Abstract
As a fundamental machining tool, the ball end milling cutter plays a crucial role in manufacturing. Due to its low thermal conductivity, the heat generated during the cutting process of titanium alloy materials is not dissipated efficiently, resulting in a substantial cutting heat. This heat leads to chip adhesion and exacerbates the wear of the ball end milling cutter, ultimately affecting its service life. Therefore, studying the residual life of the tool during the cutting process is essential to prevent significant impacts on the product’s surface quality due to tool damage and passivation. Most research on micro-texture cutters is based on experiments that analyze the wear patterns of cutters under various lubrication conditions and their influence on the cutting process. Different neural network prediction models are employed to enhance the accuracy and stability of tool life prediction models. However, the exploration of other superior models for predicting the life of micro-texture cutters remains ongoing. This paper is based on an experiment involving the milling of titanium alloy using a micro-pit-structured ball end milling cutter. It was found that the cutting force of the tool is higher during the initial and later wear stages. During the stable wear stage, the unevenness of the defective layer on the tool surface is reduced, increasing the contact area and reducing the surface pressure, thereby decreasing the cutting force. This study analyzes the influence of micro-pit structural parameters on the wear and milling force of the ball end milling cutter. By evaluating the wear value of the ball end milling cutter after each cut, the wear mechanism of the micro-texture cutter is identified. A deep-learning-based bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) neural network model for tool life prediction is developed. Through training and validation, the model’s accuracy and stability are continuously improved. A comparative analysis with different predictive models is conducted to determine whether the proposed model offers advantages over existing models, which is crucial for maximizing tool utilization and reducing manufacturing costs.
1. Introduction
Titanium alloy, known for its excellent properties such as its high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and high temperature resistance, is widely used across various fields. However, its high chemical activity, low modulus of elasticity, and strong affinity characteristics make it prone to adhesion to the milling cutter surface during machining, leading to significant tool wear and a reduced tool life. To mitigate wear, scholars have explored the application of bionic non-smooth surface technology in cutting tools, significantly enhancing tool life [1,2,3,4,5]. Tejanshu Sekhar Sahu [6] studied the wear characteristics of various micro-texture tools under dry cutting conditions for Ti6Al4V and found that the average flank face wear was reduced by 43.5% with pit texture, 32% with linear texture, and 24.7% with hybrid texture, demonstrating better tribological properties. Xu Wang’s [7,8] comparative tests on micro-texture tools for cutting SiCP/Al composites concluded that micro-texture tools reduced the cutting force by 5%–13% and provided a better cutting stability.
Along with the research on micro-texture tools, many scholars have also studied tool wear and tool life. Liang Xiaoliang [9] discovered the mechanism of the influence of the tool wear state on the surface residual stress based on the study of turning Ti6Al4V. Based on an experiment on tool wear during the micro-milling process, Alessandro Colpani [10] described in detail the effect of the feed rate on the evolution of rear face wear. It was found that the evolution of rear face wear typically exhibits decreasing, constant, and increasing tool wear slope regions, and that changes in the cutting force, roughness, and tip arc radius are related to tool wear. A statistical analysis based on Pearson correlation coefficients is also proposed to reveal the effect of the feed rate on the evolution of rear face wear, allowing rear face wear to be used as a basis for determining the tool life in the micro-milling process. Qimeng Liu [11] and other scholars, based on a tool wear test with titanium alloy machining tools, studied the impact of tool cutting wear on the cutting process, and it was concluded that with an increase in the tool continuous cutting wear time, the cutting force, residual stress, and cutting temperature obtained at each stage gradually increase and the roughness of the cutting surface obtained by continuous wear first decreases and then increases. The burrs on the cutting edge are large in the initial wear stage of the tool, while in the normal wear stage, the surface quality of the tool gradually stabilizes, but when the tool reaches the severe wear stage, the surface quality of the tool begins to decrease sharply and produces coarse burrs on the cutting edge. Jiang Wei [12], through ultrasonic-assisted machining of titanium alloy, concluded that after the application of ultrasonic vibrations, the wear of the rear face of the milling cutter is reduced, proving that the wear mechanism of the milling cutter after the application of ultrasonic vibrations is abrasive wear. The test results show that ultrasonic vibration leads to the most significant improvements in surface roughness and surface quality.
