Abstract
Whey represents the major by-product of cheese industry. One possibility to recycle the whey wastes is the use of their globular proteins as a polymer source for the production of biodegradable plastic materials. Whey protein (WP)-based films are usually obtained by protein heat treatment in the presence of glycerol (GLY) as plasticizer at pH 7, a method which would require commercially high costing process. In this work we explored the possibility of producing manageable whey-derived materials without any heat-treatment but under alkaline conditions. The reported results demonstrated that the casting at pH 12 of the unheated WP film forming solutions (FFSs), containing either 40% or 50% GLY, led to produce more resistant and flexible materials than the ones obtained at pH 7. Film opacity was observed significantly increased, being higher in the samples obtained at alkaline pH without WP heating and with higher GLY concentrations. Finally, moisture content decreased with the reduction of GLY content, both in heated and unheated WP-based films, whereas water uptake of the different films prepared at pH 12 did not significantly change.
1. Introduction
Whey is produced in huge quantities by the dairy industries during the casein coagulation process. Whey can be formed from all types (cow, goat, sheep, camel) of milk and, in particular, bovine whey is the most common whey produced in the western countries, sharing about 85%–95% of the generating milk volume and containing about 55% of the whole milk nutrients [1]. The total worldwide whey production is estimated to be more than 180 million tons/year, the major amount (approximately 70%) coming from EU and USA [1]. Whey is responsible for relevant environmental problems due to both its large volume and high organic content, and thus its disposal into municipal sewers is almost everywhere forbidden. On the other hand, land dumping creates severe pollution concerns for the environment by negatively influencing soil physicochemical characteristics. Therefore, an ecofriendly treatment of whey, when it is not recycled, is required before its disposal, even because the occurrence of numerous nutrients in whey is considered as a potential resource for the production of different value-added products. However, large amounts of whey remain generally unutilized, and thus whey still deserves attention from researchers to develop further innovative processes able to provide maximal benefits from this by-product and to limit its environmental pollution impact.
Among the various whey treatments, heating and pH modification are methods that could have a broader and easier application on industrial scale. Since aggregation depends on the repulsive and attractive forces between the particles occurring in solution, the size and the distribution pattern of whey proteins (WPs) depend on both pH and heating temperature, as well as on protein concentration [2,3]. β-Lactoglobulin is the major WP of ruminant species, and thus its molecular characteristics strongly influence WP aggregation caused by temperature or pH changes. Upon heating, it is capable of self-assembling into a variety of supramolecular structures, existing as an octamer between pH 3.5 to 5.2 and as a dimer between pH 5.2 and 7, whereas above pH 8.0, β-lactoglobulin is a monomer with a molecular weight of 18,277 Da [4]. β-Lactoglobulin is known to resist denaturation at acidic pH while, at alkaline pH, two sequential conformation changes occur in its structure, i.e., the unfolding of α-helix and of exposed β-sheet domains, similarly to its denaturation occurring in the temperature range 50–90 °C, followed by the unfolding of other β-sheets [5]. Therefore, its tunable structuring capacity makes β-lactoglobulin, and consequently, whey, a possible interesting source for material science. In fact, one possibility to re-use the whey is to turn its protein content into biodegradable/edible packaging films, that can meet consumer demands for safe, convenient, and/or healthy food products with prolonged shelf life as well as sustainability awareness [6]. Edible films, endowed with a low environmental impact, have been progressively improved to effectively protect various food products through tailored mechanical and/or barrier properties, as well as a controlled release of active ingredients [7]. In addition, these materials might replace the petroleum-based plastics, considered to be a major threat of pollution of the environment because they are not easily degradable. In fact, more than 35 million tons of wastes deriving from different plastic items are produced each year in the world and only 7% of them are recycled, the remaining waste being deposited in the landfills or dispersed in the oceans [8]. Therefore, manufacturers are trying to reduce the application of plastic materials, mainly for food packaging, and to develop innovative biodegradable films and coatings [9].
