The Microstructures and Wear Resistance of CoCrFeNi2Mox High-Entropy Alloy Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Materials and Preparation
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Materials Testing
3. Results and Discussion
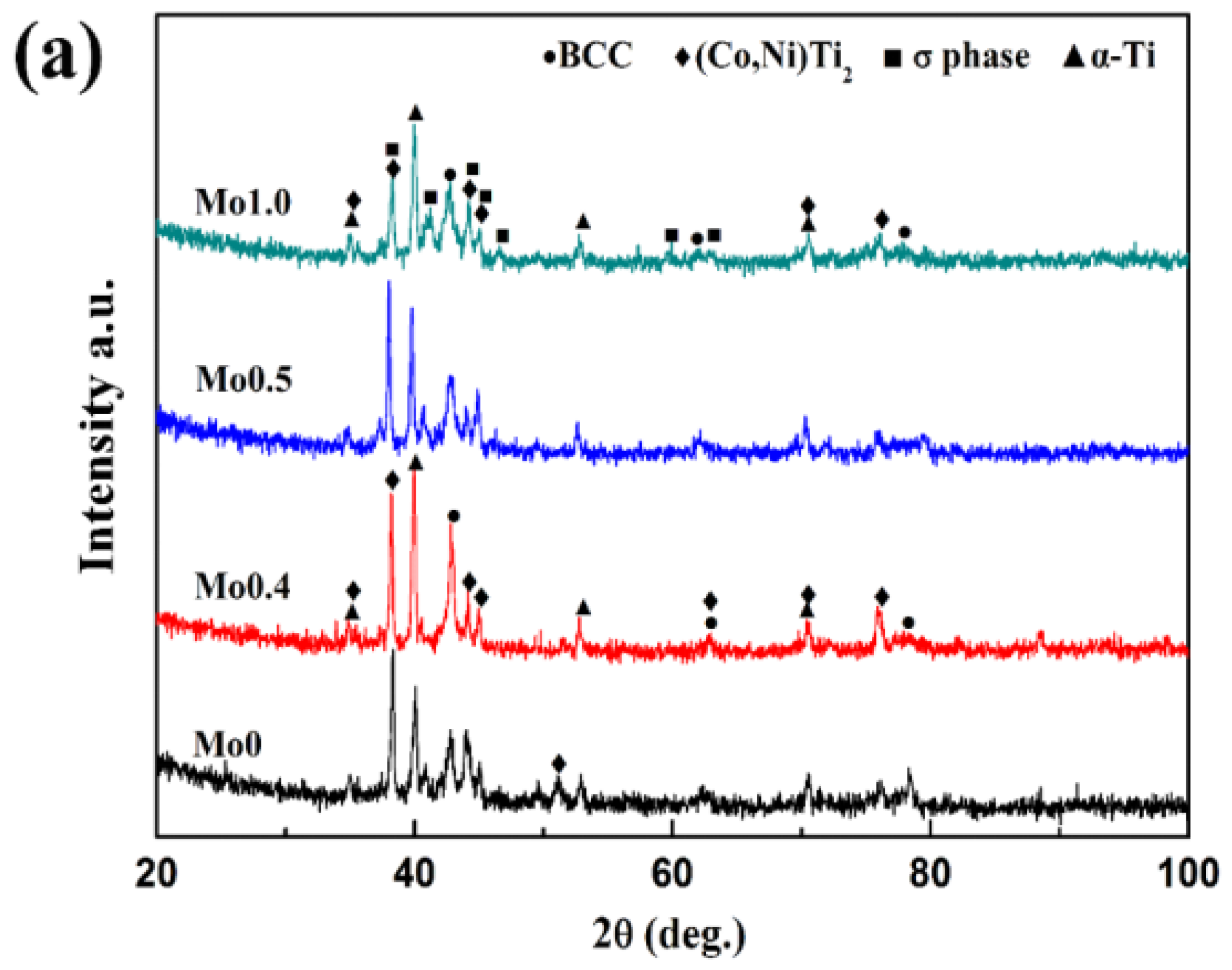
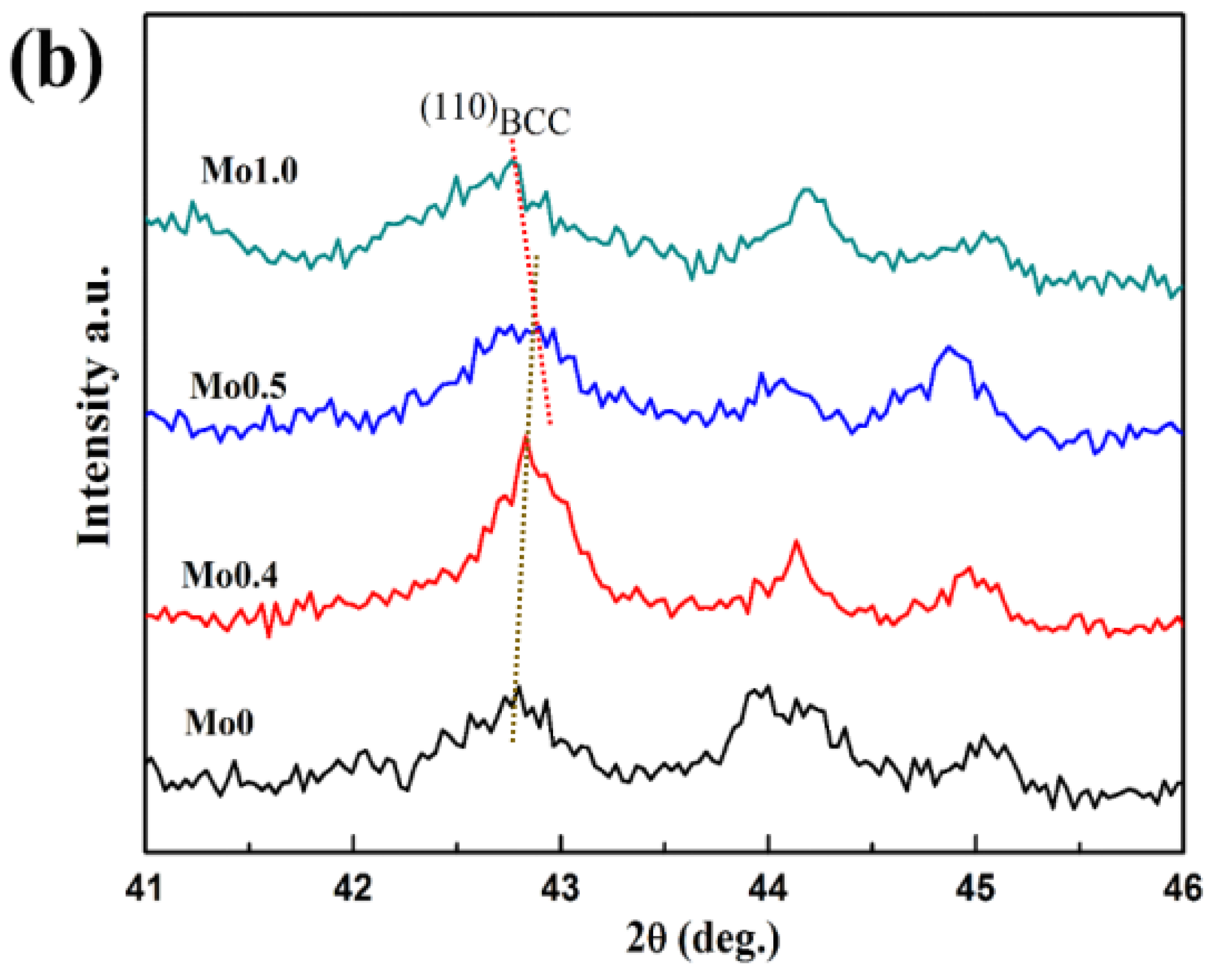
3.1. Phase Constitution
