Geometric Tuning for Enhanced Moisture-Driven Electricity Generation Enabled by Graphene-Oxide Flakes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of as-Prepared GO Powder
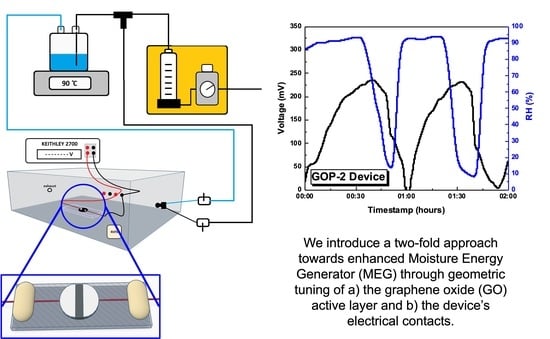
3.2. Characterisation of GO-Based MEGs Devices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogdakis, K.; Karakostas, N.; Kymakis, E. Up-Scalable Emerging Energy Conversion Technologies Enabled by 2D Materials: From Miniature Power Harvesters towards Grid-Connected Energy Systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3352–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, B.; Bocquet, M.-L.; Vuilleumier, R. Versatile Electrification of Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials in Water. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, J.; Xu, Y.; Fei, W.; Xue, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Guo, W. Emerging Hydrovoltaic Technology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Duan, Z.; Qi, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Yao, W. Harvesting Environment Energy from Water-Evaporation over Free-Standing Graphene Oxide Sponges. Carbon 2019, 148, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhou, J.; Fang, S.; Guo, W. Hydrovoltaic Energy on the Way. Joule 2020, 4, 1852–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; He, P.; Shao, Z.; Li, Z.; Kim, H.; Yao, A.M.; Peng, Y.; Xu, R.; Ahn, C.H.; Lee, S.-W.; et al. Moisture-Induced Autonomous Surface Potential Oscillations for Energy Harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Xiao, M.; Xiao, Y.; Zou, G.; Hu, L.; Zhao, B.; Liu, L.; Duley, W.W.; Zhou, Y.N. Self-Powered, Rapid-Response, and Highly Flexible Humidity Sensors Based on Moisture-Dependent Voltage Generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14249–14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Yu, Z.G.; Qu, H.; Sun, W.; Yang, J.; Suresh, L.; Zhang, X.; Koh, J.J.; Tan, S.C. An Asymmetric Hygroscopic Structure for Moisture-Driven Hygro-Ionic Electricity Generation and Storage. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, N.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. Graphene Fibers with Predetermined Deformation as Moisture-Triggered Actuators and Robots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10482–10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Chen, Z.-D.; Han, D.-D.; Mao, J.-W.; Ma, J.-N.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Sun, H.-B. Bioinspired Soft Robots Based on the Moisture-Responsive Graphene Oxide. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescetelli, S.; Agresti, A.; Viskadouros, G.; Razza, S.; Rogdakis, K.; Kalogerakis, I.; Spiliarotis, E.; Leonardi, E.; Mariani, P.; Sorbello, L.; et al. Integration of Two-Dimensional Materials-Based Perovskite Solar Panels into a Stand-Alone Solar Farm. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimanolis, K.; Rogdakis, K.; Tsikritzis, D.; Tzoganakis, N.; Tountas, M.; Krassas, M.; Bellani, S.; Najafi, L.; Martín-García, B.; Oropesa-Nuñez, R.; et al. Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells with Enhanced Lifetime and Thermal Stability Enabled by a Metallic Tantalum Disulfide Buffer Layer. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 3124–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.; Rogdakis, K.; Kymakis, E. Beneficial Impact of Materials with Reduced Dimensionality on the Stability of Perovskite-Based Photovoltaics. J. Phys. Energy 2019, 1, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, S.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Abrha, H.; Liu, M.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Liu, X. Graphene Oxide as a Versatile Platform for Emerging Hydrovoltaic Technology. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 18451–18469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Foller, T.; Jin, X.; Musso, T.; Kumar, P.; Joshi, R. Understanding Water Transport through Graphene-Based Nanochannels via Experimental Control of Slip Length. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, F.; Patterson, R.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, T.; Hu, L.; Wu, T.; Joshi, R.; Li, M.; et al. Boosting Moisture Induced Electricity Generation from Graphene Oxide through Engineering Oxygen-Based Functional Groups. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhekar, N.V.; Ramasubramaniam, A.; Ruoff, R.S.; Shenoy, V.B. Hydrogen Bond Networks in Graphene Oxide Composite Paper: Structure and Mechanical Properties. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2300–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, J.I.