Inspired by deep learning advancements, Xingwei Xu [13] proposed a parallel one-dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for feature extraction and fusion, incorporating residual connectivity and attention mechanisms, resulting in more stable and accurate tool wear predictions. Lei Nie’s [14] CNN-BiLSTM with an attention mechanism model improves the prediction accuracy using monitored data for local and temporal feature extraction. Changsen Y [15] utilized long short-term memory neural networks to predict the tool life under variable conditions, demonstrating their effectiveness. Zhu Lingfeng [16] proposed a big-data-based tool life prediction method, aligning the predicted and actual tool life. Huang [17] developed a multi-sensor fusion-based method for tool life prediction, effectively predicting tool life.
Through the analysis of the above scholars’ research, most of the analysis of micro-texture tools is performed through initial testing, studying the change rule of tool wear under different cutting conditions, and analyzing the wear mechanism of the tool. Alternatively, the impact of tool cutting wear on the cutting process can be studied, analyzing the various stages of continuous tool wear. Analysis can also be performed through auxiliary processing, which analyzes and studies the law of change in tool wear and the wear mechanism during each wear stage. The continuous development of big data and neural networks has improved the accuracy and stability of life prediction models, making neural networks common in tool life prediction.
This paper analyzes tool wear and collects cutting force and vibration signals during titanium alloy milling with a micro-pit ball end milling cutter. Using these data, a BiLSTM–Attention model is developed to predict the remaining life of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter, aiming to improve tool utilization and reduce manufacturing costs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Experimental Materials
Ti6Al4V titanium alloy has a high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature resistance and other excellent properties. During the machining process, the cutter experiences significant wear. This experiment studies the hardness, wear resistance, strength, toughness, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and other properties of an uncoated YG8 carbide ball end milling cutter in the absence of lubrication conditions on a Ti6Al4V milling workpiece. The workpieces were prepared by using slow-feeding wire cutting; the dimensions of the milling cutter are shown in Figure 1a and the physical drawing is shown in Figure 1b.
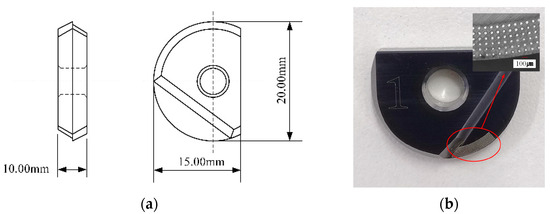
Figure 1.
Dimensions and physical images of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter. (a) Diagram of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter’s dimensions; (b) physical picture of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter.
The chemical composition of YG8 carbide is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of YG8.
The chemical composition of the Ti6Al4V workpiece is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Chemical composition of Ti6Al4V.
The workpiece dimensions are shown in the schematic diagram in Figure 2a, and the process of its preparation is shown in Figure 2b.
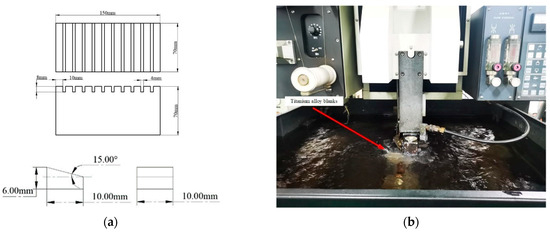
Figure 2.
Titanium alloy workpiece size and preparation. (a) Schematic diagram of workpiece dimensions; (b) preparation of workpieces by slow-feeding wire cutting.
2.2. Design of Tool Surface Texture
In our previous research, different shapes of micro-texture ball milling cutters, such as micro-pit texture, grooved texture, concentric circle texture, and ortho-intertexture cutters, were milled and milling tests were carried out; the wear and friction reduction mechanisms, the micro-texture stress distribution, and their influence on the structural strength of ball milling cutters were analyzed so as to obtain the optimal cutting performance and wear and friction reductions for ball milling cutters with a micro-pit morphology and micro-texture [18].
