Improving Prediction Model for Colorimetric Changes Due to Coating Processes with Oil-Based and UV Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
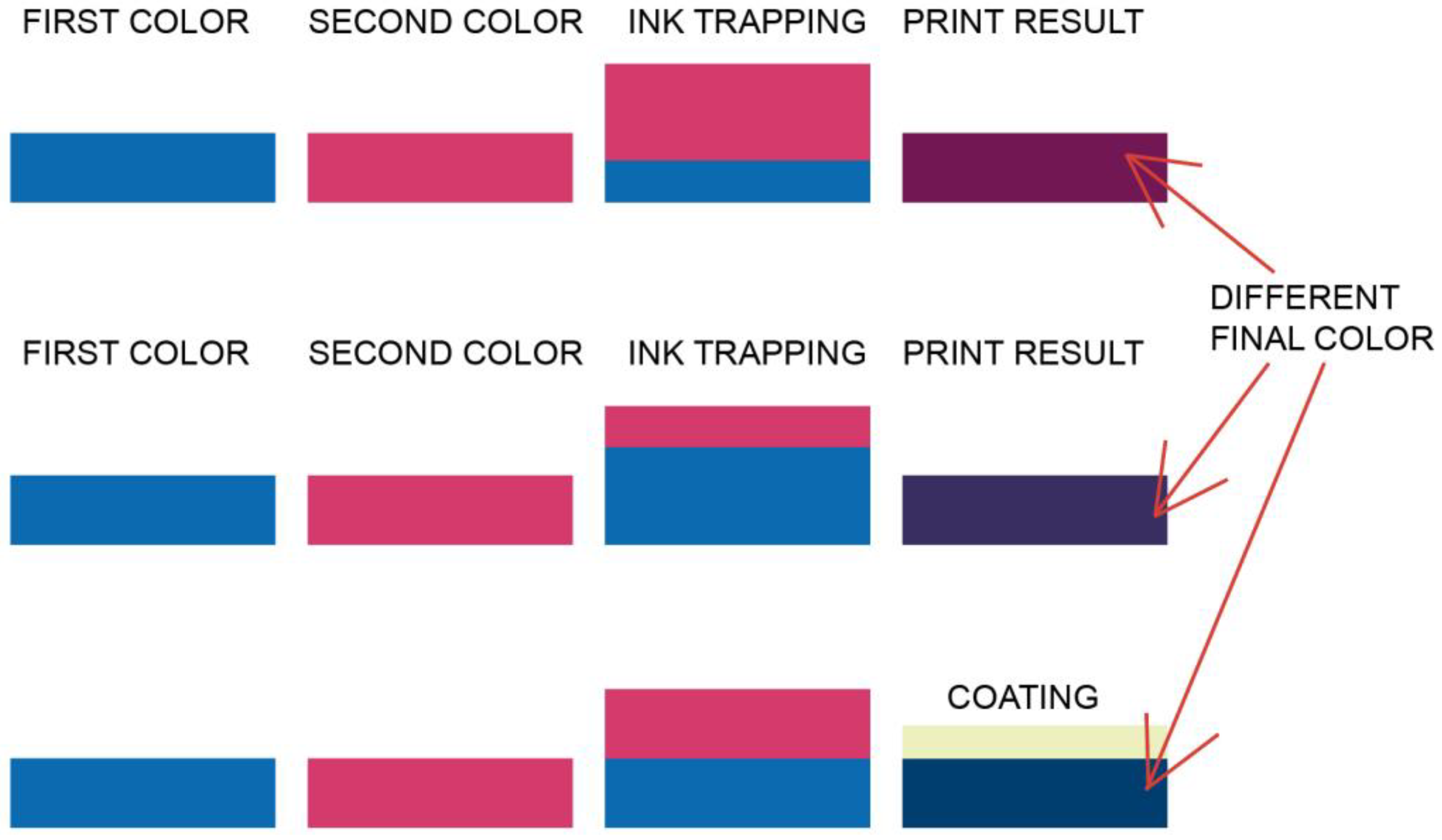
2.1. Ink Trapping
2.2. Used Substrates and Equipment
2.3. Used Inks
2.4. Printing and Spectrophotometric Measurement
2.5. ΔE00 Calculation
2.6. Gloss Measurement
2.7. Existing Mathematical Model
- X, Y, Z: the predicted tristimulus values of the overprint color;
- Xb, Yb, Zb: the measured tristimulus values of the background color;
- Xf, Yf, Zf: the measured tristimulus values of the foreground color;
- jx, jy, jz: the scaling factors of the foreground color depending on dot area;