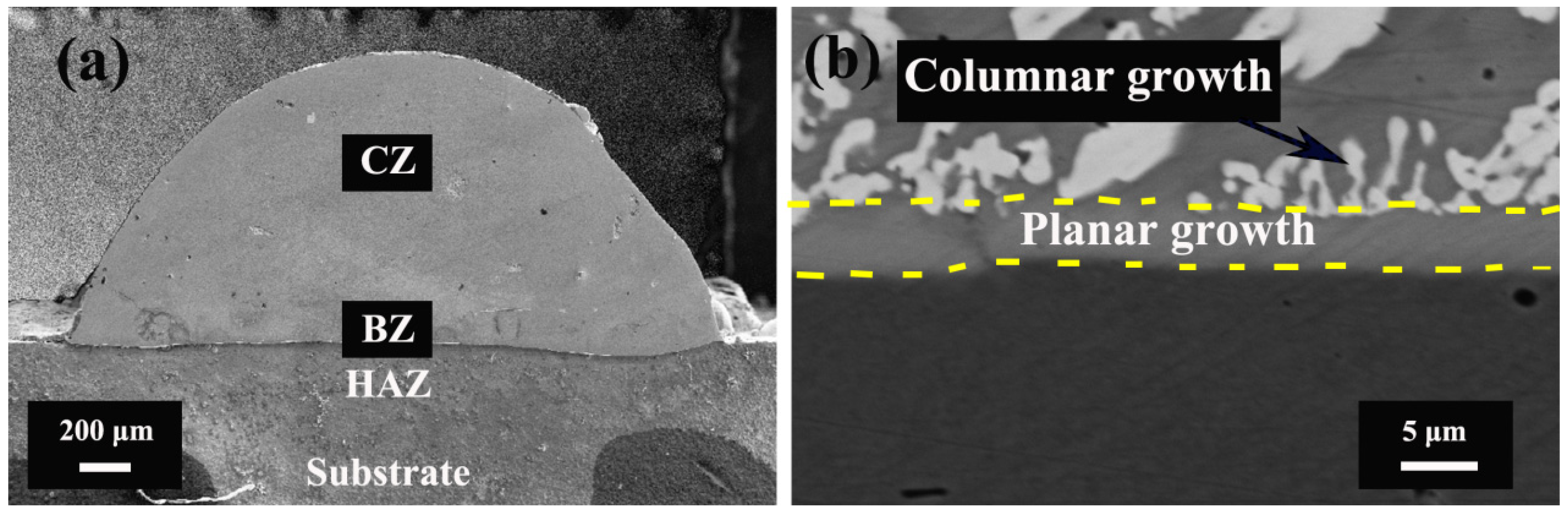
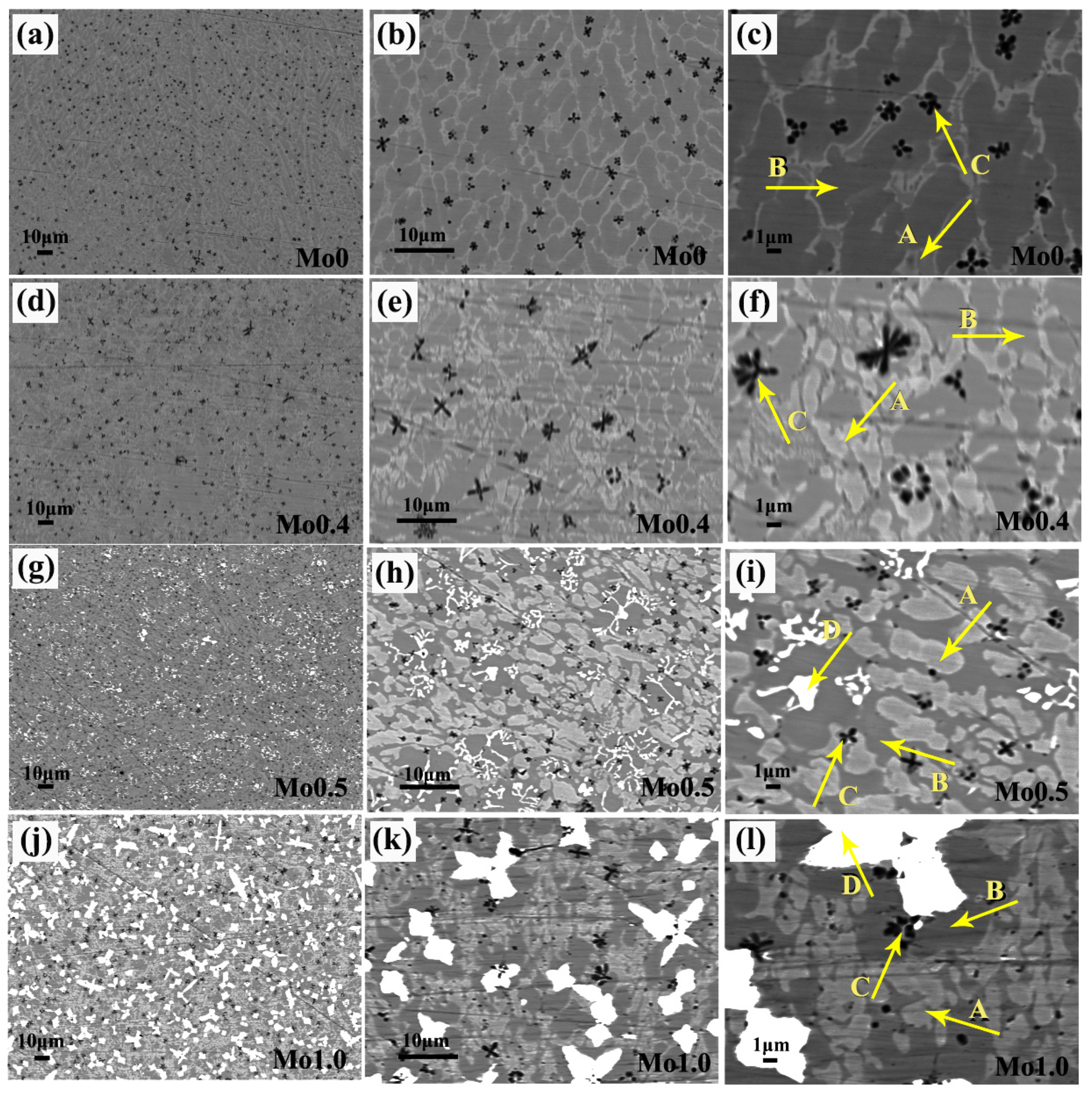
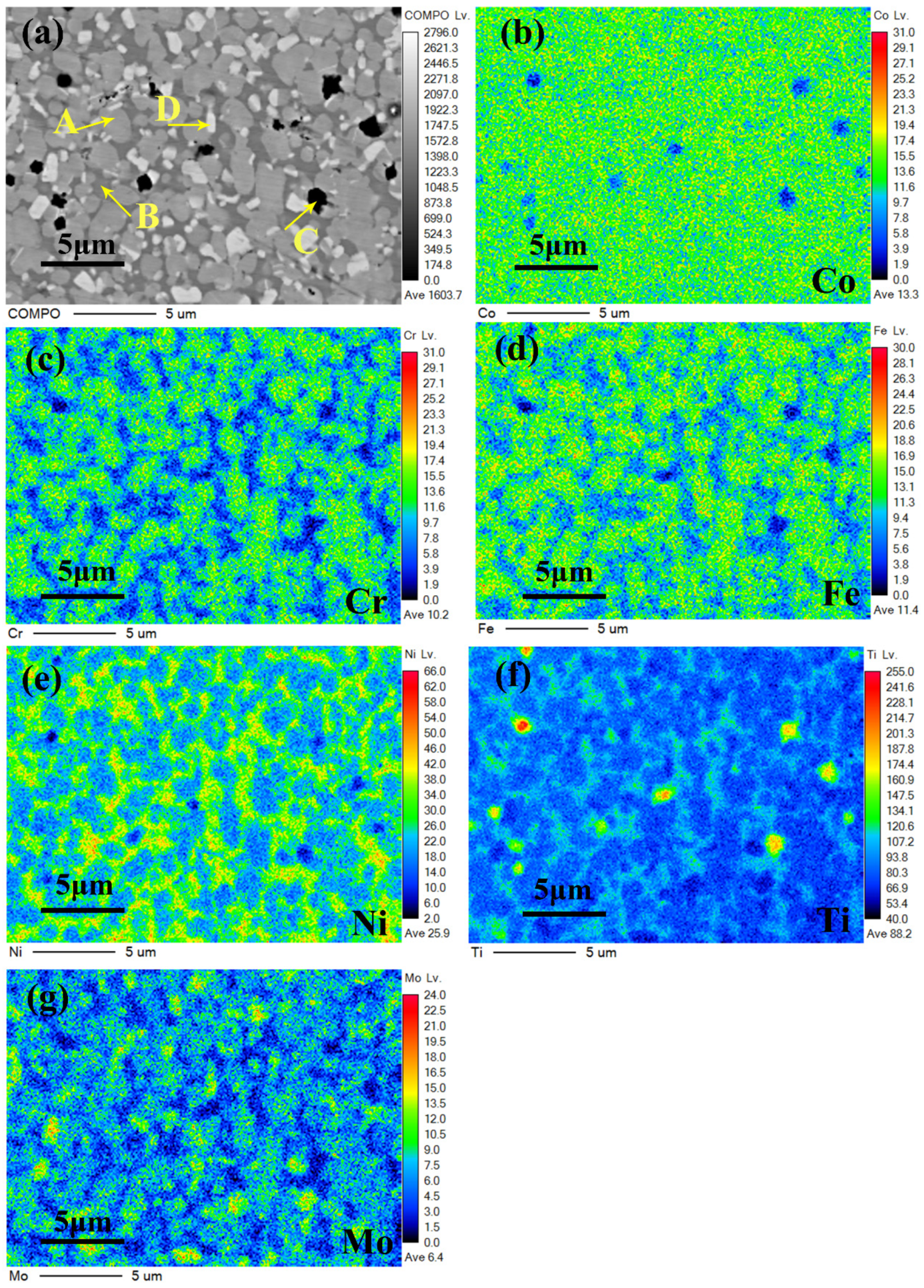
3.2. Microstructures
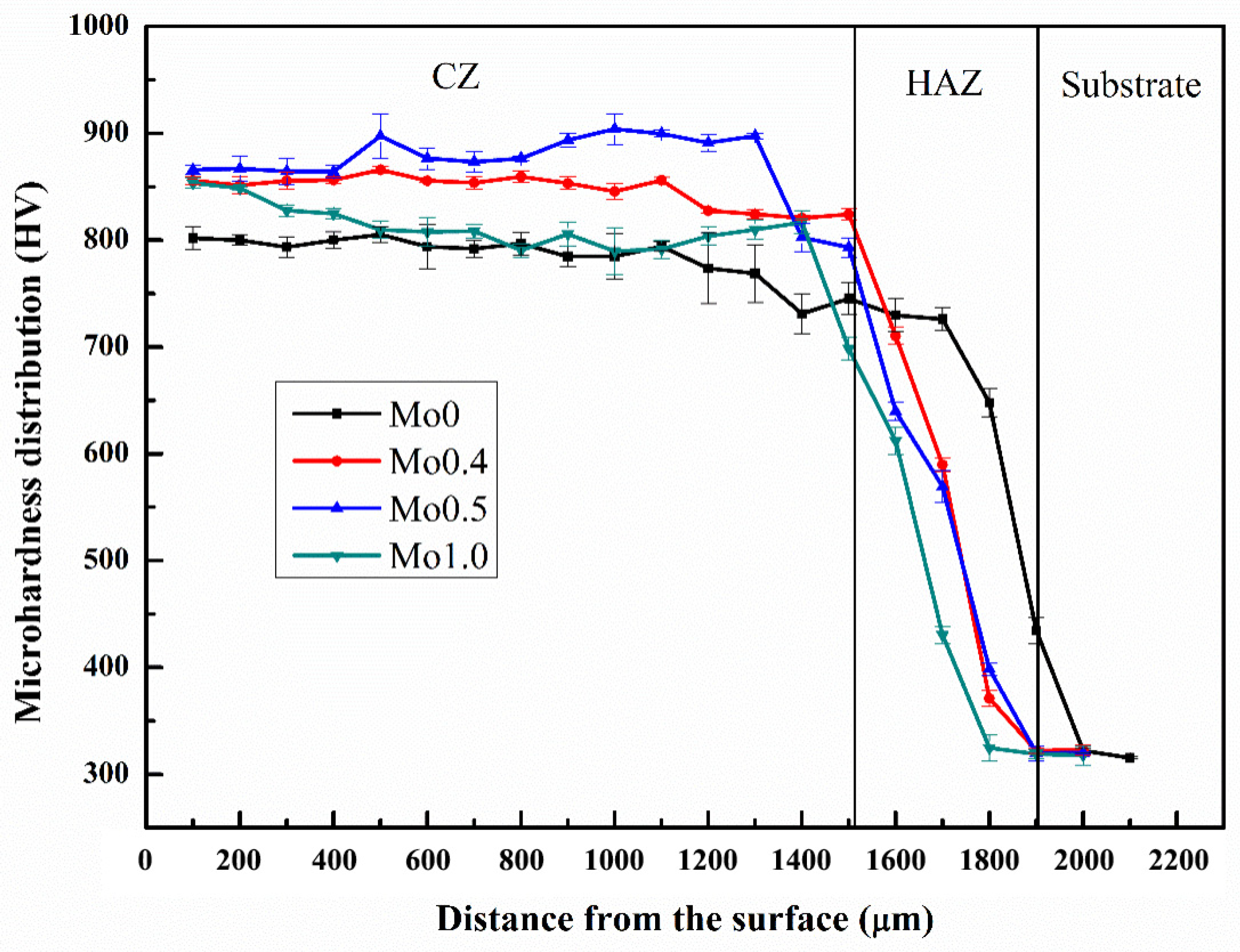
3.3. Microhardness
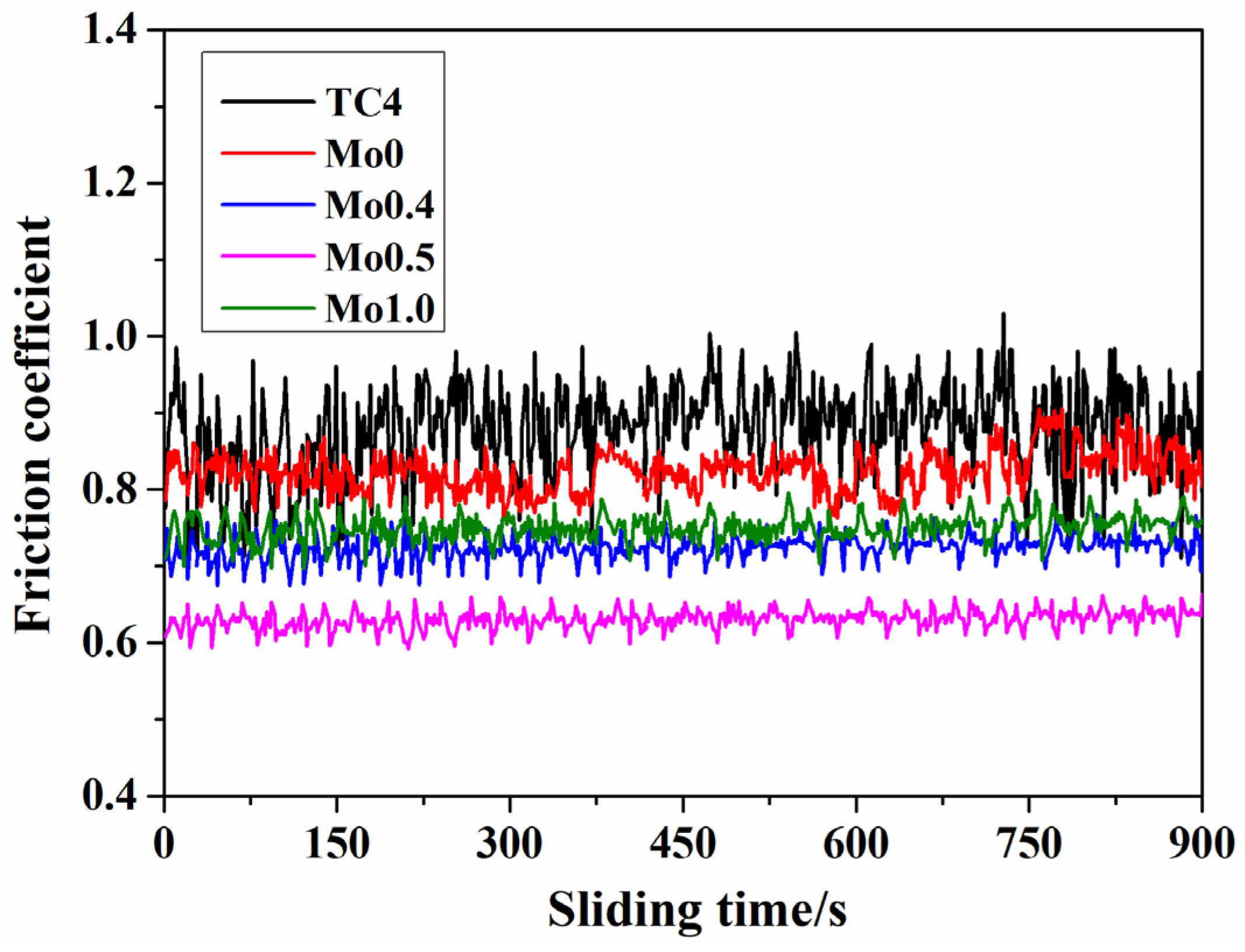
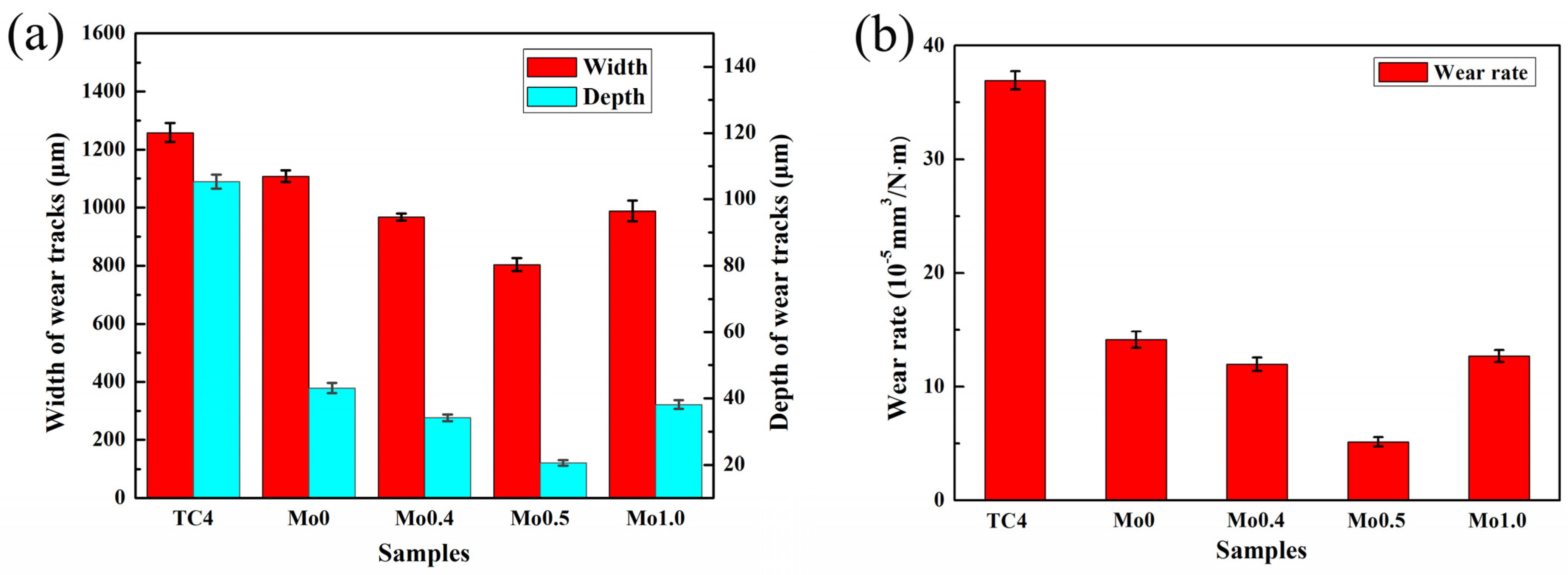
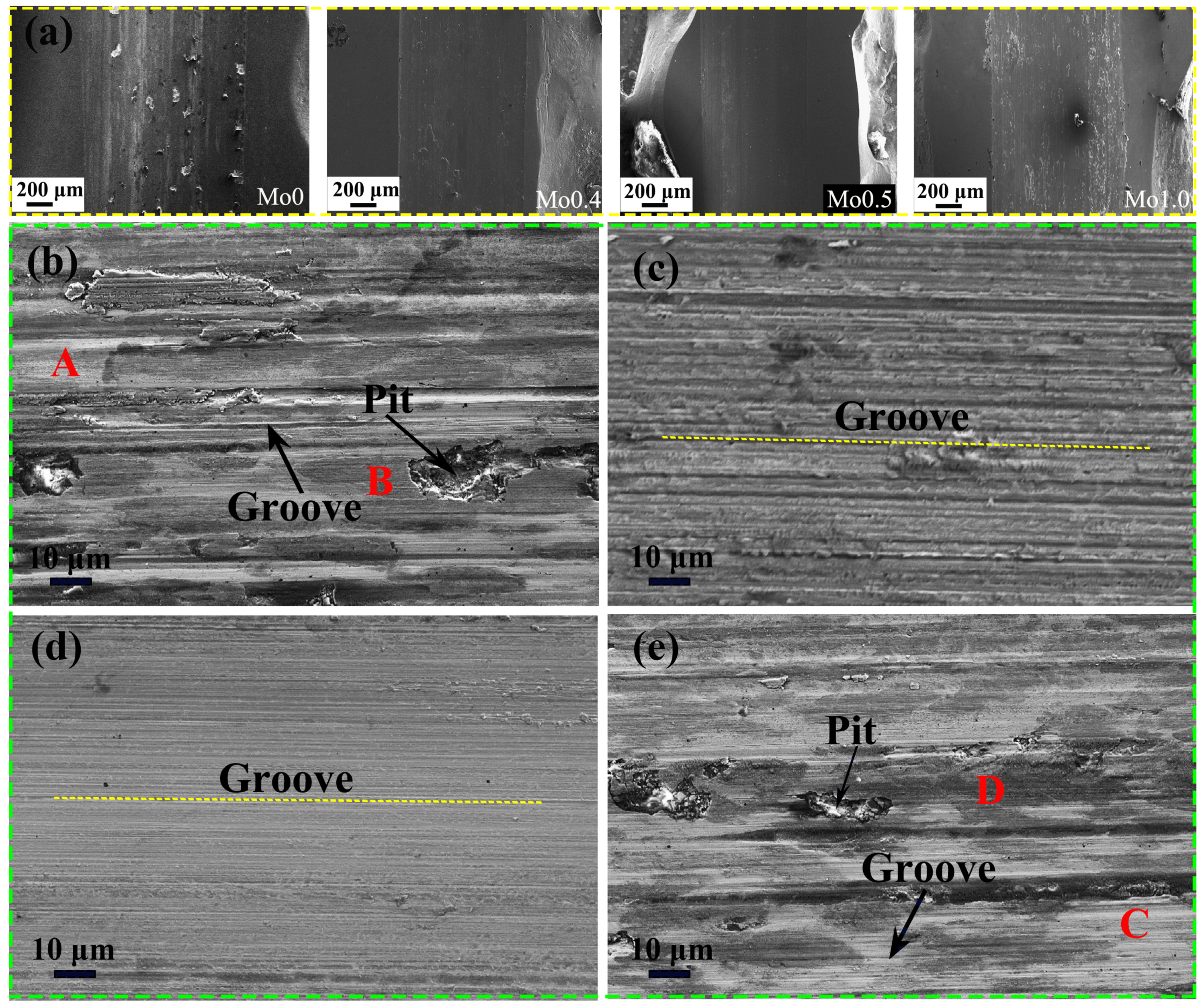