To investigate the influence of different micro-pit texture parameters on the wear of ball end milling cutters, an orthogonal simulation test scheme with four factors and three levels was designed. Through the simulation and analysis of micro-texture ball end milling cutter wear, it was concluded that the distance to the blade and micro-pit diameter are the two most significant factors affecting the wear of the flank face of a micro-texture ball end milling cutter. The optimal size parameters of the micro-pit texture are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Micro-pit texture size parameters (μm).
The dimensions of the micro-pit parameters are shown in Figure 3.
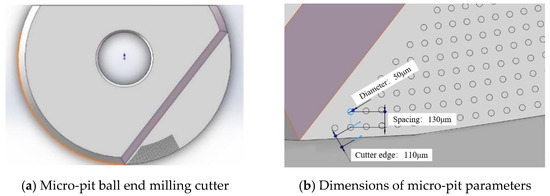
Figure 3.
Micro-pit texture parameter size.
2.3. Laser Processing Equipment
A fiber laser was used to prepare the micro-pit surface of the ball end milling cutter. The principle of operation is shown in Figure 4. Numbers were engraved on the surface of the ball end milling cutter using a laser for identification.
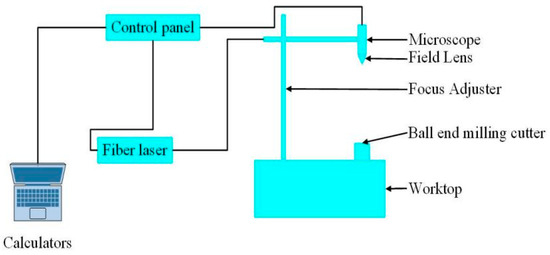
Figure 4.
Fiber laser working principle.
The fiber laser parameters are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Fiber laser parameters.
2.4. Construction of the Experimental Platform
A computer numerical control (CNC) milling machine was used in this test. The workpiece was fixed at a 15° angle to the horizontal using a sinusoidal vise to improve the surface quality and reduce tool wear, prolonging the tool’s service life [19]. The test platform and milling experiment parameters are shown in Figure 5.
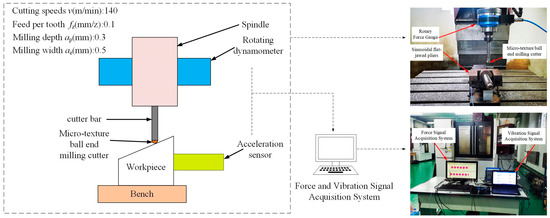
Figure 5.
Experimental platform building.
3. Analysis of Results
3.1. Tool Wear Result Analysis
An industrial camera was used to photograph and observe the wear pattern of the micro-texture milling cutter and to analyze the law between the wear of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter and the milling distance, and the acquisition device is shown in Figure 6.
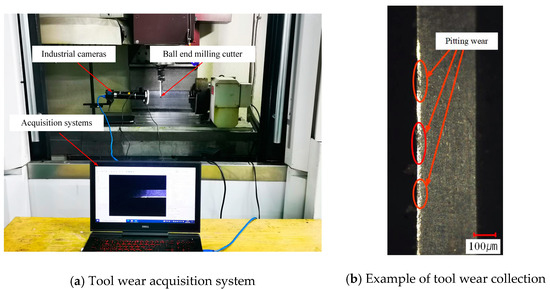
Figure 6.
Tool wear acquisition system and examples.
Ball end milling cutters consist of inserts and a cutter bar. The ball end milling cutter inserts are shown in Figure 7a, and the cutter bar is shown in Figure 7b.
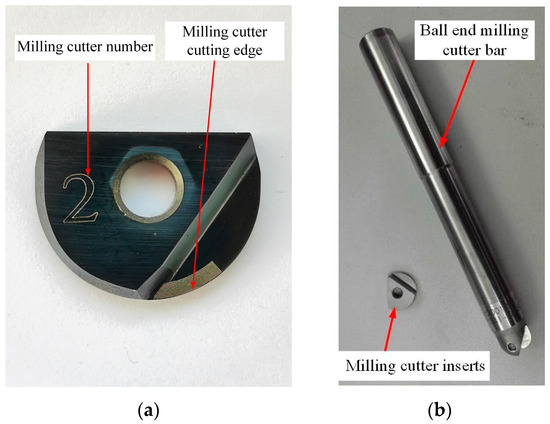
Figure 7.
