Abstract
This study investigates the production and performance of a novel nanofiltration membrane for removal of cationic dye (Methylene blue) and multivalent cations. These positively charged membranes are made by dispersing a modified cationic metal–organic framework, Cl-MIL-101(Cr), into the polyvinyl alcohol matrix as a membrane skin layer. To this end, the mobile anion (Cl−) embedded in the MIL-101(Cr) structure plays a role to create a positive partial charge on the membrane. In this study, the effects of MOF content and their types on the membrane structure were considered by FTIR, XRD, FESEM, Zeta potential and water contact angle. The results have shown that membranes filled with Cl-MIL-101(Cr) attained higher permeate flux and rejection than those of MIL-101(Cr). Particularly, this study indicates that the low irreversible resistance (19.49%) and high flux return ratio (80.50%) have been related to the membrane containing 15% cationic Cl-MIL-101(Cr). However, this membrane rejected more than 30.41% of AlCl3 salt and 99.08% of methylene blue with approximate permeate flux of 20 L/m2·h. It is recommended that the fabricated membrane be placed in the flow path process of cationic dyes purification.
1. Introduction
Wastewater from the dyeing and textile industry leads to water and environmental pollution [1,2]. In addition, the existence of dyes in water is evident even at low concentrations of 10 ppm. However, the dyes are toxic to the lentic ecosystem by harming the aesthetic temper of water and weakening the photosynthetic actions of microorganisms. Therefore, the separation of dyes from dyeing and textile wastewater is vital before discharging into the environment [3,4,5,6]. In this regard, Methylene blue (MB) cationic dye is considered as one of the most polluting dyes and is stable in an aqueous solution at room temperature due to its positive charge [7,8]. Many attempts have been made to separate this cationic dye even at deficient concentrations [9,10]. Traditional methods used for treating dye-containing effluents, e.g., chemical oxidation, precipitation, coagulation, photocatalysis and ultrafiltration, cannot separate efficiently the dyes from the effluent. These traditional methods even cause secondary contaminations at times [11,12,13]. Nanofiltration (NF) membranes have been reported to nominal cut-off molecular weight of 100–1000 Da and a pore size approximately 1 nm in terms of characteristics somewhere between ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis [14,15]. Compared to other dyeing wastewater treatment methods, NF is a relatively less costly and energy efficient method along with fewer environmental problems [13,16].
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) polymer is an attractive material in different applications due to its high hydrophilicity, non-toxicity and high mechanical strength. PVA is also known as a binder for the formation of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) into pellets [17,18,19,20]. PVA is a suitable polymer for separating hydrophilic materials from the feed stream because of its excellent film-forming ability and mechanical strength. PVA is appropriate to produce facilitated transport membranes as well [21]. PVA swells against water and loses its efficiency in the form of a membrane layer. Therefore, aldehydes cross-linking can increase the stability of the PVA membrane to water. As a result of the cross-linking reaction, some characteristics of PVA membranes may change slightly such as mechanical strength and hydrophilicity. The swelling specifications and surface properties of PVA membranes, as well as their permeability and selectivity, can be varied based on the cross-linking degree [22].
In the NF process, it is necessary to develop the membrane with high permeate flux and selectivity, while most of the polymeric membranes used for the NF process appear to have reached the maximum permissible level between permeability and selectivity [23]. Therefore, it is necessary to modify them by using several materials with different properties, including porous inorganic fillers such as SiO2 [24,25], Al2O3 [26], TiO2 [27,28], and zeolite [29] in membrane structures to improve the performance of the polymeric membranes. In this regard, compatibility between different components of membranes appears vital. Poor compatibility between inorganic particles and polymer matrix usually leads to non-selective gaps, faults in membrane structure and deterioration in its performance [30]. One of the most effective ways to improve membrane permeability and selectivity is to combine some porous fillers such as activated carbon [31] and MOFs into the membrane matrix polymer [32,33]. MOFs offer superior advantages as fillers in membrane structures due to ultra-high surface area, adjustable chemical composition, molecular sieving effect, the MOFs organic chains, and high compatibility with the polymeric membrane matrix. Besides, they are very suitable for the preparation of polymeric hybrid membranes [13,34,35]. These porous hybrid materials, also known as porous coordination polymers, are constituted from metal clusters linked together by organic ligands [36]. Reviewing different MOFs, the researchers Férey et al. [37] conducted the chromium (III)-derived MOF [Cr3O(F,OH)(H2O)2(1,4-benzene dicarboxylate)3]-25H2O, MIL-101(Cr). This MOF has mesoporous cages accessible through microporous windows together with high hydrothermal and chemical strength advantages [38]. The advantages of this structure are the potential for the creation of unsaturated chromium (III) sites in the activated framework and especially its attractiveness for feasible applications. To fill the gap, functionalization of MIL-101 (Cr) can be accomplished by binding ligands such as ethylenediamine towards unsaturated chromium (III) sites [39]. Moreover, this MOF can be functionalized by encapsulating many particles in mesoporous cages [40,41]. In addition, there are general methods capable of direct converting MIL-101(Cr) into cationic ones by simultaneously producing mobile anions [42].
