Experimental Injury Rodent Models for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Normal and Abnormal Swallowing
1.2. Injury Animal Models for Dysphagia Studies
2. Methods
3. Results
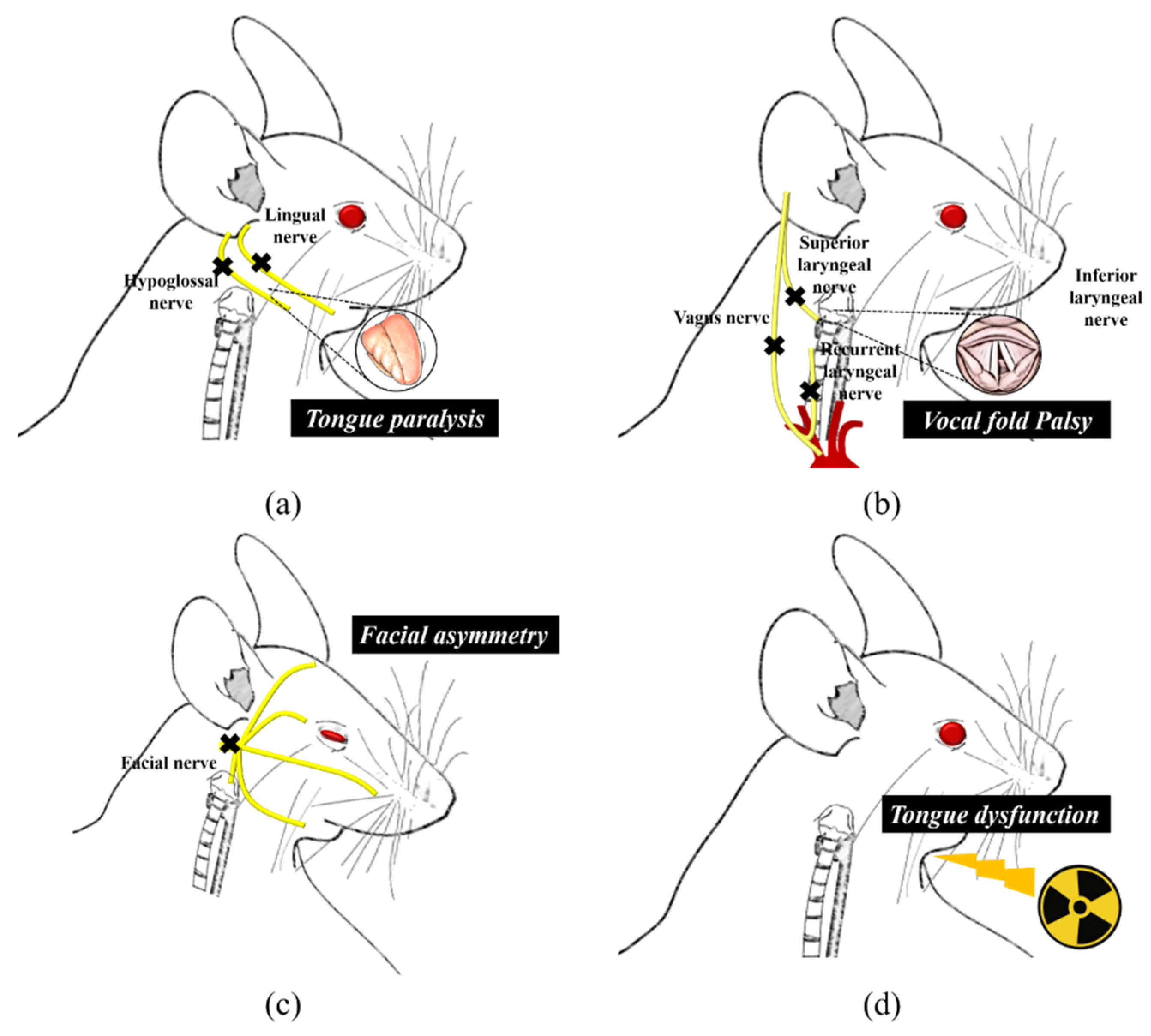
3.1. Lingual and Facial Muscles Injury
3.2. Laryngeal Injury
3.3. Radiation Injury
3.4. Others
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuo, K.; Palmer, J.B. Anatomy and Physiology of Feeding and Swallowing: Normal and Abnormal. Phys. Med. Reh. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 19, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clave, P.; Shaker, R. Dysphagia: Current reality and scope of the problem. Nat. Rev. Gastro Hepat 2015, 12, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, A. Brain stem control of swallowing: Neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 929–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, K.; Kitagawa, J.; Kurose, M.; Sugino, S.; Takatsuji, H.; Mostafeezur, R.M.; Zakir, H.M.; Yamada, Y. Neural Mechanisms of Swallowing and Effects of Taste and Other Stimuli on Swallow Initiation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfarland, D.H.; Lund, J.P. Modification of Mastication and Respiration during Swallowing in the Adult Human. J. Neurophysiol. 1995, 74, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Hiraga, K. Coordination of Swallowing and Respiration in Unconscious Subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 70, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Honda, Y. Effects of swallowing on the pattern of continuous respiration in human adults. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 132, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Magara, J.; Sakai, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Inoue, M. Changes in the frequency of swallowing during electrical stimulation of superior laryngeal nerve in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 111, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimura, T.; Tsuji, K.; Ariyasinghe, S.; Fukuhara, T.; Yamada, A.; Hayashi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Iwata, K.; Inoue, M. Differential involvement of two cortical masticatory areas in modulation of the swallowing reflex in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 528, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, A.R.; Pujara, M.S.; Petrides, M.; Murray, E.A.; Fellows, L.K. Lesion Studies in Contemporary Neuroscience. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.Z.; Crompton, A.W.; Gould, F.D.; Thexton, A.J. Animal Models for Dysphagia Studies: What Have We Learnt So Far. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desombres, A.C.; Duclos, C.; Ghannouchi, I.; Marie, J.P.; Verin, E. Effect of liquid properties on swallowing and ventilation coordination in rats. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouahchi, Y.; Marie, J.P.; Verin, E. Effect of lingual paralysis on swallowing and breathing coordination in rats. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2012, 181, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, E.J., 3rd; Gratton, M.A.; Varvares, M.A. Impact of Sensory and Motor Defects on Oral Function in an Animal Model. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 155, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welby, L.; Ukatu, C.C.; Thombs, L.; Lever, T.E. A Mouse Model of Dysphagia after Facial Nerve Injury. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, A.; Allen, J.; Haney, M.M.; Deninger, I.; Ballenger, B.; Caywood, V.; Osman, K.L.; Zitsch, B.; Hopewell, B.L.; Thiessen, A.; et al. A Surgical Mouse Model for Advancing Laryngeal Nerve Regeneration Strategies. Dysphagia 2020, 35, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, T.; Sakai, K.; Watanabe, J.; Katagiri, W.; Hibi, H. Dental pulp-derived stem cell conditioned medium to regenerate peripheral nerves in a novel animal model of dysphagia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouahchi, Y.; Bon-Mardion, N.; Marie, J.P.; Verin, E. Involvement of the aero-digestive tract in swallowing-ventilation coordination: An animal study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, e136–e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouahchi, Y.; Duclos, C.; Marie, J.P.; Verin, E. Implication of the vagus nerve in breathing pattern during sequential swallowing in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 179, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouahchi, Y.; Letelier, C.; Bon-Mardion, N.; Marie, J.P.; Tardif, C.; Verin, E. Effects of chronic aspirations on breathing pattern and ventilatory drive in vagatomized rats. