Polydopamine-Coated Copper-Substituted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of CuMSN
2.3. DOX Loading into CuMSN
2.4. PDA Coating onto CuMSN@DOX
2.5. In Vitro DOX Releasing Study
2.6. In Vitro PTT Studies
2.7. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. Cell Uptake Studies
2.9. ROS Detection Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
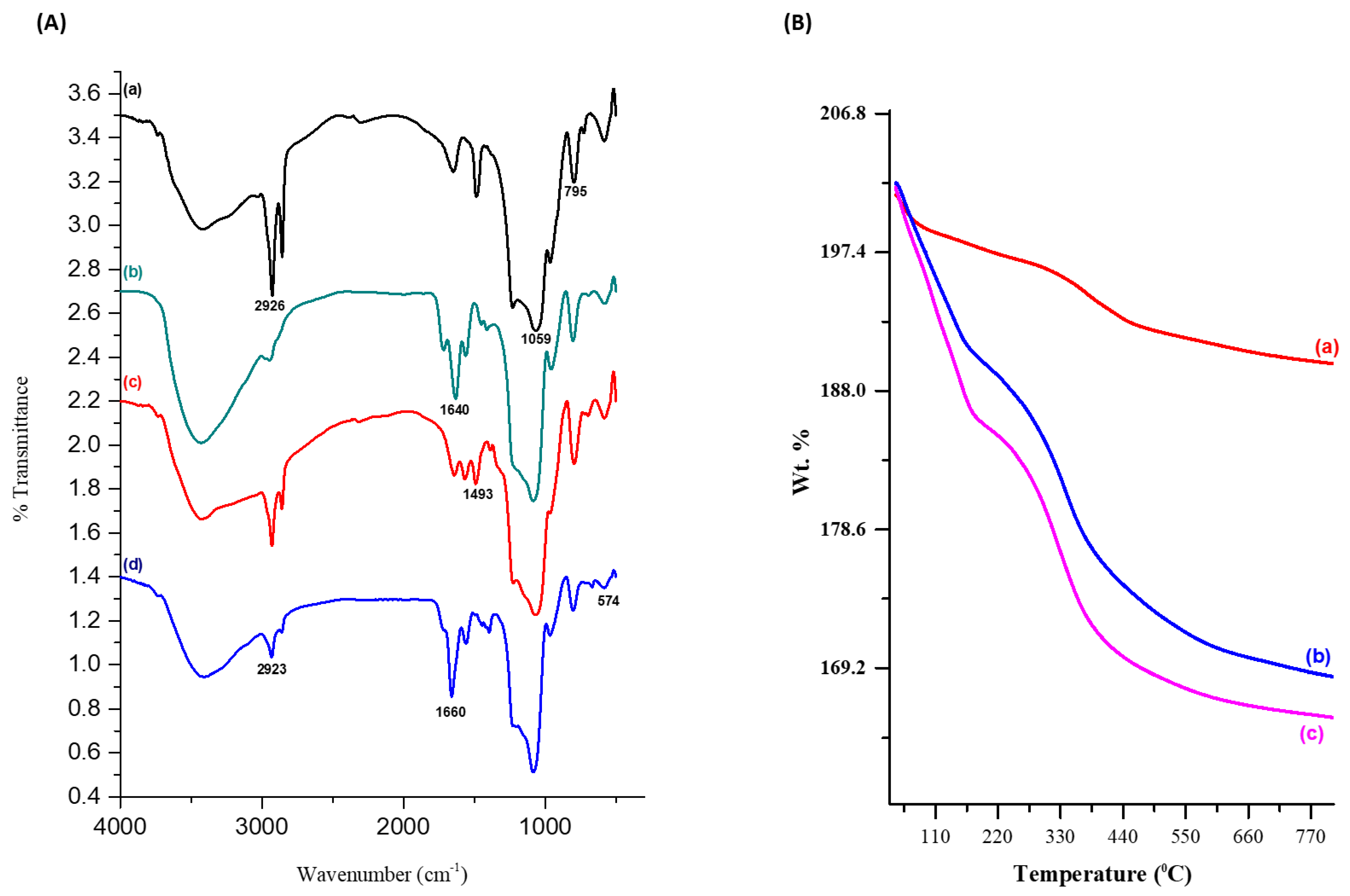
3.1. Physical Characterization
3.2. In Vitro DOX Release and PDA Photothermal Studies
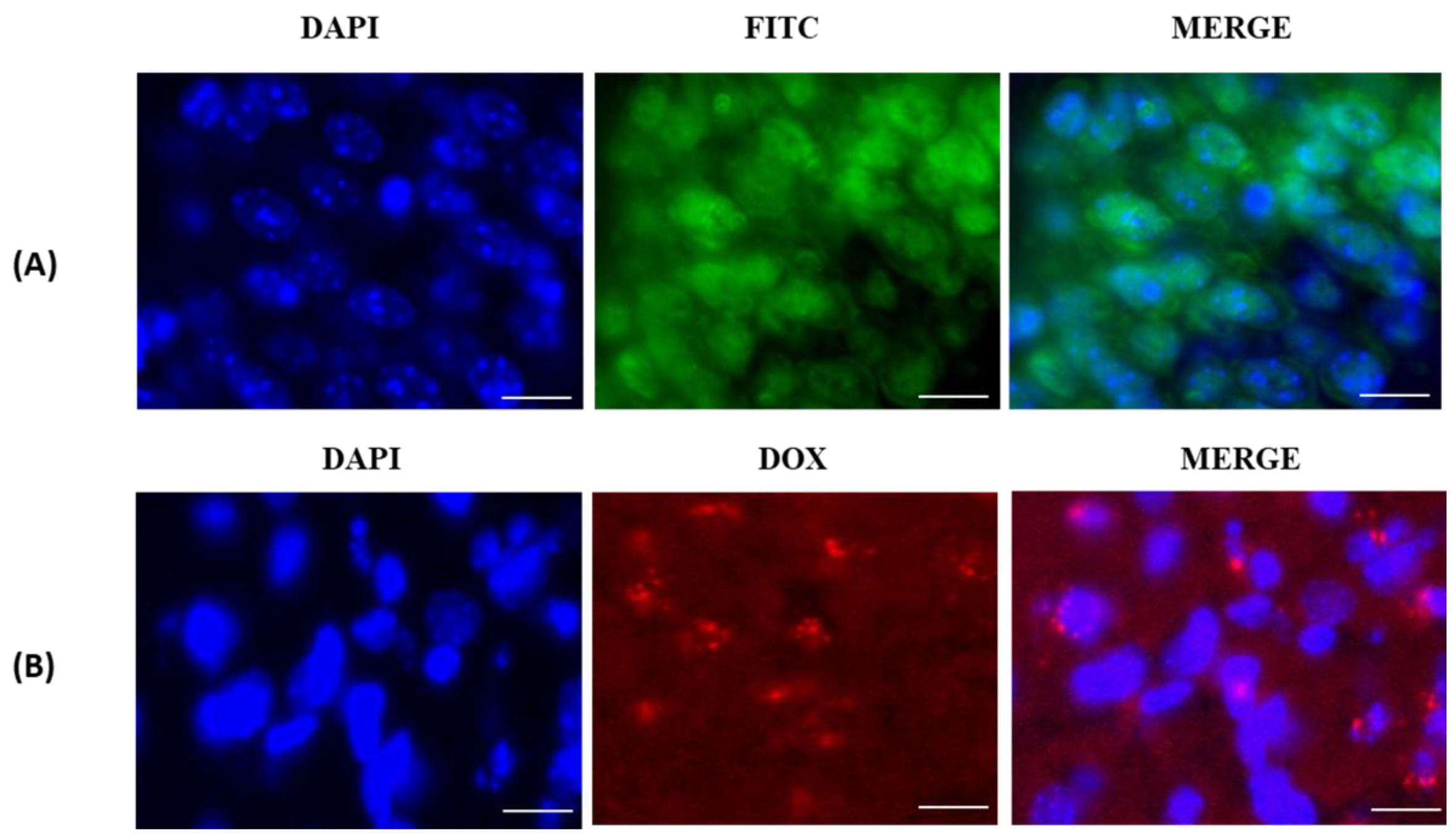
3.3. In Vitro Cellular-Uptake Studies
3.4. In Vitro Cell-Viability Studies
3.5. ROS Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahreddine, H.K. Borden Mechanisms and Insights into Drug Resistance in Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luqmani, Y.A. Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Cancer Chemotherapy. Med. Princ. Pract. 2005, 14 (Suppl. 1), 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.R.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Hemann, M.T. Hemann Understanding Resistance to Combination Chemotherapy. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer. Chemother. 2012, 15, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Y. Combination Therapy Based on Nano Codelivery for Overcoming Cancer Drug Resistance. Med. Drug Discov. 2020, 6, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, A.C.; Veeranarayanan, S.; Mohamed, M.S.; Aburto, R.R.; Mitcham, T.; Bouchard, R.; Ajayan, P.M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Multifunctional Cu2−xTe Nanocubes Mediated Combination Therapy for Multi-Drug Resistant MDA MB 453. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yu, X.; Ouyang, X.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Recent Advances in Nanomaterials-Based Chemo-Photothermal Combination Therapy for Improving Cancer Treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, T.; Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Shen, Q. Chemo-Photothermal Combination Cancer Therapy with ROS Scavenging, Extracellular Matrix Depletion, and Tumor Immune Activation by Telmisartan and Diselenide-Paclitaxel Prodrug Loaded Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 31292–31308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.-F.; Li, Y.; Long, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Li, C.-R.; Zhao, M.-X.; Lai, Y. Fabrication of Cisplatin-Loaded Polydopamine Nanoparticles via Supramolecular Self-Assembly for Photoacoustic Imaging Guided Chemo-Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 23, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, M.; Mahmoodzadeh, F.; Salehi, R.; Amirshaghaghi, A. Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Cancer Cells Using Gold Nanorod-Cored Stimuli-Responsive Triblock Copolymer. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 12777–12788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Sarkar, S.; Scott, L.; Danelisen, I.; Trush, M.A.; Jia, Z.; Li, Y.R. Doxorubicin Redox Biology: Redox Cycling, Topoisomerase Inhibition, and Oxidative Stress. React. Oxyg. Species 2016, 1, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zheng, W.; Fu, X.; Li, X.; Wong, Y.