Electrospun Bilayer PAN/Chitosan Nanofiber Membranes Incorporated with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Electrospun Bilayer Nanofiber Mats
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Studies
2.5. Mechanical Testing
3. Results and Discussion
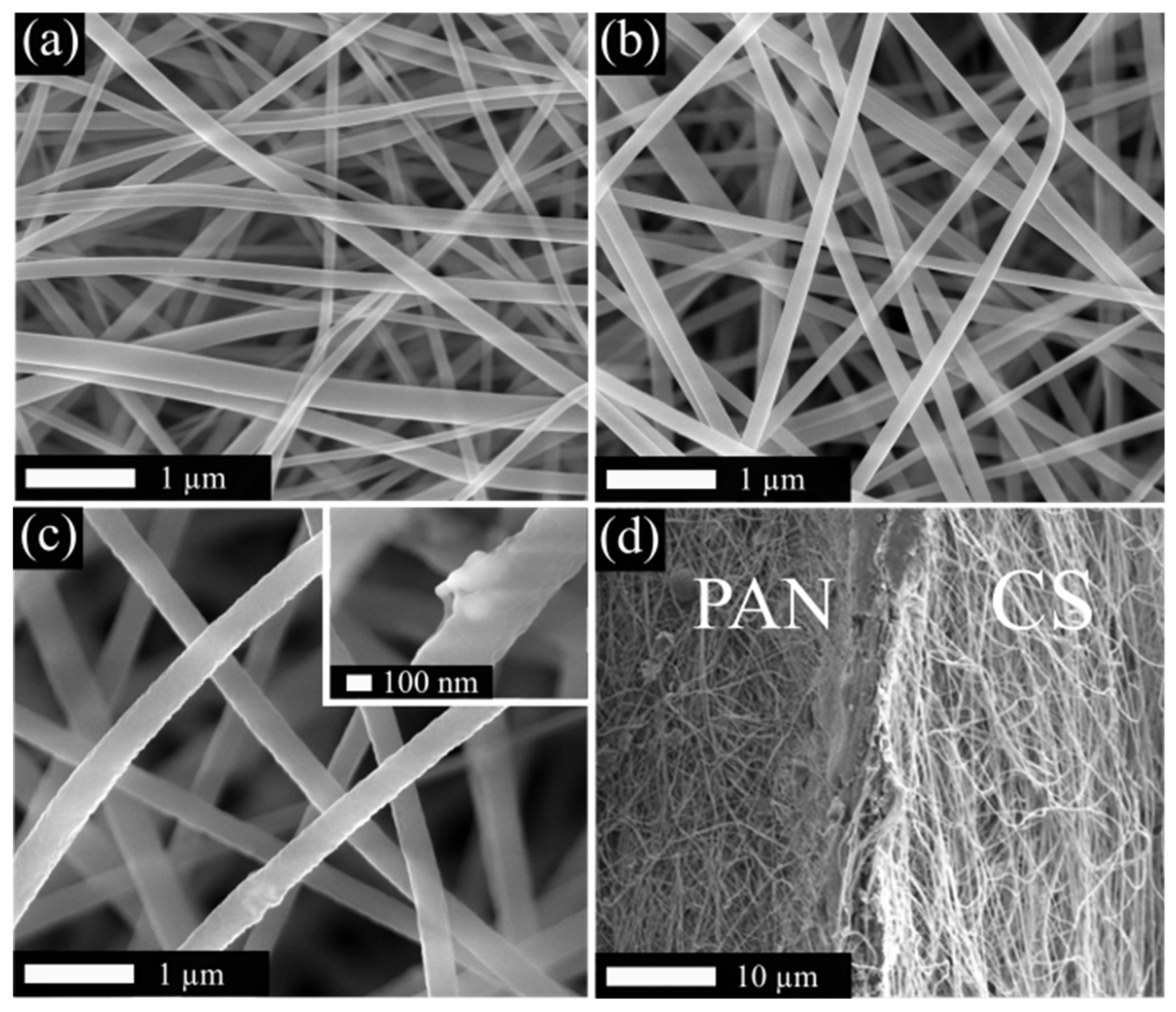
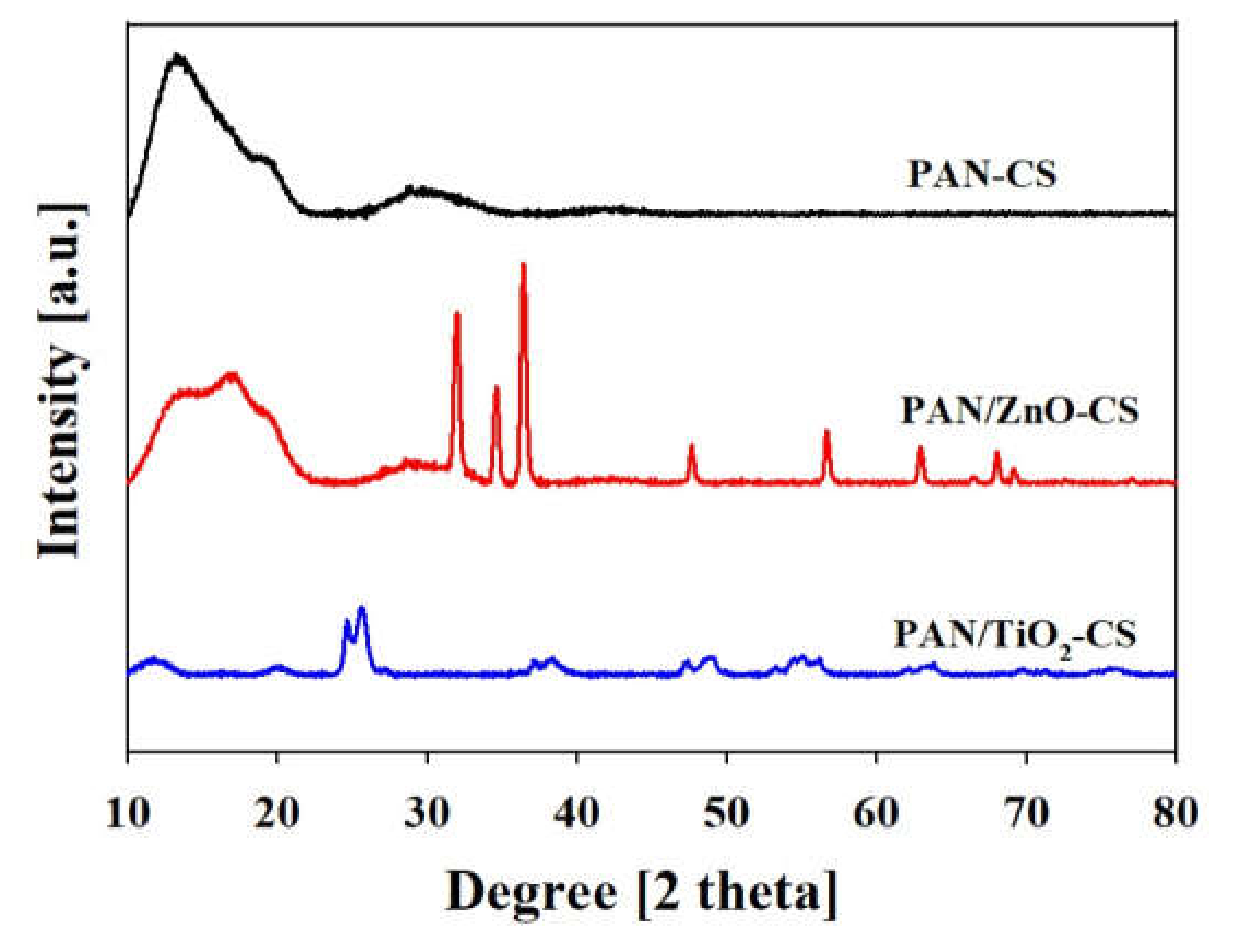
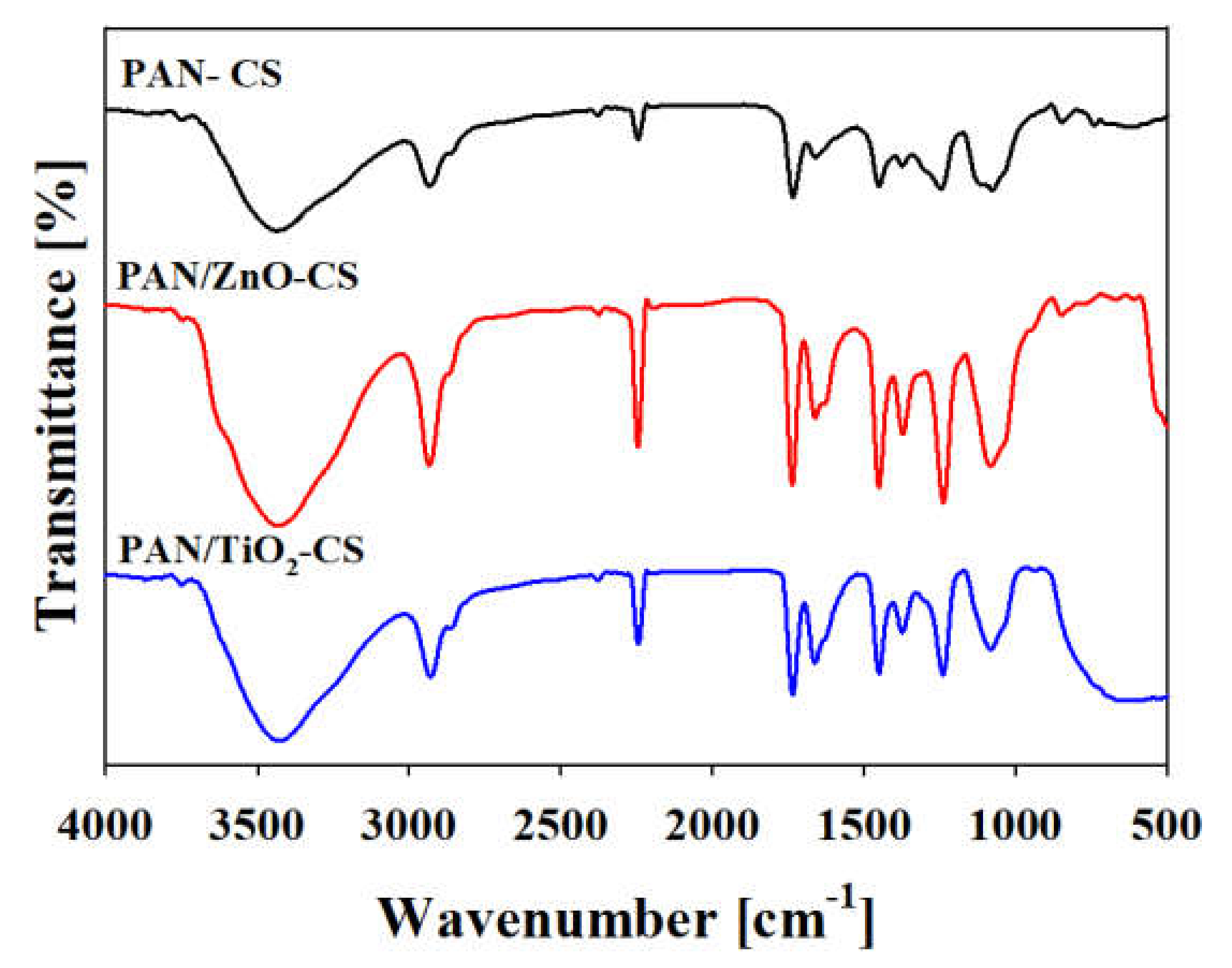
3.1. Characterization of the Bilayer Nanofiber Mat
3.2. Adsorption Study
3.2.1. pH Effect on Metal Ion Adsorption
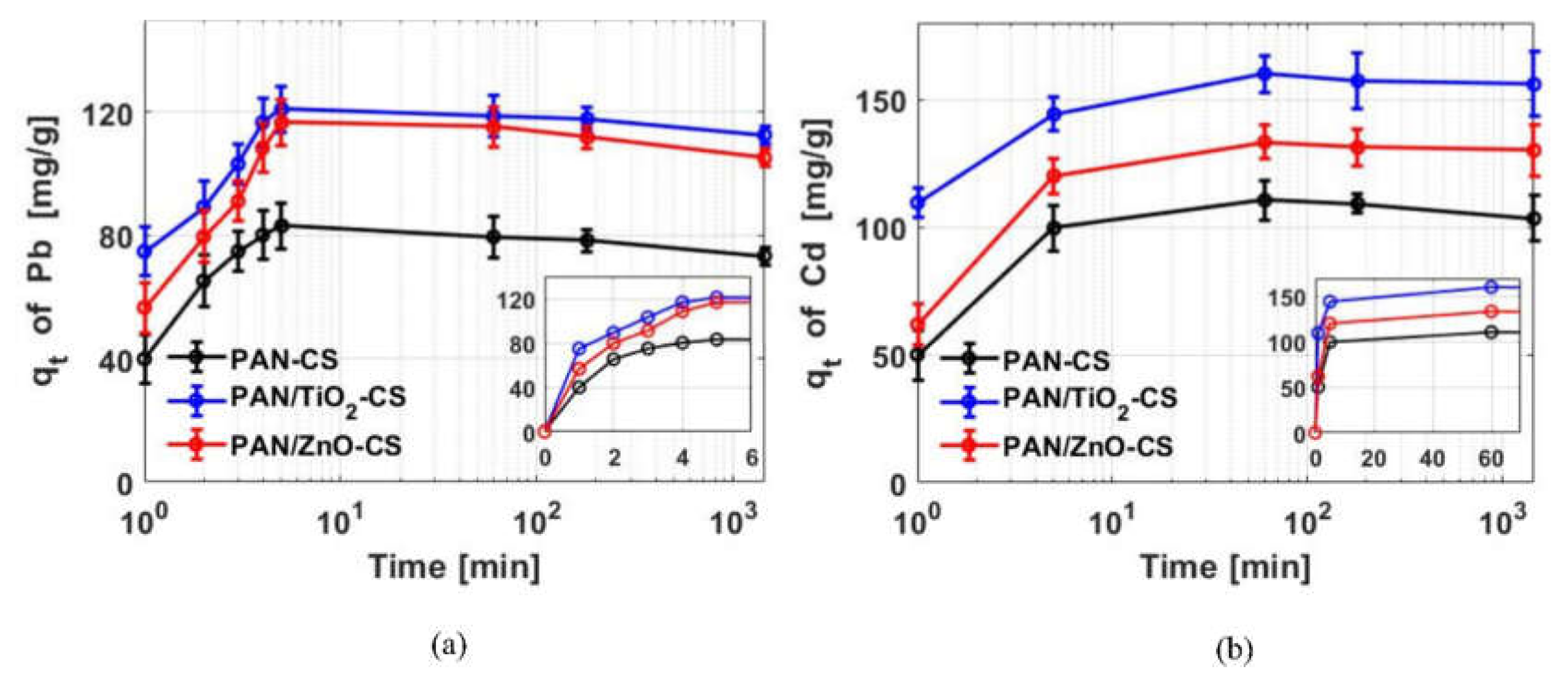
3.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
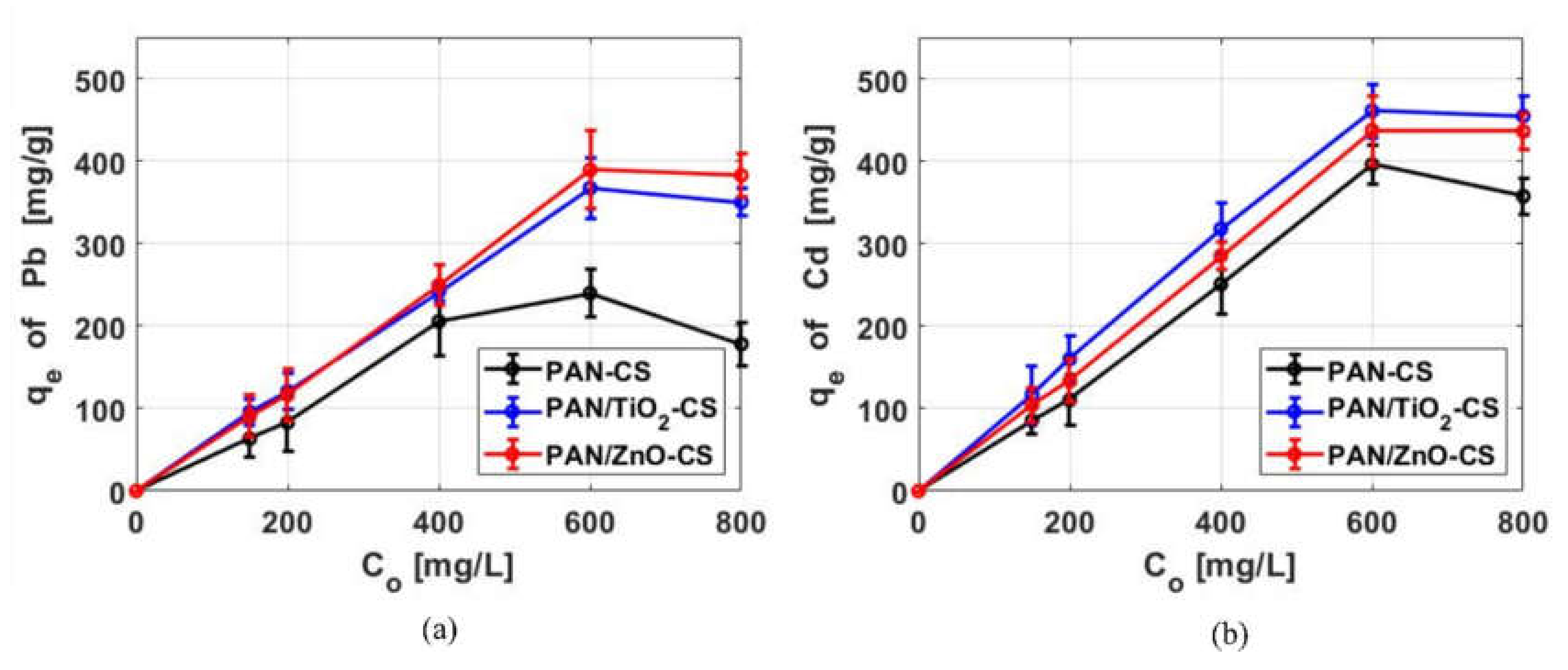
3.2.3. Metal Ions Concentration Effect on Adsorption Properties
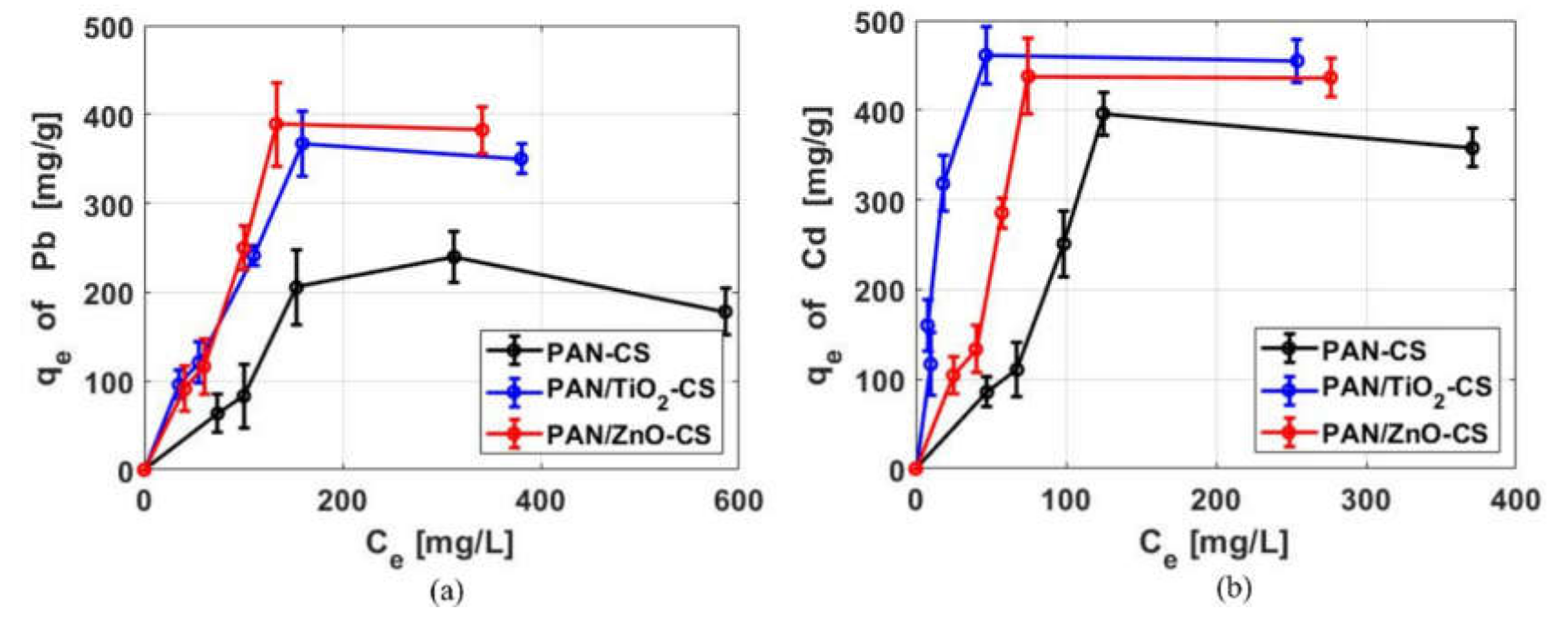
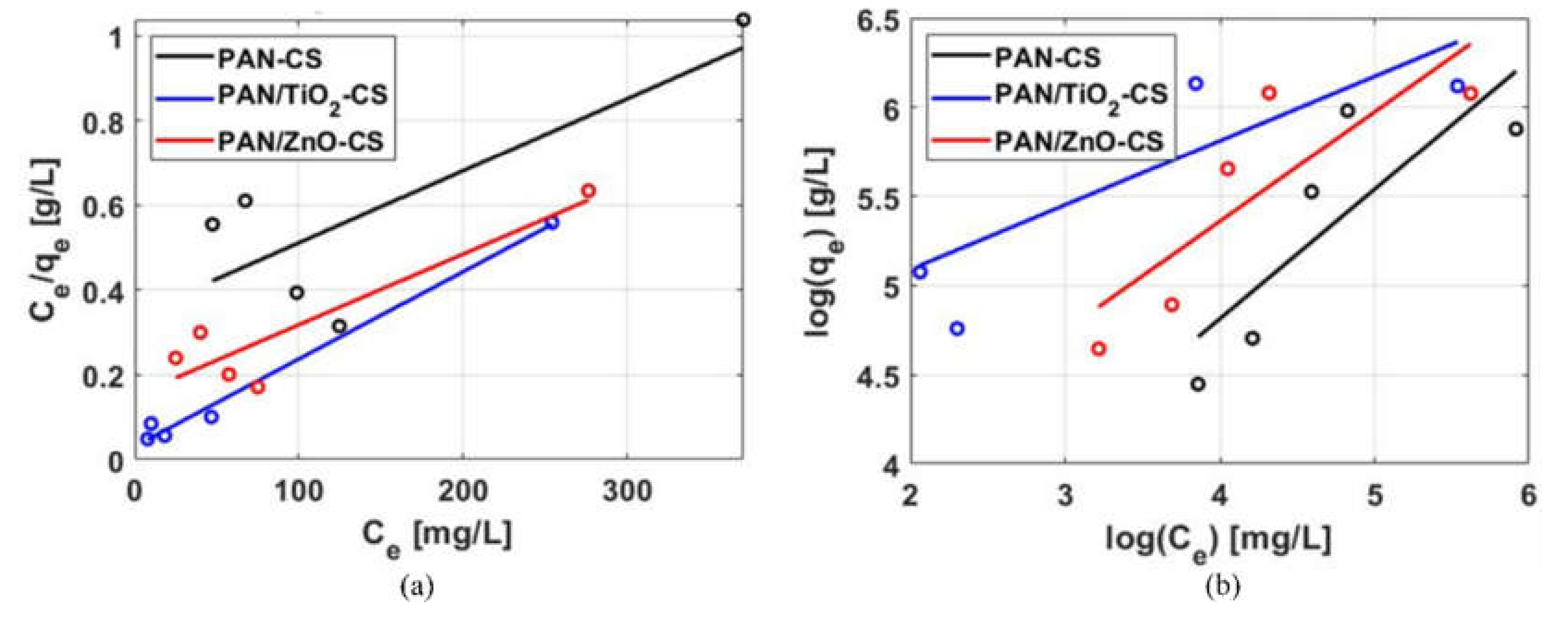
3.2.4. Adsorption Isotherm
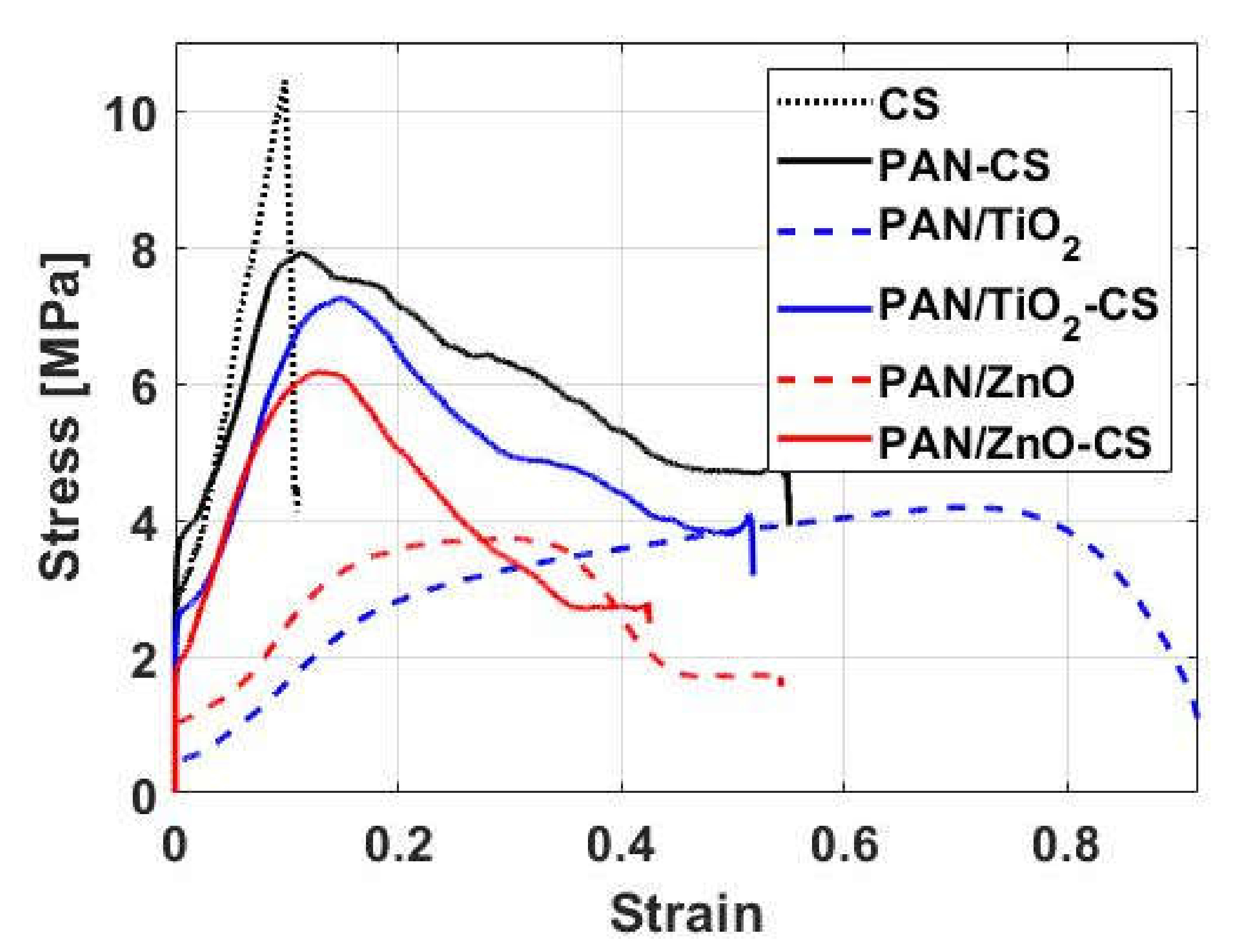
3.3. Tensile Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.M.; Hokanson, D.R.; Zhang, Q.; Czupinski, K.D.; Tang, J.X. Feasibility of water purification technology in rural areas of developing countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, D.D. Water, sanitation and hygiene for the health of developing nations. Public Health 2003, 117, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duruibe, J.O.; Ogwuegbu, M.O.C.; Egwurugwu, J.N. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Miretzky, P.; Saralegui, A.; Cirelli, A.F. Simultaneous heavy metal removal mechanism by dead macrophytes. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoushtari, A.M.; Zargaran, M.; Abdouss, M. Preparation and characterization of high efficiency ion-exchange crosslinked acrylic fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 2202–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Ko, Y.G.; Choi, U.S.; Kim, W.N. Design of high efficiency chelate fibers with an amine group to remove heavy metal ions and pH-related FT-IR analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 2060–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahaei, P.; Abdouss, M.; Edrissi, M.; Shoushtari, A.M.; Zargaran, M. Preparation of chelating fibrous polymer by different diamines and study on their physical and chemical properties. Mater. Und Werkst. 