Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis of Complete Plastomes among Aristidoideae Species (Poaceae)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material, DNA Extraction, and Sequencing
2.2. Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Repeat Sequences and SSR Analysis
2.4. Codon Usage Analysis
2.5. Comparative Genome Analysis and Divergent Hotspot Regions
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis and Taxon Removal Test
3. Results
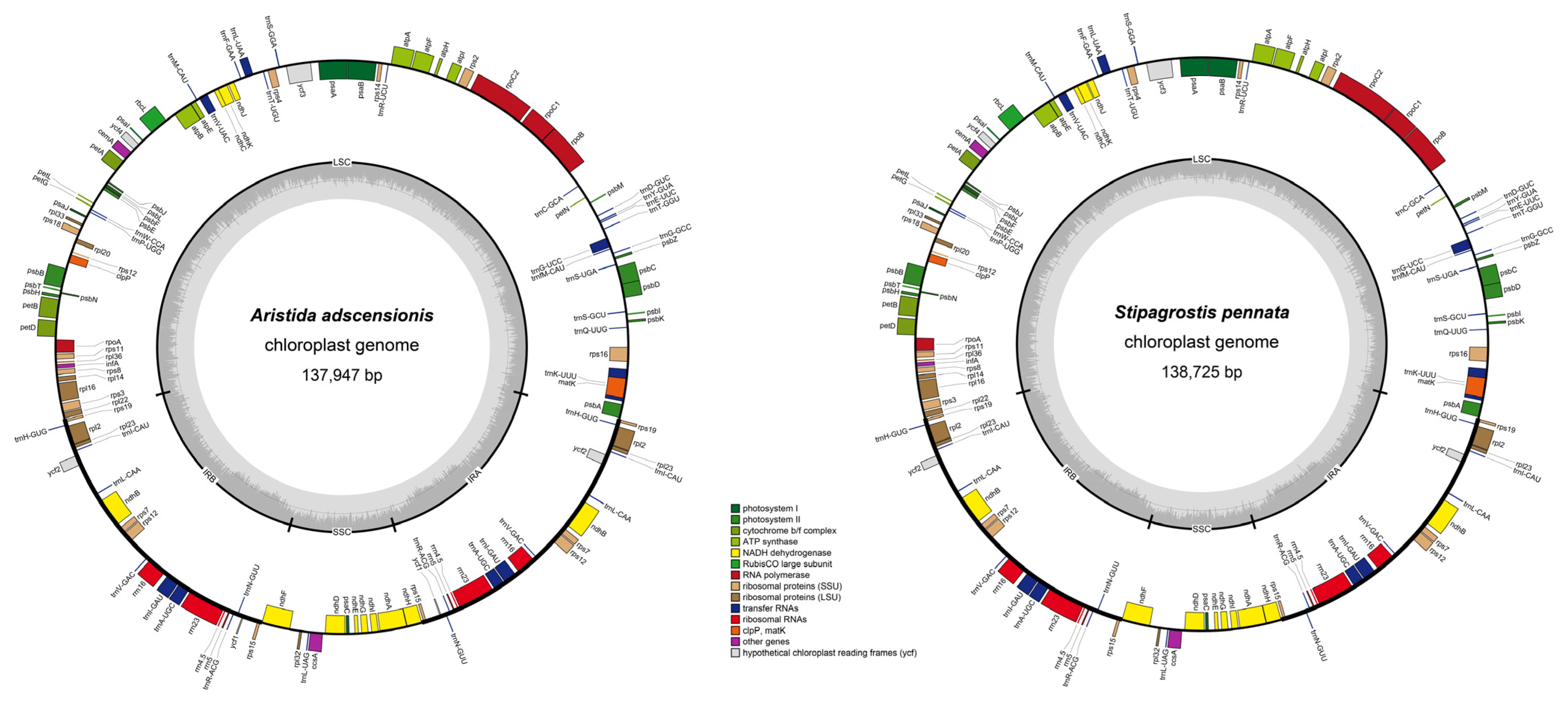
3.1. Plastome Characteristics of Aristidoideae
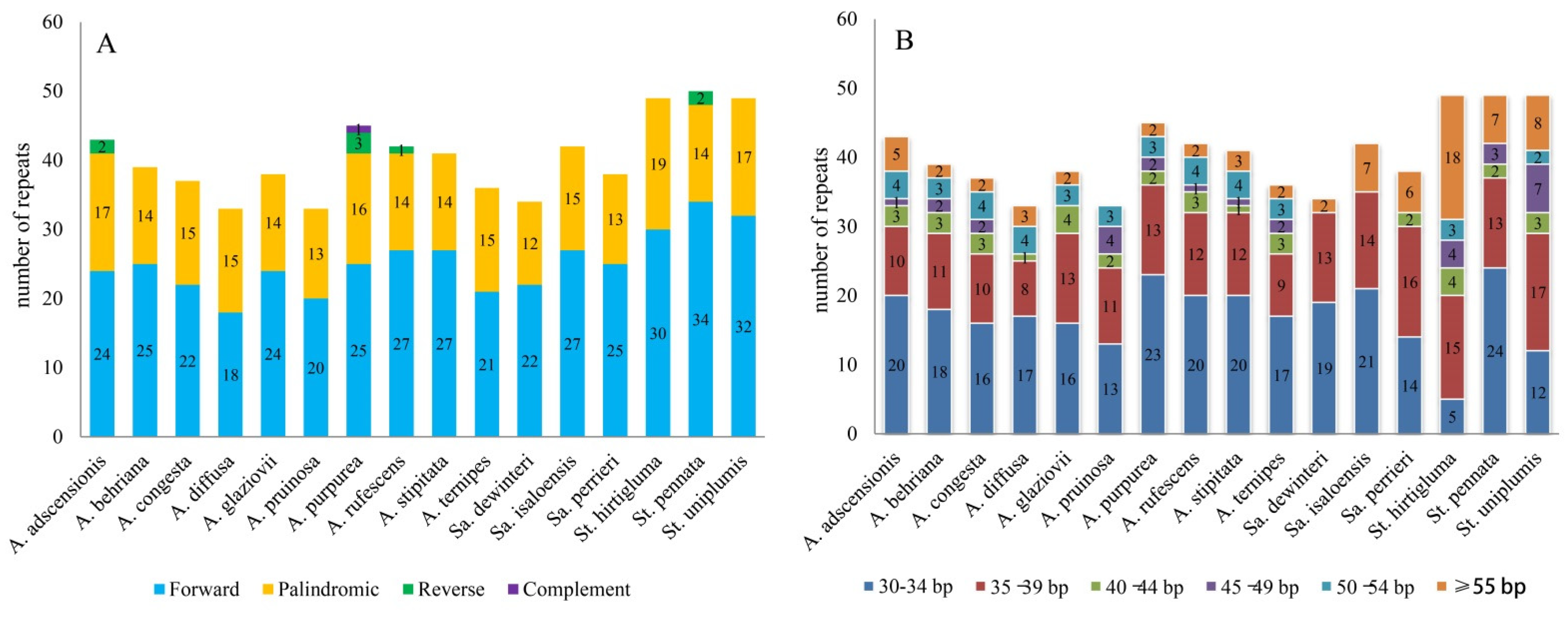
3.2. Repeat Sequence Analysis
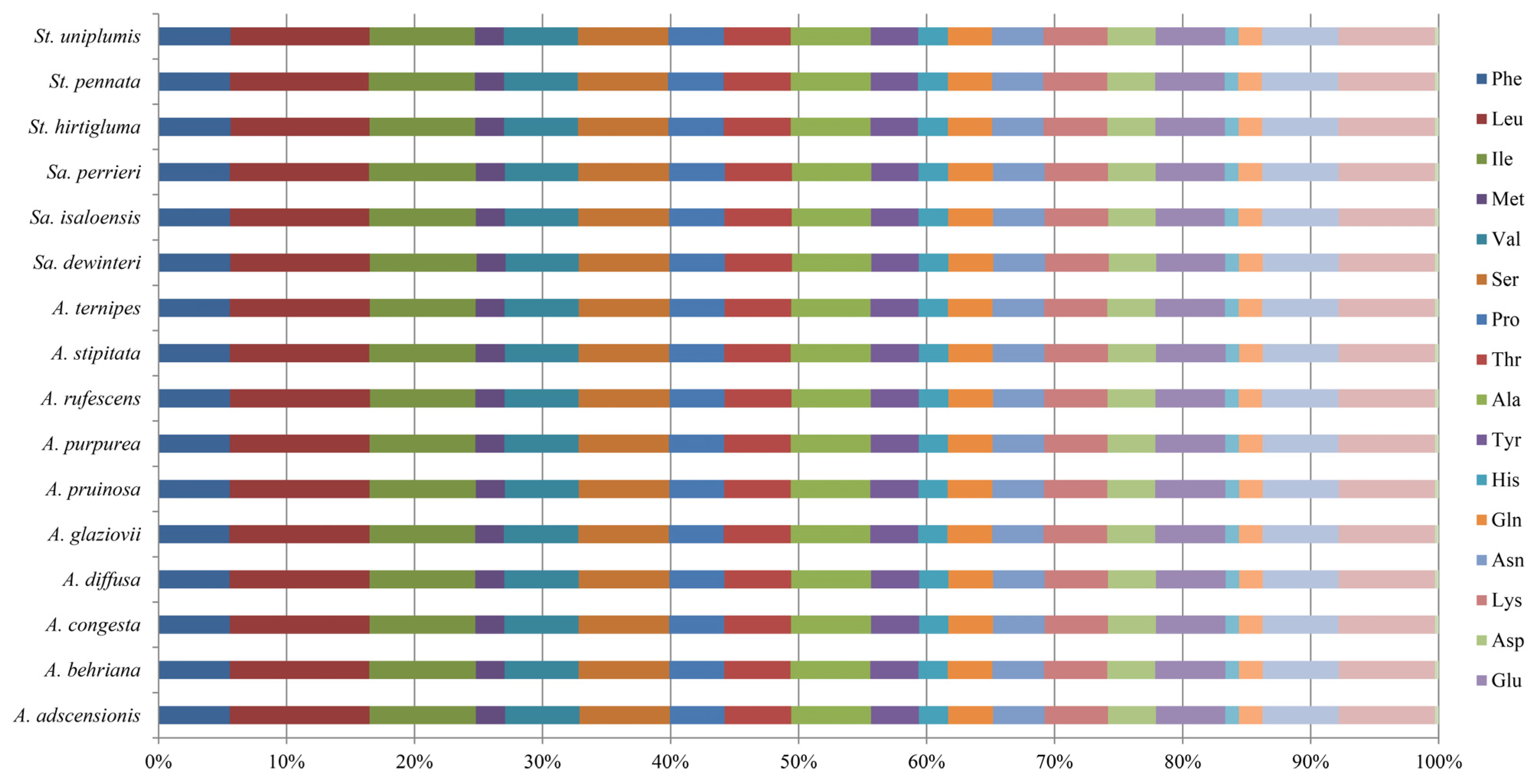
3.3. Codon Usage Analysis
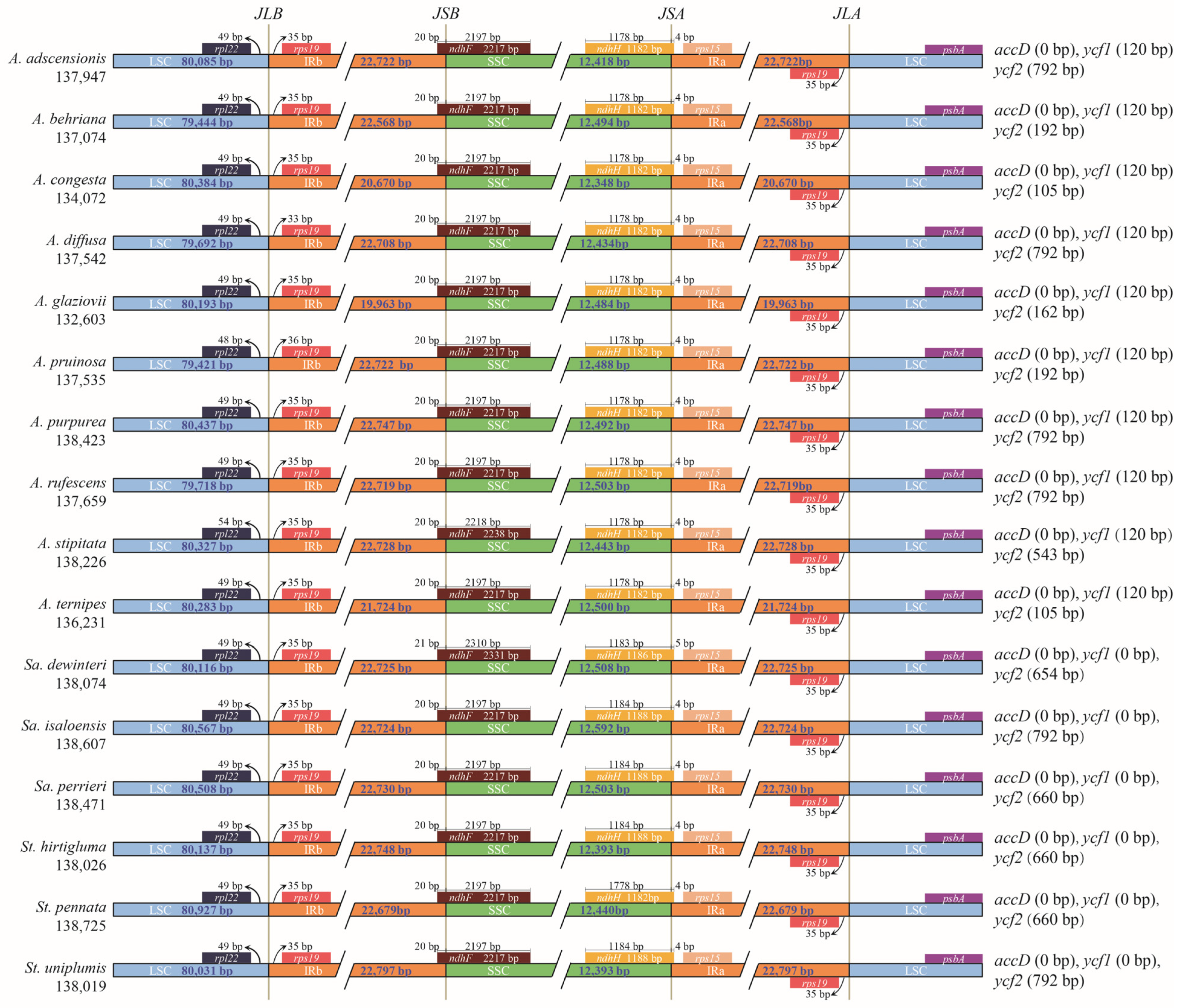
3.4. Expansion and Contraction of the IR Region
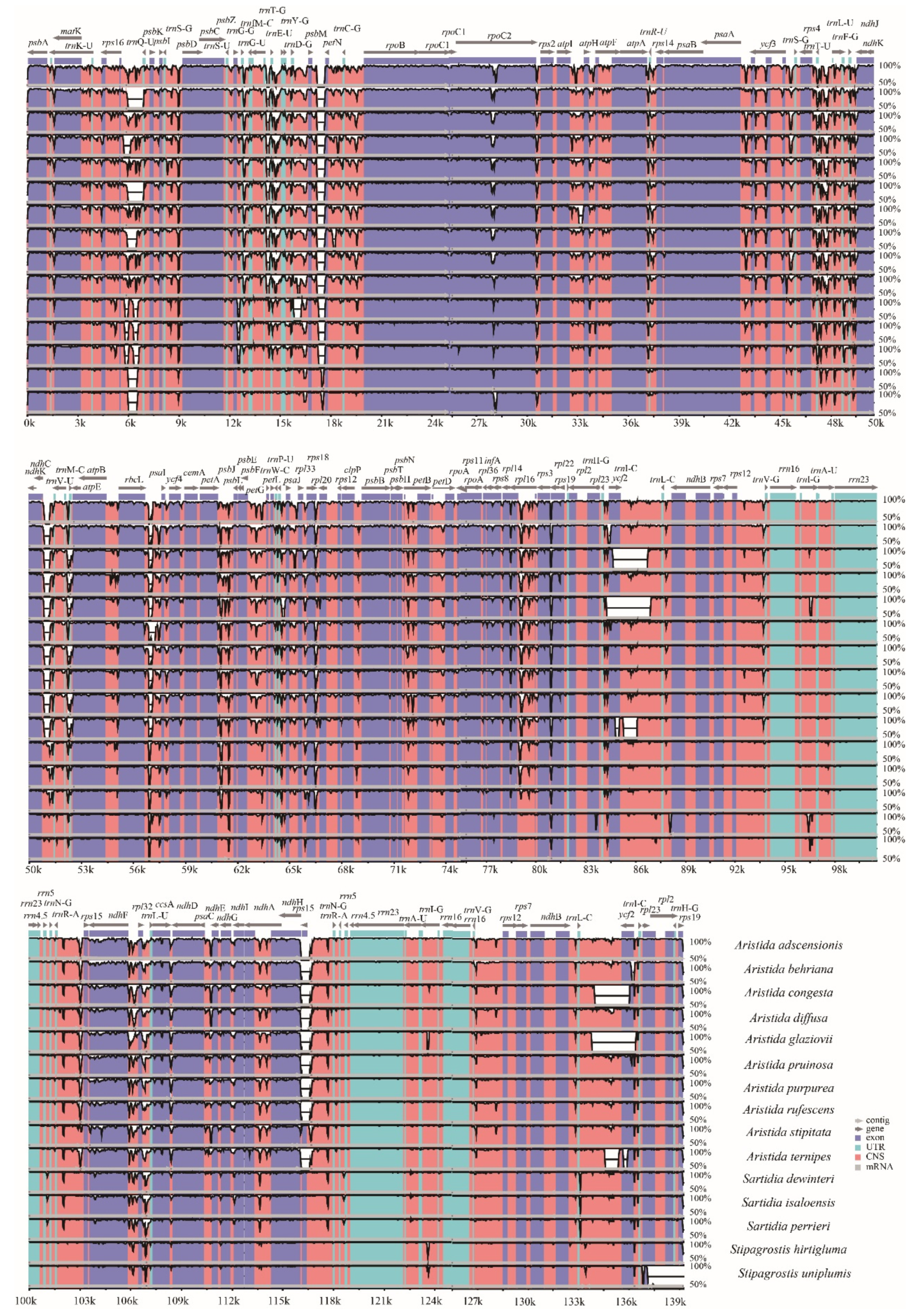
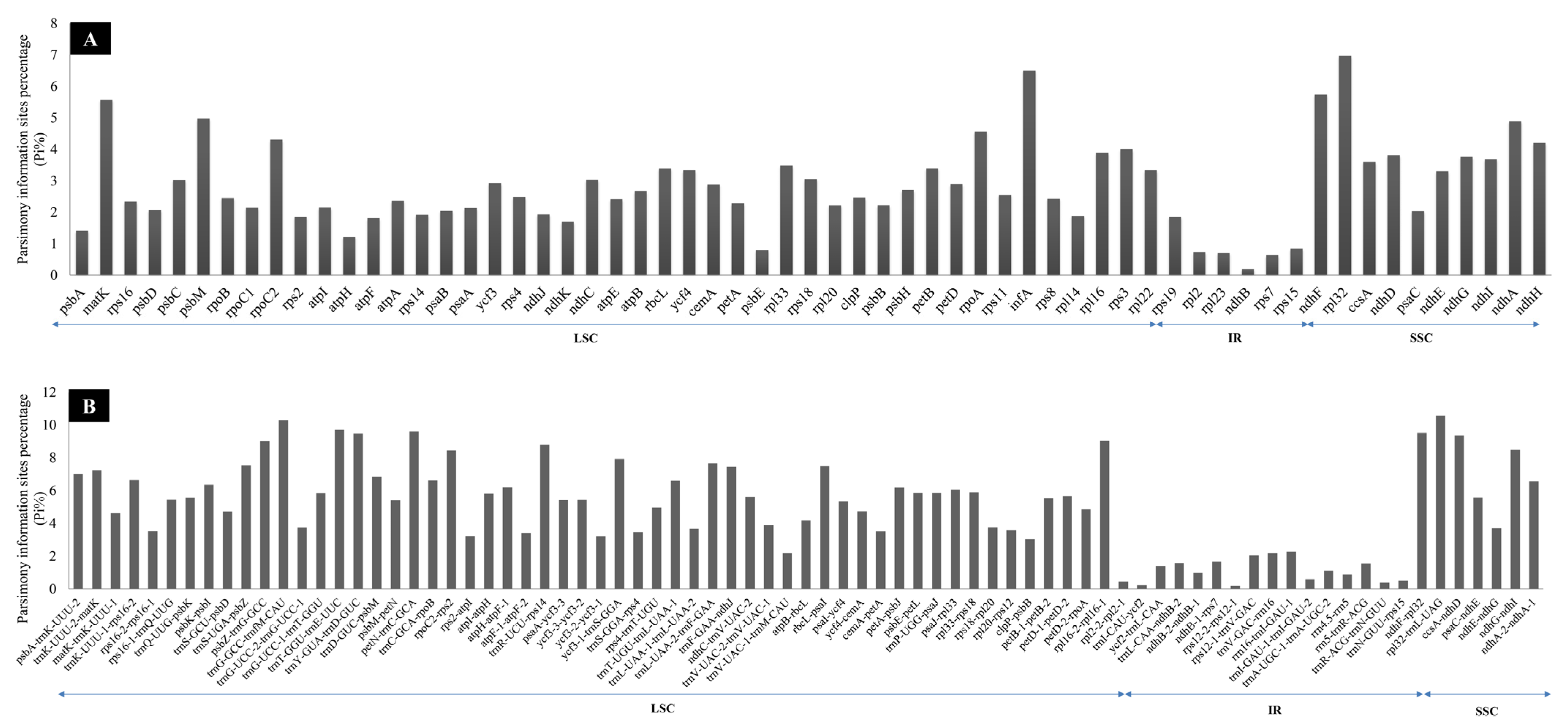
3.5. Comparative Genome Analysis and Identification of Hypervariable Regions
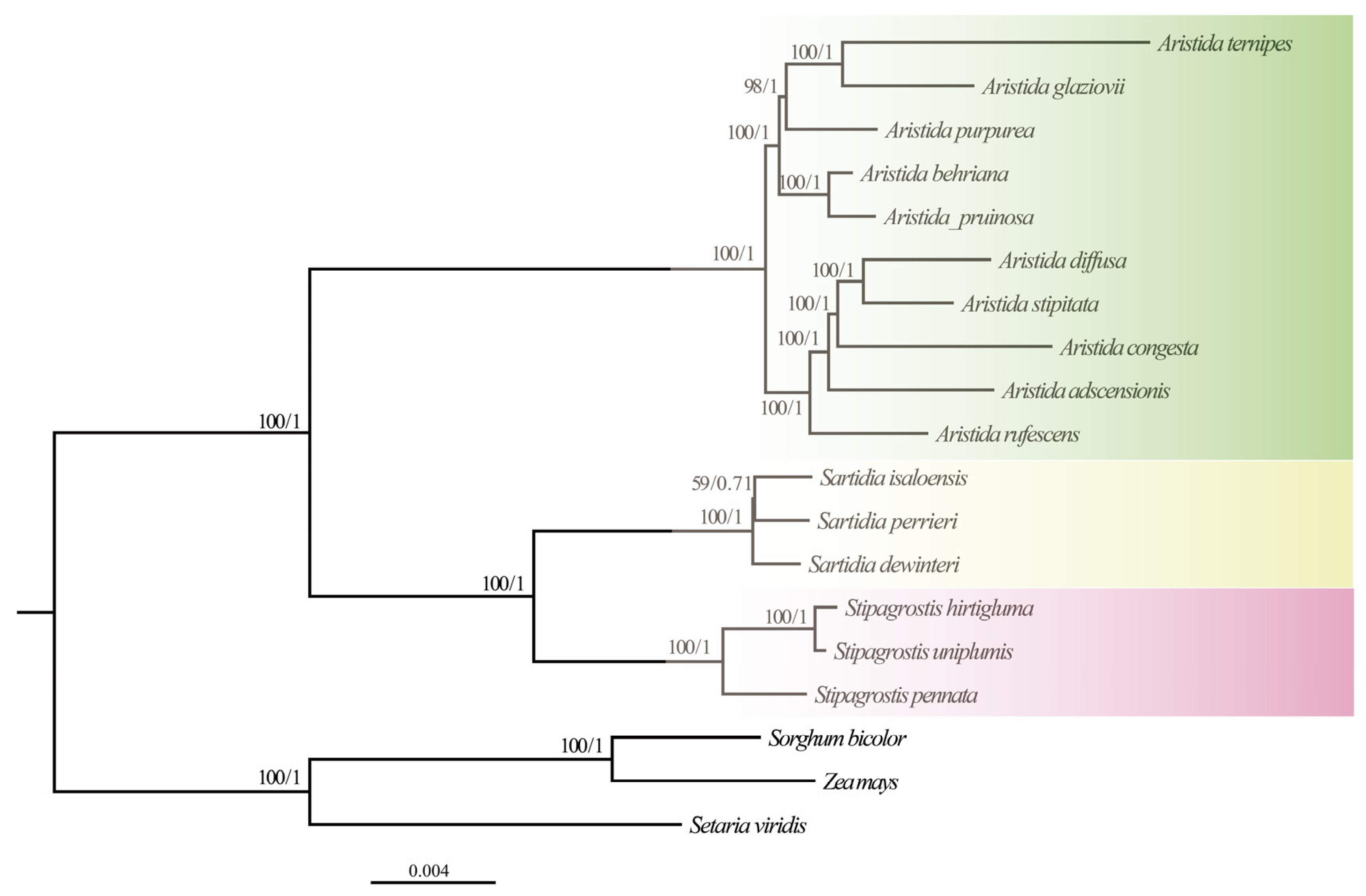
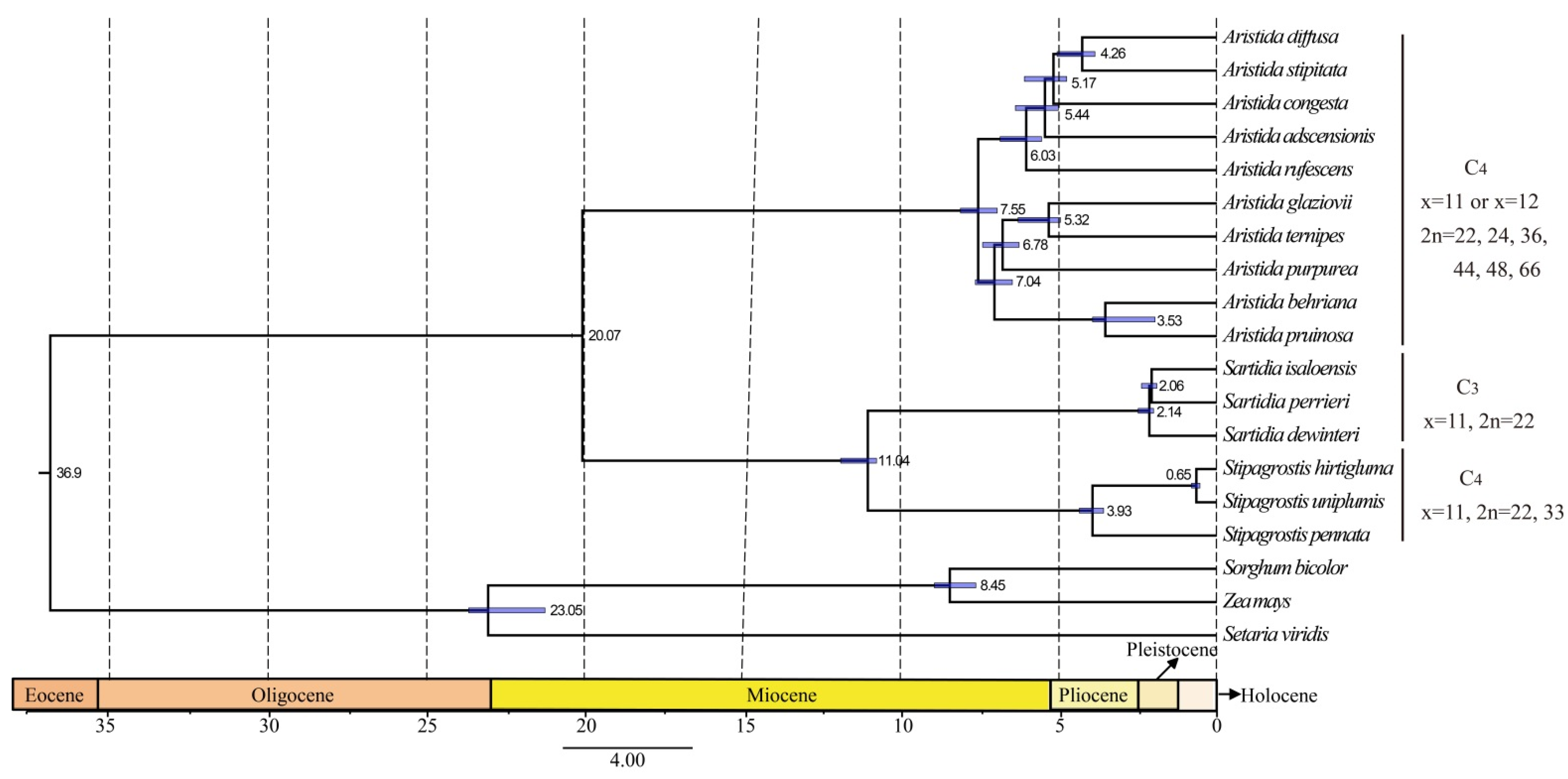
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis and Molecular Dating
4. Discussion
4.1. Basic Information of the Aristidoideae Plastomes
4.2. Phylogenetically Informative Markers
4.3. Phylogenetic Relationships of Aristidoideae
4.4. Evolutionary Implication of Aristidoideae
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grass Phylogeny Working Group II. New grass phylogeny resolves deep evolutionary relationships and discovers C4 origins. New Phytol. 2012, 193, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.L.; Chen, S.L.; Phillips, S.M. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg, E.A. Flowering Plants. Monocots; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Soreng, R.J.; Peterson, P.M.; Konstantin, R.; Gerrit, D.; Jordan, T. A worldwide phylogenetic classification of the Poaceae (Gramineae) II: An update and a comparison of two 2015 classifications. J. Syst. Evol. 2017, 55, 259–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerros-Tlatilpa, R.; Columbus, J.T. C3 photosynthesis in Aristida longifolia: Implication for photosynthetic diversification in Aristidoideae (Poaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, K.; Campbell-Young, G.J.; Fish, L.; Munday, J.; Frean, M.L.; Stalmans, M. A new species of Sartidia (Graminae), endemic to ultramafic soils. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 77, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christin, P.-A.; Besnard, G. Two independent C4 origins in Aristidoideae (Poaceae) revealed by the recruitment of distinct phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase genes. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 2234–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christin, P.-A.; Besnard, G.; Samaritani, E.; Duvall, M.R.; Hodkinson, T.R.; Savolainen, V.; Salamin, N. Oligocene CO2 decline promoted C4 photosynthesis in grasses. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, G.; Christin, P.-A.; Malé, P.-J.G.; Lhuillier, E.; Lauzeral, C.; Coissac, E.; Vorontsova, M.S. From museums to genomics: Old herbarium specimens shed light on a C3 to C4 transition. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6711–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerros-Tlatilpa, R.; Columbus, J.T.; Barker, N.P. Phylogenetic relationships of Aristida and relatives (Poaceae, Aristidoideae) based on noncoding chloroplast (trnL-F, rpl16) and nuclear (ITS) DNA sequences. