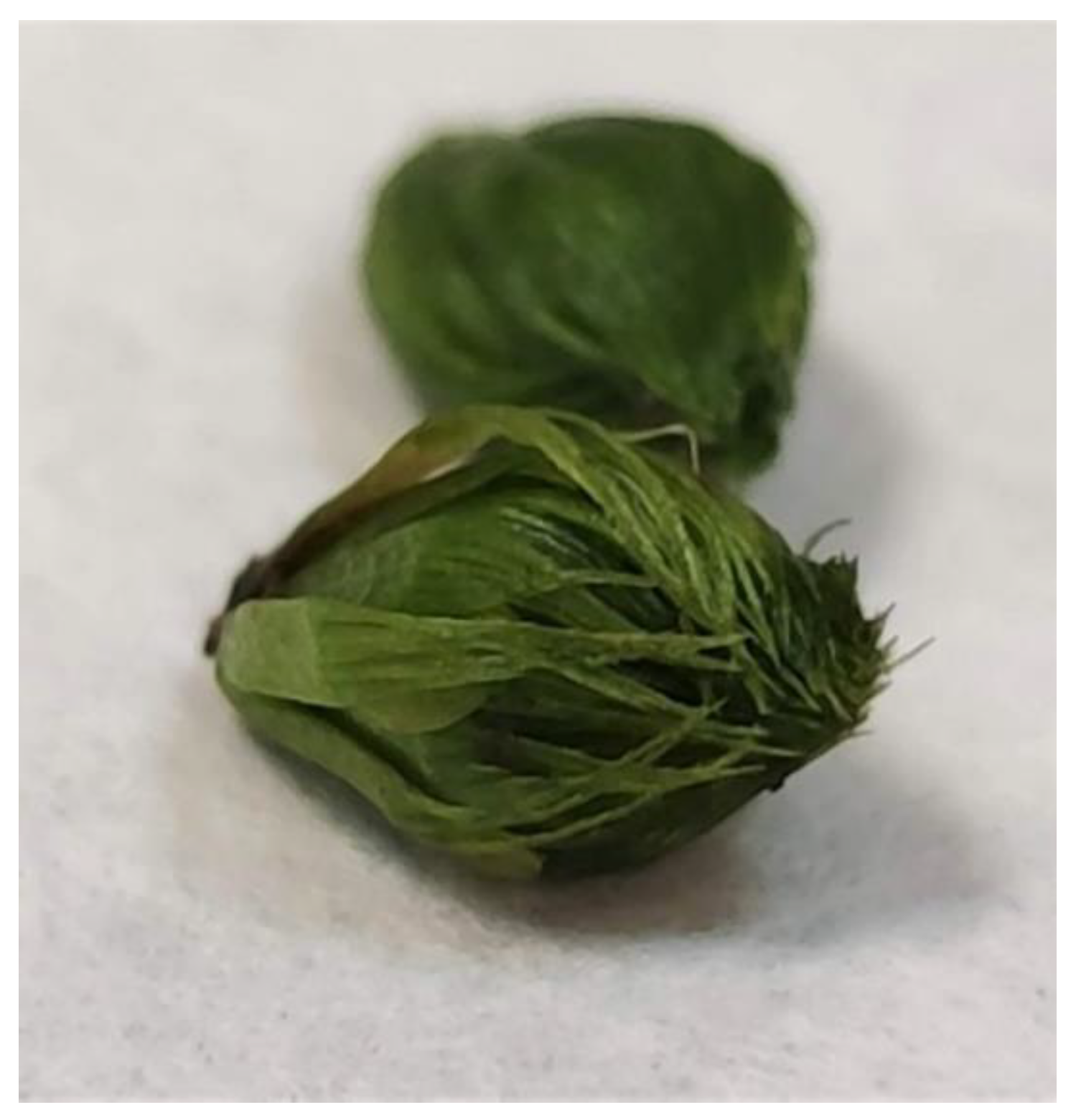
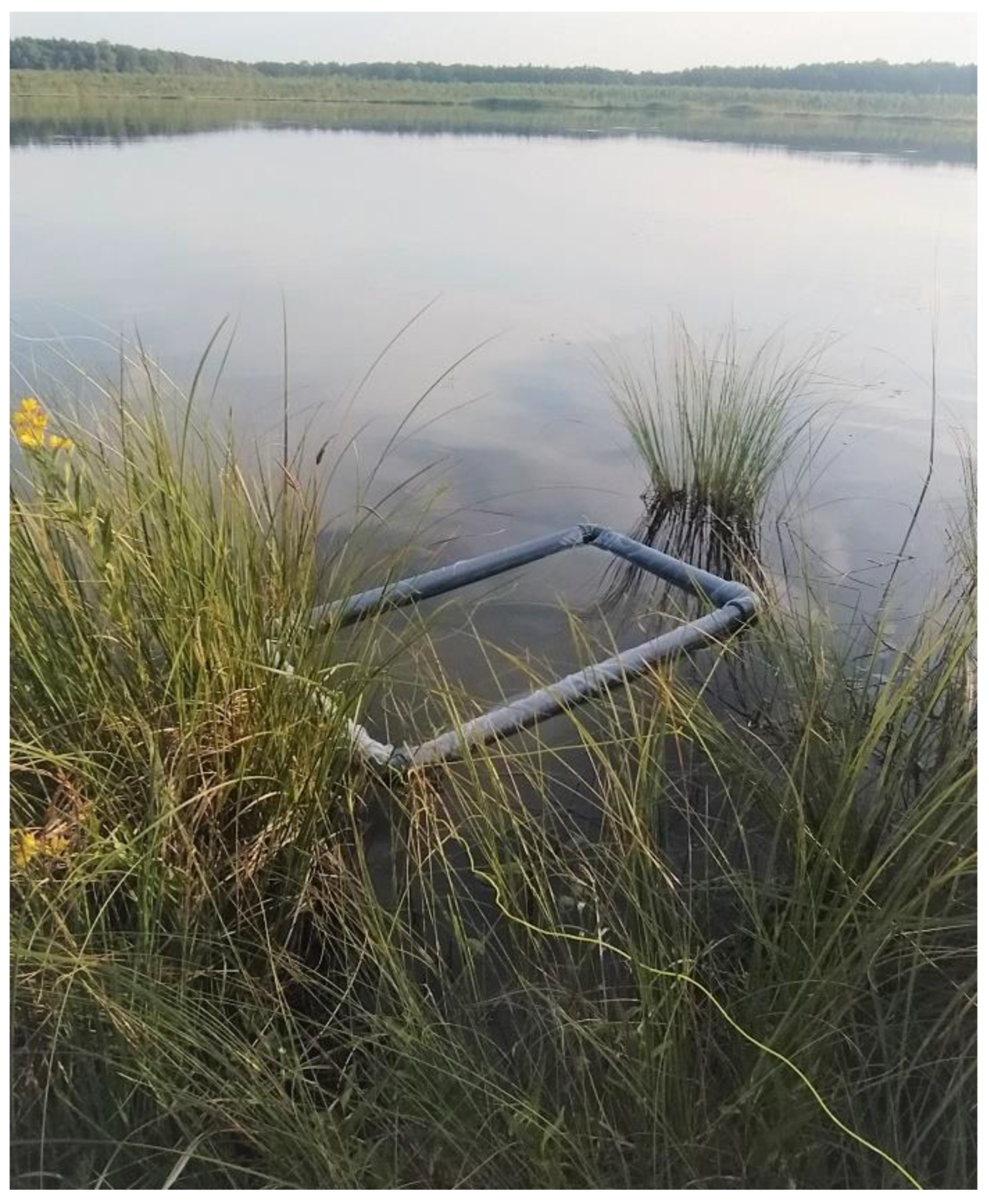
3.5. Acclimatization and Reintroduction Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamec, L. Biological flora of Central Europe: Aldrovanda vesiculosa L. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 35, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, A. Aldrovanda. The Waterwheel Plant; Redfern Natural History Productions: Pool Dorset, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann, A.; Schlauer, J.; Smith, S.A.; Givnish, T.J. Evolution of carnivory in angiosperms. In Carnivorous Plants: Physiology, Ecology and Evolution; Ellison, A.M., Adamec, L., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 22–41. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, K.M.; Wurdack, K.J.; Jobson, R.W. Molecular evidence for the common origin of snap-traps among carnivorous plants. Am. J. Bot. 2002, 89, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, A.; Cross, A.T.; Gibson, R.; Gonella, P.M.; Dixon, K.W. Systematics and evolution of Droseraceae. In Carnivorous Plants: Physciology, Ecology and Evolution; Ellison, A., Adamec, L., Eds.; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngangbam, R.D.; Devi, N.P.; Devi, M.H.; Singh, P.K. Rediscovery of Aldrovanda vesiculosa L. (Droseraceae). an endangered plant. from Manipur in India after six decades, with studies on micromorphology and physico-chemistry of water. Reinwardtia 2019, 18, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, R. Studies on the ecology of Aldrovanda vesiculosa L. I. Ecological differentiation of A. vesiculosa population under the influence of chemical factors in the habitat. Ekol. Pol. 1987, 35, 559–590. [Google Scholar]
- Poppinga, S.; Bauer, U.; Speck, T.; Volkov, A.G. Motile traps. In Carnivorous Plants: Physiology, Ecology, and Evolution; Ellison, A.M., Adamec, L., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 180–193. [Google Scholar]
- Westermeier, A.S.; Sachse, R.; Poppinga, S.; Vögele, P.; Adamec, L.; Speck, T.; Bischoff, M. How the carnivorous waterwheel plant (Aldrovanda vesiculosa) snaps. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, e20180012. Available online: www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/542035.html (accessed on 1 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.T.; Adamec, L.; Turner, S.R.; Dixon, K.W.; Merritt, D.J. Seed reproductive biology of the rare aquatic carnivorous plant Aldrovanda vesiculosa (Droseraceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 180, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Ecological requirements and the European distribution of the aquatic carnivorous plant Aldrovanda vesiculosa L. Folia Geobot. Phytotaxon. 1995, 30, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Seasonal growth dynamics and overwintering of the aquatic carnivorous plant Aldrovanda vesiculosa at experimental field sites. Folia Geobot. 