Biocompatibility of Niobium Coatings
Abstract
: Niobium coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering were evaluated as a possible surface modification for stainless steel (SS) substrates in biomedical implants. The Nb coatings were deposited on 15 mm diameter stainless steel substrates having an average surface roughness of 2 μm. To evaluate the biocompatibility of the coatings three different in vitro tests, using human alveolar bone derived cells, were performed: cellular adhesion, proliferation and viability. Stainless steel substrates and tissue culture plastic were also studied, in order to give comparative information. No toxic response was observed for any of the surfaces, indicating that the Nb coatings act as a biocompatible, bioinert material. Cell morphology was also studied by immune-fluorescence and the results confirmed the healthy state of the cells on the Nb surface. X-ray diffraction analysis of the coating shows that the film is polycrystalline with a body centered cubic structure. The surface composition and corrosion resistance of both the substrate and the Nb coating were also studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and potentiodynamic tests. Water contact angle measurements showed that the Nb surface is more hydrophobic than the SS substrate.1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
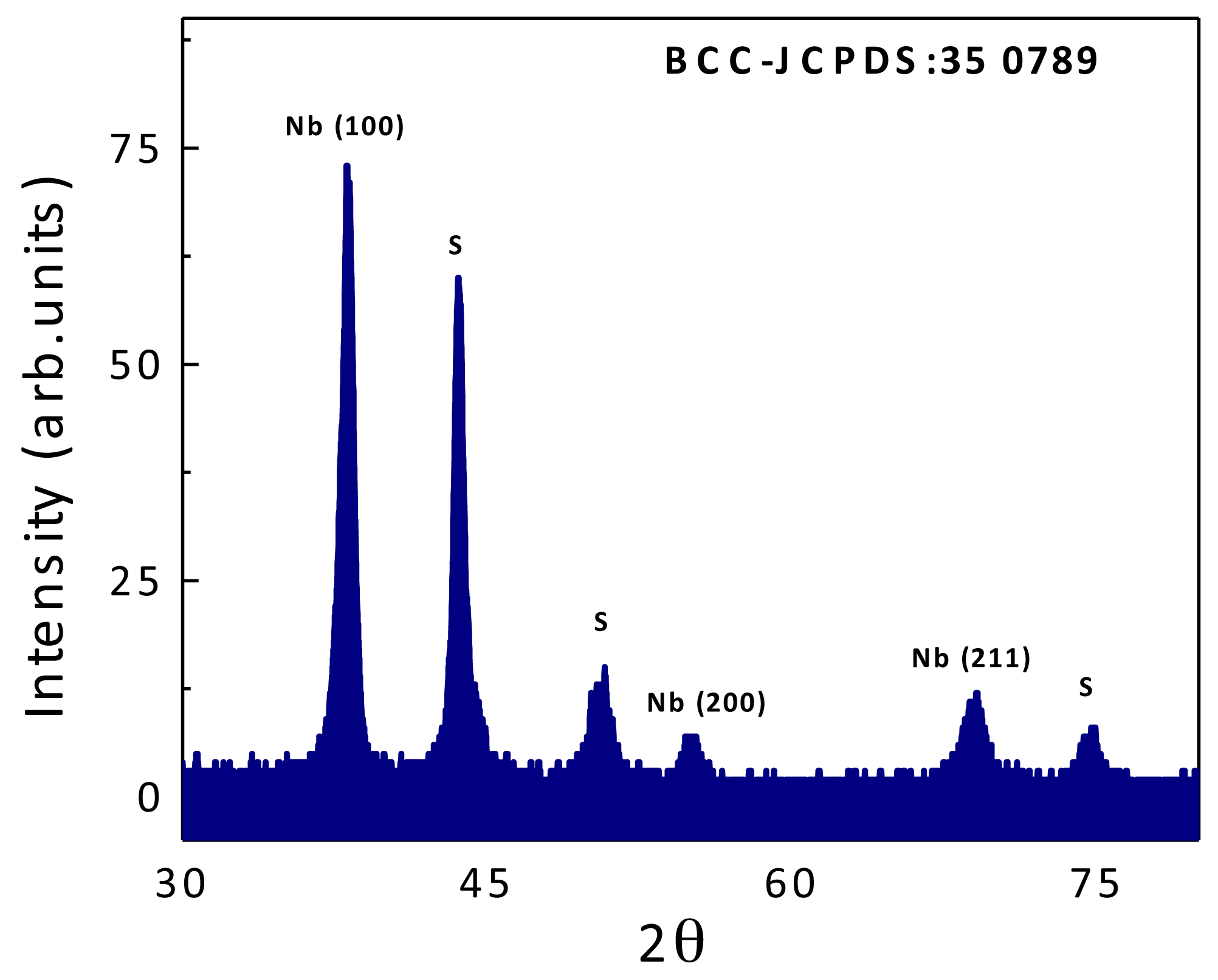
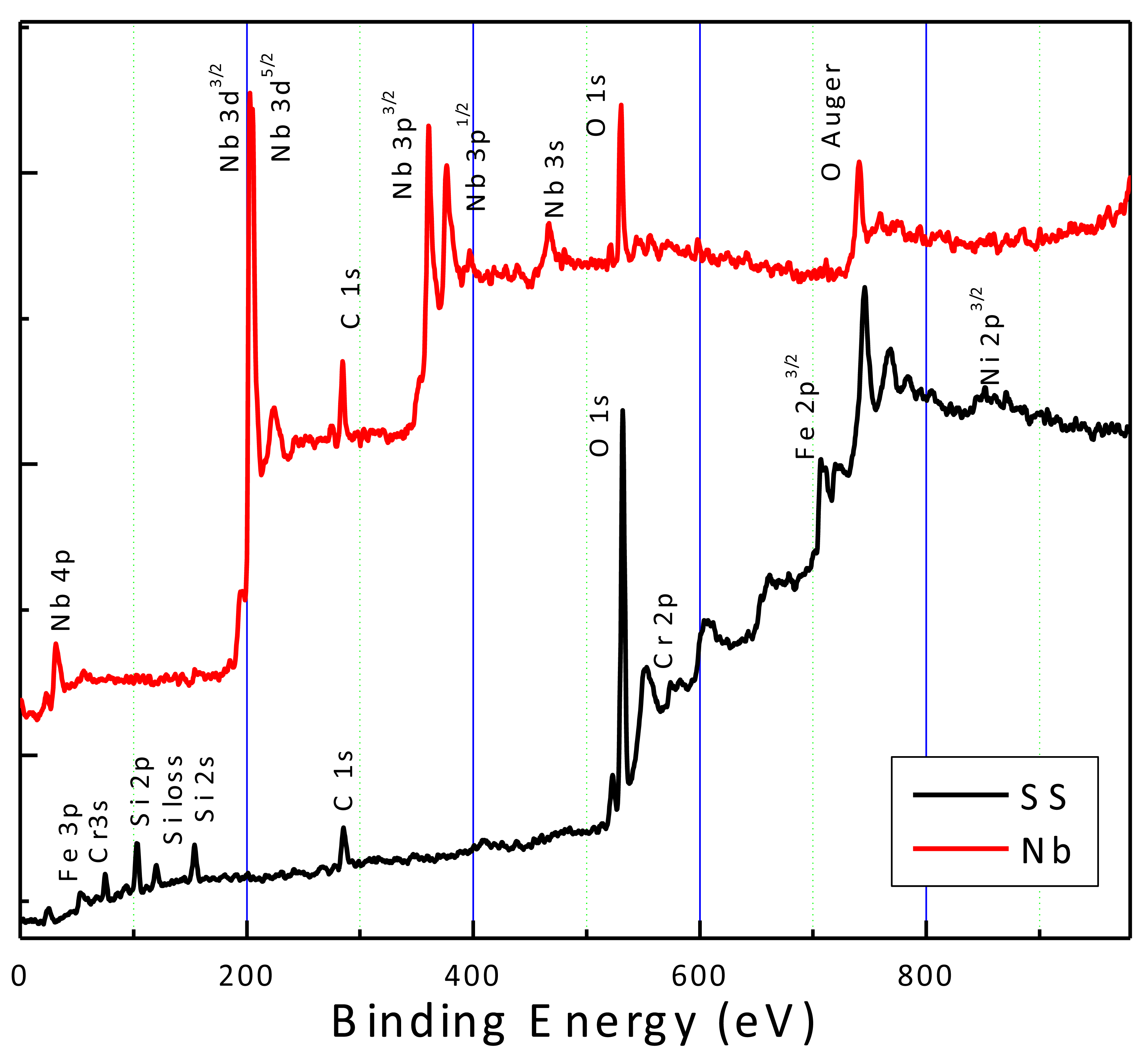
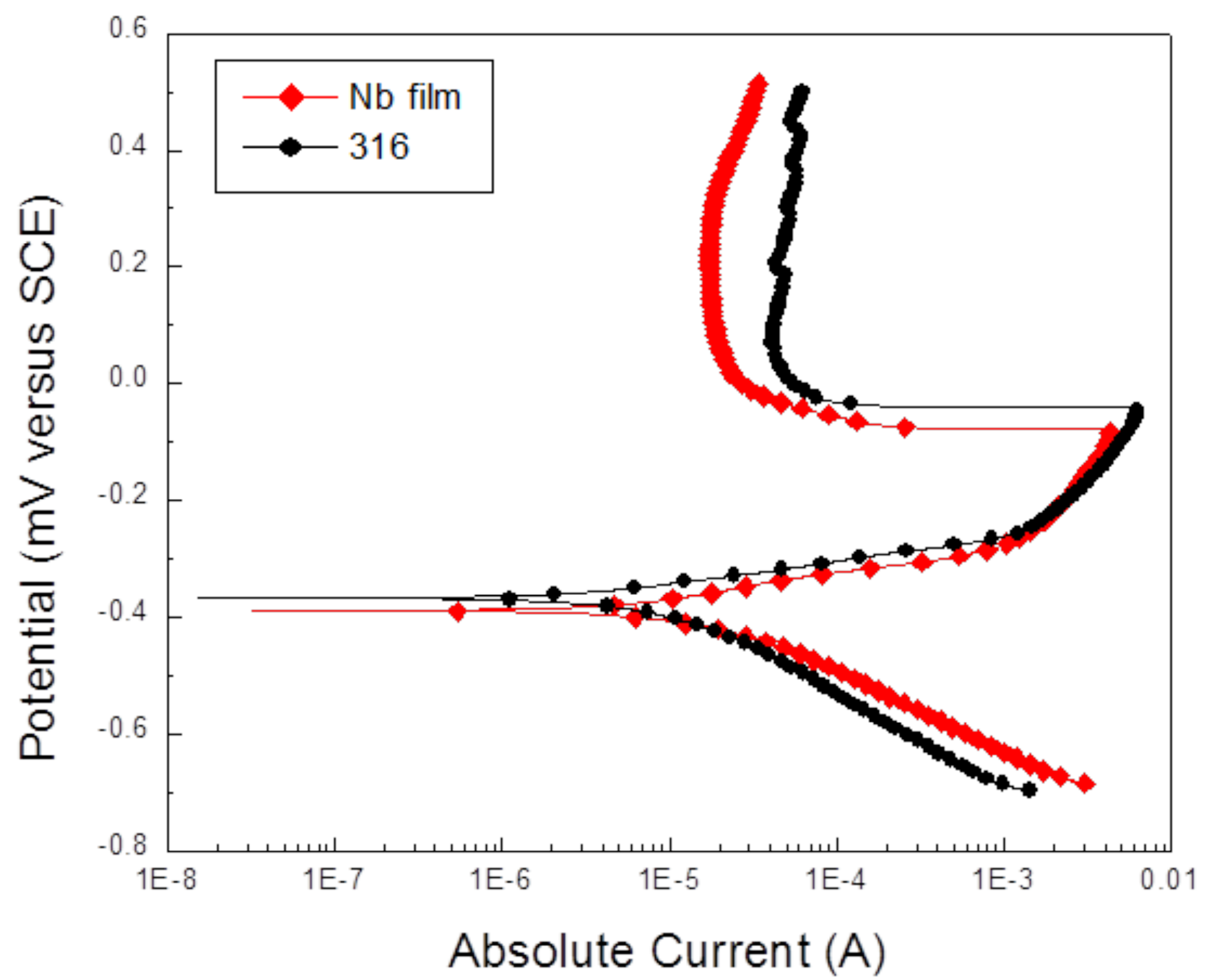
2.1. Coatings Physical Properties
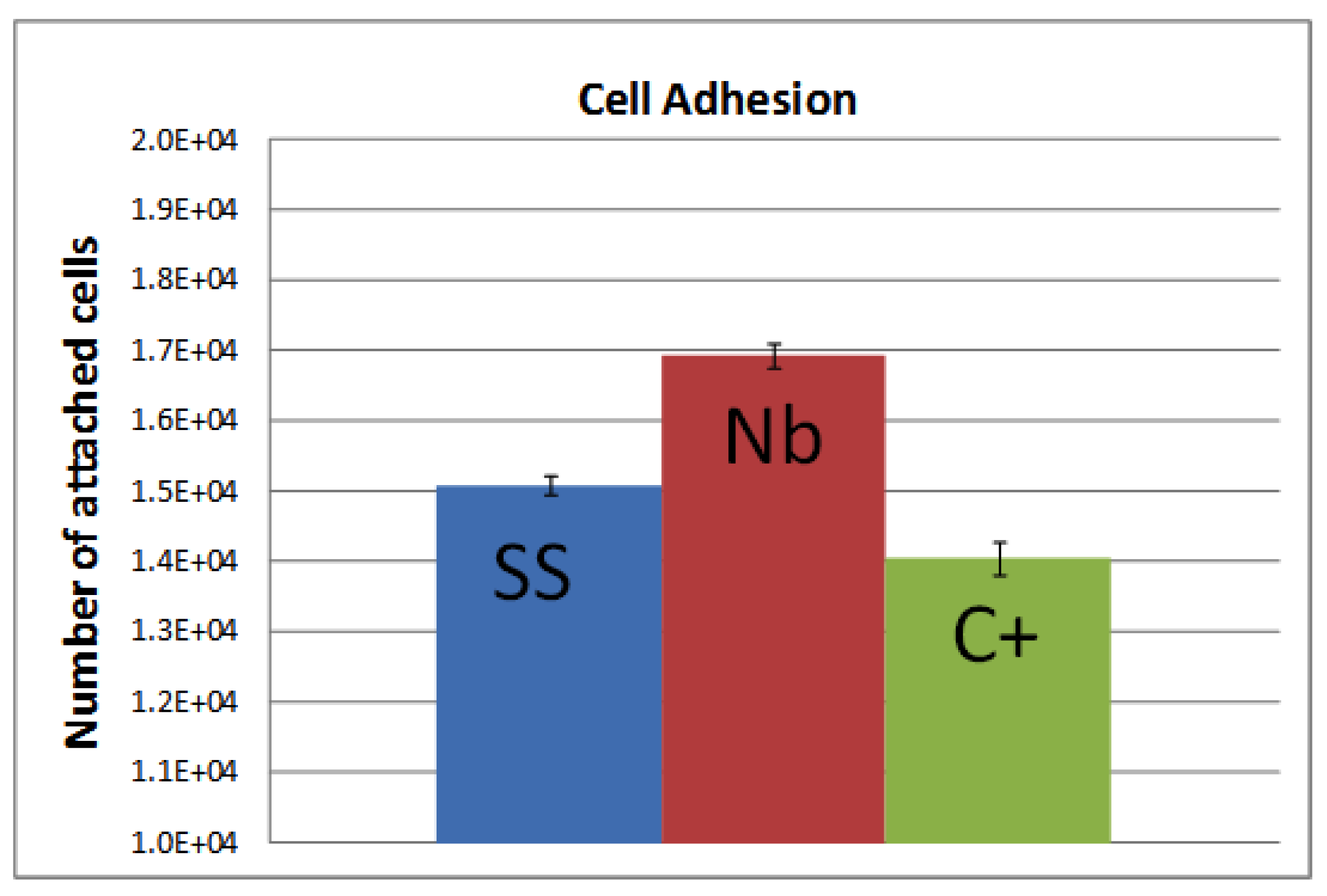
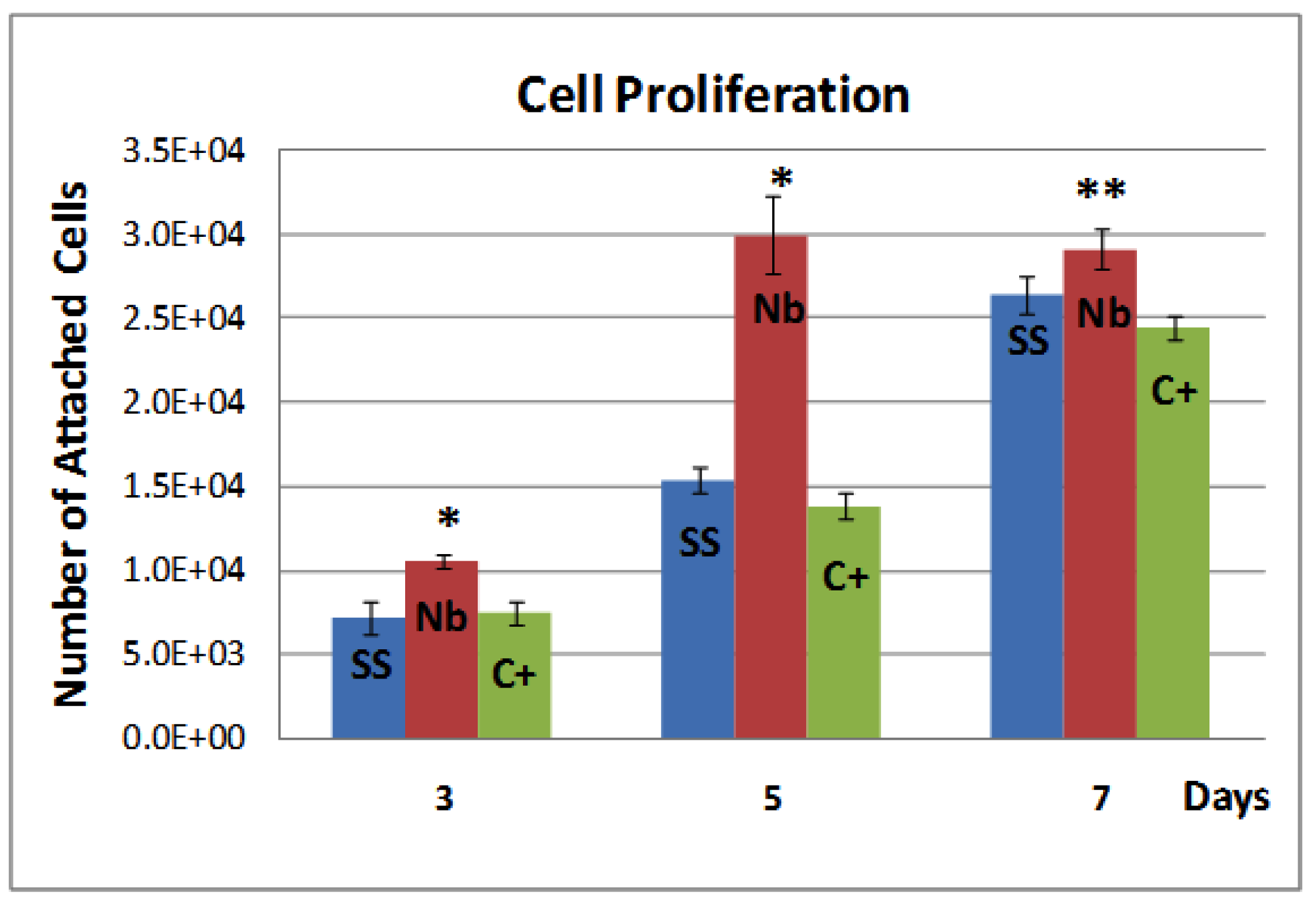
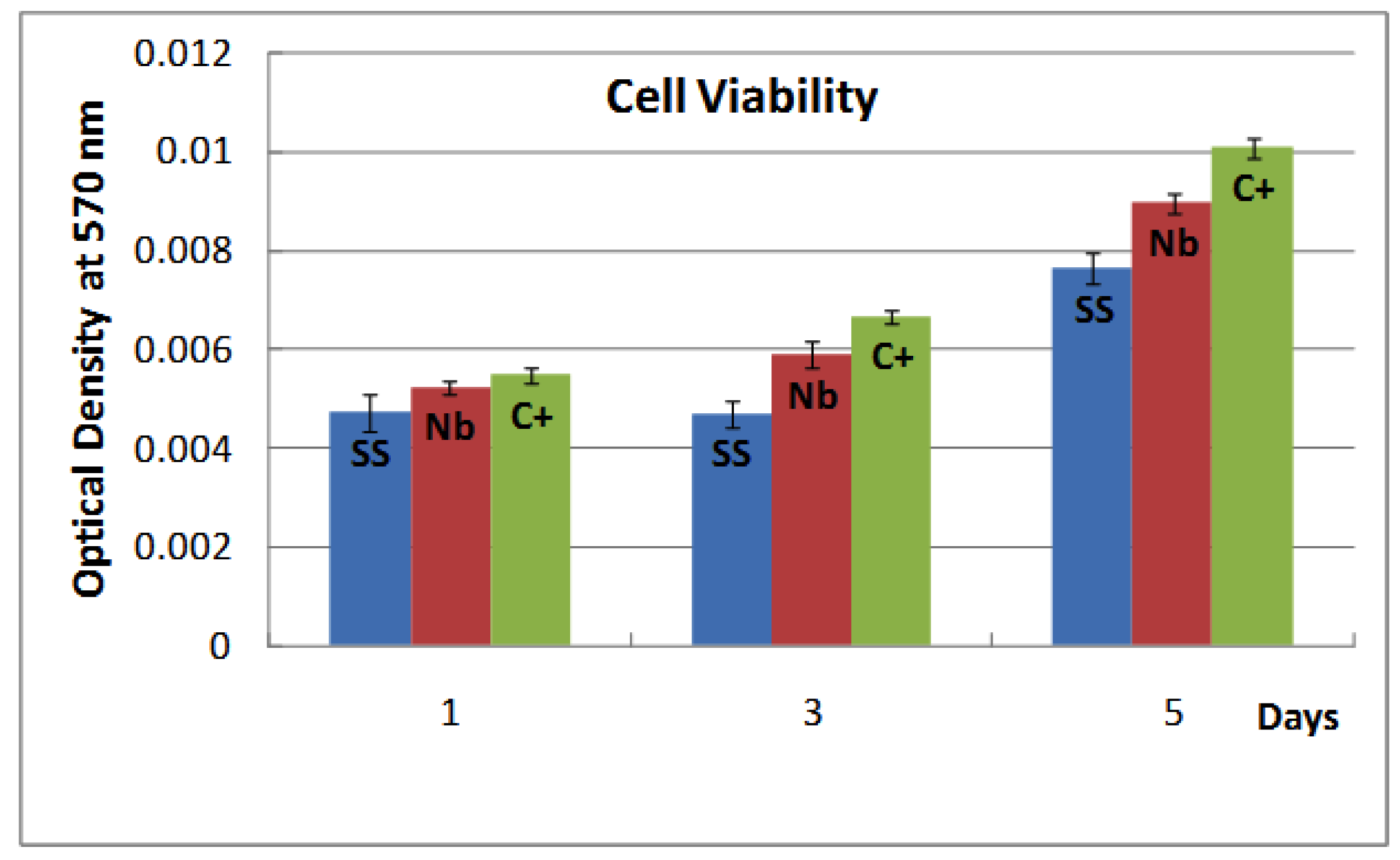
2.2. Biocompatibility
2.3. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Disks Preparation
3.2. Thin Film Deposition
3.3. Physical Properties
3.4. Cell Preparation
3.5. Biocompatibility Tests
3.6. Cellular Attachment
3.7. Cellular Proliferation
3.8. Citotoxicity, MTT Test
3.9. Morphological Characterization of the Cells Using Fluorescence Microscopy
4. Conclusions


| Roughness and Water Contact angle | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sample | Roughness (μm) | Water contact angle |
| SS | 1.79 ± 0.3 | 46 ± 0.67 |
| Nb | 1.87 ± 0.35 | 67 ± 1.25 |
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Jacobs, J.J.; Gilbert, J.L.; Urban, R.M. Corrosion of metal orthopaedic implants. J. Bone Joint Surg. 1998, 80A, 268–282. