Abstract
Expandable graphite (EG) was modified with a charring agent and organic–inorganic hybridized intumescent flame retardants (MEG) were synthesized. This study uses a cone calorimeter (CCT) and a DaqPRO 5300 radiation heat flow meter (Fourtec, Tel Aviv, Israel) to evaluate the fire-resistant properties influenced by MEG on intumescent fire-retardant coatings. The impact of MEG on the thermal degradation of these coatings was investigated through the use of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The results obtained by CCT demonstrated that the incorporation of MEG markedly diminished the heat release rate and total heat release rate of the coating, in addition to enhancing the char residue compared to coatings with only expandable graphite (EG). Furthermore, TGA results demonstrate that adding MEG increases the weight of the char residue at elevated temperatures, suggesting improved thermal stability. Based on these findings, MEG exhibits a synergistic flame-retardant effect when combined with intumescent fire-retardant (IFR) systems. This synergy not only improves the flame-retardant properties of the coatings but also enhances their overall thermal stability, making MEG a promising additive for developing more efficient fire-retardant materials. Thus, MEG-modified coatings offer superior protection against fire hazards, highlighting their potential for practical applications in fire safety.
1. Introduction
The occurrence of fire accidents caused by polymer ignition is becoming increasingly prevalent globally, resulting in significant loss of life and property. This phenomenon has emerged as a matter of societal concern [1]. So, it is essential to decrease fire hazards by some effective methods. One of the most efficacious and convenient methods for the prevention of polymer ignition is the utilization of intumescent fire protection coatings [2,3]. Indeed, the process presents several advantages. Firstly, it does not alter the intrinsic properties of the material, for example, the mechanical properties. Secondly, it is a rapid process. Thirdly, it may be used on multiple substrates, for example, metallic materials, polymers, textiles, and wood [1,4,5]. Intumescent fire protection coatings are widely recognized worldwide in the field of fire protection due to their ecological safety. They are prepared based on carbonization agents, acid sources, and blowing agents [6,7,8,9].
Expandable graphite, which is frequently employed as a blowing agent and smoke suppressant in an extensive array of flame-retardant materials, represents a graphite intercalation compound (GIC) [10,11,12,13]. When exposed to heat, EG expands strongly, forming a large barrier that separates the polymer from the fire source to provide fire protection [14]. EG exhibits high flame-retardant efficiency, low toxicity, and is smokeless, rendering it an optimal material for fire protection. Nevertheless, during the combustion process, the vermiculite structural layer formed by EG exhibits low adhesion and is susceptible to destruction by thermal convection [15]. Furthermore, the compatibility between EG and polymer is poor, which affects the materials’ mechanical and flame-retardant properties.
In order to address the aforementioned issues, this paper presents a modification of expandable graphite (MEG) with a carbonizing agent, resulting in the synthesis of an organic–inorganic hybrid intumescent flame retardant. Intumescent fire-retardant coatings are prepared based on IFR, IFR/EG, and IFR/MEG. The fire-retardant influence of MEG in the intumescent fire-retardant coating is studied by CCT, a DaqPRO 5300 radiation heat flow meter, and TGA. The results obtained can be applied to the surface of building steel structures, wood, and other substrates to form coatings with flame-retardant protection and decorative effects. In addition, the water-based fireproof coating is non-volatile and has excellent environmental protection characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The materials include melamine (MEL), pentaerythritol (PER), and ammonium polyphosphate (APP) provided by Tianjin BASF Chemical Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China, styrene-acrylic emulsion (with a solid content of 50.84%) provided Anhui Kobang Resin Technology Co., Ltd., Huangshan City, China), expandable graphite (EG) obtained from Jiangsu Xianfeng Nanomaterials Technology Institute, Nanjing, China, Phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3, A.R.), Ammonia water, and Ethanediol from Sigma-Aldrich, Shanghai, China. IFR was obtained with a mass ratio of 3:1:1 for APP, MEL, and PER.
