Structural Characteristics and Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Hemp Fiber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.3.1. Preparation of Fiber Aggregates
2.3.2. Preparation of Waste Hemp Fiber Composite Material
2.4. The Structural Characteristics and Test Method of Waste Hemp Fiber
2.4.1. Macromolecular Structure
2.4.2. Supramolecular Structure
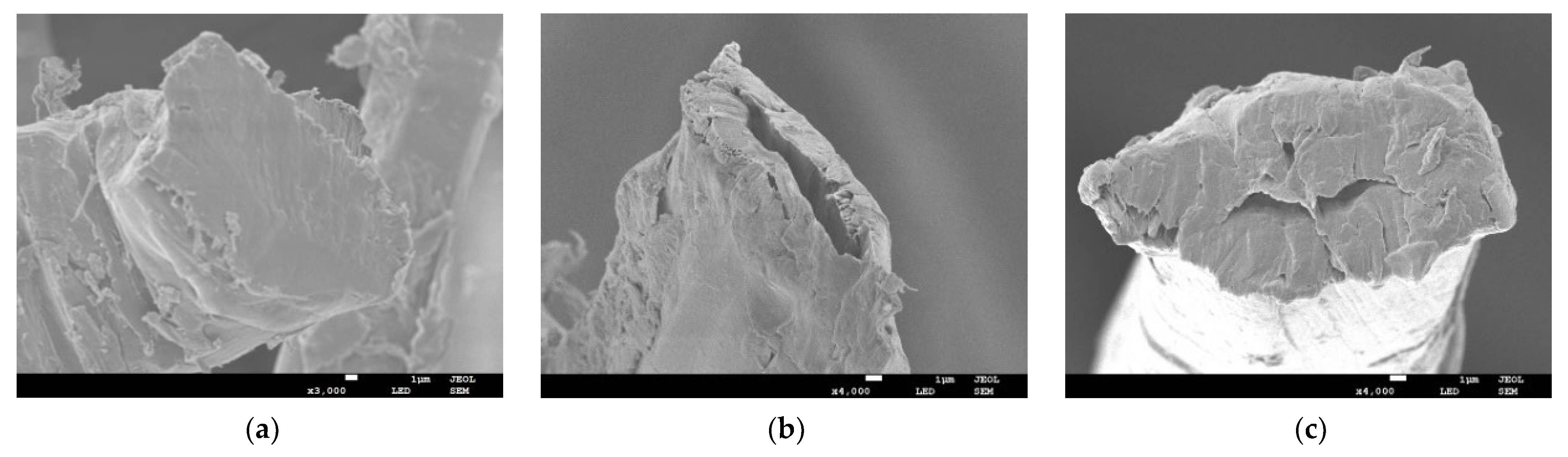
2.4.3. Morphological Structure
2.5. Parameter Calculation and Sound Absorption Test of Fiber Aggregates
2.5.1. Calculation of Volume Fraction and Bulk Density of Fiber Aggregates
2.5.2. Sound Absorption Performance Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characteristics of Waste Hemp Fiber
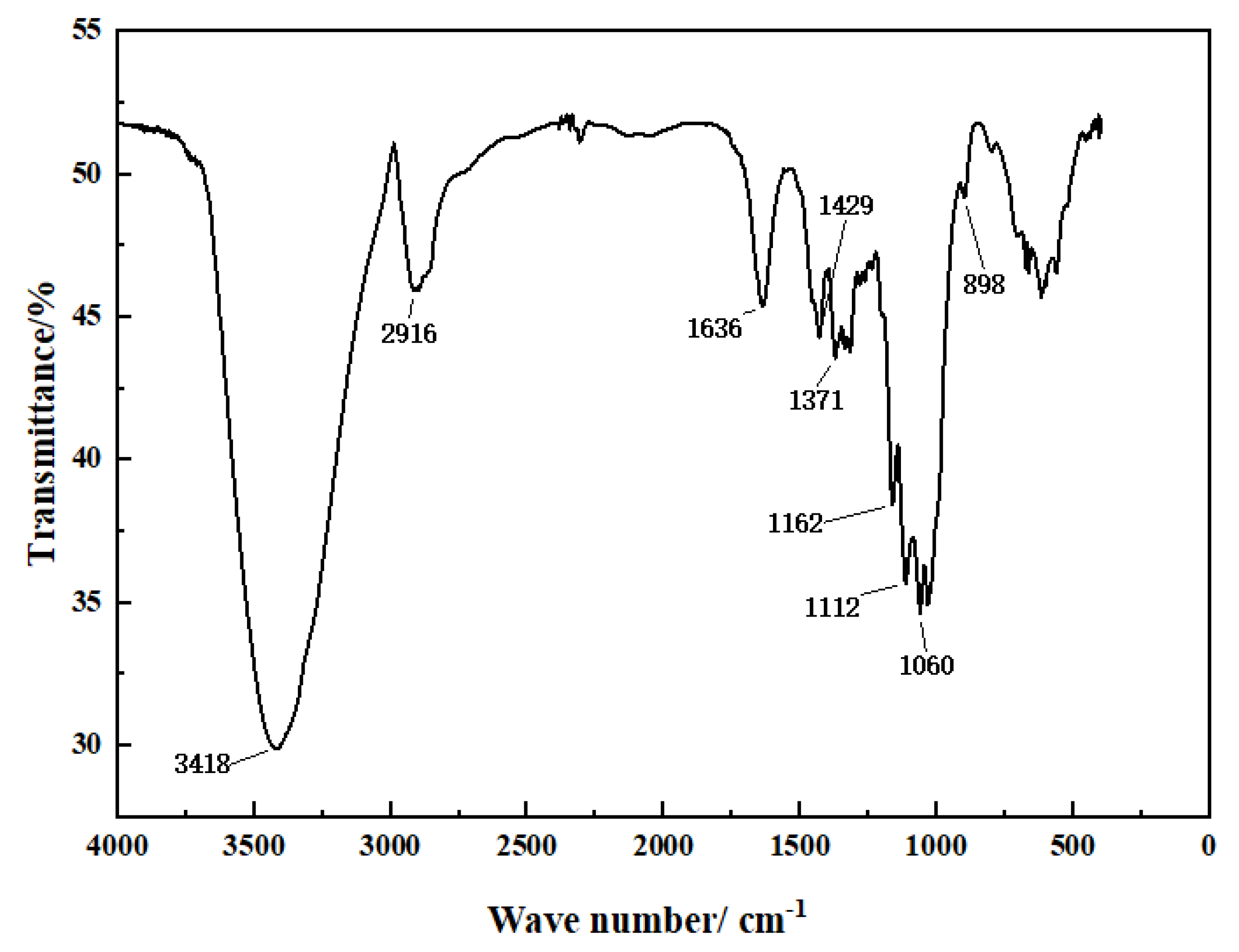
3.1.1. Macromolecular Structure
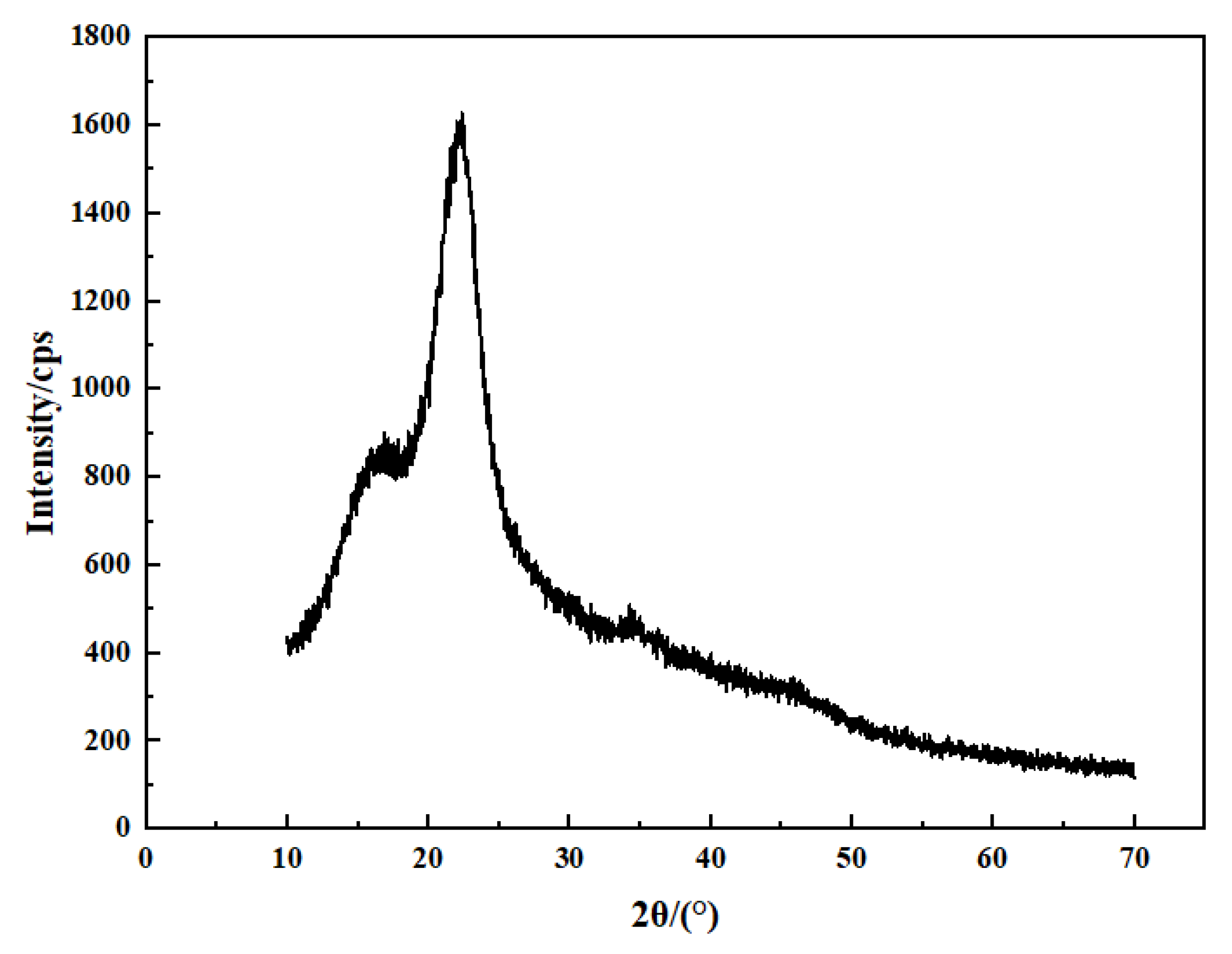
3.1.2. Supramolecular Structure
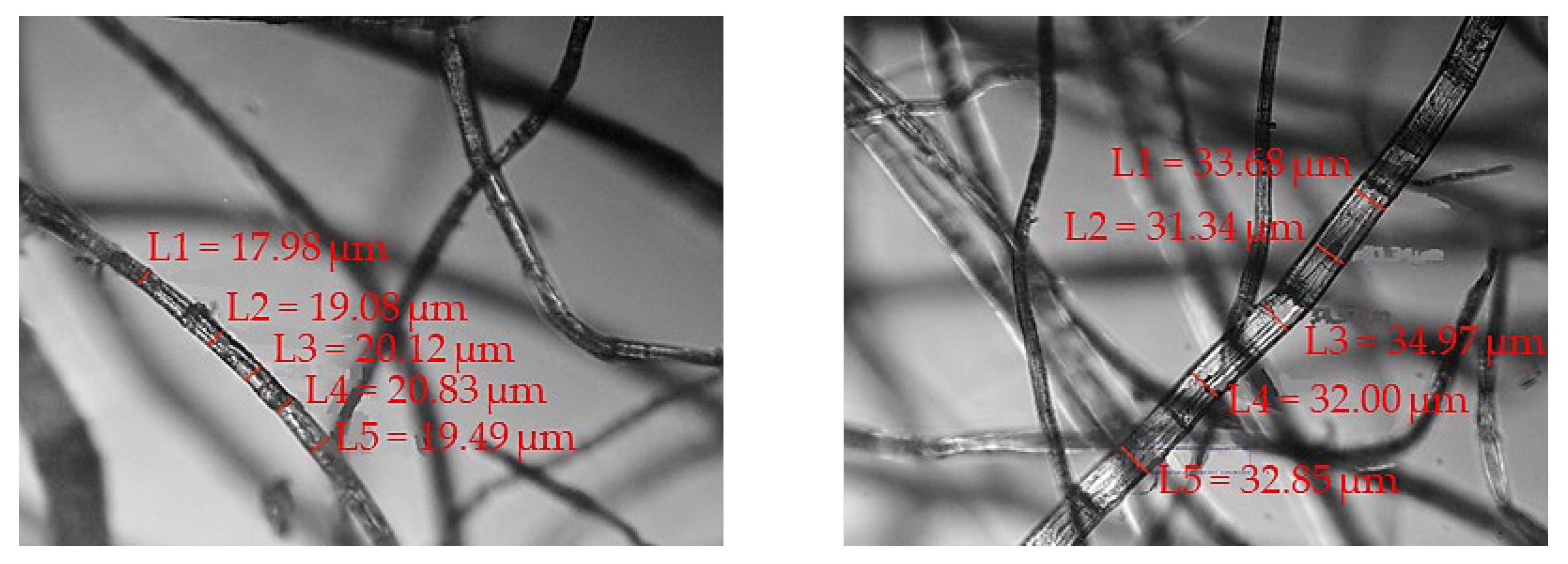
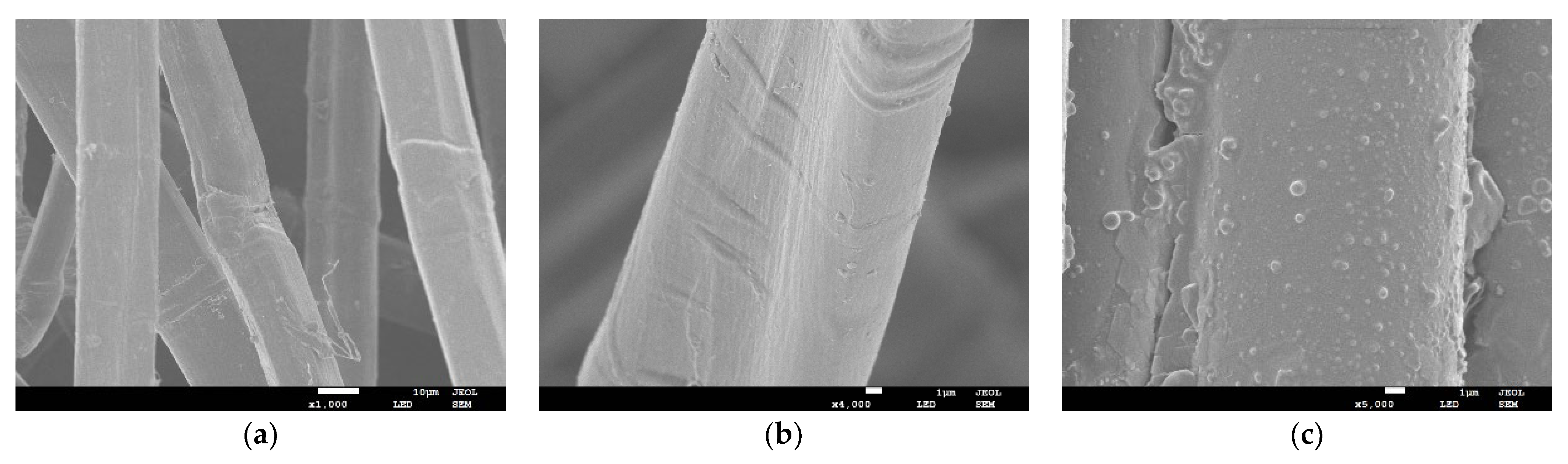
3.1.3. Morphological Structure
3.2. Test Results and Analysis of Sound-Absorbing Performance
3.2.1. Test Results and Analysis of the Sound-Absorbing Performance of Fiber Aggregates
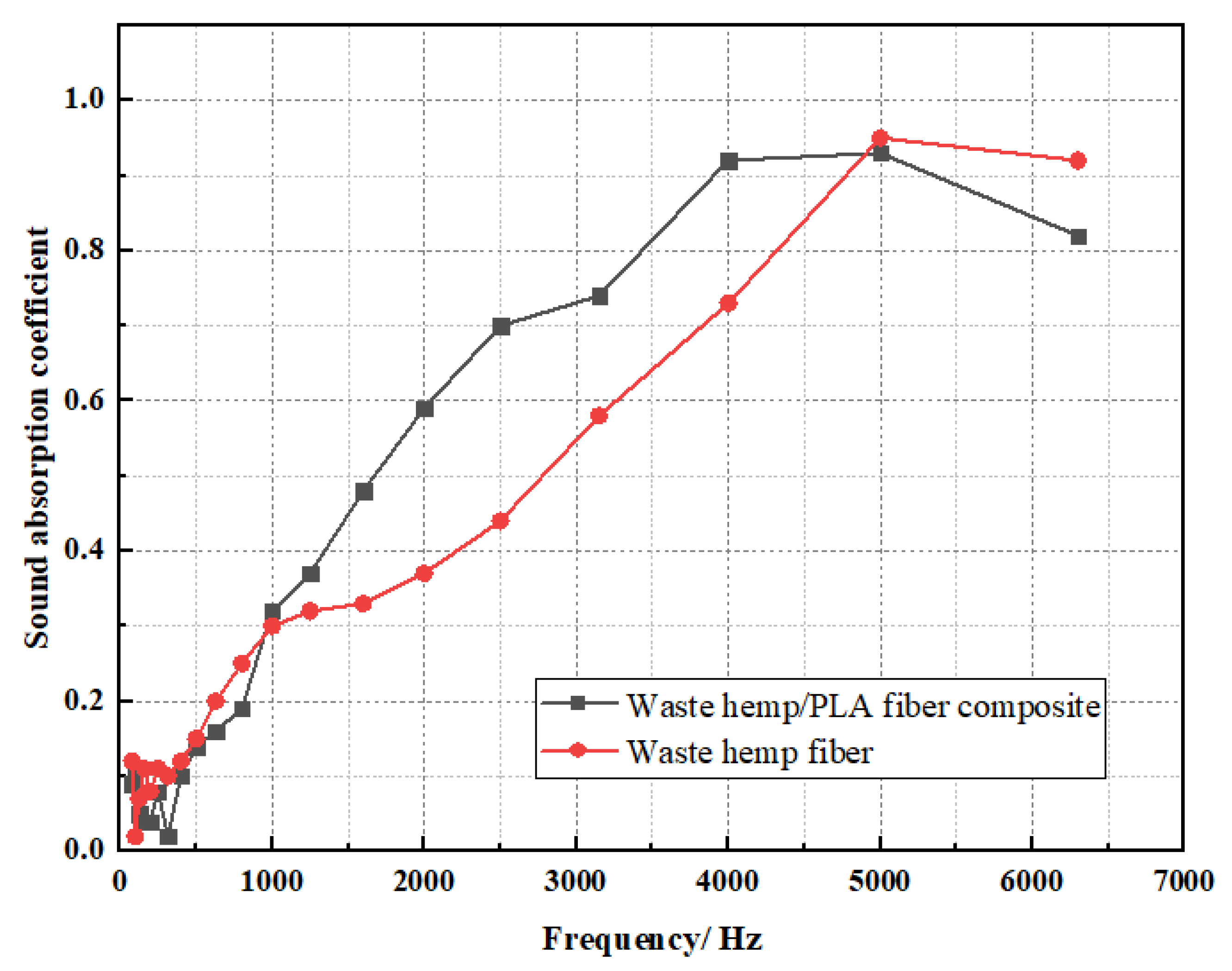
3.2.2. Test Results and Analysis of the Sound-Absorbing Performance of Waste Hemp Fiber Composite Material
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.C.; Li, H.Q.; Gong, J.X.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, J. The review of fiber-based sound-absorbing structures. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taban, E.; Amininasab, S.; Soltani, P.; Berardi, U.; Abdi, D.D.; Samaei, S.E. Use of date palm waste fibers as sound absorption material. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 41, 102752. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Q.; Yang, E. Effect of Thickness, Density and cavity depth on the sound absorption properties of wool boards. AUTEX Res. J. 2018, 2, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sakthivel, S.; Kumar, S.S.; Melese, B. Sound-absorbing recycled cotton/polyester thermal bonded nonwovens. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.; Kumar, S.S.; Mekala, N.; Dhanapriya, G. Development of sound absorbing recycled nonwoven composite materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1059, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.H.; Li, C.W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Guo, J. Sound absorption, thermal, and flame retardant properties of nonwoven wall cloth with waste fibers. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2020, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Murean, S.; Tiuc, A.E.; Neme, O.; Vermeşan, H.; Vasile, O. Innovative use of sheep wool for obtaining materials with improved sound-absorbing properties. Materials 2020, 13, 694. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Hu, L.; Xiong, X.; Yu, D.; Petrůa, M.; Yang, K. Sound absorption properties and accuracy of prediction models on natural fiber based nonwoven materials. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Raffaele, D.; Marialuisa, N.; Luca, B.; Durante, M. A study on the sound transmission loss of a new lightweight hemp/bio-epoxy sandwich structure. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 167, 107379. [Google Scholar]
- Ifeoluwa, A.; Arnab, B.; Harmandeep, S.; Shahbazi, A. A review on the current state of knowledge of growing conditions, agronomic soil health practices and utilities of hemp in the United States. Agriculture 2020, 10, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Schluttenhofer, C.; Yuan, L. Challenges towards revitalizing hemp: A multifaceted crop. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumacher AG, D.; Pequito, S.; Pazour, J. Industrial hemp fiber: A sustainable and economical alternative to cotton. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.L.; Wei, X.Y.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, C.; Long, S.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, H. Industrial hemp—An old but versatile bast fiber crop. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 6269–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Chanet, G.; Morin-Crini, N. Applications of hemp in textiles, paper industry, insulation, and building materials, horticulture, animal nutrition, food and beverages, nutraceuticals, cosmetics and hygiene, medicine, agrochemistry, energy production, and environment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1451–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.Y.; Zhang, J.C. Preparation and oil/air filtration properties of hemp paper. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 45, 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasaei, P.A.; Masumi, Z.B.; Hejazi, S.M.; Sheikhzadeh, M. Using equal cross-section theory to investigate bending properties of cellulosic fiber-reinforced cement panels. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 45, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, J.C. Effect of refined processing on the physical and chemical properties of hemp bast fibers. Text. Res. J. 2010, 80, 744–753. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Moscardo, O.; Canet, M.; Gomez-Caturla, J.; Lascano, D.; Fages, E.; Sanchez-Nacher, L. Sustainable materials with high insulation capacity obtained from wastes from hemp industry processed by wet-laid. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.L.; Jiang, S.J.; Ding, L.W. Research and production of hemp fiber properties and products. Wool Text. Sci. Technol. 