3.4. Wear Resistance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The CoCrFeNi2Mox high-entropy alloy coatings were divided vertically from top to bottom into cladding zone, bonding zone, heat affected zone, and substrate. The coatings all showed the typical dendritic morphology. When x < 0.4, the coatings were mainly composed of BCC solid solution phase, (Ni, Co)Ti2 phase, and α-Ti phase. When x ≥ 0.4, the new σ phase appeared in the coatings.
- (2)
- The average hardness values of Mo0, Mo0.4, Mo0.5, and Mo1.0 coatings were 785 HV, 850 HV, 882 HV, and 813 HV, respectively, which was much higher than the hardness of the TC4 substrate (about 320 HV), almost 2.45–2.65 times that of the substrate. In addition, as the Mo content increased from 0 to 1.0, the hardness showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. Especially when x = 0.5, the CoCrFeNi2Mo0.5 high-entropy alloy coating hardness reached a maximum (882 HV), which was 2.65 times the hardness of the TC4 substrate.
- (3)
- The friction and wear behaviors of all CoCrFeNi2Mox high-entropy alloy coatings were much more excellent than those of the TC4 substrate material, indicating that the coatings had a significant effect on improving the wear resistance of the TC4 substrate. As for the CoCrFeNi2Mox high-entropy alloy coatings, with the increase in Mo content, the widths/depths of worn tracks, wear rates, and friction coefficients of the CoCrFeNi2Mox high-entropy alloy coatings showed a trend of first decreasing and then increasing.