1999, 34, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L.; Kovářová, M. Field growth characteristics of two aquatic carnivorous plants. Aldrovanda vesiculosa and Utricularia australis. Folia Geobot. 2006, 41, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Ecophysiological characteristics of turions of aquatic plants: A review. Aquat. Bot. 2018, 148, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Turion overwintering of aquatic carnivorous plants. Carniv. Plant Newsl. 1999, 28, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Ecophysiological characterization of dormancy states in turions of the aquatic carnivorous plant Aldrovanda vesiculosa. Biol. Plant. 2003, 47, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.T. Turion development is an ecological trait in all populations of the aquatic carnivorous plant Aldrovanda vesiculosa. Carniv. Plants Newsl. 2013, 42, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Photosynthetic characteristics of the aquatic carnivorous plant Aldrovanda vesiculosa. Aquat. Bot. 1997, 59, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Ten years after the introduction of Aldrovanda vesiculosa to the Czech Republic. Acta Bot. Gall. 2005, 152, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2022-1. 2022. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats Convention Relative à la Conservation de la vie Sauvage et du Milieu Naturel de l’Europe Bern/Berne, 19.IX.1979 Appendix I–Strictly Protected Flora Species. Available online: https://rm.coe.int/CoERMPublicCommonSearchServices/DisplayDCTMContent?documentId=0900001680a2a019 (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Kaźmierczakowa, R.; Zarzycki, K.; Mirek, Z. Polska Czerwona Księga Roślin: Paprotniki I Rośliny Kwiatowe (Polish Red Data Book of Plants: Pteridophytes and Flowering Plants); Instytut Ochrony Przyrody PAN: Kraków, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiński, R. Restitution of Waterwheel plant (Aldrovanda vesiculosa L.) in Poland and recognition of factors deciding on its survival in temperate climate. Pr. Ogrodu Bot. Uniw. Wrocławskiego 2006, 8, 105. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kamiński, R. Aldrovanda vesiculosa L. In Polska Czerwona Księga Roślin: Paprotniki I Rośliny Kwiatowe, 3rd ed.; Polska Akademia Nauk: Cracow, Poland, 2014; pp. 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiński, R. Studies on the ecology of Aldrovanda vesiculosa L. II. Organic substances. physical and biotic factors and the growth and development of A. vesiculosa. Ekol. Pol. 1987, 35, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Adamec, L. How to grow Aldrovanda vesiculosa outdoors. Carniv. Plant Newsl. 