The Effect of Stabilization Conditions on Fibers from Polylactic Acid and Their Properties
Abstract
Highlights
- Additional thermal stabilization, discontinuously included in the fiber preparation, was applied in various ways to PLA fibers to improve their properties for textile applications. We monitored changes in mechanical and thermomechanical properties as well as thermal behavior;
- Under the monitored stabilization conditions, shrinkage was reduced, especially at higher stabilized temperatures above 85 °C.
- Stabilization conditions influenced the results achieved, both the stabilization medium and the stabilization temperature. Therefore, their selection depends on the potential use of PLA fibers;
- The stabilization in the air under strain showed the smallest dimensional deformation;
- The thermal stabilization of PLA fibers can improve the next process of textile processing as knitting and weaving.
Abstract
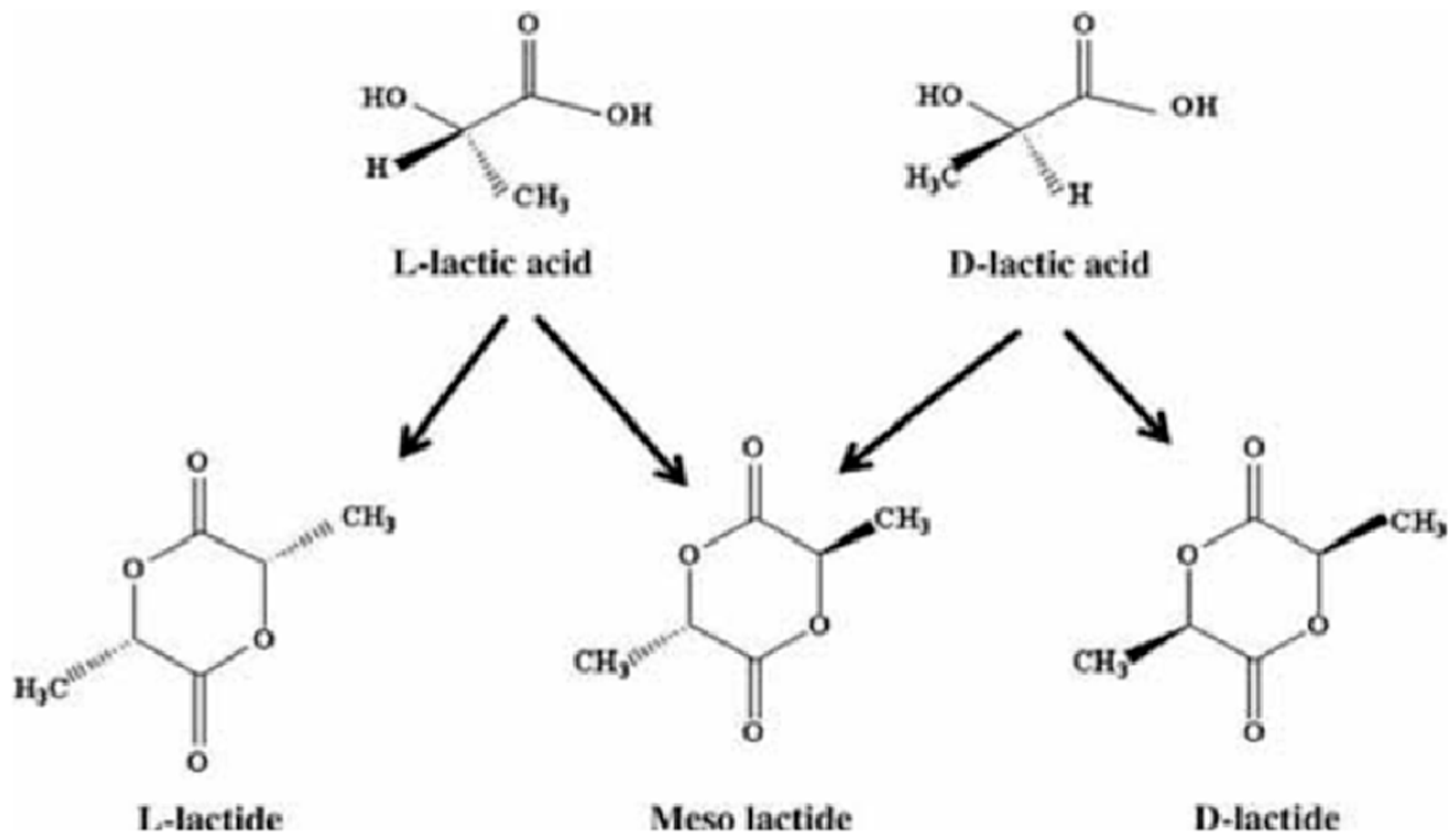
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Preparation of Polylactic Acid Fibers
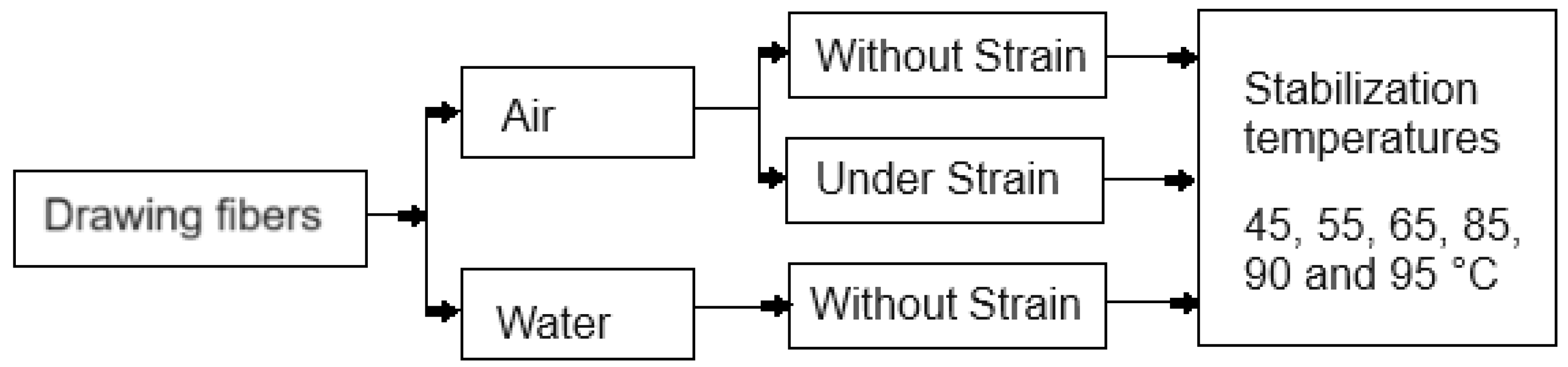
2.2. Process of Stabilization of PLA Fibers
2.3. Methods
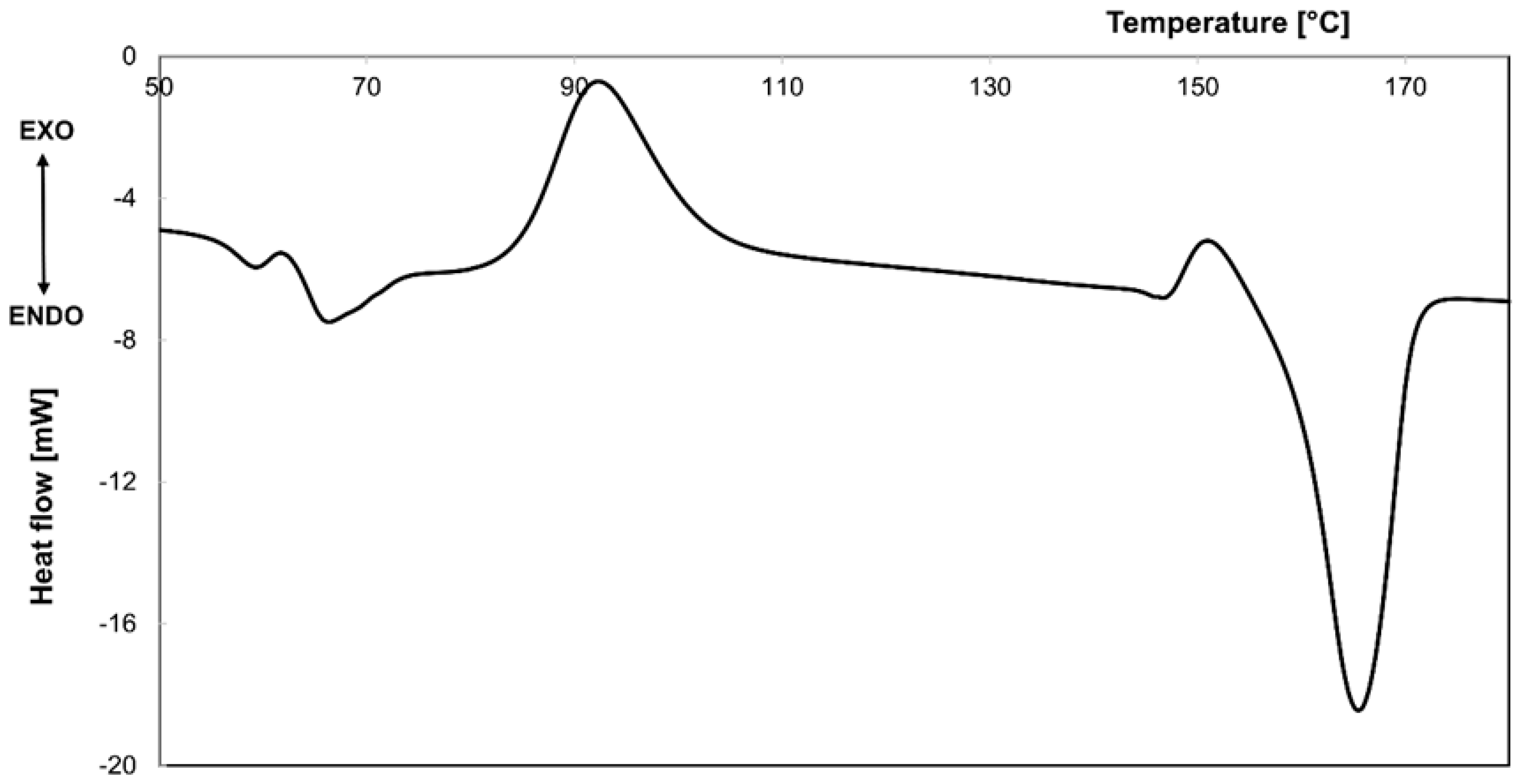
2.3.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetric
2.3.2. Mechanical Properties
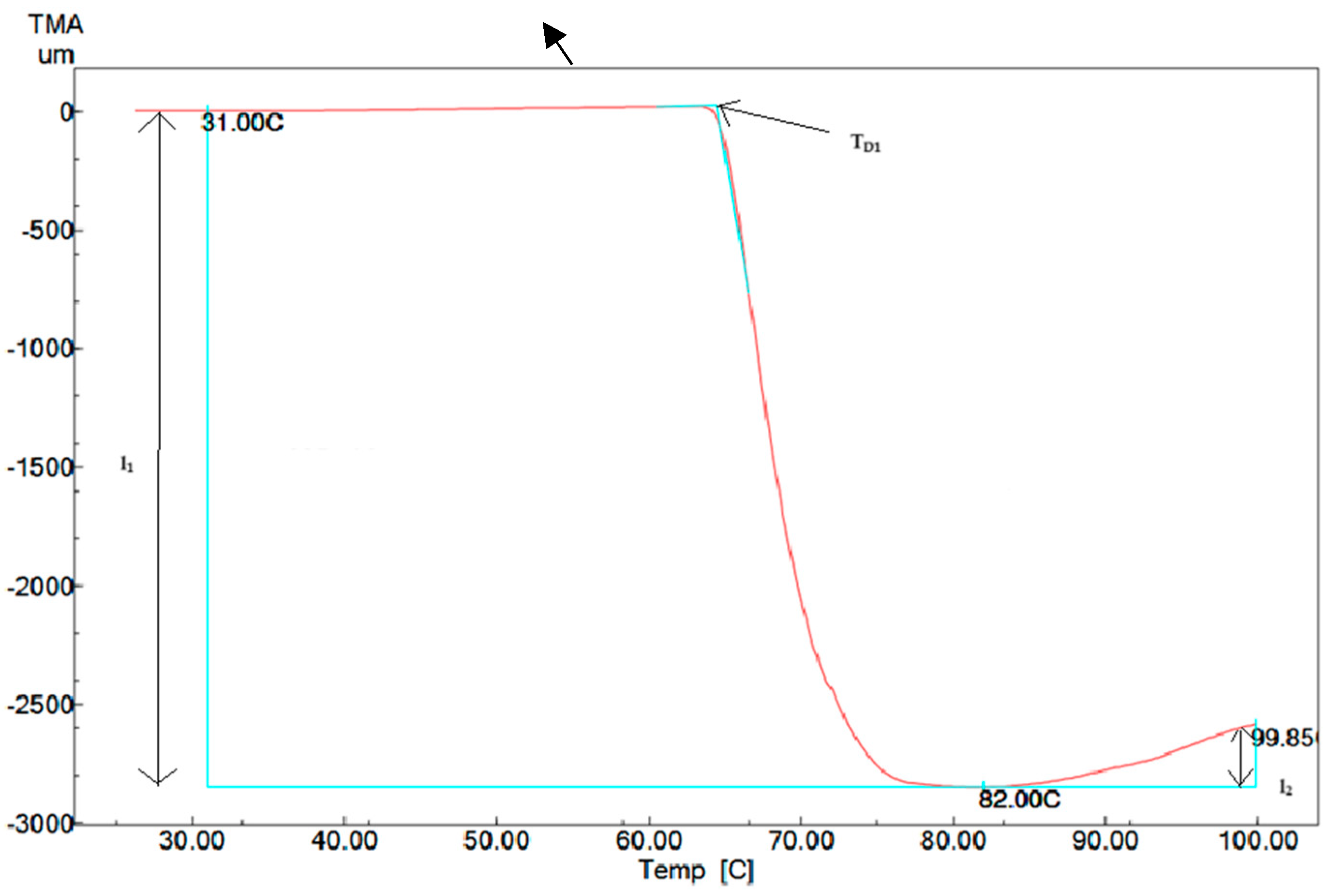
2.3.3. Thermomechanical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetric Measurements
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. Thermo-Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plavec, R.; Hlaváčiková, S.; Omaníková, L.; Feranc, J.; Vanovčanová, Z.; Tomanová, K.; Bočkaj, J.; Kruželák, J.; Madlenová, E.; Gálisová, I.; et al. Recycling possibilities of bioplastics based on PLA/PHB blends. Polym. Test. 2020, 92, 106880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, M.; Kwolek, S.; Szparaga, G.; Chrzanowski, M. Investigation of the Influence of PLA Molecular Structure on the Crystalline Forms (α’ and α) and Mechanical Properties of Wet Spinning Fibers. Polymers 2017, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, G.; Arvindh Seshadri, S.; Devnani, G.L.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Prakash Maran, J.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Environment-friendly, renewable and sustainable poly lactic acid (PLA) based natural fiber reinforced composites—A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avérous, L. Polylactic Acid: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. In Monomers, Polymers, and Composites from Renewable Resources; Belgacem, M.N., Gandini, A., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Cololia, B.P. Biodegradability and biodegradation of poly(lactide). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.S.; Jardini, A.L.; Filho, R.M. Poly (lactic acid) production for tissue engineering applications. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezghani, K.; Spruiell, J.E. High Speed Melt Spinning of Poly(L-lactic acid) Filaments. J. Polym. Sci. 1998, 36, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Revagade, N.; Anjum, N.; Atthoff, B. Preparation of Poly(lactic acid) Fiber by Dry-Jet-Wet-Spinning. I. Influence of Draw Ratio on Fiber Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Revagade, N.; Anjum, N.; Atthoff, B.; Hilborn, J. Preparation of Poly(lactic acid) Fiber by Dry-Jet-Wet Spinning. II. Effect of Process Parameters on Fiber Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 3774–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, M.; Langensiepen, F.; Seide, G. Investigation of melt spinnability of plasticized polylactic acid biocomposites-containing intumescent flame retardant. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 305–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xia, S. Structure and mechanical property of polylactide fibers manufactured by air drawing. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumright, R.E.; Gruber, P.R.; Henton, D.E. Polylactic acid Technology. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamcová, D.; Vaverková, M. Biodegradation of Degradable/Biodegradable Plastic Material in Controlled Compositing Environment. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Kervran, M.; Vagner Ch Cochez, M.; Poncot, M.; Saeb, M.R.; Vahabi, H. Thermal degradation of polylactic acid (PLA)/polyhydroxy butyrate (PHB) blends: A systematic review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 201, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tábi, T.; Ageyava, T.; Kovács, J.G. The influence of nucleating agents, plasticizers, and molding conditions on the properties of injection molded PLA products. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taweel, S.H.; Al-Ahmadi, A. Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/EVA 80 blends enhanced by NH4Cl as a nucleating agent. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 1657–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.