2.2. Synthesis of MEG
A solution of EG (20 g), POCl3 (6 mL), and 1,4-dioxane (500 mL) was placed into a reactor and heated to 60 °C for a period of 3 h. Subsequently, 9 g of PER was added to the reactor and heated to 100 °C for a further 6 h, resulting in the crude product. The resulting crude product was filtered, washed with 1,4-dioxane, and subsequently dried under a lower pressure at 80 °C for 12 h, thereby obtaining MEG, as shown in Figure 1.
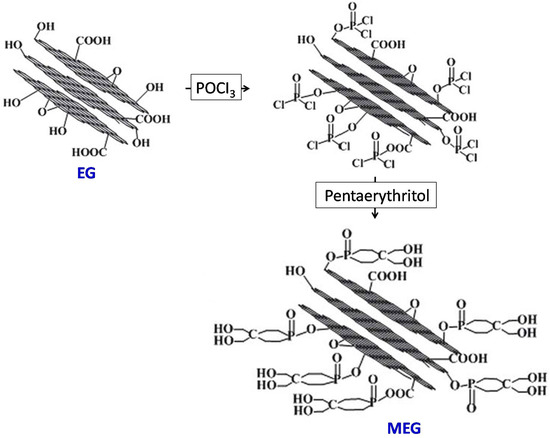
Figure 1.
Synthesis of MEG.
2.3. Preparation of Intumescent Fire-Retardant (IFR) Coatings
The preparation steps of IFR are listed below, together with the substrates used and the relationship between coatings and substrates.
- (1)
- Add IFR, EG, and MEG to an iron container according to the formula in Table 1 and stir with a high-speed dispersing agent at a speed of 1000 r/min for 20 min to prepare the coating slurry;
 Table 1. Formulations of IFR coatings.
Table 1. Formulations of IFR coatings. - (2)
- Add the styrene-acrylic emulsion to the above mixture and stir at a speed of 400 rpm for 20 min to prepare the coating;
- (3)
- Measure the solid content of each coating, then use a brush to separate the coating on wood 90 mm × 90 mm × 3 mm and 70 mm × 70 mm × 3 mm in size for the cone calorimeter test and smoke density test;
- (4)
- Brush the paint onto an iron plate with a size of 90 mm × 90 mm × 0.5 mm, which is used for the thermal insulation test;
- (5)
- Dry the finished sample at room temperature for 24 h, and then place it in a blast drying oven at a temperature of 50 °C for 24 h to obtain the final paint sample.
2.4. Measurements
The Fourier transform infrared spectrum was recorded by a spectrometer (VARIUS, Avantes, Apeldoorn, The Netherlands). Heat tests were conducted using a cone calorimeter (Shanghai Shuangxu Electronics Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The specimen size was 90 mm × 90 mm × 3 mm, wrapped in aluminum foil, with an external heat flux of 35 kW/m2. Experiments were conducted to investigate the flow of radiant heat using a radiant heat flow meter (Qingdao Jingcheng Instrumentation Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China). One end of a thermocouple was positioned at the base of an iron plate coated with a flame-retardant coating to facilitate the collection of temperature data throughout the combustion process. The other end of the thermocouple was linked to the radiant heat flow meter. Thermogravimetric analysis was conducted on a DT-50 (Setaram, Caluire-et-Cuire, France) instrument with a nitrogen protective gas. Approximately 10.0 mg of the sample was placed in a crucible and heated to 900 °C, with the heating rate set at 10 K/min.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of MEG
The production process of MEG is divided into two steps. First, POCl3 is grafted onto the EG surface. Then, P-Cl is esterified with PER. The Fourier infrared spectrometer in the experiment was Labsys Evo STA, produced by Setharam Instruments in France. The spectral resolution was 0.25 cm−1 and was determined at a high speed of 20 spectra/s. Figure 2 shows the FTIR spectra of EG and MEG. In the spectrum of EG, a solid peak appears at 3452 cm−1, which is due to the stretching vibration of the -OH and C-O groups. This stretching vibration indicates the presence of -OH in EG and its ability to react with POCl3. There are also many new absorption peaks in the MEG spectra. The peaks at 2935 cm−1 and 2873 cm−1 are carbon–hydrogen bonds, while the peak at 1213 cm−1 is P = O. The peak at 1078 cm−1 indicates cyclic P-O bonds, while the peaks at 1009 cm−1 and 826 cm−1 indicate P-O-C bonds. The infrared spectra of EG and MEG show that an organic–inorganic hybrid intumescent flame retardant was successfully synthesized by modifying MEG with a carbonylating agent.