In the present paper, MIL-101(Cr) (M101) and its positive form depicted as Cl-MIL-101(Cr) (M101Cl) are dispersed in the PVA matrix as fillers and form a skin layer onto polysulfone substrate in order to improve cationic dye separation performance. This modified MOF with excellent performance as an ion exchange agent, has been easily obtained from a hot AlCl3 solution treatment step [43]. This study aimed at amending the fouling parameters, permeability, and rejection of the state-of-the-art PVA NF membrane for MB cationic dye efficient removal from aqueous solutions. This removal has been obtained from surface modification and cationic MOF filler optimal addition in PVA matrix, which is proved to be a promising pathway for increasing membrane performance through adjusting membrane surface attributes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The polysulfone pellets were purchased from Solvay polymer. Polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400), Triton X-100 (TX-100), sodium dodecyl sulfate and N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF, ≥99.9%) solvent were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). These materials were used as ingredients and additives to fabricate the substrate membrane. PVA (MW. Approx. 72,000), Glutaraldehyde, Chromium(III) nitrate nonahydrate (Cr(NO3)3·9H2O), Aluminum (III) chloride hexahydrate (AlCl3-6H2O, crystallized, ≥99.0%), Terephthalic acid (H2BDC) (99%), MB, hydrofluoric acid (HF ≥ 40%), Sulfuric acid (98%), acetone and ethanol (99%) were also purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Deionized water produced by an ultra-water purification system was used all through this work. All the above chemicals have been used without any purification.
2.2. Synthesis of MOFs and Preparation of NF Membrane
M101, first reported by Férey, is one of the most outstanding emerging porous materials due to its noteworthy properties such as high porosity, high surface area, abundant unsaturated metal sites, physical and chemical stability, and inexpensiveness [44]. For the synthesis of M101 crystals by hydrothermal method, 1 mmol of Cr(NO3)3(9H2O), 1 mmol of terephthalic acid, and 0.05 mL of HF were mixed in 5 mL of ultra-pure water. They were transferred to a Teflon-lined autoclave at 200 °C after being stirred for 20 min. After the reaction completion in 10 h, the autoclave was returned to room temperature, and finally, the product was obtained as a green powder by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm. This powder was then washed by DMF and then hot ethanol. It was dried afterwards and stored at 100 °C for 24 h.
2.2.1. Exchanging Fluoride Ions with Chloride Ions in M101 Structure
An aqueous solution containing 0.15 wt% of AlCl3-6H2O at 90 °C was used for anion stripping of the M101. About 0.1 wt% of synthesized M101 was added to this solution, and after about 20 h, the process was completed. The products were next collected by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm and washed with water several times. Finally, the obtained powders (M101Cl) were completely dried at 100 °C and stored.
The substrate required for the production of MOF/PVA NF films was obtained by the phase inversion method. For this, 16 wt% polysulfone pellets were added to the DMF solution containing 1 wt% PEG 400 and 2 wt% TX-100 while stirring at 500 rpm. As a result, they were dissolved entirely at room temperature in 8 h. After degassing, this solution was cast onto a non-woven polyester sheet attached to glass using a casting knife with a thickness set to 160 microns. It was immediately placed in a water bath containing 1 wt% SDS to perform solvent/non-solvent transfer for 24 h.
2.2.2. Preparation of MOF/PVA NF Membranes
A total of 7 mL of PVA aqueous solution containing 42 mg, 56 mg, and 70 mg PVA was prepared by dissolving this polymer in water at 90 °C. This solution was used to cover the surface of the polysulfone membrane and create a dense skin layer. After dissolving PVA powder in deionized water at 90 °C, MOF particles were added step by step into the PVA solution under stirring and were dispersed by ultrasonic waves. MOF loadings were 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% (labeled as PM0.8, PM0.8-5, PM0.8-10, PM0.8-15 and PM0.8-20). They were calculated according to the following equation and listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Types of membranes made in this work.
The porous polysulfone membrane was mounted between two cubic cast rubber frames that were sealed by washers and four clamps. The coating solution containing PVA and dispersed MOF particles was cast onto a polysulfone substrate and dried at 50 °C for 3 h. Finally, cross-linking of the MOF-PVA membranes was performed after 20 min at room temperature with 25 mL of a solution of 0.15 wt% glutaraldehyde and 1 wt% sulfuric acid as a catalyst. After drying at room temperature, the final membranes were obtained.
2.3. Characterization
The composition of MOFs and chemical structure of their surface were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (D8 Advance, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR 8400s spectrometer, Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan). The membranes’ morphology and structure at surface and cross-section were evaluated using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, MIRA3TESCAN-XMU, Brno, Czech Republic).
The surface hydrophilicity of membrane samples was checked using measurement of the deionized water contact angle by contact angle meter (CA-ES10, Fars Overdraft Technology, Iran) at 25.0 °C. Several measurements were performed at several places of each membrane sample to ensure the accuracy of water contact angle measurements.
Membrane surface zeta potential was obtained using an electrokinetic analyzer (EKA, Anton Paar GmbH, Graz, Austria). It measured the surface streaming potential by 0.001 mol/L KCl aqueous solution at 25.0 °C and pH 7.0 according to the Helmholtz–Smoluchowski equation [45].
The MB concentration in feed and permeate was measured using UV/Vis. spectrophotometer (model T80+ UV/VIS spectrometer, PG instruments, Australia) at the wavelength corresponding to the maximum absorption (λmax = 663 nm). The calibration curve in the concentration range of 10 ppm is shown in Figure 1 (also, see Supplementary Materials).
