Wood-Based Composites with High Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness and Ultra-Low Reflection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sample
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
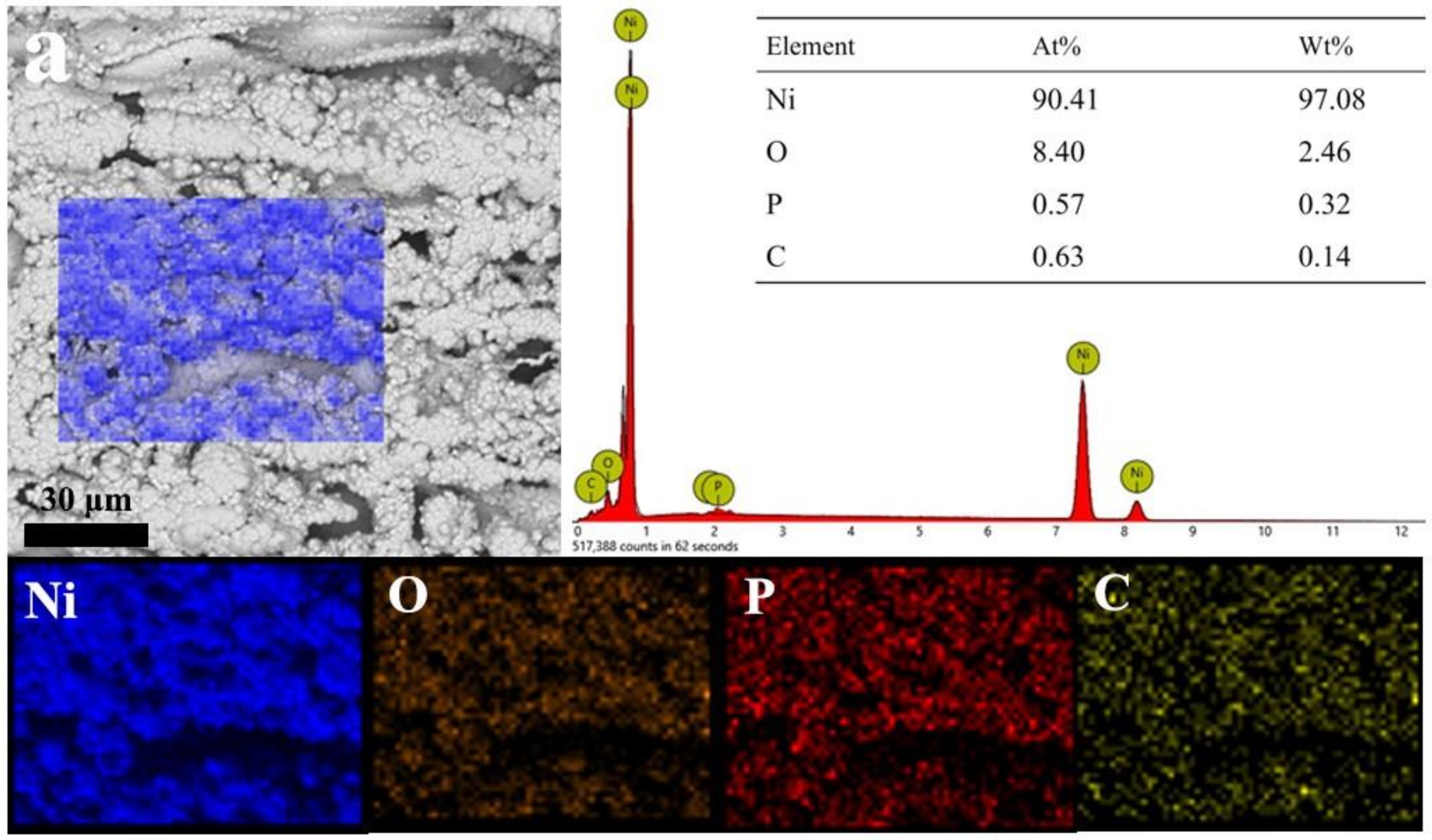
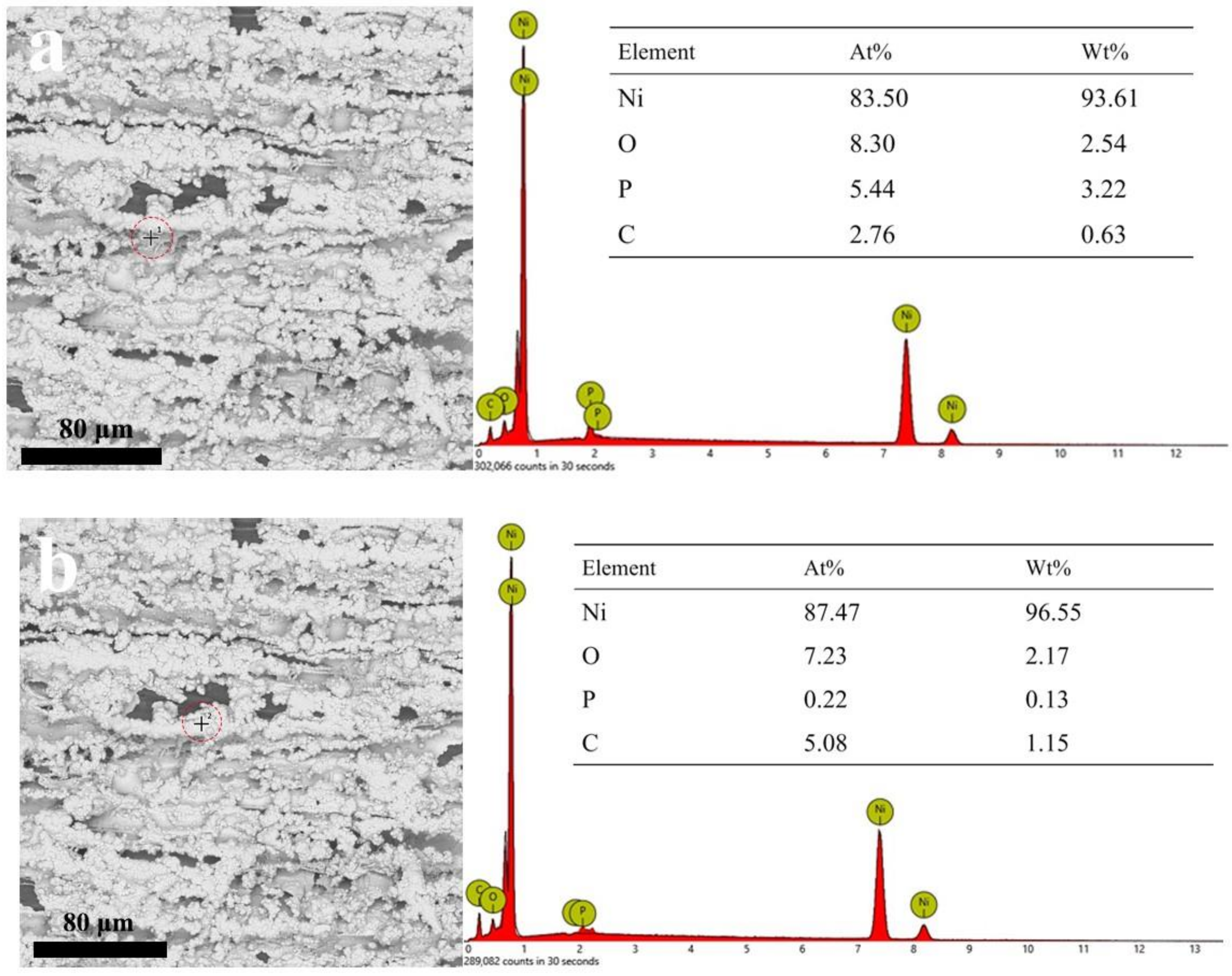
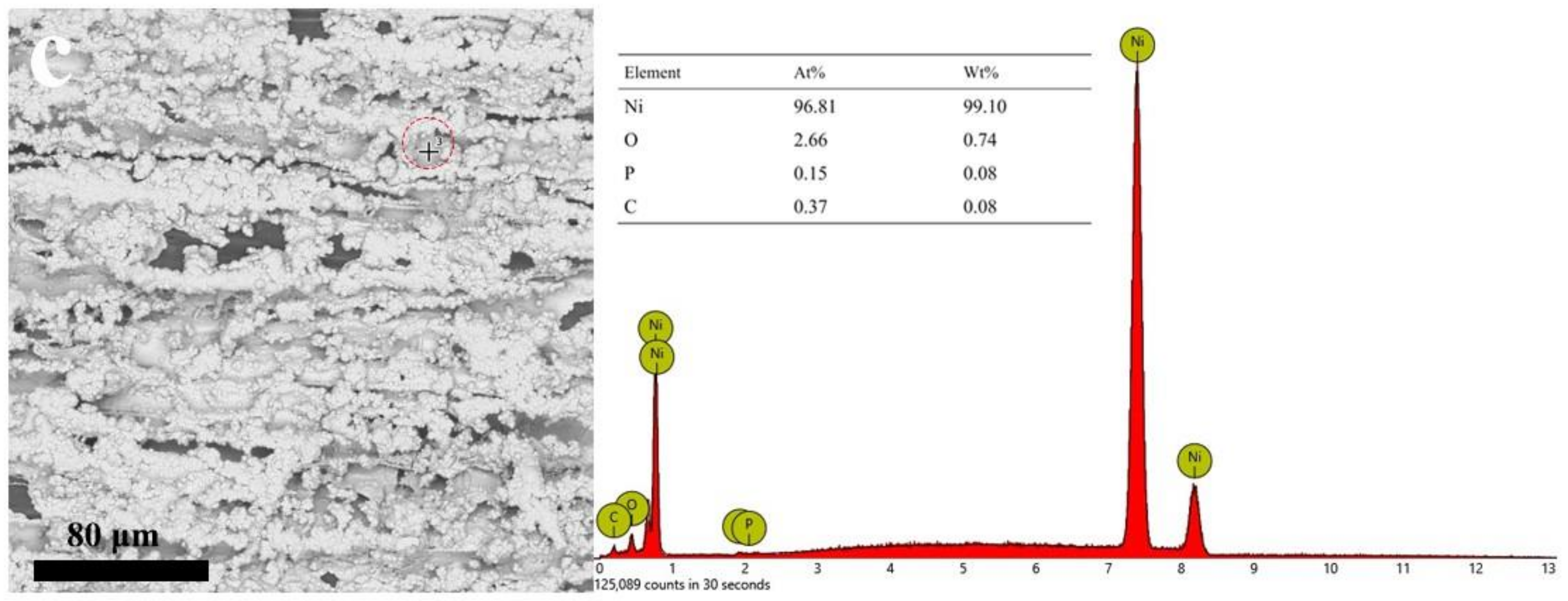
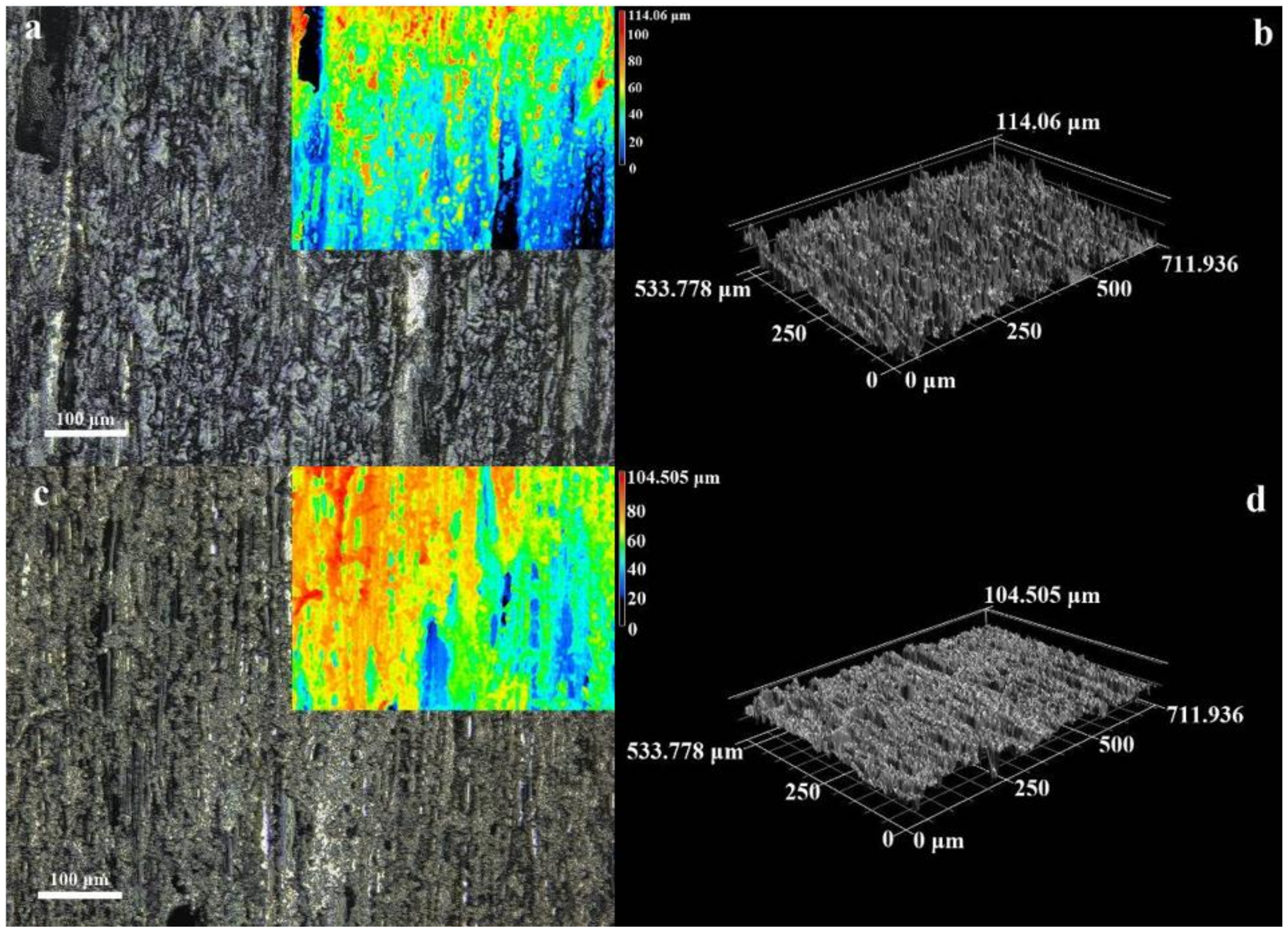
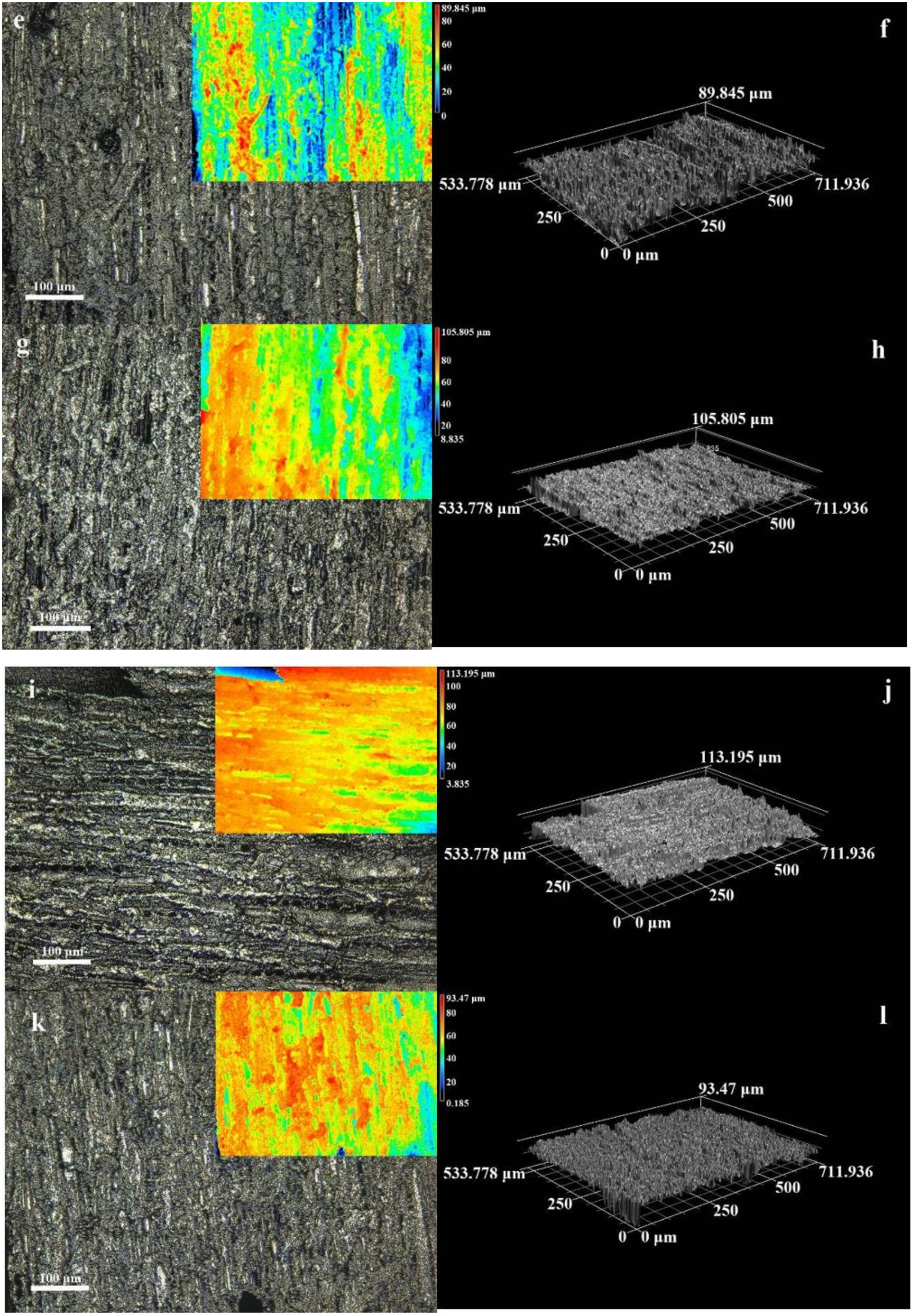
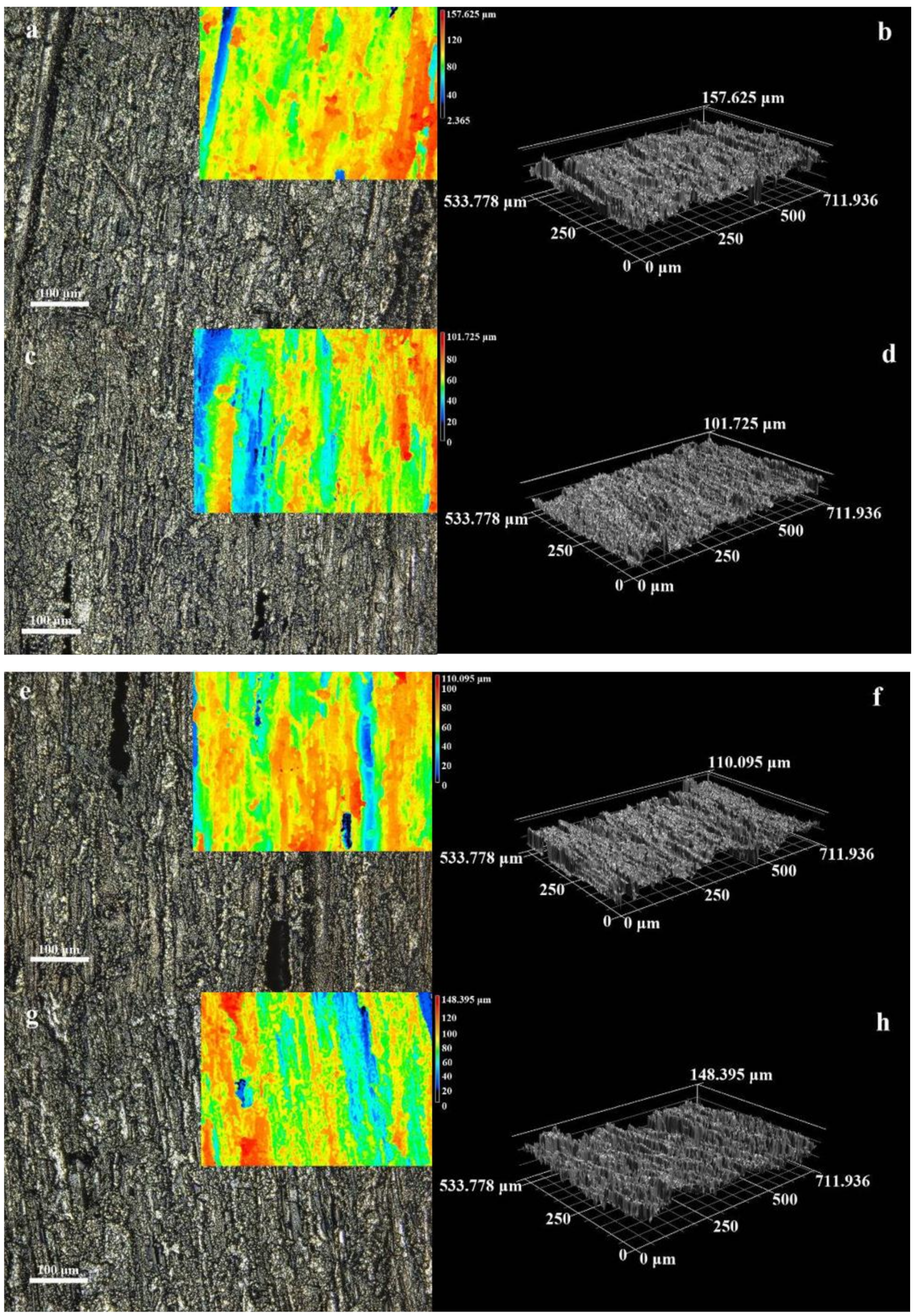
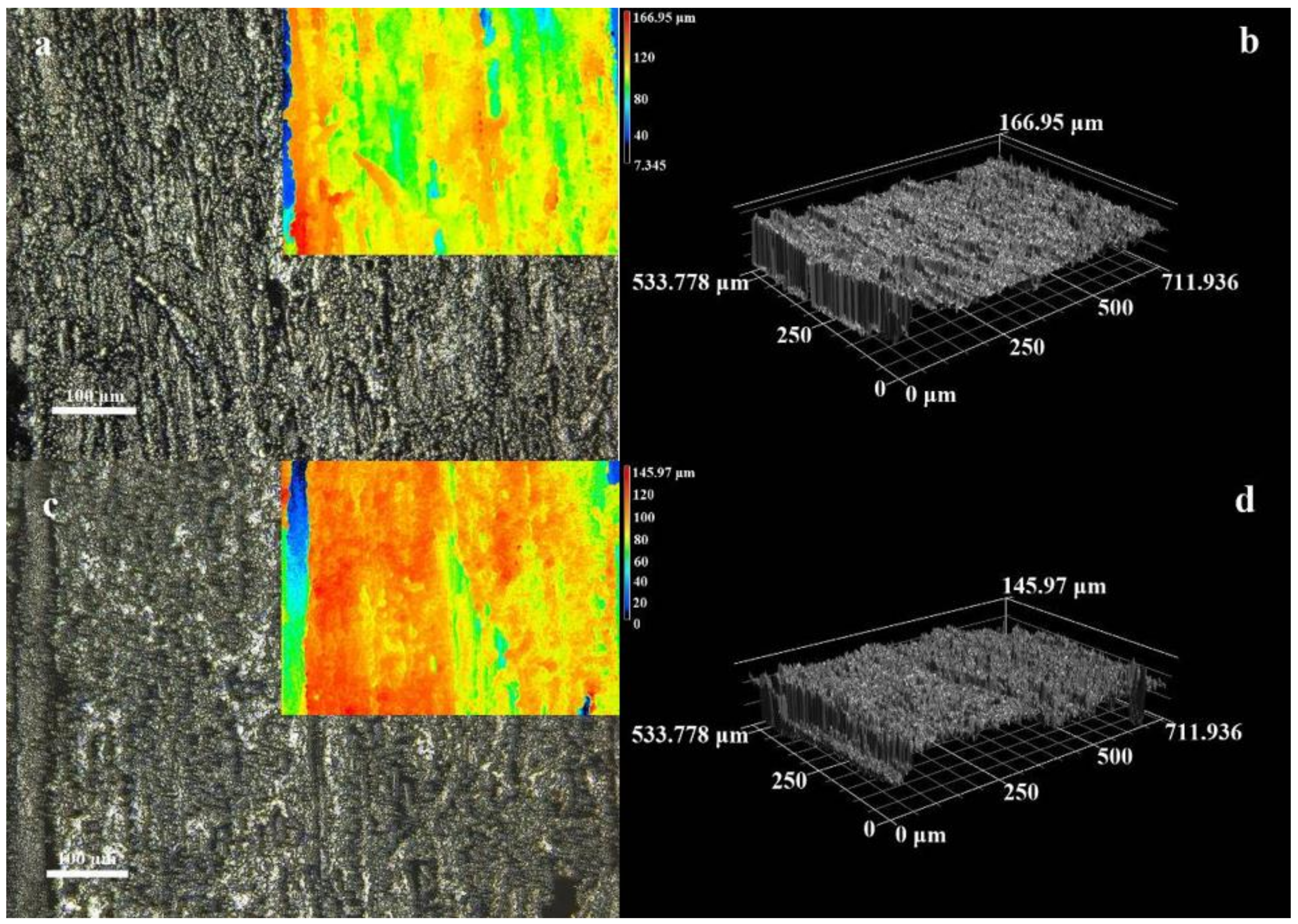
3.1. Microstructure and Morphology
3.2. Micromorphology of Composite
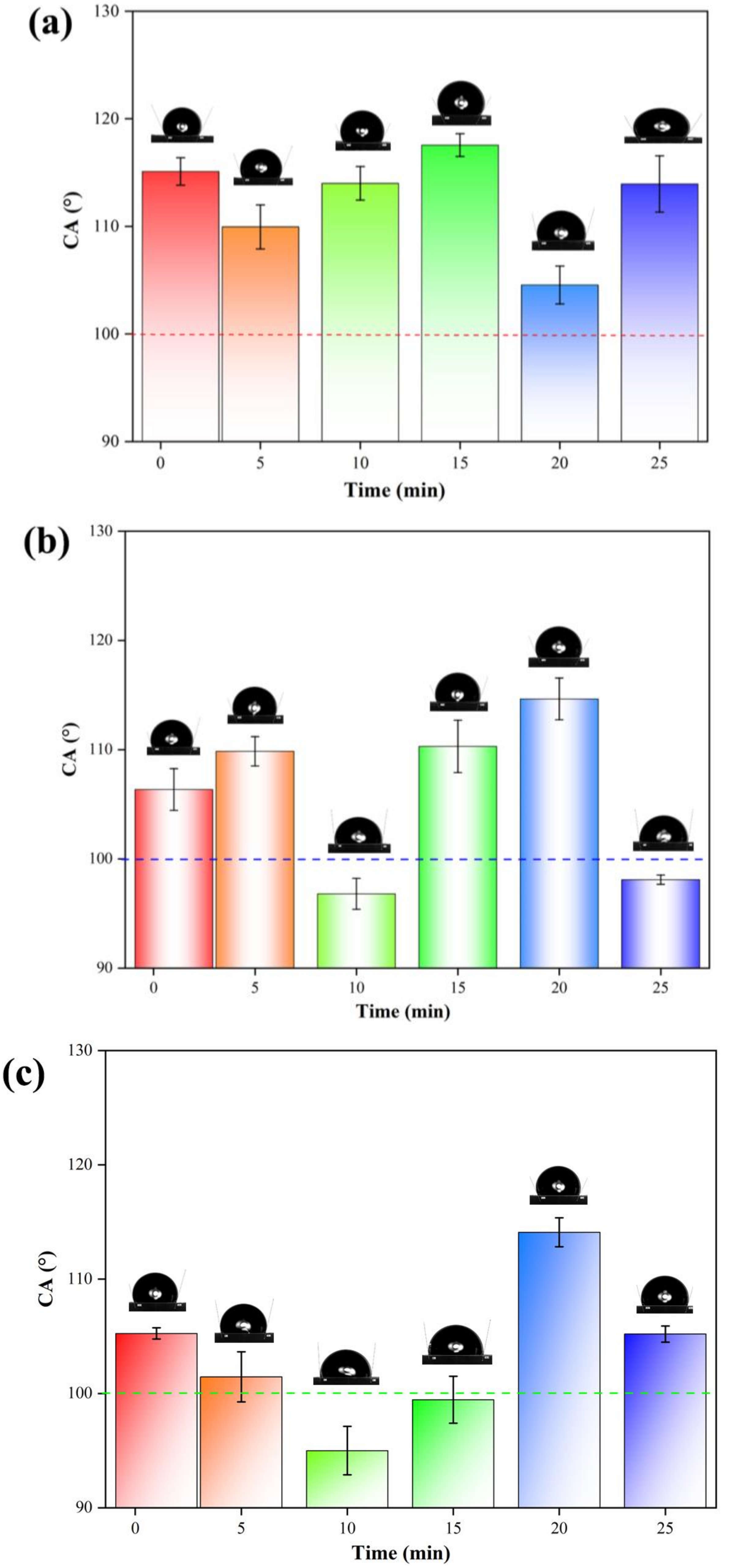
3.3. Analysis of Hydrophobic Performance
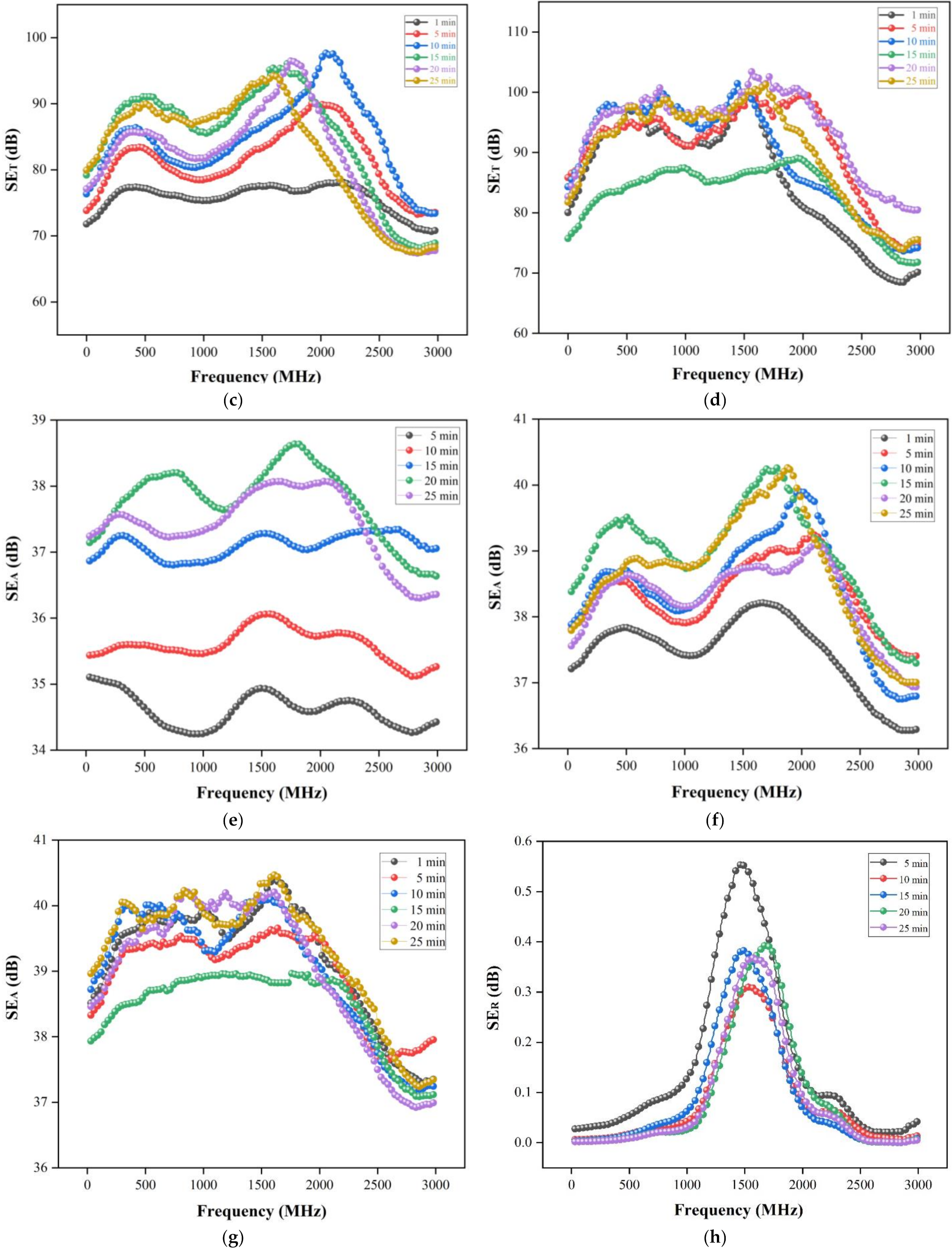
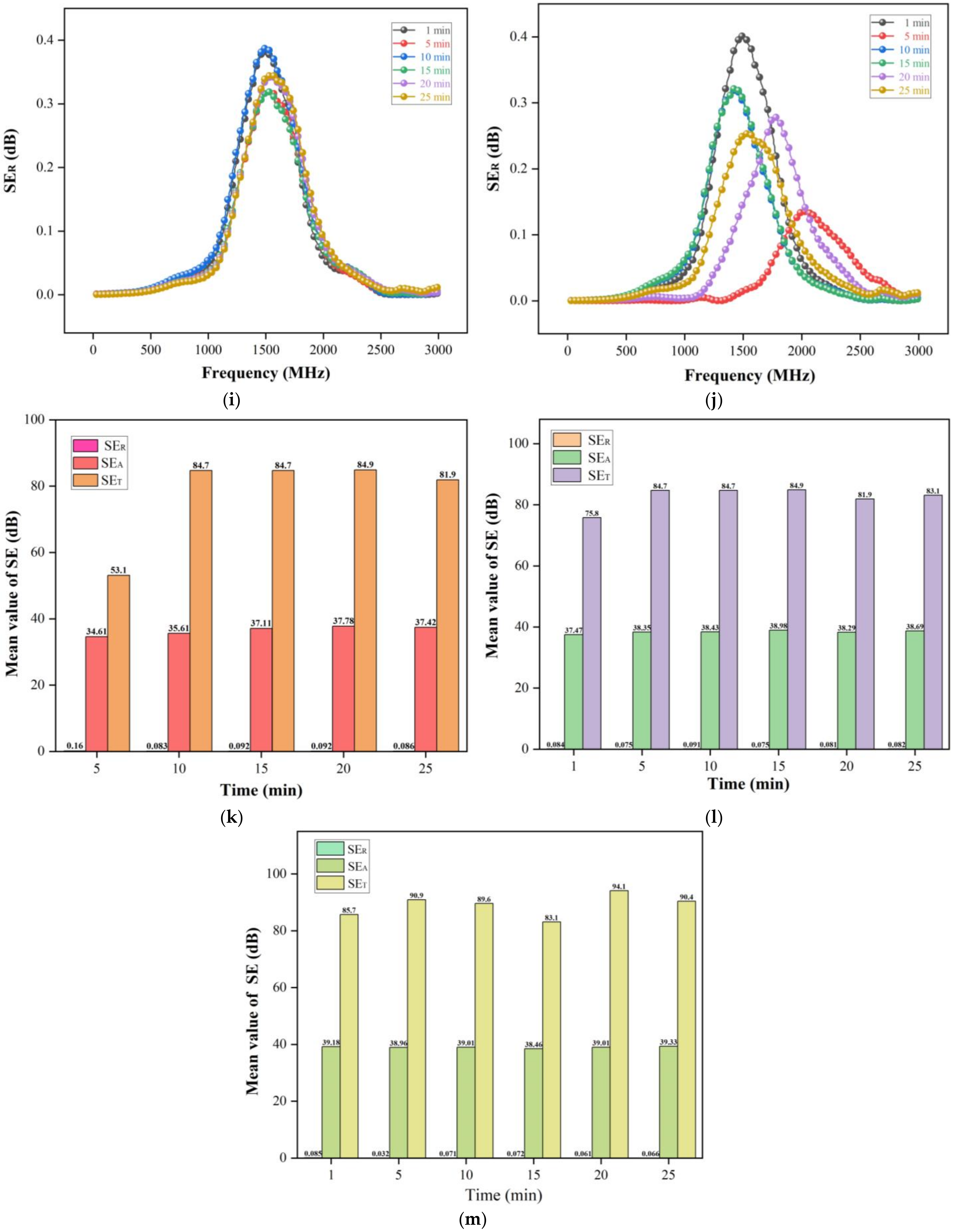
3.4. Electrical Conductivity and EMI Shielding Performance
3.5. Electromagnetic Shielding Mechanism of Wood-Based Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Mahdi, H.; Biao, Z. Layered Foam/Film Polymer Nanocomposites with Highly Efficient EMI Shielding Properties and Ultralow Reflection. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 313–330. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Tai, N.H. Carbon Materials and Their Composites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness in X-Band. Carbon 2019, 152, 159–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.F.; Yin, D.W.; Yu, X.F. Multilayer-structured wood electroless Cu-Ni composite coatings for electromagnetic interference shielding. Coatings 2020, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.W.; Liu, R.T.; Cheng, X.J. Preparation and characterization of electromagnetic shielding composites