Occurrence, Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance-Associated Markers in Campylobacter Species Isolated from Retail Fresh Milk and Water Samples in Two District Municipalities in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethical Clearance
2.2. Description of Study Area
2.3. Collection of Samples
2.4. Isolation of Campylobacter Species from Water Samples
2.5. Isolation of Campylobacter Species from Milk Samples
2.6. DNA Extraction
2.7. Molecular Confirmation Characterization and Amplification of Virulence Genes
2.8. Antibiotic Resistance of Campylobacter Isolates
2.9. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance MAR Index
2.10. Molecular Screening Of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Identification of the Genus Campylobacter
3.2. Molecular Detection of C. coli C. jejuni and C. fetus
3.3. Molecular Detection of Virulence Genes in the Identified Campylobacter Species
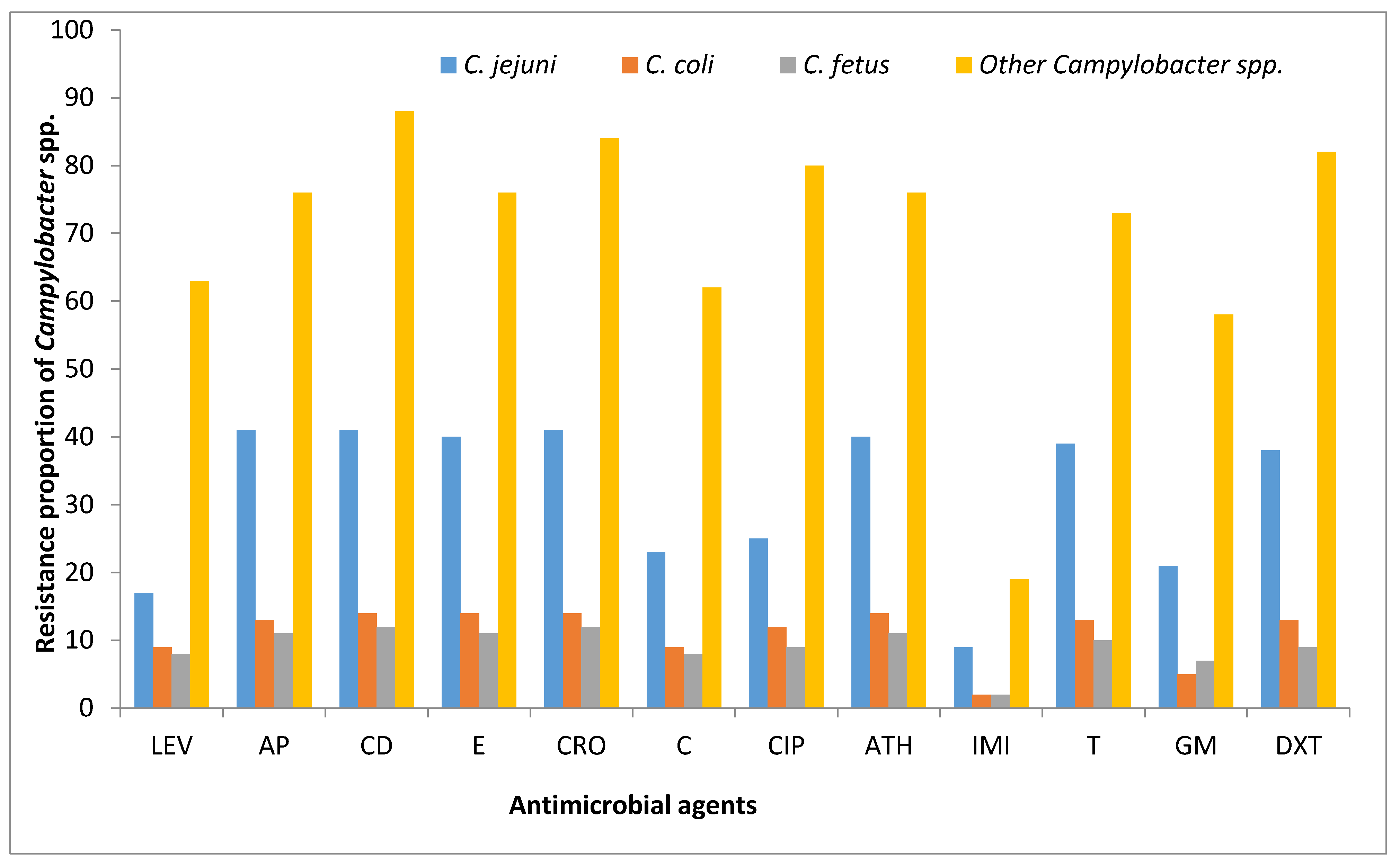
3.4. Antibiotic Phenotypic Resistance Profiles of Campylobacter Isolates
3.5. Molecular Detection of Genotypic Resistance Genes in Campylobacter Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, L.; Dennis, K.D. Campylobacter Species. Food Safety; Apple Academic Press Inc.: Waretown, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 3–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbjer, K.; Tano, E.; Chhayheng, L.; Mac-Kwashie, A.O.; Fernström, L.L.; Ellström, P.; Sokerya, S.; Sokheng, C.; Mom, V.; Chheng, K.; et al. Detection of Campylobacter in human and animal field samples in Cambodia. APMIS 2016, 124, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Brahmbhatt, M.N.; Chatur, Y.A.; Nayak, J.B. Prevalence of Campylobacter species in milk and milk products, their virulence gene profile and antibiogram. Vet. World 2015, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E.V.; Herman, K.M.; Ailes, E.C.; Fitzgerald, C.; Yoder, J.S.; Mahon, B.E.; Tauxe, R.V. Common source outbreaks of Campylobacter infection in the USA, 1997–2008. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.R. Campylobacter jejuni infections associated with raw milk consumption-Utah, 2014. MMWR 2016, 65, 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, K.G.; Falkenhorst, G.; Emborg, H.D.; Ceper, T.; Torpdahl, M.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Ethelberg, S.; Mølbak, K. Epidemiological and serological investigation of a waterborne Campylobacter jejuni outbreak in a Danish town. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 701–709. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, J.P. Water microbiology. Bacterial pathogens and water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3657–3703. [Google Scholar]
- Bitton, G. Microbiology of Drinking Water Production and Distribution, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 312, pp. 1–298. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Castillo, F.; Loera-Muro, A.; Jacques, M.; Garneau, P.; Avelar-González, F.; Harel, J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A. Waterborne pathogens: Detection methods and challenges. Pathogens 2015, 4, 307–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muirhead, R.W.; Collins, R.P.; Bremer, P.J. Numbers and transported state of Escherichia coli in runoff direct from fresh cowpats under simulated rainfall. Lett. Appl. Microb. 2006, 42, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Hellein, K.N.; Battie, C.; Tauchman, E.; Lund, D.; Oyarzabal, O.A.; Lepo, J.E. Culture-based indicators of faecal contamination and molecular microbial indicators rarely correlate with Campylobacter spp. in recreational waters. J. Water Health 2011, 9, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Country Cooperation Strategic at a Glance, South Africa, WHO/CCU/18.02/South Africa. 2018. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/136874 (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Di Giannatale, E.; Garofolo, G.; Alessiani, A.; Di Donato, G.; Candeloro, L.; Vencia, W.; Decastelli, L.; Marotta, F. Tracing back clinical Campylobacter jejuni in the Northwest of Italy and assessing their potential source. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S. Microbiological Safety Concerns of Raw Milk. Safety 2016, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sugrue, I.; Tobin, C.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Hill, C. Foodborne pathogens and zoonotic diseases. Raw Milk 2019, 12, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado, Y.A.; Glode, M.P.; Bhatia, J.; Brady, M.T.; Byington, C.L.; Davies, H.D.; Edwards, K.M.; Jackson, M.A.; Keyserling, H.L.; Murray, D.L.; et al. Consumption of raw or unpasteurized milk and milk products by pregnant women and children. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Artursson, K.; Schelin, J.; Lambertz, S.T.; Hansson, I.; Engvall, E.O. Foodborne pathogens in unpasteurized milk in Sweden. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 284, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Collo, L.P.; Karns, J.S.; Biswas, D.; Lombard, J.E.; Haley, B.J.; Kristensen, R.C.; Kopral, C.A.; Fossler, C.P.; Van Kessel, J.A.S. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of Campylobacter spp. in bulk tank milk and milk filters from US dairies. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 3470–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zamkan, M.A.; Hameed, K.G.A. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in raw milk and some dairy products. Vet. World 2016, 9, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasolofo, E.A.; St-Gelais, D.; LaPointe, G.; Roy, D. Molecular analysis of bacterial population structure and dynamics during cold storage of untreated and treated milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 138, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, A.J.; Ayers, T.; Grass, J.; Lynch, M.; Angulo, F.J.; Mahon, B.E. Nonpasteurized dairy products, disease outbreaks, and state laws-United States, 1993–2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pölzler, T.; Stüger, H.P.; Lassnig, H. Prevalence of most common human pathogenic Campylobacter spp. in dogs and cats in Styria, Austria. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 4, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Cawthraw, S.A.; van Pelt, W.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Owen, R.J. Host-pathogen interactions in Campylobacter infections: The host perspective. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, N.; García, S. Animals as sources of food-borne pathogens: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariuki, S. Chapter 11: Antimicrobial resistance in enteric pathogens in developing countries. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Developing Countries; Sosa, A.J., Byarugaba, D.K., Amábile-Cuevas, C.F., Hsueh, P., Kariuki, S., Okeke, I.N., Eds.; Springer Publishing Co. Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Omulo, S.; Thumbi, S.M.; Lockwood, S.; Verani, J.R.; Bigogo, G.; Masyongo, G.; Call, D.R. Evidence of superficial knowledge regarding antibiotics and their use: Results of two cross-sectional surveys in an urban informal settlement in Kenya. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185827. [Google Scholar]
- Rousham, E.K.; Unicomb, L.; Islam, M.A. Human, animal and environmental contributors to antibiotic resistance in low-resource settings: Integrating behavioural, epidemiological and One Health approaches. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sivagami, K.; Vignesh, V.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Divyapriya, G.; Nambi, I.M. Antibiotic usage, residues and resistance genes from food animals to human and environment: An Indian scenario. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Tian, Z.; Yu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. Distribution and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in sand settling reservoirs and drinking water treatment plants across the Yellow River, China. Water 2018, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, M.I.; Morton, V.K.; McLellan, N.L.; Huck, P.M. The occurrence of Campylobacter in river water and waterfowl within a watershed in southern Ontario, Canada. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, V.; Borella, L.; Benedetti, V.; Parisi, A.; Miccolupo, A.; Santoro, E.; Recordati, C.; Luini, M. Prevalence in bulk tank milk and epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni in dairy herds in Northern Italy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Arguello, Y.M.; Furian, T.Q.; Perdoncini, G.; Moraes, H.L.; Salle, C.T.; Rodrigues, L.B.; dos Santos, L.R.; Gomes, M.J.P.; do Nascimento, V.P. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from poultry and human samples assessed by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism assay. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, Y.; Botella, S.; Luis Alonso, J.; Ferru’s, M.A.; Herna’ndez, M.; Herna’ndez, J. Specific detection of Arcobacter and Campylobacter strains in Water and Sewage by PCR and Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki-Matsune, W.; Taguchi, M.; Seto, K.; Kawahara, R.; Kawatsu, K.; Kumeda, Y.; Kitazato, M.; Nukina, M.; Misawa, N.; Tsukamoto, T. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for identification of Campylobacter coli, Campylobacter fetus, Campylobacter hyointestinalis subsp. hyointestinalis, Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter lari and Campylobacter upsaliensis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.C.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Ramos-Cervantes, P.; Cervantes, L.E.; Jiang, X.; Pickering, L.K. Molecular characterization of invasive and noninvasive Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casabonne, C.; Gonzalez, A.; Aquili, V.; Subils, T.; Balague, C. Prevalence of seven virulence genes of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from patients with diarrhea in Rosario, Argentina. Int. J. Infect. 2016, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.L.; Rathinam, V.A.; Qi, W.; Wick, L.M.; Landgraf, J.; Bell, J.A.; Plovanich-Jones, A.; Parrish, J.; Finley, R.L.; Mansfield, L.S.; et al. Genetic diversity in Campylobacter jejuni is associated with differential colonization of broiler chickens and C57BL/6J IL10-deficient mice. Microbiology 2010, 156, 2046–2057. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Method for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria, 3rd ed.; CLSI: Wayne, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, L.K.; Martin, I.; Alfa, M.; Mulvey, M. Multiplex PCR for the detection of tetracycline resistant genes. Mol. Cell. Probes 2001, 15, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strommenger, B.; Kettlitz, C.; Werner, G.; Witte, W. Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of nine clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.S.; Fox, M.L.; Holland, S.M.; Stock, F.; Gill, V.J.; Fedorko, D.P. Resistance to multiple fluoroquinolones in a clinical isolate of Streptococcus pyogenes: Identification of gyrA and parC and specification of point mutations associated with resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 196–3198. [Google Scholar]
- Osode, A.N.; Okoh, A.I. Impact of discharged wastewater final effluent on the physicochemical qualities of a receiving watershed in a suburban community of the Eastern Cape Province. Clean-Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 938–944. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, C.; Bekal, S.; Sanschagrin, F.; Levesque, R.C.; Brousseau, R.; Masson, L.; Lariviere, S.; Harel, J. Heterogeneity among virulence and antimicrobial resistance gene profiles of extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolates of animal and human origin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5444–5452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, S.; Barbara, E.G.; Mark, J.L.; Lien, T.N.; Susan, I.H.; Ynte, H.S.; Stephen, P.O. Phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance patterns of Escherichia coli isolated from dairy cows with mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Dallenne, C.; Da Costa, A.; Decré, D.; Favier, C.; Arlet, G. Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the detection of genes encoding important β-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reich, F.; Valero, A.; Schill, F.; Bungenstock, L.; Klein, G. Characterisation of Campylobacter contamination in broilers and assessment of microbiological criteria for the pathogen in broiler slaughterhouses. Food Control 2018, 87, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, S.; Soncini, G.; Ziino, G.; Panebianco, A.; Pedonese, F.; Nuvoloni, R.; Di Giannatale, E.; Colavita, G.; Alberghini, L.; Giaccone, V. Prevalence and quantification of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. in Italian retail poultry meat: Analysis of influencing factors. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.; Kang, M.; Jang, H.K. Genetic characterization and epidemiological implications of Campylobacter isolates from wild birds in South Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Guan, X.; Zeng, H.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, X.; Yan, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance profiles and virulence-associated genes of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. isolated from ducks in a Chinese slaughterhouse. Food Control 2019, 104, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Elmal, M.; Can, H.Y. Antimicrobial susceptibility and virulence-associated genes in Campylobacter isolates from milk and wastewater in Hatay, Turkey. Cienc. Rural 2019, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Gannon, V.; Jokinen, C.C.; Kent, R.; Koning, W.; Lapen, D.R.; Medeiros, D.; Miller, J.; Neumann, N.F.; Phillips, R.; et al. A national investigation of the prevalence and diversity of thermophilic Campylobacter species in agricultural watersheds in Canada. Water Res. 2014, 61, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanska, B.; Andrzejewska, M.; Spica, D.; Klawe, J.J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from children and environmental sources in urban and suburban areas. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysok, B.; Wiszniewska-Łaszczych, A.; Uradziński, J.; Szteyn, J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter in raw milk in the selected areas of Poland. Polish J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 14, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, T.; Pintar, K.D.M.; Butler, A.J.; Nesbitt, A.; Thomas, M.K.; Marshall, B.; Pollari, F. Campylobacter spp. prevalence and levels in raw milk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, W.L.; Cardoen, S.; Daube, G.; Block, J.D.; Dewettinck, K.; Dierick, K.; De Zutter, L.; Huyghebaert, A.; Imberechts, H.; Thiange, P.; et al. Raw or heated cow milk consumption: Review of risks and benefits. Food Control 2013, 31, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2014. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 1–190. [Google Scholar]
- Bissong, M.E.; Ateba, C.N. Detection of virulent thermophilic Campylobacter species in communal chickens. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2019, 115, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samie, A.; Obi, C.L.; Barrett, L.J.; Powell, S.M.; Guerrant, R.L. Prevalence of Campylobacter species, Helicobacter pylori and Arcobacter species in stool samples from the Venda region, Limpopo, South Africa: Studies using molecular diagnostic methods. J. Infect. 2007, 54, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, M.; Tanguy, M.; Chidaine, B.; Laisney, M.J.; Mégraud, F.; Fravalo, P. Description and sources of contamination by Campylobacter spp. of river water destined for human consumption in Brittany, France. Pathol. Biol. 2011, 59, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Boto, D.; Garcia-Pena, F.J.; Abad-Moreno, J.C.; Hurtado-Pizarro, M.D.; Pérez-Cobo, I.; Aurora Echeita, M. Drinking water as the source of Campylobacter coli infection in grandparent heavy breeders. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabote, K.I.; Mbewe, M.; Ateba, C.N. Prevalence of Campylobacter contamination in fresh chicken meat and milk obtained from markets in the North-West Province, South Africa. J. Human Ecol. 2011, 36, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewska, M.; Szczepańska, B.; Śpica, D.; Klawe, J.J. Prevalence, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter spp. in raw milk, beef, and pork meat in Northern Poland. Foods 2019, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.L.; Lubna, M.M.; Islam, M.; Haque, A.Z.; Neogi, S.B.; Yamasaki, S. Isolation, molecular identification and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Campylobacter species of dairy origin: First report from Bangladesh. Vet. Sci. Dev. 2018, 8, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, E.; Sepehri, S.; Momtaz, H. Prevalence of Campylobacter species in milk and dairy products in Iran. Rev. Med. Vet. 2013, 164, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbanalizadgan, M.; Bakhshi, B.; Najar-Peerayeh, S. Heterogeneity of cytolethal distending toxin sequence types of Campylobacter jejuni and correlation to invasion/cytotoxicity potential: The first molecular survey from Iran. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R. Virulence genes detection and antibiotic resistance study on the Campylobacter isolates obtained from poultry, domestic animals and humans. Int. J. Basic Appl. Agric. Res. 2018, 16, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wysok, B.; Wojtacka, J. Detection of virulence genes determining the ability to adhere and invade in Campylobacter spp. from cattle and swine in Poland. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 115, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardoň, J.; Pudova, V.; Koláčková, I.; Karpíšková, R.; Röderová, M.; Kolář, M. Virulence and antibiotic resistance genes in Campylobacter spp. in the Czech Republic. Epidemiol. Mikrobiol. Imunol. Cas. Spol. Epidemiol. Mikrobiol. Ceske Lek. Spol. JE Purkyne 2017, 66, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Do Nascimento, V.H.; Medeiros, P.H.; Ribeiro, S.A.; Freitas, T.M.; Santos, A.K.; Amaral, M.S.; Bona, M.D.; Havt, A.; Lima, I.F.; Lima, N.L.; et al. Campylobacter jejuni virulence genes and immune-inflammatory biomarkers association with growth impairment in children from Northeastern Brazil. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lúcio, É.C.; Barros, M.R.; Mota, R.A.; Maia, R.D.C.C.; Pinheiro, J.W. Identification of Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis virulence genes in cervical mucus from cows. Braz. J. Microb. 2019, 50, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Kärenlampi, R.; Rautelin, H.; Hänninen, M.L. Evaluation of genetic markers and molecular typing methods for prediction of sources of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli infections. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1683–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Konkel, M.E.; Garvis, S.G.; Tipton, S.L.; Anderson, D.E., Jr.; Cieplak, W., Jr. Identification and molecular cloning of a gene encoding a fibronectin-binding protein (CadF) from Campylobacter jejuni. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkel, M.E.; Gray, S.A.; Kim, B.J.; Garvis, S.G.; Yoon, J. Identification of the Enteropathogens Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli based on the cadF virulence gene and its product. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lluque, A.; Riveros, M.; Prada, A.; Ochoa, T.J.; Ruiz, J. Virulence and antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter spp. from a Peruvian pediatric cohort. Scientifica 2017, 2017, 7848926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, K.; Szewczyk, R.; Osek, J. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolated from retail raw meat in Poland. Vet. Med. 2012, 57, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwet, M.; Clapa, T.; Galbas, M.; Slomski, R.; Porzucek, F. The prevalence of Campylobacter spp. and occurrence of virulence genes isolated from dogs. Polish J. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Madi, M.; Behnke, J.M.; Sharma, A.; Bearden, R.; Al-Banna, N. Prevalence of virulence/stress genes in Campylobacter jejuni from chicken meat sold in Qatari retail outlets. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156938. [Google Scholar]