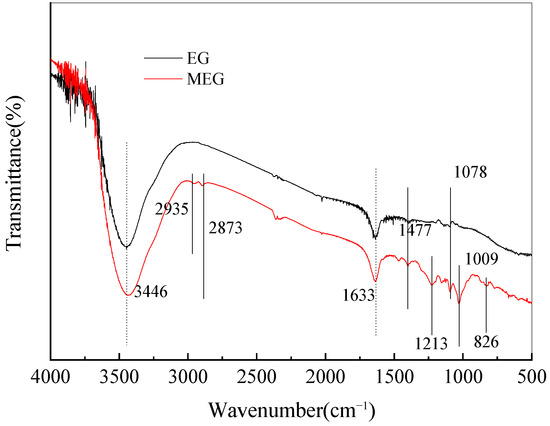
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of EG and MEG.
3.2. Cone Calorimeter Test
Cone calorimetry is an important method for flammability characterization and is based on the principle of oxygen consumption. The heat release rate (HRR) as measured by a combustion chamber thermometer (CCT) is a significant parameter in fire analysis, as it provides an indication of the intensity of a fire. Nevertheless, it is frequently employed to delineate fire hazard behaviors, as evidenced by the average HRR or peak HRR (PHRR) in actual scenarios [16,17]. The PHRR value is utilized to quantify the intensity of a fire.
3.2.1. Heat Release Rate (HRR)
Figure 3 illustrates the HRR curves of samples with distinct intumescent fire-retardant coatings, as obtained from CCT. The pertinent data from the CCT are provided in Table 2. It can be observed that sample D0, which lacks any coating, ignites rapidly, and reaches a peak heat release rate (PHRR) of 398.6 kW/m2. The heat release rate value for sample D1, which has a coating containing only IFR, is lower than that of sample D0. The addition of EG to the fire-retardant coating system results in a reduction in the PHRR value of sample D2 in comparison to sample D1. Moreover, the addition of EG results in a prolongation of the ignition time (TTI) in comparison to both D0 and D1, as presented in Table 2. Furthermore, the addition of MEG results in a further reduction in the PHRR value in comparison to sample D2, which contains EG. Sample D3, which incorporates MEG, exhibits the lowest PHRR value (232.8 kW/m2) and the longest TTI (356 s) among all samples presented in Table 2. This suggests that the incorporation of MEG in combination with IFR in this coating system provides a practical synergistic flame-retardant effect.
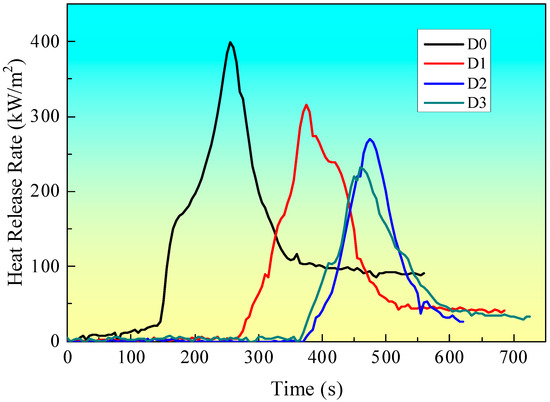
Figure 3.
HRR curves at a flux of 35 kW/m2.

Table 2.
The results of intumescent fire-retardant coatings after CCT tests.