In recent years, edible films obtained from proteins of both plant and animal sources, and particularly WPs, received increasing attention [10,11,12,13,14]. These materials are usually obtained by casting and drying of WP solutions, since the properties of extruded and molded materials derived from WPs are still unsatisfactory [15]. In addition, WP applicability in significant processes of pharmaceutical coating has not yet been really described. In fact, their use has been only proposed in obtaining films targeted as carriers of antimicrobial agents [16] and as a protective barrier to improve food shelf life [17,18], mostly because WP-based films exhibit a poor barrier capacity against water vapor. Therefore, the present paper reports studies specifically addressed to find out new experimental conditions to produce whey-derived films potentially useful for a more extensive application. In this research, the film forming capacity of WPs denatured at high temperatures and/or alkaline pH was systematically studied even in comparison with other proteins. Several properties of the WP-based films obtained at different concentrations of both plasticizer (glycerol, GLY) and structuring (poly-γ-glutamic acid, PGA) agents were also analyzed in the attempt to improve their characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Commercial WP isolate (~90% dry basis protein) was obtained from BioLine (London, UK), PGA was purchased from Xi’an Fengzu Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (Xi’an, China), and its molecular weight (between 29–30 kDa) determined by capillary viscometry according to Irurzun et al. [19]. GLY and all other reagents were purchased from Sigma (Kawasaki, Japan). Bitter vetch and grass pea seeds were obtained from a local market in Gallichio (Potenza, Italy). Soy protein concentrate was purchased from Laboratori Bio Line s.r.l. (Canaro, Roma, Italy).
2.2. Film Preparation
Film forming solutions (FFSs) were prepared by dissolving WP isolate in distilled water (1% WPs, w/v) and adjusting the pH (to 7 or 12) by 0.1 N NaOH addition. FFSs were heated or not at 80 °C for 25 min under continuous stirring. After cooling down at room temperature, GLY (30%, 40%, 50% w/w of WPs) and/or PGA (200 mg) were added just before casting 50 mL FFS into 8 cm diameter polyester Petri dishes. The derived films were then obtained by drying at 25 °C and 45% RH for 48 h and analyzed within 24 h.
Protein concentrates from bitter vetch and grass pea seeds (containing 70%–80% of proteins determined by the Kjeldahl’s method) were obtained as previously described [20,21] with some modifications. The respective flours were suspended in distilled water (10%, w/v), and then the pH was brought to pH 11 with 0.1 N NaOH. After stirring for 1 h, the suspensions were centrifuged for 20 min at 15,000× g at 4 °C and the pH of the resulting supernatants was brought to pH 5.4 with 0.1 N HCl. The obtained precipitates were dried in the climatic chamber at 25 °C and 45% RH. All FFSs were prepared by dissolving the plant protein concentrates (2 g), under stirring for 1 h, in 100 mL of distilled water alkalinized at pH 12 and containing 30% (w/v) GLY. The pH of some samples was adjusted at pH 7 with 0.1 N HCl. Finally, 50 mL of the differently diluted FFSs, containing 500 mg protein each, were poured in the Petri dishes and allowed to dry in an environmental chamber at 25 °C and 45% RH for 48 h. All the obtained films were analyzed within 24 h.
2.3. Zeta-Potential and Particle Size Measurements
1.0 mL of each WP containing FFS was analyzed for zeta-potential and particle size by using a Zetasizer Nano-ZSP (Malvern®, Worcestershire, UK). The device was equipped with a helium-neon laser of 4 mW output power operating at the fixed wavelength of 633 nm (wavelength of laser red emission). The instrument software programmer calculated the zeta-potential through the electrophoretic mobility by applying a voltage of 200 mV and by using the Henry equation [22].
