Simple Summary
The lower atmospheric partial pressure of oxygen under hypobaric hypoxia decreases oxygen saturation and arteriovenous oxygen difference. Exercise under hypoxia decreases arterial oxygen saturation, which reduces the ability to deliver oxygen to active muscles and consequently worsens aerobic capacity and exercise performance. Previous studies on metabolic and cardiac responses to submaximal exercise under hypoxia have been well documented, but information on hemorheological responses is relatively insufficient. In this regard, a review of hemorheological responses to exercise under hypoxia could provide further information on reduced aerobic capacity and exercise performance caused by acute hypoxia. We conducted a randomized crossover trial to compare the effects of acute exercise under light and moderate hypobaric hypoxia versus normoxia on metabolic parameters, cardiac function, and hemorheological properties in healthy men. The main findings of our study revealed that endurance submaximal exercise under light (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m) and moderate (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m) hypoxia induced greater metabolic and cardiac responses than exercise under normoxia. However, exercise under hypobaric hypoxia did not affect hemorheological properties, including erythrocyte deformability and aggregation. These results can be used as basic data for understanding hemorheological responses in light and moderate hypobaric hypoxia.
Abstract
We compared the effects of metabolic, cardiac, and hemorheological responses to submaximal exercise under light hypoxia (LH) and moderate hypoxia (MH) versus normoxia (N). Ten healthy men (aged 21.3 ± 1.0 years) completed 30 min submaximal exercise corresponding to 60% maximal oxygen uptake at normoxia on a cycle ergometer under normoxia (760 mmHg), light hypoxia (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m altitude), and moderate hypoxia (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m altitude) after a 30 min exposure in the respective environments on different days, in a random order. Metabolic parameters (oxygen saturation (SPO2), minute ventilation, oxygen uptake, carbon dioxide excretion, respiratory exchange ratio, and blood lactate), cardiac function (heart rate (HR), stroke volume, cardiac output, and ejection fraction), and hemorheological properties (erythrocyte deformability and aggregation) were measured at rest and 5, 10, 15, and 30 min after exercise. SPO2 significantly reduced as hypoxia became more severe (MH > LH > N), and blood lactate was significantly higher in the MH than in the LH and N groups. HR significantly increased in the MH and LH groups compared to the N group. There was no significant difference in hemorheological properties, including erythrocyte deformability and aggregation. Thus, submaximal exercise under light/moderate hypoxia induced greater metabolic and cardiac responses but did not affect hemorheological properties.
1. Introduction
The Olympic Games in 1968 were held at high altitudes in Mexico City. Since then, the effects of hypoxia on exercise performance have received considerable attention [1]. Exercise training under hypoxia has been widely accepted as a useful modality for improving athletic performance, and experimental evidence has been accumulated regarding the efficacy of hypoxic training [2,3,4,5,6]. Exercise under hypoxia decreases arterial oxygen saturation, which reduces the ability to deliver oxygen to active muscles [7]. This phenomenon augments the heart rate (HR) to supply blood flow, carbohydrate substrate mobilization with high oxygen utilization efficiency, and blood lactate levels [8,9,10]. Exercise under hypoxia is also known to achieve a greater metabolic effect and cardiac stress while maintaining the same mechanical stimulus compared with exercise under normoxia [10,11]. Therefore, sustained exercise under hypoxia might be beneficial for enhancing performance, promoting metabolic adaptation in the muscle, and improving cardiac function [2,3,12,13,14]. However, the mechanisms underlying these adaptive phenomena are not clearly understood.
Exercise under hypoxia has shown an additive improving effect on vascular function and microcirculation, arterial stiffness, and blood flow within the skeletal muscle vascular beds [10,11,15]. Hypoxia improves the endothelial-derived nitric-oxide-mediated mechanism primarily involved in the vasodilation of muscular arteries, and consequently enhances the ability of the vasculature to supply the blood to the skeletal muscle, in addition to enhancing the aerobic capacity [16,17]. In addition, chronic exercise training under hypoxia positively induces the secretion of various vasodilators (e.g., adenosine, prostaglandin, and nitric oxide) and vascular endothelial growth factor, which leads to the improvement of vasodilation and microcirculation, as well as the reduction of arterial stiffness [18,19,20].