The synergistic effect of EG and APP promotes char morphology and improves thermal stability. The formation of a char layer prevents heat transfer into the underlying material and the ingress of combustible gasses into the flame zone. Concurrently, EG and APP release non-combustible gasses, including CO2, NH3, and SO2, which dilute the combustible gasses in the gas phase. The combination of EG and APP is therefore a highly reliable IFR system, and the chemical explanation of the phenomena can be found in Refs. [2,7,8,10,17,18]. In the case of D3 with MEG, the charring agent grafted onto the surface of EG can change the structure of char residue after CCT. The charring agent can change the wormlike structure from the D2 sample into an intumescent compact char structure. The intumescent compact char structure formed from the D4 sample has good heat and mass transfer properties. So, the D3 sample shows the lowest HRR among all samples.
3.2.2. Mass
Figure 4 illustrates the weight of the char residues for all samples. It can be observed that the char residue weight of sample D2, which contains both EG and IFR, is greater than that of sample D1, which contains only IFR, throughout the entire burning period. This suggests that EG can enhance the weight of the char residue by increasing its expansion degree, which in turn improves its heat shield performance. Therefore, the char residue weight of D2 is greater than that of D1. The addition of MEG to the fire-retardant coating (sample D3) resulted in an improvement in the char residue. The char residue of sample D3, consisting of IFR and MEG, is the highest among all samples before 550 s. At this point, the percentage of char residue in sample D3 is in excess of 40 wt%. This evidence suggests that MEG can enhance the formation of char residue in this coating system. This can be explained by the fact that compact char residues form on the surface of coatings with IFR and MEG during combustion, acting as a physical protective layer. The char residue acts as a protective barrier, limiting the diffusion of oxygen to the substrate or decreasing the rate of volatilization of combustible gasses, particularly aromatic gasses which are precursors of smoke [8,10]. When the test time exceeds 550 s, the char residue weight of D3 is observed to be lower than that of D2. This phenomenon can be attributed to the formation of amorphous carbon on the surface of the D3 sample, which can undergo oxidation under conditions of high-heat radiation, resulting in a reduction in the char residue weight of the D3 sample.
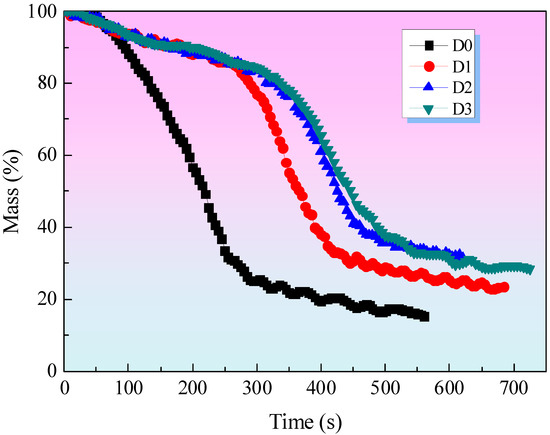
Figure 4.
Mass curves at a flux of 35 kW/m2.
3.2.3. Total Heat Release (THR)
Figure 5 illustrates the total heat release (THR) of all samples. It has been proposed that the gradient of the THR curve can be used to represent flame spread [2,17]. It can be observed that the THR value of the D0 sample is the highest among all samples. In comparison to the D0 sample, the gradient of the THR curve for the sample with only IFR is markedly diminished, thereby indicating a deceleration in the rate of flame spread. The incorporation of EG and MEG into intumescent fire-retardant coating systems results in a further reduction in the THR value in comparison to the D1 sample with only IFR. This is attributed to the formation of a substantial intumescent, compact char residue on the surface of the samples, which effectively limits the flame spread. In addition, the reduction in THR is consistent with the HRR curves in Figure 2, which show that the addition of EG or MEG can effectively reduce THR.
