Effect of NOX and SOX Contaminants on Corrosion Behaviors of 304L and 316L Stainless Steels in Monoethanolamine Aqueous Amine Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
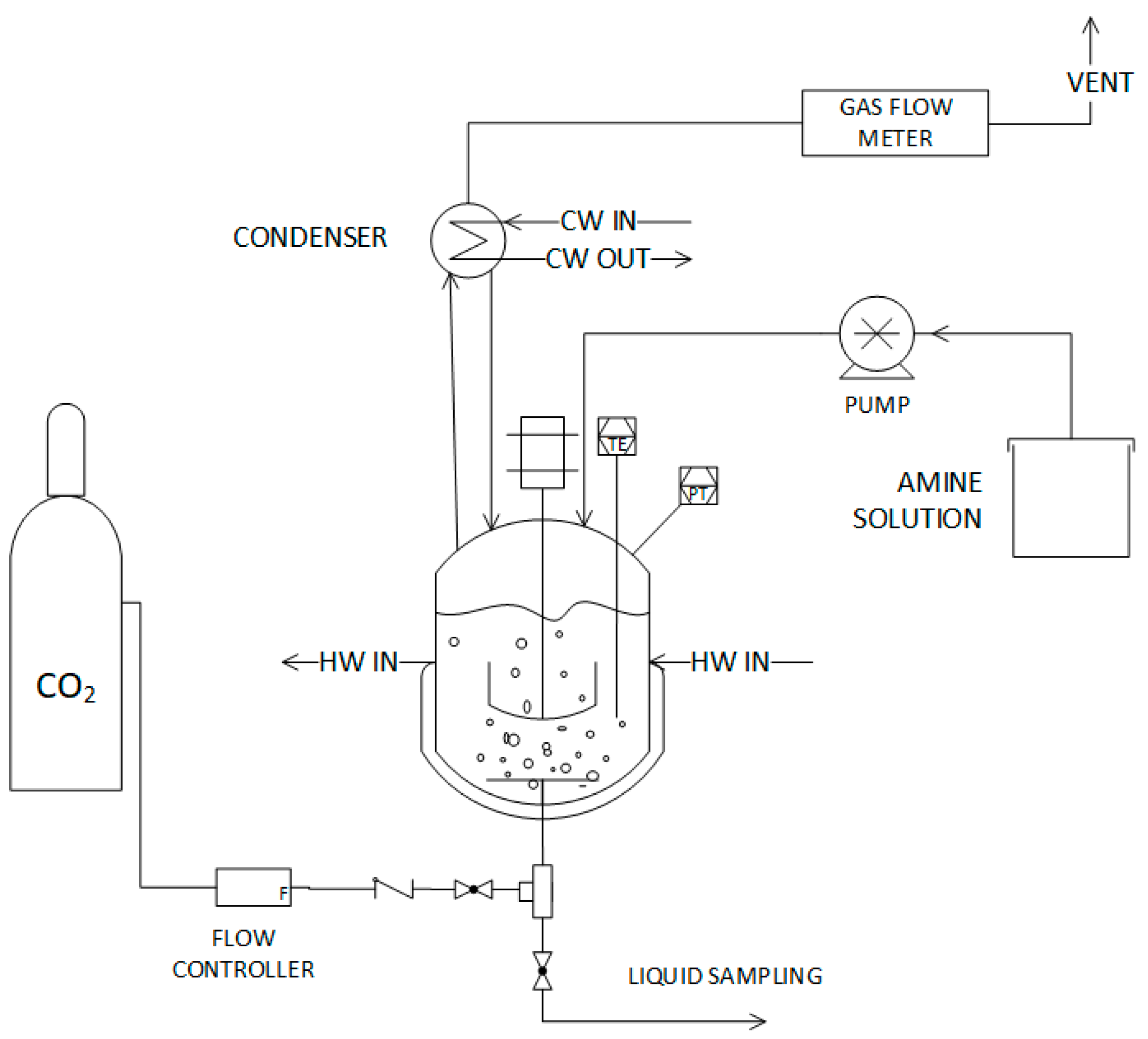
2. Materials and Methods
Amine Solvent Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
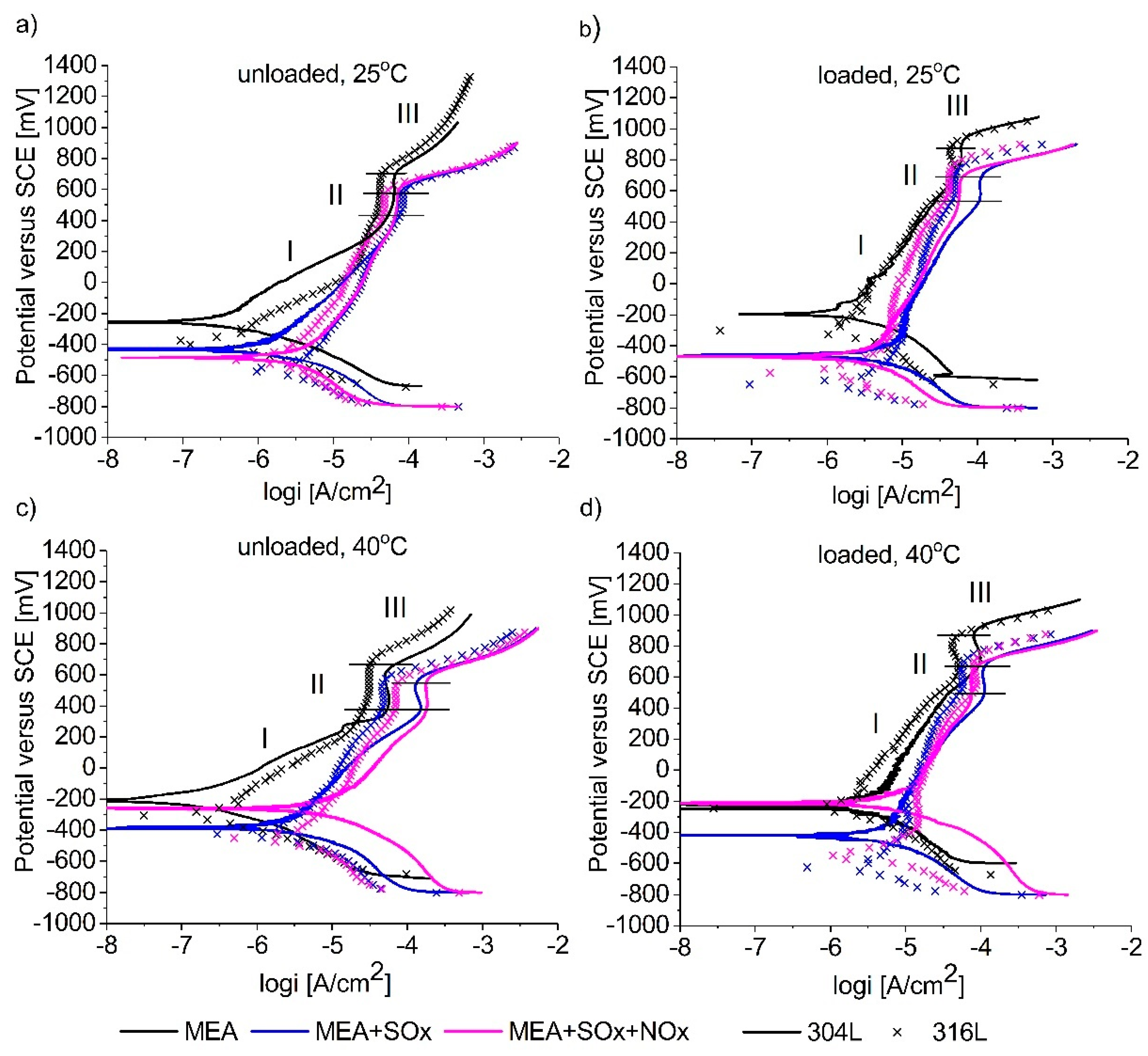
3.1. Potentiodynamic Polarization Measurements
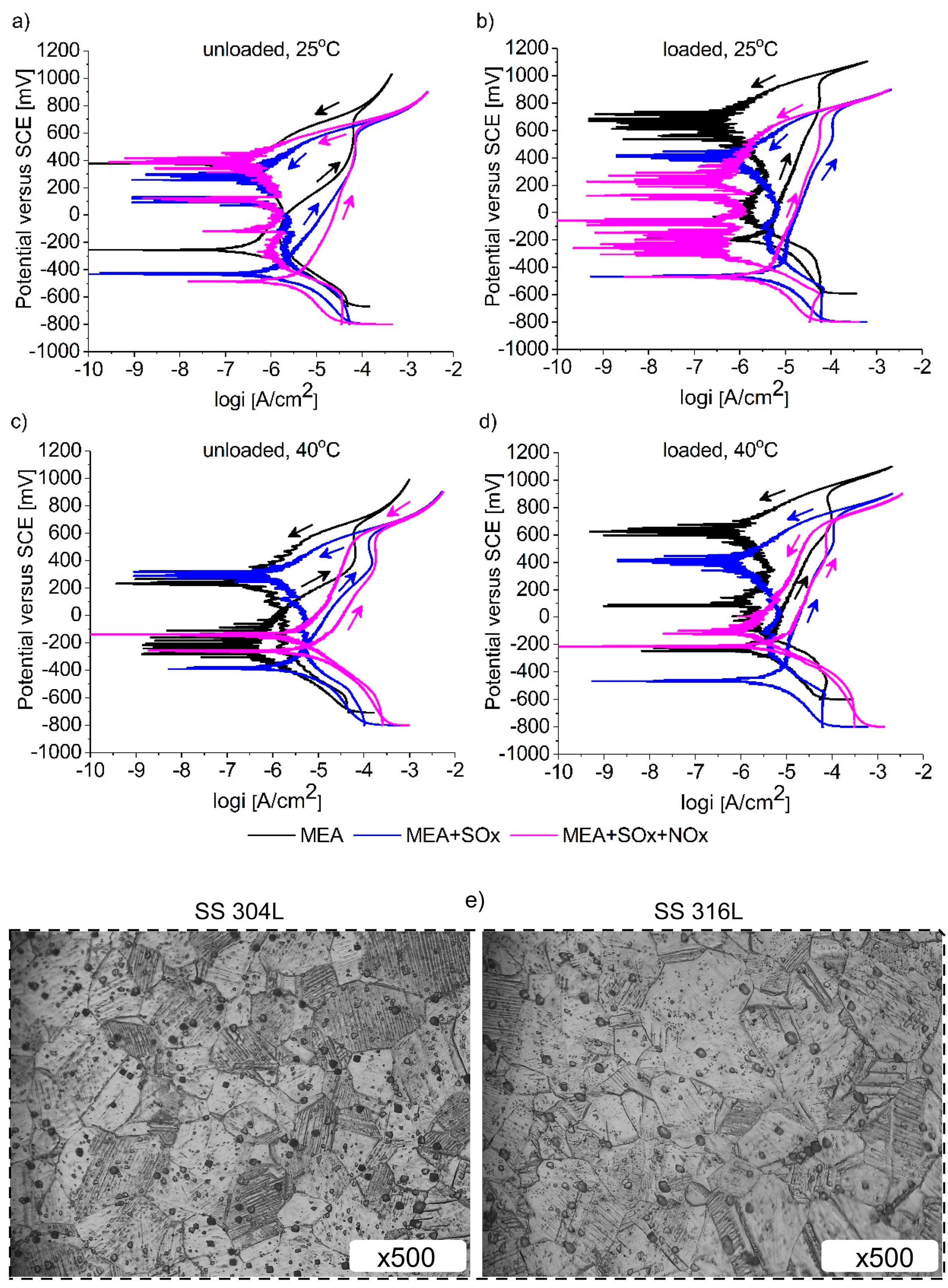
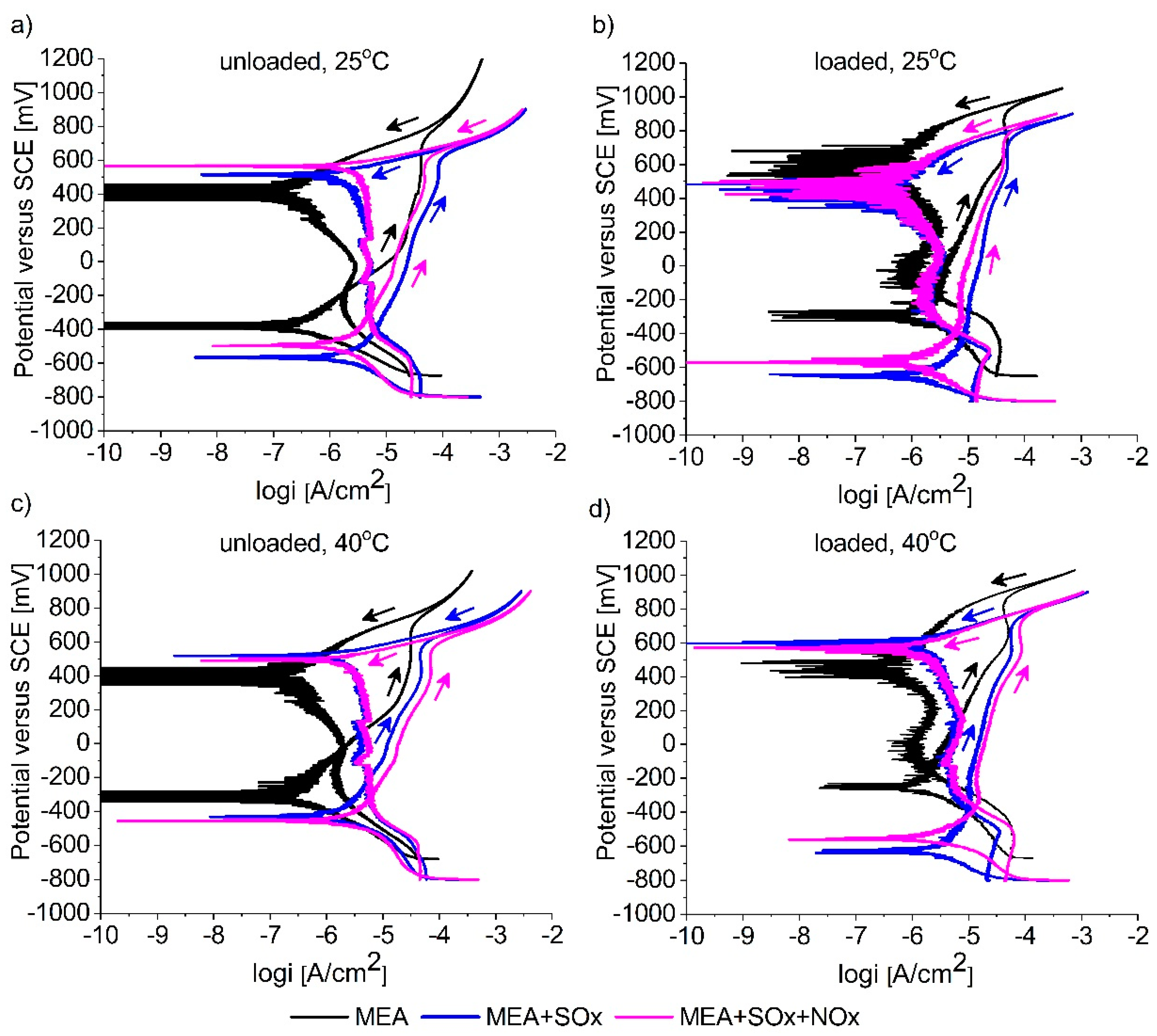
3.2. Cyclic Polarization Measurements
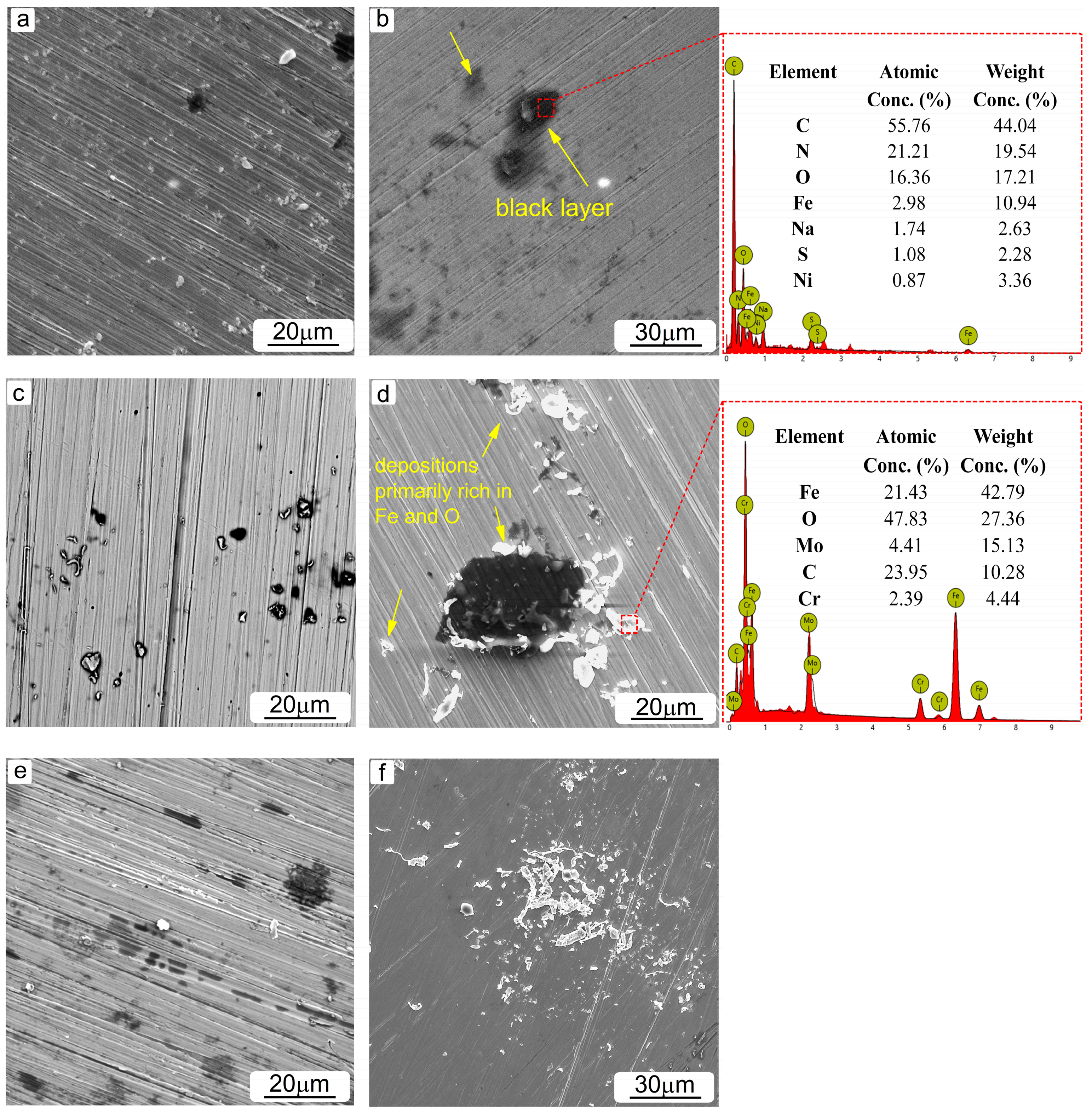
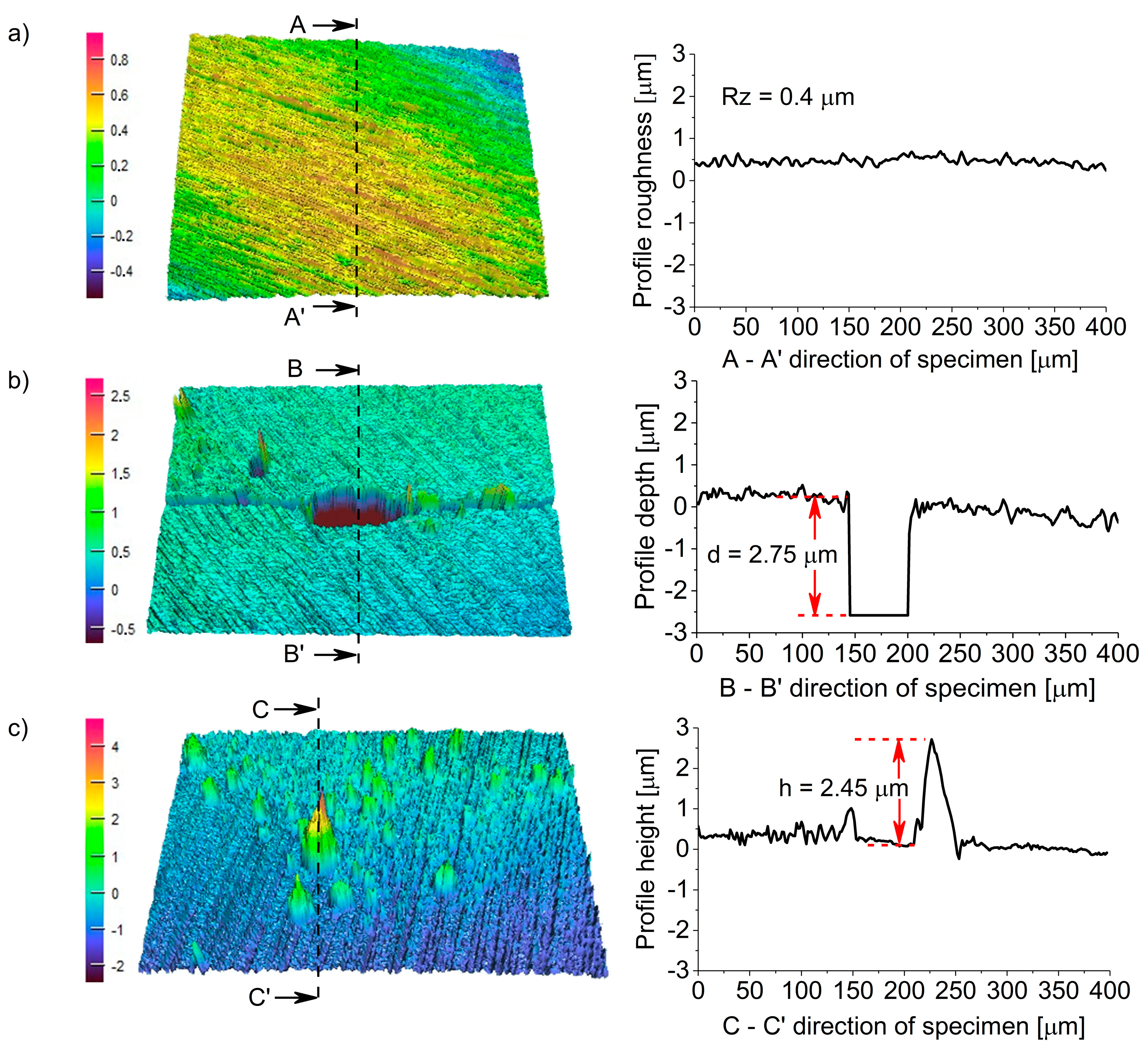
3.3. Surface and Component Characterization of Corroded Specimens
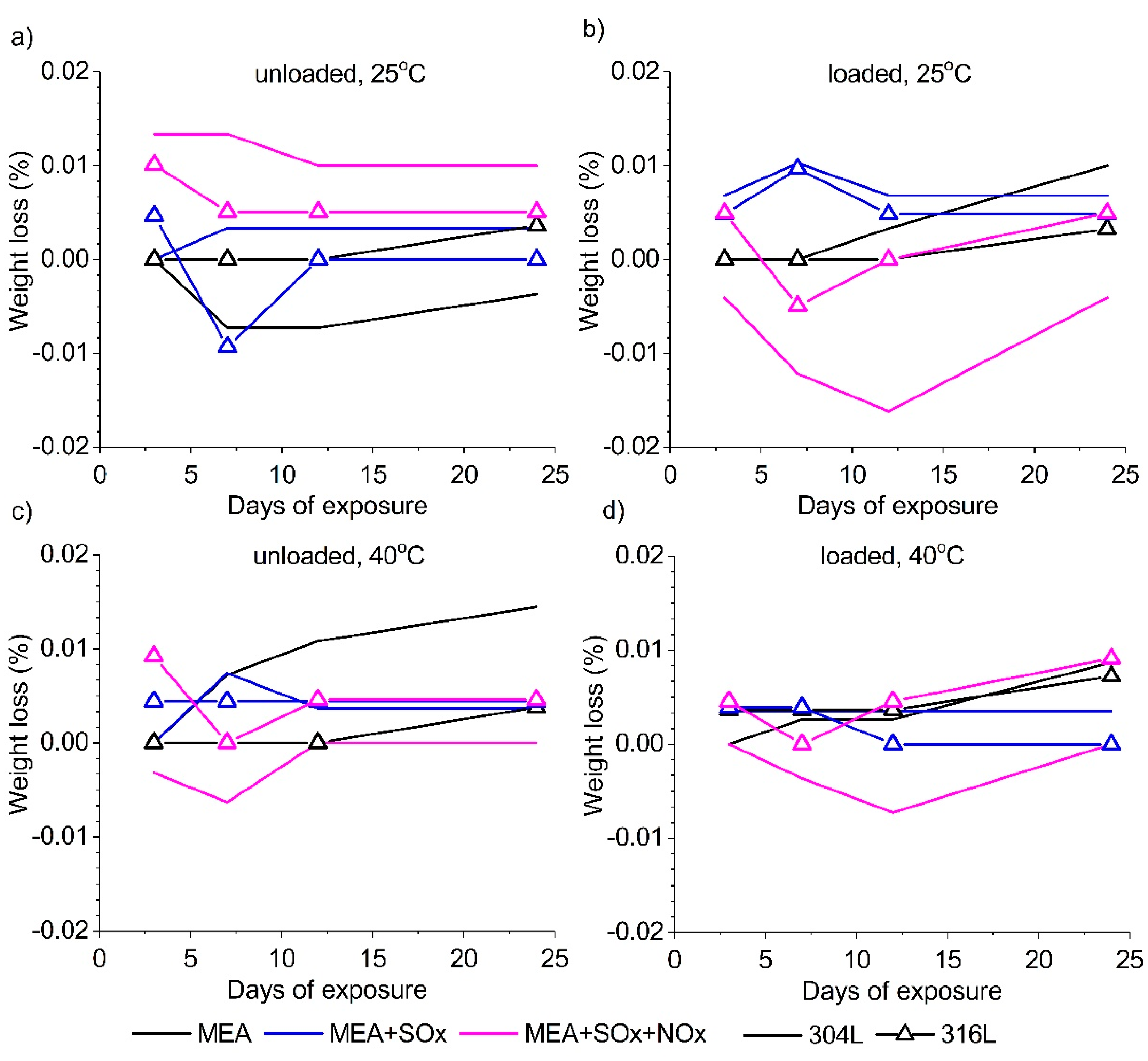
3.4. Immersion Results
4. Conclusions
- The SOX and NOX impurities had the strongest impacts on the corrosion rate over temperature and CO2 loading.
- No pitting corrosion of SS 304L or SS 316L was detected in any of the examined solutions.
- The microstructural characterization revealed the presence of various corrosion precipitations depending on the type of amine solution used. In lean MEA-based solutions, corrosion products rich in Fe and O were primarily formed, while the addition of CO2 further caused the formation of products containing Fe, O and C. Black layers likely composed of amine degradation products were identified in all solutions tested.
- The weight loss measurements showed a very low corrosion rate in all solutions at both temperatures. Also, the results reveal that maybe SOX and NOX impurities are responsible for the formation of a protective layer.