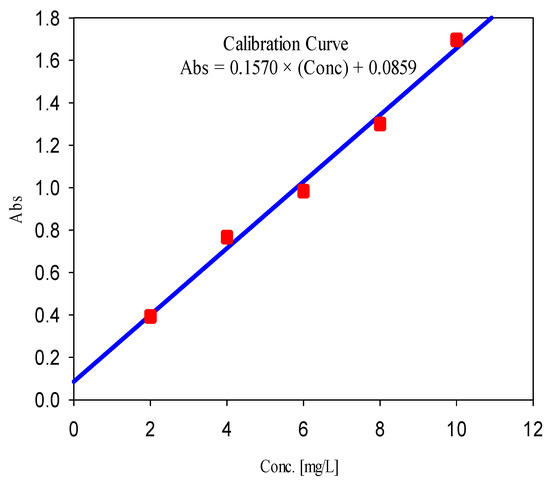
Figure 1.
The calibration curve for the measurement of MB concentration.
2.4. NF Performance Evaluation
Three main parameters, namely pure water flux, dye-containing solution permeate flux and dye rejection, were considered to evaluate the performance of different membranes. Membrane permeability tests were done using a cross-flow filtration setup. In this case, the feed was passed over the membrane surface by using a diaphragm pump with open flow of 4 LPM and head of 130 Psi. The retentate stream was returned to the feed tank and permeate was collected to measure its volume and dye concentration. Excess permeate was poured back into the feed tank to maintain its concentration to some extent. This cross-flow system involved valves that are used to control the flow rate and pressure on the membrane surface. The membrane cell was made of two cube-shaped parts with an approximately 29 cm2 flat membrane fitted between them by washers and screws. Two barometers were placed in the flow path to display the pressure before and after the membrane cell. All tests were performed at room temperature, trans-membrane pressure of 6.0 bar, pH of 7.0 ± 0.2, and cross-flow velocity of 40 L/hr.
Pure water flux (Jw) was determined following membrane compaction to achieve its steady state with deionized water at 7.0 bar. Another tank containing a 10 mg/L MB solution was then considered as feed tank, and membrane permeate flux (Jp) and rejection were measured for 30 min or up to a steady-state flux (Jws); after which, the used membranes were re-inserted into the cell and were washed with deionized water at a cross-flow rate of approximately 60 L/hr for 0.5 h to remove loosely deposited dyes from the membrane surface. Finally, the deionized water flux was measured again (JR). In addition, the AlCl3 salt solution, which is a polyvalent ion with a concentration of 500 ppm, was separated by a PM0.8-15 membrane. The amount of permeate flux passing through the membrane was calculated using the following equation [46]:
In this equation, V is the volume of liquid that seeps through the membrane at constant pressure and time of ∆t.
Rejection was also obtained from the following equation [46]:
In this equation, Cp and Cf are the concentrations of the MB in the permeate and feed, respectively, which were measured using a UV spectrophotometer. Reversible and irreversible resistances, which indicate membrane fouling, were calculated using the following equations [47]:
Additionally, the flux recovery ratio (FRR) and relative flux reduction (RFR) can be determined from the following equations [46]:
A low calculated RFR and Rir indicate better antifouling properties, while the higher flux recovery ratio value means higher cleaning efficiency. The concentration of AlCl3 in aqueous solution was measured with a conductivity meter.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Analysis of M101 and M101Cl
M101 was characterized by XRD before and after anion stripping to verify its synthesis accuracy. As depicted in Figure 2, M101’s XRD pattern showed clearly separated peaks at angles (2θ) of 9.05°, 17.8°, and 26.8°. The M101 and M101Cl graphs are in good agreement both in the literature and in this work, indicating that these MOFs were successfully synthesized [48]. The crystallinity of the material (M101Cl) was retained after anion stripping. Actually, M101Cl still maintained some characteristics of M101, such as porosity and pore structure [43].
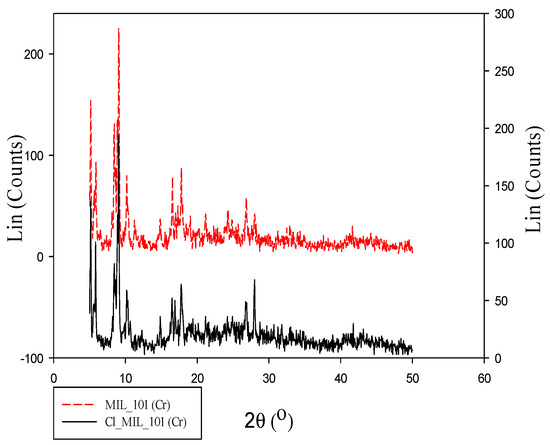
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of M101 and M101Cl.
3.2. FT-IR Analysis of M101 and M101Cl
FTIR has been used to discover the composition and chemical structure of the MOFs. FTIR graphs of M101 and M101Cl shown in Figure 3. The first characteristic peak in Figure 3 corresponds to the Cr–OH groups present in the supertetrahedra (3820.72 cm−1) [49]. The presence of ν(C–C), νs(COO), and νas(COO) vibrations between 1701.10 cm−1 and 1278.72 cm−1 are related to dicarboxylate linker in M101. The most severe peak (1400.22 cm−1) can imply the presence of M101 nanoparticles in the PVA layer [34]. For example, an intense absorption band appeared at 1400.22–1701.10 cm−1 in the spectrum corresponding to the vibration peak of the C–O stretching in the benzene ring. The moderate-intensity peak at 744.47 cm−1 and 592.11 cm−1 are attributed to stretching vibration of mono-substituted benzene and Cr–O, respectively. Since all peaks related to M101 were also observed in the M101Cl spectrum, the main composition of MOF is preserved.