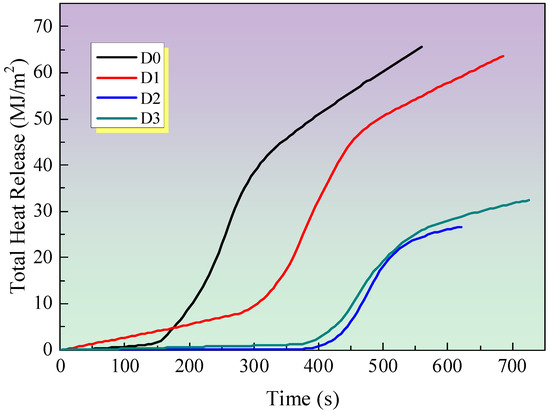
Figure 5.
THR curves of IFR coatings at a flux of 35 kW/m2.
3.2.4. Fire Performance Index (FPI) and Fire Growth Index (FGI)
Following the cone calorimeter test, the fire performance index (FPI) and fire growth index (FGI) are calculated to evaluate the fire hazard. The FPI (m2 s/kW) is the ratio of the time to ignition (TTI) to the PHRR, and the FGI (kW/m2 s) is defined as the ratio of the peak HRR to the time to PHRR (TTP) [10]. The FPI and FGI are calculated directly from the cone calorimeter test data and thus provide a direct reflection of the safety ranking of the samples. It is reasonable to assume that materials with a higher safety rank should require high FPI and low FGI values. The FPI and FGI results are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7, respectively [2,7]. Sample D3 treated with IFR/MEG has the highest FPI value and the lowest FGI value, indicating that it has a relatively high fire safety rank.
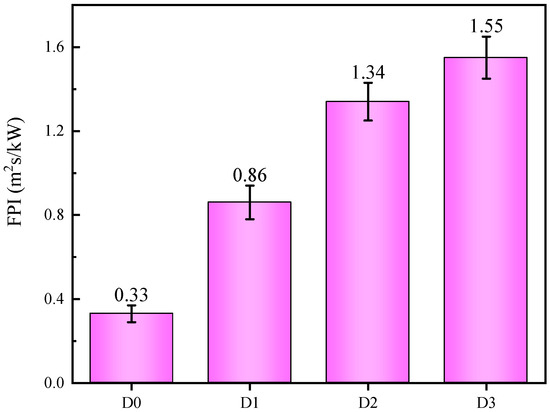
Figure 6.
FPI for IFR coatings at a flux of 35 kW/m2.
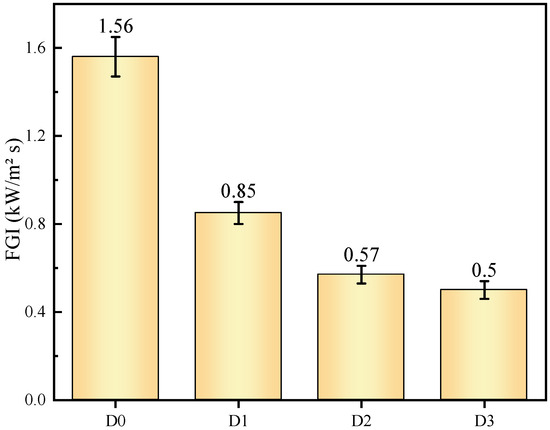
Figure 7.
FGI for IFR coatings at a flux of 35 kW/m2.
3.3. DaqPRO 5300 Radiation Heat Flow Meter Test
Figure 8 shows the temperature curves from the DaqPRO 5300 radiation heat flux meter tests. Four coating samples (from sample D0 to sample D3) are applied to an iron board, each measuring 90 mm × 90 mm × 0.5 mm. The temperature of sample D0 is higher than that of any other sample with a fire-retardant coating. The fire-retardant coating on the surface of the iron board reduces the temperature compared to D0 without any coating. When EG is incorporated into the intumescent fire-retardant coating system, the temperature of sample D2 with IFR/EG is lower than that of sample d1 with only IFR. In addition, the addition of MEG can further reduce the temperature compared to the D2 sample. In addition, MEG can improve the structure of the char residue, resulting in a good fire-retardant effect.