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, S.P.D. Comparative Study of Amine Solutions Used in Absorption/Desorption Cycles of CO2; LAP Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrucken, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Madejski, P.; Chmiel, K.; Subramanian, N.; Kuś, T. Methods and Techniques for CO2 Capture: Review of Potential Solutions and Applications in Modern Energy Technologies. Energies 2022, 15, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghel, B.; Janati, S.; Wongwises, S.; Shadloo, M.S. Review on CO2 capture by blended amine solutions. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2022, 119, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Matin, N.S.; Landon, J.; Thomas, G.A.; Liu, K. CO2 loading-dependent corrosion of carbon steel and formation of corrosion products in anoxic 30wt.% monoethanolamine-based solutions. Corros. Sci. 2016, 102, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Meng, Y.; Ju, T.; Han, S.; Lin, L.; Jiang, J. Research progress of aqueous amine solution for CO2 capture: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Cui, C.; Dong, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, H. An overview on the corrosion mechanisms and inhibition techniques for amine-based post-combustion carbon capture process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, I.M.; Alaba, P.; Mazari, S.A.; Basirun, W.J.; Lee, V.S.; Sabzoi, N. Opportunities and challenges in the development of monoethanolamine and its blends for post-combustion CO2 capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2018, 79, 212–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaoha, C.; Supap, T.; Idem, R.; Saiwan, C.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; AL-Marri, M.J.; Benamor, A. Advancement and new perspectives of using formulated reactive amine blends for post-combustion carbon dioxide (CO2) capture technologies. Petroleum 2017, 3, 10–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veawab, A.