2008, 39, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.Y.; Alharbi, H.F.; Karim, M.R.; Aijaz, M.O.; Alharthi, N.H. Preparation of TiO2 incorporated polyacrylonitrile electrospun nanofibers for adsorption of heavy metal ions. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.W.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun cellulose nanofiber as affinity membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 265, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neghlani, P.K.; Rafizadeh, M.; Taromi, F.A. Preparation of aminated-polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membranes for the adsorption of metal ions: Comparison with microfibers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazilevsky, A.V.; Yarin, A.L.; Megaridis, C.M. Co-electrospinning of core− shell fibers using a single-nozzle technique. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2311–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasian, A.; Jalali, M.; Fard, G.C.; Maleknia, L. Surfactant grafted PDA-PAN nanofiber: Optimization of synthesis, characterization and oil absorption property. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, S.; Yang, K.; Aminabhavi, T. Polyacrylonitrile-based nanofibers—A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botes, M.; Cloete, T.E. The potential of nanofibers and nanobiocides in water purification. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 36, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, S.K.; Yang, K.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Polyacrylonitrile-based nanofibers A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Chenar, M.P.; Sadeghi, M. Surface modification of PAN hollow fiber membrane by chemical reaction. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Giahi, M.; Fard, G.C.; Dehdast, S.; Maleknia, L. Removal of heavy metal ions by modified PAN/PANI-nylon core-shell nanofibers membrane: Filtration performance, antifouling and regeneration behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 1166–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampalanonwat, P.; Supaphol, P. Preparation and Adsorption Behavior of Aminated Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Mats for Heavy Metal Ion Removal. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3619–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasizadeh, S.; Keshtkar, A.R.; Mousavian, M.A. Preparation of a novel electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/titanium oxide nanofiber adsorbent modified with mercapto groups for uranium (VI) and thorium (IV) removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastbaz, A.; Keshtkar, A.R. Adsorption of Th4+, U6+, Cd2+, and Ni2+ from aqueous solution by a novel modified polyacrylonitrile composite nanofiber adsorbent prepared by electrospinning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 293, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Malik, H.N.; Singhal, D.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Malakar, D.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Electrospun polycaprolactone/ZnO nanocomposite membranes as biomaterials with antibacterial and cell adhesion properties. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlayıcı, Ş.; Yar, A.; Avcı, A.; Pehlivan, E. Removal of hexavalent chromium using polyacrylonitrile/titanium dioxide nanofiber membrane. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 16177–16183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, M.; Lim, C.X.