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, H.; Ochi, S.; Tanetani, K.; Kato, K.; Isogai, M.; Mizuno, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamagami, A. Biological test of dental biomaterials, effect of pure metals upon the mouse subcutaneous fibroblast, strain L cell in tissue cultura. Japan Soc. Dent. Appar. Mater. 1963, 4, 65–85. [Google Scholar]
- Steinemann, S.G. Corrosion of Surgical Implants—In vivo and in vitro Tests, Evaluation of Biomaterials; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Watari, F.; Uo, M.; Kawasaki, T. Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of refractoy metal implants, titanium, hafnium, niobium, tantalum and rhenium. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, D.M.; Welldon, K.; Atkins, G.J.; Howie, D.W.; Zannettino, A.C.W.; Bobyn, D. The proliferation and phenotypic expression of human osteoblasts on tantalum metal. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobyn, J.D.; Toth, K.K.; Hacking, S.A.; Tanzer, M.; Krygier, J.J. Tissue response to porous tantalum acetabular cups: A canine model. J. Arthoplasty 1999, 14, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, M.F.; Weber, H.; Sttreicher, R.M.; Schön, R. Joint replacement components made of hot-forged and surface treated Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godmann, S.B.; Davidson, J.A.; Fornasier, V.L.; Mishra, A.K. Histological