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Chakma, A. Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in the CO2 Absorption Process Using Aqueous Amine Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 3917–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emori, W.; Jiang, S.L.; Duan, D.L.; Ekerenam, O.O.; Zheng, Y.G.; Okafor, P.C.; Qiao, Y.X. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel in amine-based CO2 capture system: Effect of sodium sulfate and sodium sulfite contaminants. Mater. Corros. 2016, 68, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, J.; Gonzalez, S. Corrosion in CO2 Post-Combustion Capture with Alkanolamines—A Review. Oil Gas Sci. Technol.-Rev. D’ifp Energ. Nouv. 2014, 69, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Roy, K.; Padiyara, S.; Chen, B.; Raftery, G.M.; Lim, J.B.P. Web crippling design of cold-formed stainless steel channels under interior-two-flange loading condition using deep belief network. Structures 2023, 47, 1967–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Pan, J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, Y.; Chen, B.; Fang, Z.; Roy, K.; Lim, J.B.P. Effects of corrosion morphology on the fatigue life of corroded Q235B and 42CrMo steels: Numerical modelling and proposed design rules. Structures 2023, 57, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafat, A.; Atilhan, M.; Kahraman, R. Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in CO2 Saturated Amine and Imidazolium-, Ammonium-, and Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquid Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veawab, A.; Aroonwilas, A. Identification of oxidizing agents in aqueous amine–CO2 systems using a mechanistic corrosion model. Corros. Sci. 2002, 44, 967–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y. Corrosion issues of carbon capture, utilization, and storage. Mater. Perform. 