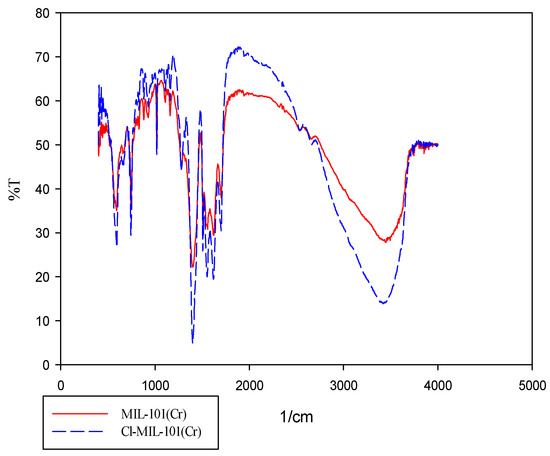
Figure 3.
FTIR results of M101 and M101Cl.
3.3. MOFs and MOF Loaded Membranes Structure and Morphology
The surface and cross-sectional FESEM images of membranes made in this study are shown in Figure 4, and a higher magnification of the membrane cross-section is presented in Figure 5. FESEM images properly confirmed that the uniformly dispersed MOF particles within the PVA matrix creating a thin skin layer placed on the upper surface of polysulfone substrate. MOF particles were compatible with the polymer due to their organic part and were therefore well dispersed in the polymer solution. This minimizes the presence of gaps at low loads. M101 morphology was investigated through FESEM images of MOF loaded membrane. As could be seen in the Figure 4c,d and Figure 5, the MOF particles morphology did not change before and after the modification. MOF particles were well distributed within the PVA matrix on the surface of the polysulfone membrane. However, the surface of the membrane fabricated with M101Cl was more integrated. This octahedral porous solid with a smooth surface had a grainy structure with a characteristic diameter of about 300 nm, while some were split or lacked angles. As seen in cross-section FESEM (Figure 4a), finger cavities were extended across the polysulfone membrane. According to the Figure 4b, a thin dense layer of PVA with a thickness of about 800 nm to 1 micron penetrated the small upper cavities of polysulfone substrate. In other words, this selective skin layer became thicker by adding MOF particles. In addition, some formless debris had been mixed with M101 crystals that are probably defective M101 crystals [50].
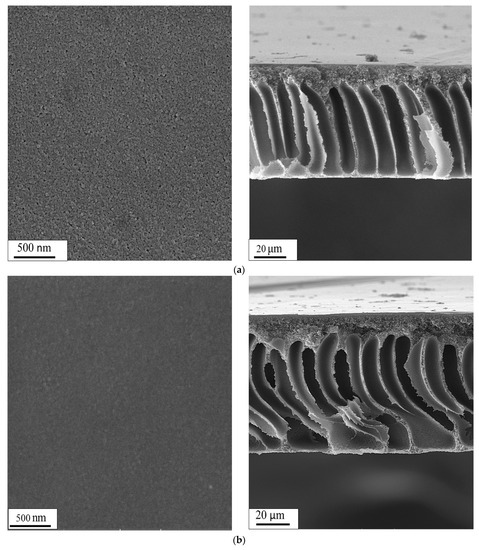
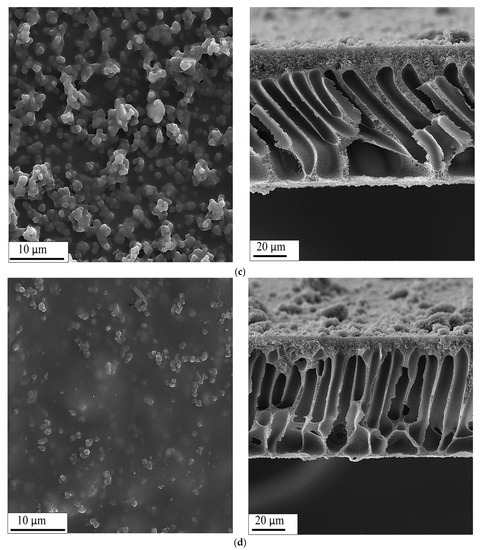
Figure 4.
FESEM images of surface (left) and cross section (right) of (a) polysulfone substrate, (b) PM0.8, (c) PM0.8-15 and (d) PM0.8-15-2.
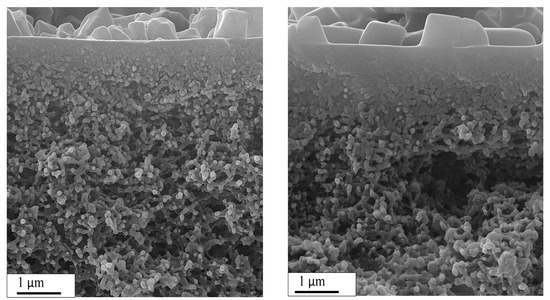
Figure 5.
Higher magnification of the membrane cross-section FESEM; left: PM0.8-15, right: PM0.8-15-2.
3.4. The Hydrophilicity and Surface Charge of the Membranes
Water contact angle results of different membranes are shown in Table 2. The results revealed that the hydrophilicity of the polysulfone membrane surface was strongly increased after coating with PVA polymer. In fact, when adding MOF particles to the polymer matrix, the hydrophilicity of the membrane surface decreased slightly due to the decrease in hydrophilic hydroxyl group density (related to the structure of the PVA) on the membrane surface.

Table 2.
Water contact angle values of different membranes.