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Graphene Oxide Dispersions in Organic Solvents. Langmuir 2008, 24, 10560–10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shao, C.; Wang, B.; Chen, N.; Jin, H.; Cheng, H.; Qu, L. Graphene Oxide Assemblies for Sustainable Clean-Water Harvesting and Green-Electricity Generation. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Duley, W.W.; Peng, P.; Xiao, M.; Feng, J.; Liu, L.; Zou, G.; Zhou, Y.N. Moisture-Enabled Electricity Generation: From Physics and Materials to Self-Powered Applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gong, T.; Zhang, K.; Lee, C. Graphene Oxide Papers with High Water Adsorption Capacity for Air Dehumidification. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lian, B.; De Luca, S.; You, Y.; Alwarappan, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Sahajwalla, V.; Smith, S.C.; Leslie, G.; Joshi, R.K. Extraordinary Water Adsorption Characteristics of Graphene Oxide. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 5106–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. Rollable, Stretchable, and Reconfigurable Graphene Hygroelectric Generators. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L.; Dai, L. Graphene Oxide Nanoribbon Assembly toward Moisture-Powered Information Storage. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. Highly Efficient Moisture-Enabled Electricity Generation from Graphene Oxide Frameworks. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z.; Deng, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, P.; Huang, Y.; Shao, H.; Qu, L. Electric Power Generation via Asymmetric Moisturizing of Graphene Oxide for Flexible, Printable and Portable Electronics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. Direct Power Generation from a Graphene Oxide Film under Moisture. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4351–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, L.; Shi, G.; Qu, L. Spontaneous Power Source in Ambient Air of a Well-Directionally Reduced Graphene Oxide Bulk. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2839–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Yang, C.; Yao, H.; Li, C.; Qu, L. All-Region-Applicable, Continuous Power Supply of Graphene Oxide Composite. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Liao, Q.; Yao, H.; Shi, G.; Qu, L. Interface-Mediated Hygroelectric Generator with an Output Voltage Approaching 1.5 Volts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, K.; Stylianakis, M.M.; Atsalakis, G.; Kosmidis, D.M.; Skouras, A.; Stavrou, I.J.; Petridis, K.; Kymakis, E. An Extensive Case Study on the Dispersion Parameters of HI-Assisted Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Graphene Oxide Precursor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 580, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konios, D.; Stylianakis, M.M.; Stratakis, E.; Kymakis, E. Dispersion Behaviour of Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Peng, Z.; Gong, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, P.; Kong, L. Mechanism of a Green Graphene Oxide Reduction with Reusable Potassium Carbonate. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11966–11972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, Y.G.; Trung, T.Q.; Yoon, O.-J.; Sohn, I.-Y.; Lee, N.-E. Nanocomposites of Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheets and Conducting Polymer for Stretchable Transparent Conducting Electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, I.A.; Berezhnytska, A.S.; Mishchenko, A. New Nanosized Systems of Polymer Metal Complexes Based β-Diketones and Lanthanides for Electroluminescent Devices. In Nanoplasmonics, Nano-Optics, Nanocomposites, and Surface Studies; Fesenko, O., Yatsenko, L., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Physics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 167, pp. 433–443. [Google Scholar]
- Sygellou, L.; Paterakis, G.; Galiotis, C.; Tasis, D. Work Function Tuning of Reduced Graphene Oxide Thin Films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon Spectra—Graphene Oxide. Available online: https://xps-database.com/carbon-spectra-graphene-oxide/ (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Sundaram, M.M.; Appadoob, D. Electrolyte with Binary Metal Oxide for Symmetric Supercapacitors: Capacitive vs. Faradaic. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 11743–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shao, H.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. Self-Powered Wearable Graphene Fiber for Information Expression. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Fang, S.; Tan, J.; Chu, W.; Rong, R.