- Aslantaş, Ö. Isolation and molecular characterization of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. in dogs and cats. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2019, 25, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Redondo, N.; Carroll, A.; McNamara, E. Molecular characterization of Campylobacter causing human clinical infection using whole-genome sequencing: Virulence, antimicrobial resistance and phylogeny in Ireland. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Abbas, F.; Ahmed, Z.; Akbar, A.; Naeem, M.; Sadiq, M.B.; Ali, I.; Bugti, F.S.; Achakzai, S.K. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility, and virulence of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from chicken meat. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, 12600. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.; Cha, S.Y.; Yoon, R.H.; Kang, M.; Roh, J.H.; Seo, H.S.; Lee, J.A.; Jang, H.K. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter spp. isolated from retail chicken and duck meat in South Korea. Food Control 2016, 62, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Maldonado, B.; Montoro-Dasi, L.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T.; Jordá, J.; Vega, S.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Marin, C. Wild Bonelli’s eagles (Aquila fasciata) as carrier of antimicrobial resistant Salmonella and Campylobacter in Eastern Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 67, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meistere, I.; Ķibilds, J.; Eglīte, L.; Alksne, L.; Avsejenko, J.; Cibrovska, A.; Makarova, S.; Streikiša, M.; Grantiņa-Ieviņa, L.; Bērziņš, A. Campylobacter species prevalence, characterisation of antimicrobial resistance and analysis of whole-genome sequence of isolates from livestock and humans, Latvia, 2008 to 2016. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhadidy, M.; Miller, W.G.; Arguello, H.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Dierick, K.; Botteldoorn, N. Molecular epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of Campylobacter coli from diarrhoeal patients and broiler carcasses in Belgium. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, Z.; Siddiqui, F.; Javed, S.; Wren, B.W.; Bokhari, H. Transmission of Multidrug Resistant Campylobacter jejuni to Children from Different Sources in Pakistan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 20, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Dulaimi, M.M.K.; Mutalib, S.A.; Ghani, M.A.; Zaini, N.A.M.; Ariffin, A.A. Multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR), plasmid profiles, and DNA polymorphisms among Vibrio vulnificus isolates. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, J.W.; Park, S. Molecular Genetics of Bacteria, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Chichester, UK, 2010; pp. 147–148. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, E.; van Belkum, A.; Ghaznavi-Rad, E. Quinolone and Macrolide-Resistant Campylobacter jejuni in Pediatric Gastroenteritis Patients from Central Iran. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, M.; Mushtaq, M.H.; Shehzad, W.; Hussain, A.; Muhammad, J.; Nagaraja, K.V.; Goyal, S.M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Campylobacter spp. isolated from retail meat in Lahore, Pakistan. Food Control 2017, 80, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathne, J.M.; Anuar, A.S.; Thung, T.Y.; Satharasinghe, D.A.; Jambari, N.N.; Abdul-Mutalib, N.A.; Huat, J.T.Y.; Basri, D.F.; Rukayadi, Y.; Nakaguchi, Y.; et al. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance against tetracycline in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli in cattle and beef meat from Selangor, Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lurchachaiwong, W.; Ruksasiri, S.; Wassanarungroj, P.; Serichantalergs, O.; Bodhidatta, L.; Crawford, J.; Shrestha, S.K.; Pandey, P. Determination of azithromycin heteroresistant Campylobacter jejuni in traveler’s diarrhea. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, W.; Lv, Z.; Xia, J.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Emerging erm (B)-mediated macrolide resistance associated with novel multidrug resistance genomic islands in Campylobacter. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 2019, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divsalar, G.; Kaboosi, H.; Khoshbakht, R.; Shirzad-Aski, H.; Ghadikolaii, F.P. Antimicrobial resistances, and molecular typing of Campylobacter jejuni isolates, separated from food-producing animals and diarrhea patients in Iran. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 65, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