Hemorheological properties such as erythrocyte deformability and aggregation affect the oxygen delivery capacity of active skeletal muscles [21,22]. The blood flow through capillaries, which are smaller in diameter than erythrocytes and microcirculation, is accompanied by erythrocyte deformability [21]. Erythrocyte deformability is an energy-dependent process, and healthy erythrocytes with high deformability show a high correlation with oxygen-carrying capacity and aerobic capacity [21,22,23]. Erythrocyte aggregation also refers to the binding of two erythrocytes, such as one-dimensional rouleaux formation. Elevated erythrocyte aggregation is frequently observed in sedentary/overweight/obese people and those with vascular diseases and diabetes mellitus. The hyper-aggregation of erythrocytes may cause flow resistance in microcirculation and yield poor oxygen delivery and aerobic capacity [21,23,24,25]. A previous study reported that a 12-week Pilates intervention under moderate hypoxia (inspired oxygen fraction (FiO2) = 14.5%, simulated 3000 m) improved erythrocyte deformability and aggregation in women with obesity compared with a Pilates intervention under normoxia [12]. These results show that exercise under hypoxia may enhance aerobic capacity and microcirculation by improving hemorheological properties.
However, studies on hypoxia-induced hemorheological responses during exercise are limited. A review of hemorheological responses to exercise under hypoxia could provide further information on reduced aerobic capacity and exercise performance caused by acute hypoxia. Therefore, it is a valuable and important task to elucidate the relationship between hypoxia and aerobic performance by investigating the effect of hypoxia on hemorheological properties such as erythrocyte deformability and aggregation, which is one of the important determinants of oxygen-delivering capacity.
We conducted a randomized crossover trial to compare the effects of acute exercise under light and moderate hypobaric hypoxia versus normoxia on metabolic parameters, cardiac function, and hemorheological properties in healthy men. We hypothesized that endurance submaximal exercise under light and moderate hypobaric hypoxia would induce greater exercise-mediated alterations in metabolic parameters, cardiac function, and hemorheological properties than exercise under normoxia.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Ten healthy men, aged 20 to 25 years old, who were nonsmokers and had no history of musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, or pulmonary diseases (age, 21.3 ± 1.0 years; height, 176.9 ± 1.4 cm; fat-free mass, 35.5 ± 1.4 kg; fat mass, 11.3 ± 1.6 kg; percent body fat, 15.5 ± 1.6%) were recruited. They had not participated in any exercise program under hypoxic conditions in the previous 6 months. The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) flow diagram is shown in Figure 1. The participants received information about the purpose and process of this study and provided informed consent prior to the start of the study. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kyung Hee University (KHSIRB 2015-020) in Korea and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
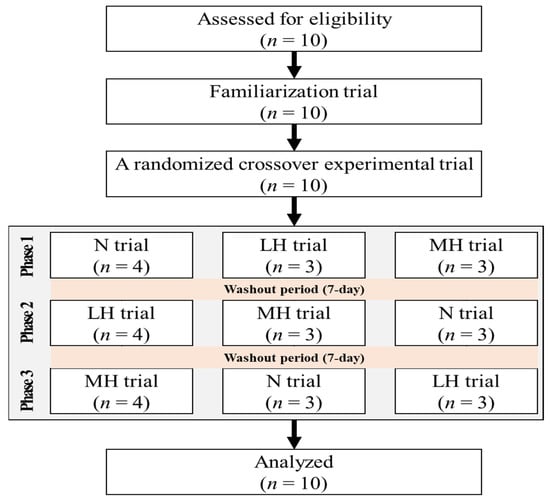
Figure 1.
The flow diagram of the consolidated standards of reporting trial. N: endurance submaximal exercise under normoxia; LH: endurance submaximal exercise under light hypoxia (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m); MH: endurance submaximal exercise under moderate hypoxia (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m).
2.2. Study Design
The design of the present study is illustrated in Figure 2. All participants visited the laboratory five times during the experimental period. During the first visit, all participants fasted for more than 8 h, and after stabilization, height and body composition were measured in the morning. Then, they performed a graded exercise test (GXT) to assess 60% maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) and determine the exercise intensity during submaximal exercise under normoxia, light hypobaric hypoxia, and moderate hypobaric hypoxia. On the second visit, they underwent a familiarization trial at sea level (760 mmHg) prior to the main trial for adaptation to the exercise program. On the third, fourth, and fifth occasions, the participants underwent randomized crossover experimental trials under normoxia (760 mmHg; N), light hypoxia (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m; LH), and moderate hypoxia (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m; MH). All participants had a washout period of at least 7 days between all trials. The order of the conditions for each experimental trial was randomized, and each participant underwent the experimental protocol at the same time at each visit. However, the participants did not undergo blinded experiments under environmental conditions.