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Lee, S.M.; Goh, K.L.; Chang, H.; Chan, E.S. Electrospun functionalized polyacrylonitrile–chitosan Bi-layer membranes for water filtration applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53882–53893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.Y.; Alharbi, H.F. Enhancement of heavy metal ion adsorption using electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers loaded with ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, K.V.H.; Tharanathan, R.N. Chitin/chitosan: Modifications and their unlimited application potential—An overview. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, C.; Li, L. Preparation of hierarchically structured PCL superhydrophobic membrane via alternate electrospinning/electrospraying techniques. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2019, 57, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Zhang, S.S.; Wang, J.N.; Liu, T.Y. Preparation of polyamides 6 (PA6)/Chitosan@FexOy composite nanofibers by electrospinning and pyrolysis and their Cr(VI)-removal performance. Catal. Today 2014, 224, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Park, S.Y. Preparation of the electrospun chitosan nanofibers and their applications to the adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from an aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M.; Ismaeili, J.; Piri, H.; Parnian, M.J. Electrospun nanofiber membrane of PEO/Chitosan for the adsorption of nickel, cadmium, lead and copper ions from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Li, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J. Dioxide/Chitosan/poly(lactide-co-caprolactone) composite membrane with efficient Cu(II) adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 580, 123687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, A.; Haspulat, B.; Üstün, T.; Eskizeybek, V.; Avcı, A.; Kamış, H.; Achour, S. Electrospun TiO 2/ZnO/PAN hybrid nanofiber membranes with efficient photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29806–29814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Wang, W.; Yu, X.; Xu, H.; Zhong, Y.; Sui, X.; Zhang, L.; Mao, Z. Preparation