Cutting Performance of a Longitudinal and Torsional Ultrasonic Vibration Tool in Milling of Inconel 718
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of LTUM Tool
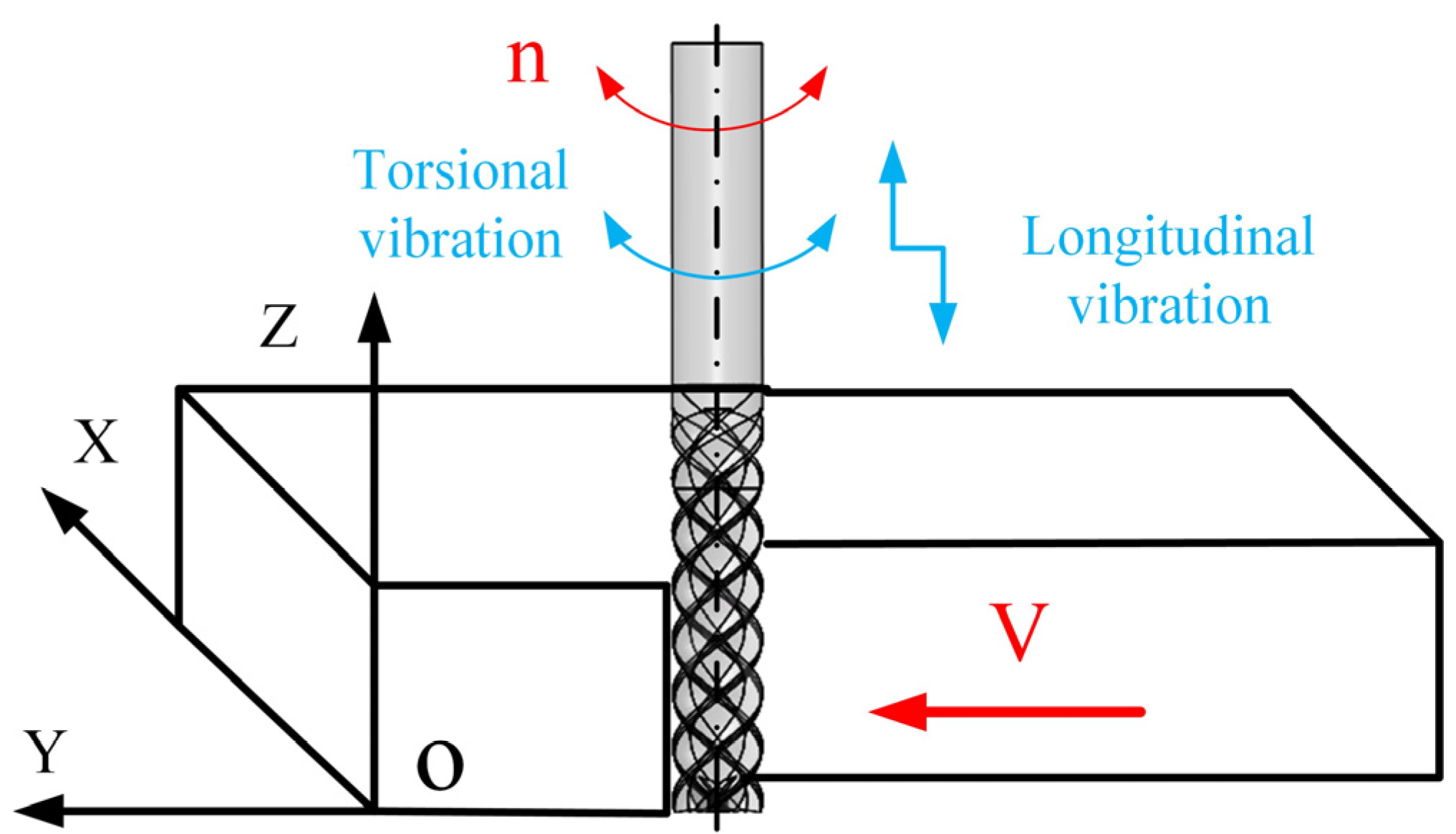
2.1. Motion Characteristic Analysis of LTUM
2.2. Design of Longitudinal-Torsional Ultrasonic Horn

| Material | Density (kg/m3) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio σ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20GrMnTi | 7800 | 207 | 0.3 |
2.3. FEM Analysis
2.4. Optimization of Ultrasonic Milling Tool
3. LTUM Tool Performance Test
3.1. Impedance Analysis
3.2. Amplitude Test Experiment
4. Milling Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Design of LTUM
4.2. Effect of LTUM on Surface Quality and Cutting Performance
4.3. Effect of LTUM Tool on Cutting Performance
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The LTUM tool was designed based on theoretical computations and finite element analysis. The resonance frequency of the tool is 21.32 kHz, the longitudinal amplitude is 6.8 µm, and the torsional amplitude is 1.4 µm. Transient dynamic analysis of the tool verified that the tool can produce a regular elliptical motion trajectory.