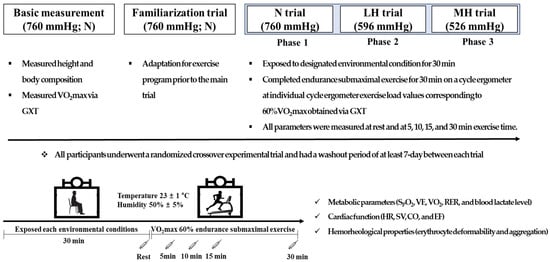
Figure 2.
Study design. N: endurance submaximal exercise under normoxia; LH: endurance submaximal exercise under light hypoxia (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m); MH: endurance submaximal exercise under moderate hypoxia (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m); VO2max: maximal oxygen uptake; GXT: graded exercise test; SpO2: oxygen saturation; VE: minute ventilation; VO2: oxygen uptake; VCO2: carbon dioxide excretion; RER: respiratory exchange ratio; HR: heart rate; SV: stroke volume; CO: cardiac output; EF: ejection fraction.
During all experimental trials, all participants were exposed to the designated environmental condition for 30 min; then, they completed endurance submaximal exercise for 30 min on a cycle ergometer (Aerobike 75XLII, Konami Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) at individual cycle ergometer exercise load values corresponding to 60% VO2max obtained via GXT. During the endurance submaximal exercise session, metabolic parameters (oxygen saturation (SpO2), minute ventilation (VE), oxygen uptake (VO2), carbon dioxide excretion (VCO2), respiratory exchange ratio (RER), and blood lactate level), cardiac function (HR, stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and ejection fraction (EF)), and hemorheological properties (erythrocyte deformability and aggregation) were measured at rest and at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min.
All experiments were performed in a 6.5 × 7.5 × 3 m (width × length × height) environmental chamber (Submersible Systems, Huntington Beach, CA, USA) at a temperature of 23 ± 1 °C and humidity of 50 ± 5% regulated by an environmental control chamber.
2.3. Measurement
Body composition (i.e., height, weight, fat-free mass, and percentage body fat) was measured after fasting for more than 8 h using a bioelectrical impedance analysis device (Inbody 770; Inbody, Seoul, Korea).
Metabolic parameters (e.g., SPO2, VE, VO2, VCO2, RER, and blood lactate level) were measured at rest and at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min of exercise time. The SPO2 was measured using a Radical-7 pulse oximeter (Masimo, Irvine, CA, USA). VE, VO2, VCO2, and RER were measured using the K4B2 auto metabolism analyzer (Cosmed, Rome, Italy) and a breathing valve in the form of a facemask during the 30 min endurance submaximal exercise. Blood lactate levels were analyzed using a YSI-1500 lactate analyzer (YSI Inc., Yellow Springs, OH, USA).
Cardiac functions, including HR, SV, CO, and EF, were noninvasively assessed at rest and at 5, 10, 15, and 30 min of exercise time using a thoracic bioelectrical impedance device (PhysioFlow PF-05, Paris, France) during the 30 min endurance submaximal exercise.