2018, 57, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Yan, M.; Choi, Y.-S.; Young, D.; Nesic, S. Time-dependent electrochemical behavior of carbon steel in MEA-based CO2 capture process. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 30, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, Z.L.; Tan, P.Y.; Tan, L.S.; Yeap, S.P. Amine-based solvent for CO2 absorption and its impact on carbon steel corrosion: A perspective review. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, M.; Wang, T.; Gao, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, F. Corrosion performance of carbon/stainless steel in amine-based solvents under different conditions for CO2 chemical absorption process. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2023, 14, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergioudi, F.; Baxevani, A.; Florou, C.; Michailidis, N.; Nessi, E.; Papadopoulos, A.I.; Seferlis, P. Corrosion Behavior of Stainless Steels in CO2 Absorption Process Using Aqueous Solution of Monoethanolamine (MEA). Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2022, 3, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Remias, J.; Neathery, J.; Liu, K. Electrochemical study of corrosion behaviour of carbon steel A106 and stainless steel 304 in aqueous monoethanolamine. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G38-01; Standard practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- Tzirakis, F.; Tsivintzelis, I.; Papadopoulos, A.I.; Seferlis, P. Experimental measurement and assessment of equilibrium behaviour for phase change solvents used in CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 199, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.; Corrigan, P.; Cole, I.S.; Birbilis, N. Use of Aqueous Solutions to Simulate Supercritical CO2 Corrosion. Corrosion 2012, 68, 045004-1–045004-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalib, L.; Ali, B.S.; Mazari, S.; Saeed, I.M. Modeling the Effect of Piperazine on Carbon Steel Corrosion Rate in Carbonated Activated MDEA Solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 4560–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanaphan, P. Studies and Prevention of Carbon Steel Corrosion and Solvent Degradation During Amine-Based CO2 Capture from Industrial Gas Streams; The University of Regina: Regina, SK, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, R.R. Handbook of Corrosion Engineering; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Chapter 2; p. 67. [Google Scholar]
- Widyanto, B.; Putri, S. Corrosion Behavior of ASTM A1008 Carbon Steel in Mixtures of HNO3, H2SO4, and HCl Using Immersion and Polarization Methods. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.K.; Jafar, S.A.; Humadi, J.I.; Sehgal, S.; Saxena, K.K.; Abdullah, G.H.; Saeed, L.I.; Salman, M.S.; Abdullah, W.S. Investigation of carbon steel corrosion rate in different acidic environments. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Xie, W.; Ni, S.; He, X. Comparative study of A106 steel corrosion in fresh and dirty MEA solutions during the CO2 capture process: Effect of NO3−. Corros. Sci. 2020, 167, 108521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekatou, A.; Sioulas, D.; Karantzalis, A.E.; Grimanelis, D. A comparative study on the microstructure and surface property evaluation of coatings produced from nanostructured and conventional WC–Co powders HVOF-sprayed on Al7075. Surface Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailzadeh, S.