- (2)
- Under side milling, the surface roughness of LTUM is 0.418 μm, which is significantly lower than that of CM, and the surface morphology is obviously improved. Under the two processing methods, the surface roughness value increases with the increase in the radial depth of cutting and decreases with the increase in the speed of the main spindle. Under slot milling, the burr height under LTUM is significantly reduced, which reduces the adhesion of the material on the bottom surface of the slot, and a regular micro-texture is generated at the bottom of the slot, which proves that LTUM can improve the surface quality of Inconel 718.
- (3)
- Compared with CM, the milling force after adding LTUM is significantly reduced. With increases in feed speed, feed per tooth, and radial depth of cutting, the milling force of two kinds of side milling increases, and with the increase in the speed of the main spindle, the milling force of two kinds of side milling decreases. The factors affecting the milling force of Inconel 718 are in the order of: radial cutting depth > speed of main spindle > feed per tooth > feed speed. It is proven that LTUM can improve the cutting performance of Inconel 718.
- (4)
- The flank wear width of the two side milling methods increases with the increase in the speed of the main spindle and feed per tooth. The milling force of LTUM is less than that of CM under the same machining parameters. LTUM processing improves the chip breaking ability, the chip size is small, and more debris is generated.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Ming, W.; An, Q.; Chen, M. Cutting performance and tool wear of SiAlON and TiC-whisker-reinforced Si3N4 ceramic tools in side milling Inconel 718. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 3096–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pei, Z.J.; Cong, W.L. A feeding-directional cutting load model for end surface grinding of CFRP composites using rotary ultrasonic machining with elliptical ultrasonic vibration. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 152, 103540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Chang, B.Q.; Wang, X.B. System design and experimental research on ultrasonic assisted elliptical vibration grinding of Nano-ZrO2 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 24865–24877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, M.; Amini, S.; Aghayar, Z.; Sajjady, S.A.; Farid, A.A. Effect of 3D elliptical ultrasonic assisted boring on surface integrity. Measurement 2020, 163, 108008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.L.; Qi, M.; Zhu, Y.F.; Liu, M.X.; Bie, W.B. Ultrasonic rolling strengthening effect on the bending fatigue behavior of 12Cr2Ni4A steel gears. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2023, 279, 109024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, N.; Liu, D.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Wu, S.C. Improved fretting fatigue mechanism of surface-strengthened Ti-6Al-4V alloy induced by ultrasonic surface rolling process. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 170, 107567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, X.K.; Zhao, B.; Li, G.X.; Xie, Z.J. Surface and subsurface analysis of TC18 titanium alloy subject to longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic vibration-assisted end milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 929, 167259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, K.-L. Ultrasonic vibrating system design and tool analysis. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, s225–s231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F. Study on the simulativeand experiment of ultrasonic-assisted vibration drilling of Ti6Al4V. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2242, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Jiao, Y.; Deines, T.W.; Pei, Z.J.; Treadwell, C. Rotary ultrasonic machining of ceramic matrix composites: Feasibility study and designed experiments. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, E.; Bertolini, R.; Bruschi, S.; Ghiotti, A. Design and development of an ultrasonic vibration assisted turning system for machining bioabsorbable magnesium alloys. Procedia CIRP 2018, 77, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.W.; Liu, Z.Q.; Han, L.C.; Wang, B.; Xin, M.Z.; Cai, Y.K.; Song, Q.H. Optimizing amplitude to improve machined surface quality in longitudinal ultrasonic vibration-assisted side milling 2.5 DC/SiC composites. Compos. Struct. 2022, 297, 115963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namlu, R.H.; Yılmaz, O.D.; Lotfisadigh, B.; Kılıç, S.E. An experimental study on surface quality of Al6061-T6 in ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling with minimum quantity lubrication. Procedia CIRP 2022, 108, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; He, Y.J.; Yu, T.B. Surface quality and milling force of SiCp/Al ceramic for ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 33819–33834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.Q.; Zhu, L.; Wiercigroch, M.; Ren, T.Y.; Hao, Y.P.; Ning, J.S.; Zhao, J. Material removal and surface generation in longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic assisted milling. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 227, 107375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.M.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhao, S.C.; Li, X.; Geng, D.X.; Zhang, D.Y. Tool wear and its effect on the surface integrity and fatigue behavior in high-speed ultrasonic peening milling of Inconel 718. Tribol. Int. 2023, 178, 108070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.B.; Zhu, L.D.; Liu, C.F.; Yang, Z.C. Analytical modeling of tool-workpiece contact rate and experimental study in ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling of Ti–6Al–4V. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 142, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zou, Y.H.; Qin, X.D.; Liu, J.; Feng, Q.; Ren, C.Z. Geometrical texture and surface integrity in helical milling and ultrasonic vibration helical milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 278, 116494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.Q.; Yi, Z.X.; Cao, X.B.; Duan, J.A. Defect suppression and grain refinement during ultrasonic vibration-assisted side milling of GH4169 superalloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 85, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.J. Design for torsional transducer in ultrasonic machining based on equivalent circuit. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), Macao, China, 18–20 July 2017; pp. 953–958. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.J.; Nie, W.Z.; Lu, J.M.; Chen, H. Study on surface quality of BK7 optical glass by longitudinal torsional composite ultrasonic vibration milling. Mater. Sci. Forum 2020, 984, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, N.; Feng, J.; Bo, Z.; Guo, F.G.; Jing, J.N. Theoretical investigation of machining-induced residual stresses in longitudinal torsional ultrasonic–assisted milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 3689–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.X.; Zhang, D.Y.; Xu, Y.G.; He, F.T.; Liu, D.P.; Duan, Z.H. Rotary ultrasonic elliptical machining for side milling of CFRP: Tool performance and surface integrity. Ultrasonics 2015, 59, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.P.; Zhang, J.F.; Feng, P.F.; Wang, J.J. Controllable fabrication of microstructures on the metallic surface using oblique rotary ultrasonic milling. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 237, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.F.; Han, L.; Qiu, X.; Chen, W.S.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, J.J. Development of a high-precision piezoelectric ultrasonic milling tool using longitudinal-bending hybrid transducer. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 222, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.A.; Chuang, W.Y.; Hsu, K.; Pham, H.T. Design of a Bézier-profile horn for high displacement amplification. Ultrasonics 2011, 51, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Dong, Z.G.; Bao, Y.; Kang, R.K.; Du, W.H.; Pan, Y.N. Development and optimization of ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting device based on single excitation. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2021, 143, 081005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, K.H.; Qureshi, M.A.M.; Raza, S.F. Novel ultrasonic horn design for machining advanced brittle composites: A step forward towards green and sustainable manufacturing. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Geng, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X. Cutting performance and surface integrity for rotary ultrasonic elliptical milling of Inconel 718 with the ball end milling cutter. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 319, 118094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Xia, Z.; Su, T.; Xiang, D.; Zhao, B. Cutting force model of longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic-assisted milling Ti-6Al-4V based on tool flank wear. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 291, 117042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Tong, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, B. A study ofthe surface microstructure and tool wear of titanium alloys after ultrasonic longitudinal-torsional milling. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


























| Parameter | Numerical Value (Unit) | Parameter | Numerical Value (Unit) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resonance frequency Fs | 21.32 kHz | Half power point F2 | 21.33 kHz |
| Anti-resonance frequency Fp | 21.46 kHz | Dynamic resistor R1 | 107 Ω |
| Half power point F1 | 21.31 kHz | Dynamic capacitance C1 | 0.07 nF |
| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Gr | Ni | Co | Ri | Fe | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.08 | <0.015 | 0.002 | 18.37 | 53.37 | 0.23 | 0.98 | 1.78 | 0.50 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 8220 |
| Elastic modulus (GPa) | 210 |
| Hardness (HV) | 390 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.3 |
| Yield strength (MPa) | 955 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 1150 |
| Parameters | Specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| CM | LTUM | |
| Speed of main spindle (r/min) | 1000, 1500, 2000 | 1000, 1500, 2000 |
| Feed speed (m/min) | 100, 150, 200 | 100, 150, 200 |
| Feed per tooth (mm/z) | 0.025, 0.0375, 0.05 | 0.025, 0.0375, 0.05 |
| Radial cutting depth (mm) | 1, 2, 3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Axial cutting depth (mm) | 5 | 5 |
| Frequency (kHz) | - | 21,000 |
| Alon (µm) | 0 | 6.8 |
| Ator (µm) | 0 | 1.4 |
| Parameters | Specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| CM | LTUM | |
| Speed of main spindle (r/min) | 1000, 1500, 2000 | 1000, 1500, 2000 |
| Feed speed (m/min) | 100, 150, 200 | 100, 150, 200 |
| Feed per tooth (mm/z) | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| Cutting depth (mm) | 1, 2, 3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Frequency (kHz) | - | 21,000 |
| Alon (µm) | 0 | 6.8 |
| Ator (µm) | 0 | 1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Su, G.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Sun, Y.; Du, J.; Fang, B. Cutting Performance of a Longitudinal and Torsional Ultrasonic Vibration Tool in Milling of Inconel 718. Coatings 2024, 14, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060719
Zhang H, Su G, Xia Y, Zhang P, Li B, Sun Y, Du J, Fang B. Cutting Performance of a Longitudinal and Torsional Ultrasonic Vibration Tool in Milling of Inconel 718. Coatings. 2024; 14(6):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060719
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hang, Guosheng Su, Yan Xia, Peirong Zhang, Binxun Li, Yujing Sun, Jin Du, and Bin Fang. 2024. "Cutting Performance of a Longitudinal and Torsional Ultrasonic Vibration Tool in Milling of Inconel 718" Coatings 14, no. 6: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060719
APA StyleZhang, H., Su, G., Xia, Y., Zhang, P., Li, B., Sun, Y., Du, J., & Fang, B. (2024). Cutting Performance of a Longitudinal and Torsional Ultrasonic Vibration Tool in Milling of Inconel 718. Coatings, 14(6), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060719