- (4)
- When x = 0.5, the CoCrFeNi2Mo0.5 high-entropy alloy coating had the smallest friction coefficient (0.63), widths/depths of worn tracks (width: 803.690 μm; depth: 20.630 μm), and wear rate (5.136 × 10−5 mm3/(N·m)), which was one order of magnitude smaller than that of substrate (3.694 × 10−4 mm3/(N·m)), demonstrating the best wear resistance, which was mainly due to the appropriate proportion of hard α-Ti and σ phases effectively played a supporting role in resisting wear, while the relatively soft and dispersed BCC and (Ni, Co)Ti2 phases could effectively prevent the occurrence of brittle fracture during wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, M.; Qian, Y. Principle and Design of Tribology; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kusinski, J.; Kac, S.; Kopia, A.; Radziszewska, A.; Rozmus-Górnikowska, M.; Major, B.; Major, L.; Marczak, J.; Lisiecki, A. Laser modification of the materials surface layer—A review paper. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2012, 60, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Vilar, R.; Shen, J. Dry sliding wear behavior of laser clad TiVCrAlSi high entropy alloy coatings on Ti-6Al-4V substrate. Mater. Des. 2012, 41, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, M.; Qi, C.; Cui, N.; Wang, Y. Characterization and friction-reduction performances of composite coating produced by laser cladding and ion sulfurizing. Mater. Lett. 2015, 150, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.-B.; Fan, J.-W.; He, X.-M.; Shi, S.-H.; Fu, G.-Y.; Wang, M.-D.; Chen, S.-F. Microstructure and wear behaviors of laser clad NiCr/Cr3C2-WS2 high temperature self-lubricating wear-resistant composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3757–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafali, M.; Doleker, K.M.; Erdogan, A.; Sunbul, S.E.; Icin, K.; Yildiz, A.; Gok, M.S. Wear, corrosion and oxidation characteristics of consolidated and laser remelted high entropy alloys manufactured via powder metallurgy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 467, 129704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Axinte, E.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Du, J.; Qiao, P.; Wang, Y. CoCrFeNi(W1−xMox) high-entropy alloy coatings with excellent coatings with excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance prepared by mechanical alloying and hot pressing sintering. Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Sui, S.; Kayani, S.H.; Seol, J.B.; Zhu, P.; Guo, A.; Lin, X.; Huang, W. The influence of chemical short-range order on the nanoindentation properties of high-entropy alloys prepared via laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Charact. 2024, 207, 113560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarasamy, M.; Kumar, N.; Tang, Z.; Mishra, R.S.; Liaw, P.K. Effect of microstructure on the deformation mechanism of frictin stri-processed Al0.1CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2015, 3, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of high-entropy stabilized solid solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2012, 132, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.H.; Liu, N.; Yang, W.; Zhu, Z.X.; Lu, Y.P.; Wang, X.J. Microstructure and solidification behavior of multicomponent CoCrCuxFeMoNi high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 642, 142–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yeh, J. Effect of aluminum content on plasma-nitrided AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2009, 40, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, A.; Sunbul, S.E.; Icin, K.; Doleker, K.M. Microstructure, wear and oxidation behavior of AlCrFeNiX (X = Cu, Si, Co) high entropy alloys produced by powder metallurgy. Vac. Technol. Appl. Ion Phys. 2021, 187, 110143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, J. Effect of nitriding on the tribological properties of Al1.3CoCuFeNi2 high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 725, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licavoli, J.J.; Gao, M.C.; Sears, J.S.; Jablonski, P.D.; Hawk, J.A. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of high entropy alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 114, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Han, G.; Qiu, L. Laser cladding Al0.4CoCu0.6NiSi0.2Ti0.25 layer of abrasion resistance and high entropy alloys forming mechanism analysis. Hot Work. Technol. 2018, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.; Liang, X.; Tong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Preparation and characterization of NbMoTaW high entropy alloy coating. Appl. Laser 2018, 38, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Wei, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X. Study on wear resistance of NiCoFeCrTi high entropy alloy coating by laser cladding. Laser Technol. 2016, 40, 432–435. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Mao, C.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Wang, K. On the enhanced wear resistance of laser-clad CoCrCuFeNiTix high-entropy alloy coatings at elevated temperature. Tribol. Int. 2022, 174, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, H.; Pan, X.; Cao, Z.; Deng, D.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Phase evolution and properties of Al2CrFeNiMox high-entropy alloys coatings by laser cladding. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2015, 24, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, W.; Duan, R.; Yang, W.; Chan, K.C.; Ren, F.; Yang, X.-S. Laser surface treatment-introduced gradient nanostructured TiZrHfTaNb refractory highentropy alloy with significantly enhanced wear resistance. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 110, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-G.; Che, P.-C.; Yang, X.-K.; Huang, Y.-J.; Ning, Z.-L.; Sun, J.-F.; Fan, H.-B. Enhanced tensile properties and wear resistance of additively manufactured CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy at cryogenic temperature. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, W.; Cao, Z.; Li, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a CoFeNi2V0.5Nb0.75 eutectic high entropy alloy in as-cast and heat-treated conditions. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Z. Enhancing cryogenic yield strength and ductility of the Al0.1CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy by synergistic effect of nanotwins and dislocations. Scr. Mater. 