based on graphene nanosheets-loaded nonwoven fabric. Coatings 2021, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, R. Lightweight and Easily Foldable MCMB-MWCNTs Composite Paper with Exceptional Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10600–10608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parit, M.; Prather, C.; Adams, M. Polypyrrole and cellulose nanofiber based composite films with improved physical and electrical properties for electromagnetic shielding applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, C.K.; Mahendra, K.; Madhukar, B.S. Incorporation of graphite into iron decorated polypyrrole for dielectric and EMI shielding applications. Synth. Met. 2020, 267, 116450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, M. Lightweight, thermally insulating and stiff carbon honeycomb induced graphene composite foams with a horizontal laminated structure for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2017, 123, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipa, M.; Gusmão, R. Recent advances in the electromagnetic interference shielding of 2D materials beyond graphene. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 3048–3071. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Sabet, S.; Pilla, S. Polydopamine coating improves electromagnetic interference shielding of delignified wood derived carbon scaffold. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 10915–10925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Song, Y.J.; Gao, T. Lightweight and hydrophobic three-dimensional wood-derived anisotropic magnetic porous carbon for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40802–40814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, M. Stiff, Thermally Stable and Highly Anisotropic Wood-Derived Carbon Composite Monoliths for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21371–21381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.B.; Qiu, H.; Song, P. Ultra-light MXene Aerogel/Wood-Derived Porous Carbon Composites with Wall-Like “Mortar/Brick” Structures for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Voit, B.; Qi, H.S. Multifunctional cellulose/rGO/Fe3O4 composite aerogels for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22088–22098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, F.; Alhabeb, M.; Hatter, C.B. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 2016, 353, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.P.; Xu, C.; Ma, C.Q. Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Jin, H.; Chen, M. Lightweight and anisotropic porous MWCNT/WPU composites for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liao, X.; Li, J. Light-weight and flexible silicone rubber/MWCNTs/Fe3O4 nanocomposite foams for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 181, 107670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Hu, L.; Li, Y. Co3O4 Nanocages for High-Performance Anode Material in LithiumIon Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 7227–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Mei, X.; Liang, L. Structure-function integrated poly (aryl ether ketone)-grafted MWCNTs/poly (ether ether ketone) composites with low percolation threshold of both conductivity and electromagnetic shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 217, 109032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Chang, S.; Song, Y.F. Novel PVP-encapsulated CoFe2O4/rGO composites with controllable electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Lei, Z.W.; Ma, X.D. A lightweight MXene-Coated nonwoven fabric with excellent flame Retardancy, EMI Shielding, and Electrothermal/Photothermal conversion for wearable heater. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Zhang, X.N.; Ding, Y.Q. Multifunctional carbon fiber@NiCo/polyimide films with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhou, C.G. Lightweight and robust Carbon nanotube/Polyimide foam for efficient and heat-resistant electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 8704–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Zhu, H.; Gao, J. Asymmetric conductive polymer composite foam for absorption dominated ultra-efficient electromagnetic interference shielding with extremely low reflection characteristics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 9146–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, G. Gradient structure design of flexible waterborne polyurethane conductive films for ultraefficient electromagnetic shielding with low reflection characteristic. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19143–19152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, X.; Liang, S. 2D Carbide MXene Ti2CTx as a novel high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding material. Carbon 2019, 146, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chen, M.; He, G. Stretchable microwave absorbing and electromagnetic interference shielding foam with hierarchical buckling induced by solvent swelling. Carbon 2020, 157, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.X.; Niu, H.T. A Waterborne Coating System for Preparing Robust, Self-healing, Superamphiphobic Surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fan, S.; Li, Y. Copper nanowires/thermally annealed graphene aerogel/epoxy nanocomposites with excellent thermal conductivities and outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 128, 105670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.J.; Zhao, H.H.; Zhang, J. Fabrication and electromagnetic interference shielding performance of open-cell foam of a Cu-Ni alloy integrated with CNTs. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J. Multifunctional and corrosion resistant poly (phenylene sulfide)/Ag composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 129052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, T. Sulfur-doped wood-derived porous carbon for optimizing electromagnetic response performance. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 16084–16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Feng, J. Preparation of Thermally Conductive Polymer Composites with Good Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Efficiency Based on Natural Wood-Derived Carbon Scaffolds. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6259–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wu, F. Microporous Polythiophene (MPT)-Guest Complex Derived Magnetic Metal Sulfides/Carbon Nanocomposites for Broadband Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 100, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Han, X. MXene/wood-derived hierarchical cellulose scaffold composite with superior electromagnetic shielding. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X. An Angle-Insensitive Electromagnetic Absorber Enabling a Wideband Absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 113, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. Lightweight Fe3C@Fe/C Nanocomposites Derived from Wasted Cornstalks with High Efficiency Microwave Absorption and Ultrathin Thickness. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ma, Z.; Lan, D. Synergistic Polarization Loss of MoS2-Based Multiphase Solid Solution for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Huang, Y.; Deng, C. Hierarchically Porous Biochar Derived from Orthometric Integration of Wooden and Bacterial Celluloses for High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 218, 109184. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, A.; Ren, W.; Yang, Y. Multilayer WPU conductive composites with controllable electro-magnetic gradient for absorption-dominated electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 129, 105692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Materials | Density (g/cm3) | EMI Shielding Performance (SE) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni/PC | 0.288 | 50.8 | [11] |
| WCM@N-G@AgNWs | - | 60 | [12] |
| MXene aerogel/wood | - | 69.4 | [13] |
| Cellulose/rGO/Fe3O4 aerogels | - | 52.4 | [14] |
| Ti3C2Tx film | - | 92 | [15] |
| Graphene/PDMS | 0.06 | 30 | [16] |
| MWCNT/WPU | 0.02 | 20 | [17] |
| MWCNTs/Fe3O4 foam | 0.48 | 27.5 | [18] |