- kx, ky, kz: the constants of the foreground color depending on dot area.
- Xpw, Ypw, Zpw: the tint percentage printed on white (substrate);
- Xpk, Ypk, Zpk: the same tint percentage printed on black;
- Xw, Yw, Zw: the white (substrate) without overprint;
- Xk, Yk, Zk: the solid black without overprint.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gloss Values
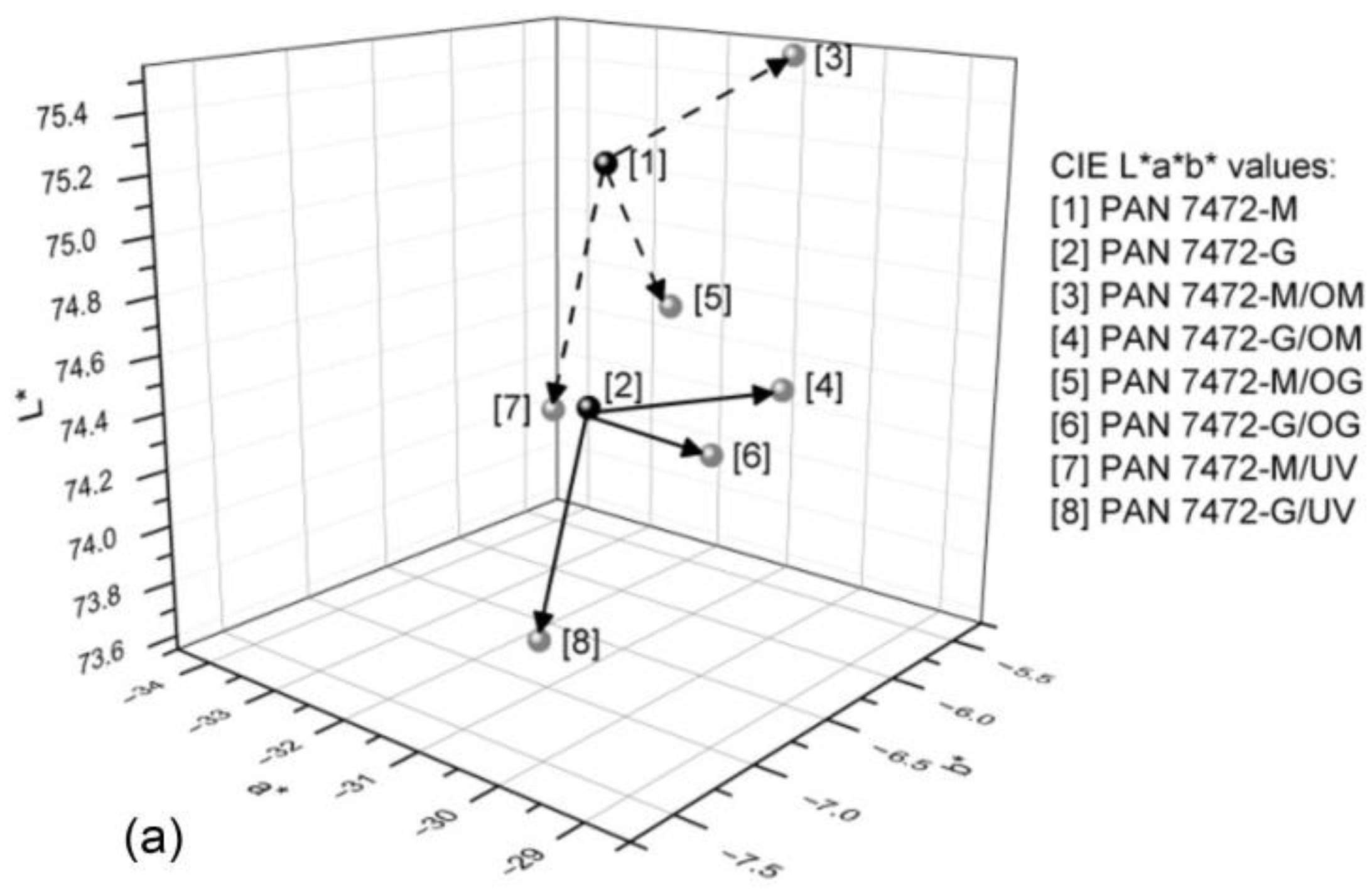
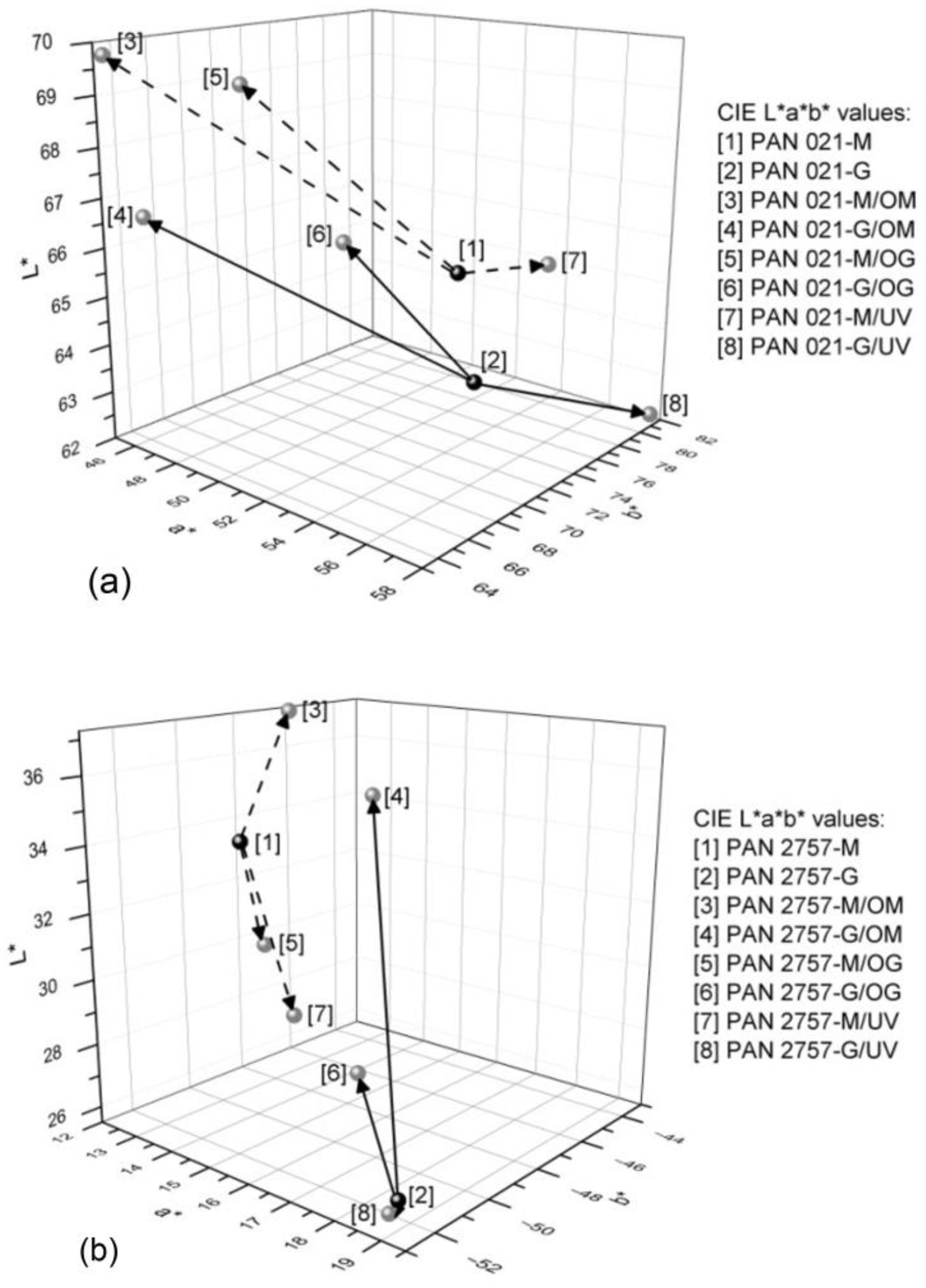
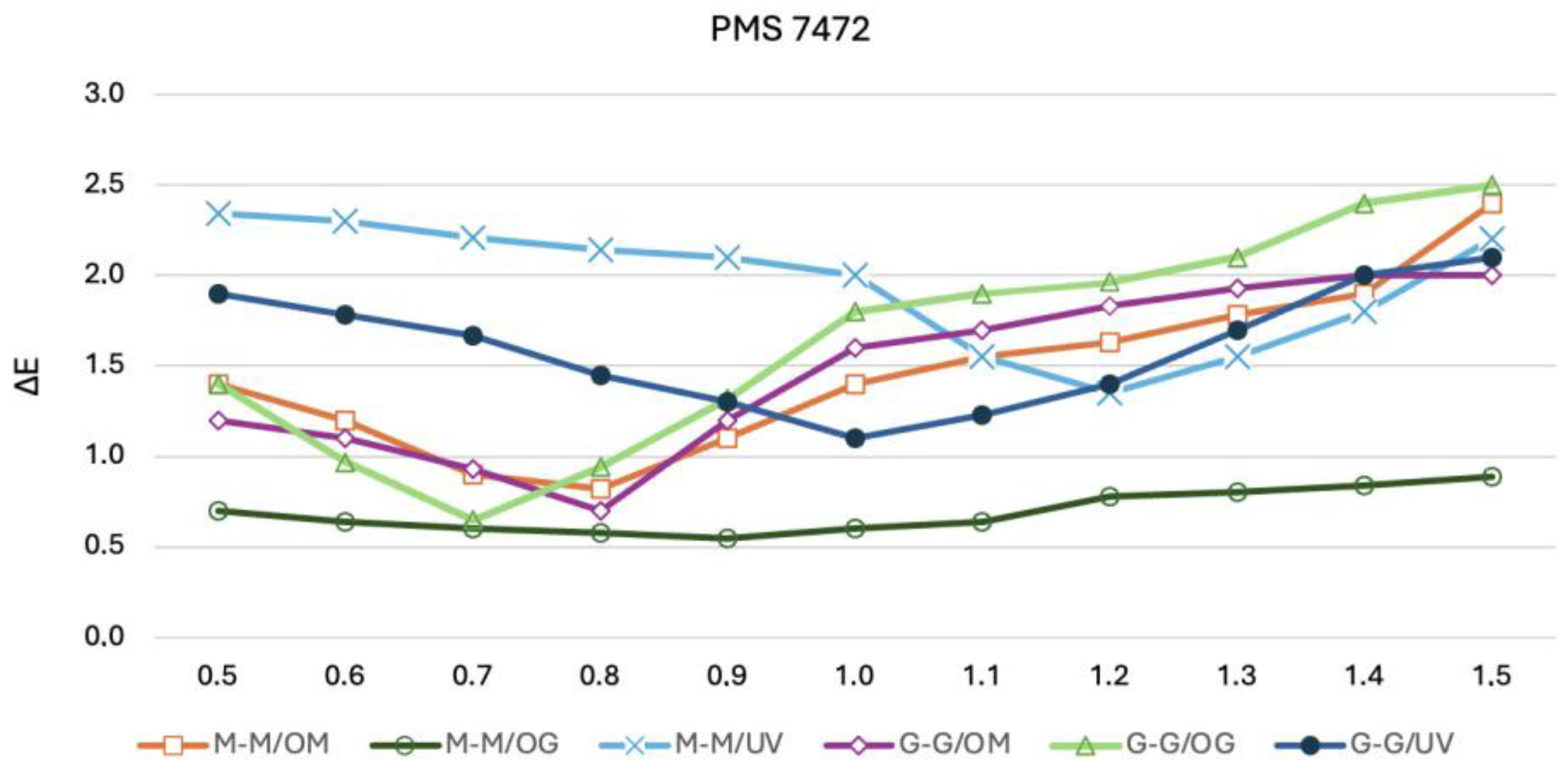
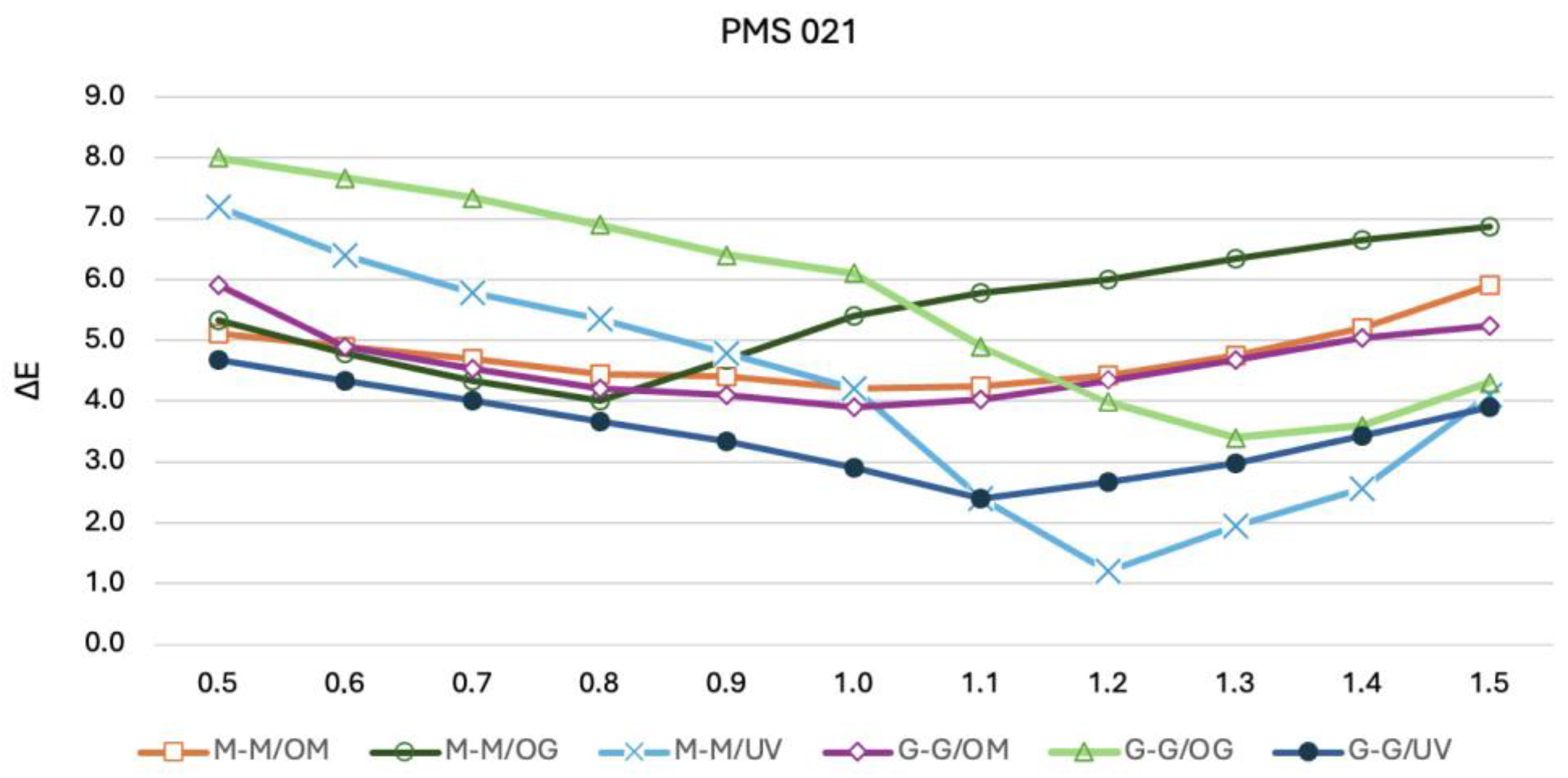
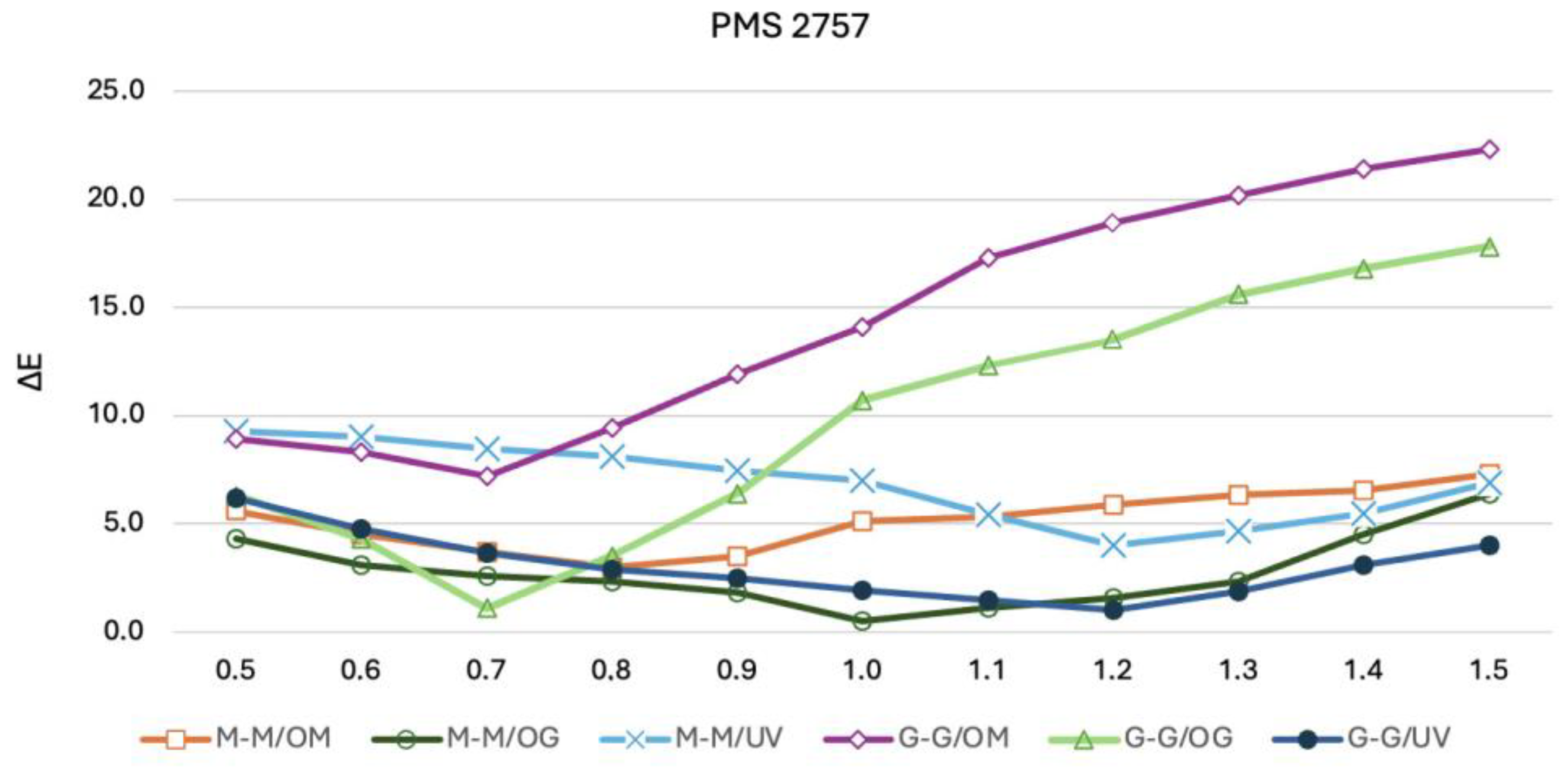
3.2. CIE L*a*b* and ∆E00 Values
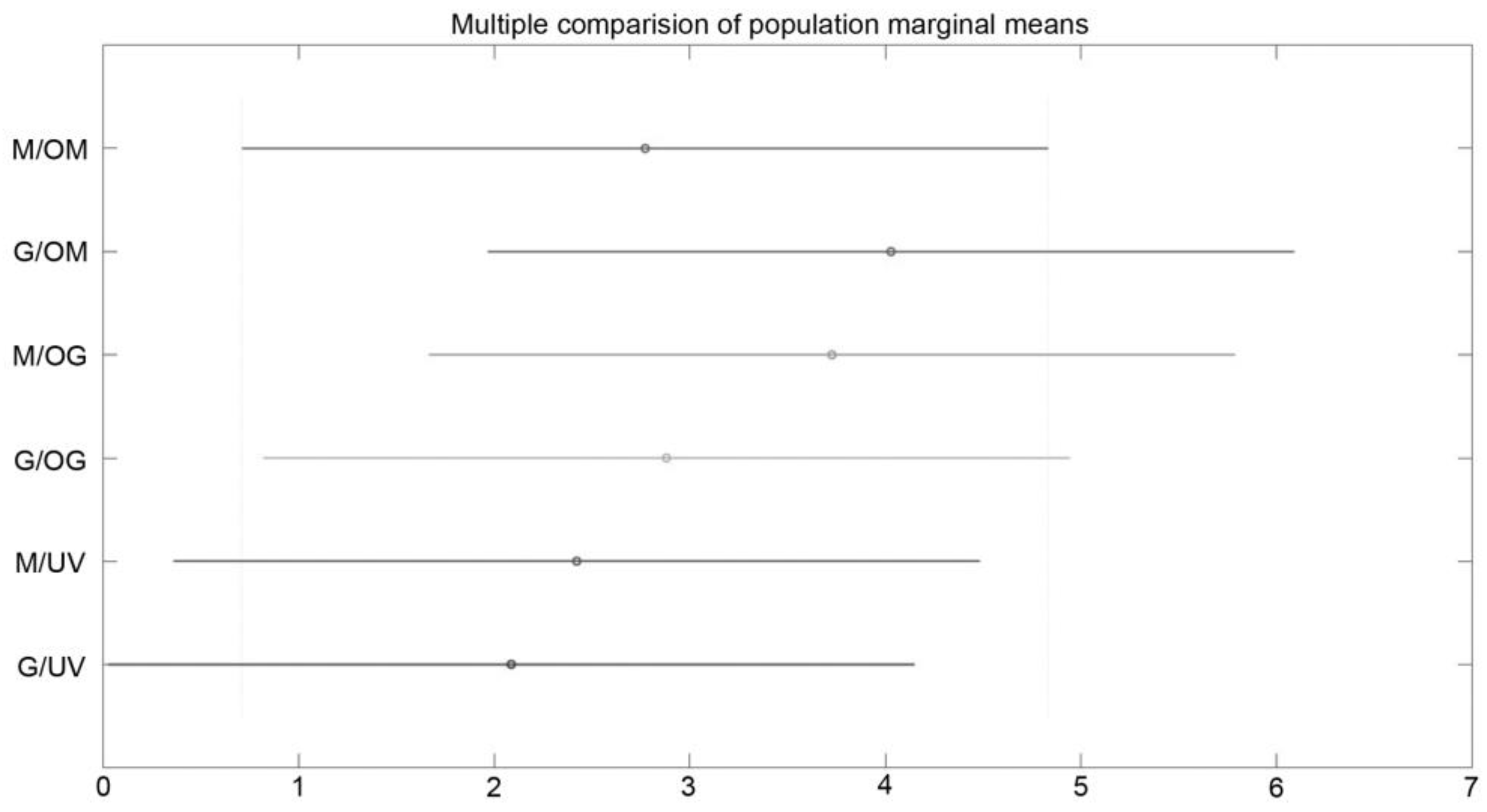
