An Experimental Investigation into Residual Stress Control of 24CrNiMo Alloy Steel by Selective Laser Melting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
2.2. The SLM Machining
2.3. Microstructural and Properties Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Scanning Strategy on Residual Stress in the SLM Process
3.2. The Effect of Preheating Temperature on Residual Stress in the SLM Process
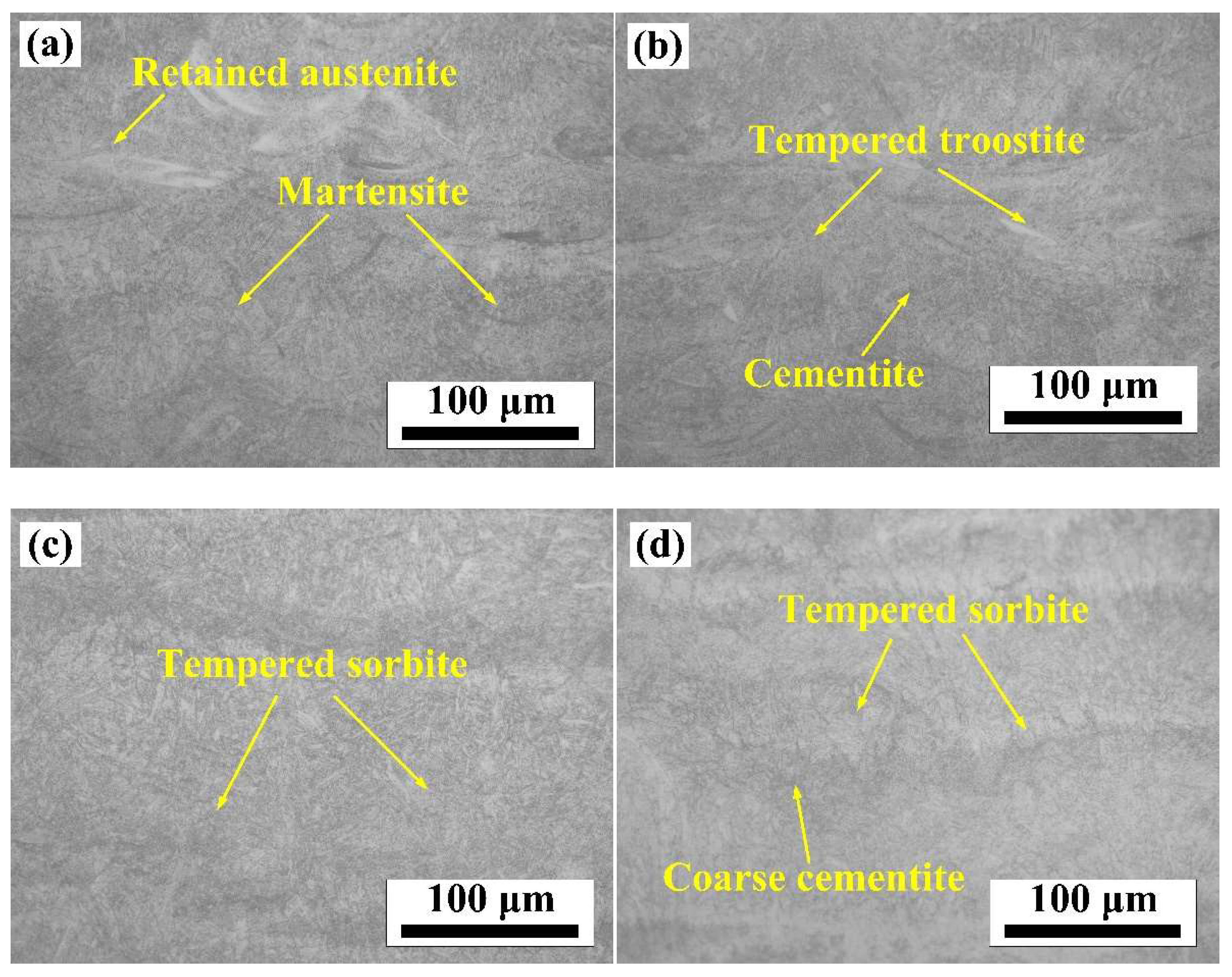
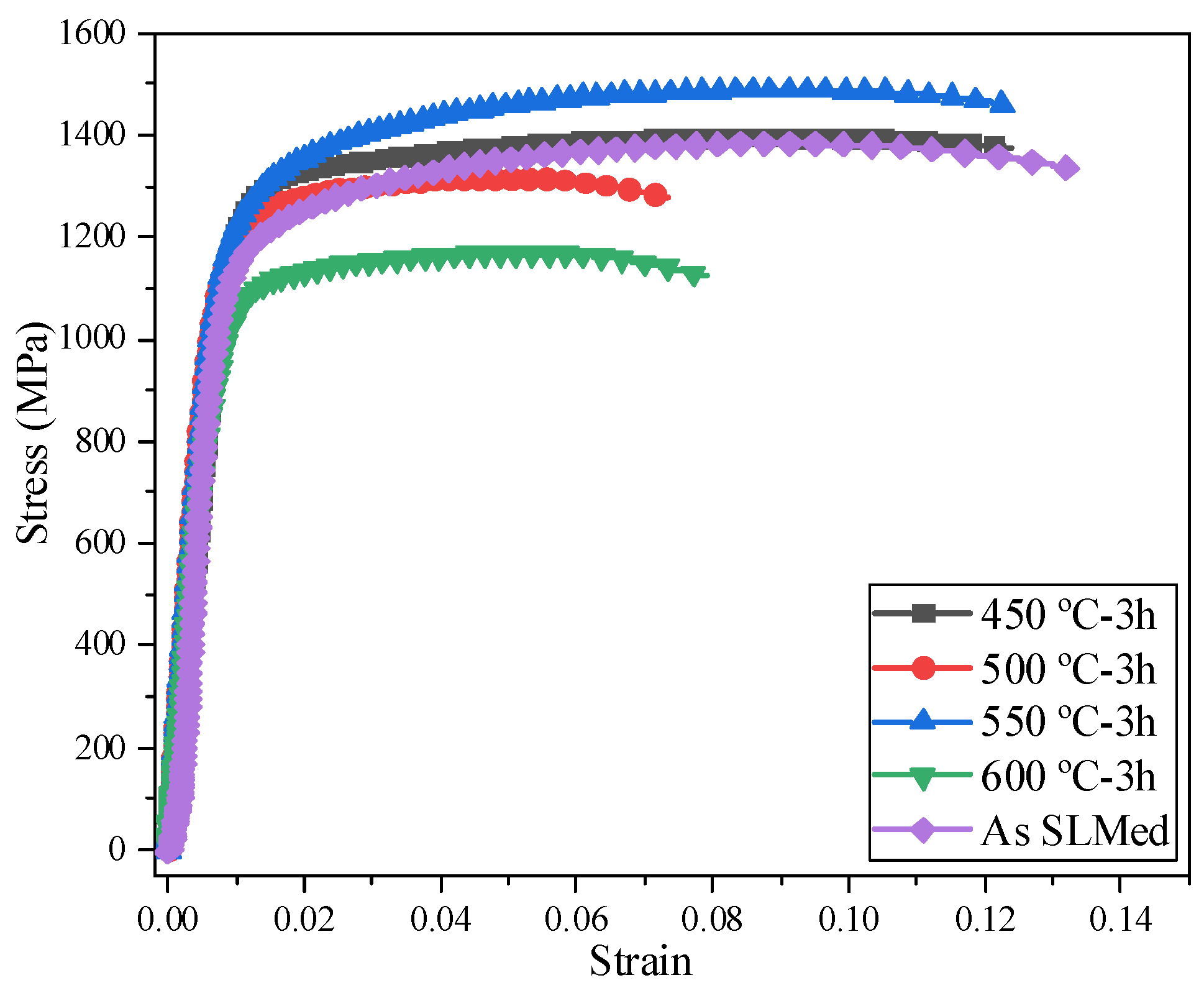
3.3. The Effect of Stress Relief Heat Treatment on Residual Stress
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasebani, S.; Ghayoor, M.; Badwe, S.; Irrinki, H.; Atre, S. Effects of atomizing media and post processing on mechanical properties of 17-4 ph stainless steel manufactured via selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, X.; Dong, S.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X.; Ren, L. Effects of process parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 24crnimo steel fabricated by selective laser melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 128, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.B.; Dong, S.Y. Additive manufacturing of 24crnimo low alloy steel by selective laser melting: Influence of volumetric energy density on densification, microstructure and hardness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 809, 140957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Chen, S.; Xi, L.; Liang, J.; Liu, C. Selective laser melting of 24crnimo steel for brake disc: Fabrication efficiency, microstructure evolution, and properties. