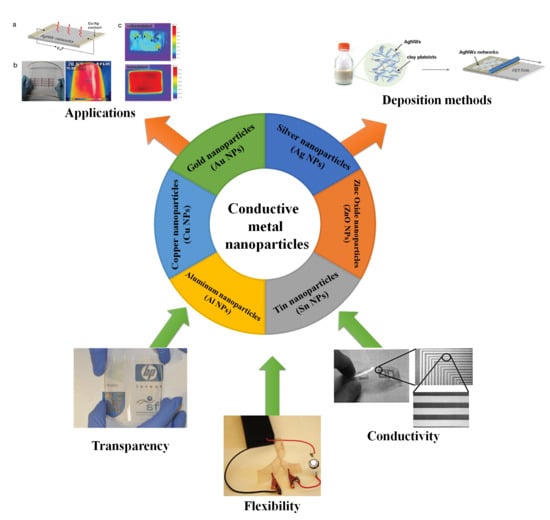
A Review of Conductive Metal Nanomaterials as Conductive, Transparent, and Flexible Coatings, Thin Films, and Conductive Fillers: Different Deposition Methods and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Why Are Conductive Nanomaterials Used in Coatings and Thin Films?
1.2. Why Is Flexibility Needed in Some Cases and Transparency in Others?
1.2.1. Cost
1.2.2. Brittleness
1.2.3. Poor Choice for Use as a Conductive Coating (Electrode) on Organic Substrates
1.2.4. Limited Chemical Stability
1.2.5. Poor Choice for Use as an Electrode in Solar Cells
1.2.6. Lack of an Easy and Cost-Effective Deposition Technique
1.3. Solution
1.4. Application of Conductive Nanomaterials as Nanofiller and Percolation Threshold
1.5. Percolation Theory
2. Conductive Metal Nanomaterials
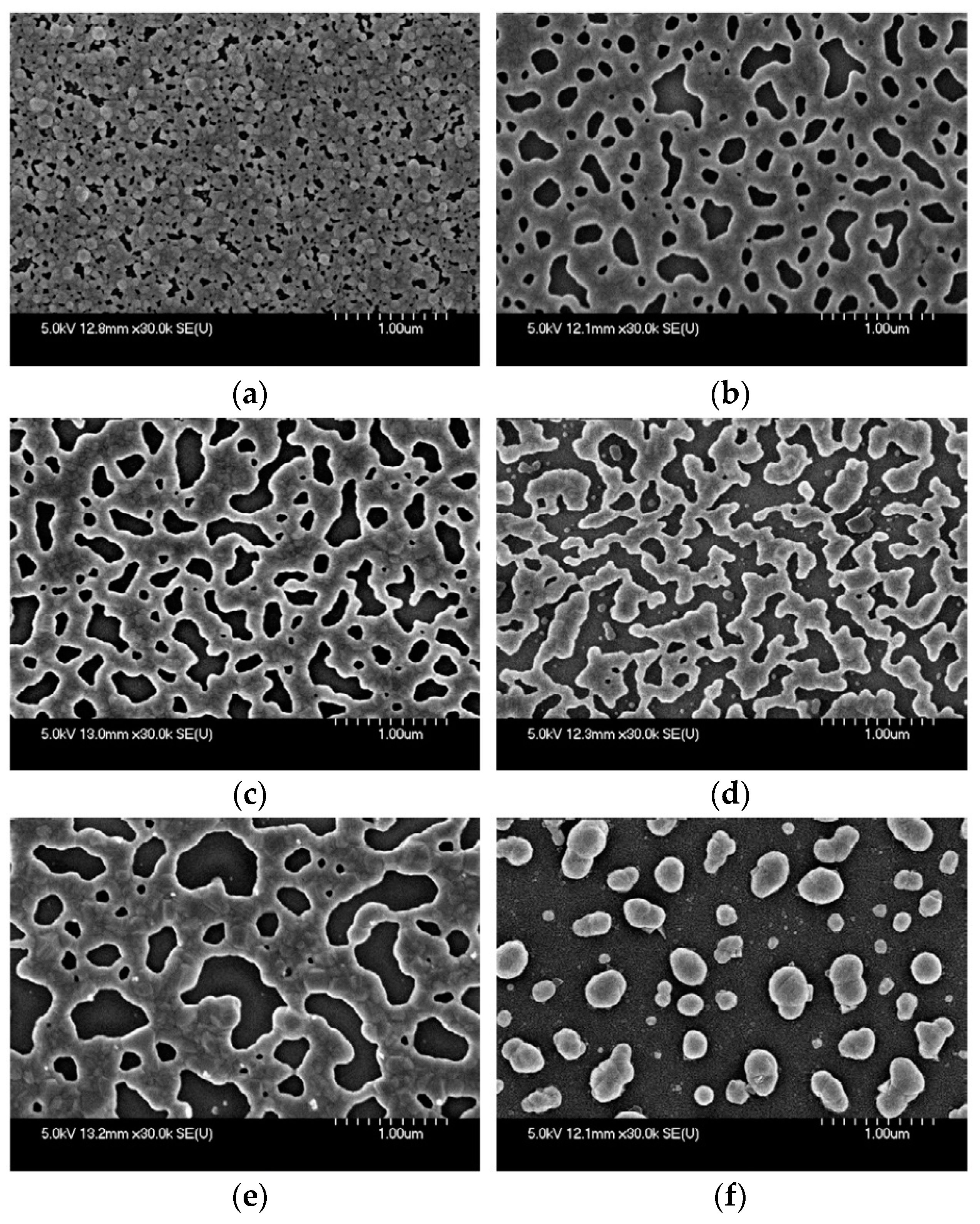
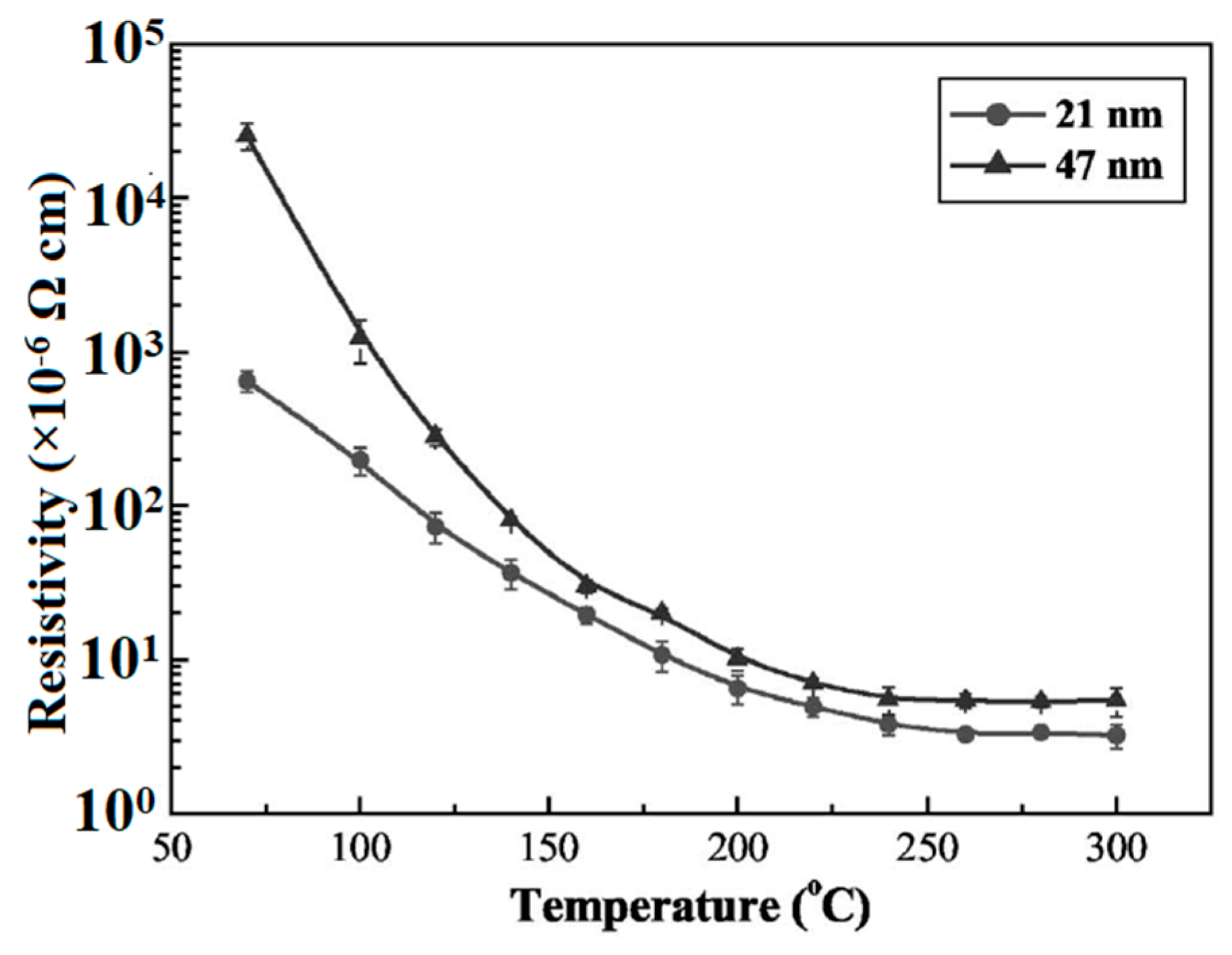
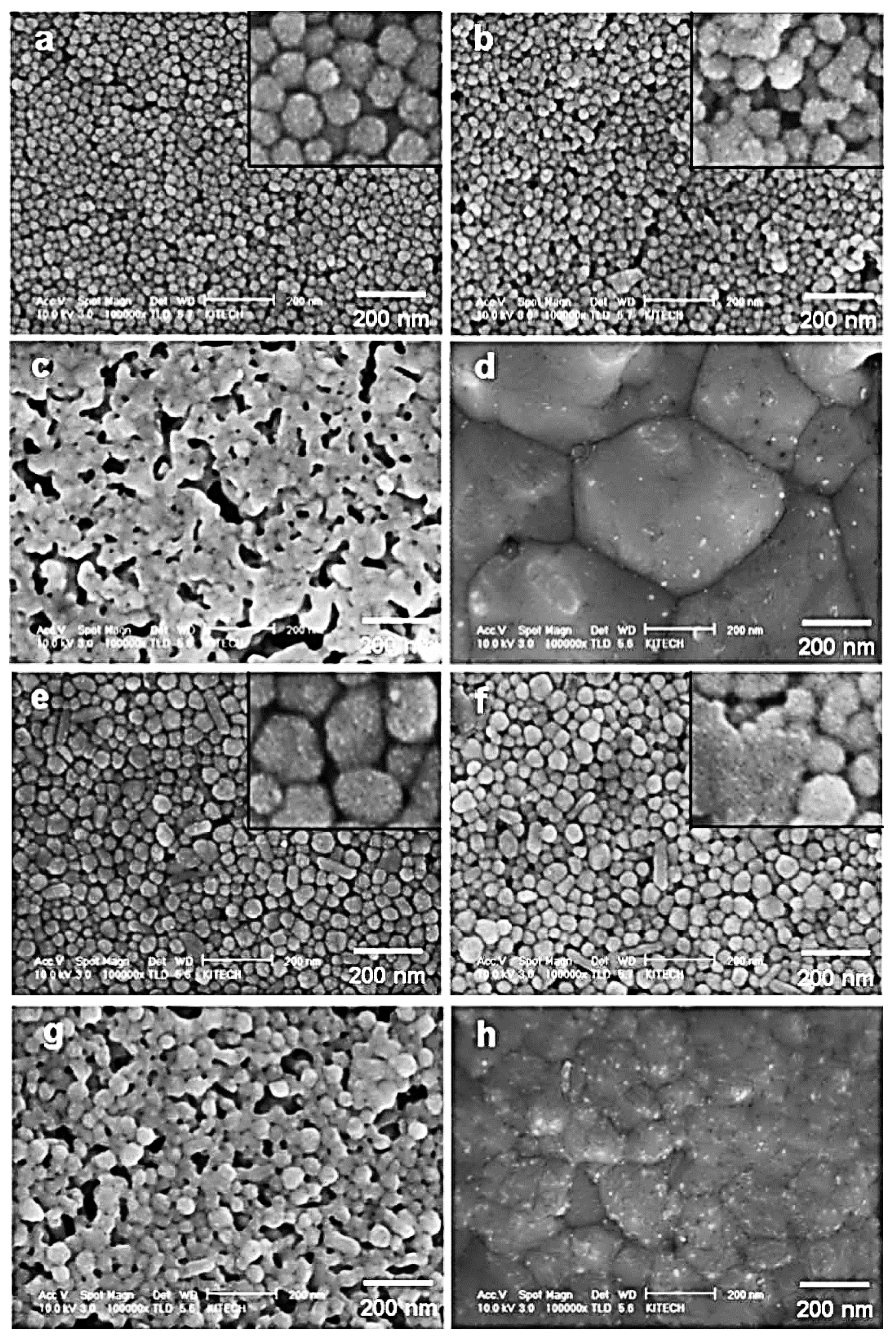
2.1. Sintering of Metal Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.2. Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Nanowires (Ag NPs and Ag NWs)
2.3. Ag NPs and Ag NWs as Filler
2.4. Gold Nanoparticles (Au NP)
2.5. Copper Nanoparticles and Nanowires (Cu NPs and NWs)
2.6. Cu NPs and NWs as filler
2.7. Other Conductive Metal Nanoparticles
3. Deposition Methods
3.1. Ink-Jet Printing
3.2. Spin Coating
3.3. Rod Coating
3.4. Spray Coating
3.5. Vacuum Filtration or Transfer Printing Method
3.6. Dip Coating
3.7. Other Deposition Methods
4. Application of Conductive Thin Films and Coatings
4.1. Solar Cells
4.2. OLED
4.3. Supercapacitor
4.4. Circuitry
4.5. Transistor
4.6. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding
4.7. Transparent Film Heaters
4.8. Dielectric
4.9. Conductive Thread
4.10. Aerospace Industry
4.11. Medical Applications
4.12. Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIB)
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| AZO | Al-doped zinc oxide | Al | Aluminum |
| Cu | Copper | EMI | Electromagnetic interference |
| FTO | Fluorine tin oxide | Au | Gold |
| HMDS | Hexamethyldisilazane | HCl | Hydrogen chloride |
| ITO | Indium tin oxide | LED | Light emitting diode |
| LCD | Liquid crystal display | LIB | Lithium-ion batterie |
| NP | Nanoparticle | OLED | Organic light-emitting diode |
| OPV | Organic photovoltaic cell | PEDOT:PSS | Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) poly(styrenesulfonate) |
| PDMS | Poly(dimethylsiloxane) | PVP | Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate | Ag | Silver |
| NW | Nanowire | TFT | Thin film transistor |
| Sn | Tin | ZnO | Zinc oxide |
References
- Farhan, M.S.; Zalnezhad, E.; Bushroa, A.R.; Sarhan, A.A.D. Electrical and optical properties of indium-tin oxide (ITO) films by ion-assisted deposition (IAD) at room temperature. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahng, W.S.; Francis, A.H.; Moon, H.; Nanos, J.I.; Curtis, M.D. Is indium tin oxide a suitable electrode in organic solar cells? Photovoltaic properties of interfaces in organic p/n junction photodiodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 093504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Connor, S.T.; Cui, Y.; Peumans, P. Solution-processed metal nanowire mesh transparent electrodes. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathmell, A.R.; Bergin, S.M.; Hua, Y.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Wiley, B.J. The growth mechanism of copper nanowires and their properties in flexible, transparent conducting films. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3558–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghdi, S.; Sajjadi, M.