2023, 232, 115495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. Solid solution alloys of AlCoCrFeNiTix with excellent room-temperature mechanical properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 181904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.W.; Liu, C.G. Microstructure and properties of Al2CrFeCoCuTiNix high-entropy alloys prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Gao, F.; Li, L. Manufacturing of FeCoCrNiCux medium-entropy alloy coating using laser cladding technology. Mater. Des. 2017, 133, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, P.; He, Y.Z. Synthesis and characterization of FeCoNiCrCu high-entropy alloy coating by laser cladding. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Ye, F.; Yang, C.; Wu, S. Effect of alloying elements on microstructure, mechanical and damping properties of Cr-Mn-Fe-V-Cu high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Ence Technol. 2018, 34, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.I. Microstructure and properties of laser cladding AlBxCoCrNiTi high-entropy alloy coating on titanium alloys. Surf. Technol. 2017, 46, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, Y.L.; Yeh, J.W.; Shih, H.C. The effect of molybdenum on the corrosion behaviour of the high-entropy alloys Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5Mox in aqueous environments. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2571–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.S.; Liang, Y.C.; Ming, H.C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multiprincipal component CoCrFeNiMox alloys. Mater. Charact. 2012, 60, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.H.; Lu, Z.P.; He, J.Y.; Luan, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, C. Ductile CoCrFeNiMox high entropy alloys strengthened by hard intermetallic phases. Acta Mater. 2016, 116, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Effects of annealing treatment on microstructure and hardness of bulk AlCrFeNiMo0.2 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 82, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, C.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Guan, M.; Tan, J. Laser surface alloying of FeCoCrAlNi high-entropy alloy on 304 stainless steel to enhance corrosion and cavitation erosion resistance. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 84, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staia, M.H.; Carrasquero, E. Wear behaviour of HVOF thermally sprayed WC-14Co-3Cr coatings. Surf. Eng. 2013, 16, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Huang, C.; Du, L.; Zhang, W.; Lan, Y. Preparation and tribological properties of atmospheric plasma-sprayed NiCr/Cr3C2-hBN wear-resistant coatings. Surf. Technol. 2015, 44, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Yin, X.Y.; Lin, Z.Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. Microstructure and wear behaviors of laser cladding in-situ synthetic (TiBx+TiC)/(Ti2Ni+TiNi) gradient composite coatings. Vacuum 2020, 176, 109305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | Samples | Atomic Percent/at.% | Mass Percent/wt.% | Mass/g (Total Mass = 20 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo0 | Co | 1.0 | 20.7397 | 4.1479 |
| Cr | 1.0 | 18.2984 | 3.6597 | |
| Fe | 1.0 | 19.6536 | 3.9307 | |
| Ni | 2.0 | 41.3083 | 8.2617 | |
| Mo0.4 | Co | 1.0 | 18.2720 | 3.6544 |
| Cr | 1.0 | 16.1212 | 3.2242 | |
| Fe | 1.0 | 17.3152 | 3.4630 | |
| Ni | 2.0 | 36.3933 | 7.2787 | |
| Mo | 0.4 | 11.8983 | 2.3797 | |
| Mo0.5 | Co | 1.0 | 17.7442 | 3.5488 |
| Cr | 1.0 | 15.6555 | 3.1311 | |
| Fe | 1.0 | 16.8150 | 3.3630 | |
| Ni | 2.0 | 35.3420 | 7.0684 | |
| Mo | 0.5 | 14.4433 | 2.8887 | |
| Mo1.0 | Co | 1.0 | 15.5048 | 3.1010 |
| Cr | 1.0 | 13.6797 | 2.7359 | |
| Fe | 1.0 | 14.6929 | 2.9386 | |
| Ni | 2.0 | 30.8817 | 6.1763 | |
| Mo | 1.0 | 25.2410 | 5.0482 |
| Samples | Phase | Lattice Constant a/Å | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (110) | (200) | (211) | Average Value | ||
| Mo0 | BCC | 2.1134 | 1.4923 | 1.2198 | 1.6085 |
| Mo0.4 | BCC | 2.1088 | 1.4800 | 1.2299 | 1.6062 |
| Mo0.5 | BCC | 2.1112 | 1.4944 | 1.2241 | 1.6099 |
| Mo1.0 | BCC | 2.1144 | 1.4969 | 1.2207 | 1.6106 |
| Sample | Region | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Mo | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo0 | A | 15.91 | 23.79 | 19.98 | 19.66 | … | 20.66 |
| B | 19.76 | 7.33 | 11.01 | 36.34 | … | 25.56 | |
| C | 6.33 | 6.21 | 6.50 | 12.64 | … | 68.32 | |
| Mo0.4 | A | 11.77 | 21.45 | 21.08 | 15.73 | 8.34 | 21.63 |
| B | 16.95 | 6.38 | 9.96 | 38.35 | 4.16 | 24.20 | |
| C | 6.18 | 6.29 | 5.15 | 9.54 | 2.63 | 70.21 | |
| Mo0.5 | A | 8.56 | 22.21 | 17.25 | 16.09 | 7.06 | 28.83 |
| B | 13.83 | 5.57 | 9.86 | 22.32 | 4.79 | 43.63 | |
| C | 5.93 | 6.98 | 6.31 | 10.13 | 3.29 | 67.36 | |
| D | 2.71 | 19.54 | 25.51 | 3.31 | 23.62 | 25.31 | |
| Mo1.0 | A | 14.06 | 18.92 | 15.21 | 16.17 | 8.05 | 27.59 |
| B | 18.72 | 5.52 | 8.21 | 21.74 | 4.40 | 41.41 | |
| C | 6.01 | 6.05 | 6.27 | 11.11 | 6.20 | 64.36 | |
| D | 2.11 | 16.98 | 23.14 | 1.92 | 38.23 | 17.62 |
| Sample | Region | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Mo | Ti | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo0 | A | 18.20 | 19.13 | 18.84 | 35.46 | … | 3.86 | 4.51 |
| B | 8.37 | 7.93 | 8.16 | 14.84 | … | 4.59 | 56.11 | |
| Mo0.4 | Entirety | 17.86 | 16.72 | 18.10 | 34.14 | 7.28 | 3.51 | 2.39 |
| Mo0.5 | Entirety | 16.95 | 17.66 | 17.83 | 32.66 | 8.70 | 3.12 | 3.08 |
| Mo1.0 | C | 16.13 | 16.44 | 15.81 | 30.03 | 16.20 | 3.26 | 2.13 |
| D | 7.81 | 6.97 | 7.73 | 15.50 | 7.62 | 1.56 | 52.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, H.; Hou, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Cao, Z. The Microstructures and Wear Resistance of CoCrFeNi2Mox High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Coatings 2024, 14, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060760
Liang H, Hou J, Liu J, Xu H, Li Y, Jiang L, Cao Z. The Microstructures and Wear Resistance of CoCrFeNi2Mox High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Coatings. 2024; 14(6):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060760
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Hui, Jinxin Hou, Jianhong Liu, Hongtai Xu, Yaning Li, Li Jiang, and Zhiqiang Cao. 2024. "The Microstructures and Wear Resistance of CoCrFeNi2Mox High-Entropy Alloy Coatings" Coatings 14, no. 6: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060760
APA StyleLiang, H., Hou, J., Liu, J., Xu, H., Li, Y., Jiang, L., & Cao, Z. (2024). The Microstructures and Wear Resistance of CoCrFeNi2Mox High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Coatings, 14(6), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060760