4. Mean, Confidence Interval, Standard Deviation, Median, and Coefficient of Variation Calculations
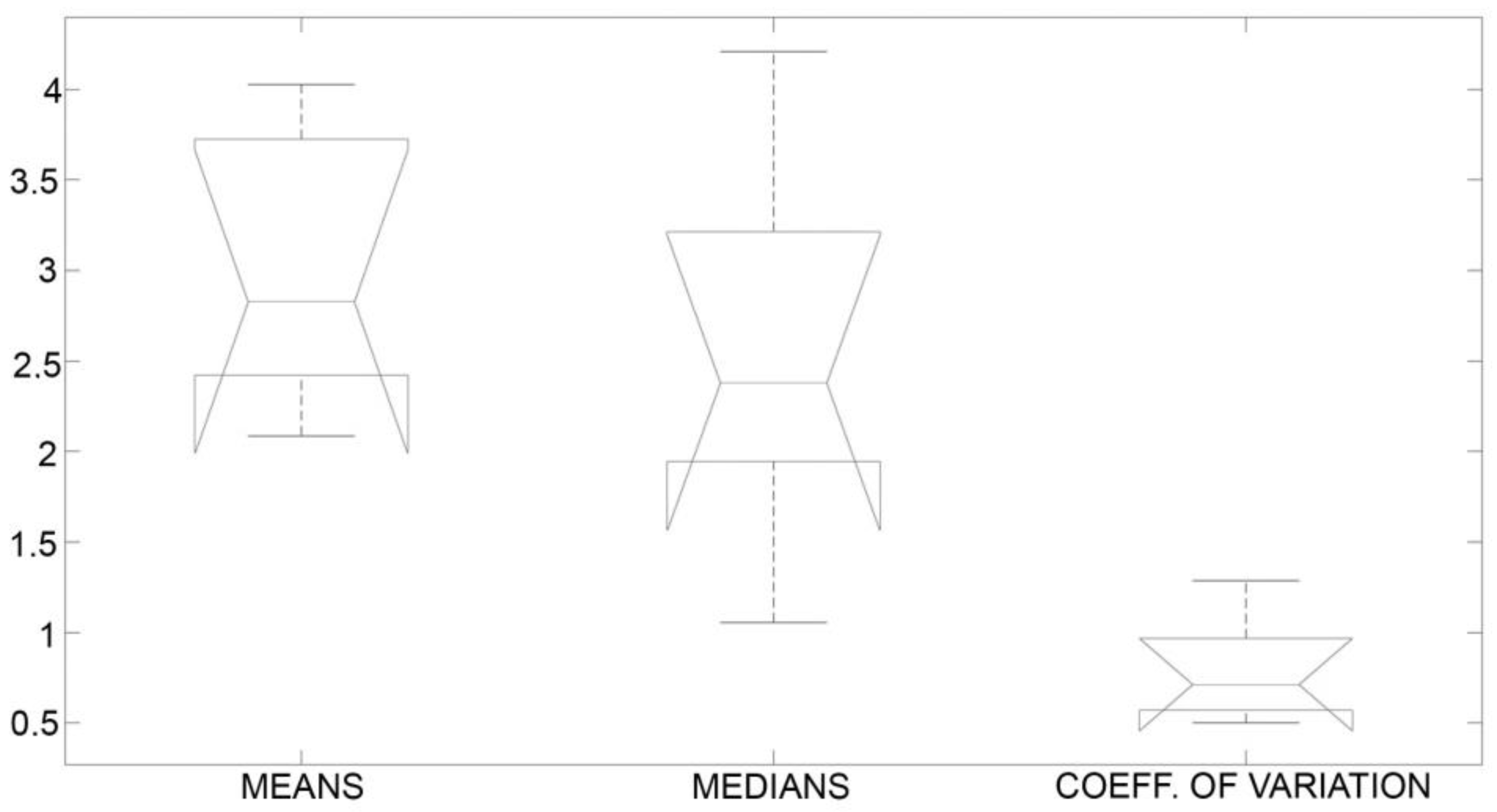
| Printing Substrate/Varnish Type | Mean, Confidence Interval (5% Sign. Level) | Standard Deviation | Median | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/OM | 2.7717 (1.0387–4.5046) | 1.6513 | 2.52 | 0.5958 |
| M/OG | 3.7267 (0.4978–6.9556) | 3.0678 | 3.215 | 0.8256 |
| M/UV | 2.4217 (0.9784–3.8649) | 1.3753 | 1.945 | 0.5679 |
| G/OM | 4.0283 (1.9170–6.1396) | 2.0118 | 4.21 | 0.4994 |
| G/OG | 2.88 (−0.0378–5.7978) | 2.7804 | 2.235 | 0.9654 |
| G/UV | 2.0867 (−0.7295–4.9029) | 2.6835 | 1.055 | 1.286 |
| ΔE | 2.9858 (2.1978–3.7739) | 0.7509 | 2.825 | 0.2515 |
5. Model Improvement Recommendation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kipphan, H. Handbook of Print Media; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 206–219. ISBN 978-3-540-67326-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rossitza, S. Offset Printing without Isopropyl Alcohol in Damping Solution. Energy Procedia 2015, 74, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sang, R.; Yang, S.; Fan, S. Effects of MDF Substrate Surface Coating Process on UV Inkjet Print Quality. Coatings 2023, 13, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, B.H. Investigation into the Coating Surface Topography and Properties of Paper Related to Drying Condition. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 233–255, 1614–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnaric, I.; Morić, M.; Valdec, D.; Milkovic, K. The Effect of Applying UV LED-Cured Varnish to Metalized Printing Elements during Cold Foil Lamination. Coatings 2004, 14, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sublistar. Discover the Print Difference. Available online: https://shop.subli-star.com/blogs/news/the-differences-between-water-based-and-uv-varnishes (accessed on 18 October 2024.).