2.4. Film Mechanical Properties
All dried films were cut into 1 cm × 8 cm strips using a sharp scissor and conditioned at 25 °C and 50% RH for 2 h by placing them into a glass chamber over a saturated solution of Mg(NO3)2 before being tested. Film thickness was measured in six different points with a micrometer (Electronic digital micrometer (Metrocontrol, Srl, Casoria, Italy; sensitivity 0.001 mm) and film tensile strength (TS), elongation at break (EB) and Young’s modulus (YM) were determined on five specimens of each sample (5 cm gage length, 1 kN load and 5 mm/min speed) by using an Instron universal testing instrument model no. 5543A (Instron Engineering Corp., Norwood, MA, USA).
2.5. Film Transmittance and Transparency
Each WP film was cut into 1 cm × 4 cm strip and placed in a quartz cuvette and its whole light transmittance and absorbance spectra were obtained by using a Agilent UV-vis spectrophotometer (Santa Clara, CA, USA) in the range of 200–800 nm with a scan rate of 250 nm/min. The transparency analyses were performed as described by Galus and Kadzinska [23] by calculating film opacity as follows:
where A600nm was the absorbance at 600 nm and X was the film thickness (mm).
Opacity = A600nm/X
2.6. Film Moisture Content and Uptake
Moisture content test was performed by evaluating the mass loss of the film sample after 24 h at 105 °C as previously described [23]. Analyses in triplicate of each film were made and film moisture content was calculated as:
where W1 is the initial weight of the film and W2 is the film weight after drying.
Film moisture content (%) = (W1 − W2)/W1 × 100
Film moisture uptake tests were carried out by a gravimetric method described by Manrich et al. [24]. The analysis was performed by determining the mass of film samples after drying at 105 °C for 24 h and the mass after the samples were put in a conditioning environment at RH 50% (saturated solution of Mg(NO3)2) for other 24 h. The moisture uptake was finally calculated as:
where Ws and Wd are the weight of swollen and dried films, respectively.
Film moisture uptake (%) = (Ws − Wd)/Ws × 100
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All data were analyzed by means of JMP software 5.0 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA), used for all statistical analyses. The data were subjected to analysis of variance, and the means were compared using the Tukey–Kramer HSD test. Differences were considered to be significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Zeta-Potential and Particle Size
Micro- and nano-particle charge can be quantified by measuring their zeta potential, a quantitative parameter monitoring the particle mobility in an electrical field. It is known that FFS pH value and components may influence the zeta potential of the dissolved or suspended particles. The data reported in Table 1 indicate that both heated and unheated WP FFSs prepared at pH 7 and 12 were quite stable. In particular, zeta-potential values of the FFSs prepared at pH 12 were markedly more negative (around −36 mV) than those detected with FFSs prepared at pH 7 (around −25 mV), with an average particle size between 400 and 600 nm regardless of GLY concentrations and heat-treatment. Therefore, the WP FFSs prepared at pH 12 exhibit a higher stability due to the repulsive forces and, as consequence, should give rise to a more homogeneous distribution of WP nanoparticles during FFS drying and, potentially, to films with improved performance.

Table 1.
Zeta-potential and Z-average measurements of whey protein (WP) film forming solutions (FFSs) prepared at pH 7 or 12 and subjected or not to heat treatment.
3.2. Film Mechanical Properties
After the analyses of the stability of all the WP FFSs prepared under different experimental conditions, the mechanical properties only of the handleable films obtained were investigated. In more detail, TS, EB, and YM of the films derived from the FFSs, heated and unheated, prepared at pH 12 in the presence of different amounts of GLY were determined. Conversely, it was possible to evaluate the mechanical properties only of the films derived from the FFSs heated and prepared at pH 7 in the presence of 40% or 50% GLY. In fact, very brittle films were obtained under the same experimental conditions in the presence of 30% GLY, whereas unmanageable sticky materials were obtained with unheated FFS at the same pH and at all GLY concentrations. The results reported in Table 2 indicate that the unheated FFSs, prepared at pH 12 and containing 50% GLY, led to obtain more flexible materials, as demonstrated by the highest EB and the lowest YM detected. In addition, these values were also much higher and lower, respectively, than those observed with counterpart films obtained at pH 7 from heated FFSs in the presence of 50% GLY (Table 3).

