The Effect of Carbon Ink Rheology on Ink Separation Mechanisms in Screen-Printing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterisation of Ink Rheology and TGA
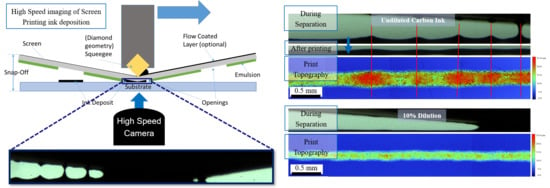
2.2. Visualisation of Screen-Printing Process
2.3. Characterisation of Print Topography and Electrical Properties
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of Ink Rheology and TGA
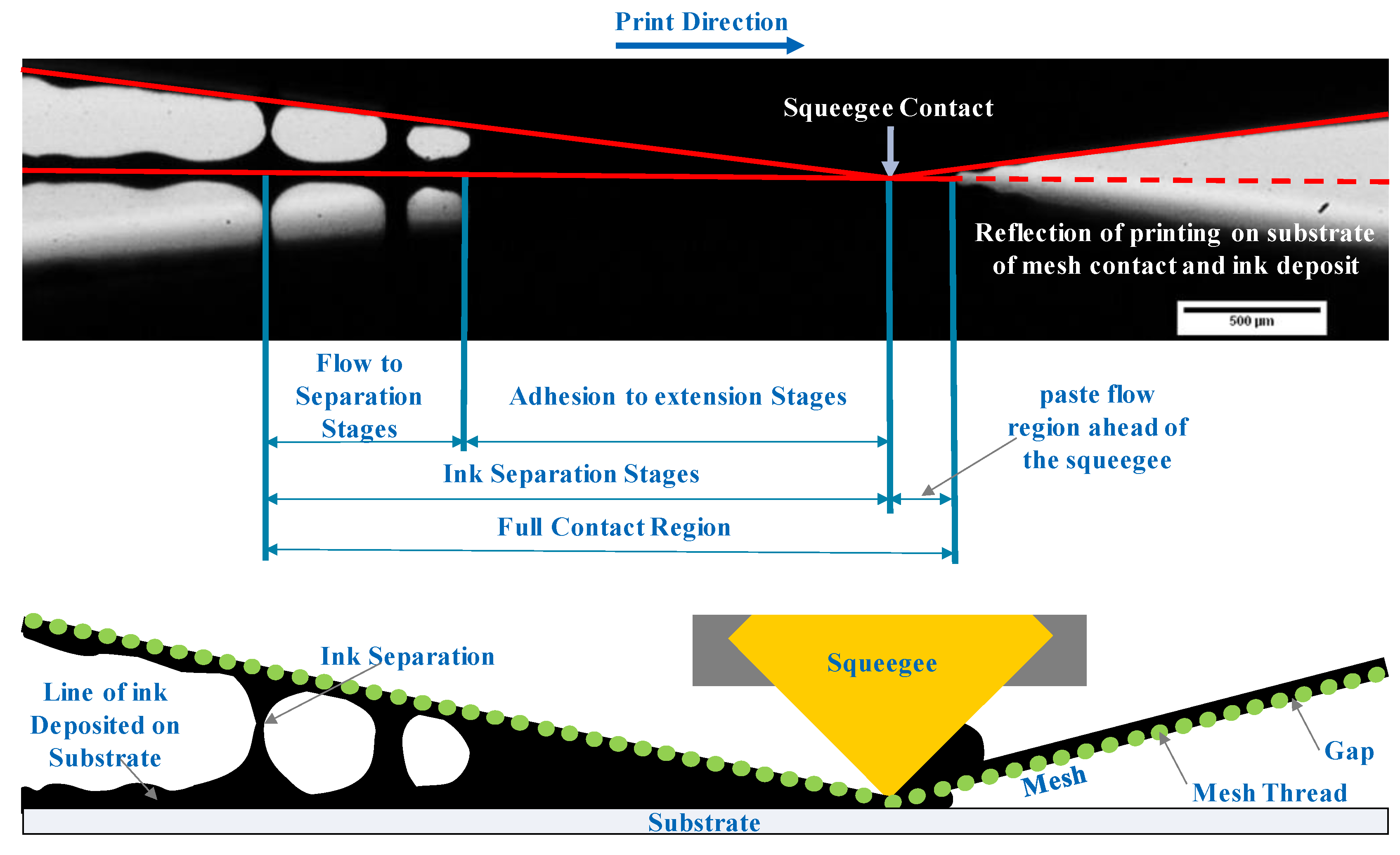
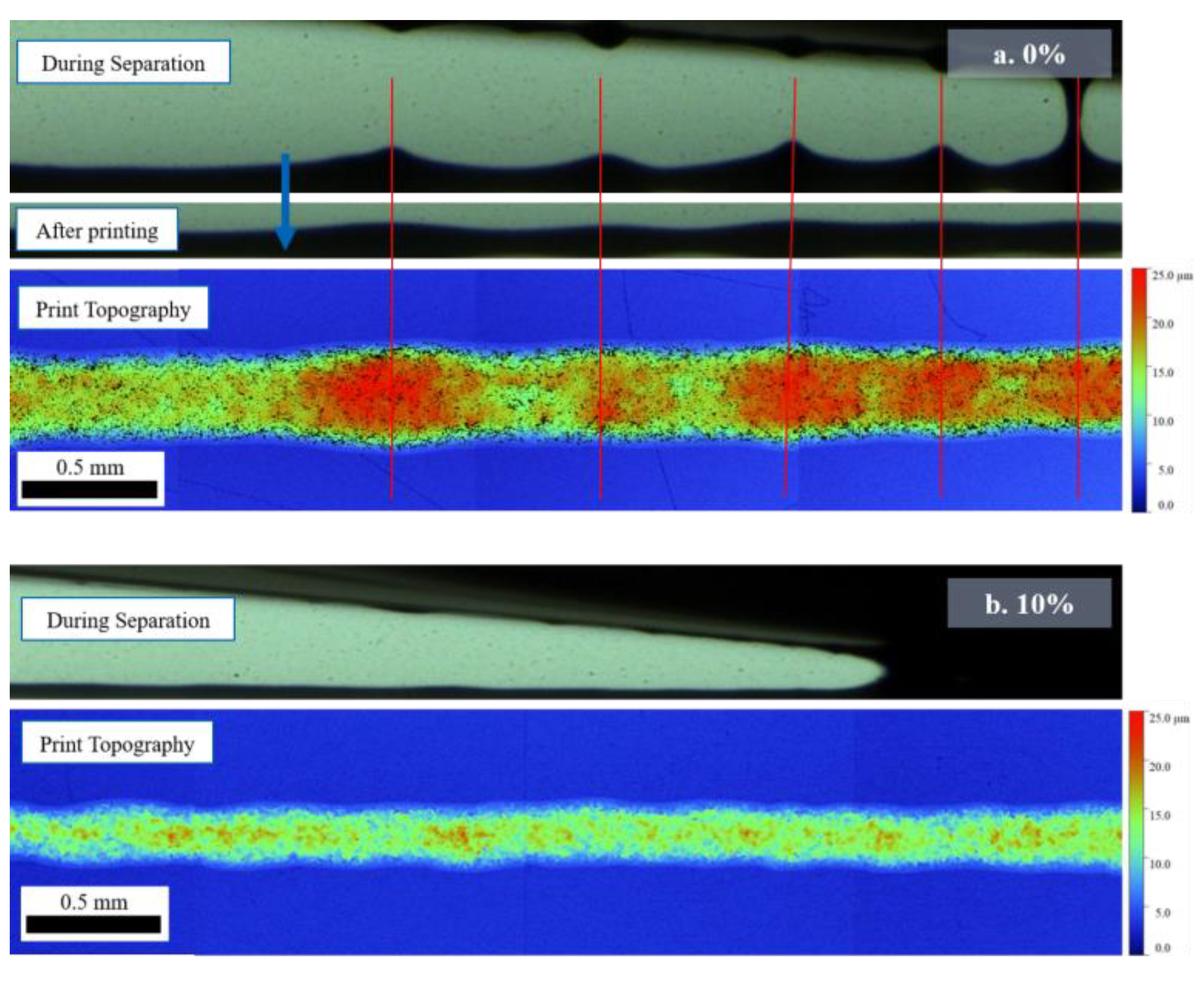
3.2. Ink Separation Mechanisms
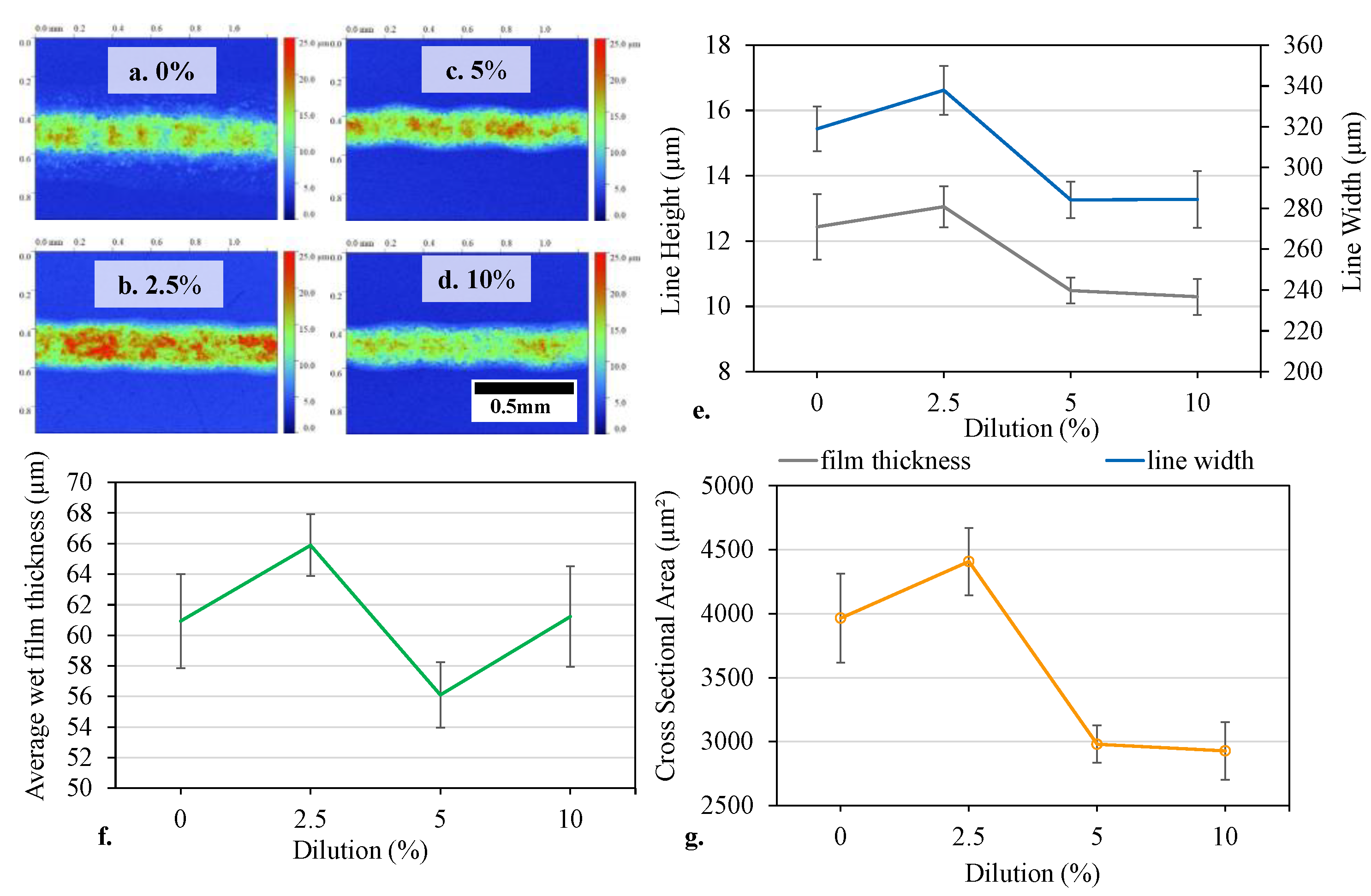
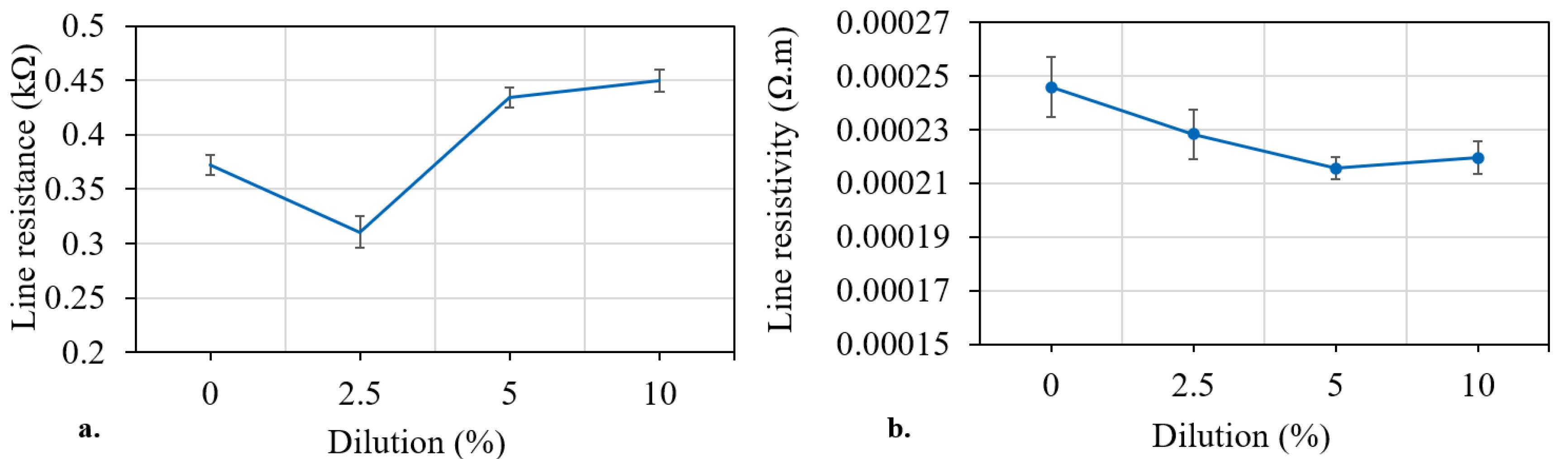
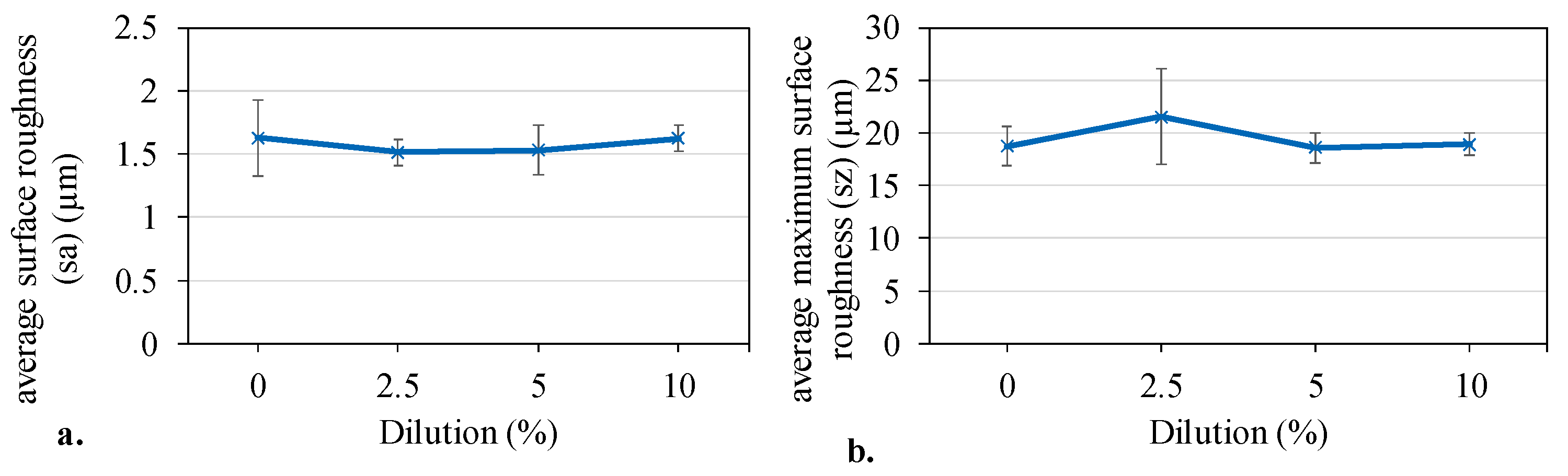
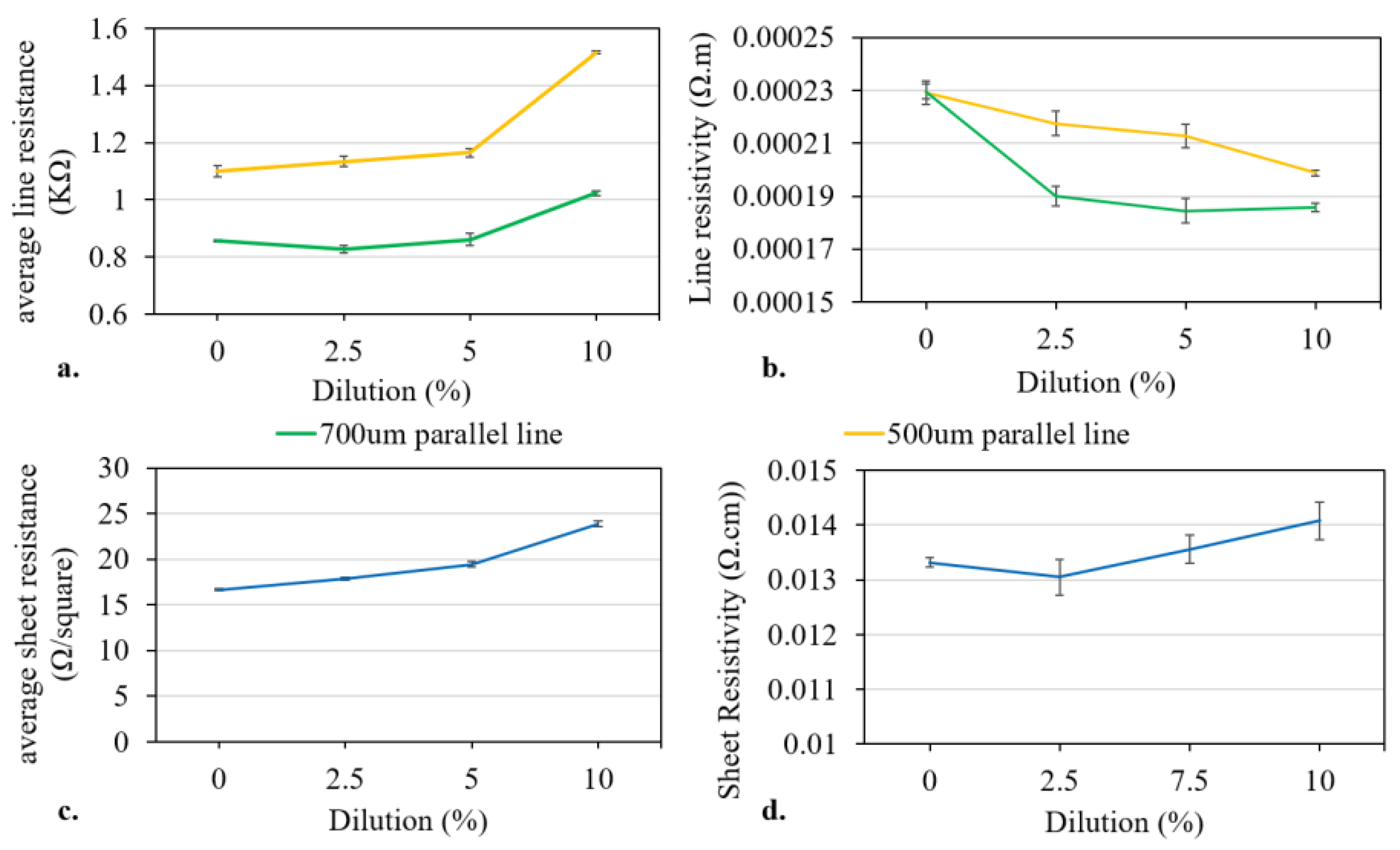
3.3. Print Characterisation
3.3.1. Custom Screen-Printing Apparatus
3.3.2. Full Scale Printing Press
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Philip, B.; Jewell, E.; Greenwood, P.; Weirman, C. Material and process optimization screen printing carbon graphite pastes for mass production of heating elements. J. Manuf. Process. 2016, 22, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, S.K.; Bae, S.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, B.H. High-performance graphene-based transparent flexible heaters. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5154–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, Z.; Burwell, G.; Azmi, M.M.; Castaing, A.; Rickman, R.; Almarashi, J.; Dunstan, P.; Miran Beigi, A.; Doak, S.H.; Guy, O.J. Generic epitaxial graphene biosensors for ultrasensitive detection of cancer risk biomarker. 2D Mater. 