Microfabrication micro-texture ball end milling cutter and shanks. (a) Micro-texture ball end milling cutter inserts, (b) milling cutter inserts and cutter bar.
Its flank face wear values at different travel distances are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
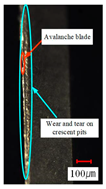
Micro-texture ball end milling cutter wear diagram.
The milling process of the micro-pit structure ball end milling cutter is shown in Figure 8.
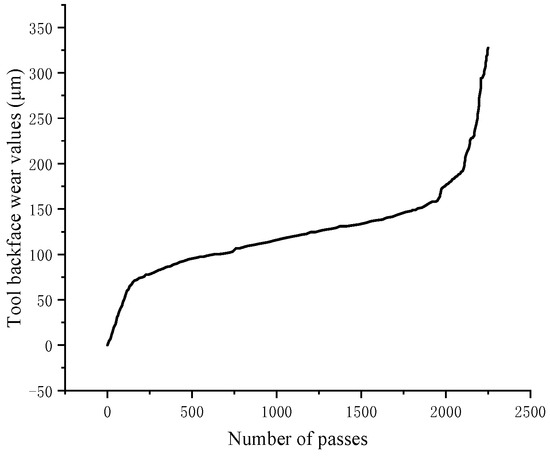
Figure 8.
Micro texture ball end milling cutter wear relationship diagram.
In the milling process of the micro-texture structure ball end milling cutter, the micro-texture structure ball end milling cutter’s wear process can be mainly divided into three stages: the initial wear stage, the normal wear stage and the sharp wear stage.
- (1)
- Initial wear stage
The micro-pit structure ball end milling cutter has just started to cut into the workpiece with incomplete removal of the remelted layer on the surface and rough surface, resulting in severe tool wear.
- (2)
- Intermediate wear stage
As the surface of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter, after a period of milling the surface remelting layer, is smoothed, increasing the contact area and reducing the surface pressure, the tool wear rate is reduced and the micro-texture ball end milling cutter’s wear value is relatively stable.
- (3)
- Later wear stage
The surface quality of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter begins to decline sharply and the wear increases sharply; in this stage, the tool boundary easily breaks and flaking and micro-chipping phenomena are often observed, resulting in the performance failure of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter, and the milling cutter’s life comes to an end.
3.2. Analysis of Workpiece Surface Quality
A white light interferometer was used to measure the surface roughness of the workpiece at different cutting stages. For accuracy, measurements were taken at three points along the radial direction of the tool, and the average was calculated. Table 6 shows the surface roughness results for different cutting stages; it can be found that the workpiece’s surface roughness decreases first and then increases, and the surface quality of the workpiece is better in the stage of normal wear.

Table 6.
Surface roughness of the workpiece at different cutting stages.
3.3. Preliminary Analysis of Cutting Forces and Vibration Signals
Vibration and force signals during each tool pass in the milling test of titanium alloy using a micro-texture ball end milling cutter were collected. The vibration data from the first to the fourth second of each tool pass were selected for corresponding analysis. Because the wear process of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter is divided into three stages, the vibration signal and force signal in the tool passing process were taken once in each of the three stages for a brief analysis, and the vibration signal analysis is shown in Figure 9.
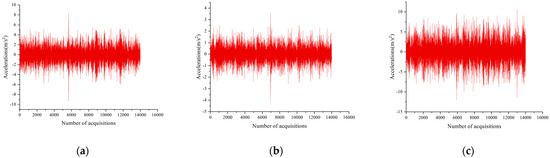
Figure 9.
The vibration signals of the tool under different cutting numbers. (a) Vibration signal at the 30th pass of the tool; (b) vibration signal at the 1000th pass of the tool; (c) vibration signal at the 2000th pass of the tool.