of ZnO:(Al, La)/polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nonwovens with low infrared emissivity via electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2015, 143, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L. Size-controlled synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their photoluminescence properties. J. Lumin. 2007, 122, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, G.; Zinadini, S.; Rajabi, L.; Dadari, S. Fabrication of high flux and antifouling mixed matrix fumarate-alumoxane/PAN membranes via electrospinning for application in membrane bioreactors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Shin, S.R.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, S.I. Swelling characterizations of chitosan and polyacrylonitrile semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.; Qureshi, U.A.; Muqeet, M.; Mahar, R.B.; Ahmed, F.; Khatri, Z. Removal of lead from aqueous solution using polyacrylonitrile/magnetite nanofibers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 3557–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Hota, G. Iron oxide nanoparticle-immobilized PAN nanofibers: Synthesis and adsorption studies. Rsc Adv. 2016, 6, 15402–15414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.S.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, K.P. Sorption of copper by dye-treated oil-palm fibres. Bioresour. Technol. 1993, 44, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalhmunsiama; Lee, S.M.; Tiwari, D. Manganese oxide immobilized activated carbons in the remediation of aqueous wastes contaminated with copper(II) and lead(II). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaran, P. Zeta potential of apatite in aqueous solutions and its change during equilibration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 27, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. Surface Charging and Points of Zero Charge, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Chao, H.