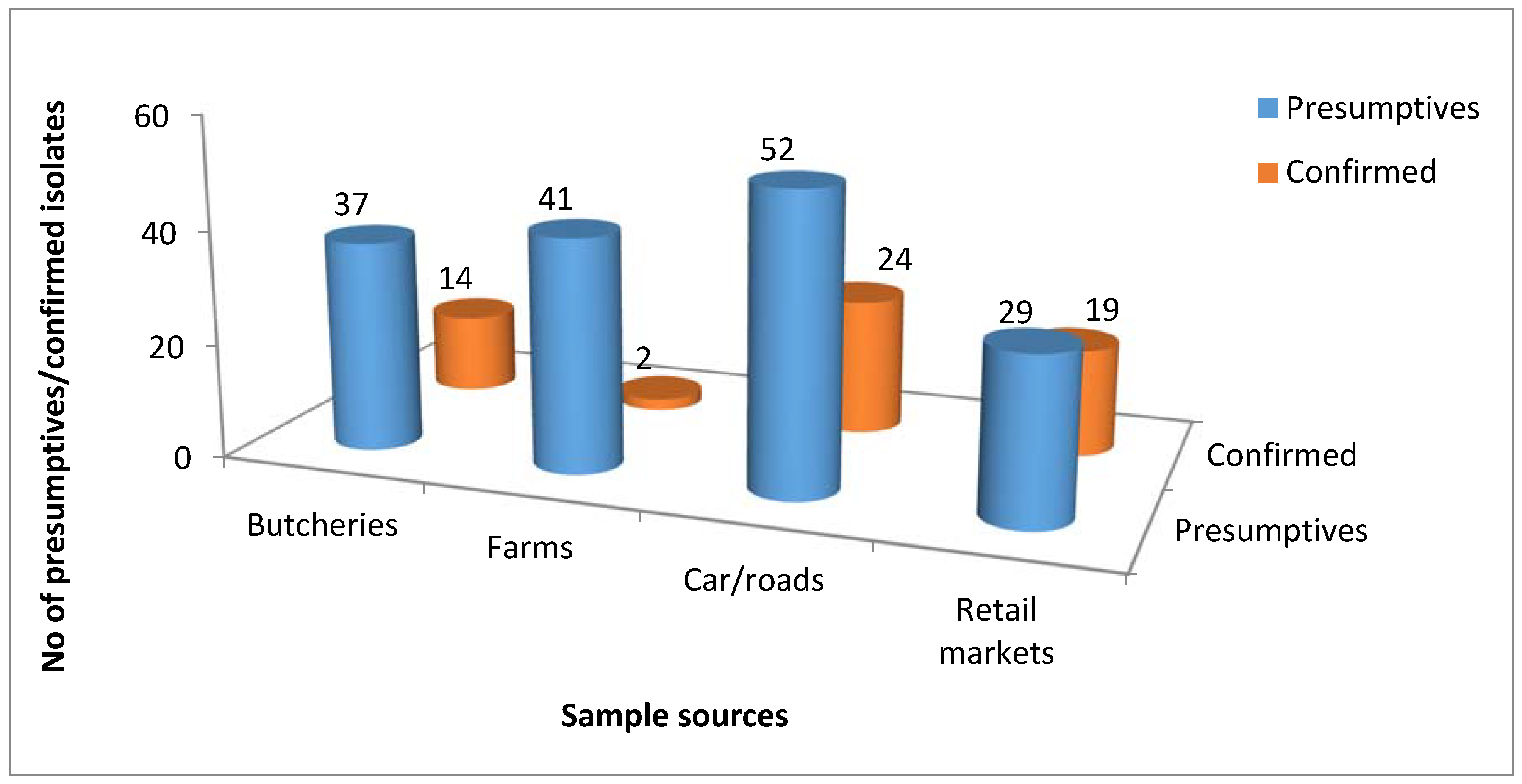
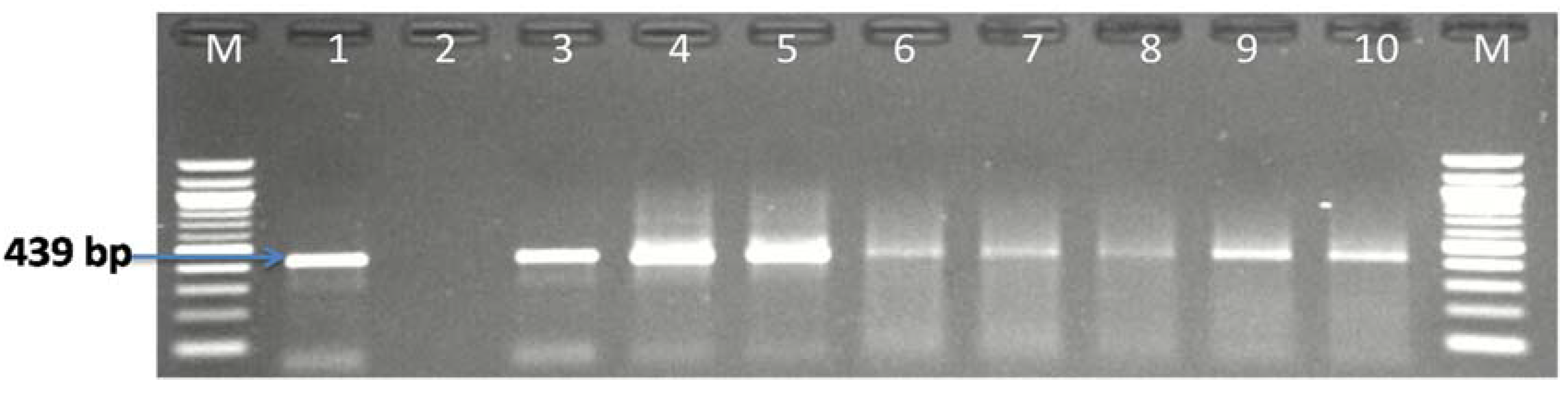
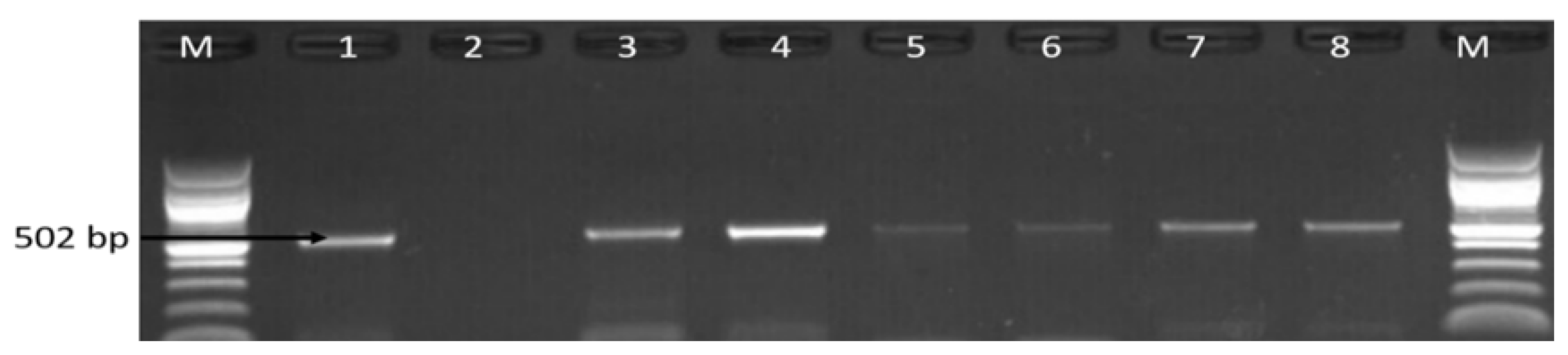
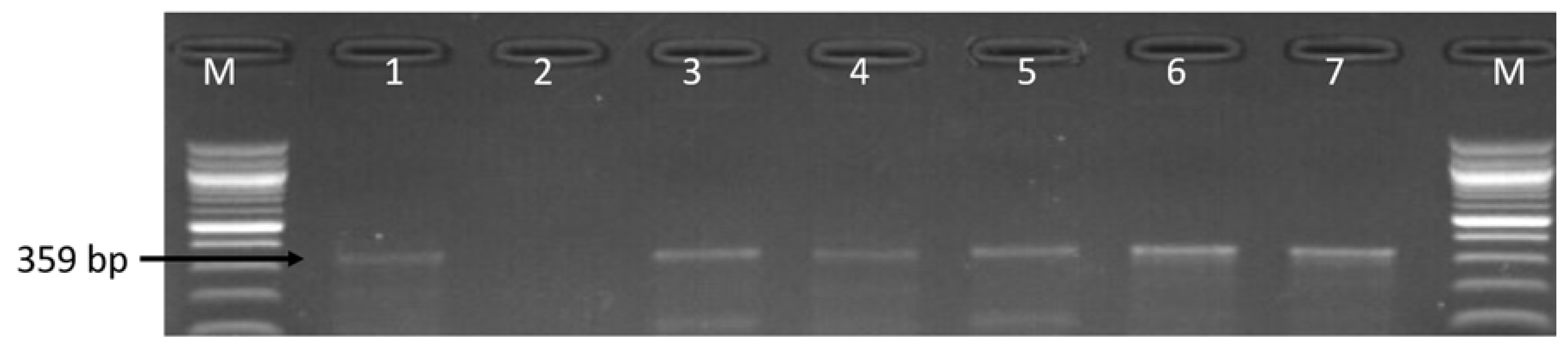
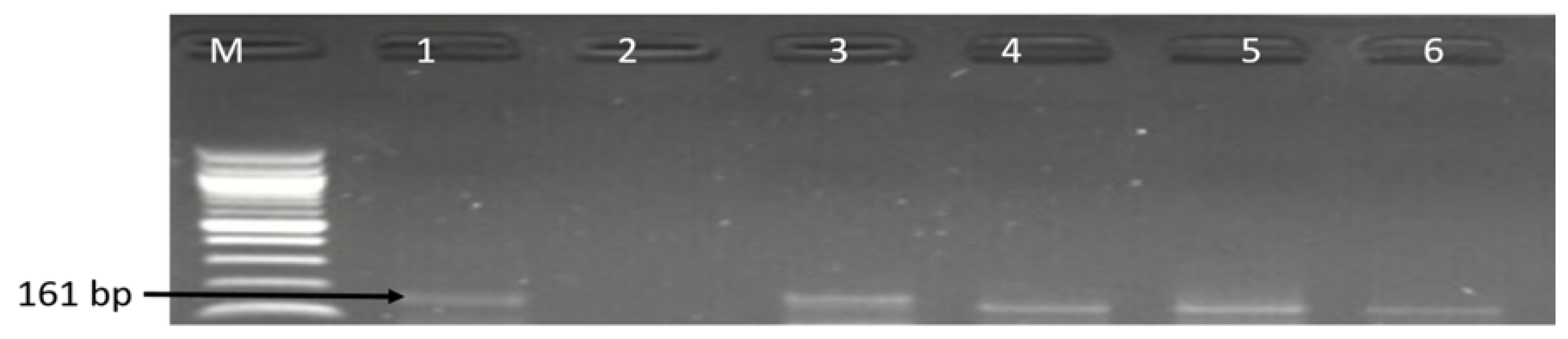
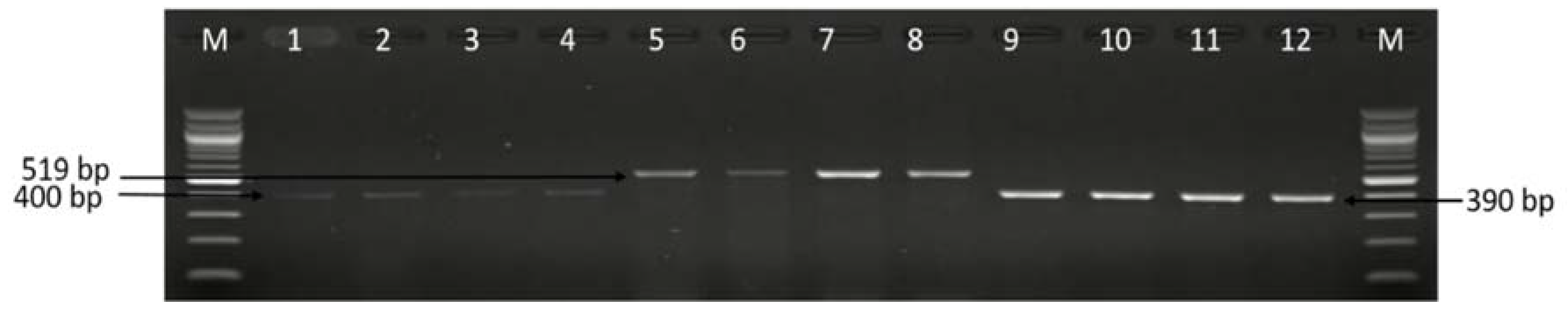
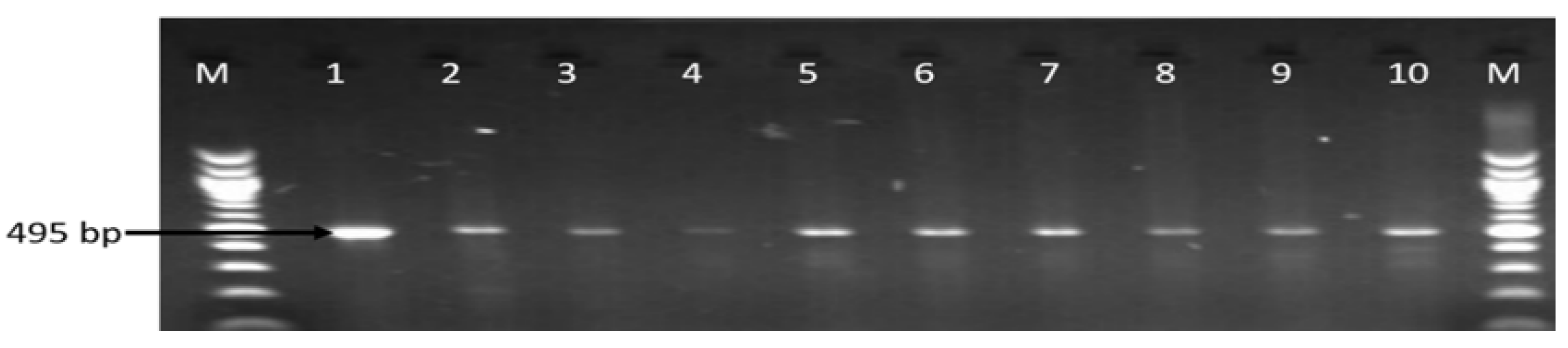
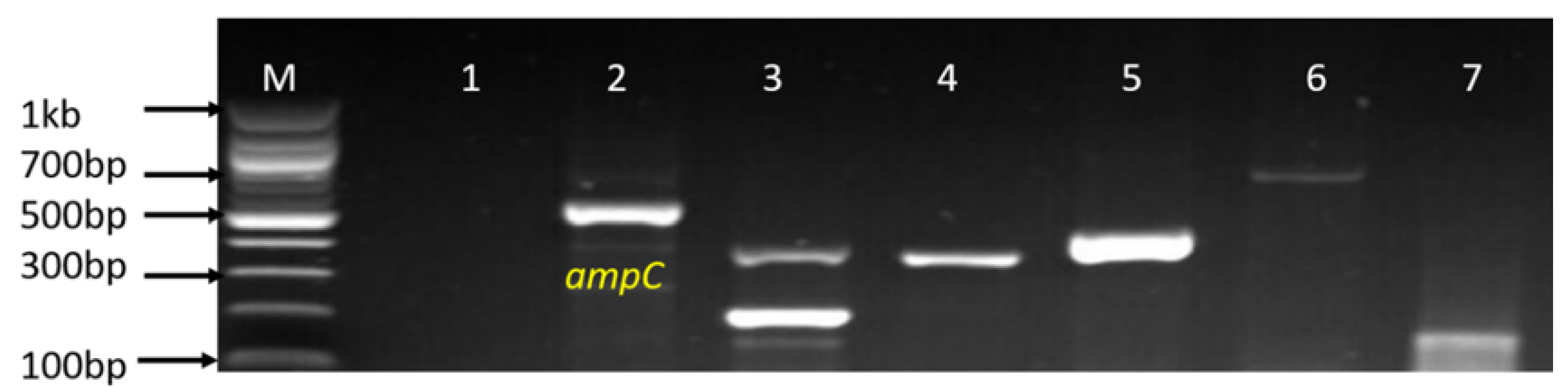
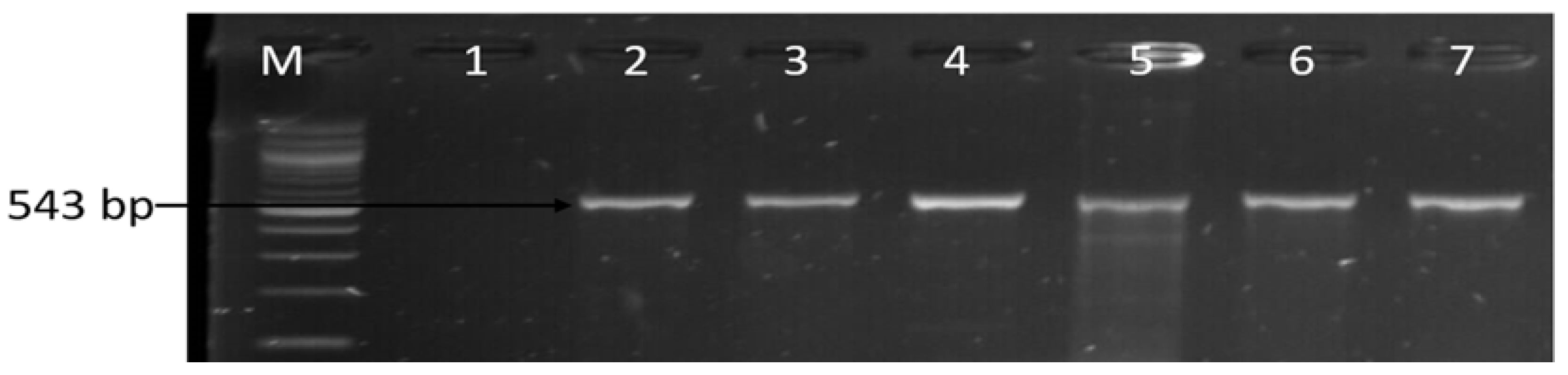
| Sample Sources | C. fetus (%) | C. jejuni (%) | C. coli (%) | C. lari (%) | No of Isolates That Belong to Other Campylobacter Species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 6 (10.17) | 4 (6.78) | 6 (10.17) | 0 | 43 (72.88) |
| Water | 6 (5.83) | 40 (38.83) | 8 (7.77) | 0 | 49 (47.57) |
| Water Samples | Milk Samples | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campylobacter spp. | No of Isolate | Virulence Genes Screened (%) | No of Isolates | Virulence Genes Screened (%) | ||||||||||
| iam | flaA | cadF | flgR | cdtB | ciaB | iam | flaA | cadF | flgR | cdtB | ciaB | |||
| C. coli | 8 | 4 (50) | - | 3 (37.) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (12.5) | - | 6 | 4 (66.7) | - | - | 6 (100) | - | - |
| C. jejuni | 40 | 14 (35) | - | - | 2 (5) | 3 (7.5) | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| C. fetus | 6 | 1 (16.7) | - | - | 1 (16.7) | - | - | 6 | - | - | 1 (16.7) | 4 (66.7) | - | - |
| No | Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns | Sample Source | No of Isolates | Total | MAR Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Milk | C. coli | C. jejuni | C. fetus | ||||
| 1 | CRO-E-CD-AP | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 0.33 | |
| 2 | CRO-E-CD-T-DXT-AP | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| 3 | E-ATH-CD-T-DXT-AP | 2 | - | 1 | - | 2 | 0.5 | |
| 4 | CRO-C-E-ATH-CD-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.5 | |
| 5 | LEV-C-CIP-E-ATH-CD | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| 6 | LEV-CRO-CIP-E-ATH-CD-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.58 | |
| 7 | CRO-E-ATH-CD-T-DXT-AP | 3 | - | 3 | - | 3 | 0.58 | |
| 8 | E-ATH-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.58 | |
| 9 | CRO-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.58 | |
| 10 | CRO-E-ATH-CD-T-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.58 | |
| 11 | CRO-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 0.67 |
| 12 | CRO-C-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-AP | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 0.67 | |
| 13 | CRO-C-CIP-E-CD-T-DXT-AP | 3 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.67 | |
| 14 | CRO-C-E-ATH-CD-T-DXT-AP | 3 | - | 3 | - | 3 | 0.67 | |
| 15 | CRO-E-ATH-IMI-CD-T-DXT-AP | 2 | - | 2 | - | 2 | 0.67 | |
| 16 | CRO-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.67 | |
| 17 | LEV-CRO-C-CIP-E-ATH-CD-DXT | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 0.67 | |
| 18 | CRO-E-ATH-IMI-CD-T-GM-AP | 2 | - | 2 | - | 2 | 0.67 | |
| 19 | CRO-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.67 | |
| 20 | CRO-C-E-ATH-IMI-CD-T-DXT-AP | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 0.75 | |
| 21 | CRO-C-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | - | 2 | - | 2 | 0.75 | ||
| 22 | LEV-C-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-AP | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 0.75 | |
| 23 | CRO-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 0.75 | |
| 24 | C-CIP-E-ATH-IMI-CD-T-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.75 | |
| 25 | LEV-CRO-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.75 | |
| 26 | LEV-CRO-C-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.83 | |
| 27 | LEV-CRO-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 0.83 | |
| 28 | CRO-C-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 0.83 | |