-S.; Chen, T. Strategy to Enhance the Therapeutic Effect of Doxorubicin in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Selenocystine, a Synergistic Agent that Regulates the ROS-Mediated Signaling. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2853–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijäs, H.; Shen, B.; Heuer-Jungemann, A.; Keller, A.; Kostiainen, M.A.; Liedl, T.; Ihalainen, J.; Linko, V. Unraveling the Interaction between Doxorubicin and DNA Origami Nanostructures for Customizable Chemotherapeutic Drug Release. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 3048–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; van der Zanden, S.Y.; Wander, D.P.A.; Borràs, D.M.; Song, J.-Y.; Li, X.; van Duikeren, S.; van Gils, N.; Rutten, A.; van Herwaarden, T.; et al. Uncoupling DNA Damage from Chromatin Damage to Detoxify Doxorubicin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, C.; Yao, W.; Zhou, H.; Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Qiao, W. Endogenous Reactive Oxygen Species Burst Induced and Spatiotemporally Controlled Multiple Drug Release by Traceable Nanoparticles for Enhancing Antitumor Efficacy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4968–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, S.; Yoo, H.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Yum, K.; Kim, K.; Kim, H. Overcoming Anticancer Resistance by Photodynamic Therapy-Related Efflux Pump Deactivation and Ultrasound-Mediated Improved Drug Delivery Efficiency. Nano Converg. 2020, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, Y.; Kamareddine, M.H.; Tawk, A.; Elia, C.; El Mahmoud, A.; Terro, K.; El Harake, N.; El-Baba, B.; Makdessi, J.; Farhat, S. Inorganic Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems and Their Potential Role in the Treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819853241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, T.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mei, L. Inorganic Nano-Carriers Based Smart Drug Delivery Systems for Tumor Therapy. Smart Mater. Med. 2020, 1, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, C.; Cheng, J.; Yuan, Z. Recent Advances on Inorganic Nanoparticle-Based Cancer Therapeutic Agents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthati, Y.; Busa, P.; Tummala, S.; Rao, V.; Davuluri, V.; Ho, Y.-P.; Wong, C.-S. Mesoporous Polydopamine Nanoparticles Attenuate Morphine Tolerance in Neuropathic Pain Rats by Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Restoration of the Endogenous Antioxidant System. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Che, E.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, V.-C. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Bio-Applications. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lei, C.; Yu, C. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Protein Protection and Delivery. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthati, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Busa, P.; Lin, S.-X.; Deng, J.-P.