Hemorheological properties, erythrocyte deformability, and aggregation were analyzed as suggested in previous studies [21,24]. A 20G catheter (Sewoonmedical Co., Ltd., Cheonan-si, Chungcheongnam-do, Korea) was inserted in the forearm vein and connected using a three-way extension line (Sewoonmedical Co., Ltd., Cheonan-si, Chungcheongnam-do, Korea). The blood (6 mL) was collected in two K3-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) tubes (Greiner Bio-One Ltd., Chon Buri, Thailand) at rest and during exercise (5, 10, 15, and 30 min). We refrained from using a tourniquet as much as possible because the use of a tourniquet during venous blood sampling can decrease erythrocyte deformability and increase erythrocyte aggregation [25]. However, if necessary, the use of a tourniquet was limited to 5 s. All blood samples were analyzed within 3 h of collection at room temperature (25 °C) using a Rheoscan-D (Rheo Meditech Inc., Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea) [12,21]. Erythrocyte deformability was evaluated using the elongation index (EI) by the following process: after transferring the sample to a 2 mL microfuge tube, it was diluted in 700 μL of 5.5% polyvinylpyrrolidone (360 kDa) dissolved in 1 mmol phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4; osmolality: 300 mOsmol/kg) in a K3-EDTA tube (Greiner Bio-one, Chon Nuri, Thailand). Thereafter, this solution (0.5 mL) was analyzed using a D-test kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Rheo Meditech Inc., Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea). The accuracy of erythrocyte EI was measured using a Lineweaver–Burk plot model [21,24]. Erythrocyte aggregation was evaluated using the aggregation index (AI) by the following process: 8 μL of the whole-blood sample was analyzed using an A-test kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Rheo Meditech Inc., Seongbuk-gu, Seoul, Korea) [12,21].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 25.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) for Windows. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. To determine the sample size, we focused on identifying meaningful differences in SPO2 during submaximal exercise, as previously suggested [26]. An a priori power analysis, which was performed using G-power, indicated that a minimum sample size of 8 participants would be required to provide 80% power at an α-level of 0.05. Anticipating a dropout rate > 10%, we aimed for a starting sample size of 10 participants. The normality of the distribution of all outcome variables was verified using the Shapiro–Wilk W-test prior to parametric tests. A two-way analysis (trial × time) of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measures was used to assess the presence of interactions (trial × time) and main effects (trial or time). When ANOVA revealed a significant interaction or main effect within the trial, a Bonferroni post-hoc test was used to identify within-trial differences at each time point. The level of significance was set a priori at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Metabolic Parameters
As shown in Figure 3, there was no significant interaction between VE, VO2, VCO2, and RER; however, SPO2 (p = 0.008, η2 = 0.213) and blood lactate level (p < 0.001, η2 = 0.529) showed a significant interaction. Post-hoc analysis indicated the significant reduction in SPO2 as the hypoxia became more severe in the order of MH > LH > N (main effect for trial, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.883); blood lactate levels were significantly higher in the MH group than in LH and N groups (main effect for trial, p < 0.001, η2 = 0.700).
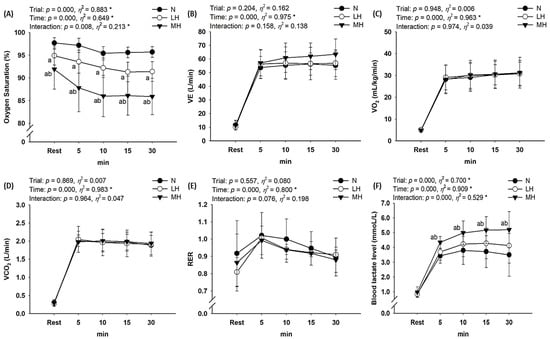
Figure 3.
Changes in metabolic parameters at rest and during endurance submaximal exercise. (A) SPO2, (B) VE, (C) VO2, (D) VCO2, (E) RER, (F) blood lactate level. SPO2: oxygen saturation; VE: minute ventilation; VO2: oxygen uptake; VCO2: carbon dioxide excretion; RER: respiratory exchange ratio; N: endurance submaximal exercise under normoxia; LH: endurance submaximal exercise under light hypoxia (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m); MH: endurance submaximal exercise under moderate hypoxia (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m). The bars indicate the mean ± S.D. *: Significant interaction or main effect; a: significant difference vs. normoxia; b: significant difference vs. light hypoxia.
3.2. Cardiac Function
Figure 4 presents the cardiac function results during submaximal exercise between different groups. No significant interaction was observed between SV, CO, and EF; however, HR showed a significant interaction (p < 0.001, η2 = 0.529). Post-hoc analysis indicated that HR was significantly higher for MH and LH groups than for the N group (main effect for trial, p = 0.029, η2 = 0.326). In addition, CO showed an increased tendency in the MH group compared with N and LH groups (p = 0.054, η2 = 0.277).
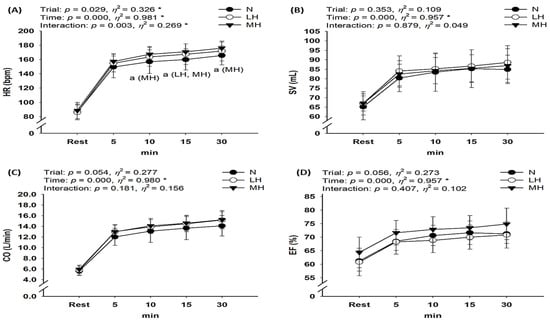
Figure 4.