-Y.; Zhang, K.; Ren, J.; Zhan, H. Melt rheology of polylactide/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheriasl, D.; Carreau, P.J. Shear rheology of polylactide (PLA)–cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) nanocomposites. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1885–1897. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10570-016-0914-1 (accessed on 20 January 2024). [CrossRef]
- Salehiyan, R.; Hyun, K. Effect of organoclay on non-linear rheological properties of poly(lactic acid)/poly(caprolactone) blends. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiardo, M.; Frisoni, G.; Scandola, M.; Rimelen, M.; Lips, D.; Ruffieux, K.; Wintermantel, E. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Plasticized poly (L-lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, T.; Garmabi, H. The effects of processing parameters on the morphology of PLA/PEG melt electrospun fibers. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.L. Reactive Blending of Biodegradable Polymers: PLA and Starch. J. Polym. Environ. 2000, 8, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wolcott, M.P.; Zhang, J. Study of biodegradable polylactide/poly(butylenes adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, J.P.; Dijkstra, H.; Pennings, A.J. Preparation and properties of absorbable fibres from L-lactide copolymers. J. Polym. 1993, 34, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dou, Q. Influence of the combination of nucleating agent and plasticizer on the non-isothermal crystallization kinetics and activation energies of poly(lactic acid). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 1069–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, J.A.; Dorgan, J.R.; Janzen, J.; Garrett, J.; Runt, J.; Lin, J.S. Supramolecular Morphology of Two-Step, Melt-Spun Poly(lactic acid) Fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 2828–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, Z.; Varshney, S. Thermal properties of polylactides—Effect of molecular mass and nature of lactide isomer. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 95, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xie, F.; Yu, L.; Chen, L. Thermal processing of starch-based polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1348–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, J.A.; Dorgan, J.R. Physical Properties and Fiber Morphology of Poly(lactic acid) Obtained from Continuous Two-Step Melt Spinning. J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, O.; Basoli, V.; Boschetto, F.; Rondinella, A.; Lanzutti, A.; Zhu, W.; Greco, E.; Thieringer, F.M.; Xu, H.; Marin, E. Simple Electrospinning Method for Biocompatible Polycaprolactone β-Carotene Scaffolds: Advantages and Limitations. J. Polym. 