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2011, 176, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, P.A.; Ruiz, R.; Verma, A.; Dion, G.R.; Oh, P.; Wang, B.; Ahmed, O.H.; Hiwatashi, N.; Bing, R.; Victor, K.; et al. The effects of concurrent chemoradiation therapy to the base of tongue in a preclinical model. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, S.N.; Fletcher, B.; Kimbel, B.; Bonomo, N.; Pitts, T. Adaptations to Oral and Pharyngeal Swallowing Function Induced by Injury to the Mylohyoid Muscle. Dysphagia 2020, 35, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.A.; Connor, N.P. Effects of age and radiation treatment on function of extrinsic tongue muscles. Radiat. Oncol. (Lond. Engl.) 2014, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holson, R.R.; Adams, J.; Ferguson, S.A.; Scalzo, F.M. Retinoic acid exposure on gestational days 11 to 13 impairs swallowing in rat offspring. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2000, 22, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.L.; Bohnsack, B.L. What’s retinoic acid got to do with it? Retinoic acid regulation of the neural crest in craniofacial and ocular development. Genesis 2019, 57, e23308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foecking, E.M.; Fargo, K.N.; Coughlin, L.M.; Kim, J.T.; Marzo, S.J.; Jones, K.J. Single session of brief electrical stimulation immediately following crush injury enhances functional recovery of rat facial nerve. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2012, 49, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odebode, T.O.; Ologe, F.E. Facial nerve palsy after head injury: Case incidence, causes, clinical profile and outcome. J. Trauma 2006, 61, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.M.; Wang, R.; Kwartowitz, G. Unilateral Vocal Fold Paralysis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salik, I.; Winters, R. Bilateral Vocal Cord Paralysis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.A.; Santeerapharp, A.; Alnouri, G.; Park, J.; Sataloff, R.T.; Franco, R.A., Jr. The Poor Validity of Asymmetric Laryngoscopic Findings in Predicting Laterality in Vocal Fold Paresis. J. Voice Off. J. Voice Found. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Xu, W.; Cheng, L. The Causes and Laryngeal Electromyography Characteristics of Unilateral Vocal Fold Paralysis. J. Voice Off. J. Voice Found. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logemann, J.A.; Pauloski, B.R.; Rademaker, A.W.; Lazarus, C.L.; Gaziano, J.; Stachowiak, L.; Newman, L.; MacCracken, E.; Santa, D.; Mittal, B. Swallowing disorders in the first year after radiation and chemoradiation. Head Neck J. Sci. Spec. 2008, 30, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polizzotti, B.D.; Ganapathy, B.; Haubner, B.J.; Penninger, J.M.; Kuhn, B. A cryoinjury model in neonatal mice for cardiac translational and regeneration research. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bos, E.J.; Mees, B.M.E.; de Waard, M.C.; de Crom, R.; Duncker, D.J. A novel model of cryoinjury-induced myocardial infarction in the mouse: A comparison with coronary artery ligation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart C 2005, 289, H1291–H1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, L.; Moretti, A.I.S.; Abrahao, T.B.; de Souza, H.P.; Hamblin, M.R.; Parizotto, N.A. Low-level laser therapy (808 nm) contributes to muscle regeneration and prevents fibrosis in rat tibialis anterior muscle after cryolesion. Laser. Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neel, H.B., 3rd; Farrell, K.H.; DeSanto, L.W.; Payne, W.S.; Sanderson, D.R. Cryosurgery of respiratory structures. I. Cryonecrosis of trachea and bronchus. Laryngoscope 1973, 83, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somogyi, G.T.; Yokoyama, T.; Szell, E.A.; Smith, C.P.; de Groat, W.C.; Huard, J.; Chancellor, M.B. Effect of cryoinjury on the contractile parameters of bladder strips: A model of impaired detrusor contractility. Brain Res. Bull. 2002, 59, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Injury | Author (Year) | Animal/Sex, Age or BW | Method Inducing Dysphagia | Main Damage | Dysphagia Screening | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation | Result | |||||