However, when the MOF load was high, the water contact angle decreased again. This may be due to the large number of MOF particles with high porosity and specific surface area on the membrane surface, surface roughness, and the gap between PVA and MOFs. In other words, under the same MOF load, the hydrophilicity of the membrane loaded with M101Cl was slightly higher than that of M101. This higher hydrophilicity can increase water permeation.
In addition to the hydrophilicity of the membrane surface, the surface charge also affected the removal of cationic contaminants, thereby improving the performance and fouling properties of NF membranes. Membrane surface charge has been evaluated through the measurement of static surface zeta potential and reported in Table 3. The results indicate that the surface of the anion-stripped M101 modified membrane has a more positive charge under neutral pH compared with that of the initial MOF and MOF-free membranes. This more positive charge can be attributed to the M101Cl particles in the membrane surface.

Table 3.
Zeta potential values of different membranes.
The M101 was modified by AlCl3 hot solution due to the charge balance of M101 framework. In fact, affinity of F− to Al3+ was stronger than that of Cr3+. Therefore, mobile Cl− anion in MOF structure was replaced by F−. Therefore, the cationic porous framework of M101Cl with mobile anions was easily and successfully synthesized. It suggested as an ion-exchanger and cationic filler to adsorb anionic contaminants and repel cationic organic contaminants, respectively. Several simple experiments consisted of the adsorption of anionic and cationic dye molecules showed that F− is replaced by Cl−, and Cl− can be easily removed from the framework. Under such conditions, positively charged M101Cl was more acceptable to the anionic dye, and hence ion exchange also occurred during the adsorption process.
3.5. Water Permeation and Dye Rejection of Membranes Filled with Different Amounts of M101 and M101Cl
Figure 6 shows that increasing the amount of PVA in the coating solution leads to a decrease in the pure water and dye solution flux, and this decrease was steep at higher values. In other words, thickening the membrane skin layer with increasing the amount of PVA leads to increased methylene blue rejection.
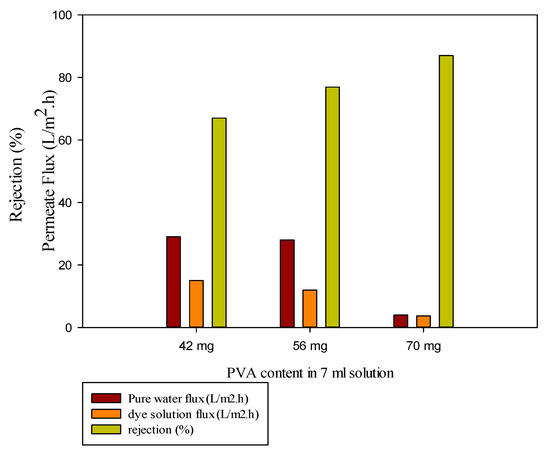
Figure 6.
Performance of membranes containing different amount of PVA.
A constant amount of each MOF has been loaded on the membrane skin layer to compare the dye separation performance of NF membranes. For this purpose, 15% of M101 incorporated in the PVA matrix and coated on the surface of polysulfone substrate following anion stripping (M101Cl). In addition, different percentages of MOF, including 0%, 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% were investigated to obtain the desired amount of M101Cl in the PVA matrix, in which the permeate flux, rejection and antifouling properties of the membrane were optimal. The trends of permeate flux, dye rejection and fouling resistance changes for these synthesized membranes are shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
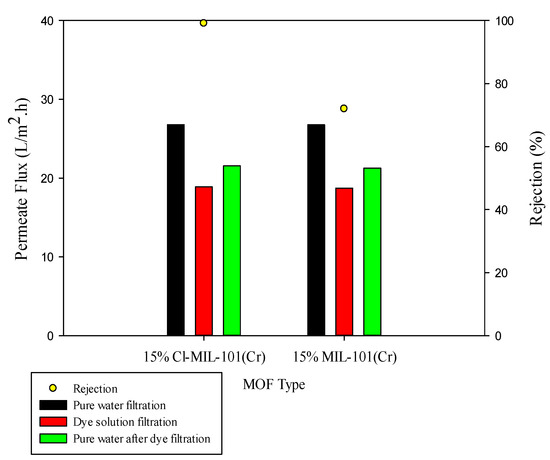
Figure 7.
Performance of membranes containing 15% of M101 and M101Cl.
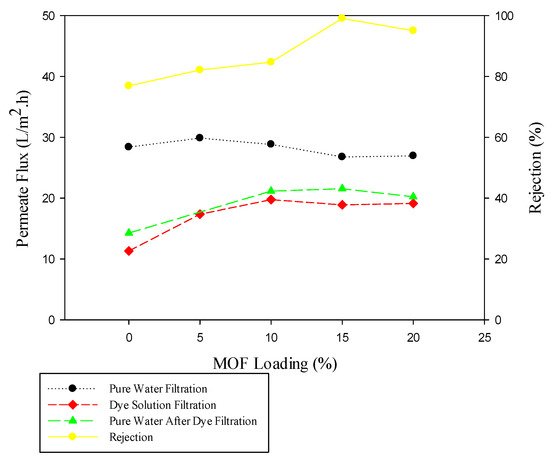
Figure 8.
Performance of membranes with different M101Cl loading.