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Rhee, K.Y.; Sajadi, S.M.; Jaleh, B. Cuscuta reflexa leaf extract mediated green synthesis of the Cu nanoparticles on graphene oxide/manganese dioxide nanocomposite and its catalytic activity toward reduction of nitroarenes and organic dyes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 86, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J. Shape-Dependent Magnetic Properties and Phase Transformation of Annealed Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. JOM 2017, 69, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Rhee, K.Y.; Jaleh, B.; Park, S.J. Altering the structure and properties of iron oxide nanoparticles and graphene oxide/iron oxide composites by urea. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watté, J.; Van Zele, M.; De Buysser, K.; Van Driessche, I. Recent Advances in Low-Temperature Deposition Methods of Transparent, Photocatalytic TiO2 Coatings on Polymers. Coatings 2018, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyamin, Z.Y.; Kelly, P.Y.; West, G.; Boardman, J. Electrical and optical properties of fluorine doped tin oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Coatings 2014, 4, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-S.; Huang, K.-C.; Lee, H.-H. Fabrication and sintering effect on the morphologies and conductivity of nano-Ag particle films by the spin coating method. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ong, B.S. Facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles useful for fabrication of high-conductivity elements for printed electronics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3266–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-H.; Chou, K.-S.; Huang, K.-C. Inkjet printing of nanosized silver colloids. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Moon, J. Highly conductive ink jet printed films of nanosilver particles for printable electronics. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2005, 8, J30–J33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, S.; Park, B.K.; Moon, J. Direct writing of silver conductive patterns: Improvement of film morphology and conductance by controlling solvent compositions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 264101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, S.; Shin, H.; Xia, Y.; Moon, J. Heterogeneous Interfacial Properties of Ink-Jet-Printed Silver Nanoparticulate Electrode and Organic Semiconductor. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3084–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Higgins, T.M.; Lyons, P.E.; Doherty, E.M.; Nirmalraj, P.N.; Blau, W.J.; Boland, J.J.; Coleman, J.N. Silver nanowire networks as flexible, transparent, conducting films: Extremely high DC to optical conductivity ratios. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layani, M.; Gruchko, M.; Milo, O.; Balberg, I.; Azulay, D.; Magdassi, S. Transparent conductive coatings by printing coffee ring arrays obtained at room temperature. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3537–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.K.; Yu, R.M.; Lu, C.Z. A new transparent conductor: Silver nanowire film buried at the surface of a transparent polymer. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4484–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Yu, X. Silver nanowire-based transparent, flexible, and conductive thin film. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, I.; Jo, Y.H.; Kim, I.; Lee, H.M. A simple process for synthesis of Ag nanoparticles and sintering of conductive ink for use in printed electronics. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaria, A.R.; Kumar, A.; Zhou, C. Large scale, highly conductive and patterned transparent films of silver nanowires on arbitrary substrates and their application in touch screens. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 245201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, T.; Kim, W.S. Reversibly stretchable transparent conductive coatings of spray-deposited silver nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.; Yang, W.S.; Suh, K.S. Uniformly interconnected silver-nanowire networks for transparent film heaters. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, P.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.S.; Ko, S.H. Very long Ag nanowire synthesis and its application in a highly transparent, conductive and flexible metal electrode touch panel. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6408–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Gao, Y.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Su, J.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, J. Transferable self-welding silver nanowire network as high performance transparent flexible electrode. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 335202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Zhu, Y. Highly conductive and stretchable silver nanowire conductors. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5117–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Narasimhan, V.K.; Kong, D.; Lee, H.R.; Cui, Y. Performance enhancement of metal nanowire transparent conducting electrodes by mesoscale metal wires. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madaria, A.R.; Kumar, A.; Ishikawa, F.N.; Zhou, C. Uniform, highly conductive, and patterned transparent films of a percolating silver nanowire network on rigid and flexible substrates using a dry transfer technique. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Bai, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Deng, S.; Du, X.; Li, W. The Preparation of Ag Nanoparticle and Ink Used for Inkjet Printing of Paper Based Conductive Patterns. Materials 2017, 10, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Moon, K.-S.; Li, Y.; Wong, C. Surface functionalized silver nanoparticles for ultrahigh conductive polymer composites. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2969–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, W.; Pei, Q. Silver Nanowire-Polymer Composite Electrodes for Efficient Polymer Solar Cells. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4453–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; He, R.; Lan, Q.; Wu, W.; Duan, F.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, Q.; Wu, J.; Liu, J. Screen-Printed Fabrication of PEDOT:PSS/Silver Nanowire Composite Films for Transparent Heaters. Materials 2017, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scardaci, V.; Coull, R.; Lyons, P.E.; Rickard, D.; Coleman, J.N. Spray deposition of highly transparent, low-resistance networks of silver nanowires over large areas. Small 2011, 7, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieri, N.; Chung, J.; Haferl, S.; Poulikakos, D.; Grigoropoulos, C. Microstructuring by printing and laser curing of nanoparticle solutions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 3529–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Liao, F.; Molesa, S.; Redinger, D.; Subramanian, V. Plastic-compatible low resistance printable gold nanoparticle conductors for flexible electronics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, G412–G417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieri, N.; Chung, J.; Poulikakos, D.; Grigoropoulos, C. Manufacturing of nanoscale thickness gold lines by laser curing of a discretely deposited nanoparticle suspension. Superlattices Microstruct. 