C9 Petroleum Resin and Polyethylene-Based High-Viscosity Modified Asphalt Binder Proportioning Optimization and Performance Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Design Method
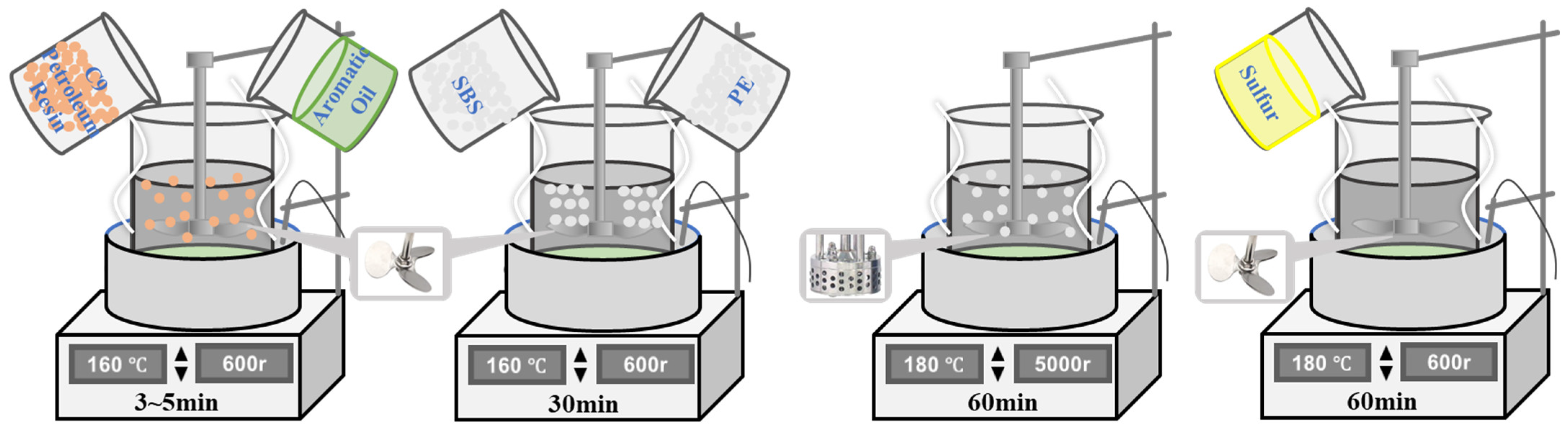
2.3. Preparation Method
- Place the asphalt binders in a 160 °C oven and heat it until fully melted. Add aromatic oil and C9 petroleum resin, and stir thoroughly at 600 rpm for 3–5 min until evenly dispersed;
- Add SBS and PE modifiers, and stir thoroughly at 600 rpm for 30 min at 160 °C;
- Perform high-speed shear at 5000 rpm for 60 min at 180 °C;
- Add stabilizers, and stir at 600 rpm for 60 min at 180 °C. The high-viscosity modified asphalt binder product is obtained and immediately poured into molds for subsequent tests. The specific preparation process is shown in Figure 2.
2.4. Test Method
- Basic Indicators
- 2.
- Aging Resistance
- 3.