- Car, I.; Majnaric, I.; Lozo, B. Colorimetric changes caused by uv varnishing. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Information and Graphic Arts Technology (CIGT 2018), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 7−8 June 2018; pp. 37–40, ISBN 978-961-6900-24-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tracton, A.A. Coatings Technology Handbook, 3rd ed.; CRC Press-Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maass, A.; Hirn, U. Long term curl of printing paper due to ink solvent migration. Mater. Des. 2024, 237, 112593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienke, A.; Hoffmann, G.A.; Koch, J.; Jäschke, P.; Overmeyer, L.; Kaierle, S. Ablation and functionalization of flexographic printing forms using femtosecond lasers for additively manufactured polymer-optical waveguides. Procedia CIRP 2020, 94, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, Z.; Dedijer, S.; Draganov, S.; Karlović, I.; Juric, I. Offset Printing. In Printing on Polymers, Fundamentals and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigula, T.; Hudika, T.; Tomasegovic, T. Lightfastness, surface and interfacial properties of colour-printed paper substrates coated with PCL/ZnO and PCL/TiO2 nanocomposites. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillat, U.; Vergara, P.; Carlos, L.V.; Gomez, N. Structural properties of coated papers with cellulosic nanofibres using different metering systems and drying technologies. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 179, 107543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, S.; Bhardwaj, N.K.; Varadhan, R. Calcium sulphate as pigment for improved functional properties of coated paper. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 79, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lae Lee, H. Novel method for the evaluation of mechanical property of pigment coating layer and its application: Influence of spreading of latex binder on final properties of coating layer. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 163, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, N. Fundamentals of Nanomaterials and Polymer Nanocomposites. In Nanomaterials and Polymer Nanocomposites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balea, A.; Fuente, E.; Monte, M.C.; Merayo, N.; Campano, C.; Negro, C.; Blanco, A. Industrial Application of Nanocelluloses in Papermaking: A Review of Challenges, Technical Solutions, and Market Perspectives. Molecules 2020, 25, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 12647-2:2017; Graphic Technology—Process Control for the Production of Half-Tone Color Separations, Proof and Production Prints—Part I1: Offset Lithographic Processes. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Available online: https://printhouse.co.uk/2010/01/what-is-trapping-and-how-is-it-used-in-print/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Tran, T.T.T.; Bach, L.H.; Hoang, T.K.N. Effect of Ink Transfer on Color Values in Lithographic Printing. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangermano, M.; Meier, P.; Tzavalas, S. Infrared Spectroscopy as a Tool to Monitor Radiation Curing. In Infrared Spectroscopy-Materials Science, Engineering and Technology; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://repository.rit.edu/theses/3902/ (accessed on 19 October 2024).
- Wongchi, X.; Shisheng, Z.; Yinlin, X. New Algorithm for Ink Trapping Ratio Based on Transmittance. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2016, 312, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quyen, D.H.; Nguyen, T.K. Effect of Ink Tack Value on the Ink Trapping in Lithographic Printing. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 9, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Liao, L.Z. Coating and printing processes. In Solution Processed Metal Oxide Thin Films for Electronic Applications; Cui, Z., Korotcenkov, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 536-2:2019; Paper and Board—Determination of Grammage. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 8254-1:2009; Paper and Board—Measurement of Specular Gloss, Part 1: 75 Degree Gloss with a Converging Beam, TAPPI Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- ISO 2470-2:2008; Paper, Board and Pulps—Measurement of Diffuse Blue Reflectance Factor, Part 2: Outdoor Daylight Conditions (D65 Brightness). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 2471:2008; Paper and Board—Determination of Opacity (Paper Backing)—Diffuse Reflectance Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 8254-2:2016; Paper and Board—Measurement of Specular Gloss, Part 2: 75 Degree Gloss with a Parallel Beam, DIN Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 8791-4:2021; Paper and Board—Determination of Roughness/Smoothness (Air Leak Methods), Part 4: Print-Surf Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 13655:2009; Graphic Technology—Spectral Measurement and Colorimetric Computation for Graphic arts Images. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Korytkowski, P.; Olejnik-Krugly, A.; Zaikin, O. A Framework for a Quality Assurance in Offset Printing. In Proceedings of the 13th IFAC Symposium on Information Control Problems in Manufacturing, Moscow, Russia, 3–5 June 2009; pp. 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.hhgrfx.com/special-effects-screen-printing-uv-coatings/gloss-matte-printing/ (accessed on 19 October 2024).
- Kašiković, N.; Novaković, D.; Milić, N.; Vladić, G.; Zeljković, Ž.; Stančić, M. Thermovision and spectrophotometric analysis of ink volume and material characteristics influence on colour changes of heat treated printed substrates. Teh. Vjesn. 2015, 22, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszecki, G.; Stiles, W.S. Color Science: Concepts and Methods, Quantitative Data and Formulae; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipour, H.; Witzel, C. Colour expectations across illumination changes. Vis. Res. 2024, 222, 108451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, K.; Green, P. A simplified method of predicting the colorimetry of spot color overprints. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth Color and Imaging Conference: Color Science and Engineering Systems, Technologies, and Applications, San Antonio, TX, USA, 8–12 November 2010; pp. 213–216, ISBN ISBN/ISSN 978-0-89208-294-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatela, S.; Sole, A.S. Visually Significant Dimensions and Parameters for Gloss. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.rhopointinstruments.com/faq/how-is-gloss-measured/ (accessed on 19 October 2024).