Changes in the cardiac function at rest and during endurance submaximal exercise. (A) HR, (B) SV, (C) CO, (D) EF. HR: heart rate; SV: stroke volume; CO: cardiac output; EF: ejection fraction; N: endurance submaximal exercise under normoxia; LH: endurance submaximal exercise under light hypoxia (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m); MH: endurance submaximal exercise under moderate hypoxia (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m). The bars indicate the mean ± S.D. *: Significant interaction or main effect; a: significant difference vs. normoxia.
3.3. Hemorheological Properties
As shown in Figure 5, there was no significant interaction with erythrocyte aggregation; however, erythrocyte deformability showed a significant interaction (p = 0.008, η2 = 0.189). Post-hoc analysis indicated no significant difference in erythrocyte deformability between the groups (main effect for trial, p = 0.071, η2 = 0.255).
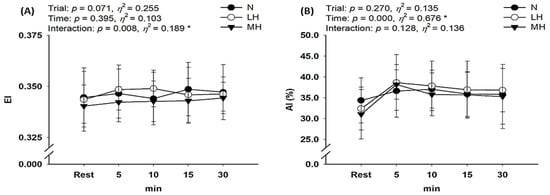
Figure 5.
Changes in hemorheological properties at rest and during endurance submaximal exercise. (A) Erythrocyte deformability (EI) and (B) Erythrocyte aggregation (AI). EI: elongation index; AI: aggregation index; N: endurance submaximal exercise under normoxia; LH: endurance submaximal exercise under light hypoxia (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m); MH: endurance submaximal exercise under moderate hypoxia (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m). The bars indicate the mean ± S.D. *: Significant interaction or main effect.
4. Discussion
According to our hypothesis, endurance submaximal exercise under light and moderate hypobaric hypoxia induces greater responses in some metabolic parameters (e.g., SPO2 and blood lactate level) and cardiac function (e.g., HR) than exercise under normoxia. However, there were no significant changes in VE, VO2, VCO2, RER, SV, CO, or EF between LH or MH groups and the N group. In addition, exercise under hypoxia did not affect hemorheological properties, including erythrocyte deformability and aggregation, compared with exercise under normoxia.
The lower atmospheric partial pressure of oxygen under hypobaric hypoxia decreases SpO2 and the arteriovenous oxygen difference and worsens the aerobic capacity and exercise performance [1,7,21,26]. Hypoxia also reduces oxygen availability in active muscles owing to reduction in the oxygen delivery capacity of the blood, resulting in decreased VO2 during endurance submaximal exercise at the same relative intensity (same mechanical load), as well as a decrease in VO2max [26,27]. In the present study, we confirmed the significant decrease in SpO2 as hypoxia became more severe (MH > LH > N). However, we did not observe any significant differences in VO2 during endurance submaximal exercise between all environmental conditions. It is likely that the energy consumption was the same because the mechanical load was similar during endurance submaximal exercise under all environmental conditions [28,29,30]. Several previous studies have reported no significant differences in VO2 during submaximal exercise at the same mechanical load between normoxia and hypoxia. There was no difference in VO2 during submaximal exercise between normoxia and hypoxia conditions, which may be explained by changes in cardiac function, especially the increase in HR and CO in response to reduced oxygen availability in active muscles following reduction in the oxygen delivery capacity of the blood [7,10,26]. Moon et al. [26] evaluated the effects of hypoxia (FiO2 = 16.5%, 14.5%, 12.8%, and 11.2%) versus normoxia (FiO2 = 20.9%) on metabolic parameters and cardiac function during constant load (116.7 ± 20.1 watts and 60 rpm, 70% maximal HR under normoxia) submaximal bicycle exercise. These authors reported that submaximal exercise under hypoxia (FiO2 = 14.5% and below) might be associated with an increase in blood lactate level, VE, HR, EF, and CO. These changes are an acute compensation response to reduced aerobic capacity owing to decreased oxygen delivery and utilization capacity under hypoxia. Regarding cardiac function, our study showed that HR was significantly higher in MH and LH groups than in the N group. This result is consistent with previous studies reporting that hypoxia reduces the ability to deliver and utilize oxygen to active muscles, but cardiac stress such as increase in HR raises the energy requirement during submaximal exercise with the same workload [7,10,26,28,29,30]. Unlike previous studies, the present study did not show changes in CO or EF during endurance submaximal exercise between environmental conditions. Considering that Moon et al. [26] observed higher CO and EF under severe hypoxia than under normoxia, no difference in CO and EF between LH, MH, and N conditions is considered a reasonable finding. However, considering that CO showed an increased tendency in the MH group compared to the N and LH groups in the present study, if the sample size was larger, it is considered that the statistical significance of CO would have been reached in response to reduced oxygen availability in active muscles following reduction in the oxygen-delivery capacity of the blood under hypoxia, as in most previous studies [7,10,26].