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 1868–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, J.L.; Wysocki, W.P.; Clark, L.G.; Kelchner, S.A.; Pires, J.C.; Edger, P.P.; Mayfield-Jones, D.; Duvall, M.R. Resolving deep relationships of PACMAD grasses: A phylogenomic approach. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, J.M.; Burke, S.V.; Wysocki, W.P.; Barrett, M.D.; Duvall, M.R. A 250 plastome phylogeny of the grass family (Poaceae): Topological support under different data partitions. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grass Phylogeny Working Group. Phylogeny and Subfamilial Classification of the Grasses (Poaceae). Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2001, 88, 373–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exell, A.W. Flora Zambesiaca. 1971, Volume 10, pp. 67–70. Available online: https://www.zobodat.at/pdf/Mitt-Bot-StaatsS-Muenchen_10_0069-0070.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Zhu, L. Systematic Studies on the Genus of Aristida. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, W. GrassBase—The Online World Grass Flora; Royal Botanic Gardens: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Ohme, M.; Tanaka, M.; Wakasugi, T.; Sugiura, M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: Its gene organization and expression. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1986, 5, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, K.; Fukuzawa, H.; Kohchi, T.; Shirai, H.; Sano, T.; Sano, S.; Umesono, K.; Shiki, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Chang, Z. Chloroplast gene organization deduced from complete sequence of liverwort Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast DNA. Nature 1986, 322, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Stein, D.B. Conservation of chloroplast genome structure among vascular plants. Curr. Genet. 1986, 10, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, R.; Knoop, V. Genomics of Chloroplasts and Mitochondria; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, E.B. The dynamic history of plastid genomes in the Campanulaceae sensu lato is unique among angiosperms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11097–11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.Q.; Guisinger, M.; Kim, H.G.; Ruck, E.; Blazier, J.C.; Mcmurtry, V.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.; Jansen, R.K. Extensive reorganization of the plastid genome of Trifolium subterraneum (Fabaceae) is associated with numerous repeated sequences and novel DNA insertions. J. Mol. Evol. 2008, 67, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao-Lun, W.; Blazier, J.C.; Madhumita, G.; Jansen, R.K. Reconstruction of the ancestral plastid genome in Geraniaceae reveals a correlation between genome rearrangements, repeats, and nucleotide substitution rates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumley, T.W.; Palmer, J.D.; Mower, J.P.; Fourcade, H.M.; Calie, P.J.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Pelargonium × hortorum: Organization and evolution of the largest and most highly rearranged chloroplast genome of land plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Li, D.Z. Advances in phylogenomics based on complete chloroplast genomes. Plant Divers. Resour. 2011, 33, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, M.T.; Gaut, B.S.; Learn, G.H., Jr.; Morton, B.R. Rates and patterns of chloroplast DNA evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6795–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.J.; Wang, T.; Shu, X.C.; Wang, N.; Zhuang, W.B.; Wang, Z. Complete chloroplast genomes and comparative analyses of L. chinensis, L. anhuiensis, and L. aurea (Amaryllidaceae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.Y.; Li, M.Z.; Xu, W.K.