2004, 35, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Ko, S.; Bieri, N.R.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; Poulikakos, D. Conductor microstructures by laser curing of printed gold nanoparticle ink. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczech, J.; Megaridis, C.; Zhang, J.; Gamota, D. Ink jet processing of metallic nanoparticle suspensions for electronic circuitry fabrication. Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 2004, 8, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieri, N.; Chung, J.; Poulikakos, D.; Grigoropoulos, C. An experimental investigation of microresistor laser printing with gold nanoparticle-laden inks. Appl. Phys. A 2005, 80, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.; Moon, J.; Kim, J.S. Direct writing of copper conductive patterns by ink-jet printing. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 7706–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Woo, K.; Kim, D.; Lim, S.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, H.; Xia, Y.; Moon, J. Controlling the thickness of the surface oxide layer on Cu nanoparticles for the fabrication of conductive structures by ink-jet printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-G.; Park, H.J.; Ahn, S.H.; Guo, L.J. Transparent Cu nanowire mesh electrode on flexible substrates fabricated by transfer printing and its application in organic solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmell, A.R.; Wiley, B.J. The synthesis and coating of long, thin copper nanowires to make flexible, transparent conducting films on plastic substrates. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4798–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Rathmell, A.R.; Stewart, I.E.; Ha, Y.-C.; Wilson, A.R.; Chen, Z.; Wiley, B.J. A rapid synthesis of high aspect ratio copper nanowires for high-performance transparent conducting films. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2562–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Pan, D. Large-Scale synthesis of well-dispersed copper nanowires in an electric pressure cooker and their application in transparent and conductive networks. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 4440–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Wang, R.; Lu, Y.; Pei, Q. An elastomeric transparent composite electrode based on copper nanowires and polyurethane. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.; Kim, A.; Yang, W.; Jeong, S.; Moon, J. A highly stretchable, helical copper nanowire conductor exhibiting a stretchability of 700%. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.-G.; Jung, S.-H.; Jin, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, I.D.; Bae, B.-S. Flexible transparent conducting hybrid film using a surface-embedded copper nanowire network: A highly oxidation-resistant copper nanowire electrode for flexible optoelectronics. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10973–10979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Gelves, G.A.; Sundararaj, U. Copper nanowire/polystyrene nanocomposites: Lower percolation threshold and higher EMI shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.; Kim, A.; Lee, D.; Yang, W.; Woo, K.; Jeong, S.; Moon, J. Annealing-free fabrication of highly oxidation-resistive copper nanowire composite conductors for photovoltaics. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Zeng, H. Superstable transparent conductive Cu@Cu4Ni nanowire elastomer composites against oxidation, bending, stretching, and twisting for flexible and stretchable optoelectronics. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6298–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, T.; Izumi, K.; Kuroiwa, N.; Senjuh, A.; Fujimoto, A.; Adachi, M.; Yamamoto, T. Preparation of electrically conductive nano-powder of zinc oxide and application to transparent film coating. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 480, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.H.; Jung, I.; Choi, C.S.; Kim, I.; Lee, H.M. Synthesis and characterization of low temperature Sn nanoparticles for the fabrication of highly conductive ink. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 225701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathalingam, A.; Kesavan, K.; Jeon, J.; Kim, H.-S. Analysis of Sn Concentration Effect on Morphological, Optical, Electrical and Photonic Properties of Spray-Coated Sn-Doped CdO Thin Films. Coatings 2018, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, C.; Lee, H.M. Synthesis of oxide-free aluminum nanoparticles for application to conductive film. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 055602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Ko, S.H.; Grigoropoulos, C.P. Thermal sintering of solution-deposited nanoparticle silver ink films characterized by spectroscopic ellipsometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 234104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ong, B.S.; Liu, P.; Gardner, S.; Chiang, B. High-Performance organic thin-film transistors with solution-printed gold contacts. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdassi, S.; Grouchko, M.; Toker, D.; Kamyshny, A.; Balberg, I.; Millo, O. Ring stain effect at room temperature in silver nanoparticles yields high electrical conductivity. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10264–10267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoni, A.; Azoubel, S.; Magdassi, S. Inkjet printing of flexible high-performance carbon nanotube transparent conductive films by “coffee ring effect”. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11084–11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermanaki Farahani, R.; Gagne, M.; Klemberg-Sapieha, J.E.; Therriault, D. Electrically Conductive Silver Nanoparticles-Filled Nanocomposite Materials as Surface Coatings of Composite Structures. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kandel, H.R.; Dervishi, E.; Saini, V.; Xu, Y.; Biris, A.R.; Lupu, D.; Salamo, G.J.; Biris, A.S. Comparative study on different carbon nanotube materials in terms of transparent conductive coatings. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slegers, S.; Linzas, M.; Drijkoningen, J.; D’Haen, J.; Reddy, N.K.; Deferme, W. Surface Roughness Reduction of Additive Manufactured Products by Applying a Functional Coating Using Ultrasonic Spray Coating. Coatings 2017, 7, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Gao, S.; Eslamian, M. Fundamental study on the effect of spray parameters on characteristics of P3HT: PCBM active layers made by spray coating. Coatings 2015, 5, 488–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwa, Y.; Goldthorpe, I.A. Metal-nanowire coated threads for conductive textiles. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 14th International Conference on Nanotechnology, Toronto, ON, Canada, 18–21 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Meulendijks, N.; Burghoorn, M.; van Ee, R.; Mourad, M.; Mann, D.; Keul, H.; Bex, G.; van Veldhoven, E.; Verheijen, M.; Buskens, P. Electrically conductive coatings consisting of Ag-decorated cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 2017, 24, 2191–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, N.; Czerw, R.; Xing, S.; Iyer, P.; Carroll, D.L. Properties of polyvinylidene difluoride-carbon nanotube blends. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitl, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Gaur, A.; Jeon, S.; Usrey, M.L.; Strano, M.S.; Rogers, J.A. Solution casting and transfer printing single-walled carbon nanotube films. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Minami, N.; Zhu, W.; Kazaoui, S.; Azumi, R.; Matsumoto, M. Langmuir–Blodgett films of single-wall carbon nanotubes: Layer-by-layer deposition and in-plane orientation of tubes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, 7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, N.; Gabriel, J.-C.; Grüner, G. Quasi-Langmuir–Blodgett thin film deposition of carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 3228–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Marks, T.J.; Grüner, G. Indium tin oxide modified transparent nanotube thin films as effective anodes for flexible organic light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, H.; Hatsuta, N.; Wachi, M.; Takei, Y.; Takashiri, M. Combination of Electrodeposition and Transfer Processes for Flexible Thin-Film Thermoelectric Generators. Coatings 2018, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Jaleh, B.; Ehsani, A. Electrophoretic deposition of graphene oxide on aluminum: Characterization, low thermal annealing, surface and anticorrosive properties. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 88, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Jaleh, B.; Shahbazi, N. Reversible wettability conversion of electrodeposited graphene oxide/titania nanocomposite coating: Investigation of surface structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 368, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, G.B.; Fincher, C.; Gao, F. Polyaniline nanotube composites: A high-resolution printable conductor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1290–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J. Transfer-Free chemical vapor deposition of graphene on silicon substrate at atmospheric pressure: A sacrificial catalyst. Thin Solid Films 2018, 657, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, D.S.; Thomas, D.; Hu, L.; Ladous, C.; Lam, T.; Park, Y.; Irvin, G.; Drzaic, P. Carbon-Nanotube film on plastic as transparent electrode for resistive touch screens. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2009, 17, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Niu, X.; Liu, Z.; Pei, Q. Intrinsically Stretchable Polymer Light-Emitting Devices Using Carbon Nanotube-Polymer Composite Electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3989–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, F. Buckling of aligned carbon nanotubes as stretchable conductors: A new manufacturing strategy. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.; Niu, X.; Yu, Z.; Hu, W.; Brochu, P.; Pei, Q. Compliant Silver Nanowire-Polymer Composite Electrodes for Bistable Large Strain Actuation. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Le, T.-H.; Park, C.S.; Park, G.