- Rheological Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Test Results Analysis
3.2. Regression Analysis
3.2.1. Linear Regression
3.2.2. Nonlinear Regression
3.3. Correlation Analysis
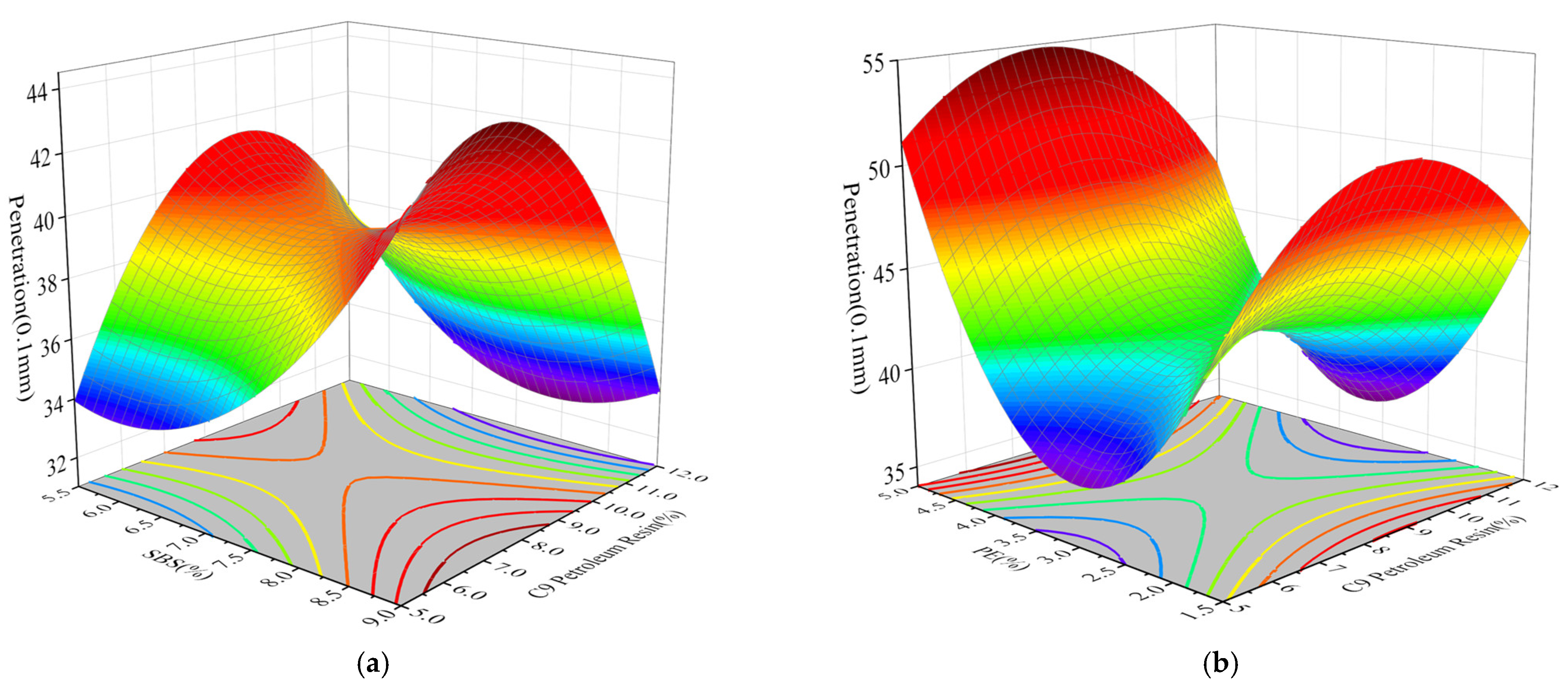
3.3.1. Penetration
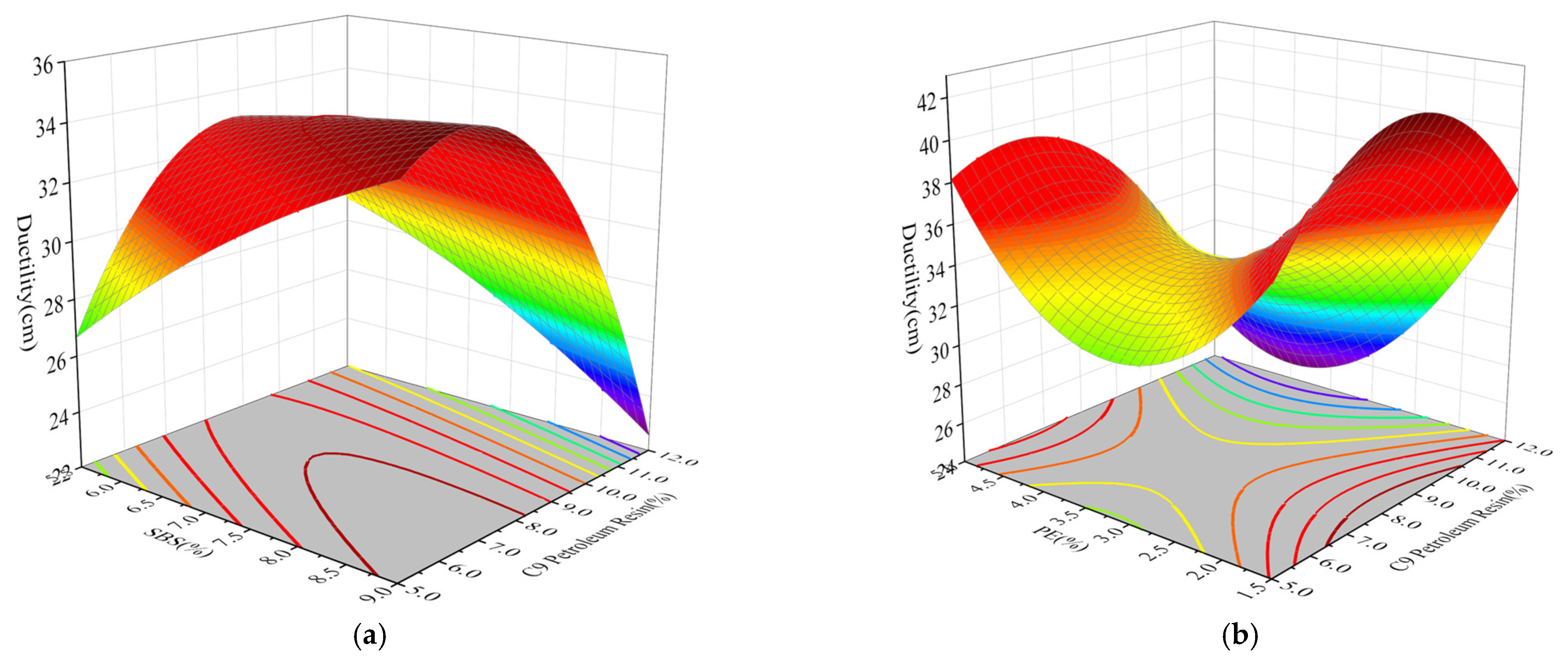
3.3.2. Ductility
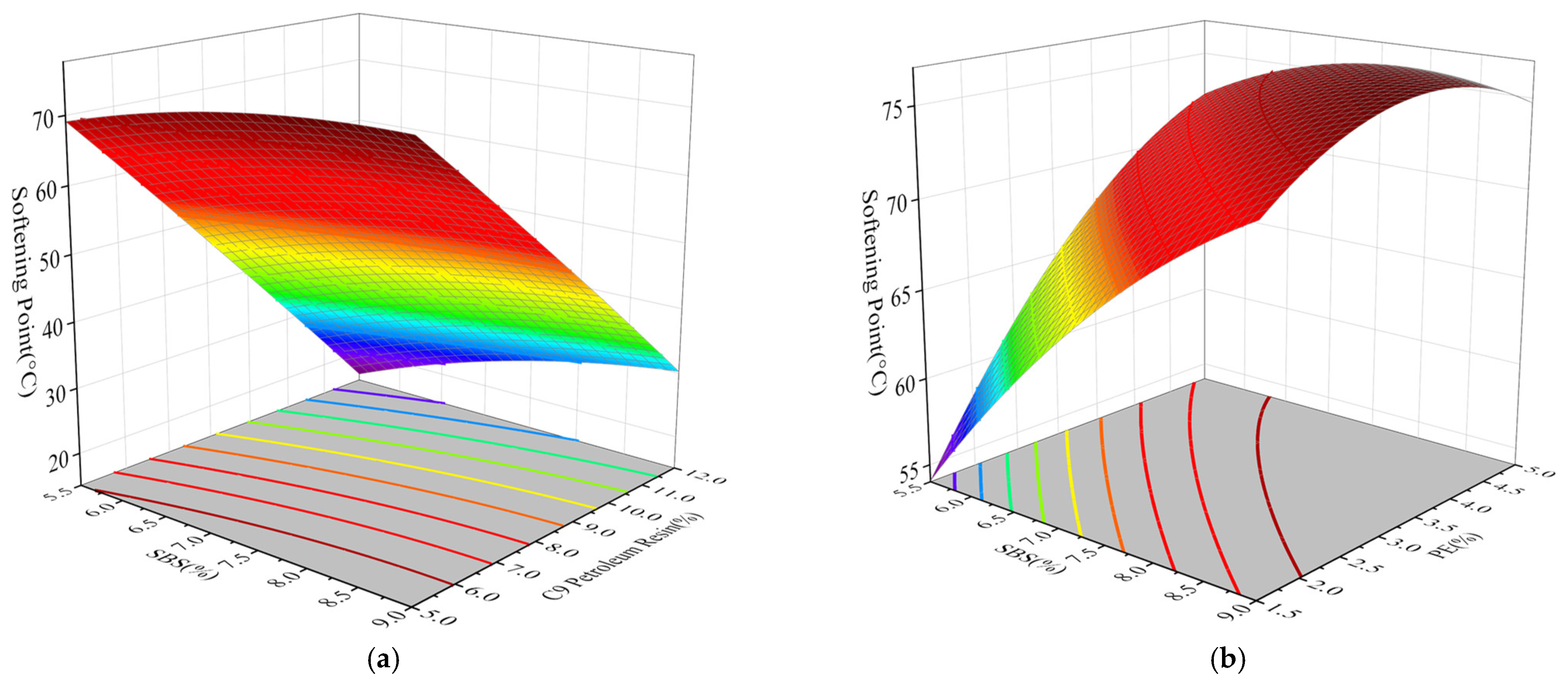
3.3.3. Softening Point