2004, 6, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.N. Study on sound absorption performance of hemp fiber. Text. Sci. Technol. Prog. 2008, 5, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Research and Development of Hemp/Polypropylene Textile Sound-Absorbing Composites. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin Polytechnic University, Tianjin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Santoni, A.; Bonfiglio, P.; Fausti, P.; Marescotti, C.; Mazzanti, C.; Mollica, F.; Pompoli, F. Improving the sound absorption performance of sustainable thermal insulation materials: Natural hemp fibers. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 150, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.B.; Zhang, S.Y.; Tang, X.N. Sound absorption of hemp fibers (Cannabis sativa L.) based nonwoven fabrics and composites: A review. J. Nat. Fiber 2020, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Boominathan, S.; Bhuvaneshwari, M.; Sangeetha, K.; Pachiyappand, K.M.; Devaki, E. Influence of fiber blending on thermal and acoustic properties nonwoven material. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hu, L.; Xiong, X.; Petru, M.; Noman, M.T.; Mishra, R.; Militky, J. Sound absorption properties of natural fibers: A review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.C. Lignocellulosic Chemistry, 4th ed.; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 166–180. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.M.; Li, X.X. Sound absorption mechanism of polymer based composite foams. Noise Vib. Control 2000, 5, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, S.S. Discussion on feasibility of nonwoven sound-absorbing materials used for road noise-deafening barrier. Zhejiang Fash. Inst. Technol. 