According to Figure 9, from the 30th cut to the 1000th cut, and then to the 2000th cut, the vibration signal data show that as the number of cuts increases, both the maximum value and the peak-to-peak value of the vibration signals gradually increase.
The influence of tool wear on the vibration signal in the milling test with the micro-texture ball end milling cutter is shown in Figure 10.
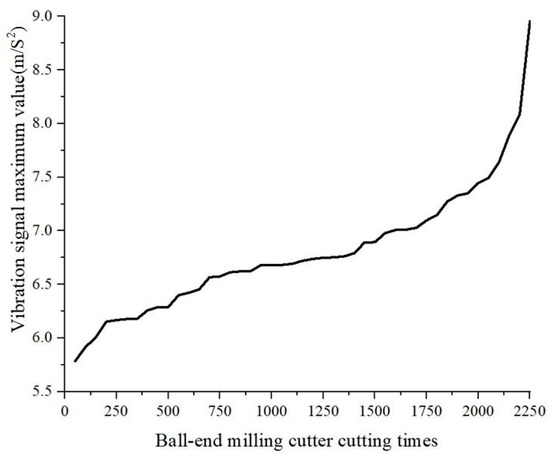
Figure 10.
Effect of tool wear on vibration signals.
The force signal is briefly analyzed in Figure 11.
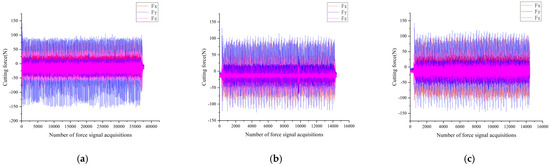
Figure 11.
The force signal of the tool under different cutting numbers. (a) Force signal at the 30th pass of the tool; (b) force signal at the 1000th pass of the tool; (c) force signal at the 2000th pass of the tool.
From Figure 11, it is evident that the cutting force of the tool is higher during the initial and later wear stages. During the stable wear stage, the unevenness of the defective layer on the tool’s surface smooths out, increasing the contact area, reducing the surface pressure, and thereby decreasing the cutting force. The law of the influence of tool wear on milling force is illustrated in Figure 12.
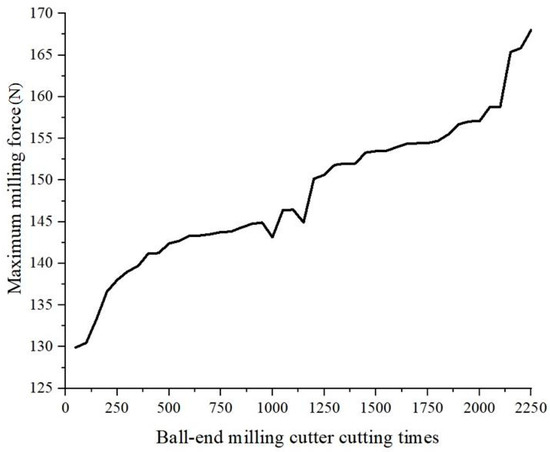
Figure 12.
Effect of tool wear on milling force.
3.4. Preprocessing of Cutting Forces and Vibration Signals
The signals collected in the milling test are extensive and disorganized, making the relationship with tool wear unclear. However, time-domain signals can directly reflect the change rules of signals, necessitating the extraction of features from the original signal. During milling tests, the cutting performance and machine tool spindle vibrations affect the test results, which are reflected in time-domain characteristics, frequency-domain characteristics, and time–frequency-domain characteristics.
In this study, the time-domain, frequency-domain, and time–frequency characteristic values of the signal were extracted using IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0.1.0 software, spectrum analysis, and wavelet transform analysis. The time-domain features describe the waveform of the target signal with time as the independent variable. During the milling test, until the service life of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter ends, certain dimensional feature values (absolute mean, root mean square, root amplitude, skewness, and peak value) will increase. The dimensionless feature values (peak factor, pulse factor, margin factor, and waveform factor) indicate the extreme degree of the peak value in the waveform, the instantaneous peak value in the vibration signal, and the wear status of the machined component, respectively.