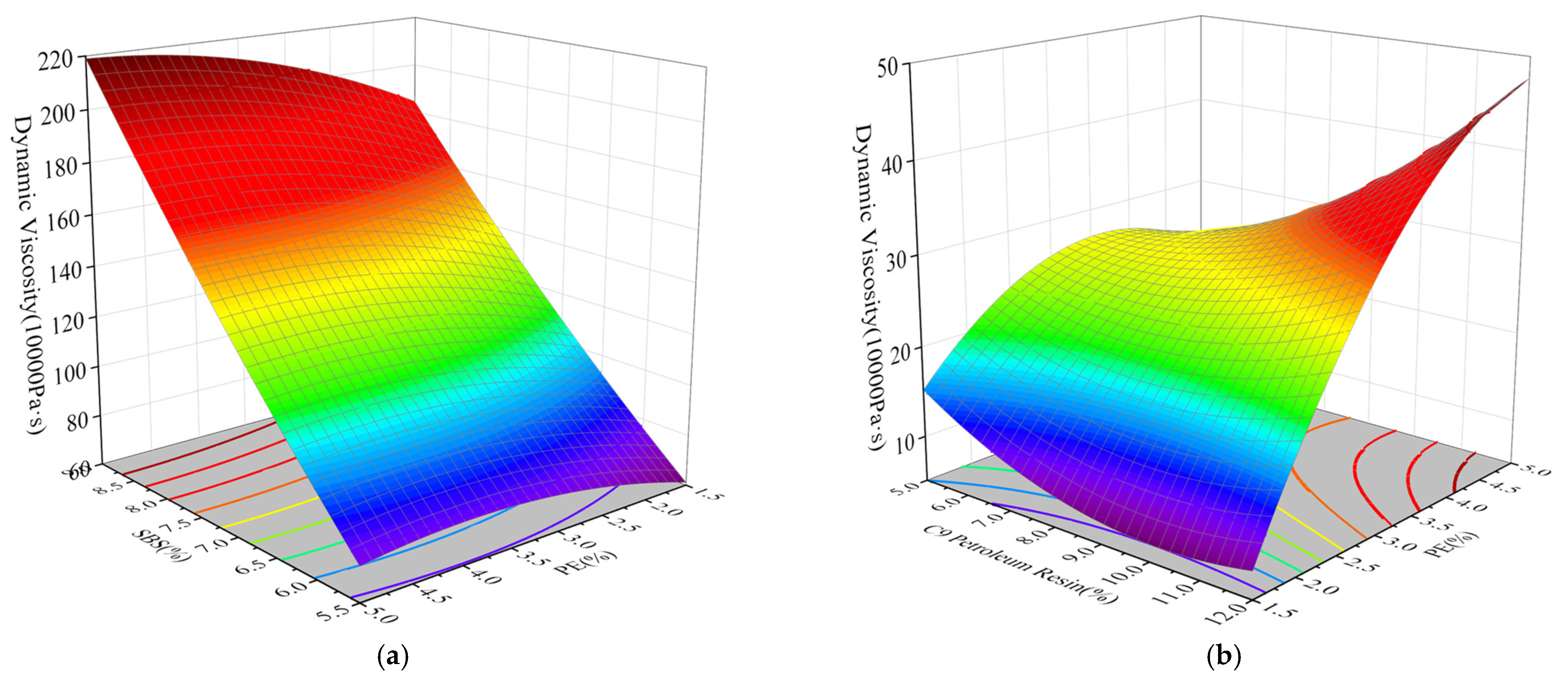
3.3.4. Dynamic Viscosity
3.4. Optimal Ratio of Modifier
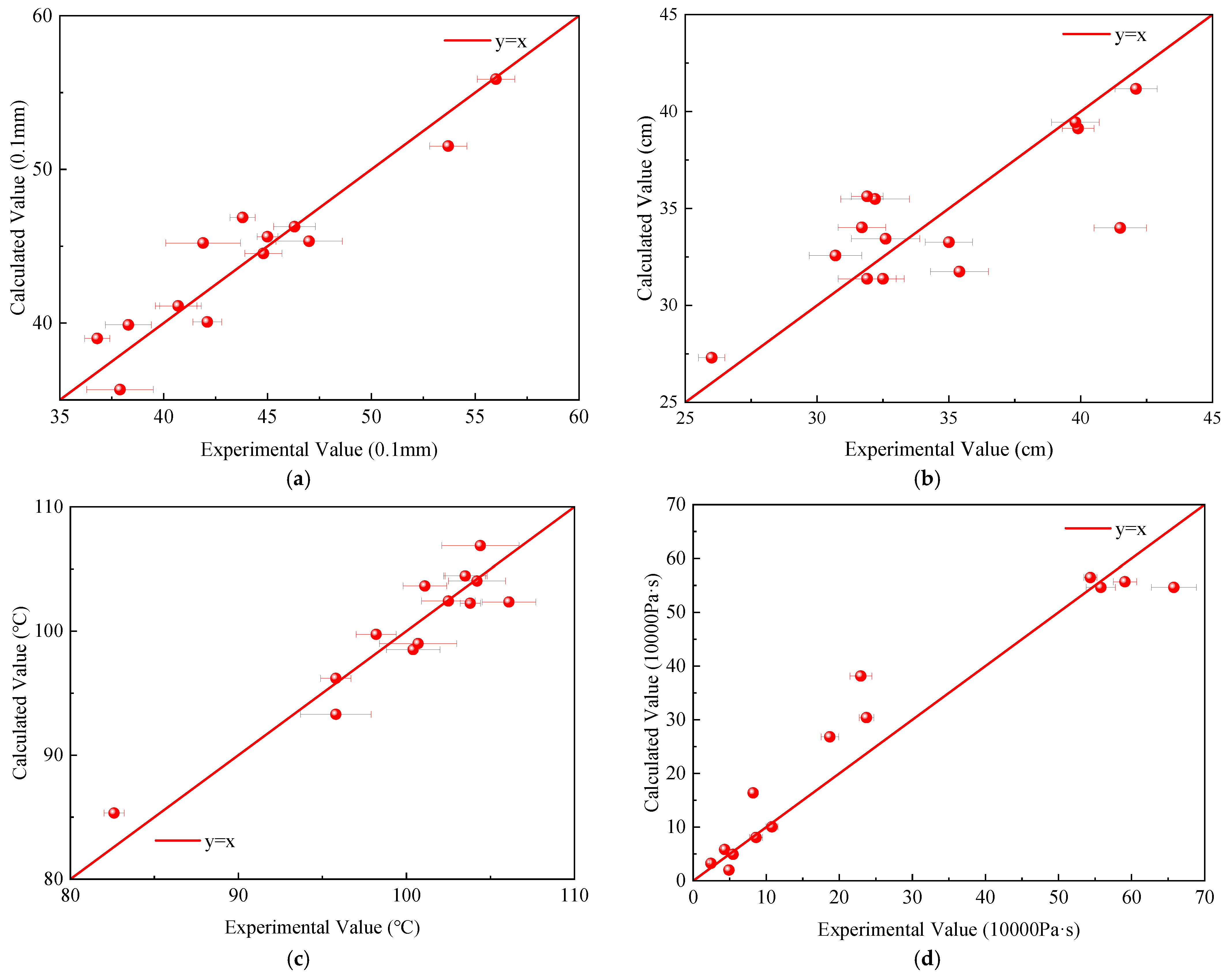
3.4.1. Model Validation
3.4.2. Modifier Ratio Determination
3.5. Performance Evaluation
3.5.1. Ageing Resistance
3.5.2. Rheological Properties
4. Conclusions
- SBS, PE, and C9 petroleum resin significantly influence asphalt binder performance. Penetration and softening point are primarily driven by the positive effects of SBS and PE, while C9 petroleum resin has a smaller impact. Ductility is mainly dominated by the positive contribution of C9 petroleum resin, but high dosages may lead to negative effects. Dynamic viscosity strongly depends on the synergistic effects of SBS and PE, with C9 petroleum resin playing a relatively limited role.
- Based on multivariate nonlinear regression model analysis, the optimal proportioning ratio is SBS 7.5%, C9 petroleum resin 6.0%, and PE 5.0%. Under this ratio, the high-viscosity modified asphalt binders meet technical standards for key performance indicators, including penetration, ductility, softening point, and dynamic viscosity.