2009, 2, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bei, W.; Mohini, S.; Kristiina, O. Study of structural morphology of hemp fiber from the micro to the nanoscale. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2007, 14, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zimniewska, M. Hemp fibre properties and processing target textile: A review. Materials 2022, 15, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutek, K.; Masek, A. Hemp and Its derivatives as a universal industrial raw material (with particular emphasis on the polymer industry)—A review. Materials 2022, 15, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, Z. Order in cellulosics: Historical review of crystal structure research on cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Lyu, L.H.; Xiong, X.Q. Structural characteristics and sound absorption properties of poplar seed fibers. Text. Res. J. 2020, 90, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthamaraikannan, P.; Kathiresan, M. Characterization of raw and alkali treated newnatural cellulosic fiber from Coccinia grandis L. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrum, P.R.; Amanda, J.T. Characterization of the crystallographic properties of bamboo plants, natural and viscose fibers by X-ray diffraction method. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 112, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.J.; Wang, Z.; Bao, F.C.; Chang, L. Research status and development trend of natural plant fiber/biodegradable plastic biomass composites. For. Sci. 2008, 441, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.H.; Yu, L. Study on the performance of xinjiang flax fiber. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.D. Textile Materials Science, 1st ed.; China Textile and Apparel Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 147–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.L. The Study on the Spinnability and Blended Yarn Development of Hemp Fiber. Master’s Thesis, Donghua University, Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, R.A.; Aracil, M.B.; Paya, J.G.; del Rey, R.; Picó, R. Influence of fineness, length and hollow section of fibers on acoustic absorption. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, P.; Zarrebini, M. The analysis of acoustic characteristics and sound absorption coefficient of needle punched nonwoven fabrics. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2013, 9, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Joo, C. Sound absorption properties of recycled polyester fibrous assembly absorbers. AUTEX Res. J. 2003, 2, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, W.L.; Sang, W.P. Effect of fiber cross section shape on the sound absorption and the sound insulation. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar]
- Kunikazu, H. Numerical study on the influence of fiber cross-sectional shapes on the sound absorption efficiency of fibrous porous materials. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 164, 107222. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Sound-absorption properties of kapok fiber nonwoven fabrics at low frequency. J. Nat. Fibers 2015, 12, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Mevlut, T. Effects of total surface area and fabric density on the acoustical behavior of needlepunched nonwoven fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Hoda, S.S.; Nermin, M.A.; Ali, M.A.; Elshakankery, M. Investigation on sound absorption properties for recycled fibrous materials. J. Ind. Text. 2013, 43, 56–73. [Google Scholar]