1997, 26, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Adamec, L. Rootless aquatic plant Aldrovanda vesiculosa: Physiological polarity, mineral nutrition, and importance of carnivory. Biol. Plant. 2000, 43, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. The influence of prey capture on photosynthetic rate in two aquatic carnivorous plant species. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 89, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Respiration of turions and winter apices in aquatic carnivorous plants. Biologia 2008, 63, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L.; Sirová, D.; Vrba, J. Contrasting growth effects of prey capture in two carnivorous plant species. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2010, 176, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Bi, W.L.; Shukla, M.R.; Cannings, S.; Bennett, B.; Saxena, P.K. Micropropagation and cryopreservation of Yukon Draba (Draba yukonensis), a Special Concern Plant Species Endemic to Yukon Territory, Canada. Plants 2021, 10, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Saxena, A.; Ayyanath, M.M.; Harpur, C.; Shukla, M.R.; Saxena, P.K. Conservation. propagation and redistribution (CPR) of hill’s thistle: Paradigm for plant species at risk. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2021, 145, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F.S.; Zavaleta, E.S.; Eviner, V.T.; Naylor, R.I.; Vitousek, P.M.; Reynolds, H.L.; Hooper, D.U.; Lavorel, S.; Sala, O.E.; Hobbie, S.E.; et al. Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 2020, 405, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.S.; Porter-Morgan, H.A.; Stevens, H.; Boom, B.; Krupnick, G.A.; Acevedo-Rodriguez, P.; Fleming, J.; Gensler, M. Addressing target two of the global strategy for plant conservation by rapidly identifying plants at risk. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 21, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volis, S. Complementarities of two existing intermediate conservation approaches. Plant Divers. 2017, 39, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasan, V.A.; Cripps, R.; Ramsay, M.M.; Atherton, C.; McMichen, M.; Prendercast, G.; Rowntree, J. Conservation in vitro of threatened plants—Progress in the past decade. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2006, 42, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, N.; Gonçalves, S.; Romano, A. Endemic Plant Species Conservation: Biotechnological Approaches. Plants 2020, 9, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam, A.; Tariq, R.; Chuadhary, S.; Azmat, R.; Javed, S.; Khanam, S.A. Review: Role of tissue culture (in-vitro) techniques in the conservation of rare and endangered species. Pac. J. Life Sci. 2014, 2, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Qarshi, L.A.; Nazir, H.; Ullah, I. Plant tissue culture: Current status and opportunities. Recent Adv. Plant Vitr. Cult. 2012, 6, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Fay, M.F. Conservation of rare and endangered plants using in vitro methods. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 1992, 28, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasheva, K.; Kosturkova, G. Role of Biotechnology for Protection of Endangered Medicinal Plants. In Enviromental Biology; Petre, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotova, L.G.; Ivanova, T.A.; Bogdanova, Y.Y.; Gussev, C.V.; Stanilova, M.I.; Bosseva, Y.Z.; Stoeva, T.D. In vitro cultivation of plant species from sandy dunes along the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Phytol. Balc. 2008, 14, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kułak, V.; Longboat, S.; Brunet, N.D.; Shukla, M.; Saxena, P. In vitro technology in plant conservation: Relevance to biocultural diversity. Plants 2022, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misic, D.M.; Chalawenji, N.A.; Grubisic, D.V.; Konjevic, R.M. Micropropagation and reintroduction of Nepeta rtanjensis. an endemic and critically endangered perennial of Serbia. Phyton-Ann. Rei Bot. 2005, 45, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pence, V.C. In vitro collecting (IVC). 1. The effect of collecting method and antimicrobial agents on contamination in temperate and tropical collections. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2005, 41, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, M.F. In what situations is in vitro culture appropriate to plant conservation? Biodivers. Conserv. 1994, 3, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.R.; Senaratna, T.; Bunn, E.; Tan, B.; Dixon, K.W.; Touchell, D.H. Cryopreservation of shoot tips from six endangered Australian species using a modified vitrification protocol. Ann. Bot. 2001, 87, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.; Singh, N.; Varma, S. Plant tissue culture: A biotechnological tool for solving the problem of propagation of multipurpose endangered medicinal plants in India. J. Agric. Technol. 2012, 8, 305–318. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley, S.E.; Bunn, E.; Menon, A.; Mancera, R.L.; Turner, S.R. Ex situ conservation of the endangered species Androcalva perlaria (Malvaceae) by micropropagation and cryopreservation. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2016, 125, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzejczyk, I.; Morozowska, M.; Nowińska, R.; Jagodziński, A. Primula veris plants derived from in vitro cultures and from seeds: Genetic stability, morphology, and seed characteristics. Turk. J. Bot. 2018, 42, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitek, E.; Nowak, B.; Fecowicz, M.; Gajewski, Z.; Dańda, P.; Kapała, K.; Dąbek-Kozik, B. Application of horticultural and tissue culture methods for ex situ conservation of endangered Primula farinosa L. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2020, 89, 8913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzymies, M.; Pogorzelec, M.; Głąbocka, K.; Śliwińska, E. Genetic stability of the endangered species Salix lapponum L. regenerated in vitro during the reintroduction process. Biology 2020, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelec, M.; Parzymies, M.; Banach-Albińska, B.; Serafin, A.; Szczurowska, A. Experimental reintroduction of the boreal species Salix lapponum L. to refuges at the southern limit of its range–short-term results. Boreal Environ. Res. 2020, 25, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Pogorzelec, M.; Parzymies, M.; Bronowicka-Mielniczuk, U.; Banach, B.; Serafin, A. Pollen viability and tissue culture initiation of Salix lapponum, an endangered species in Poland. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2015, 14, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Adamec, L.; Pásek, K. Medium optimization for growing Aldrovanda vesiculosa in vitro. Carniv. Plant Newsl. 2000, 29, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Kokubugata, G.; Varghese, S.B.; Itoyama, M.; Breckpot, C.; Kromer, K.; Kamiński, R. Conservation of endangered Aldrovanda vesiculosa by tissue culture. Carniv. Plant Newsl. 1997, 26, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamborg, O.L.; Miller, R.A.; Ojima, K. Nutrient requirement suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1968, 50, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, K.; Atsuzawa, K.; Takatori, A.; Kaneko, Y.; Matsushima, H. Studies on the endangered aquatic carnivorous plant Aldrovanda vesiculosa–1. In vitro propagation and ex vitro conservation. Plant Cell Physiol. Suppl. S 2003, 44, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Parzymies, M. Nano-Silver Particles Reduce Contaminations in Tissue Culture but Decrease Regeneration Rate and Slows Down Growth and Development of Aldrovanda vesiculosa Explants. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, M.E.; Gilman, E.F.; Jenks, M.A.; Sheehan, T.J. Micropropagation of aquatic plant Cryptocoryne lucens. HortScience 1990, 25, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanapoom, K.; Chunui, P.; Kanchanapoom, K. Micropropagation of Anubis barteri var. Nana from shoot tip culture and the analysis of ploidy stability. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2012, 40, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendy, J.A.; Chew, H.H.; Zainuddin, R.; Zawawi, D.D.; Nguang, S.I. Micro-propagation of aquatic Brazilian micro sword (Lileaopsis brasiliensis). J. Agrobiotechnol. 2019, 10 (Suppl. S1), 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hook, I.L.I. Naphthoquinone contents of in vitro cultured plants and cell suspensions of Dionaea muscipula and Drosera species. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2001, 67, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, L. Foliar mineral nutrient uptake in carnivorous plants: What do we know and what should we know? Front. Plants Sci. 2013, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banasiuk, R.; Kawiak, A.; Królicka, A. In vitro cultures of carnivorous plants from the Drosera and Dionaea genus for the production of biologically active secondary metabolites. BioTechnologia 2012, 93, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.; Kim, K.; Park, R. Micropropagation of venus fly trap by shoot culture. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2003, 72, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grevenstuk, T.; Coelho, N.; Gonçalves, S.; Romano, A. In vitro propagation of Drosera intermedia in a single step. Biol. Plant. 2010, 54, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadczak, P.; Kulpa, D.; Zbrojewska, A. In vitro micropropagation of Drosera rotundifolia. World Sci. News WSN 2017, 66, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Rejthar, J.; Viehmannova, I.; Cepkova, P.H.; Fernandez, E.; Millella, L. In vitro propagation of Drosera intermedia as influenced by cytokinins, pH, sucrose, and nutrient concentration. Plant Tissue Cult. 2014, 26, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovič, A.; Singerová, L.; Demko, V.; Hudák, J. Feeding enhances photosynthetic efficiency in the carnivorous pitcher plant Nepenthes talangensis. Ann. Bot. 2009, 104, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Media Type | Contaminated Explants (%) | Contamination-Free Explants (%) | Of Which: | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regenerating (%) | Necrotic (%) | |||
| Liquid | 9 | 91 | 68 | 32 |
| Solidified | 13 | 87 | 3.5 | 96.5 |
| Medium | Regeneration (%) | Length of Main Shoot (mm) | Plants with Lateral Shoots (%) | Number of Lateral Shoots/Explant | Length of Lateral Shoots (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/5 MS | 100% | 76.80 a * | 100 a | 4.80 b | 33.18 a |
| 1/5 B5 | 60% | 50.00 ab | 33 a | 10.0 a | 17.40 b |
| 1/2 MS 500 KNO3 | 60% | 25.32 b | 66.7 a | 2.5 b | 12.50 bc |
| 1/2 B5 500 KNO3 | 60% | 24.32 b | 0 a | - | - |
| Length of Main Shoot (mm) | Length Increase (mm) | Number of Lateral Shoots/Shoot | Increase in Number of Lateral Shoots | Length of Lateral Shoots (mm) | Increase in Length of Lateral Shoots (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/5 MS | 96.80 a * | 20.0 a | 6.2 ab | 1.4 a | 38.20 a | 5.02 ab |
| 1/5 B5 | 69.0 ab | 19.0 ab | 10.0 a | 0 b | 27.20 ab | 9.80 a |
| 1/2 MS 500 KNO3 | 27.32 b | 2.0 b | 2.5 b | 0 b | 14.60 bc | 1.10 b |
| 1/2 B5 500 KNO3 | 27.32 b | 3.0 ab | 2.0 b | 2.0 a | 11.0 c | 0 b |