| Hypoglossal nerve injury | Desombreset al. (2017) [12] | Rat/male, 250–374 g | Unilateral section of the hypoglossal nerve | Unilateral lingual paralysis |
|
|
| Ouahchi et al. (2012) [13] | Rat/male, 250–350 g | Unilateral section of the hypoglossal nerve | Lingual motor deficits |
|
| |
| Doyleet al. (2016) [14] | Rat/male, 250–350 g | Transection of the hypoglossal nerve or hypoglossal and lingual nerve. | A combined functional impact on swallowing of tongue sensory (lingual n.) and motor (hypoglossal n.) loss |
|
| |
| Facial nerve injury | Welby et al. (2020) [15] | Mouse/male and female, 6–12 months old | Transection of the main trunk of the facial nerve | Facial asymmetry, synkinesis, ocular sequelae, dysphagia |
|
|
| Injury | Author (Year) | Animal/Sex, Age or BW | Method Inducing Dysphagia | Main Damage | Dysphagia Screening | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation | Result | |||||
| RLN or SLN or ILN injury | Mok et al. (2019) [16] | Mouse/male and female, 3–12 months old | RNL transection (unilateral and bilateral), SLN transection (unilateral and bilateral) | Ipsilateral VF immobility, dysphagia, dysphonia, dyspnea |
|
|
| Tsuruta et al. (2018) [17] | Rat/male, 300–330 g, 9–10 weeks old | Bilateral SLN injury using a vascular clip | Swallowing difficulty |
|
| |
| Ouahchi et al. (2011) [18] | Rat/male and female 2–3 months, 290–350 g | Unilateral laryngeal paralysis: 1) sectioning of right ILN, 2) 5% lidocaine given orally | (1) Right unilateral vocal cord paralysis, (2) oropharyngeal anesthesia |
|
| |
| Unilateral cervical vagotomy | Ouahchi et al. (2017) [19] | Rat/male, 7–11 weeks old, 260–400 g | A right or left cervical vagotomy under the SLN and above the ILN | A right or left laryngeal paralysis |
|
|
| Ouahchi et al. (2011) [20] | Rats/male, 2–3 months old, 290–350 g | A unilateral vagotomy above the ILN and under the SLN | Bronchial aspirations, unilateral vocal cord paralysis |
|
| |
| Injury | Author (Year) | Animal/Sex, Age or BW | Method Inducing Dysphagia | Main Damage | Dysphagia Screening | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation | Result | |||||
| Radiation injury | Benedict et al. (2018) [21] | Rat/male, adult | CCRT to head and neck | Tongue dysfunction |
|
|
| King et al. (2020) [22] | Rat/male, 8.5–9 months old, 450–500 g | Bilateral cyroinjuries to the belly of the mylohyoid muscle | Prominent inflammation and necrosis, fibrosis |
|
| |
| Russell and Connor (2014) [23] | Rat/male, 9 and 32 months | Delivery of two fractions of 11 Gy | Radiation injury to tongue muscle |
|
| |
| Injury | Author (Year) | Animal/Sex, Age or BW | Method Inducing Dysphagia | Main Damage | Dysphagia Screening | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation | Result | |||||
| Gestational retinoid exposure | Holson et al. (2000) [24] | Rat/pups | Gestational exposure to all-trans-retinoic acid daily on GDs 11 through to 13 | Impairment in swallowing |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-Y. Experimental Injury Rodent Models for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Biology 2021, 10, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050360
Kim J-Y. Experimental Injury Rodent Models for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Biology. 2021; 10(5):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050360
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ji-Youn. 2021. "Experimental Injury Rodent Models for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia" Biology 10, no. 5: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050360
APA StyleKim, J.-Y. (2021). Experimental Injury Rodent Models for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. Biology, 10(5), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050360