In addition, our study shows that blood lactate levels significantly increased in the MH group compared to the LH and N groups. Acute exposure to hypoxia results in sympathetic activation that raises blood epinephrine [31,32] and consequently lactate turnover in resting men and those engaged in submaximal exercises at given exercise power outputs [32,33]. Hypoxia also decreases metabolic and cardiac functions, which may increase the dependence on glycolysis—that is, anaerobic energy metabolism. This phenomenon induces an increase in VE, VCO2, RER, and blood lactate levels during exercise [26,34]. Endurance exercise under hypoxia decreases SpO2, resulting in an increase in the energy supply via the glycolytic system and consequently augmenting the blood lactate level in the active muscle [7,8,9]. In addition, the increase in VE during endurance exercise is indicative of an acid–base response by the bicarbonate buffer system that also occurs with an increase in blood lactate level [7,8,9]. Lühker et al. [35] investigated acid–base response differences during endurance exercise under normoxia and severe hypoxia (FiO2 = 12%, simulated 4500 m), and reported that severe hypoxia significantly decreased the pH and increased blood lactate levels during endurance submaximal exercise compared with normoxia. On the other hand, Sumi et al. [8] confirmed the effects of acid–base response differences on high-intensity interval exercise under moderate hypoxia (14.5% FiO2, simulated 3000 m) and normoxia in endurance athletes. These authors reported that high-intensity interval exercise under moderate hypoxia induced an increase in the blood pH, bicarbonate, and lactate levels compared with an equivalent level of exercise under normoxia. Although the acid–base response was not examined in our study, there was no significant difference in VE, VCO2, or RER between LH, MH, and N conditions. The discrepancy between previous studies is thought to be associated with the differences in hypoxic conditions, exercise type, and exercise intensity. Our results are considered reasonable because hypoxia the was not severe (more than simulated 4000 m) but light (simulated 2000 m) and moderate (simulated 3000 m), and the exercise type was not high-intensity interval exercise.
Hemorheological properties can help evaluate the oxygen delivery and utilization capacity in various subjects, for different exercise methods and exercise intensities, and between sexes [23,36,37,38]. In particular, hemorheological properties, including erythrocyte deformability and aggregation, are very important parameters because they are related to the surrounding microcirculation tissue and facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide [22]. In their study related to hypoxia and hemorheological properties, Grau et al. [39] investigated the impact of mild-to-severe hypoxia on human erythrocyte-nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-dependent nitric oxide production, protein S-nitrosylation, and deformability. These authors reported that the activation of erythrocyte-NOS decreased under mild hypoxia with an increase in hypoxia and erythrocyte deformability, which is influenced by erythrocyte-NOS activation, but surprisingly increased under severe hypoxia in vivo and in vitro. Moon et al. [21] reported that erythrocyte deformability was more reduced in healthy men under severe hypoxia (12.8% FiO2, simulated 4000 m and 11.2% FiO2, simulated 5000 m) than under normoxia, and was associated with a decrease in SpO2 concomitant with a compensatory increase in HR and a decrease in aerobic capacity, as reflected by an increase in blood lactate level. In addition, Lin et al. [40] confirmed that an acute bout of exercise under severe hypoxia (FiO2 = 12%, simulated 4500 m) increases erythrocyte aggregation and facilitates erythrocyte senescence in sedentary men. As such, most of the previous studies showed a decrease in erythrocyte deformability and an increase in erythrocyte aggregation during exercise under hypoxia compared to under normoxia, and these responses were confirmed to be prominent during exercise under severe hypoxia. Our study showed no significant differences between all trials in terms of erythrocyte deformability and aggregation. In the future, we believe that it is necessary to investigate erythrocyte deformability and aggregation under various conditions because the hemorheological properties are also greatly affected by hypoxic conditions, exercise type, exercise intensity, and exercise time.