Table 2.
Mechanical properties of whey protein (WP) films obtained at pH 12.

Table 3.
Mechanical properties of whey protein (WP) films obtained at pH 7.
Among the numerous studies on WP-based films recently reviewed by Zink et al. [13], only few investigations were carried out under experimental conditions similar to those described in the present paper. It has been reported that (i) films obtained from native WP isolates dissolved in water, and plasticized with 30% GLY, were weaker and less extendible than films obtained with heat-denatured WPs, and (ii) the pH (in the range 3–8) of the FFS did not influence the mechanical properties of films made with both native and heat-denatured WPs [25]. The present results, conversely, indicate that WPs denatured at alkaline pH give rise, in the presence of 50% GLY, to films still resistant (TS more than 1 MPa) but more stretchable (EB over 60% and a YM of 24.1 MPa) than those previously obtained at lower pH with heat-denatured WPs and 30% GLY, which exhibited only 8%–18% EB and a YM in the range of 141–472 MPa [25].
Finally, the only way to obtain WP films at pH values lower than 12, without a previous protein denaturation, needed the presence of further additives to the FFS. Table 4 reports the mechanical properties of films prepared in the pH range between 6 and 12 with unheated WPs but in the presence of not only of a plasticizing (GLY) but also of a structuring agent (PGA) [26].

Table 4.
Effect of poly-γ-glutamic acid (PGA) on the mechanical properties of whey protein (WP) films prepared at different pHs and containing 50% GLY *.
However, the feature to give rise to plasticized films at pH 12 but not at pH 7, perfectly manipulable, and thus suitable to be studied, seems to be quite specific of WPs. In fact, other protein-based films, such as those derived from bitter vetch, grass pea, and soy seed proteins, were easily obtained at both pH values, in the presence of only 30% GLY, and their mechanical properties also investigated (Table 5).

Table 5.
Mechanical properties of glycerol (GLY)-plasticized films obtained at pH 7 and 12 from plant protein sources.
3.3. Film Transparency
Since the appearance of the coated products plays an important role in consumer acceptability, the opacity of the obtained WP films was evaluated by measuring light transmission through the films at a wavelength of 600 nm [23]. Table 6 clearly indicates that only slight differences were detected between the films prepared at pH 12 and pH 7. Nevertheless, opacity was observed to significantly change, being higher in the films obtained at pH 12 without FFS heating and, when FFS was heated, at higher GLY concentrations. The opacity values detected, which resulted from the same order of magnitude of those of films prepared by Galus and Kandiska at pH 7 from a heated WP isolate [27], were also compared with ones exhibited by traditional commercial plastics such as cellulose triacetate and polypropylene, which resulted more and much less transparent, respectively, than the WP films.

Table 6.
Opacity of whey protein (WP)-based films obtained under different experimental conditions.
It is worthy to note that no differences were observed among the absorbance and transmittance profiles obtained analyzing the various films prepared at different GLY concentrations and pH values, as well as with heated or unheated WPs. A typical film obtained from an FFS prepared at pH 12 and containing unheated WPs and 50% GLY is shown in Figure 1, together with its whole transmittance and absorbance spectra. Furthermore, the low transmittance of all the films at UV wavelengths should be considered a further interesting feature of the WP-based materials, being potentially able to prevent possible physicochemical alterations of coated/wrapped foods or drugs.
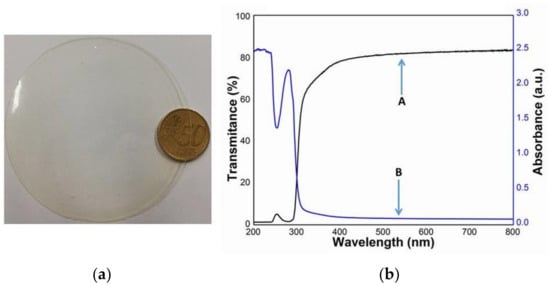
Figure 1.