| MS Concentration | Nitrogen Concentration | Number of Regenerating Explants (%) | Main Shoot Length (mm) | Mean for Medium | Main Shoot Weight (mg) | Mean for Medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 2N | 0 | - | - | - | |
| 1N | 0 | - | ||||
| 1/2N | 93 | 22.73 d * | 32.63 ab | |||
| 1/2 MS | 2N | 45 | 20.5 d | 23.56 C | 20.18 b | 31.86 A |
| 1N | 95 | 22.24 d | 29.39 b | |||
| 1/2N | 100 | 26.26 c | 39.66 a | |||
| 1/5 MS | 2N | 97.5 | 22.56 d | 27.96 B | 18.18 c | 26.15 BC |
| 1N | 60 | 31.77 ab | 31.84 ab | |||
| 1/2N | 100 | 29.50 bc | 28.35 b | |||
| 1/10 MS | 2N | 100 | 30.85 ac | 31.66 A | 29.12 b | 30.38 AB |
| 1N | 100 | 35.64 a | 32.27 ab | |||
| 1/2N | 100 | 28.49 bc | 29.75 b | |||
| Mean for nitrogen concentration | 2N—22.91 B 1N—27.61 A 1/2N—26.75 A | 2N—20.64 C 1N—28.73 B 1/2N—32.62 A | ||||
| MS Concentration | Nitrogen Concentration | Number of Explants with Lateral Shoots (%) | Number of Lateral Shoots | Mean for Medium | Length of Lateral Shoots (mm) | Mean for Medium | Weight of Lateral Shoots (mg) | Mean for Medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 2N | - | - | 1.15 | - | 8.18 B | - | 13.75 |
| 1N | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 1/2N | 50.0 | 1.15 a * | 8.18 ab | 13.75 ab | ||||
| 1/2 MS | 2N | 47.0 | 1.25 a | 1.24 | 7.60 ab | 8.03 B | 5.62 ab | 16.82 |
| 1N | 55.3 | 1.09 a | 8.13 ab | 12.76 ab | ||||
| 1/2N | 44.7 | 1.41 a | 8.12 ab | 25.78 a | ||||
| 1/5 MS | 2N | 25.6 | 1.10 a | 1.48 | 6.64 ab | 11.95 | 9.32 ab | 19.29 |
| 1N | 60.0 | 1.50 a | 12.61 a | 23.36 a | ||||
| 1/2N | 79.5 | 1.58 a | 12.65 a | 19.63 a | ||||
| 1/10 MS | 2N | 53.8 | 1.05 a | 1.11 | 13.27 a | 13.70 | 13.69 ab | 15.50 |
| 1N | 66.7 | 1.19 a | 15.0 a | 15.90 ab | ||||
| 1/2N | 41.0 | 1.06 a | 13.53 a | 17.21 ab | ||||
| Mean for nitrogen concentration | 2N—0.87 1N—1.11 1/2N—1.35 | 2N—8.32 1N—10.78 1/2N—10.94 | 2N—8.82 1N—15.13 1/2N—19.14 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parzymies, M.; Pogorzelec, M.; Świstowska, A. Optimization of Propagation of the Polish Strain of Aldrovanda vesiculosa in Tissue Culture. Biology 2022, 11, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101389
Parzymies M, Pogorzelec M, Świstowska A. Optimization of Propagation of the Polish Strain of Aldrovanda vesiculosa in Tissue Culture. Biology. 2022; 11(10):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101389
Chicago/Turabian StyleParzymies, Marzena, Magdalena Pogorzelec, and Alicja Świstowska. 2022. "Optimization of Propagation of the Polish Strain of Aldrovanda vesiculosa in Tissue Culture" Biology 11, no. 10: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101389
APA StyleParzymies, M., Pogorzelec, M., & Świstowska, A. (2022). Optimization of Propagation of the Polish Strain of Aldrovanda vesiculosa in Tissue Culture. Biology, 11(10), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101389