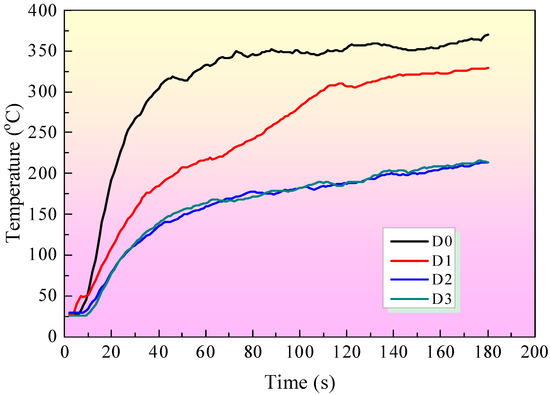
Figure 8.
Temperature curves of IFR coatings by DaqPRO 5300 radiation heat flow meter test.
Figure 9 illustrates the char residues of intumescent fire-retardant coatings following the DaqPRO 5300 radiation heat flow meter test. The formation of an effective carbon layer can impede the transfer of heat between the combustion zone and the underlying substrate. It can be seen that the D1 sample with only IFR has relatively high char residue. But it is not compact enough. The D2 sample containing both IFR and EG has high and regular char residues. In the case of the D3 sample with IFR and MEG, the most intumescent compact char residues are found among all samples. This indicates that MEG can contribute to forming char residue and prevent heat from passing through fire-retardant coating systems.
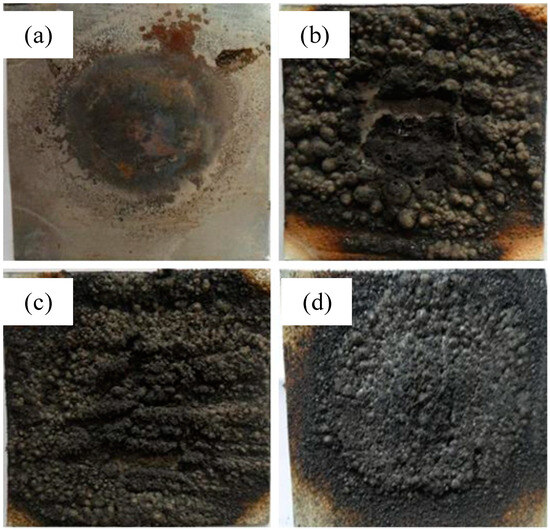

Figure 9.
Char residues of IFR coatings after DaqPRO 5300 radiation heat flow meter, (a) D0 sample, (b) D1 sample, (c) D2 sample, (d) D3 sample.
3.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
TGA is an efficient way to assess the thermal stability of diverse materials. Additionally, it provides insight into the degradation of polymers at varying temperatures by quantifying the onset of degradation (T5.0%), defined as the temperature at which a 5 wt% mass loss is observed, with the temperature corresponding to the maximum degradation rate (Tmax) and the residual char [8,18].
Figure 10 illustrates the thermogravimetric (TGA) curves for the samples. The D1 sample, which comprises only IFR, initiates its decomposition at approximately 250 °C, exhibiting a weight loss of 5 wt%. The char residue of D1 is lower than that of the D2 sample with IFR/EG or the D3 sample with IFR/M-EG the whole time. It also can be seen that D1 with only IFR is less stable than the D2 and D3 samples between 250 °C and 450 °C. Adding EG improves thermal stability compared with D1, which only has IFR. Moreover, the addition of MEG to the intumescent fire-retardant coating resulted in the highest char residue of D3 among all samples. This indicates that MEG contributes to the improvement of carbon residue in the IFR coating system, which is consistent with the mass results after CCT.