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.; Kwon, O.S.; Lim, G.T.; Yoon, H. A Solution-Processable, Nanostructured, and Conductive Graphene/Polyaniline Hybrid Coating for Metal-Corrosion Protection and Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuznetzov, A.A.; Lee, S.B.; Zhang, M.; Baughman, R.H.; Zakhidov, A.A. Electron field emission from transparent multiwalled carbon nanotube sheets for inverted field emission displays. Carbon 2010, 48, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.G.; Xu, T.; Park, H.J.; Luo, X.; Guo, L.J. Efficiency enhancement of organic solar cells using transparent plasmonic Ag nanowire electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4378–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaynor, W.; Burkhard, G.F.; McGehee, M.D.; Peumans, P. Smooth nanowire/polymer composite transparent electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Connor, S.T.; Cui, Y.; Peumans, P. Semitransparent organic photovoltaic cells with laminated top electrode. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Xu, Y.; Lu, G.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Transparent graphene/PEDOT:·PSS composite films as counter electrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, Z.; Hu, W.; Chang, C.H.; Chen, Q.; Pei, Q. Efficient Flexible Phosphorescent Polymer Light-Emitting Diodes Based on Silver Nanowire-Polymer Composite Electrode. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5563–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Hu, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, M.; Grüner, G.; Pei, Q. Fully bendable polymer light emitting devices with carbon nanotubes as cathode and anode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Grüner, G.; Marks, T. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes with transparent carbon nanotube electrodes: Problems and solutions. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 155202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Sun, M.; Lei, G.; Pei, Q. Highly flexible polymer light-emitting devices using carbon nanotubes as both anodes and cathodes. J. Photonics Energy 2011, 1, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artukovic, E.; Kaempgen, M.; Hecht, D.; Roth, S.; Grüner, G. Transparent and flexible carbon nanotube transistors. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gupta, M.C.; Dudley, K.L.; Lawrence, R.W. Novel carbon nanotube-polystyrene foam composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Huang, Y.; Du, F.; He, X.; Lin, X.; Gao, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Eklund, P.C. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of single-walled carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekitani, T.; Noguchi, Y.; Hata, K.; Fukushima, T.; Aida, T.; Someya, T. A rubberlike stretchable active matrix using elastic conductors. Science 2008, 321, 1468–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Dang, Z.-M. Carbon nanotube composites with high dielectric constant at low percolation threshold. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 042903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, N.; Huang, C.; Ren, K.; Zhang, Q. Microstructure and electromechanical properties of carbon nanotube/poly (vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene-chlorofluoroethylene) composites. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1897–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-W.; Joo, M.; Ahn, J.; Lee, T.-I.; Kim, T.-S.; Im, S.G.; Lee, J.-Y. Facilitated embedding of silver nanowires into conformally-coated iCVD polymer films deposited on cloth for robust wearable electronics. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3399–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Yuan, W.; Brochu, P.; Gruner, G.; Pei, Q. Highly stretchable, conductive, and transparent nanotube thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 161108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.-F.; Hu, L.; Choi, J.W.; Cui, Y. Light-Weight free-standing carbon nanotube-silicon films for anodes of lithium ion batteries. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3671–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