- Luc, A. Biodegradable multiphase systems based on plasticized starch: A review. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C Polym. Rev. 2004, 44, 231–274. [Google Scholar]



| Researcher | Raw Material | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Xu Fan et al. [20] | hemp, wool, cotton fibers, ramie, and flax | The sound absorption coefficients of hemp, wool, cotton fiber, ramie, and flax were compared in the middle and low frequency bands. |
| Jing Zhang [21] | hemp staple fibers and polypropylene fibers | Composite sound absorption properties of hemp/polypropylene fiber composites varied under different preparation conditions. |
| Santoni et al. [22] | hemp fiber | The effects of each treatment on the physical properties of the hemp fiber composites and their sound absorption coefficients were investigated. |
| Liao et al. [23] | hemp fiber | Summarized the methods for improving the sound absorption of hemp fiber materials. |
| Boominathan et al. [24] | Sansevieria stuckyi, banana, and hemp fiber | The nonwoven mat made with blended fibers had a higher maximum sound absorption coefficient than single fiber nonwoven mats. The higher the proportion of hemp fiber, the greater the thickness of nonwovens, and the greater the sound absorption coefficient. |
| Wavenumber/cm−1 | Characteristic Peak Attribution | Characteristic Peak |
|---|---|---|
| 3418 | O–H telescopic vibration | Lignin and cellulose |
| 2916 | C–O telescopic vibration | Lignin |
| 1636 | C=O telescopic vibration | Lignin |
| 1429 | CH2 bending vibration | Cellulose and lignin |
| 1371 | CH bending vibration | Cellulose and hemicellulose |
| 1162 | C–O–C telescopic vibration | Cellulose and lignin |
| 1060 | C=O telescopic vibration | Cellulose and hemicellulose |
| 898 | β-glucosidic bond vibration | Carbohydrate characteristic peak |
| Length Range/mm | Number of Roots/Root |
|---|---|
| 20–40 | 67 |
