Microcrater-Arrayed Chemiluminescence Cell Chip to Boost Anti-Cancer Drug Administration in Zebrafish Tumor Xenograft Model
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coating with Waxy Film on Glass Substrate
2.2. Laser Direct Writing on Waxy Film-Coated Slide Substrate
2.3. Microcrater-Arrayed (µCA) Chip
2.4. Zebrafish Xenograft Model
2.5. Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity (ZFET) Testing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
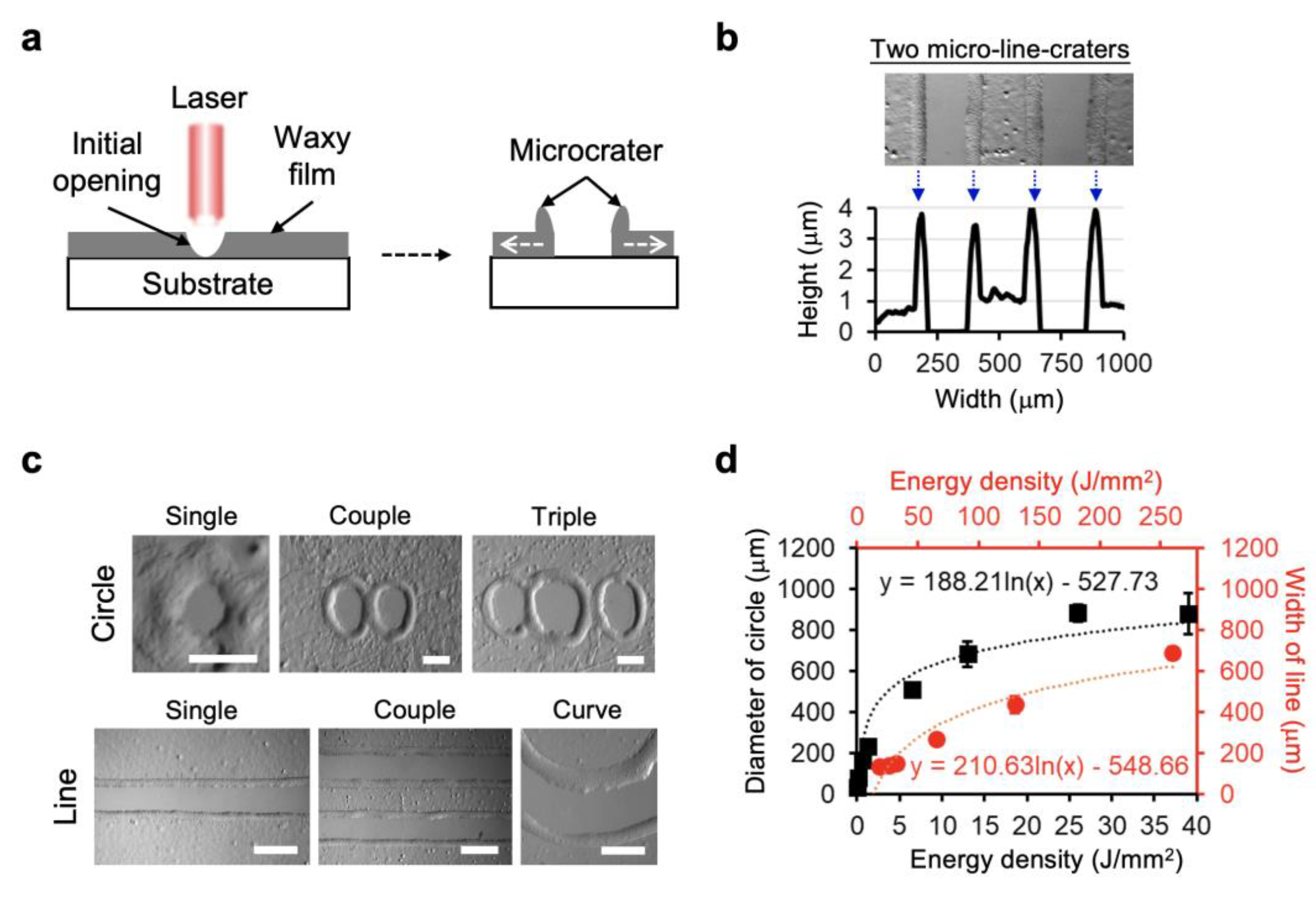
3.1. Laser Direct Patterning of Microcrater Wax Structures
3.2. High-Throughput Drug Screening by Microcrater-Arrayed (µCA) Chip
3.3. Successful Translation of the Selected Optimal Drug Combination into Zebrafish Tumor Xenograft Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, M.-Y.; Kumar, R.A.; Sukumaran, S.M.; Hogg, M.G.; Clark, D.S.; Dordick, J.S. Three-dimensional cellular microarray for high-throughput toxicology assays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berthuy, O.I.; Muldur, S.K.; Rossi, F.; Colpo, P.; Blum, L.J.; Marquette, C.A. Multiplex cell microarrays for high-throughput screening. Lab A Chip 2016, 16, 4248–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Fan, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Yan, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Poznansky, M.C.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; et al. Biomechani-cally primed liver microtumor array as a high-throughput mechanopharmacological screening platform for stromarepro-grammed combinatorial therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 124, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Feng, X.; Du, W.; Koehler, S.A.; Demirci, U.; Luo, B.F. Rapid Assembly of Heterogeneous 3D Cell Microenvironments in a Microgel Array. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3543–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiung, L.C.; Yang, C.H.; Chiu, C.L.; Chen, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Lee, H.; Cheng, J.Y.; Ho, M.C.; Wo, A.M. A planar interdig-itated ring electrode array via dielectrophoresis for uniform patterning of cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Onuki-Nagasaki, R.; Ikuta, K.; Hara, Y. A simple method for producing multiple copies of controlled release small molecule microarrays for cell-based screening. Biofabrication 2016, 9, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, A.A.; Schillo, S.M.; Demir, K.; Ueda, E.; Nesterov-Mueller, A.; Levkin, P.A. Droplet-Array (DA) Sandwich Chip: A Versatile Platform for High-Throughput Cell Screening Based on Superhydrophobic–Superhydrophilic Micropatterning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5217–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popova, A.A.; Demir, K.; Hartanto, T.G.; Schmitt, E.; Levkin, P.A. Droplet-microarray on superhydropho-bic-superhydrophilic patterns for high-throughput live cell screenings. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 38263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carstens, M.R.; Fisher, R.C.; Acharya, A.P.; Butterworth, E.A.; Scott, E.; Huang, E.H.; Keselowsky, B.G. Drug-eluting microarrays to identify effective chemotherapeutic combinations targeting patient-derived cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8732–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, P.K.; Yu, F.; Shahangian, A.; Cheng, G.; Sun, R.; Ho, C.M. Closed-loop control of cellular functions using combina-tory drugs guided by a stochastic search algorithm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5105–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, A.; Ding, X.; Van Beijnum, J.R.; Wong, I.; Wong, T.J.; Berndsen, R.H.; Dormond, O.; Dallinga, M.; Shen, L.; Schlingemann, R.O.; et al. Rapid optimization of drug combinations for the optimal angiostatic treatment of cancer. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.; Lee, B.-Y.; Clemens, D.L.; Kee, T.; Ding, X.; Ho, C.-M.; Horwitz, M.A. Output-driven feedback system control platform optimizes combinatorial therapy of tuberculosis using a macrophage cell culture model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2172–E2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iadevaia, S.; Lu, Y.; Morales, F.C.; Mills, G.B.; Ram, P.T. Identification of optimal drug combinations targeting cellular net-works: Integrating phospho-proteomics and computational network analysis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6704–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Pritchard, J.R.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Hemann, M.T. Addressing Genetic Tumor Heterogeneity through Computationally Predictive Combination Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.Y.; Hsiung, L.C.; Wang, C.H.; Chiang, C.L.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, C.S.; Wo, A.M. A Novel 96well-formatted Micro-gap Plate Enabling Drug Response Profiling on Primary Tumour Samples. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kenny, H.A.; Lal-Nag, M.; White, E.A.; Shen, M.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Mitra, A.K.; Zhang, Y.; Curtis, M.W.; Schryver, E.M.; Bettis, S.; et al. Quantitative high throughput screening using a primary human three-dimensional organotypic culture predicts in vivo efficacy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monjezi, M.; Rismanian, M.; Jamaati, H.; Kashaninejad, N. Anti-Cancer Drug Screening with Microfluidic Technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, E.; Bai, L.; Huang, H.; Yun, K.; Wang, M. Droplet-based microfluidic platform for high-throughput screening of Streptomyces. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Hattori, K.; Yanagawa, F.; Sugiura, S.; Kanamori, T.; Nakazawa, K. Detachably assembled microfluidic device for perfusion culture and post-culture analysis of a spheroid array. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Iliescu, F.S.; Iliescu, C. A Comprehensive Review on Perfusion Cell Culture System. Informacije Midem 2016, 4, 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Shembekar, N.; Chaipan, C.; Utharala, R.; Merten, C.A. Droplet-based microfluidics in drug discovery, transcriptomics and high-throughput molecular genetics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1314–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Ueda, E.; Levkin, P.A. Droplet Microarrays: From Surface Patterning to High-Throughput Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eduati, F.; Utharala, R.; Madhavan, D.; Neumann, U.P.; Longerich, T.; Cramer, T.; Saez–Rodriguez, J.; Merten, C.A. A mi-crofluidics platform for combinatorial drug screening on cancer biopsies. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, G.S.; Pan, J.Z.; Zhao, S.P.; Zhu, Y.; den Toonder, J.M.J.; Fang, Q. Cell-Based Drug Combination Screening with a Mi-crofluidic Droplet Array System. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6740–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, F.B.; Laurenson, S.; Willams, L.C.; Dodd, A.; Copp, B.R.; Love, D.R. Chemical discovery and global gene expres-sion analysis in zebrafish. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-T.; Wang, J.-Y.; Wo, A.M.; Chen, B.P.C.; Lee, H. ParaStamp and Its Applications to Cell Patterning, Drug Synergy Screening, and Rewritable Devices for Droplet Storage. Adv. Biosyst. 2017, 1, 1700048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-T.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lu, S.-R.; Lai, Y.-S.; Chang, H.-H.; Hsieh, J.-T.; Wo, A.M.; Chen, B.P.C.; Lu, J.-H.; Lee, H. A nanodroplet cell processing platform facilitating drug synergy evaluations for anti-cancer treatments. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Wei, Y.; Yang, H. A novel xenograft model in zebrafish for high-resolution inves-tigating dynamics of neovascularization in tumors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21768. [Google Scholar]
- Barriuso, J.; Nagaraju, R.; Hurlstone, A. Zebrafish: A New Companion for Translational Research in Oncology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fior, R.; Povoa, V.; Mendes, R.V.; Carvalho, T.; Gomes, A.; Figueiredo, N.; Ferreira, M.G. Single-cell functional and chemo-sensitive profiling of combinatorial colorectal therapy in zebrafish xenografts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8234–E8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haldi, M.; Ton, C.; Seng, W.L.; McGrath, P. Human melanoma cells transplanted into zebrafish proliferate, migrate, produce melanin, form masses and stimulate angiogenesis in zebrafish. Angiogenesis 2006, 9, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, M.G.; Moore, L.H.; Blackburn, J.S. Drug Screening of Primary Patient Derived Tumor Xenografts in Zebrafish. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 158, e60996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, J.; Elson, D.; Greenwood, J.; Tanguay, R.; Kolluri, S. The Zebrafish Xenograft Models for Investigating Cancer and Cancer Therapeutics. Biology 2021, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corkery, D.; Dellaire, G.; Berman, J.N. Leukaemia xenotransplantation in zebrafish-chemotherapy response assay in vivo. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 153, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.-Y.; Wei, C.-W.; Hsu, K.-H.; Young, T.-H.J.S. Direct-write laser micromachining and universal surface modification of PMMA for device development. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 99, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Tu, T.