2014, 1, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrin, A.; Killard, A.J.; Smyth, M.R. Electrochemical characterization of commercial and home-made screen-printed carbon electrodes. Anal. Lett. 2003, 36, 2021–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tehrani, Z.; Korochkina, T.; Govindarajan, S.; Thomas, D.J.; O’Mahony, J.; Kettle, J.; Claypolea, T.C.; Gethin, D.T. Ultra-thin flexible screen printed rechargeable polymer battery for wearable electronic applications. Org. Electron. 2015, 26, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suren, S.; Kheawhom, S. Development of a high energy density flexible zinc-air battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A846–A850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, J.; Hooper, K.; Meroni, S.; Pockett, A.; McGettrick, J.; Wei, Z.; Escalante, R.; Oskam, G.; Carnie, M.; Watson, T. High throughput fabrication of mesoporous carbon perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 18643–18650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, L.; Hu, M.; Yang, Y.; Mei, A.; Han, H. The effect of carbon counter electrodes on fully printable mesoscopic perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9165–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxfall, H.; Ariu, G.; Gkourmpis, T.; Rychwalski, R.W.; Rigdahl, M. Effect of carbon black on electrical and rheological properties of graphite nanoplatelets/poly(ethylene-butyl acrylate) composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, C.; Al-Ahmadi, A.; Potts, S.J.; Claypole, T.; Deganello, D. The effect of graphite and carbon black ratios on conductive ink performance. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9520–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, H.; Pitt, W.G.; McGrath, L.K.; Ho, C.K. Resistivity measurements of carbon-polymer composites in chemical sensors: Impact of carbon concentration and geometry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 101, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, E.H.; Hamblyn, S.M.; Claypole, T.C.; Gethin, D.T. The impact of carbon content and mesh on the characteristics of screen printed conductive structures. Circuit World 2013, 39, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, E.; Philip, B.; Greenwood, P. Improved manufacturing performance of screen printed carbon electrodes through material formulation. Biosensors 2016, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philip, B.; Jewell, E.; Worsley, D. The impact of solvent characteristics on performance and process stability of printed carbon resistive materials. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 13, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Tonkay, G.L.; Quintero, A. Screen printing process design of experiments for fine line printing of thick film ceramic substrates. J. Electron. Manuf. 1999, 9, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molamphy, T.A.; Stephenson, M.I.; Murphy, E.A. Application of experimental design to the solder paste screen printing process. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 1992, 11, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, E.H.; Claypole, T.C.; Gethin, D.T. The Impact of ink rheology on the image transfer mechanism in screen printing. In Proceedings of the Institute of Non Newtonian fluid mechanics, Conference on Rheology, Cardiff, UK, April 2003; Institute of Non Newtonian fluid mechanics: Cardiff, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Cheng, K.; Wang, Z. Optimization of Screen Printing Process. In Proceedings of the 7th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 05EX1233C), Singapore, 7–9 December 2005; IEEE: Singapore, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, I.J.; Bohan, M.F.J.; Claypole, T.C.; Gethin, D.T. Film thickness prediction in halftone screen-printing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2003, 217, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, S.H.; Ekere, N.N.; Ismail, I.; Lo, E.K. Squeegee deformation study in the stencil printing of solder pastes. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. Part A 1994, 17, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, E.H.; Claypole, T.C.; Gethin, D.T. Viscosity control in the screen printing of ceramic transfers. Surf. Coat. Int. Part B Coat. Trans. 2003, 86, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemer, D.E. The direct emulsion screen as a tool for high resolution thick film printing. In Proceedings of the 21st Electronic Component Conference Proceedings, Washington, DC, USA, 10–12 May 