| 40–60 | 27 |
| 60–75 | 6 |
| Sample Code | Type of Fiber | 125 Hz | 250 Hz | 500 Hz | 1000 Hz | 2000 Hz | 4000 Hz | α | NRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | Cotton fiber | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.86 | 0.33 | 0.25 |
| b | Waste hemp fiber | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.37 | 0.73 | 0.29 | 0.25 |
| c | Wool fiber | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.58 | 0.25 | 0.20 |
| d | Polyester | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.3 | 0.49 | 0.22 | 0.20 |
| Fiber Tape | Fiber Density/(g/cm3) | Fiber Volume Fraction/% | Fiber Fineness/μm | Fiber Length/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton fiber | 1.58 | 4.029 | 16–22 | 25–35 |
| Waste hemp fiber | 1.50 | 4.244 | 19–38 | 20–50 |
| Wool fiber | 1.32 | 4.832 | 10–50 | 30–70 |
| Polyester fiber | 1.38 | 4.613 | 28–40 | 51–76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Lyu, L. Structural Characteristics and Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Hemp Fiber. Coatings 2022, 12, 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121907
Zhang D, Zhou X, Gao Y, Lyu L. Structural Characteristics and Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Hemp Fiber. Coatings. 2022; 12(12):1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121907
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Duoduo, Xinghai Zhou, Yuan Gao, and Lihua Lyu. 2022. "Structural Characteristics and Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Hemp Fiber" Coatings 12, no. 12: 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121907
APA StyleZhang, D., Zhou, X., Gao, Y., & Lyu, L. (2022). Structural Characteristics and Sound Absorption Properties of Waste Hemp Fiber. Coatings, 12(12), 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121907