-Y.; Jong, D.-S.; Wo, A.M. Patch clamping on plane glass—fabrication of hourglass aperture and high-yield ion channel recording. Lab A Chip 2009, 9, 2370–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Yen, M.H.; Kuo, C.T.; Young, T.H. A transparent cell-culture microchamber with a variably controlled con-centration gradient generator and flow field rectifier. Biomicrofluidics 2008, 2, 24105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, C.-T.; Chen, C.-C. Biomimetic Wax Interfaces Facilitating Rehealable Polymer Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-T.; Chiang, C.-L.; Chang, C.-H.; Liu, H.-K.; Huang, G.-S.; Huang, R.Y.-J.; Lee, H.; Huang, C.-S.; Wo, A.M. Modeling of cancer metastasis and drug resistance via biomimetic nano-cilia and microfluidics. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-T.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lin, Y.-F.; Wo, A.M.; Chen, B.P.C.; Lee, H. Three-dimensional spheroid culture targeting versatile tissue bioassays using a PDMS-based hanging drop array. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-T.; Lu, S.-R.; Chen, W.-M.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-C.; Chang, H.-H.; Wo, A.M.; Chen, B.P.C.; Lee, H. Facilitating tumor spheroid-based bioassays and in vitro blood vessel modeling via bioinspired self-formation microstructure devices. Lab A Chip 2018, 18, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Characteristics | µCA Chip | 96-Well Plate | Zebrafish Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell number | 100 | 4000 | 300 | |
| Culture scale (per well) | Volume of medium | 0.2 µL | 100 µL | 0.01 µL |
| Volume density | 500 cells µL−1 | 40 cells µL−1 | 30,000 cells µL−1 | |
| Surface area | 6.4 × 105 µm2 | 3.2 × 107 µm2 | Nil | |
| Surface density | 1.6 × 10−4 cells µm−2 | 1.3 × 10−4 cells µm−2 | Nil | |
| Material | Substrate | Glass | Polystyrene | Nil |
| Well | Wax | Polystyrene | Nil | |
| Total product area | 484 mm2 (for 9 × 9 wells) | 10,920 mm2 (for 12 × 8 well) | Nil | |
| Viability assay | Cell-Titer Glo | MTT assay | DiI |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, C.-T.; Lai, Y.-S.; Lu, S.-R.; Lee, H.; Chang, H.-H. Microcrater-Arrayed Chemiluminescence Cell Chip to Boost Anti-Cancer Drug Administration in Zebrafish Tumor Xenograft Model. Biology 2022, 11, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010004
Kuo C-T, Lai Y-S, Lu S-R, Lee H, Chang H-H. Microcrater-Arrayed Chemiluminescence Cell Chip to Boost Anti-Cancer Drug Administration in Zebrafish Tumor Xenograft Model. Biology. 2022; 11(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Ching-Te, Yu-Sheng Lai, Siang-Rong Lu, Hsinyu Lee, and Hsiu-Hao Chang. 2022. "Microcrater-Arrayed Chemiluminescence Cell Chip to Boost Anti-Cancer Drug Administration in Zebrafish Tumor Xenograft Model" Biology 11, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010004
APA StyleKuo, C.-T., Lai, Y.-S., Lu, S.-R., Lee, H., & Chang, H.-H. (2022). Microcrater-Arrayed Chemiluminescence Cell Chip to Boost Anti-Cancer Drug Administration in Zebrafish Tumor Xenograft Model. Biology, 11(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010004