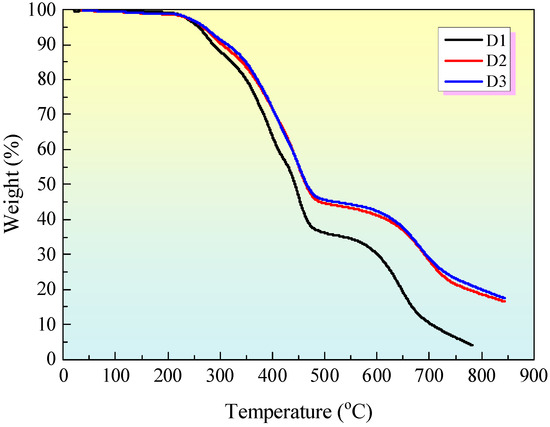
Figure 10.
TGA curves of IFR coatings.
Figure 11 shows the derivative thermogravimetric (DTG) curves for IFR coatings. The thermal degradation of IFR coatings occurs in four distinct stages. The temperatures of the maximum mass loss rate (Tmax) of sample D1 with IFR and sample D2 with IFR/EG are observed to be lower than that of sample D3 with IFR/MEG throughout the degradation process. Furthermore, the addition of MEG is observed to accelerate the initial stage of thermal degradation. Melamine and APP degrade between 300 and 500 °C, releasing N2 and NH3. PER and MEL also decompose in this temperature range. [19]. When MEG was added to these coatings, the thermal stability of the second and third degradation stages was significantly enhanced. The amorphous carbon formed in the previous stages is decomposed, so that a fourth degradation stage occurs between 500 and 800 °C. The presented evidence lends support to the proposition that MEG enhances the thermal stability of these intumescent fire-retardant coatings.
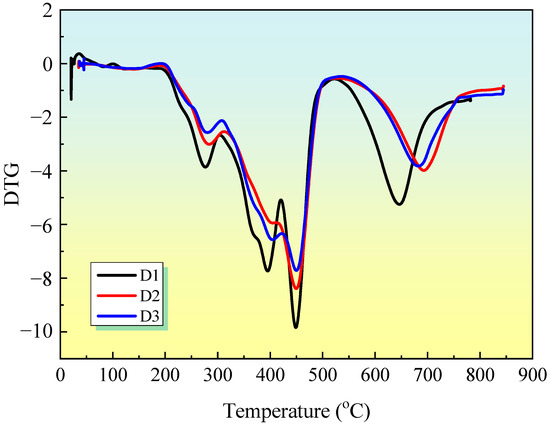
Figure 11.
DTG curves of IFR coatings.
4. Conclusions
An organic–inorganic hybrid intumescent flame retardant was successfully synthesized by modifying expandable graphite (MEG) with a charring agent. The conclusions can be drawn as follows:
- (1)
- MEG can significantly reduce the HRR and THR of fire-resistant coating samples and improve the carbon formation of the coating.
- (2)
- MEG can reduce the heat generated by the sample combustion and extend the combustion time, improving the high-temperature thermal stability of the sample and the sample carbon formation.