- Jeff, C.F.; Michael, S.H. Experiments: Planning, Analysis, and Optimization, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Wei, P.; Deng, L. Research on the factorial effect of science and technology innovation (STI) policy mix using multifactor analysis of variance (ANOVA). J. Innov. Knowl. 2022, 7, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.F. Chapter 15-ANOVA: Testing for Differences Among Many Samples, and Much More Practical Business Statistics, 6th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


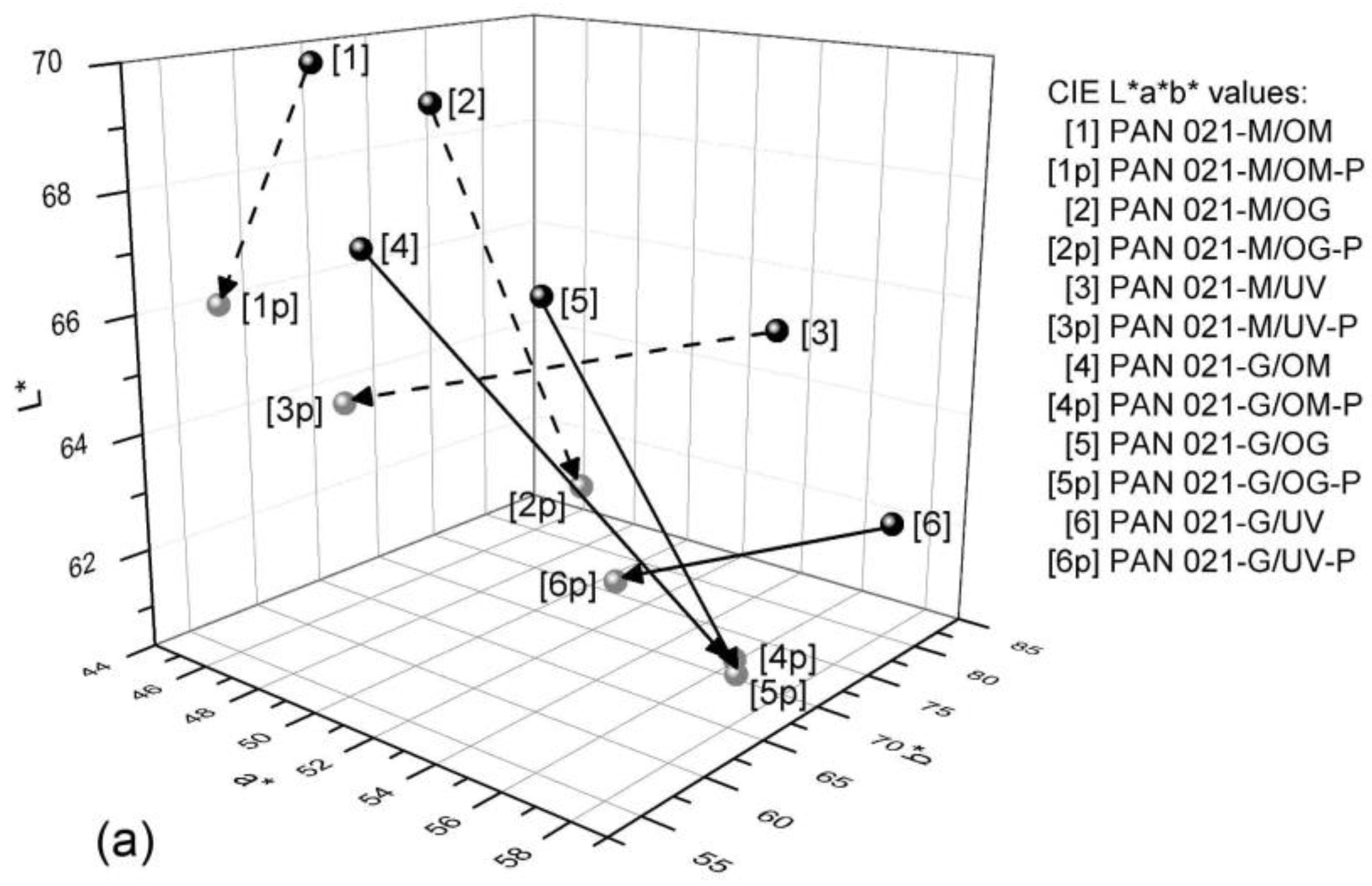

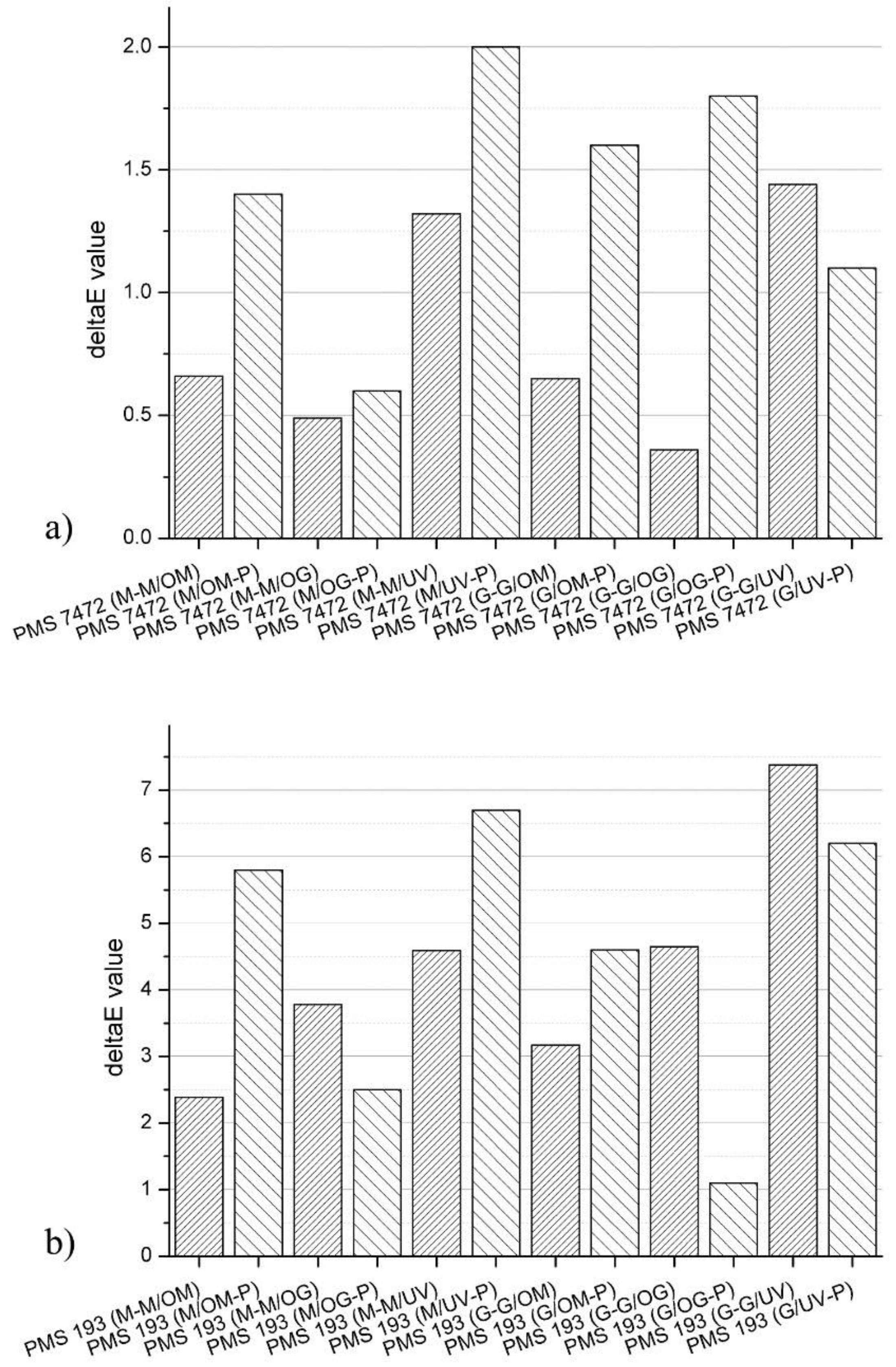
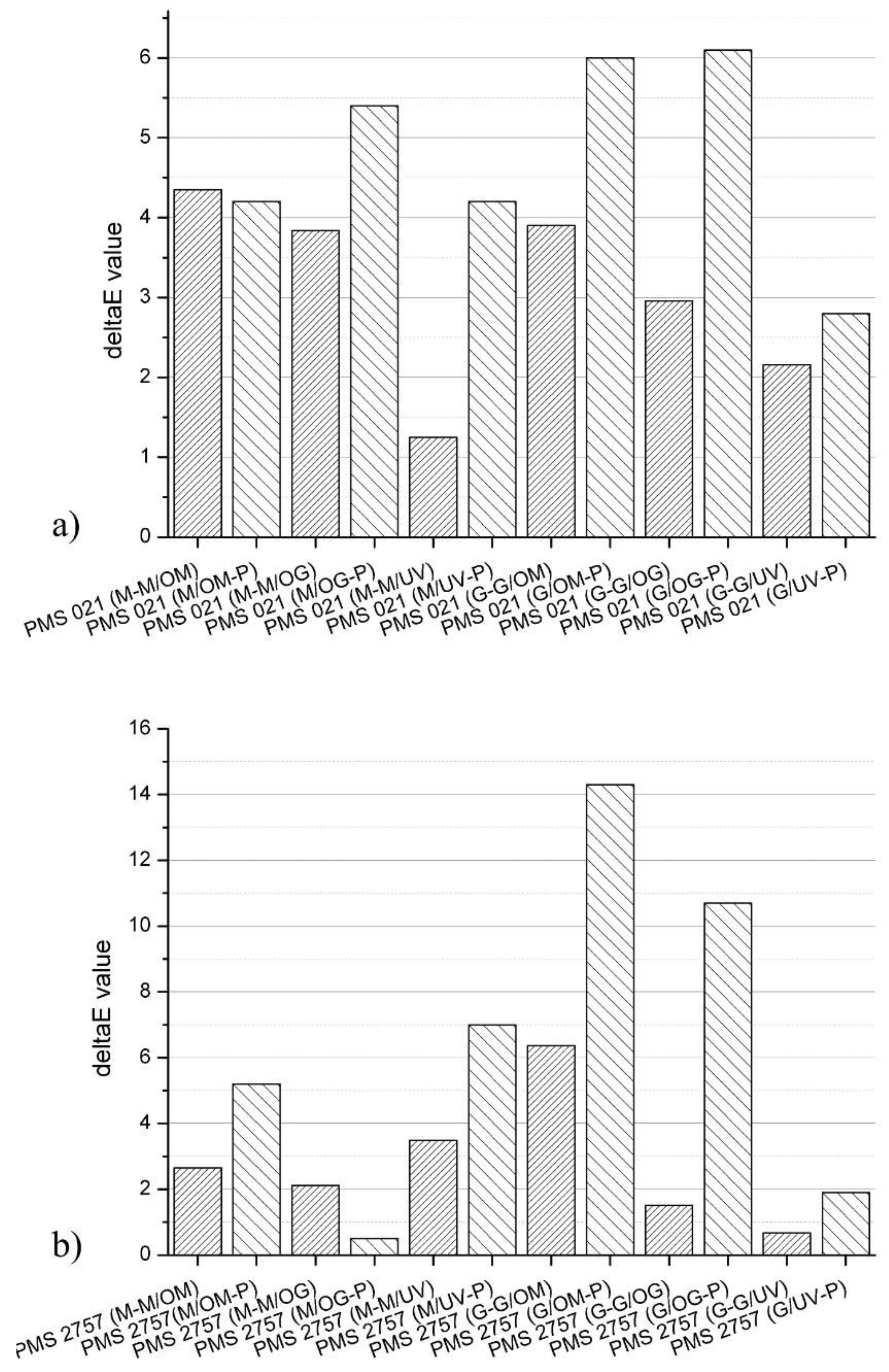

| Characteristics | Standard | Measure | Value Matte/Coated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basis Weight | ISO 536 [26] | g/m2 | 300/300 |
| Gloss Hunter | ISO 8254-1 [27] | % | 55/75 |
| Brightness D65 | ISO 2470-2 [28] | % | 9793 |
| CIE Whiteness | % | 127/126 | |
| Opacity | ISO 2471 [29] | % | 98.8/98.7 |
| Gloss Lehmann | ISO 8254-2 [30] | % | 52/71 |
| Smoothness PPS 10 | ISO 8791-4 [31] | μm | 2.5/0.93 |
| UV Varnish | Offset Coating Gloss | Offset Coating Matte | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Coating | After Coating | Before Coating | After Coating | Before Coating | After Coating | |
| Glossy paper | 71 | 88 | 71 | 79 | 71 | 74 |
| Matte paper | 52 | 82 | 52 | 58 | 52 | 54 |
| Group X | Group Y | Lower CI | Mean Estimate | Upper CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/OM | G/OM | −5,379 | −1.2567 | 2.8657 | 0.9363 |
| M/OM | M/OG | −5.0773 | −0.955 | 3.1673 | 0.9799 |
| M/OM | G/OG | −4.2307 | −0.1083 | 4.014 | 1 |
| M/OM | M/UV | −3.7723 | 0.35 | 4.4723 | 0.9998 |
| M/OM | G/UV | −3.4373 | 0.685 | 4.8073 | 0.9956 |
| G/OM | M/OG | −3.8207 | 0.3017 | 4.424 | 0.9999 |
| G/OM | G/OG | −2.974 | 1.1483 | 5.2707 | 0.9559 |
| G/OM | M/UV | −2.5157 | 1.6067 | 5.729 | 0.8402 |