-P. Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: A comparison study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2671–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 1998, 70, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.-P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Wang, Y.; Zou, W.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J. Comparison of linear and nonlinear analysis in estimating the Thomas model parameters for methylene blue adsorption onto natural zeolite in fixed-bed column. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfferich, F.G. Principles of adsorption & adsorption processes, by D.M. Ruthven, John Wiley & Sons, 1984, xxiv + 433 pp. Aiche J. 1985, 31, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. The Adsorption in Physical Chemistry; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1906. [Google Scholar]
- Vasanth Kumar, K.; Sivanesan, S. Equilibrium data, isotherm parameters and process design for partial and complete isotherm of methylene blue onto activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 134, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.R.; Eagleton, L.C.; Acrivos, A.; Vermeulen, T. Pore- and Solid-Diffusion Kinetics in Fixed-Bed Adsorption under Constant-Pattern Conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1966, 5, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V. Comments on “Equilibrium studies for the adsorption of Acid dye onto modified hectorite”. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1252–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M. The Equation of the Characteristic Curve of Activated Charcoal. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1947, 55, 327–329. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, J.P. Physical adsorption isotherms extending from ultrahigh vacuum to vapor pressure. J. Phys. Chem. 1969, 73, 2720–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ali, S.; Jaouali, I.; Souissi-Najar, S.; Ouederni, A. Characterization and adsorption capacity of raw pomegranate peel biosorbent for copper removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3809–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noei, H.; Qiu, H.; Wang, Y.; Löffler, E.; Wöll, C.; Muhler, M. The identification of hydroxyl groups on ZnO nanoparticles by infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 7092–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, S.; Jalali, M.; Afkhami, A. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4, ZnO, and CuO nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Qian, Q.; Machida, M.; Tatsumoto, H. Effect of ZnO loading to activated carbon on Pb(II) adsorption from aqueous solution. Carbon 2006, 44, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, D.W.; Kim, B.C. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the physical properties of polyacrylonitrile. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Adsorbents | Adsorption of Lead | Adsorption of Cadmium | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1/min) | (mg/g) | (mg/g) | MAAE % | (1/min) | (mg/g) | (mg/g) | MAAE % | |
| PAN–CS | 0.0077 | 83.8 | 88.5 | 0.6 | 0.0078 | 110.5 | 114.0 | 2.5 |
| PAN/TiO2–CS | 0.0056 | 127.9 | 131.2 | 2.8 | 0.0136 | 160.1 | 159.2 | 0.7 |
| PAN/ZnO–CS | 0.0029 | 119.0 | 126.4 | 1.6 | 0.0067 | 133.3 | 137.4 | 2.3 |
| Adsorbents | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | MAAE % | n | KF (mg/g)/(mg/L)n | R2 | MAAE % | |
| PAN–CS | 234.45 (268.5) | 0.0086 (0.008) | 0.82 | 14.7 (15.4) | 1.86 (2.92) | 8.25 (25.2) | 0.59 | 17.5 (103.4) |
| PAN/TiO2–CS | 491.74 (502.9) | 0.0079 (0.008) | 0.90 | 7.4 (7.8) | 1.63 (2.23) | 11.82 (27.69) | 0.85 | 11.7 (70.6) |
| PAN/ZnO–CS | 662.56 (592.7) | 0.0048 (0.007) | 0.71 | 10.4 (10.5) | 1.34 (1.99) | 6.68 (22.7) | 0.80 | 14.8 (124.4) |
| Adsorbents | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | MAAE % | n | KF (mg/g)/ (mg/L)n | R2 | MAAE % | |