- (3)
- MEG exhibits a synergistic flame-retardant effect when combined with intumescent fire-retardant (IFR) systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M., Q.S., F.D. and J.L.; methodology, L.M., Q.S. and F.D.; software, Q.S. and J.L.; validation, F.D.; formal analysis, L.M.; investigation, L.M., Q.S. and F.D.; resources, J.L.; data curation, F.D.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M., Q.S., F.D. and J.L.; writing—review and editing, Q.S. and Z.X.; supervision, F.D.; project administration, L.M., H.Y. and F.D.; funding acquisition, L.M., H.Y. and F.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52005517); the State Key Laboratory for High-Performance Complex Manufacturing, Central South University, China (No. ZZYJKT2022-02); the Science and Technology Research and Development Command Plan Project of Zhangjiakou, China (No. 2311005A); and the 2024 Graduate Innovation Fund project of Hebei University of Architecture (No. XY2024080).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Jianlin Liu is employed by CRRC Qingdao Sifang Co., Ltd. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Huo, S.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Song, P. Two-dimensional nanomaterials for flame-retardant polymer composites: A mini review. Adv. Nanocompos. 2024, 1, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Shao, W.; Xiao, F. Benign design of intumescent fire protection coatings for steel structures containing biomass humic acid as carbon source. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Moon, H.; Jee, S.; Lee, K.C.; Jung, H.W.; Paik, H.; Noh, S.M. Characteristics of phosphorus-nitrogen based flame-retardant monomers for UV-curable coatings on battery PET pouches. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 195, 108665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhai, C.; Yang, R. Expanded charring flame retardant effect of caged polysilsesquioxane containing Schiff base structure on poly(ethylene terephthalate) combustion. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 227, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, N.F.; Elashery, S.E.A.; El-Sayed, F.; Mohamed, M.; Osama, R.; Elmahdy, E.; Abd-Ellah, M.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Hawash, H.B.; Ameen, H. Recent advances in nanobased flame-retardant coatings for textile fabrics. Nano-Struct. Nano-Obj. 2024, 38, 101180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, B.K.; Horrocks, A.R. Complex char formation in flame-retarded fibre-intumescent combinations—II. Thermal analytical studies. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1996, 54, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Chai, W.; Liu, Y.; Su, X.; Liao, C.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Z. Facile fabrication of starch-based, synergistic intumescent and halogen-free flame retardant strategy with expandable graphite in enhancing the fire safety of polypropylene. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 184, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, M.; Li, B. Synthesis of a novel phosphorus and nitrogen-containing flame retardant and its application in rigid polyurethane foam with expandable graphite. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 173, 109077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dai, B.; Meng, C.; Guo, Z. Fabrication of cellulose-based halogen-free flame retardant and its synergistic effect with expandable graphite in polypropylene. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, G.; Gu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.; Jin, X. Preparation of a novel supramolecular intumescent flame retardants containing P/N/S/Fe/Zn and its application in polylactic acid. Fire Saf. J. 2022, 128, 103536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panczek, P.; Ostrysz, R.; Krassowski, D. Flame Retardants 2000. In Proceedings of the 9th Flame Retardants 2000 Conference, London, UK, 8–9 February 2000; pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Okisaki, F. FLAMECUT GREP series new non-halogenated flame-retardant systems. In Proceedings of the New Developments and Future Trends in Fire Safety on a Global Basis International Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–19 March 1997; pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Krassowski, D.W.; Hutchings, D.A.; Oureshi, S.P. Tomorrow’s Trends in Fire-retardant Regulations, Testing, Applications, and Current Technologies. In Proceedings of the Fire-Retardant Chemicals Association Fall Conference, Naples, FL, USA, 13–16 October 1996; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Sun, L.; Ding, L.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y. A UV-curable coating constructed from bio-based phytic acid, D-sorbitol and glycine for flame retardant modification of rigid polyurethane foam. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 227, 110892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.; Guan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, M.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.; Jiao, C.; Chen, X. A green organic-inorganic PAbz@ZIF hybrid towards efficient flame-retardant and smoke-suppressive epoxy coatings with enhanced mechanical properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 217, 110534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tawiah, B.; Noor, N.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J.; Yuen, R.K.K.; Fei, B. A facile and sustainable approach for simultaneously flame retarded, UV protective and reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites using fully bio-based complexing couples. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 215, 108833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Mu, J.; Sun, X.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, J. Application of intumescent flame retardant containing aluminum diethyphosphinate, neopentyl glycol, and melamine for polyethylene. Saf. Sci. 2020, 131, 104849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Hwang, S.; Liu, S. Flame retardancy and thermal stability of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer nanocomposites with alumina trihydrate and montmorillonite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Z.; Feng, J.Q.; Tsui, C.P.; Tang, C.Y.; Liu, D.F.; Zhang, S.D.; Huang, W.F. Mechanical properties and flame-retardant of PP/MRP/Mg(OH)2/Al(OH)3 composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 71, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).