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Phototherapeutic Spectrum Expansion through Synergistic Effect of Mesoporous Silica Trio-Nanohybrids against Antibiotic-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 169, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; Lozano, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Carriers for Therapeutic Biomolecules. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Quan, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, B.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug and Gene Delivery. Acta Pharm. Sinica. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Kankala, R.K.; Busa, P.; Lee, C.-H. Hydrophobicity-Tuned Periodic Mesoporous Organo-Silica Nanoparticles for Photodynamic Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, N. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Classification, Drug Loading, Pharmacokinetics, Biocompatibility, and Application in Drug Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzeciak, K.; Chotera-Ouda, A.; Bak-Sypien, I.; Potrzebowski, M. Mesoporous Mesoporous Silica Particles as Drug Delivery Systems—The State of the Art in Loading Methods and the Recent Progress in Analytical Techniques for Monitoring These Processes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wang, H.; Ducheyne, P. Polymer-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Controlled Release of Macromolecules. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3429–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, K.K.; Mishra, D.K.; Rosling, A.; Rosenholm, J.M. Therapeutic Potential of Polymer-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zheng, H.; Cao, Y.; Che, S. Coordination Polymer Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Drug Release. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6433–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Han, S.; Cao, S. Mesoporous Silica-Coated Gold Nanorods with a Thermally Responsive Polymeric Cap for Near-Infrared-Activated Drug Delivery. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 7165–7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.R.; Jang, D.J.; Kim, S.; An, S.; Lee, J.; Oh, E.; Kim, J. Polymer-Coated Spherical Mesoporous Silica for pH-Controlled Delivery of Insulin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, X.; Cui, Y.; He, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, A.; Fei, J.; Li, J. Preparation of Polymer-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Used for Cellular Imaging by a “Graft-from” Method. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5731–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, W.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C. Recent Development of pH-Responsive Polymers for Cancer Nanomedicine. Molecules 2019, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsehli, M. Polymeric Nanocarriers as Stimuli-Responsive Systems for Targeted Tumor (Cancer) Therapy: Recent Advances in Drug Delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Ito, A.; Sogo, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsuji, N.M.; Ohno, T. Biodegradable Metal Ion-Doped Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Stimulate Anticancer Th1 Immune Response in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 43538–43544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasbi, L.; Sedaghat, T.; Motamedi, H.; Kooti, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Supported Copper(II) and Nickel(II) Schiff Base Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial Activity and Enzyme Immobilization. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 258, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Parshad, B.; Li, W.; Haag, R. Novel Dendritic Polyglycerol-Conjugated, Mesoporous Silica-Based Targeting Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and Tariquidar to Overcome Multidrug Resistance in Breast Cancer stem Cells. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, C.S.; Ray, P.; Alam, S.; Kale, N.; Aishwarya, R.; Morshed, M.; Dutta, D.; Hudziak, C.; Banerjee, S.K.; Mallik, S.; et al. Chemical Architecture of Block Copolymers Differentially Abrogate Cardiotoxicity and Maintain the Anticancer Efficacy of Doxorubicin. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 4676–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, H.; Peng, C.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. Polydopamine-Coated Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Multimodal Cancer Theranostics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Achazi, K.; Steinhilber, D.; Kratz, F.; Dernedde, J.; Haag, R. A Facile Approach for Dual-Responsive Prodrug Nanogels Based on Dendritic Polyglycerols with Minimal Leaching. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pada, A.-K.; Desai, D.; Sun, K.; Govardhanam, N.P.; Törnquist, K.; Zhang, J.; Rosenholm, J.M. Comparison of Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanorods and Spheres for the Delivery of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Shi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Guo, J.; Song, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, M.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; et al. Recent Developments in Mesoporous Polydopamine-Derived Nanoplatforms for Cancer Theranostics. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, C.; Xia, H.; Wang, Z. pH and Ultrasound Dual-Responsive Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9974–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Sun, C.; Jiang, T.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S. Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Multi-Responsive Drug Delivery and Combined Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2019, 105, 110103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Q.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, H.; Kong, D.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L. Robust Nanovaccine Based on Polydopamine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Effective Photothermal-Immunotherapy Against Melanoma. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Polydopamine-Doped Virus-like Mesoporous Silica Coated Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheets for Chemo-Photothermal Synergetic Therapy. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 35, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Q.; Bhave, M.; Xu, G.; Sun, C.; Yu, A. Synthesis of Polydopamine Hollow Capsules via a Polydopamine Mediated Silica Water Dissolution Process and Its Application for Enzyme Encapsulation. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Chen, H. DOX-Loaded pH-Sensitive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Coated with PDA and PEG Induce Pro-Death Autophagy in Breast Cancer. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39641–39650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Wei, E.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, L.; Ge, B. Polydopamine and Peptide Decorated Doxorubicin-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Targeted Drug Delivery System for Bladder Cancer Therapy. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.; Sweetman, M.; Song, Y.; Plush, S.; Garg, S. Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for Doxorubicin: Drug Loading and Release. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Chen, T.; Liu, H.; Su, S. Preparation and Adsorption Performance Research of Large-Volume Hollow Mesoporous Polydopamine Microcapsules. MRS Commun. 2019, 9, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liang, C.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Gao, N.; Tao, W.; Luo, L.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. TPGS-Functionalized Polydopamine-Modified Mesoporous Silica as Drug Nanocarriers for Enhanced Lung Cancer Chemotherapy against Multidrug Resistance. Small 2017, 13, 1700623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busa, P.; Koutavarapu, R.; Lee, D.-Y.; Shim, J.; Kuthati, Y. Hierarchical Two-Dimensional Layered Double Hydroxide Coated Polydopamine Nanocarriers for Combined Chemodynamic and Photothermal Tumor Therapy. Coatings 2021, 11, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Lin, S.-X.; Kankala, R.K.; Busa, P.; Deng, J.-P.; Lue, S.-I.; Liu, C.-L.; Weng, C.-F.; Lee, C.-H. Surface-Functionalized Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocontainers as Bile Acid Sequestrants for Lowering Hyperlipidemia. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X. Multiple-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Highly Accurate Drugs Delivery to Tumor Cells. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4306–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthati, Y.; Busa, P.; Davuluri, V.N.G.; Wong, C.S. Manganese Oxide Nanozymes Ameliorate Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Partial Sciatic Nerve-Transection Induced Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 10105–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Kang, J.; Lin, L.-R.; Chen, W.-T.; Liu, J.-X.; Wu, X.-L.; Lu, T.-L. Cinnamaldehyde and Doxorubicin Co-Loaded Graphene Oxide Wrapped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Enhanced MCF-7 Cell Apoptosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 10285–10304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Cai, K. Mesoporous Polydopamine Nanoparticles with Co-Delivery Function for Overcoming Multidrug Resistance via Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8781–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-J.; Li, W.