response to cylinders of a low modulus Titanium alloy (Ti-13Nb-13Zr) and a wear resistant Zirconium alloy (Zr-2.5Nb) implanted in the rabbit tibia. J. Appl. Biomater. 1993, 4, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metikoš-Huković, M.; Kwokal, A.; Piljac, J. The influence of niobium and vanadium on passivity of titanium-based implants in physiological solution. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenbarth, E.; Velten, D.; Müller, M.; Thull, R.; Brene, J. Biocompatibility of β-stabilizing elements of titanium alloys. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5705–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castner, D.G.; Ratner, B.D. Biomedical surface science: Foundations to frontiers. Surf. Sci. 2002, 500, 28–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemo, B. Biological surface science. Surf. Sci. 2002, 500, 656–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, B.D. Surface modifications of polymers: Chemical, biological and surface analytical challenges. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.L. Thin Film Deposition: Principles and Practice; Mc Graw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Stals, L.M.M.; Nesladek, M.; Quayhaegens, C. Current industrial practice critical issue in hard PVD and PA-CVD coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1997, 91, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.M.; Rohde, S.; Sproul, W.D.; Matthews, A. Recent developments in plasma assisted physical vapour deposition. J. PhysD: Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, R173–R186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolz, A. Application of thin film technology in biomedical engineering. In Encyclopedic Handbook of Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Part B: Applications; Wise, D.L., Trantolo, D.J., Altobelli, D.E., Yaszemski, M.J., Schwartz, E.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mandl, S.; Rauschenbach, B. Improving the biocompatibility of medical implants with plasma inmersion ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 156, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.K.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, L.P.; Huang, N. Plasma-surface modification of biomaterials. Mat. Sci. Eng. R. 2002, 36, 143–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzoferrato, A.; Ciapetti, G.; Stea, S.; Cenni, E.; Arciola, C.A.; Granchi, D.; Savarino, L. Cell culture methods for testing biocompatibility. Clin. Mater. 