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Hydrovoltaic Technology: From Mechanism to Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 4902–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, H.; Ward, J.E.; Liu, X.; Yin, B.; Fu, T.; Chen, J.; Lovley, D.R.; Yao, J. Power Generation from Ambient Humidity Using Protein Nanowires. Nature 2020, 578, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniwal, A.; Ganguly, P.; Aliyana, A.K.; Khandelwal, G.; Dahiya, R. Screen-Printed Graphene-Carbon Ink Based Disposable Humidity Sensor with Wireless Communication. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 374, 132731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigler, S.; Enzelberger-Heim, M.; Grimm, S.; Hofmann, P.; Kroener, W.; Geworski, A.; Dotzer, C.; Röckert, M.; Xiao, J.; Papp, C.; et al. Wet Chemical Synthesis of Graphene. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3583–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Kumar, N.; Krayev, A.; Chaigneau, M. In Situ Topographical Chemical and Electrical Imaging of Carboxyl Graphene Oxide at the Nanoscale. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Childres, I.; Jauregui, L.A.; Park, W.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.P. Raman Spectroscopy of Graphene and Related Materials; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Khenfouch, M.; Buttner, U.; Baïtoul, M.; Maaza, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Mass Produced High Quality Few Layered Graphene Sheets via a Chemical Method. Graphene 2014, 3, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cançado, L.G.; Jorio, A.; Ferreira, E.H.M.; Stavale, F.; Achete, C.A.; Capaz, R.B.; Moutinho, M.V.O.; Lombardo, A.; Kulmala, T.S.; Ferrari, A.C. Quantifying Defects in Graphene via Raman Spectroscopy at Different Excitation Energies. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3190–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidano, R.P.; Fischbach, D.B.; Willis, L.J.; Loehr, T.M. Observation of Raman Band Shifting with Excitation Wavelength for Carbons and Graphites. Solid State Commun. 1981, 39, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Hafiz, S.; Ritikos, R.; Whitcher, T.J.; Md. Razib, N.; Bien, D.C.S.; Chanlek, N.; Nakajima, H.; Saisopa, T.; Songsiriritthigul, P.; Huang, N.M.; et al. A Practical Carbon Dioxide Gas Sensor Using Room-Temperature Hydrogen Plasma Reduced Graphene Oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Díaz, D.; López Holgado, M.; García-Fierro, J.L.; Velázquez, M.M. Evolution of the Raman Spectrum with the Chemical Composition of Graphene Oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 20489–20497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniyoor, A.; Ramaprabhu, S. A Raman Spectroscopic Investigation of Graphite Oxide Derived Graphene. AIP Adv. 2012, 2, 032183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.-B.; Lin, M.-L.; Cong, X.; Liu, H.-N.; Tan, P.-H. Raman Spectroscopy of Graphene-Based Materials and Its Applications in Related Devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1822–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.H.; Kuila, T.; Lee, J.H. Simultaneous Reduction, Functionalization and Stitching of Graphene Oxide with Ethylenediamine for Composites Application. J. Mater. Chem. A 2012, 1, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| % Carbon Components Concentration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-C sp2 | C-C sp3 | C-OH | C=O | COOH |
| 37.5 | 3.7 | 45.5 | 9.8 | 3.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anagnostou, K.; Veisakis, G.; Kalogerakis, I.; Viskadouros, G.; Rogdakis, K.; Kymakis, E. Geometric Tuning for Enhanced Moisture-Driven Electricity Generation Enabled by Graphene-Oxide Flakes. Coatings 2022, 12, 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121970
Anagnostou K, Veisakis G, Kalogerakis I, Viskadouros G, Rogdakis K, Kymakis E. Geometric Tuning for Enhanced Moisture-Driven Electricity Generation Enabled by Graphene-Oxide Flakes. Coatings. 2022; 12(12):1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121970
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnagnostou, Katerina, George Veisakis, Ioannis Kalogerakis, George Viskadouros, Konstantinos Rogdakis, and Emmanuel Kymakis. 2022. "Geometric Tuning for Enhanced Moisture-Driven Electricity Generation Enabled by Graphene-Oxide Flakes" Coatings 12, no. 12: 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121970
APA StyleAnagnostou, K., Veisakis, G., Kalogerakis, I., Viskadouros, G., Rogdakis, K., & Kymakis, E. (2022). Geometric Tuning for Enhanced Moisture-Driven Electricity Generation Enabled by Graphene-Oxide Flakes. Coatings, 12(12), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121970