According to the data extraction of time-domain characteristics by SPSS software, there are minor peaks and minimal changes in the root mean square value during the early wear stage of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter. However, due to the high sensitivity of the pulse factor, margin factor, and kurtosis factor to changes in the tool’s health state, these factors show a trend of first increasing and then decreasing in the later stages. The waveform factor and the number of tool passes exhibit a strong correlation, indicating differences in the correlation between each characteristic value and the time-domain signal. Time-domain feature values are more significant in the analysis of periodic stationary signals. For nonlinear signals in milling data, time-domain analysis alone may not accurately characterize the signal data features. Therefore, to study the milling signal more in depth, frequency-domain feature processing is combined with time-domain features to predict the tool wear and service life.
The original signal of the titanium alloy milling process is influenced by the machine tool system, cutting parameters, and tool wear, making it a typical nonlinear, complex random signal. Frequency-domain analysis is used to enhance the features of the milling data of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter by analyzing the frequency component and energy of the time-domain signal, extracting effective information, and improving the correlation between tool wear and the characteristic value of the milling signal. Frequency-domain signals are extracted using spectral analysis. The data show that frequency information changes with tool wear. By monitoring tool wear under different conditions, the frequency-domain characteristics of multi-source signal data can be analyzed, identifying the cutting state and providing a basis for predicting tool life.
Since milling signals are non-periodic and non-stationary under tool wear, single time-domain or frequency-domain methods cannot identify the correlation between characteristic values, time, and frequency. Wavelet transform analysis is used to analyze signal characteristics in the time–frequency domain. Time–frequency domain feature extraction can monitor signal characteristics in the time domain and frequency domain and monitor the signal amplitude, accurately explaining the effective characteristics of the cutter signal during milling. Through analysis of force signals, vibration signals, and wear data of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter in the time domain, frequency domain, and time–frequency domain, the characteristics of these signals are highly correlated with the residual life of the cutter.
3.5. Tool Residual Life Modeling
This paper presents a prediction model for remaining tool life based on feature extraction using LSTM [14], constructing a BiLSTM–Attention tool-remaining-life prediction model with the attention mechanism method and MATLAB 2016a software. The prediction process is shown in Figure 13.
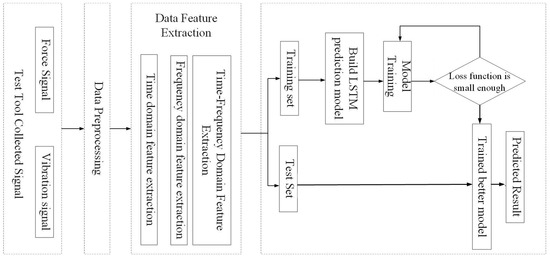
Figure 13.
Flowchart of tool remaining life prediction based on deep learning.
3.5.1. Tool-Remaining-Life Prediction Model Training
The force and vibration signal data collected during the milling of titanium alloy by the micro-texture ball end milling cutter are recorded as A1 to A4, B1 to B4, and C1 to C4. A1, A3, A4, B1, B2, B4, C2, C3, and C4 are used as the training set data, while A2, B3, and C1 are used as the validation set data. These are input into the trained BiLSTM–Attention model to predict the tool’s remaining life.
The root mean square error is chosen as the loss function during model training, calculated as follows:
where —the predicted value of the remaining service life of the tool and —the actual measured value of the remaining service life of the tool.
As the number of training iterations increases, the loss function decreases until convergence, indicating the predicted values are approaching the actual values, shown in Figure 14. The horizontal axis represents the number of training iterations, and the vertical axis represents the loss function size. The analysis shows that the BiLSTM–Attention prediction model for remaining tool life has an excellent generalization ability.
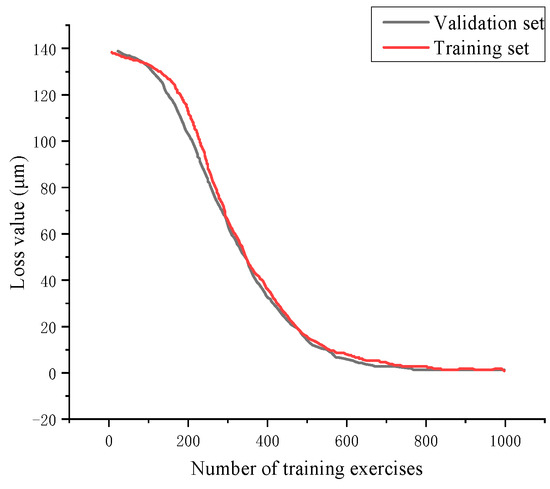
Figure 14.