| Ni/poplar/Ni composite | 0.618 | 94.1 | This work |
| Type (min) | Wood Thickness (μm) | Thickness of Composite (μm) | Coatings Thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–1 | 437 | 465 | 28 |
| 1–5 | 323 | 378 | 55 |
| 1–10 | 269 | 326 | 57 |
| 1–15 | 303 | 368 | 65 |
| 1–20 | 219 | 290 | 71 |
| 1–25 | 257 | 338 | 81 |
| 2–20 | 322 | 430 | 108 |
| 3–5 | 296 | 432 | 136 |
| Type | Area 1 (μm) | Area 2 (μm) | Area 3 (μm) | Area 4 (μm) | Area 5 (μm) | Mean Value (μm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 min | 1 deposition Ni | 13.3 | 18.34 | 12.59 | 12.92 | 15.38 | 14.51 |
| 2 deposition Ni | 11.16 | 12.47 | 10.02 | 12.7 | 15.36 | 12.34 | |
| 3 deposition Ni | 14.98 | 10.82 | 11.37 | 9.58 | 13.95 | 12.14 | |
| 5 min | 1 deposition Ni | 11.66 | 18.69 | 10.52 | 7.16 | 9.72 | 11.55 |
| 2 deposition Ni | 14.17 | 13.01 | 8.21 | 10.96 | 12.89 | 11.85 | |
| 3 deposition Ni | 15.5 | 13.1 | 16.29 | 11.16 | 14.78 | 14.17 | |
| 10 min | 1 deposition Ni | 11.93 | 8.61 | 13.06 | 8.14 | 18.41 | 12.03 |
| 2 deposition Ni | 12.68 | 9.46 | 14.44 | 11.68 | 8.45 | 11.34 | |
| 3 deposition Ni | 21.01 | 15.87 | 20.51 | 22.79 | 12.67 | 18.57 | |
| 15 min | 1 deposition Ni | 14.35 | 16.64 | 7.62 | 9.26 | 9 | 11.37 |
| 2 deposition Ni | 20.17 | 15.53 | 13.47 | 12.87 | 10.85 | 14.58 | |
| 3 deposition Ni | 11.75 | 12.89 | 22.59 | 11.91 | 10.79 | 13.99 | |
| 20 min | 1 deposition Ni | 12.49 | 8.38 | 8.17 | 8.63 | 14.02 | 10.34 |
| 2 deposition Ni | 20.5 | 17.23 | 19.99 | 9.79 | 12.86 | 16.07 | |
| 3 deposition Ni | 13.5 | 15.84 | 14.47 | 14.59 | 14.89 | 14.66 | |
| 25 min | 1 deposition Ni | 8.52 | 7.46 | 7.52 | 8.06 | 10.16 | 8.34 |