As a result, the paper found that dye rejection went up rapidly by using anion stripped M101 instead of its initial state. Consequently, adding MOF contents increases the surface charge and improves the dye rejection. For PM0.8-20 with a MOF load greater than 20%, the potential for gaps between MOF particles and the polymer increased and the dye rejection was lower than PM0.8-15. The existence of a mobile anion in the MOF structure and thus a positive partial charge on the MOF surface can cause higher cationic particle rejection through electrostatic repulsion. Likewise, according to the FESEM images, the dispersion of cationic MOF particles on the surface of the membrane was more uniform, and this uniform thickness leads to better performance of the membrane. The pure water flux for M101Cl loaded membrane was almost similar to that of M101. The reason for this similarity was that the morphology and structure of the MOFs and the membranes fabricated with these two types of MOFs did not change; it was less than the membrane without MOFs because of the thickening of the skin layer (according to cross-section FESEM figures). Surface porosity and additional path for water permeate enhanced with increasing MOF loading in PVA matrix. These factors can improve the pure water flux, but the effect of coating solution concentration has been dominant on reducing the flux of pure water. However, in the case of dye solution permeate flux, for the PM0.8-15-2 membrane, the permeate flux was slightly lower than PM0.8-15 because of the membrane fouling effect, less rejection, and concentration polarization. According to the results, M101Cl has a better impact than M101 on membrane performance and can be used as filler in the PVA matrix. It is expected that the dye solution permeate flux would increase by adding positive MOF particles in the membrane structure. Due to the creation of electrostatic repulsion, fewer dye molecules have entered the pores of the membrane. Consequently, membrane fouling has been optimized. At short-term permeate flux evaluation, the dye solution permeate flux has been slightly lessening for MOF loading of about 15% due to the effect of concentration and thickness of the coating solution. However, for PM0.8-20 with 20% MOF loading, the dye solution permeate flux increased slightly as a result of the possibility of gaps between the MOF particles and the polymer matrix.
3.6. Evaluation of Membranes Resistance, Antifouling Property and Cleaning Efficiency
Examination of other membrane parameters related to antifouling properties and cleaning efficiencies such as reversible and irreversible resistances, relative flux reduction, and flux reversal ratio were depicted in Figure 9 and Figure 10. The results show that the addition of cationic M101 reduce the irreversible fouling resistance and the flux drop of the membranes. Therefore, it can be expected that in the long-term tests, dye solution permeates for the membranes fabricated with up to 15% cationic MOF as filler is associated with higher stability and was at a high level for a more extended period. Moreover, the membrane constructed with the initial MOF had more irreversible resistance and a lower flux ratio than that of modified positive MOF.
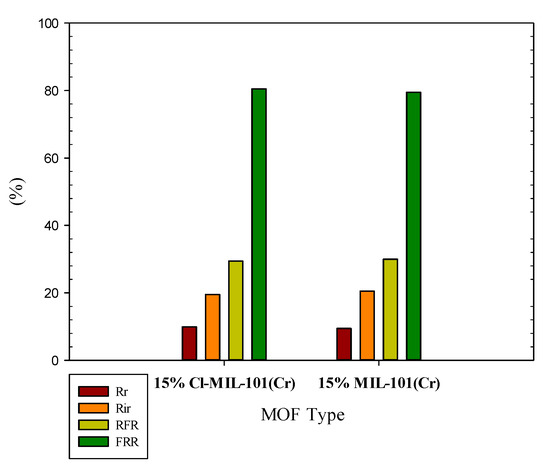
Figure 9.
Comparison of resistances, relative flux reduction (RFR) and water recovery ratio (FRR) for membranes containing 15% of M101Cl with M101.
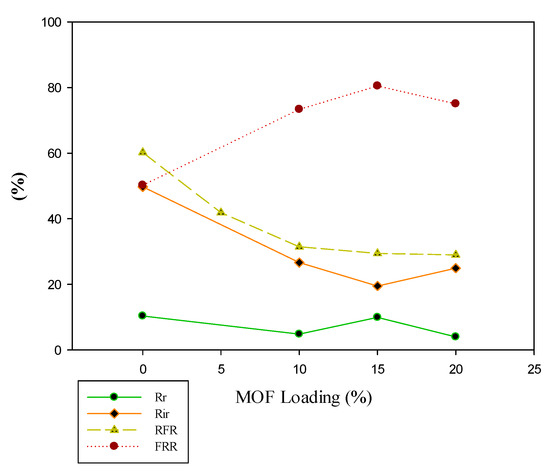
Figure 10.
Resistances, relative flux reduction (RFR) and water recovery ratio (FRR) for membranes with different M101Cl loading.
It is clear that the dye rejection increased up to 99.08% for PM0.8-15 with MOF loading until 15%. It also projected acceptable permeability (approximately 18.90 L/m2·h), high rejection, and low fouling resistance, making it the most ideal membrane fabricated in this study. This membrane (P0.8-15) rejected 30.41% of AlCl3 polyvalent ion from an aqueous solution. According to the results, the performance of the membrane made in this study is competitive with the results of many studies in the field of dye separation and can be used in dye purification in industry [51,52].