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Sarlak, H. Interpretation of Cyclic Potentiodynamic Polarization Test Results for Study of Corrosion Behavior of Metals: A Review. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2018, 54, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, M.A. A Review of Monoethanolamine Chemistry; U.S. Naval Research Laboratory: Washington DC, USA, 1962; Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/AD0277031.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Dixon, B.E.; Williams, R.A. Reaction of iron with monoethanolamine. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1950, 69, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fostås, B.; Gangstad, A.; Nenseter, B.; Pedersen, S.; Sjøvoll, M.; Sørensen, A.L. Effects of NOx in the flue gas degradation of MEA. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pearson, P.; Yang, Q.; Puxty, G.; Feron, P.; Xiao, D. A study of designer amine 4-amino-1-propyl-piperidine against the corrosion of carbon steel for application in CO2 capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2020, 94, 102929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H. Synergistic effect of O2, H2S and SO2 impurities on the corrosion behavior of X65 steel in water-saturated supercritical CO2 system. Corros. Sci. 2016, 107, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugstad, A.; Halseid, M.; Morland, B. Effect of SO2 and NO2 on Corrosion and Solid Formation in Dense Phase CO2 Pipelines. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhou, C.; Li, Z.; Ni, W. Impact of SO2 concentration on the corrosion rate of X70 steel and iron in water-saturated supercritical CO2 mixed with SO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 58, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Effect of High-Concentration O-2 on Corrosion Behavior of X70 Steel in Water-Containing Supercritical CO2 with SO2. Corrosion 2016, 73, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| % | C | Cr | Mn | Si | P | Ni | S | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS 304L | 0.03 | 18 | 2 | 1 | 0.0045 | 8 | 0.03 | - | Bal. |
| SS 316L | 0.022 | 17.5 | 1.8 | - | 0.003 | 10 | 0.54 | 2 | Bal. |
| Amine Type | Ecorr [mV vs. SCE] 25 °C/40 °C | Icorr [μA/cm2] 25 °C/40 °C | βc [mV] 25 °C/40 °C | βa [mV] 25 °C/40 °C | Cor. r. [μm/Y] 25 °C/40 °C | Ipassive [μA/cm2] 25 °C/40 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS 304L | Lean MEA | −374/−301 | 0.1/0.2 | −205.7/−155.8 | 100/225 | 1.4/2.8 | −4.2/−4.2 |
| Lean MEA with SOX | −431.4/−392.9 | 1.9/2.3 | −234.6/−347.7 | 324.5/470.1 | 22.8/27.4 | −4.1/−3.8 | |
| Lean MEA with SOX/NOX | −570/−272.7 | 3.6/5.9 | −233.9/−209.1 | 475.5/354.8 | 42.6/69.6 | −4.1/−3.7 | |
| Loaded MEA | −195.8/−229 | 1.45/4.5 | −184.4/−278 | 444/960 | 28.1/47.6 | −4.3/−4 | |
| MEA loaded with SOX | −449.2/−475.7 | 2.8/3.9 | −233.5/−312 | 277.6/787.8 | 32.8/45.4 | −3.9/−3.9 | |
| MEA loaded with SOX/NOX | −483.2/−218.7 | 3.9/4.4 | −305.1/−168.5 | 529.7/225.6 | 45.3/51.9 | −4.2/−4.1 | |
| SS 316L | Lean MEA | −393/−291 | 0.4/0.6 | −155.7/−210.2 | 242/286.1 | 4.2/6.7 | −4.4/−4.5 |
| Lean MEA with SOX | −570/−436 | 1.8/2.2 | −171.5/−167 | 386.1/189.8 | 20.8/25 | −4.1/−4.3 | |
| Lean MEA with SOX/NOX | −505/−464 | 2.4/3.3 | −319.3/−263.9 | 419.4/362.4 | 28.1/38.8 | −4.2/−4.1 | |