| 2 deposition Ni | 13.73 | 13.98 | 13.97 | 15.3 | 13.12 | 14.02 | |
| 3 deposition Ni | 21.97 | 16.34 | 13.16 | 14.49 | 9.45 | 15.08 | |
| Type | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|
| 1–1 | 116.0 |
| 1–5 | 111.4 |
| 1–10 | 115.1 |
| 1–15 | 118.3 |
| 1–20 | 105.8 |
| 1–25 | 115.8 |
| 2–1 | 105.0 |
| 2–5 | 108.9 |
| 2–10 | 97.8 |
| 2–15 | 108.6 |
| 2–20 | 116.0 |
| 2–25 | 98.4 |
| 3–1 | 105.6 |
| 3–5 | 103.0 |
| 3–10 | 96.5 |
| 3–15 | 100.9 |
| 3–20 | 115.0 |
| 3–25 | 105.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Dai, M.; Zhao, H.; Hu, N.; Guo, Q.; Huang, J. Wood-Based Composites with High Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness and Ultra-Low Reflection. Coatings 2022, 12, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12081117
Pan Y, Dai M, Zhao H, Hu N, Guo Q, Huang J. Wood-Based Composites with High Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness and Ultra-Low Reflection. Coatings. 2022; 12(8):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12081117
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yanfei, Mayin Dai, Hongwei Zhao, Nianguang Hu, Qiang Guo, and Jintian Huang. 2022. "Wood-Based Composites with High Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness and Ultra-Low Reflection" Coatings 12, no. 8: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12081117
APA StylePan, Y., Dai, M., Zhao, H., Hu, N., Guo, Q., & Huang, J. (2022). Wood-Based Composites with High Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness and Ultra-Low Reflection. Coatings, 12(8), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12081117