5. Conclusions
The present study demonstrates that in comparison with endurance submaximal exercise under normoxia, endurance submaximal exercise under light (596 mmHg, simulated 2000 m) and moderate (526 mmHg, simulated 3000 m) hypobaric hypoxia induced greater metabolic (e.g., SPO2 and blood lactate level) and cardiac responses (e.g., HR). However, exercise under hypobaric hypoxia did not affect hemorheological properties, including erythrocyte deformability and aggregation, compared to exercise under normoxia.
Author Contributions
Study conception and design, H.-Y.P., J.-W.K. and S.-S.N.; data curation, H.-Y.P., J.-W.K. and S.-S.N.; formal analysis, H.-Y.P., J.-W.K. and S.-S.N.; investigation, H.-Y.P., J.-W.K. and S.-S.N.; methodology, H.-Y.P., J.-W.K. and S.-S.N.; writing—original draft, H.-Y.P.; writing—review and editing, H.-Y.P. and S.-S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kyung Hee University (KHSIRB 2015-020) in Korea and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the KU Research Professor Program of Konkuk University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kasperowski, D. Constructing altitude training standards for the 1968 Mexico Olympics: The impact of ideals of equality and uncertainty. Int. J. Hist. Sport 2009, 26, 1263–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feriche, B.; García-Ramos, A.; Morales-Artacho, A.J.; Padial, P. Resistance training using different hypoxic training strategies: A basis for hypertrophy and muscle power development. Sports Med. Open 2017, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czuba, M.; Wilk, R.; Karpiński, J.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Zajac, A.; Langfort, J. Intermittent hypoxic training improves anaerobic performance in competitive swimmers when implemented into a direct competition mesocycle. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocherie, F.; Girard, O.; Faiss, R.; Millet, G.P. Effects of repeated-sprint training in hypoxia on sea-level performance: A meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinex, J.A.; Chapman, R.F. Hypoxic training methods for improving endurance exercise performance. J. Sport Health Sci. 2015, 4, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiss, R.; Girard, O.; Millet, G.P. Advancing hypoxic training in team sports: From intermittent hypoxic training to repeated sprint training in hypoxia. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, i45–i50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.-S.; Park, H.-Y. Effects of endurance exercise under hypoxia on acid-base and ion balance in healthy males. Phys. Act. Nutr. 2020, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, D.; Kojima, C.; Kasai, N.; Goto, K. The effects of endurance exercise in hypoxia on acid-base balance and potassium kinetics: A randomized crossover design in male endurance athletes. Sports Med. Open 2018, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, D.; Kasai, N.; Ito, H.; Goto, K. The effects of endurance exercise in hypoxia on acid-base balance, potassium kinetics, and exogenous glucose oxidation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Seo, J.; Jung, W.-S.; Kim, J.; Park, H.-Y.; Lim, K. Effects of an acute Pilates program under hypoxic conditions on vascular endothelial function in Pilates participants: A randomized crossover trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, O.; Malatesta, D.; Millet, G.P. Walking in hypoxia: An efficient treatment to lessen mechanical constraints and improve health in obese individuals? Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Kim, J.; Park, H.-Y.; Jung, W.-S.; Lim, K. Hypoxic Pilates intervention for obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serebrovska, T.V.; Serebrovska, Z.O.; Egorov, E. Fitness and therapeutic potential of intermittent hypoxia training: A matter of dose. Fiziol. Zh. 2016, 62, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verges, S.; Chacaroun, S.; Godin-Ribuot, D.; Baillieul, S. Hypoxic conditioning as a new therapeutic modality. Front. Pediatr. 2015, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacaroun, S.; Borowik, A.; Vega-Escamilla, Y.G.I.; Doutreleau, S.; Wuyam, B.; Belaidi, E.; Tamisier, R.; Pepin, J.L.; Flore, P.; Verges, S. Hypoxic exercise training to improve exercise capacity in obese individuals. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, L.; Passino, C.; Serebrovskaya, Z.; Serebrovskaya, T.; Appenzeller, O. Respiratory and cardiovascular adaptations to progressive hypoxia. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serebrovskaya, T.V.; Manukhina, E.B.; Smith, M.L.; Downey, H.F.; Mallet, R.T. Intermittent hypoxia: Cause of or therapy for systemic hypertension? Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 627–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, G.P.; Debevec, T.; Brocherie, F.; Malatesta, D.; Girard, O. Therapeutic use of exercising in hypoxia: Promises and limitations. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuenberger, U.A.; Gray, K.; Herr, M.D. Adenosine contributes to hypoxia-induced forearm vasodilation in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, E.; Sun, D.; Koller, A.; Wolin, M.; Kaley, G. Role of endothelium-derived prostaglandins in hypoxia-elicited arteriolar dilation in rat skeletal muscle. Circ. Res. 1992, 71, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.-W.; Shin, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Park, H.-Y.; Sunoo, S.; Nam, S.-S. Effects of various acute hypoxic conditions on the hemorheological response during exercise and recovery 1. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2016, 63, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bor-Kucukatay, M.; Colak, R.; Erken, G.; Kilic-Toprak, E.; Kucukatay, V. Altitude training induced alterations in erythrocyte rheological properties: A controlled comparison study in rats. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2014, 58, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connes, P.; Tripette, J.; Mukisi-Mukaza, M.; Baskurt, O.K.; Toth, K.; Meiselman, H.J.; Hue, O.; Antoine-Jonville, S. Relationships between hemodynamic, hemorheological and metabolic responses during exercise. Biorheology 2009, 46, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskurt, O.; Boynard, M.; Cokelet, G.; Connes, P.; Cooke, B.M.; Forconi, S.; Liao, F.; Hardeman, M.; Jung, F.; Meiselman, H. New guidelines for hemorheological laboratory techniques. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2009, 42, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cengiz, M.; Ulker, P.; Meiselman, H.J.; Baskurt, O.K. Influence of tourniquet application on venous blood sampling for serum chemistry, hematological parameters, leukocyte activation and erythrocyte mechanical properties. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.-W.; Sunoo, S.; Park, H.-Y.; Lee, D.-J.; Nam, S.-S. Effects of various acute hypoxic conditions on metabolic parameters and cardiac function during exercise and recovery. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrlin, J.P.; Hallén, J. Linear decrease in. VO2max and performance with increasing altitude in endurance athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 96, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.; Stacey, M.; Woods, D. Energy at high altitude. J. R. Army Med. Corps 2011, 157, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, R.S. Physiological responses to exercise at altitude. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbet, J.; Boushel, R.; Rådegran, G.; Søndergaard, H.; Wagner, P.D.; Saltin, B. Determinants of maximal oxygen uptake in severe acute hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R291–R303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, R.S.; Brooks, G.A.; Butterfield, G.E.; Podolin, D.A.; Wolfel, E.E.; Reeves, J.T. Acclimatization to high altitude increase muscle sympathetic activity both at rest and during exercise. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, R201–R207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A. The science and translation of lactate shuttle theory. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 757–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, G.A.; Wolfel, E.E.; Butterfield, G.E.; Cymerman, A.; Roberts, A.C.; Mazzeo, R.S.; Reeves, J.T. Poor relationship between arterial [lactate] and leg net release during exercise at 4,300 m altitude. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, R1192–R1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofner, M.; Wonisch, M.; Frei, M.; Tschakert, G.; Domej, W.; Kröpfl, J.M.; Hofmann, P. Influence of acute normobaric hypoxia on physiological variables and lactate turn point determination in trained men. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2014, 13, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lühker, O.; Berger, M.M.; Pohlmann, A.; Hotz, L.; Gruhlke, T.; Hochreiter, M. Changes in acid-base and ion balance during exercise in normoxia and normobaric hypoxia. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connes, P.; Caillaud, C.; Py, G.; Mercier, J.; Hue, O.; Brun, J.-F. Maximal exercise and lactate do not change red blood cell aggregation in well trained athletes. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2007, 36, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Muravyov, A.; Draygin, S.; Eremin, N.; Muravyov, A. The microrheological behavior of young and old red blood cells in athletes. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2002, 26, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcin, O.; Erman, A.; Muratli, S.; Bor-Kucukatay, M.; Baskurt, O.K. Time course of hemorheological alterations after heavy anaerobic exercise in untrained human subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, M.; Lauten, A.; Hoeppener, S.; Goebel, B.; Brenig, J.; Jung, C.; Bloch, W.; Suhr, F. Regulation of red blood cell deformability is independent of red blood cell-nitric oxide synthase under hypoxia. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2016, 63, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-L.; Wang, J.-S.; Fu, T.-C.; Hsu, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-C. Hypoxic exercise training elevates erythrocyte aggregation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).