| G/OM | G/UV | −2.1807 | 1.9417 | 6.064 | 0.7075 |
| M/OG | G/OG | −3.2757 | 0.8467 | 4.969 | 0.9883 |
| M/OG | M/UV | −2.8173 | 1.305 | 5.4273 | 0.926 |
| M/OG | G/UV | −2.4823 | 1.64 | 5.7623 | 0.8285 |
| G/OG | M/UV | −3.664 | 0.4583 | 4.5807 | 0.9994 |
| G/OG | G/UV | −3.329 | 0.7933 | 4.9157 | 0.9913 |
| M/UV | G/UV | −3.7873 | 0.335 | 4.4573 | 0.9999 |
| M-M/OM | M-M/OG | M-M/UV | G-G/OM | G-G/OG | G-G/UV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMS7472 | 0.85 | 0.95 | 1.20 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 1.85 |
| PMS193 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 1.10 | 0.90 | 1.22 | 1.90 |
| PMS021 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 1.25 | 0.95 | 1.30 | 1.10 |
| PMS2757 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 1.20 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 1.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zjakić, I.; Galić, E.; Ljevak, I.; Matijević, M. Improving Prediction Model for Colorimetric Changes Due to Coating Processes with Oil-Based and UV Coatings. Coatings 2024, 14, 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14121488
Zjakić I, Galić E, Ljevak I, Matijević M. Improving Prediction Model for Colorimetric Changes Due to Coating Processes with Oil-Based and UV Coatings. Coatings. 2024; 14(12):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14121488
Chicago/Turabian StyleZjakić, Igor, Eduard Galić, Ivana Ljevak, and Mile Matijević. 2024. "Improving Prediction Model for Colorimetric Changes Due to Coating Processes with Oil-Based and UV Coatings" Coatings 14, no. 12: 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14121488
APA StyleZjakić, I., Galić, E., Ljevak, I., & Matijević, M. (2024). Improving Prediction Model for Colorimetric Changes Due to Coating Processes with Oil-Based and UV Coatings. Coatings, 14(12), 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14121488