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 107, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.; Hufenbach, J.; Bleckmann, M.; Giebeler, L.; Wendrock, H.; Oswald, S.; Gemming, T.; Eckert, J.; Kühn, U. Selective laser melting of ultra-high-strength trip steel: Processing, microstructure, and properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 4944–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Zheng, D.; Li, H.; Jia, X.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.L.; Qian, M.; Yan, M. Selective laser melting of h13: Microstructure and residual stress. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 12476–12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Kang, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y. Huang. Laser powder bed fusion of zr-modified al–cu–mg alloy: Crack-inhibiting, grain refinement, and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2022, 838, 142618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frkan, M.; Konecna, R.; Nicoletto, G.; Kunz, L. Microstructure and fatigue performance of slm-fabricated ti6al4v alloy after different stress-relief heat treatments. Transp. Res. Procedia 2019, 40, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Ghadbeigi, H.; Mumtaz, K. Effect of scanning strategies on residual stress and mechanical properties of selective laser melted ti6al4v. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Yue, S.; Wang, H. On the solidification behaviour and cracking origin of a nickel-based superalloy during selective laser melting. Mater. Charact. 2019, 148, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, J.; Hong, R.; Weng, C.; Wang, H. Microstructure and machinability of selective laser melted high-strength maraging steel with heat treatment. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 288, 116906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Fang, Y.; He, Z. A short review on selective laser melting of h13 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 2453–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Huang, C.; Wu, C. Review on residual stress in selective laser melting additive manufacturing of alloy parts. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 129, 106283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Kumar, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure, surface quality, residual stress, fatigue behavior and damage mechanisms of selective laser melted 304l stainless steel considering building direction. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sun, J.; Yan, B. An approach to predict the residual stress and distortion during the selective laser melting of alsi10mg parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 3535–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, S.; Guo, K.; Sun, J. Fem analysis of thermal and residual stress profile in selective laser melting of 316l stainless steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 66, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiraei, H.; Rezadoost, P. Development of a probability distribution model for the SCFs in tubular X-connections retrofitted with FRP. Structures 2022, 36, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiraei, H.; Rezadoost, P. Stress concentration factors in tubular T-joints reinforced with external ring under in-plane bending moment. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, 112551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, I.A. Investigation of Residual Stresses in the Laser Melting of Metal Powders in Additive Layer Manufacturing. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wolverhampton, West Midlands, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, K.; Pal, D.; Teng, C.; Stucker, B.E. Evaluations of effective thermal conductivity of support structures in selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 6, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, G.B.; Park, J.H.; Kim, W.R.; Hyun, S.; Park, H.; Lee, T.W.; Kim, H.G. Study on the effect of preheating temperature of slm process on characteristics of cocrmo alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 841, 143020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaohui, J.; Chunbo, Y.; Honglan, G.; Shan, G.; Yong, Z. Effect of supporting structure design on residual stresses in selective laser melting of alsi10mg. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 118, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugwagwa, L.; Dimitrov, D.; Matope, S.; Yadroitsev, I. Influence of process parameters on residual stress related distortions in selective laser melting. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 21, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H. Scanning strategy in selective laser melting (slm): A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 2413–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Shrestha, S.; Chou, K. Stress and deformation evaluations of scanning strategy effect in selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 12, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Xiao, H.; Ye, F.; Li, Z.; Tang, W.; Zhu, F.; Chen, C.; Zhu, C. Numerical analysis of the effect of the scan strategy on the residual stress in the multi-laser selective laser melting. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Ghadbeigi, H.; Mumtaz, K. Processing parameter effects on residual stress and mechanical properties of selective laser melted ti6al4v. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 4059–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Q.; Thomas, S.; Birbilis, N.; Cizek, P.; Hodgson, P.D.; Fabijanic, D. The effect of post-processing heat treatment on the microstructure, residual stress and mechanical properties of selective laser melted 316l stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 821, 141611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Tan, S. Effects of vacuum annealing treatment on microstructures and residual stress of alsi10mg parts produced by selective laser melting process. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 30, 1650255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. The Study on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Melting Additive Manufactured 24CrNiMo Alloy Steel. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Jilin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
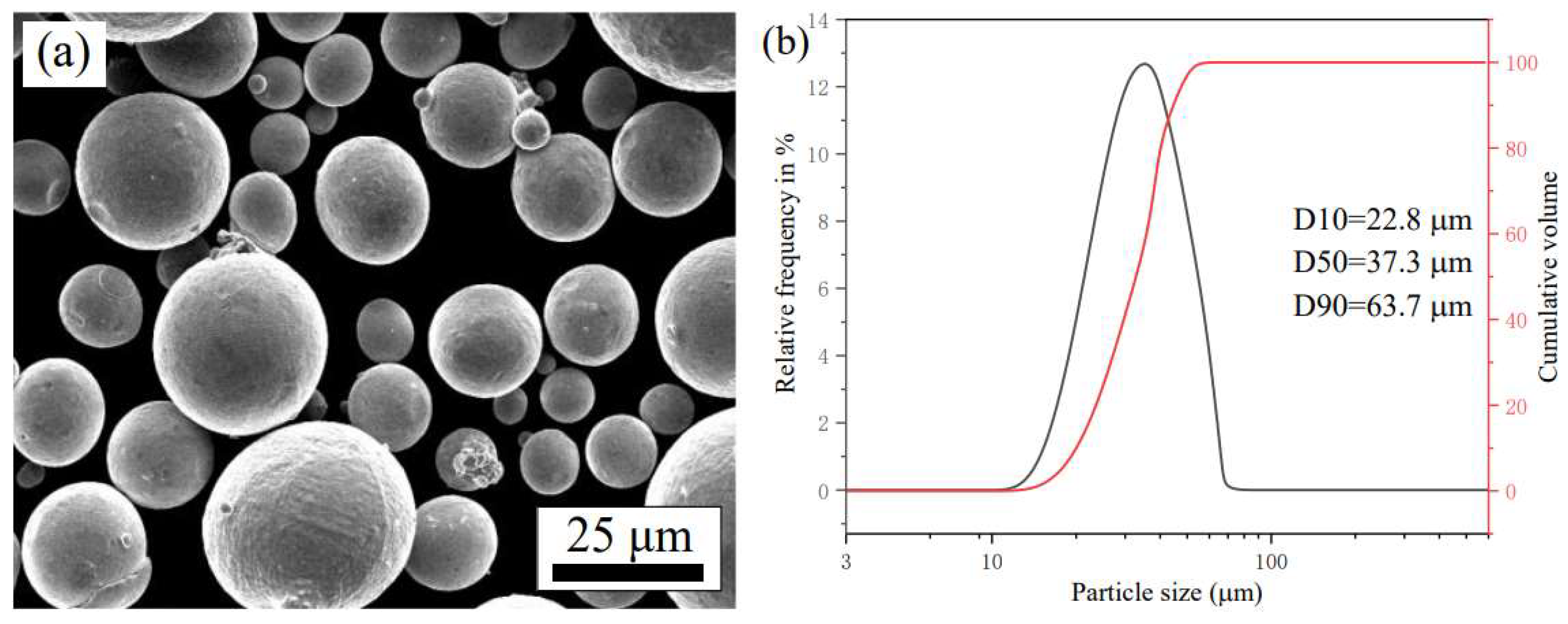
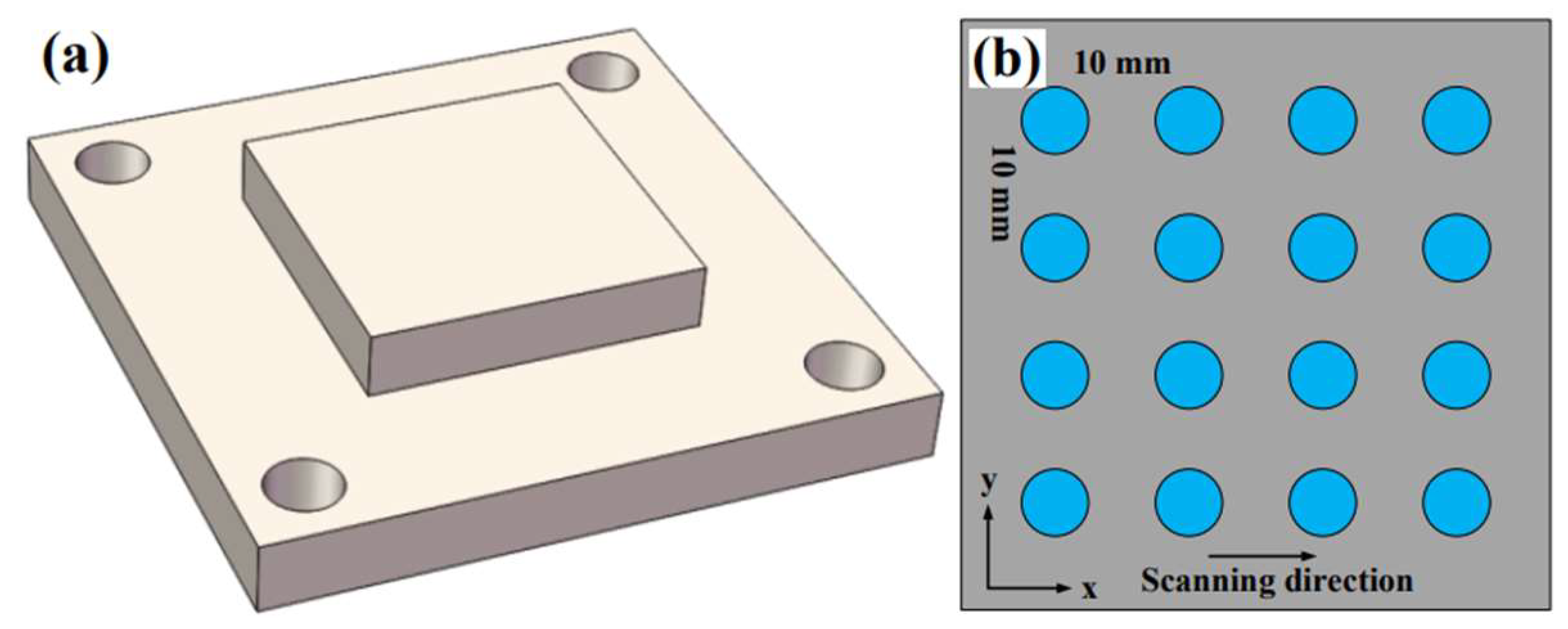



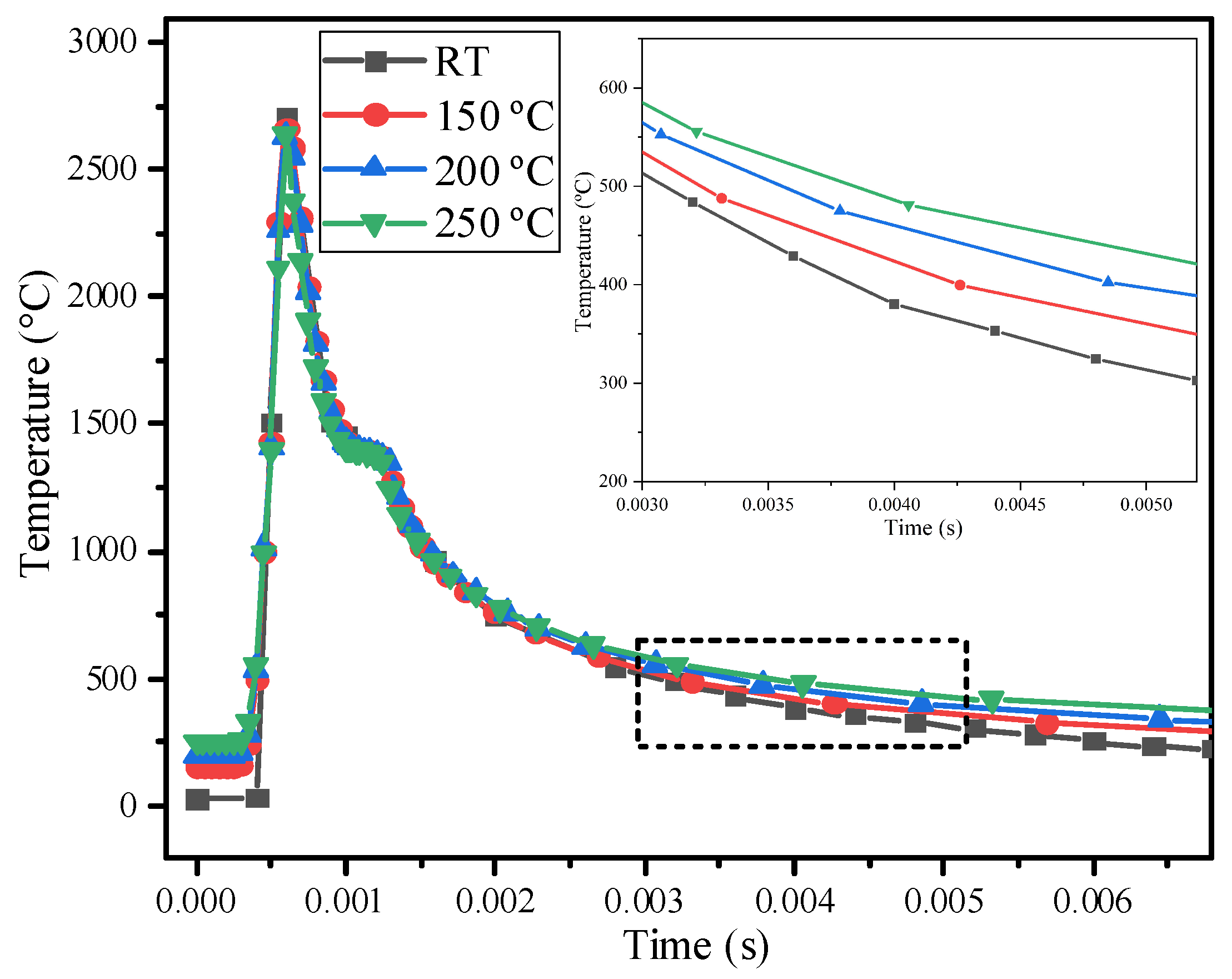
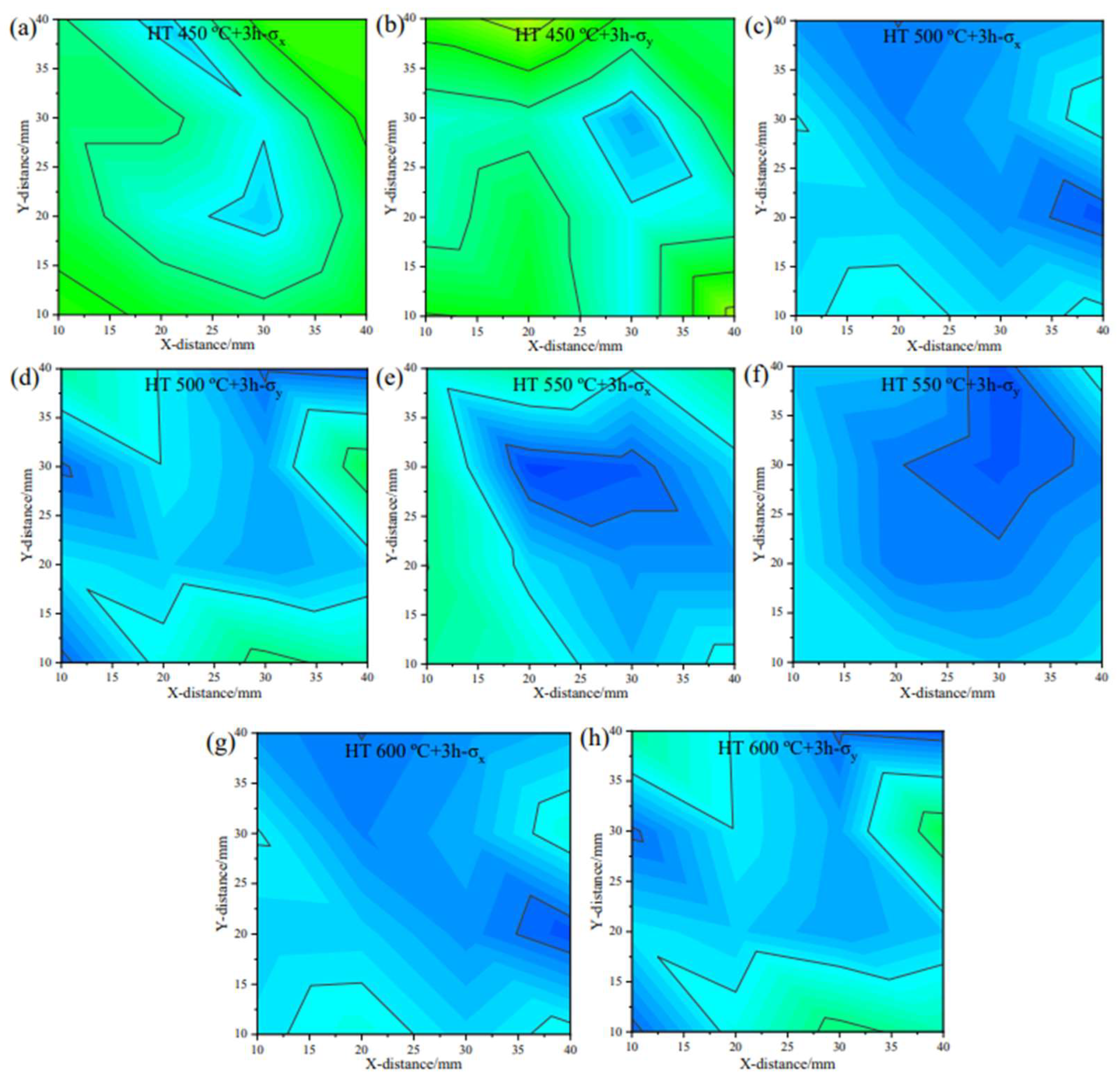
| Element | C | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.23 | 1.15 | 1.84 | 0.48 | 0.78 | 0.19 | <0.003 | Bal. |
| Laser Power P (W) | Scanning Speed v (mm/s) | Scanning Spacing h (mm) | Powder Layer Thickness t (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 280 | 550 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Rong, P.; Men, X.; Deng, A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L. An Experimental Investigation into Residual Stress Control of 24CrNiMo Alloy Steel by Selective Laser Melting. Coatings 2023, 13, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020321
Chen Y, Rong P, Men X, Deng A, Liu Y, Chen H, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Ren L. An Experimental Investigation into Residual Stress Control of 24CrNiMo Alloy Steel by Selective Laser Melting. Coatings. 2023; 13(2):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020321
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yong, Peng Rong, Xiangnan Men, Ailin Deng, Yan Liu, Hui Chen, Zhenlin Zhang, Yue Liu, and Lisha Ren. 2023. "An Experimental Investigation into Residual Stress Control of 24CrNiMo Alloy Steel by Selective Laser Melting" Coatings 13, no. 2: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020321
APA StyleChen, Y., Rong, P., Men, X., Deng, A., Liu, Y., Chen, H., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., & Ren, L. (2023). An Experimental Investigation into Residual Stress Control of 24CrNiMo Alloy Steel by Selective Laser Melting. Coatings, 13(2), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020321