Film obtained at pH 12 with unheated whey proteins (WPs) in the presence of 50% glycerol (GLY) (a) and its whole transmittance (A) and absorbance (B) spectra (b).
3.4. Film Moisture Content and Moisture Uptake
The prepared WP films were also analyzed for moisture content and moisture uptake, as these features are important for food packaging applications, particularly when the water activity is high or when the film should act as a food protective barrier [28]. In fact, a high moisture content of the coating material considerably limits its use for packaging foods. The results reported in Table 7 showed that the moisture content of the films prepared at pH 12 decreased when the FFS was previously heated, as well as when the amount of GLY was lower in both heated and unheated samples. Conversely, film water uptake did not seem to significantly change in all films cast at pH 12. Finally, the moisture uptake values were found significantly lower when the films were prepared at pH 7.

Table 7.
Moisture content and uptake of whey-protein (WP)-based films obtained under different experimental conditions.
4. Conclusions
Since it is known that denaturation and aggregation of WPs are pH dependent, with strong alkalis producing rod-like microstructures able to form fine-stranded fiber-like matrices, the possibility of obtaining GLY-plasticized materials by using WP isolate treated at pH 12 without heating was investigated and demonstrated. Conversely, at pH 7, it was necessary not only to previously heat at 80 °C for 25 min the WP-containing FFS, but also to increase to at least 40% the GLY concentration to obtain handleable films. The developed experimental conditions allowed the production of hydrocolloid films with higher flexibility with respect to the WP-based films so far obtained at pH 7 following FFS heat treatment, probably because WPs denatured under alkaline conditions form small primary aggregates able to combine into large clusters [29].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.P., P.D.P. and C.V.L.G.; Methodology, M.A., M.E., M.F.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.A. and C.V.L.G.; Writing—Review and Editing, R.P.; Supervision, C.V.L.G. and R.P.; Software, M.A. and P.D.P.; Validation, R.P. and C.V.L.G.; Formal Analysis, M.A.; Investigation, R.P.; Resources, R.P.; Data Curation, C.V.L.G.; Visualization M.E. and M.A.; Project Administration, R.P.; Funding Acquisition, R.P.
Funding
This research was financially supported by a grant from the Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation to P.D.P. (CUP: E68D18000130001).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yadav, J.S.S.; Yan, S.; Pilli, S.; Kumar, L.; Tyagi, R.; Surampalli, R. Cheese whey: A potential resource to transform into bioprotein, functional/nutritional proteins and bioactive peptides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 756–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, L.; Schmitt, C.; Bovetto, L.; Rouvet, M. Mechanism of formation of stable heat-induced β-lactoglobulin microgels. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.; McClements, D. Optimizing preparation conditions for heat-denatured whey protein solutions to be used as cold-gelling ingredients. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, A.R.; Pereira, C.I.; Gomes, A.M.; Pintado, M.E.; Malcata, F.X.; Gomes, A.M.; Pintado, M.M. Bovine whey proteins–Overview on their main biological properties. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobert, J.-M. Milk protein modification to improve functional and biological properties. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, 1st ed.; Taylor, S.L., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 47, pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Di Pierro, P.; Mariniello, L.; Giosafatto, V.L.; Esposito, M.; Sabbah, M.; Porta, R. Dairy whey protein-based edible films and coatings for food preservation. In Food Packaging and Preservation, 1st ed.; Grumezescu, A., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier-Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 9, pp. 439–456. [Google Scholar]