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of Avena: Insights into evolutionary dynamics and phylogeny. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.F.; Yu, H.X.; Price, M.; Xie, C.; Deng, Y.Q.; Chen, J.P.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, S.D.; He, X.J. Phylogeny of Chinese Allium species in section Daghestanica and adaptive evolution of Allium (Amaryllidaceae, Allioideae) species revealed by the chloroplast complete Genome. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.; Doyle, J. A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissues. Phytochemistry 1986, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.J.; Fan, S.J.; Wicke, S.; Yi, T.S. Plastome reduction in the only parasitic gymnosperm Parasitaxus is due to Losses of photosynthesis but not housekeeping genes and apparently involves the secondary gain of a large inverted repeat. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 2789–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.J.; Moore, M.J.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. PGA: A software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, K.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Enno, O.; Chris, S.; Jens, S.; Robert, G. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Xie, D.F.; He, X.J.; Zhou, S.D. Comparative chloroplast genomics of Fritillaria (Liliaceae), inferences for phylogenetic relationships between Fritillaria and Lilium and plastome evolution. Plants 2020, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, F. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.W.; Nie, L.P.; Xu, Z.C.; Li, P.; Yao, H. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of three Paeonia Section Moutan Species (Paeoniaceae). Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somaratne, Y.; Guan, D.L.; Abbood, N.N.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.Q.; Xu, S.Q. Comparison of the complete Eragrostis pilosa chloroplast genome with its relatives in Eragrostideae (Chloridoideae; Poaceae). Plants 2019, 8, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Qu, X.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. Plastomes of Mimosoideae: Structural and size variation, sequence divergence, and phylogenetic implication. Tree Genet. Genom. 2017, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.A.; O’Meara, B.C. treePL: Divergence time estimation using penalized likelihood for large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2689–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicentini, A.; Barber, J.C.; Aliscioni, S.S.; Giussani, L.M.; Kellogg, E.A. The age of the grasses and clusters of origins of C4 photosynthesis. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2963–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchenak-Khelladi, Y.; Verboom, G.A.; Hodkinson, T.R.; Salamin, N.; Francois, O.; Chonghaile, G.N.; Savolainen, V. The origins and diversification of C4 grasses and savanna-adapted ungulates. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 15, 2397–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1985, 19, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, A.; Ruf, S.; Calsa, T.; Carrer, H.; Bock, R. The two largest chloroplast genome-encoded open reading frames of higher plants are essential genes. Plant J. 2000, 22, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, R.; Guo, X.X.; Zhang, X.J.; Qu, X.J.; Fan, S.J. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of complete chloroplast genomes in Eragrostideae (Chloridoideae, Poaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-D.; Lee, S.-K.; Yun, D.-W.; Sun, H.-J.; Kang, H.-G.; Lee, H.-Y.; Xi, H.; Park, J.; Lee, B. The complete chloroplast genome of Zoysia macrostachya (Poaceae): Insights into intraspecific variations and species delimitation of the Zoysia species. Korean J. Plant Taxon 2021, 51, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timme, R.E.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. A comparative analysis of the Lactuca and Helianthus (Asteraceae) plastid genomes: Identification of divergent regions and categorization of shared repeats. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Jeong, W.J.; Bae, J.M.; Bang, J.W.; Liu, J.R.; Harn, C.H. Characterization of the plastid-encoded carboxyltransferase subunit (accD) gene of potato. Mol. Cells 2004, 17, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Ruan, Q.Y.; Peng, C. Phylogeny in structure alterations of Poaceae cpDNA. Chin. Agr. Sci. Bull. 2011, 27, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.J.; Lv, S.Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Du, X.H.; Wang, L.; Biradar, S.S.; Tan, X.F.; Wan, F.H.; Song, W.N. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major invasive species, Crofton Weed (Ageratina adenophora). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Gao, L.; Wang, B.; Su, Y.J.; Wang, T. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Cephalotaxus oliveri (Cephalotaxaceae): Evolutionary comparison of Cephalotaxus chloroplast DNAs and insights into the loss of inverted repeat copies in Gymnosperms. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Ma, P.-F.; Li, D.-Z. High-throughput sequencing of six Bamboo chloroplast genomes: Phylogenetic implications for temperate woody Bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenv, D.; Chase, M.W.; Kelly, L.J.; Leitch, I.J.; Macas, J.; Novak, P.; Mathieu, P.; Hanna, W.-S.; Leitch, A.R. Genomic repeat abundances contain phylogenetic signal. Syst. Biol. 2015, 64, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Chen, Z.H. Chloroplast genome evolution in Actinidiaceae: clpP Loss, heterogenous divergence and phylogenomic practice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsztein, D.C.; Amos, W.; Leggo, J.; Goodburn, S.; Jain, S.; Li, S.-H.; Margolis, R.L.; Ross, C.A.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A. Microsatellite evolution-evidence for directionality and variation in rate between species. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Li, W.L.; Xu, F.S.; Wang, X.M. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of species in Gentiana section Cruciata (Gentianaceae) and the development of authentication markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.H.; Dong, B.; Xu, L.; Tembrock, L.R.; Zheng, S.Y.; Wu, Z.Q. The complete chloroplast genome of Heimia myrtifolia and comparative analysis within Myrtales. Molecules 2018, 23, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, K.; Zhang, X.J.; Chen, W.L.; Qu, X.J.; Fan, S.J. Comparative plastomes and phylogenetic analysis of Cleistogenes and closely related genera (Poaceae). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 638597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.L.; Ma, L.; Gong, P.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.Q. Development and application of EST–SSRs markers for analysis of genetic diversity in erect milkvetch (Astragalus adsurgens Pall.