-T.; Li, Z.-H.-R.; Zhang, L.-P.; Gai, C.-C.; Zhang, W.-F.; Ding, D.-J. Iron-Chelated Polydopamine Decorated Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanodevices for Reactive Oxygen Species Enhanced Cancer Combination Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Mori, A.; Huang, L. Role of Liposome Size and RES Blockade in Controlling Biodistribution and Tumor Uptake of GM1-Containing Liposomes. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1992, 1104, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; He, Q.; Gao, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loading Doxorubicin Reverse Multidrug Resistance: Performance and Mechanism. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4314–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, R.; Sheng, L.; Wu, W.; Pan, G.; Feng, Q.; Cui, W. Doxorubicin-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Composite Nanofibers for Long-Term Adjustments of Tumor Apoptosis. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Khan, T.A.; Patil, Y.P.; Pagariya, D.; Kishore, N.; Tapryal, S.; Naik, A.D.; Naik, S.G. Bio-Affinity of Copper(II) Complexes with Nitrogen and Oxygen Donor Ligands: Synthesis, Structural Studies and in Vitro DNA and HSA Interaction of Copper(II) Complexes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 174, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, G.; Tao, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, F.; Pan, J.; Mei, L.; Pan, G. A Drug-Self-Gated Mesoporous Antitumor Nanoplatform Based on pH-Sensitive Dynamic Covalent Bond. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahoui, N.; Jiang, B.; Hegazy, M.; Taloub, N.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; Huang, Y.D. Gold Modified Polydopamine Coated Mesoporous Silica Nano-Structures for Synergetic Chemo-Photothermal Effect. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, X.; Soeriyadi, A.H.; Sagnella, S.M.; Lu, X.; Scott, J.A.; Lowe, S.B.; Kavallaris, M.; Gooding, J.J. Stimuli-Responsive Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Release in Response to Various Biological Stimuli. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Tao, W.; Mei, L.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X. Polydopamine-Based Surface Modification of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as pH-Sensitive Drug Delivery Vehicles for Cancer Therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 463, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.P.; Bhattarai, D.P.; Maharjan, B.; Ko, S.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Polydopamine-Based Implantable Multifunctional Nanocarpet for Highly Efficient Photothermal-Chemo Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wu, H.; Luo, K.; Hao, W.; Wang, S.; Huang, M. Magnetic Silica Nanosystems With NIR-Responsive and Redox Reaction Capacity for Drug Delivery and Tumor Therapy. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 567652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, M.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y. Doxorubicin-Metal Coordinated Micellar Nanoparticles for Intracellular Codelivery and Chemo/Chemodynamic Therapy in Vitro. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4703–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Tang, Y.; Cao, W.; Cui, Y.; Qian, G. Highly Efficient Encapsulation of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride in Metal-Organic Frameworks for Synergistic Chemotherapy and Chemodynamic Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4999–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Y. Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoscale Metal-Organic Framework for Tumor-Targeting Combined Chemotherapy and Chemodynamic Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4615–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tang, W.; Jiang, D.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P. Hyaluronic Acid Conjugated Polydopamine Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Synergistic Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11012–11024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Zhang, R.; Lu, J.; Zhao, C.; Deng, X.; Wu, Y. Mesoporous Silica Coated Polydopamine Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide for Synergistic Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Eltayeb, O.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Tumor Microenvironment Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual Delivery of Doxorubicin and Chemodynamic Therapy (CDT) agent. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 2578–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Deng, C.; Aras, O.; Zhou, M.; Wu, C.; An, F. Chemodynamic Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinard, B.; Neo, S.Z.Y.; Yeo, E.L.L.; Heng, H.P.S.; Neoh, K.G.; Kah, J.C.Y. Polydopamine Nanoparticles Enhance Drug Release for Combined Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 21125–21136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




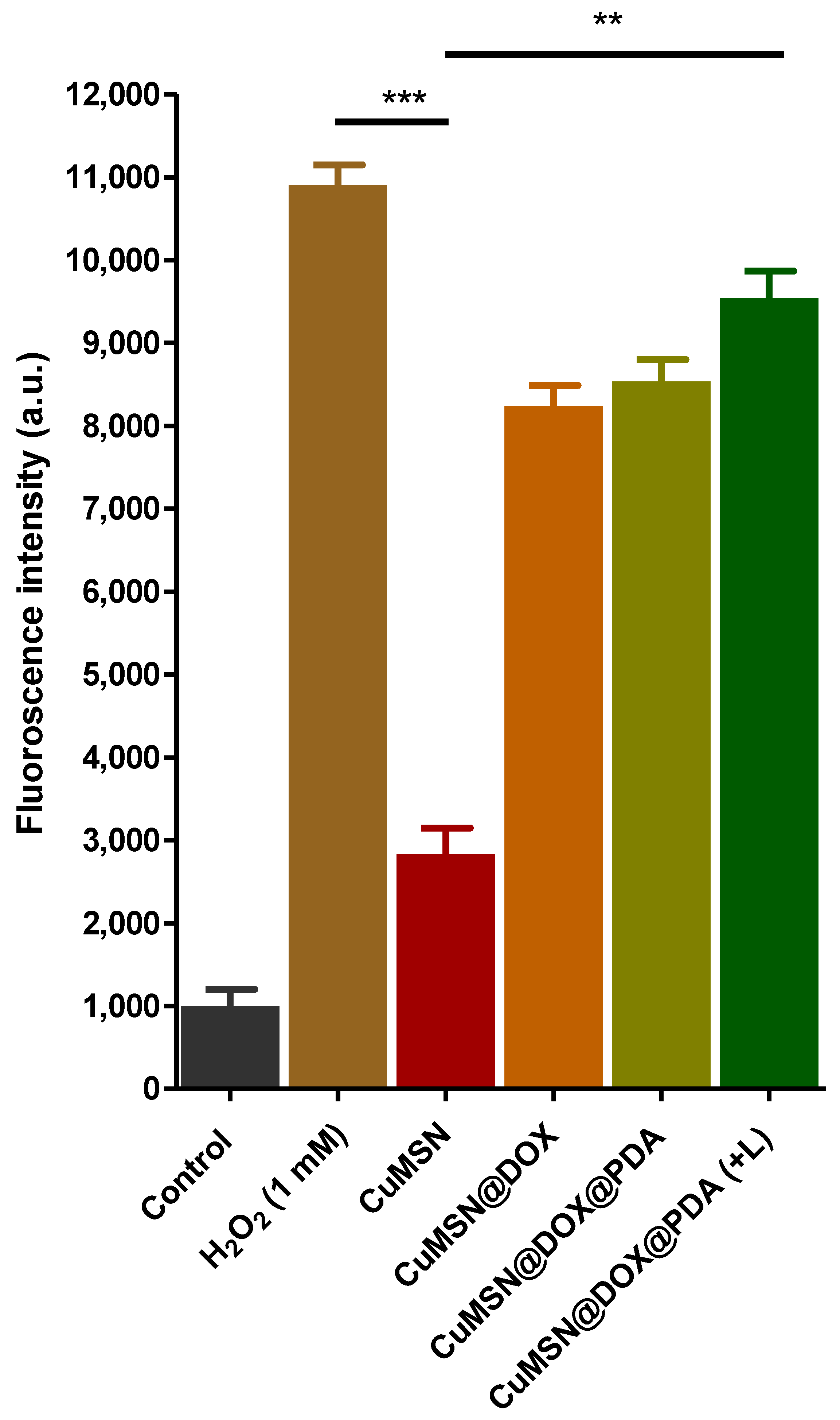
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Busa, P.; Koutavarapu, R.; Kuthati, Y. Polydopamine-Coated Copper-Substituted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual Cancer Therapy. Coatings 2022, 12, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010060
Busa P, Koutavarapu R, Kuthati Y. Polydopamine-Coated Copper-Substituted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual Cancer Therapy. Coatings. 2022; 12(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleBusa, Prabhakar, Ravindranadh Koutavarapu, and Yaswanth Kuthati. 2022. "Polydopamine-Coated Copper-Substituted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual Cancer Therapy" Coatings 12, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010060
APA StyleBusa, P., Koutavarapu, R., & Kuthati, Y. (2022). Polydopamine-Coated Copper-Substituted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Dual Cancer Therapy. Coatings, 12(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010060