- In aging resistance tests, the high-viscosity modified asphalt binders exhibited excellent anti-aging performance, with an elastic recovery ratio exceeding 95%, significantly surpassing the technical standard requirements. Rheological test results indicate that the asphalt binders maintain a high rutting factor at elevated temperatures, demonstrating superior rutting resistance and temperature adaptability.
- This study primarily focused on optimizing modifier dosages and their effects on the performance of high-viscosity modified asphalt binders. However, further research is required to address aspects such as long-term durability, freeze–thaw cycles, mixture adaptability, and life cycle assessment (costs and environment). Future studies should also incorporate microstructural characterization techniques to comprehensively explore the mechanisms underlying performance optimization of asphalt binders and their mixtures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, L.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Li, H. Modified asphalt based on polyethylene with broad molecular weight distribution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Han, Y.; Guangxun, E.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Lin, Z. Recycling of waste polyethylene in asphalt and its performance enhancement methods: A critical literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 142072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Li, R.; Hu, M.; Zou, L. Determination of low-temperature crack control parameter of binding asphalt materials based on gray correlation analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 217, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, P.; Zhao, C.; Ling, J.; Wu, T.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Sun, B. Anti-rutting performance evaluation of modified asphalt binders: A review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2021, 8, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Pei, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Cheng, P.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Abdukadir, A.; Xiong, Y.; Yi, J. Study on the development and performance optimization of gussasphalt containing high percent of fine reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 420, 135557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y. Performance optimization of high viscosity modified asphalt with SBS composite modifier and comparison of different high viscosity modified asphalts. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Sun, J. Using SBS Terpene-styrene Resin Blends as a Novel High-viscosity Asphalt Modifier. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, F.; Wang, J. Low Temperature Performance Characteristics of Polyethylene Modified Asphalts—A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Hu, G.; Zhang, J. Study on anti-aging performance enhancement of polymer modified asphalt with high linear SBS content. Polymers 2023, 15, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.S.; RN, G.R.; Ravindranath, S.S. Performance evaluation of long-term laboratory-aged asphalt mixtures containing different molecular structures of SBS copolymers. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2023, 35, 4023191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmoorian, F.; Liyanapathirana, S.; Yeaman, J.; Egwurube, J. Performance of hot-mix asphalt and modified binders containing polyethylene. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2023, 149, 4023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, S.; Chen, A.; Li, Y. Modification mechanism and technical performance of recycled PE-modified asphalt. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghrafy, Y.M.; El-Badawy, S.M.; Abd Alla, E.M. Rheological and environmental evaluation of sulfur extended asphalt binders modified by high-and low-density polyethylene recycled waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assolie, A.A.; Al-Migdady, A.; Borowski, G.; Alsaqoor, S.; Ali, A.S.B.; Alahmer, A. Utilizing waste polyethylene for improved properties of asphalt binders and mixtures: A review. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2025, 19, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boarie, A.; Abdelsalam, M.; Gamal, A.; Rabah, M. Laboratory and Environmental Assessment of Asphalt Mixture Modified with a Compound of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement and Waste Polyethylene. Buildings 2024, 14, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalfattah, I.A.; Mogawer, W.S.; Stuart, K.D. Recycled polyethylene modified asphalt binders and mixtures: Performance characteristics and environmental impact. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022, 2676, 202–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Mainieri, J.J.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Ghabchi, R. Effects of waste high-density polyethylene (HDPE) on asphalt binder and airfield mixes. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2024, 25, 2303661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuniarti, R.; Ahyudanari, E.; Prastyanto, C.A. Performance Comparison of Conventional and Biopolymer-modified Asphalt Mixtures for Airport Pavement. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Hou, T.; Yao, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, C. Effect of C9 petroleum resins on improvement in compatibility and properties of SBS-modified asphalt. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Deng, W.; Zhang, Y. Study on Rheological Behavior and Modification Mechanism of SBS/Tackifying Resin Composite High-Viscosity Modified Asphalt. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2024, 36, 4024130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, S.; Pei, Z.; Zhan, S.; Lin, S.; Ma, K.; Lei, J.; Yi, J. Study of the Properties and Modification Mechanism of SBS-Modified Asphalt by Dry Process. Materials 2024, 17, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdukadir, A.; Pei, Z.; Zhou, W.; Yi, J. Optimization of composite-modified asphalt ratio and performance evaluation of rich bottom layer mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, N.; Kamaruddin, I.; Napiah, M.; Sutanto, M.H. Polymer nanocomposite-modified asphalt: Characterisation and optimisation using response surface methodology. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 4233–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajikarimi, P.; Ehsani, M.; Haloui, Y.E.; Tehrani, F.F.; Absi, J.; Nejad, F.M. Fractional viscoelastic modeling of modified asphalt mastics using response surface method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 317, 125958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, G. Preparation, Performance, and modification mechanism of high viscosity modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, D.; Xia, L.; Du, R.; Shi, Z.; Dong, R.; Wang, X. Study on cohesion and adhesion of high-viscosity modified asphalt. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 394–402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, C. Preparation and properties of high viscosity modified asphalt. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Jin, K.; Zhou, Z. Properties and mechanism of SBS/crumb rubber composite high viscosity modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Chaohui, W.; Cheng, S.; Luqing, L. Research Progress and Performance Evaluation of SBS/CR-modified Asphalt. China J. Highw. Transp. 2021, 34, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Xiong, Q.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, F. Study On Wind Load Coefficient Variation Law Of Heliostat Group Based On Uniform Design Method. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2023, 44, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Lu, Q.; Ai, C.; Rahman, A.; Qiu, Y. Optimization of hard modified asphalt formula for gussasphalt based on uniform experimental design. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, C.; Temitope, A.A.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, G.; Guo, P. Effect of SBS and crumb rubber on asphalt modification: A review of the properties and practical application. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2022, 9, 836–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, P.; Fan, W.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Ouyang, J. Facile preparation and application performance evaluation of SBS/C9 petroleum resin blends as modifier for high viscosity asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jexembayeva, A.; Konkanov, M.; Aruova, L.; Kirgizbayev, A.; Zhaksylykova, L. Performance Optimization Approach of Polymer-Modified Asphalt Mixtures with PET and PE Waste. Polymers 2024, 16, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukkanen, O.; Soenen, H.; Winter, H.H.; Seppälä, J. Low-temperature rheological and morphological characterization of SBS modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 179, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. Performance Study of Waste PE-Modified High-Grade Asphalt. Polymers 2023, 15, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Zhang, T.; Hu, K.; Gillani, S.T.A.; Zhang, W. Evaluation of the Effect of C9 Petroleum Resin on Rheological Behavior, Microstructure, and Chemical Properties of Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene Modified Asphalt. Buildings 2024, 14, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qiu, L.; Liu, J.; Hu, K.; Zou, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, F.; Zang, J. Modification mechanism of C9 petroleum resin and its influence on SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Test Item | Test Value | Test Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | 82.5 | T 0604 2011 | |
| Softening point (℃) | 46.8 | T 0606 2011 | |
| Ductility (15 °C, cm) | >100 | T 0605 2011 | |