| 29 | CRO-CIP-E-ATH-IMI-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.83 | |
| 30 | LEV-CRO-C-CIP-E-ATH-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 11 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 16 | 0.92 |
| 31 | CRO-C-CIP-E-ATH-IMI-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | 0.92 | |
| 32 | LEV-CRO-C-CIP-E-ATH-IMI-CD-T-GM-DXT-AP | 7 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 1 | |
| No | Sample Source | Campylobacter Species | Multiple Resistance Genes Harbored | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Sample | Milk Sample | C. jejuni | C. coli | C. fetus | ||
| 1 | + | - | 2 | - | - | tetA, catII |
| 2 | - | + | 1 | - | - | catII, ermB |
| 3 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | tetA, ampC |
| 4 | - | + | - | - | 1 | tetA, tetM, ampC |
| 5 | + | - | - | - | 1 | tetA, ampC, gyrA |
| 6 | + | - | 1 | - | - | tetK, ampC, catII |
| 7 | + | - | 1 | - | - | tetA, catII, gyrA |
| 8 | + | - | 6 | - | - | tetA, tetB, ampC |
| 9 | + | + | 4 | - | - | tetA, ampC, catII |
| 10 | + | - | - | 1 | - | tetM, ampC, gyrA |
| 11 | - | + | - | 2 | - | tetA, ampC, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 12 | - | + | - | - | 1 | tetA, catII, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 13 | + | + | - | - | 2 | tetA, tetM, ampC, catII |
| 14 | + | - | 2 | - | - | tetA, tetB, ampC, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 15 | + | - | 1 | - | - | tetA, tetB, ampC, ermB |
| 16 | + | - | 1 | - | - | tetA, tetB, ampC, catII |
| 17 | + | - | - | 1 | - | tetM, ampC, catII, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 18 | + | - | 1 | - | - | tetA, catII, ermB, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 19 | + | - | - | 1 | 1 | tetA, ampC, gyrA, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 20 | + | - | 2 | - | - | tetA, tetB, ampC, catII, gyrA |
| 21 | + | 4 | 3 | - | tetA, ampC, catII, gyrA, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a | |
| 22 | + | - | 1 | - | - | tetA, tetM, catII, ermB, gyrA |
| 23 | + | - | 1 | - | - | tetA, tetB, ampC, catII, gyrA |
| 24 | - | + | - | 1 | - | tetM, ampC, catII, gyrA, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 25 | + | + | 2 | 2 | tetA, tetM, ampC, catII, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a | |
| 26 | + | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | tetA, tetM, ampC, catII, gyrA |
| 27 | + | - | 3 | - | - | tetA, tetB, ampC, ermB, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 28 | + | - | 2 | - | - | tetA, tetB, ampC, ermB, gyrA |
| 29 | + | - | - | 1 | - | tetA, tetM, ampC, catII, ermB, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
| 30 | + | - | 2 | - | - | tetA, tetM, ampC, catII, gyrA, aac(3)-IIa-(aacC2)a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Igwaran, A.; Okoh, A.I. Occurrence, Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance-Associated Markers in Campylobacter Species Isolated from Retail Fresh Milk and Water Samples in Two District Municipalities in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070426
Igwaran A, Okoh AI. Occurrence, Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance-Associated Markers in Campylobacter Species Isolated from Retail Fresh Milk and Water Samples in Two District Municipalities in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(7):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070426
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgwaran, Aboi, and Anthony Ifeanyi Okoh. 2020. "Occurrence, Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance-Associated Markers in Campylobacter Species Isolated from Retail Fresh Milk and Water Samples in Two District Municipalities in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa" Antibiotics 9, no. 7: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070426
APA StyleIgwaran, A., & Okoh, A. I. (2020). Occurrence, Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance-Associated Markers in Campylobacter Species Isolated from Retail Fresh Milk and Water Samples in Two District Municipalities in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Antibiotics, 9(7), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070426