| Loaded MEA | −359/−256 | 0.9/2.5 | −163.6/−267.5 | 309.4/425.1 | 10.9/29.5 | −4.4/−4.3 | |
| MEA loaded with SOX | −650/−626 | 2.1/2.7 | −157.9/−236.7 | 109.9/189.8 | 24.5/31.8 | −4.3/−4.2 | |
| MEA loaded with SOx/NOX | −590/−568 | 2.5/3.5 | −227.1/−148 | 358.4/220.5 | 29.7/40.7 | −4.4/−4.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamprou, E.; Stergioudi, F.; Skordaris, G.; Michailidis, N.; Nessi, E.; Papadopoulos, A.I.; Seferlis, P. Effect of NOX and SOX Contaminants on Corrosion Behaviors of 304L and 316L Stainless Steels in Monoethanolamine Aqueous Amine Solutions. Coatings 2024, 14, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070842
Lamprou E, Stergioudi F, Skordaris G, Michailidis N, Nessi E, Papadopoulos AI, Seferlis P. Effect of NOX and SOX Contaminants on Corrosion Behaviors of 304L and 316L Stainless Steels in Monoethanolamine Aqueous Amine Solutions. Coatings. 2024; 14(7):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070842
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamprou, Eleni, Fani Stergioudi, Georgios Skordaris, Nikolaos Michailidis, Evie Nessi, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, and Panagiotis Seferlis. 2024. "Effect of NOX and SOX Contaminants on Corrosion Behaviors of 304L and 316L Stainless Steels in Monoethanolamine Aqueous Amine Solutions" Coatings 14, no. 7: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070842
APA StyleLamprou, E., Stergioudi, F., Skordaris, G., Michailidis, N., Nessi, E., Papadopoulos, A. I., & Seferlis, P. (2024). Effect of NOX and SOX Contaminants on Corrosion Behaviors of 304L and 316L Stainless Steels in Monoethanolamine Aqueous Amine Solutions. Coatings, 14(7), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070842