BiLSTM–Attention loss function change curve.
3.5.2. Tool-Remaining-Life Prediction Analysis
The evaluation indexes for the tool residual life prediction model are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Predictive performance evaluation indicators.
The square error (MSE) is used to reflect how closely the model’s predicted values approximate the true values, calculated as:
where —predicted value and —true value.
The average absolute percentage error (MAPE) is used to determine the prediction accuracy, calculated as:
The evaluation metrics described in the table above are mainly used to evaluate the accuracy of the tool residual life prediction model by calculating the mean square error and mean absolute percentage error.
The validation set data, A2, B3, and C1, collected for the milling cutter are input into the BiLSTM–Attention toolremaining-life prediction model to obtain the predicted value of the remaining life of the tool. This predicted value and the true value are plotted as the curve shown in Figure 15. The predicted results exhibit the same trend as the actual tool wear, demonstrating the model’s effectiveness.
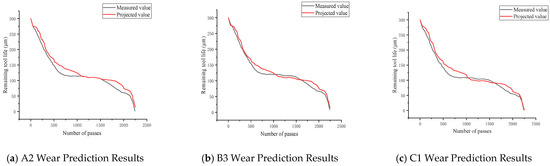
Figure 15.
BiLSTM–Attention tool wear prediction results.
After calculating and analyzing the above three sets of graphs, the average absolute percentage error is 11.64%, which is less than 20%, proving that the model is able to accurately predict the remaining life of the micro-pit ball end milling cutter.
3.5.3. Predictive Model Comparison Test
A comparison test was conducted between the BiLSTM–Attention tool-remaining-life prediction model and other models, including the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) and a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN).
The validation set data (A2, B3, C1) were input into the Hidden Markov Prediction Model (HMM) and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) prediction model to obtain the predicted values of the remaining life of the tool. The graphs of predicted and measured values are shown in Figure 16 and Figure 17, respectively.
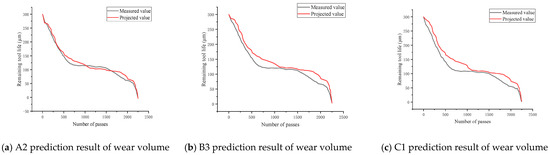
Figure 16.
HMM tool wear prediction results.
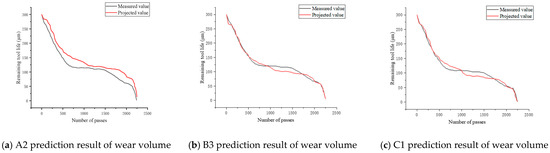
Figure 17.
CNN tool wear prediction results.
The predicted and measured values for each model were used to calculate the mean square error and average absolute percentage error, shown in Table 8.

Table 8.
The prediction results of different prediction models.
The BiLSTM–Attention model exhibited an average absolute percentage error of 11.64%, significantly lower than the HMM (24.82%) and CNN (18.74%) models, proving its higher accuracy and better stability.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on the experimental study of milling titanium alloy with a micro-texture ball end milling cutter, it was found that the amplitude of the milling force and vibration signals increases with tool wear as the milling distance increases.
- (2)
- The wear evolution of the micro-texture ball end milling cutter is divided into three stages: the initial wear stage, the mid-wear stage, and the late wear stage. In the initial wear stage, due to the presence of the tool’s remelted layer, micro-pit wear occurs, resulting in significant tool wear. In the intermediate wear stage, the remelted layer smooths out, increasing the contact area and reducing the surface pressure, leading to a lower tool wear rate, mainly due to crescent pits. In the late wear stage, the surface quality of the ball end milling cutter declines sharply, producing thick edge burrs, which cause a significant increase in wear. During this stage, boundary breakage, flake peeling, and micro-chipping occur, leading to the tool’s failure.