- Janjarasskul, T.; Krochta, J.M. Edible packaging materials. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 415–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, A.; Burgos, N.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M. Natural pectin polysaccharides as edible coatings. Coatings 2015, 5, 865–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, A.L.; Duarte, M.P.; Vatsanidou, A.; Alexopoulou, E. Environmental aspects of fiber crops cultivation and use. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 68, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaldia, K.; Pérez, C.; Banon, S.; Desobry, S.; Hardy, J. Milk proteins for edible films and coatings. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammann, F.; Schmid, M.; Drelich, J.W. Determination quantification of molecular interactions in protein films: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 7975–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coltelli, M.B.; Wild, F.; Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lindner, M.; Schmid, M.; Weckel, V.; Müller, K.; Rodriguez, P.; Staebler, A.; et al. State of the art in the development and properties of protein-based films and coatings and their applicability to cellulose based products: An extensive review. Coatings 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, J.; Wyrobnik, T.; Prinz, T.; Schmid, M.; Taubert, A.; Qin, Q. Physical, chemical and biochemical modifications of protein-based films and coatings: An extensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calva-Estrada, S.J.; Jiménez-Fernández, M.; Lugo-Cervantes, E. Protein-based films: Advances in the development of biomaterials applicable to food packaging. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, M.; Gomes, D.; Pereira, C. Whey protein edible coatings: Recent developments and applications. In Emerging and Traditional Technologies for Safe, Healthy and Quality Food, 1st ed.; Nedovic, V., Raspor, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 176–196. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Pérez, O.B.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Rojas, R.; Aguilar-González, M.A.; Aguilar, C.N. Whey protein-based edible films: Progress and prospects. In Applied Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 1st ed.; Haghi, A.K., Faria Ribeiro, A.C., Eds.; Apple Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 5, pp. 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- Di Pierro, P.; Sorrentino, A.; Mariniello, L.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Porta, R.; Giosafatto, C.V.L. Chitosan/whey protein film as active coating to extend Ricotta cheese shelf-life. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 2324–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Dallmann, K.; Bugnicourt, E.; Cordoni, D.; Wild, F.; Lazzeri, A.; Noller, K. Properties of whey-protein-coated films and laminates as novel recyclable food packaging materials with excellent barrier properties. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 2012, 562381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irurzun, I.; Bou, J.J.; Pérez-Camero, G.; Abad, C.; Campos, A.; Muñoz-Guerra, S.; Pérez-Camero, G.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Mark-houwink parameters of biosynthetic poly(γ-glutamic acid) in aqueous solution. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 3253–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, R.; Di Pierro, P.; Roviello, V.; Sabbah, M. Tuning the functional properties of bitter vetch (vicia ervilia) protein films grafted with spermidine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giosafatto, C.; Al-Asmar, A.; D’Angelo, A.; Roviello, V.; Esposito, M.; Mariniello, L. Preparation and characterization of bioplastics from grass pea flour cast in the presence of microbial transglutaminase. Coatings 2018, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, M.; Di Pierro, P.; Cammarota, M.; Dell’Olmo, E.; Arciello, A.; Porta, R. Development and properties of new chitosan-based films plasticized with spermidine and/or glycerol. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Moisture sensitivity, optical, mechanical and structural properties of whey protein-based edible films incorporated with rapeseed oil. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 54, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrich, A.; Moreira, F.K.; Otoni, C.G.; Lorevice, M.V.; Martins, M.A.; Mattoso, L.H. Hydrophobic edible films made up of tomato cutin and pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Gago, M.B.; Krochta, J. Denaturation time and temperature effects on solubility, tensile properties, and oxygen permeability of whey protein edible films. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunleye, A.; Irorere, V.U.; Williams, C.; Hill, D.; Bhat, A.; Radecka, I. Poly-γ-glutamic acid: Production, properties and applications. Microbiology 2015, 161, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Whey protein edible films modified with almond and walnut oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejdan, A.; Ojagh, S.M.; Adeli, A.; Abdollahi, M. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the physico-mechanical and ultraviolet light barrier properties of fish gelatin/agar bilayer film. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwulata, C.I.; Isobe, S.; Tomasula, P.M.; Cooke, P.H. Properties of whey protein isolates extruded under acidic and alkaline conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).