4. Conclusions
Anion stripped M101 was placed into the membrane skin layer due to positive charge to repel the cationic dye molecules. M101 and M101Cl were added to the PVA matrix at different content. The FESEM results show that the MOF particles’ morphology does not change before and after anion stripping, that it was well distributed within the PVA matrix on the surface of the polysulfone membrane. The membrane of M101Cl was observed, indicating the membrane had a better performance than its initial state, with a maximum efficiency at 15% filler content. The highest MB rejection (99.08%) is concerned with 15% filler content while filler contents made dye rejection decrease higher than 15%, due to the gaps between MOF particles and the polymer. Hence, the results present the best permeation flux of the dye solution at PM-0.8-10; however, the optimal conditions of film composition obtained at PM-0.8-15 appear to be due to its low irreversible fouling resistance and higher flux return ratio.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/coatings12081148/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.G.; methodology, M.M.G. and A.B.; software, A.B.; validation, M.M.G. and A.B.; formal analysis, M.M.G. and A.B.; investigation, A.B.; resources, A.B.; data curation, M.M.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B.; writing—review and editing, A.B.; visualization, M.M.G.; supervision, M.M.G.; project administration, M.M.G.; funding acquisition, M.M.G. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Santos, D.H.; Duarte, J.L.S.; Tavares, M.G.R.; Tavares, M.G.; Friedrich, L.C.; Meili, L.; Pimentel, W.R.O.; Tonholo, J.; Zanta, C. Electrochemical degradation and toxicity evaluation of reactive dyes mixture and real textile effluent over DSA® electrodes. Chem. Eng. Proc. Proc. Int. 2020, 153, 107940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.Q.Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.Q. Fabrication of Chitosan Nanofiltration Membranes by the Film Casting Strategy for Effective Removal of Dyes/Salts in Textile Wastewater. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, X.; Zou, J.; Guo, H. N-TiO2-Coated SiC Foam for the Treatment of Dyeing Wastewater under Blue Light LED Irradiation. Coatings 2022, 12, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keharia, H.; Madamwar, D. Textile and Dye Effluent. In Concise Encyclopedia of Bioresource Technology; Pandey, A., Ed.; The Haworth Press: Binghamton, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Luna de, L.A.V.; da Silva, T.H.G.; Nogueirab, R.F.P.; Kummrow, F.; Umbuzeiro, G.A. Aquatic toxicity of dyes before and after photo-Fenton treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punzi, M.; Nilsson, F.; Anbalagan, A.; Svensson, B.M.; Jönsson, K.; Mattiasson, B.; Jonstrup, M. Combined anaerobic–ozonation process for treatment of textile wastewater: Removal of acute toxicity and mutagenicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 292, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.K.; Du, K.F.; Zhao, Z.M. Fabrication of spherical cellulose/carbon tubes hybrid adsorbent anchored with welan gum polysaccharide and its potential in adsorbing MB. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200–202, 452–458. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, V.; Masiello, D.; Trifuoggi, M.; Serio, M.D.; Tesser, R. Design of an adsorption column for methylene blue abatement over silica: From batch to continuous modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing-Jyh, L.; Keng-Ta, L.; Yi-Ming, K. Cheng-Hsien Tsai, Preparation of High-Transparency, Superhydrophilic Visible Photo-Induced Photocatalytic Film via a Rapid Plasma-Modification Process. Coatings 2021, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alardhi, S.M.; Albayati, T.M.; Alrubaye, J.M. A hybrid adsorption membrane process for removal of dye from synthetic and actual wastewater. Chem. Eng. Proc. Proc. Int. 2020, 157, 108113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Moutinho, J.; Shao, J.; Zydney, A.L.; He, Y. Recovery of small dye molecules from aqueous solutions using charged ultrafiltration membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 284, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Improved salts transportation of a positively charged loose nanofiltration membrane by introduction of poly(ionic liquid) functionalized hydrotalcite nanosheets. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3292–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ji, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.R. Coordination-driven in situ self-assembly strategy for the preparation of metal-organic framework hybrid membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9775–9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafiz, M.; Hawari, A.H.; Alfahel, R.; Hassan, M.K.; Altaee, A. Comparison of nanofiltration with reverse osmosis in reclaiming tertiary treated municipal wastewater for irrigation purposes. Membranes 2021, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, E. Chapter 15—Nanofiltration. In Basic Equations of Mass Transport through a Membrane Layer, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 417–428. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Ji, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.R. One-step self-assembly fabrication of amphiphilic hyperbranched polymer composite membrane from aqueous emulsion for dye desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) recent contributions to engineering and medicine. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Luo, C.; Luo, F. Preparation and properties of self-healable and conductive PVA-agar hydrogel with ultra-high mechanical strength. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 124, 109465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdoğan, A.; Aksakal, B.; Yargi, O. Film formation and mechanical properties of an opaque titanium dioxide and transparent polyvinyl alcohol composite films. Polym. Compos. 2019, 41, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökpinar, S.; Ernst, S.J.; Hastürk, E.; Möllers, M.; Aita, I.E.; Wiedey, R.; Tannert, N.; Nießing, S.; Abdpour, S.; Schmitz, A.; et al. Air-Con metal–organic frameworks in binder composites for water adsorption heat transformation systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 21493–21503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, B.U.; Aytac, A. Development and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol) and casein blend films. Polym. Int. 2019, 68, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkowska, E.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Marais, S.; Kujawa, J.; Kujawski, W. Chemically and thermally cross-linked PVA-based membranes: Effect on swelling and transport behavior. Polymers 2019, 11, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zornoz, B.; Tellez, C.; Coronas, J.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Metal-organic framework based mixed matrix membranes: An increasingly important field of research with a large application potential. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 166, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariazadeh, M.; Farashi, Z.; Azizi, N.; Khajoue, M. Influence of functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles on the morphology and CO2/CH4 separation efficiency of Pebax-based mixed-matrix membranes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, W.K.; Chiang, K.Y. Silica applied as mixed matrix membrane inorganic filler for gas separation: A review. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nematollahi, M.H.; Saeedi Dehaghani, A.H.; Pirouzfar, V.; Akhondi, E. Mixed Matrix Membranes Comprising PMP Polymer with Dispersed Alumina Nanoparticle Fillers to Separate CO2/N2. Macromol. Res. 2016, 24, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, F.A.; Mustafa, Y.H.; Muhammed, O.A.; Abdulaziz, K.A.; Mohammed, R.K. Electrospun Bilayer PAN/Chitosan Nanofiber Membranes Incorporated with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption. Coatings 2020, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, W.; Li, J.; Sun, F.; Dong, W. Ultrasonication favors TiO2 nano-particles dispersion in PVDF ultrafiltration membrane to effectively enhance membrane hydrophilicity and anti-fouling capability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 9503–9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castruita-de León, G.; Yeverino-Miranda, C.Y.; Montes-Luna, A.d.J.; Meléndez-Ortiz, H.I.; Alvarado-Tenorio, G.; García-Cerda, L.A. Amine impregnated natural zeolite as filler in mixed matrix membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, N.; Ji, S.; Yan, H.; Zhang, G. Nanodisperse ZIF-8/PDMS hybrid membranes for biobutanol permselective pervaporation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 20947–20957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fynn, W.; Prokopios, G.; Sergey, S.; Volkan, F.; Torsten, B.; Volker, A. Development and Characterization of Defect-Free Matrimid® Mixed-Matrix Membranes Containing Activated Carbon Particles for Gas Separation. Polymers 2018, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; She, Q.; Huo, F.; Tang, C.Y. Metal-organic framework-based porous matrix membranes for improving mass transfer in forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Davies, R.P.; Braddock, D.C.; Livingston, A.G. Improving the permeance of hybrid polymer/metal-organic framework (MOF) membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN)—Development of MOF thin films via interfacial synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9668–9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorribas, S.; Gorgojo, P.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.; Livingston, A.G. High flux thin film nanocomposite membranes based on metal-organic frameworks for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15201–15208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echaide-Górriz, C.; Sorribas, S.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. MOF nanoparticles of MIL- 68(Al), MIL-101(Cr) and ZIF-11 for thin-film nanocomposite organic solvent nanofiltration membranes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 90417–90426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.T.; Space, B.; Chang, Z.; Bu, X.H. Metal-organic materials with triazine-based ligands: From structures to properties and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213518. [Google Scholar]
- Férey, G.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Dutour, J.; Surble’, S.; Margiolaki, I. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science 2005, 309, 2040–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Jeremias, F.; Boldog, I.; Nguyen, B.; Henninger, S.K.; Janiak, C. High-Yield, Fluoride-Free and Large-Scale Synthesis of MIL-101(Cr)). Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 16791–16801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasinathan, P.; Seo, Y.K.; Shim, K.E.; Hwang, Y.K.; Lee, U.H.; Hwang, D.W.; Hong, D.Y.; Halligudi, S.B.; Chang, J.S. Effect of diamine in amine-functionalized MIL-101 for knoevenagel condensation. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 2073–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Yue, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Lin, Y.; Pan, Y.; Sun, D.; Liu, Y. The encapsulation of POM clusters into MIL-101(Cr) at molecular level: LaW10O36@MIL-101(Cr), an efficient catalyst for oxidative desulfurization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 311, 110694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, J.X.; Ding, L.L.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.M.; Han, Z.B. Palladium nanoparticles encapsulated in the MIL-101-Catalyzed one-pot reaction of alcohol oxidation and aldimine condensation. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 13586–13593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Kudla, R.A.; Zuo, F.; Zhao, X.; Mueller, L.J.; Bu, X.; Feng, P. Anion stripping as a general method to create cationic porous framework with mobile anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7579–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, C.; Qin, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, P.; Ye, F. Preparation of cationic MOFs with mobile anions by anion stripping to remove 2,4-D from water. Materials 2017, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebedev, O.I.; Millange, F.; Serre, C.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Férey, G. First direct imaging of giant pores of the Metal-organic framework MIL-101. Chem. Mater. 2013, 17, e6525–e6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgın, S.; Salgın, U.; Tuzlalı, N. Determination of correct zeta potential of polyether sulfone membranes using CLC and AGC: Ionic environment effect. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 26031–26040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutharasi, Y.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Arumugham, T.; Banat, F.; Kapavarapu, M.S.R.S. Antifouling and photocatalytic properties of 2-D Zn/Al layered double hydroxide tailored low-pressure membranes. Chem. Eng. Proc. Proc. Int. 2020, 158, 108191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.R.; Isloor, A.M.; Bhat, U.K.; Ismail, A.F.; Obaidd, A.; Funde, H.K. Preparation and performance studies of polysulfone-sulfated nano-titania (S-TiO2) nanofiltration membranes for dye removal. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yu, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, A.; Dou, Z.; Yang, Y. A low cytotoxic cationic metal-organic framework carrier for controllable drug release. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5679–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, P.L.; Bourrelly, S.; Serre, C.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Hamon, L.; Weireld, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Hong, D.Y.; Hwang, Y.K.; et al. High uptakes of CO2 and CH4 in mesoporous metal-organic frameworks MIL-100 and MIL-101. Langmuir 2008, 24, 7245–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hu, Q.; Gao, L.; Hao, Q.; Wang, P.; Qin, D. Adsorption characteristics of metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr) towards sulfamethoxazole and its persulfate oxidation regeneration. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 27623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelhamid, A.E.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Khalil, A.M. Polysulfone nanofiltration membranes enriched with functionalized graphene oxide for dye removal from wastewater. J. Polym. Eng. 2020, 40, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, K.; Zhao, C. Polyvinylidene fluoride membrane modified by tea polyphenol for dye removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).