2024, 16, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
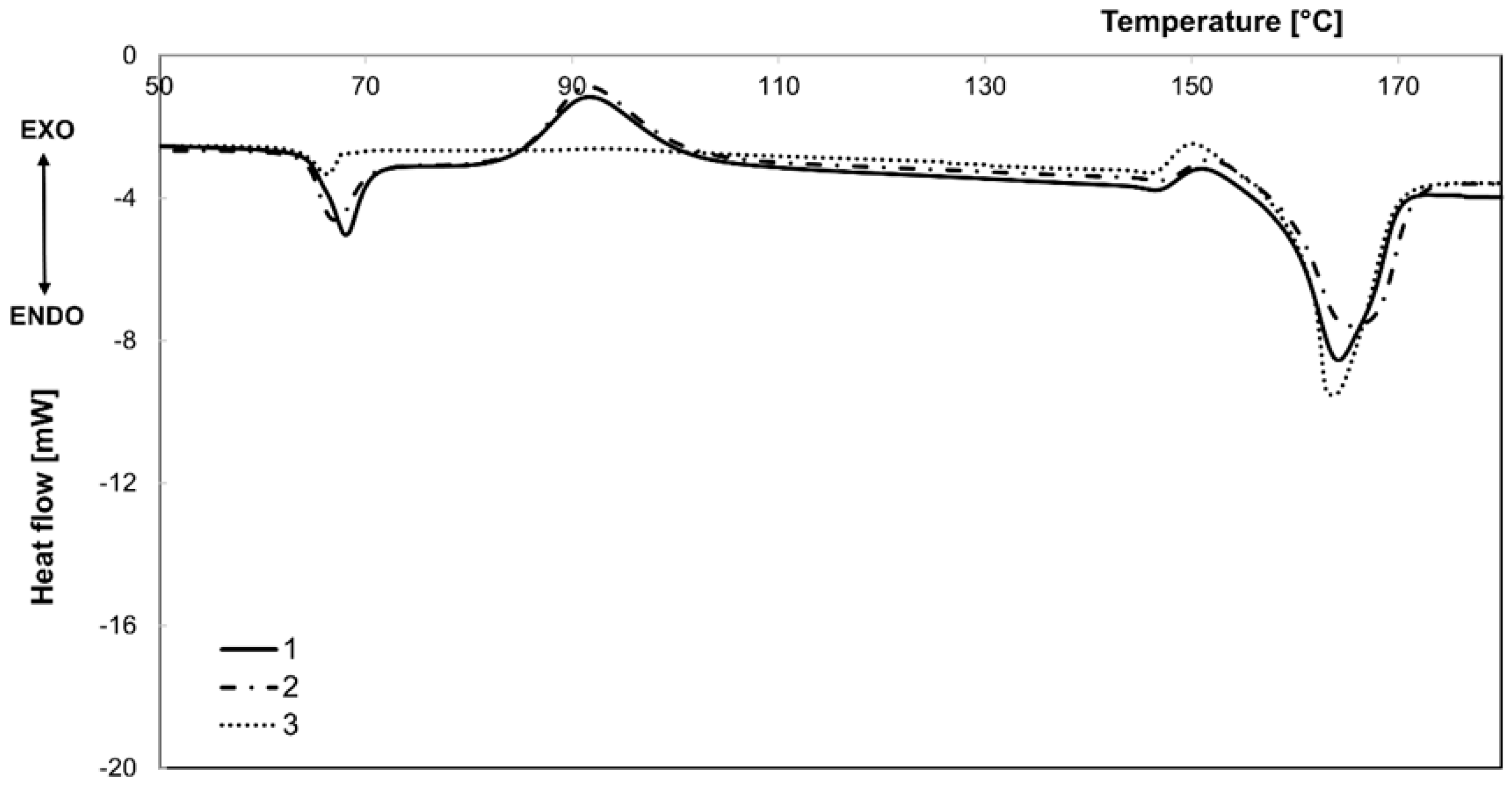
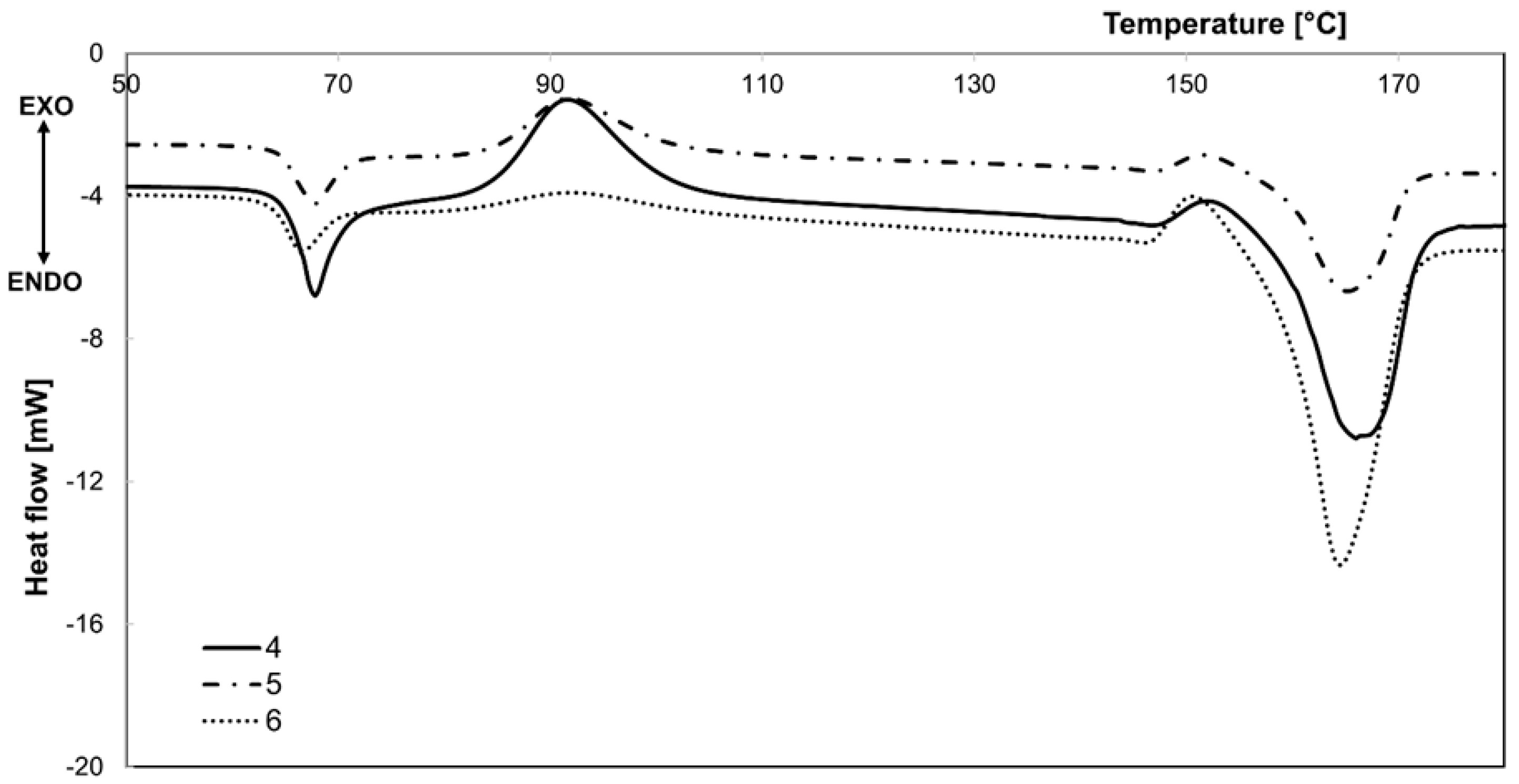
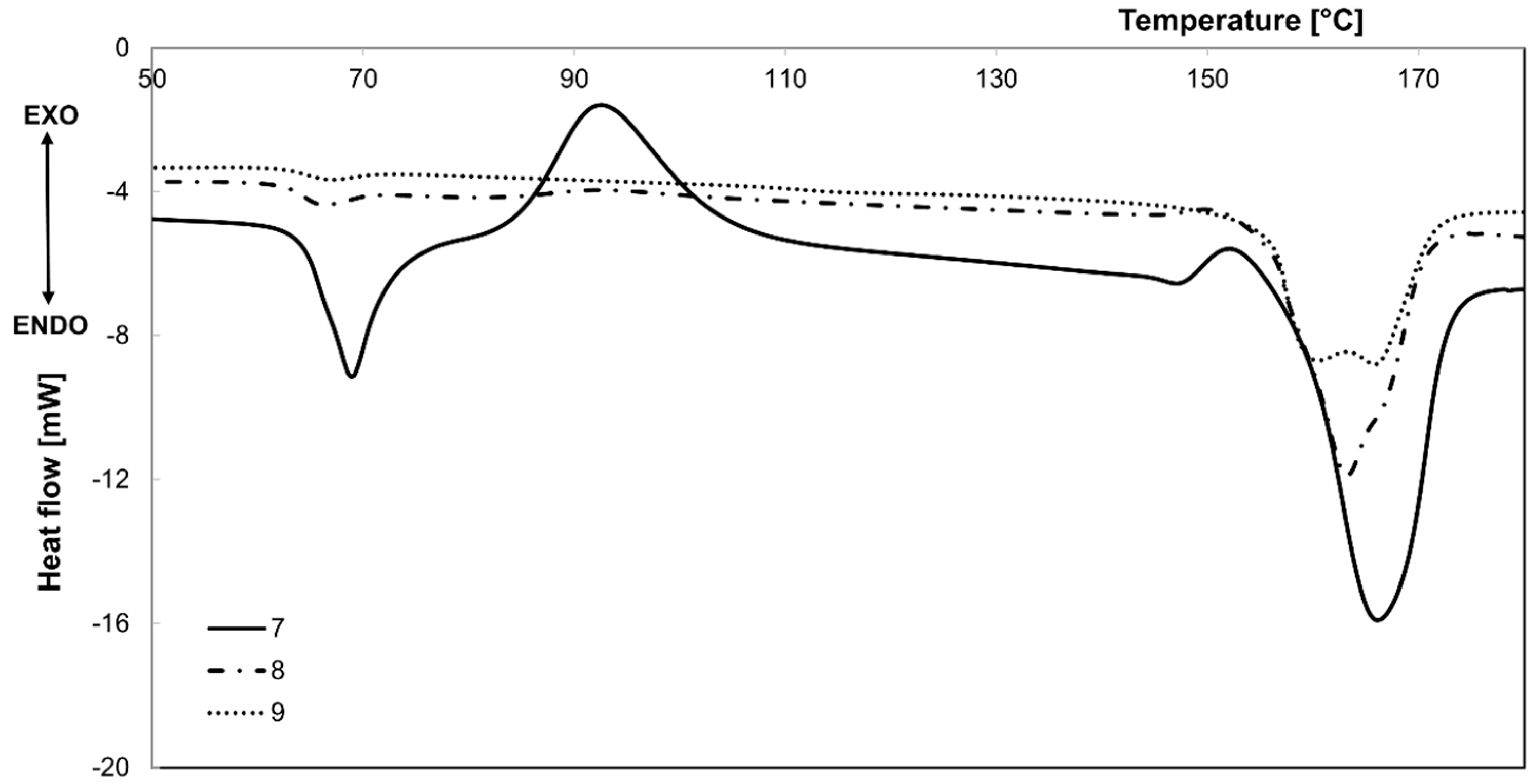
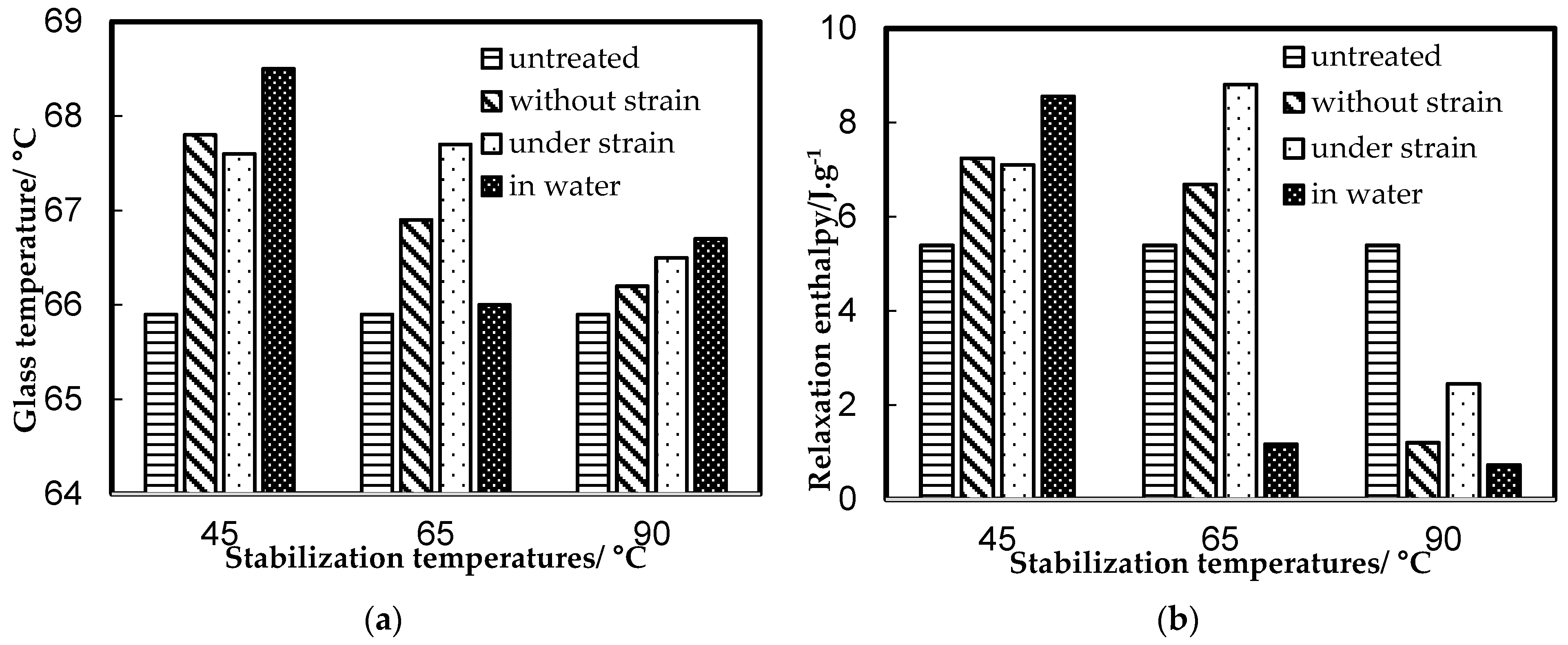
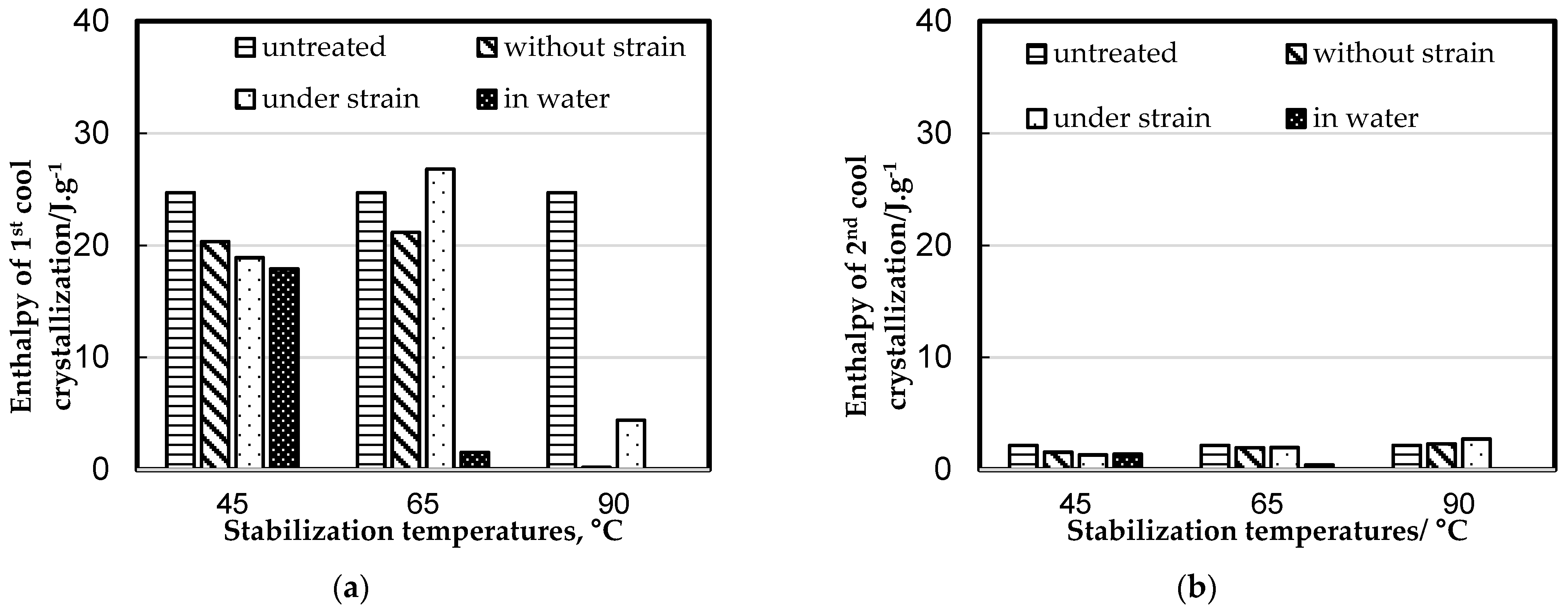
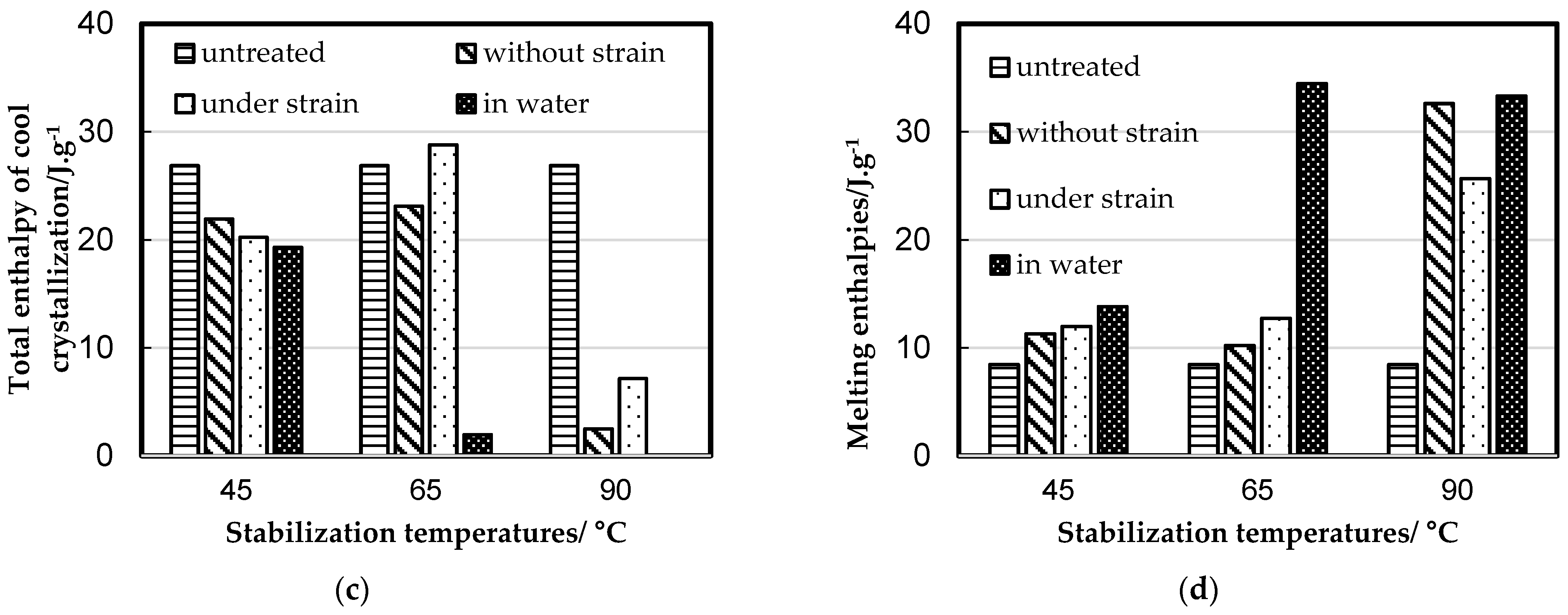
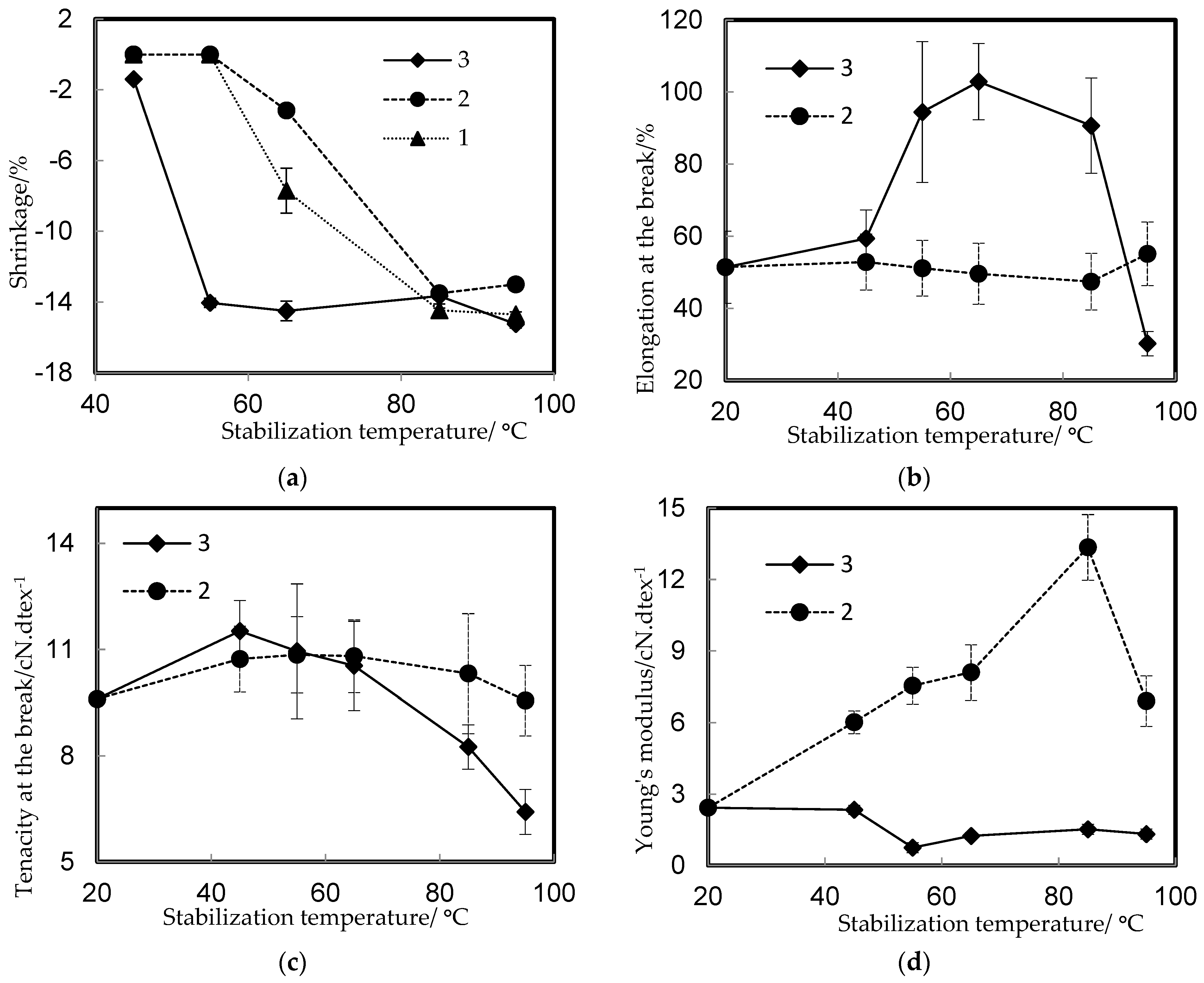
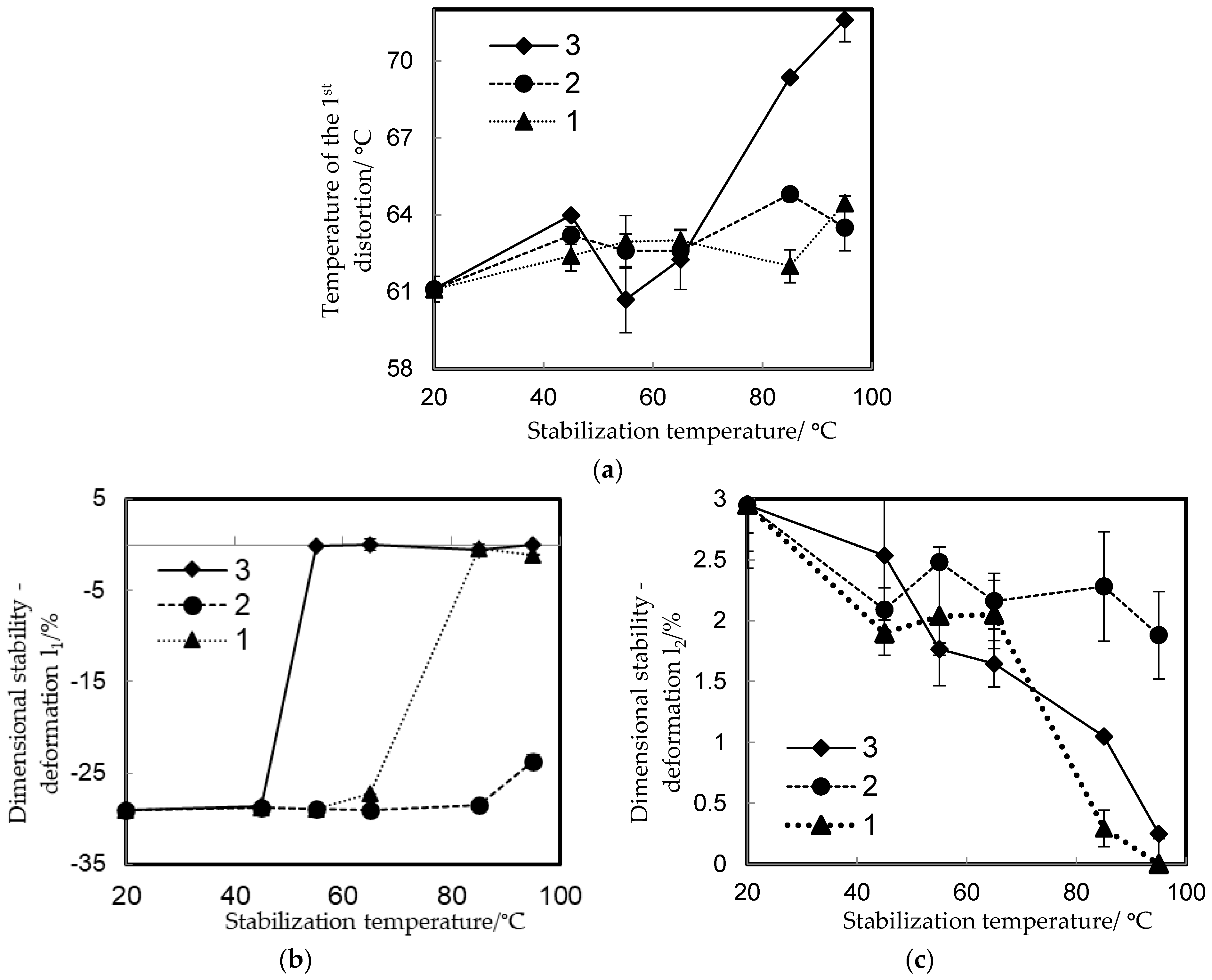
| Num. of Sample | Stabilization Process | Stabilization Temperature, °C |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Non-stabilized | - |
| 1 | without strain—hot air | 45 |
| 2 | 65 | |
| 3 | 90 | |
| 4 | under strain—hot air | 45 |
| 5 | 65 | |
| 6 | 90 | |
| 7 | without strain—in water | 45 |
| 8 | 65 | |
| 9 | 90 |
| Num. of Sample | Stabilization Process | Stabilization Temperature, °C | Tcc1, °C | Tcc2, °C | Tm, °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | untreated | - | 92.1 | 164.5 | |
| 1 | without strain—hot air | 45 | 91.6 | 150.9 | 163.8 |
| 2 | 65 | 91.6 | 151.5 | 165.2 | |
| 3 | 90 | 93.9 | 150.1 | 163.1 | |
| 4 | under strain—hot air | 45 | 91.5 | 152.0 | 165.5 |