| PAN–CS | 588.4 (530.3) | 0.005 (0.008) | 0.63 | 13.3 (13.6) | 1.38 (2.23) | 6.80 (28.4) | 0.66 | 18.0 (154) |
| PAN/TiO2–CS | 486.5 (529.3) | 0.064 (0.06) | 0.98 | 8.4 (8.9) | 2.77 (3.98) | 78.95 (125.2) | 0.67 | 15.8 (29.7) |
| PAN/ZnO–CS | 600.6 (588.7) | 0.011 (0.014) | 0.84 | 11.8 (12.2) | 1.63 (49.7) | 18.26 (2.48) | 0.69 | 17.3 (46.1) |
| Nanofiber Mat | Maximum Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break |
| CS | 11.72 ± 0.96 | 0.11 ± 0.09 |
| PAN–CS | 7.91 ± 0.74 | 0.55 ± 0.06 |
| PAN/TiO2 | 4.18 ± 0.53 | 0.92 ± 0.07 |
| PAN/TiO2–CS | 7.25 ± 0.65 | 0.52 ± 0.05 |
| PAN/ZnO | 3.73 ± 0.35 | 0.54 ± 0.05 |
| PAN/ZnO–CS | 6.18 ± 0.71 | 0.43 ± 0.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, H.F.; Haddad, M.Y.; Aijaz, M.O.; Assaifan, A.K.; Karim, M.R. Electrospun Bilayer PAN/Chitosan Nanofiber Membranes Incorporated with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption. Coatings 2020, 10, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030285
Alharbi HF, Haddad MY, Aijaz MO, Assaifan AK, Karim MR. Electrospun Bilayer PAN/Chitosan Nanofiber Membranes Incorporated with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption. Coatings. 2020; 10(3):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030285
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Hamad F., Mustafa Y. Haddad, Muhammed Omer Aijaz, Abdulaziz K. Assaifan, and Mohammed R. Karim. 2020. "Electrospun Bilayer PAN/Chitosan Nanofiber Membranes Incorporated with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption" Coatings 10, no. 3: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030285
APA StyleAlharbi, H. F., Haddad, M. Y., Aijaz, M. O., Assaifan, A. K., & Karim, M. R. (2020). Electrospun Bilayer PAN/Chitosan Nanofiber Membranes Incorporated with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption. Coatings, 10(3), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030285