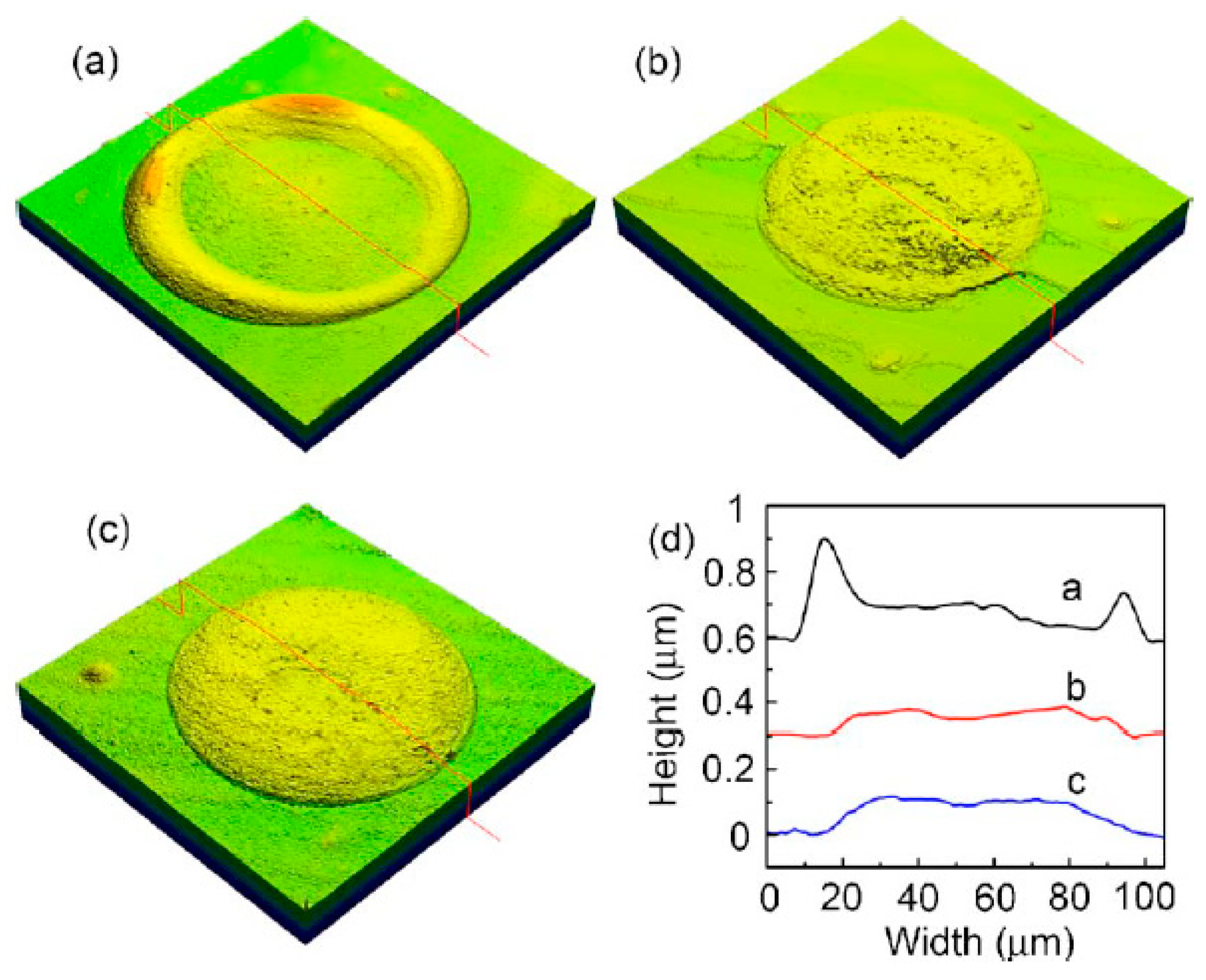
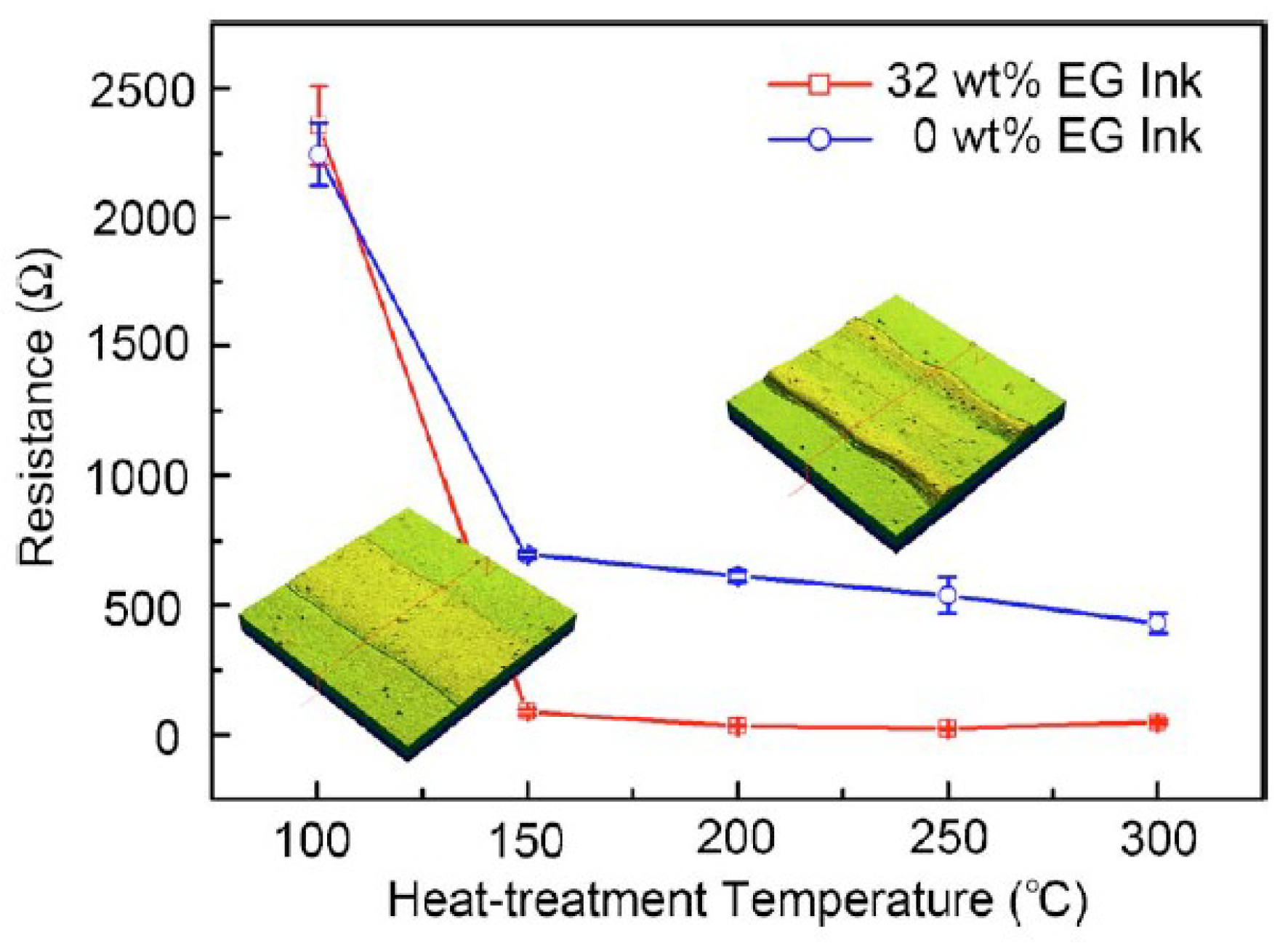
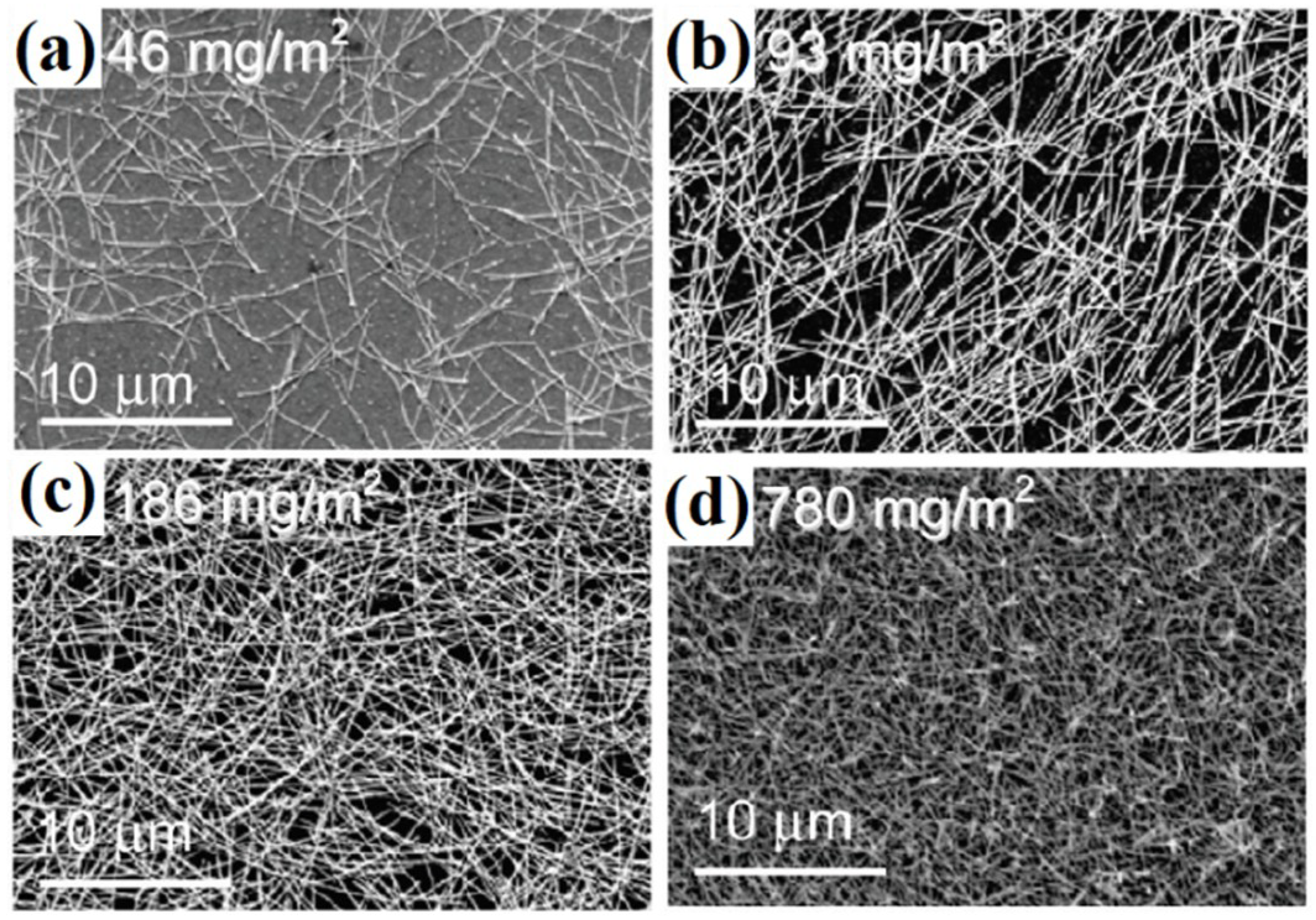
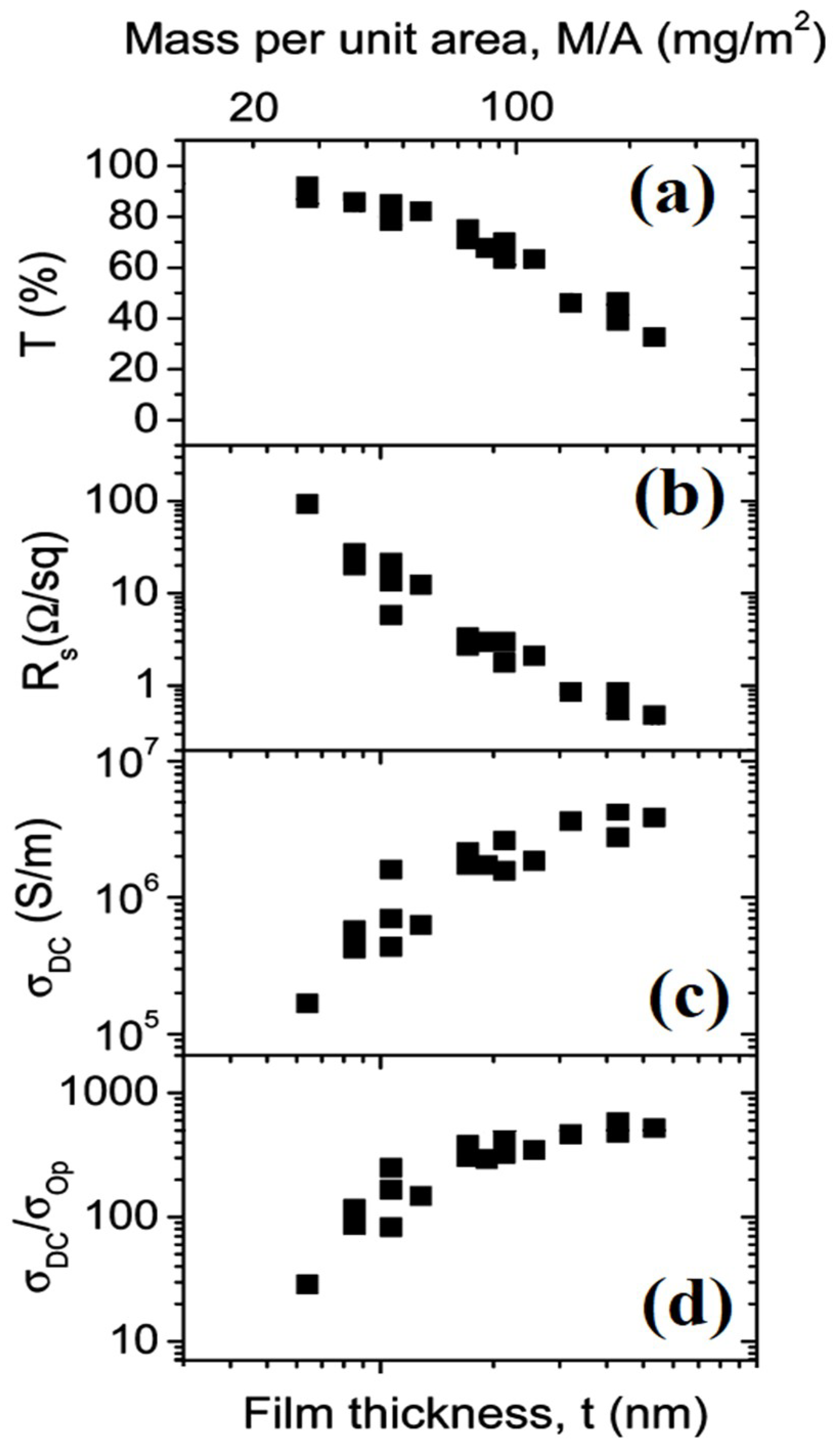
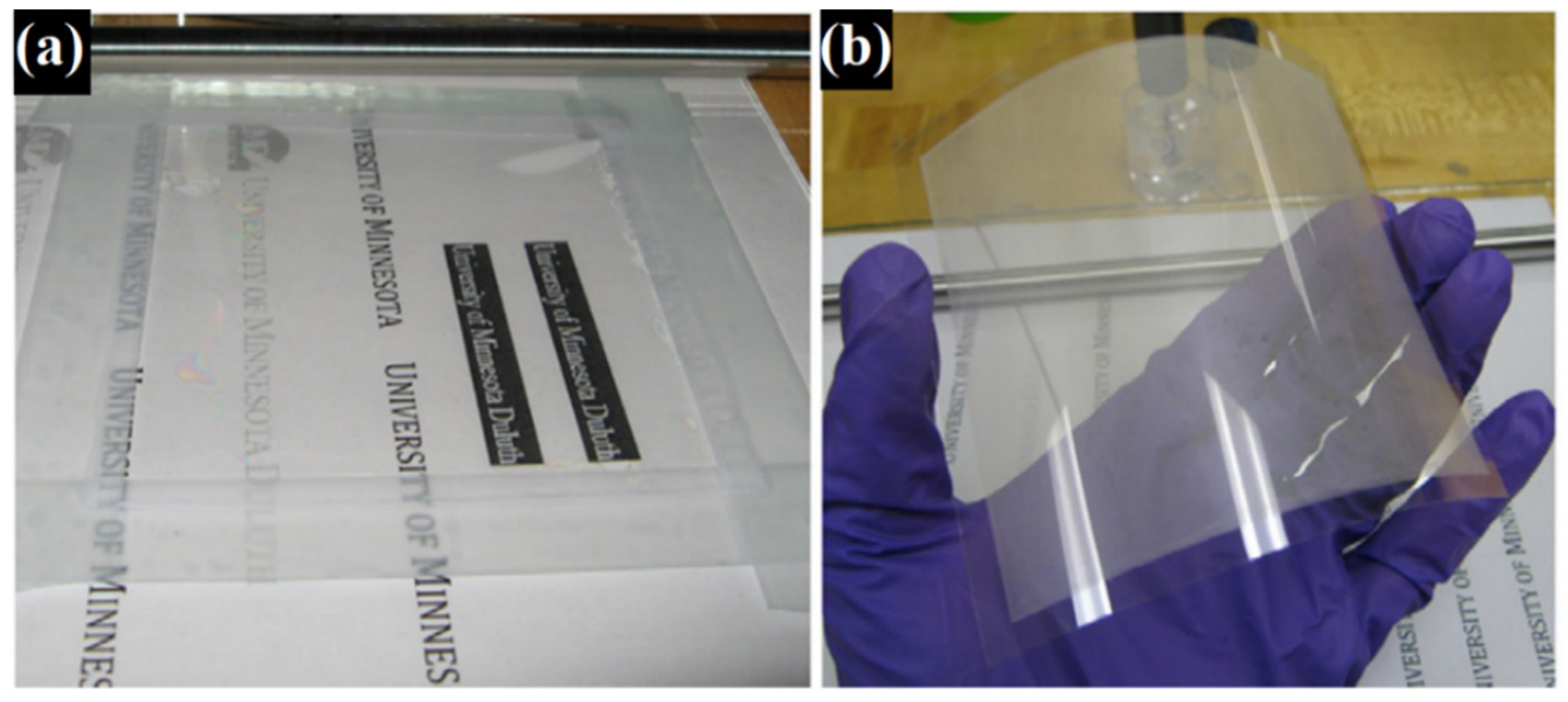
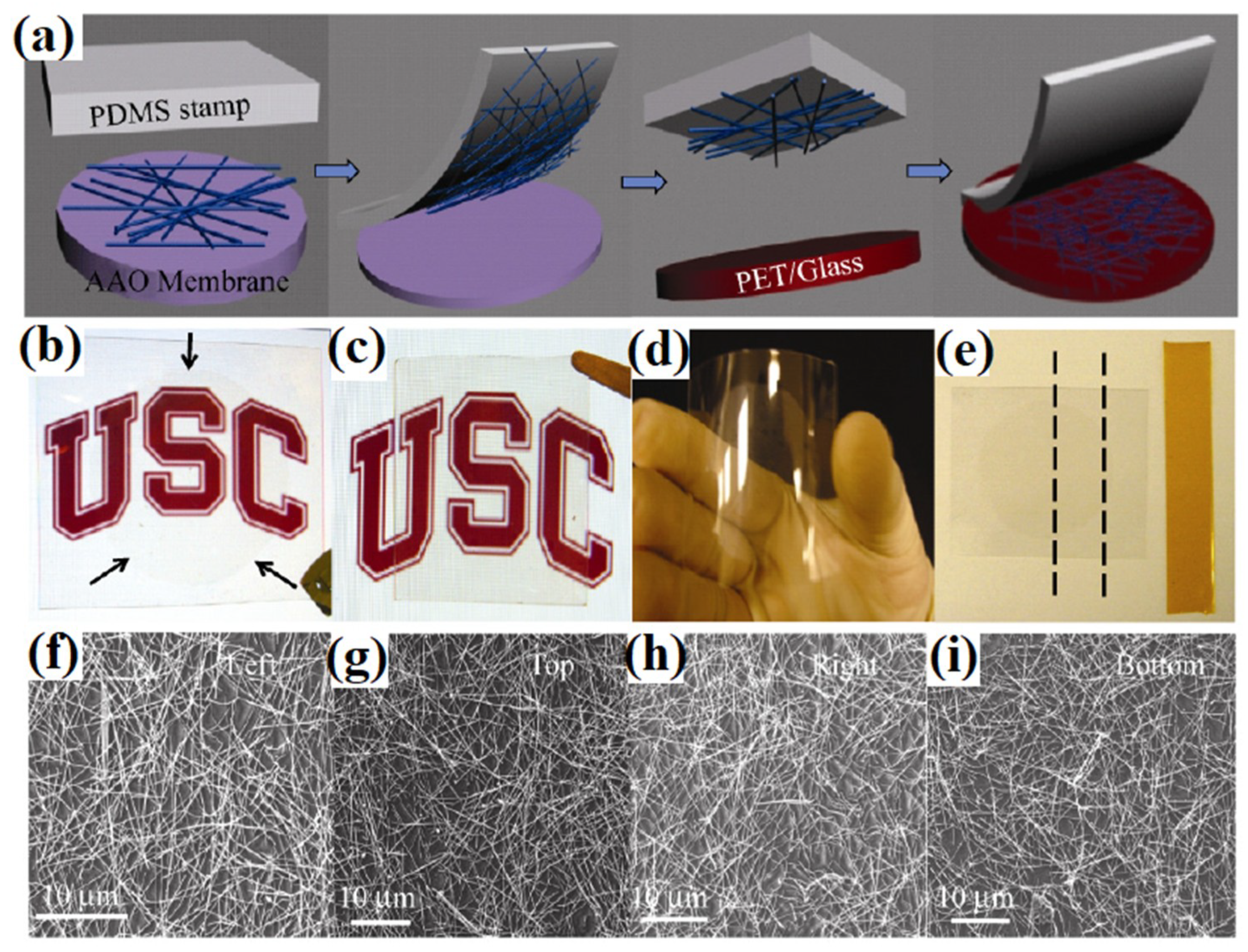
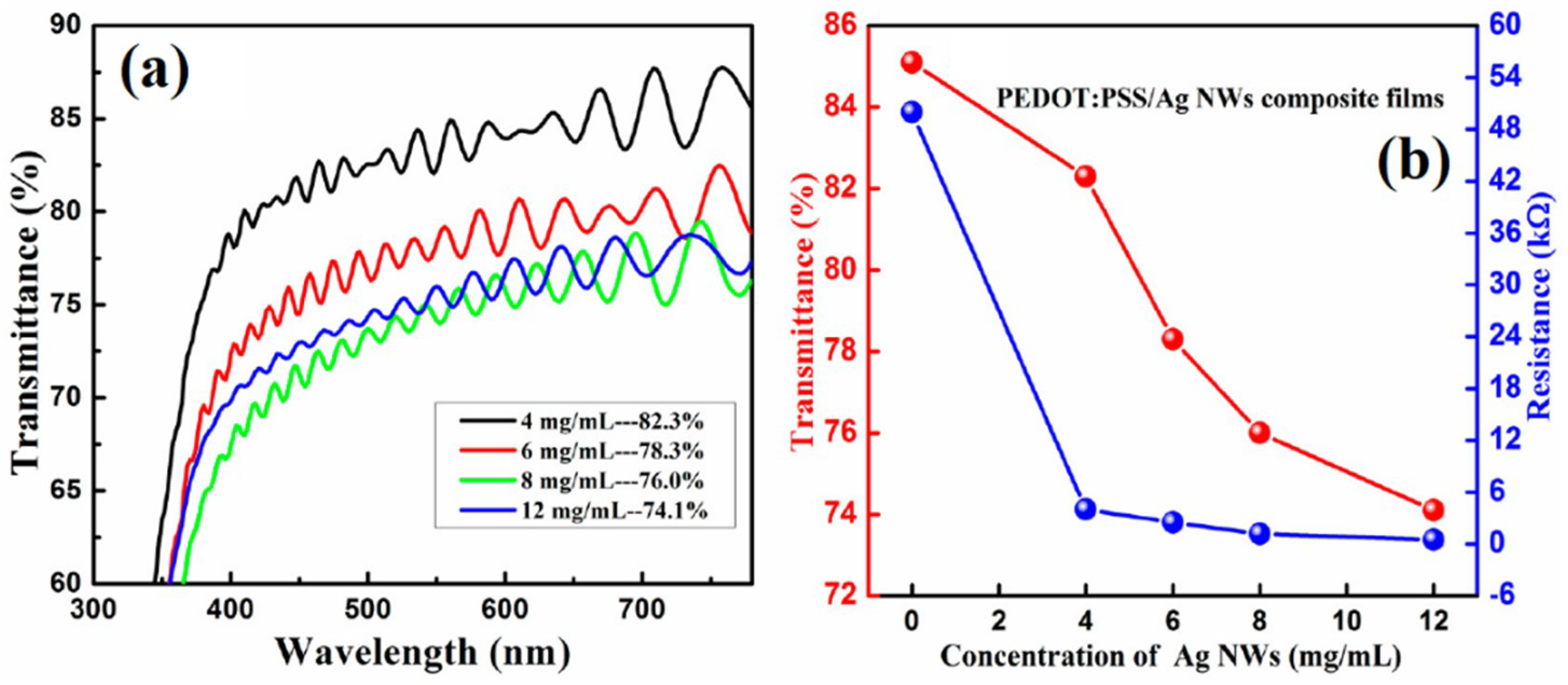
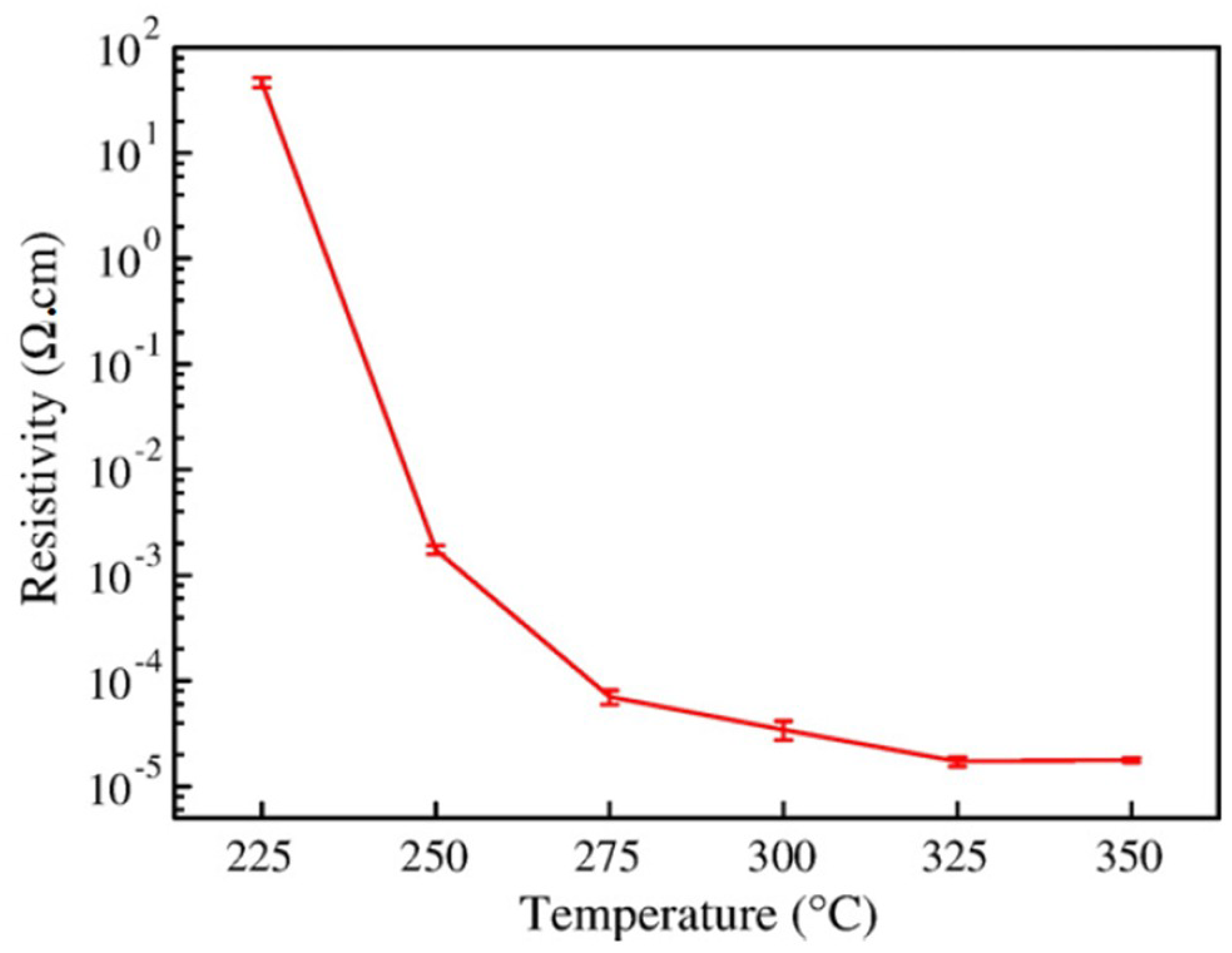
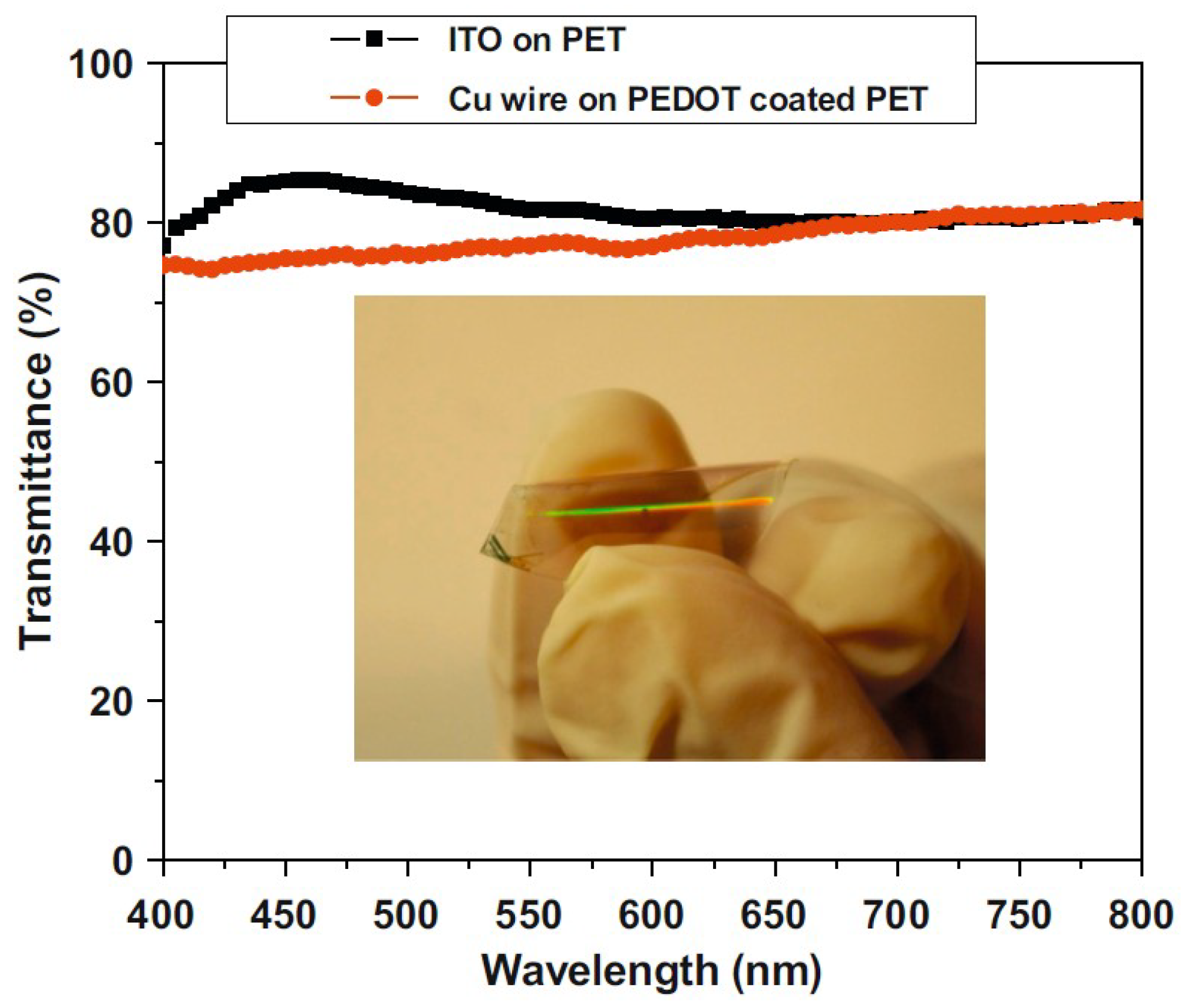
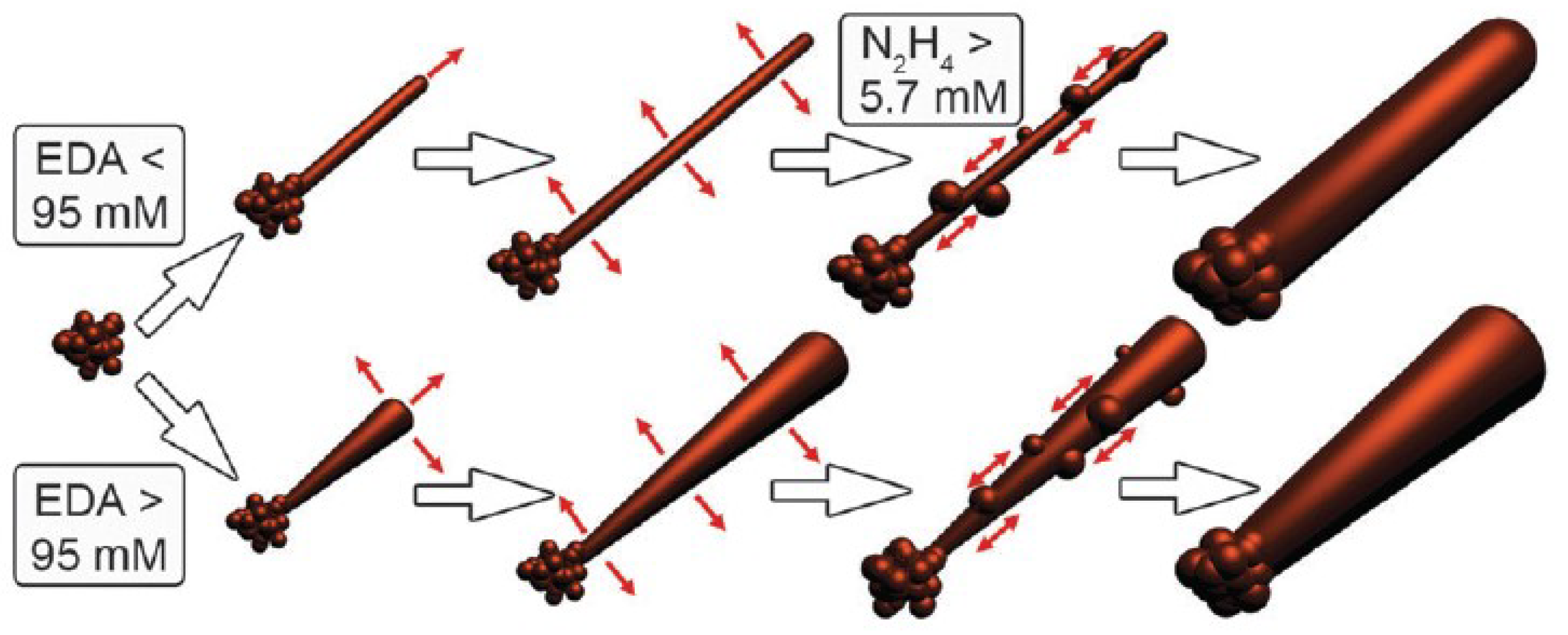
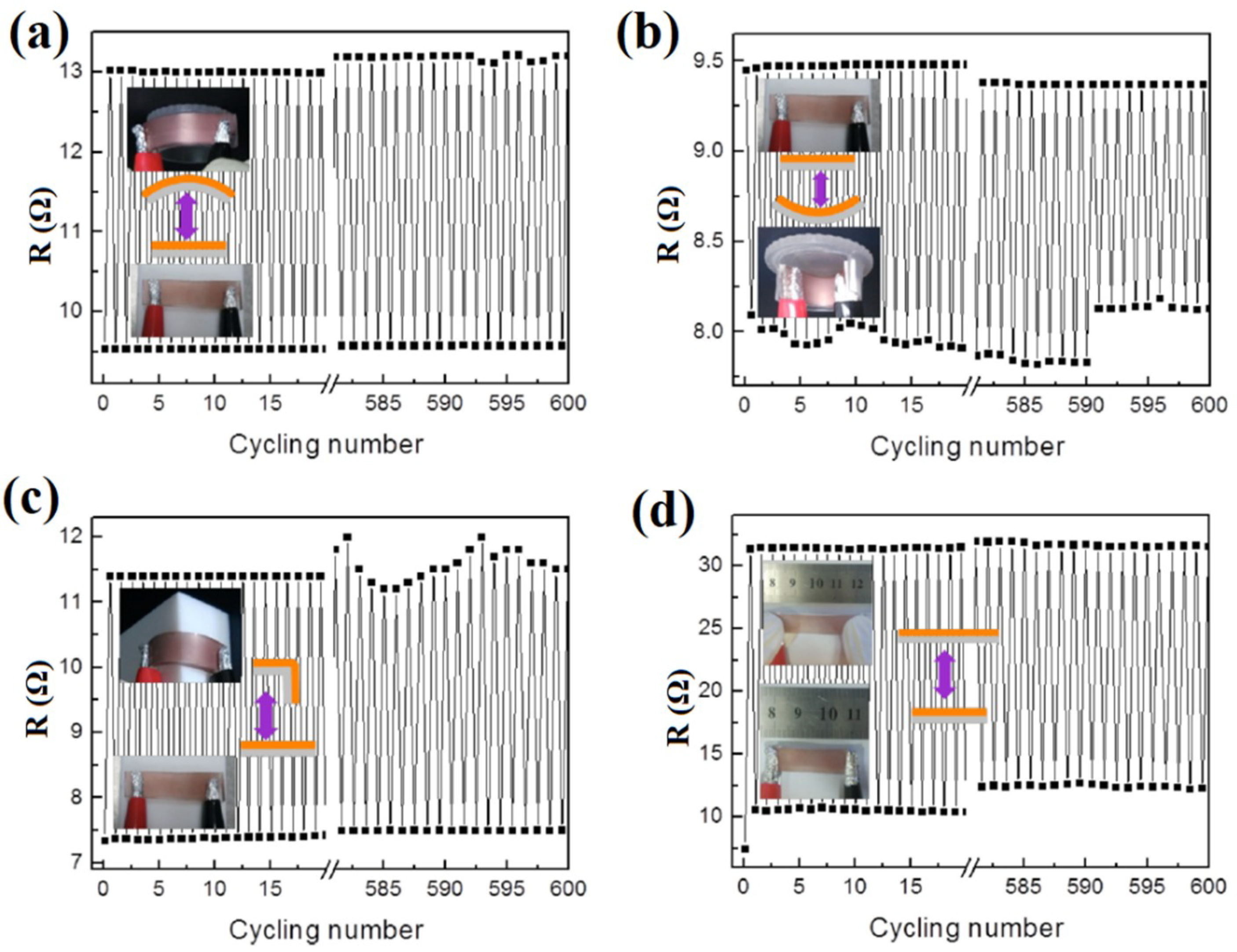
| Ref. | Material | Coating Method | Coating Thickness (nm) | Transparency (%) | Electronic Factor | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | Ag NPs | Spin coating | 82 | Not available | 2.4 × 10−5 Ω cm | Not available |
| [12] | Ag NPs | Ink-jet printing | 530 | Not available | 1.6 × 10−5 Ω cm | Not available |
| [14] | Ag NPs | Ink-jet printing | 100 | Not available | 3.5 × 10−6 Ω cm | Not available |
| [3] | Ag NWs | Solution-processed | 100 | 85 (solar) | 10 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| [16] | Ag NWs | Vacuum filtration (transfer) | 107 | 85 | 13 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| [17] | Ag NPs | Ink-jet printing | 300 | 95 | 4 ± 0.5 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| [19] | Ag NWs | Rod-coating | Not available | 75 | 175 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| [21] | Ag NWs | Spray deposition | Not available | 85 | 33 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| [22] | Ag NWs | Spray deposition | Not available | 80 | 35 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| Stretchable | ||||||
| [24] | Ag NWs | Vacuum filtration | Not available | 89 | 9 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| 95 | 69 Ω/sq | |||||
| [25] | Ag NWs | Rod-coating | Not available | 91 | 13 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| [28] | Ag NWs | Vacuum filtration | Not available | 85 | 10 Ω/sq | Flexible |
| [33] | Ag NWs | Spray deposition | Not available | 90 | 50 Ω/sq | Not available |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naghdi, S.; Rhee, K.Y.; Hui, D.; Park, S.J. A Review of Conductive Metal Nanomaterials as Conductive, Transparent, and Flexible Coatings, Thin Films, and Conductive Fillers: Different Deposition Methods and Applications. Coatings 2018, 8, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8080278
Naghdi S, Rhee KY, Hui D, Park SJ. A Review of Conductive Metal Nanomaterials as Conductive, Transparent, and Flexible Coatings, Thin Films, and Conductive Fillers: Different Deposition Methods and Applications. Coatings. 2018; 8(8):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8080278
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaghdi, Samira, Kyong Yop Rhee, David Hui, and Soo Jin Park. 2018. "A Review of Conductive Metal Nanomaterials as Conductive, Transparent, and Flexible Coatings, Thin Films, and Conductive Fillers: Different Deposition Methods and Applications" Coatings 8, no. 8: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8080278
APA StyleNaghdi, S., Rhee, K. Y., Hui, D., & Park, S. J. (2018). A Review of Conductive Metal Nanomaterials as Conductive, Transparent, and Flexible Coatings, Thin Films, and Conductive Fillers: Different Deposition Methods and Applications. Coatings, 8(8), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8080278