- (3)
- By building a BiLSTM–Attention tool-remaining-life prediction model and inputting feature data for training and validation, the model achieved an average absolute percentage error of 11.64%. In a comparative analysis with the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) prediction models suggested by other researchers, the BiLSTM–Attention tool was revealed to have a significantly higher accuracy (24.82%) for predicting the remaining life of micro-textured ball end milling cutters compared to both the HMM (24.82%) and CNN (18.74%) models. This finding attests to the efficacy and reliability of the proposed BiLSTM–Attention tool in this domain.
5. Research Outlook
This study focused on preparing micro-pits on cemented carbide tool materials. Future research can explore other micro-structure types and sizes and the impact of different texturing techniques on wear performance and further refine the predictive model to include additional variables for an even higher accuracy.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. proposed the prediction model and general ideas. Y.F. is responsible for experimental design, data analysis, and instrument operation. Q.L. was responsible for creating and optimizing data images. K.Z. facilitated constructive discussion and analyzed the article. K.L. was responsible for translating and polishing the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51875144).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request due to restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest in the publication of this paper. The research in this paper is in the field of metalworking and does not involve humans or animals. This paper strictly adheres to recognized principles of ethics and professional conduct.
References
- Yang, S.; Zhou, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Tong, X.; Liu, W.W. Prediction of surface roughness of titanium alloy milled by Micro-pit configuration ball-end milling cutter. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2017, 3, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hexi, J.; Kexiang, W.; Jianming, L.; Jianyu, Z.; Wenjing, P. Research progress of titanium alloy for aviation. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2015, 2, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y. Research on Tool Failure Mechanism of Titanium Alloy Milling Process. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lianyao, T.; Tang, L.; Li, P.; Qiu, X. A new species of the genus Lepidoptera (Lepidoptera, Lepidoptera, Lepidoptera). Research progress on cutting titanium alloys by micro-texture tools. Aerosp. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xinmin, F.; Xin, L.; Zuo, W. Research status of micro-texture tool wear. Mech. Des. Manuf. 2023, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, T.S.; George, A.; Kuriachen, B.; Mathew, J.; Dhanish, P.B. Experimental investigations on the wear behaviour of micro-EDM-fabricated textured tools during dry turning of Ti6Al4V. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2022, 74, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Popov, V.L.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Yu, H. Evaluation of the cutting performance of mi-cro-groove-textured PCD tool on SiCp/Al composites. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 32389–32398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Popov, V.L.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, H. Study on cutting performance of SiCp/Al composite using textured YG8 carbide tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 119, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X. Research on the influence law of tool wear state on the surface integrity of machining titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Ph.D. Dissertation, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Colpani, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Ceretti, E.; Attanasio, A. Tool wear analysis in micromilling of titanium alloy. Precis. Eng. 2019, 57, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Yu, H. Experimental study on the influence of tool wear on the cutting process of Ti6Al4V. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2021, 1838, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. Experimental Research on Machining Titanium Alloy by Circular Milling Cutter under Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Li, X.; Ming, W.; Chen, M. A novel multi-scale CNN and attention mechanism method with multi-sensor signal for remaining useful life prediction. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 169, 108204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Cai, W.; Yang, H. Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Milling Cutters Based on CNN-BiLSTM and Attention Mechanism. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, E.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Z. Milling cutter wear prediction method under variable working conditions based on LRCN. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 2647–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingfeng, Z.; Longxian, C.; Fujun, Z.; Anhui, K.; Dazun, L. A new genus and species of the genus Lepidoptera (Hymenoptera, Braconidae). Research on tool life prediction based on big data analysis technology. Mech. Manuf. Autom. 2022, 4, 148–151. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Qian, C.; Li, C.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H. Tool Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method Based on Multi-Sensor Fusion under Variable Working Conditions. Machines 2022, 10, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X. Research on Surface Quality of Titanium Alloy Milling by Micro-Pit Configuration Ball End Milling Cutter. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, T.; Kim, H.; Lee, S. Selection of the Machining Inclination Angle in High-Speed Ball End Milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2001, 17, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).