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, M.; Vekemans, X.; Gode’, C.c.; Fre´rot, H.l.n.; Castric, V.; Saumitou-Laprade, P. Nuclear and chloroplast DNA phylogeography reveals vicariance among European populations of the model species for the study of metal tolerance, Arabidopsis halleri (Brassicaceae). New Phytol. 2012, 193, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Wu, Z.Q.; Zhao, K.K.; Yang, Z.J.; Tembrock, L.R.; Xu, D.P. Comparative analyses of five complete chloroplast genomes from the genus Pterocarpus (Fabacaeae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Yang, J.; Park, J.; Yamada, T.; Kim, S.C. Comparison of whole plastome sequences between thermogenic Skunk Cabbage Symplocarpus renifolius and Nonthermogenic S. nipponicus (Orontioideae; Araceae) in East Asia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, R.; Gautier, C.; Gouy, M. Codon frequencies in 119 individual genes confirm consistent choices of degenerate bases according to genome type. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 1893–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, R.; Gautier, C.; Gouy, M.; Jacobzone, M.; Mercier, R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981, 9, 43–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.F.; Xu, D.; Kleinhofs, A.; Zhou, J.Z. Quantitative relationship between synonymous codon usage bias and GC composition across unicellular genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2004, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olejniczak, M.; Uhlenbeck, O.C. tRNA residues that have coevolved with their anticodon to ensure uniform and accurate codon recognition. Biochimie 2006, 88, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, Y.; Kawamata, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Chikashige, Y. Codon usage bias is correlated with gene expression levels in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genes Cells 2010, 14, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.P.; Xue, Q.Z. Comparative studies on codon usage pattern of chloroplasts and their host nuclear genes in four plant species. J. Genet. 2005, 84, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Nie, X.J.; Jia, X.O.; Zhao, C.Z.; Biradar, S.S.; Wang, L.; Du, X.H.; Song, W.N. Analysis of codon usage patterns of the chloroplast genomes in the Poaceae family. Aust. J. Bot. 2012, 60, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablok, G.; Nayak, K.C.; Vazquez, F.; Tatarinova, T.V. Synonymous codon usage, GC(3), and evolutionary patterns across plastomes of three pooid model species: Emerging grass genome models for monocots. Mol. Biotechnol. 2011, 49, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Long, W.; Li, X. Patterns of synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genomes of seed plants. For. Stud. China 2008, 11, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Deng, F.; Wang, H.L.; Hu, Z.H. An extensive analysis on the global codon usage pattern of baculoviruses. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Nuggent, J.M.; Herbon, L.A. Unusual structure of geranium chloroplast DNA: A triple-sized inverted repeat, extensive gene duplications, multiple inversions, and two repeat families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, X.J.; Guo, Y.B.; Wu, H.Z. Comparative analysis of four Zantedeschia chloroplast genomes: Expansion and contraction of the IR region, phylogenetic analyses and SSR genetic diversity assessment. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.I.; Soreng, R.J. Migration of endpoints of two genes relative to boundaries between regions of the plastid genome in the grass family (Poaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 874–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goremykin, V.V.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Stefan, W.; Hellwig, F.H. Analysis of the Amborella trichopoda chloroplast genome sequence suggests that amborella is not a basal angiosperm. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, F.; Hu, Z.; Jin, S.; Diao, Y. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of five Miscanthus species, and comparative analyses with other grass plastomes. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 162, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.S.; Wolfe, K.H. Nucleotide substitution rates in legume chloroplast DNA depend on the presence of the inverted repeat. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 55, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Mao, S.Y.; Gao, L.Z. Thirteen Camellia chloroplast genome sequences determined by high-throughput sequencing: Genome structure and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K. Complete chloroplast genome of Camellia japonica genome structures, comparative and phylogenetic analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, S.J.; Ding, Y.M.; Xu, J.; Li, M.F.; Zhu, S.F.; Chen, N.Z. Chloroplast genomic resource of Paris for species discrimination. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, K.; Nobis, M.; Myszczyński, K.; Klichowska, E.; Sawicki, J. Plastid super-barcodes as a tool for species discrimination in feather grasses (Poaceae: Stipa). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchenak-Khelladi, Y.; Salamin, N.; Savolainen, V.; Forest, F.; Hodkinson, T.R. Large multi-gene phylogenetic trees of the grasses (Poaceae): Progress towards complete tribal and generic level sampling. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 2008, 47, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soreng, R.J.; Peterson, P.M.; Romaschenko, K.; Davidse, G.; Zuloaga, F.O.; Judziewicz, E.J.; Filgueiras, T.S. A worldwide phylogenetic classification of the Poaceae (Gramineae). J. Syst. Evol. 2015, 53, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, M.R.; Burke, S.V.; Clark, D.C. Plastome phylogenomics of Poaceae: Alternate topologies depend on alignment gaps. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 192, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsova, M.S.; Haevermans, T.; Haevermans, A.; Razanatsoa, J.; Lundgren, M.R.; Besnard, G. The genus Sartidia (Poaceae: Aristidoideae) in Madagascar. Syst. Bot. 2015, 40, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lu, S.L. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae; Chen, S., Ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990; Volume 10, pp. 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cerling, T.E.; MacFaddenb, B.J. Fossil horses and carbon isotopes: New evidence for Cenozoic dietary, habitat, and ecosystem changes in North America. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1994, 107, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.L.; Koch, P.L. Tertiary history of C4 biomass in the Great Plains, USA. Geology 2003, 31, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, E.J.; Smith, S.A. Phylogenetic analyses reveal the shady history of C4 grasses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spriggs, E.L.; Christin, P.-A.; Edwards, E.J. C4 photosynthesis promoted species diversification during the Miocene grassland expansion. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Y.C.; Wang, G. Spatial distribution patterns of the soil seed bank of Stipagrostis pennata (Trin.) de Winter in the Gurbantonggut Desert of north-west China. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 63, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mable, B.K. Breaking down taxonomic barriers in polyploidy research. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltis, D.E.; Albert, V.A.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Bell, C.D.; Paterson, A.H.; Zheng, C.; Sankoff, D.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Wall, K.; Soltis, P.S. Polyploidy and angiosperm diversification. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Accession Number | Species | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphipogon turbinatus | NC_035521 | Cortaderia selloana | NC_036681 |
| Aristida adscensionis | MZ373986 | Eleusine coracana | MW262987 |
| Aristida behriana | NC_046729 | Eriachne mucronata | NC_035529 |
| Aristida congesta | NC_046731 | Isachne distichophylla | NC_025236 |
| Aristida diffusa | NC_046732 | Merxmuellera tsaratananensis | NC_036122 |
| Aristida glaziovii | NC_046413 | Oryza sativa | NC_031333 |
| Aristida pruinosa | NC_042836 | Sartidia dewinteri | NC_027147 |
| Aristida purpurea | NC_025228 | Sartidia isaloensis | NC_036117 |
| Aristida rufescens | NC_036130 | Sartidia perrieri | NC_027146 |
| Aristida stipitata | NC_046730 | Setaria viridis | NC_028075 |
| Aristida ternipes | NC_037164 | Sorghum bicolor | NC_008602 |
| Arundo plinii | NC_034652 | Stipagrostis hirtigluma | NC_036112 |
| Bambusa bambos | NC_026957 | Stipagrostis pennata | MZ373985 |
| Brachyelytrum aristosum | NC_027470 | Stipagrostis uniplumis | MF460973 |
| Centropodia glauca | NC_029411 | Thysanolaena latifolia | NC_025238 |
| Chloris virgata | NC_032034 | Zea mays | NC_001666 |
| Species | Genome Size (bp) | LSC (bp) | IR (bp) | SSC (bp) | GC Content (%) | Number of Genes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | IR | LSC | SSC | Total | CDS | rRNAs | tRNAs | |||||
| Aristida adscensionis | 137,947 | 80,085 | 22,722 | 12,418 | 38.4 | 43.9 | 36.2 | 32.4 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida behriana | 137,074 | 79,444 | 22,568 | 12,494 | 38.6 | 44 | 36.4 | 32.6 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida congesta | 134,072 | 80,384 | 20,670 | 12,348 | 38.3 | 44.1 | 36.2 | 32.6 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida diffusa | 137,542 | 79,692 | 22,708 | 12,434 | 38.4 | 43.9 | 36.2 | 32.5 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida glaziovii | 132,603 | 80,193 | 19,963 | 12,484 | 38.4 | 44.3 | 36.3 | 32.6 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida pruinosa | 137,353 | 79,421 | 22,722 | 12,488 | 38.5 | 44 | 36.4 | 32.6 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida purpurea | 138,423 | 80,437 | 22,747 | 12,492 | 38.5 | 43.9 | 36.3 | 32.6 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida rufescens | 137,659 | 79,718 | 22,719 | 12,503 | 38.5 | 43.9 | 36.4 | 32.6 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida stipitata | 138,226 | 80,327 | 22,728 | 12,443 | 38.4 | 44 | 36.2 | 32.4 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Aristida ternipes | 136,231 | 80,283 | 21,724 | 12,500 | 38.5 | 44.1 | 36.4 | 32.5 | 134 | 88 | 8 | 38 |
| Sartidia dewinteri | 138,074 | 80,116 | 22,725 | 12,508 | 38.4 | 44 | 36.2 | 32.3 | 132 | 86 | 8 | 38 |
| Sartidia isaloensis | 138,607 | 80,567 | 22,724 | 12,592 | 38.4 | 43.9 | 36.2 | 32.3 | 132 | 86 | 8 | 38 |