1994, 15, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitãão, E.; Barbosa, M.A.; De Groot, K. In vitro testing of surface-modified biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. in Med. 1998, 9, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, M.; Ogueta, S.; Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; García, J.P.; Martínez-Duart, J.M. Testing biomaterials by in-situ evaluation of cell response. Biomol. Eng. 2002, 19, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaya, J.J.; Rodil, S.E.; Muhl, S. Comparative study of niobium nitride coatings deposited by unbalanced and balanced magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 8319–8326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, G.; Rodil, S.E.; Arzate, H.; Muhl, S.; Olaya, J.J. Niobium based coatings for dental implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2555–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselin, E.; Ahmed, T.M.; Alfantazi, A. Corrosion of niobium in sulphuric and hydrochloric solutions at 75 and 95 °C. Corr. Sci. 2007, 49, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, P.J. Human endosteal osteoblastic cells: Relationship with bone formation. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1995, 56, S13–S16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.; Kaspar, D.; Sarkar, M.R.; Claes, L.E.; Ignatius, A.A. A scanning electron microscopy study of human osteoblast morphology on five orthopedic metals. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 63, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, G.; Wiedmann-Al-Ahmad, M.; Otten, J.E.; Hubner, U.; Schmelzeisen, S.W. The titanium surface texture effects adherence and growth of human gingival keratinocytes and human maxillar osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2799–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselme, K.; Bigerelle, M.; Noel, B.; Iost, A.; Hardouin, P. Effect of grooved titanium substratum on human osteoblastic cell growth. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodil, S.E.; Olaya, J.J. Unbalanced magnetic field configuration: Plasma and film properties. J. Phys: Condens. Matter 2006, 18, S1703–S1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G5-4 “Standard reference test method for making potentiostatic and potentyodinamic anodic polarization measurements”. In Annual Book of ASTM standards; 2000; 3, 02 Wear and Erosion; metal Corrosion; p. 57.
- Chou, W.J.; Yu, G.P.; Huang, J.H. Corrosion resistance of ZrN films on AISI 304 stainless steel substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 167, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodil, S.E.; Olivares, R.; Arzate, H.; Muhl, S. Properties of carbon films and their biocompatibility using in vitro tests. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Olaya, J.J.; Ramírez, C.; Rodil, S.E. Biocompatibility of Niobium Coatings. Coatings 2011, 1, 72-87. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings1010072
Olivares-Navarrete R, Olaya JJ, Ramírez C, Rodil SE. Biocompatibility of Niobium Coatings. Coatings. 2011; 1(1):72-87. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings1010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlivares-Navarrete, René, Jhon Jairo Olaya, Claudia Ramírez, and Sandra Elizabeth Rodil. 2011. "Biocompatibility of Niobium Coatings" Coatings 1, no. 1: 72-87. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings1010072
APA StyleOlivares-Navarrete, R., Olaya, J. J., Ramírez, C., & Rodil, S. E. (2011). Biocompatibility of Niobium Coatings. Coatings, 1(1), 72-87. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings1010072