1971; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Riemer, D.E. The theoretical fundamentals of the screen printing process. Microelectron. Int. 1989, 6, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemer, D.E. Analytical engineering model of the screen printing process: Part I. Solid State Technol. 1988, 8, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Riemer, D.E. Analytical engineering model of the screen printing process: Part II. Solid State Technol. 1988, 9, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Messerschmitt, E. Rheological considerations for screen printing inks. Screen Print. 1982, 72, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Potts, S.J.; Phillips, C.; Jewell, E.; Clifford, B.; Lau, Y.C.; Claypole, T. High-speed imaging the effect of snap-off distance and squeegee speed on the ink transfer mechanism of screen-printed carbon pastes. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020, 17, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potts, S.J.; Phillips, C.; Claypole, T. High Speed Imaging of Ink Separation in Screen-Printing. In Advances in Printing and Media Technology, Proceedings of the 46th International Research Conference of Iarigai, Stuttgart, Germany, 15–18 September 2019; Ridgway, C., Ed.; The International Association of Research Organizations for the Information, Media and Graphic Arts Industries: Darmstadt, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda, M.M.; Auscher, M.C.; Fulchiron, R.; Perie, T.; Martin, G.; Sonntag, P.; Cassagnau, P. Rheology and applications of highly filled polymers: A review of current understanding. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 66, 22–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A. A Handbook of Elementary Rheology, 1st ed.; The University of Wales Institute of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, Department of Mathematics: Wales, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Holder, A.J.; Claypole, J.; Claypole, T.; Cooper, P.G.; Williams, P.R.; Curtis, D.J. Fourier transform controlled stress parallel superposition (FT-CSPS): Validation and application in processing printable functional materials. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 077105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claypole, A.; Claypole, J.; Holder, A.; Claypole, T.C.; Kilduff, L. Rheology of high-aspect-ratio nanocarbons dispersed in a low-viscosity fluid. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020, 17, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, F.M. Measurement of sheet resistivities with the four-point probe. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1958, 37, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, V.; Weitz, D.A. Scaling of the viscoelasticity of weakly attractive particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amari, T.; Uesugi, K.; Suzuki, H. Viscoelastic properties of carbon black suspension as a flocculated percolation system. Prog. Org. Coat. 1997, 31, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, S.J.; Lau, Y.C.; Dunlop, T.; Claypole, T.; Phillips, C. Effect of photonic flash annealing with subsequent compression rolling on the topography, microstructure and electrical performance of carbon-based inks. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8163–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jewell, E.; Hamblyn, S.; Claypole, T.; Gethin, D. Deposition of high conductivity low silver content materials by screen printing. Coatings 2015, 5, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willfahrt, A. Screen printed thermoelectric devices. Linköping Stud. Sci. Technol. 2014, 1663, 49. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potts, S.-J.; Phillips, C.; Claypole, T.; Jewell, E. The Effect of Carbon Ink Rheology on Ink Separation Mechanisms in Screen-Printing. Coatings 2020, 10, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10101008
Potts S-J, Phillips C, Claypole T, Jewell E. The Effect of Carbon Ink Rheology on Ink Separation Mechanisms in Screen-Printing. Coatings. 2020; 10(10):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10101008
Chicago/Turabian StylePotts, Sarah-Jane, Chris Phillips, Tim Claypole, and Eifion Jewell. 2020. "The Effect of Carbon Ink Rheology on Ink Separation Mechanisms in Screen-Printing" Coatings 10, no. 10: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10101008
APA StylePotts, S.-J., Phillips, C., Claypole, T., & Jewell, E. (2020). The Effect of Carbon Ink Rheology on Ink Separation Mechanisms in Screen-Printing. Coatings, 10(10), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10101008