| TFOT Residue | Mass Loss (%) | −0.12 | T 0609 2011 |
| Penetration Ratio (25 °C, %) | 76.8 | ||
| Ductility (5 cm/min,15 °C) | 105.9 | ||
| Factor | SBS (A) | C9 Petroleum Resin (B) | PE (C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.5% | 5.0% | 1.5% |
| 2 | 6.0% | 6.0% | 2.0% |
| 3 | 6.5% | 7.0% | 2.5% |
| 4 | 7.0% | 8.0% | 3.0% |
| 5 | 7.5% | 9.0% | 3.5% |
| 6 | 8.0% | 10.0% | 4.0% |
| 7 | 8.5% | 11.0% | 4.5% |
| 8 | 9.0% | 12.0% | 5.0% |
| Test Number | Level | Combination | Factor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | SBS | C9 | PE | ||
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 7 | A1B4C7 | 5.50% | 8.0% | 4.5% |
| 2 | 2 | 8 | 5 | A2B8C5 | 6.00% | 12.0% | 3.5% |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | A3B3C3 | 6.50% | 7.0% | 2.5% |
| 4 | 4 | 7 | 1 | A4B7C1 | 7.00% | 11.0% | 1.5% |
| 5 | 5 | 2 | 8 | A5B2C8 | 7.50% | 6.0% | 5.0% |
| 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | A6B6C6 | 8.00% | 10.0% | 4.0% |
| 7 | 7 | 1 | 4 | A17B1C4 | 8.50% | 5.0% | 3.0% |
| 8 | 8 | 5 | 2 | A8B5C2 | 9.00% | 9.0% | 2.0% |
| Test Number | Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | Ductility (5 °C, cm) | Softening Point (°C) | Dynamic Viscosity (Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Requirement | 40–60 | ≥30 | ≥80 | ≥200,000 |
| 1 | 45.0 | 35.4 | 98.2 | 24,243 |
| 2 | 37.9 | 26.0 | 95.8 | 48,941 |
| 3 | 42.1 | 32.2 | 100.4 | 43,008 |
| 4 | 43.8 | 42.1 | 82.6 | 107,770 |
| 5 | 53.7 | 39.9 | 106.1 | 237,157 |
| 6 | 40.7 | 32.5 | 103.5 | 657,860 |
| 7 | 36.8 | 35.0 | 104.4 | 590,908 |
| 8 | 47.0 | 31.9 | 103.8 | 543,591 |
| Indicator | Multivariate Linear Regression Model | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration | 0.36 | |
| Ductility | 0.97 | |
| Softening Point | 0.30 | |
| Dynamic Viscosity | 0.64 |
| Indicator | Multivariate Nonlinear Regression Model | R2 | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration | 0.88 | 3.17 | |
| Ductility | 0.99 | 4.29 | |
| Softening Point | 0.88 | 3.64 | |
| Dynamic Viscosity | 0.95 | 13.59 |
| Type | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBS Content (%) | 7.0 | 6.5 | 8.0 | |
| C9 Petroleum Resin Content (%) | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.0 | |
| PE Content (%) | 4.5 | 4.5 | 2.4 | |
| Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | Experimental Value | 41.9 | 44.8 | 38.3 |
| Calculated Value | 45.2 | 44.5 | 39.9 | |
| Error | −3.31 | 0.27 | −1.59 | |
| Ductility (5 °C, cm) | Experimental Value | 31.7 | 30.7 | 41.5 |
| Calculated Value | 34.0 | 32.6 | 34.0 | |
| Error | −2.33 | −1.88 | 7.50 | |
| Softening Point (°C) | Experimental Value | 101.1 | 102.5 | 100.7 |
| Calculated Value | 103.6 | 102.4 | 99.0 | |
| Error | −2.54 | 0.07 | 1.70 | |
| Dynamic Viscosity (10,000 Pa·s) | Experimental Value | 18.7 | 8.2 | 22.9 |
| Calculated Value | 17.8 | 10.1 | 25.3 | |
| Error | 0.9 | −1.9 | −2.4 | |
| Type | SBS | C9 Petroleum Resin | PE | Aromatic Oil | Sulfur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 7.5 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 0.20% |
| Type | Test Value | Requirement | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | 53.7 | 40–60 | T 0604 2011 |
| Ductility (5 °C, cm) | 39.3 | ≥30 | T 0606 2011 |
| Softening Point (°C) | 106.1 | ≥80 | T 0605 2011 |
| Dynamic Viscosity (Pa·s) | 237,157 | ≥200,000 | T 0620 2011 |
| Type | Test Value | Requirement | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass Loss (%) | 0.30 | ≤±1.0 | T 0609 2011 |
| Penetration Ratio (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | 75.3% | ≥75 | T 0604 2011 |
| Ductility (5 °C,cm) | 30.7 | ≥20 | T 0606 2011 |
| G*/sinδ (85 °C) | 2.64 | ≥2.2 | T 0628 2011 |
| Elastic Recovery Ratio (25 °C) | 97.5% | ≥60 | T 0662 2000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Abdukadir, A.; Lei, J.; Yi, J.; Pei, Z. C9 Petroleum Resin and Polyethylene-Based High-Viscosity Modified Asphalt Binder Proportioning Optimization and Performance Study. Coatings 2025, 15, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030343
Chen Z, Wang W, Abdukadir A, Lei J, Yi J, Pei Z. C9 Petroleum Resin and Polyethylene-Based High-Viscosity Modified Asphalt Binder Proportioning Optimization and Performance Study. Coatings. 2025; 15(3):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030343
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zining, Wei Wang, Abduhaibir Abdukadir, Junwen Lei, Junyan Yi, and Zhongshi Pei. 2025. "C9 Petroleum Resin and Polyethylene-Based High-Viscosity Modified Asphalt Binder Proportioning Optimization and Performance Study" Coatings 15, no. 3: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030343
APA StyleChen, Z., Wang, W., Abdukadir, A., Lei, J., Yi, J., & Pei, Z. (2025). C9 Petroleum Resin and Polyethylene-Based High-Viscosity Modified Asphalt Binder Proportioning Optimization and Performance Study. Coatings, 15(3), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030343