| Sartidia perrieri | 138,471 | 80,508 | 22,730 | 12,503 | 38.4 | 44 | 36.2 | 32.3 | 132 | 86 | 8 | 38 |
| Stipagrostis hirtigluma | 138,026 | 80,137 | 22,748 | 12,393 | 38.5 | 43.9 | 36.3 | 32.9 | 132 | 86 | 8 | 38 |
| Stipagrostis pennata | 138,725 | 80,927 | 22,679 | 12,440 | 38.4 | 44 | 36.4 | 32.8 | 132 | 86 | 8 | 38 |
| Stipagrostis uniplumis | 138,019 | 80,031 | 22,797 | 12,394 | 38.5 | 43.9 | 36.4 | 32.8 | 132 | 86 | 8 | 38 |
| Term | Plastome Size | GC Content | Total SSRs | P1% | P2% | P3% | P4% | P5% | P6% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastome Size | 1 | ||||||||
| GC content | 0.2473 | 1 | |||||||
| Total SSRs | −0.4087 | 0.1868 | 1 | ||||||
| P1% | −0.589 * | −0.0325 | 0.766 ** | 1 | |||||
| P2% | 0.661 ** | −0.1420 | −0.3807 | −0.590 * | 1 | ||||
| P3% | 0.0761 | 0.565 * | −0.0616 | −0.0010 | −0.1244 | 1 | |||
| P4% | 0.3473 | 0.0234 | −0.677 ** | −0.845 ** | 0.2253 | −0.2124 | 1 | ||
| P5% | 0.1996 | −0.1588 | −0.2326 | −0.2800 | 0.2742 | 0.1881 | −0.1428 | 1 | |
| P6% | 0.0992 | −0.1604 | 0.2575 | −0.0327 | 0.3447 | −0.3606 | −0.0262 | −0.16742 | 1 |
| Species | CC | ENC | GC | T3s | C3s | A3s | G3s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aristida adscensionis | 16,986 | 49.51 | 0.389 | 0.4643 | 0.1712 | 0.4263 | 0.1739 |
| Aristida behriana | 17,016 | 49.75 | 0.39 | 0.4631 | 0.1728 | 0.4237 | 0.177 |
| Aristida congesta | 17,004 | 49.63 | 0.39 | 0.4637 | 0.1719 | 0.425 | 0.175 |
| Aristida diffusa | 17,004 | 49.65 | 0.39 | 0.4638 | 0.1721 | 0.4242 | 0.1758 |
| Aristida glaziovii | 17,005 | 49.79 | 0.391 | 0.4627 | 0.1726 | 0.4235 | 0.1772 |
| Aristida pruinosa | 17,023 | 49.72 | 0.39 | 0.4631 | 0.1722 | 0.4245 | 0.1767 |
| Aristida purpurea | 17,003 | 49.89 | 0.391 | 0.4615 | 0.174 | 0.4233 | 0.1774 |
| Aristida rufescens | 17,066 | 49.82 | 0.391 | 0.4622 | 0.1727 | 0.4234 | 0.1777 |
| Aristida stipitata | 17,011 | 49.66 | 0.39 | 0.4639 | 0.172 | 0.4245 | 0.1758 |
| Aristida ternipes | 17,001 | 49.87 | 0.391 | 0.4617 | 0.1738 | 0.4226 | 0.1779 |
| Sartidia dewinteri | 17,072 | 49.62 | 0.39 | 0.4636 | 0.1723 | 0.4257 | 0.1744 |
| Sartidia isaloensis | 17,034 | 49.55 | 0.39 | 0.4641 | 0.1718 | 0.4257 | 0.1739 |
| Sartidia perrieri | 17,034 | 49.57 | 0.39 | 0.464 | 0.1719 | 0.4251 | 0.1744 |
| Stipagrostis hirtigluma | 17,101 | 49.74 | 0.391 | 0.4616 | 0.1756 | 0.4243 | 0.1744 |
| Stipagrostis pennata | 17,055 | 49.75 | 0.391 | 0.4613 | 0.1753 | 0.4249 | 0.174 |
| Stipagrostis uniplumis | 17,101 | 49.73 | 0.391 | 0.4618 | 0.1755 | 0.4242 | 0.1745 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.-X.; Qu, X.-J.; Zhang, X.-J.; Fan, S.-J. Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis of Complete Plastomes among Aristidoideae Species (Poaceae). Biology 2022, 11, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010063
Guo X-X, Qu X-J, Zhang X-J, Fan S-J. Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis of Complete Plastomes among Aristidoideae Species (Poaceae). Biology. 2022; 11(1):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010063
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiu-Xiu, Xiao-Jian Qu, Xue-Jie Zhang, and Shou-Jin Fan. 2022. "Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis of Complete Plastomes among Aristidoideae Species (Poaceae)" Biology 11, no. 1: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010063
APA StyleGuo, X.-X., Qu, X.-J., Zhang, X.-J., & Fan, S.-J. (2022). Comparative and Phylogenetic Analysis of Complete Plastomes among Aristidoideae Species (Poaceae). Biology, 11(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010063