| 5 | 65 | 91.6 | 151.4 | 164.9 | |
| 6 | 90 | 92.2 | 150.5 | 163.8 | |
| 7 | without strain—in water | 45 | 92.6 | 151.9 | 165.3 |
| 8 | 65 | 92.7 | 149.6 | 162.6 | |
| 9 | 90 | - | - | 160.1 165.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petková, M.; Ujhelyiová, A.; Ryba, J.; Hrabovská, V.; Kurtulík, M. The Effect of Stabilization Conditions on Fibers from Polylactic Acid and Their Properties. Fibers 2025, 13, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib13040044
Petková M, Ujhelyiová A, Ryba J, Hrabovská V, Kurtulík M. The Effect of Stabilization Conditions on Fibers from Polylactic Acid and Their Properties. Fibers. 2025; 13(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib13040044
Chicago/Turabian StylePetková, Mária, Anna Ujhelyiová, Jozef Ryba, Veronika Hrabovská, and Martin Kurtulík. 2025. "The Effect of Stabilization Conditions on Fibers from Polylactic Acid and Their Properties" Fibers 13, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib13040044
APA StylePetková, M., Ujhelyiová, A., Ryba, J., Hrabovská, V., & Kurtulík, M. (2025). The Effect of Stabilization Conditions on Fibers from Polylactic Acid and Their Properties. Fibers, 13(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib13040044







