Current Issues and Perspectives in Patients with Possible Sepsis at Emergency Departments
Abstract
1. Introduction
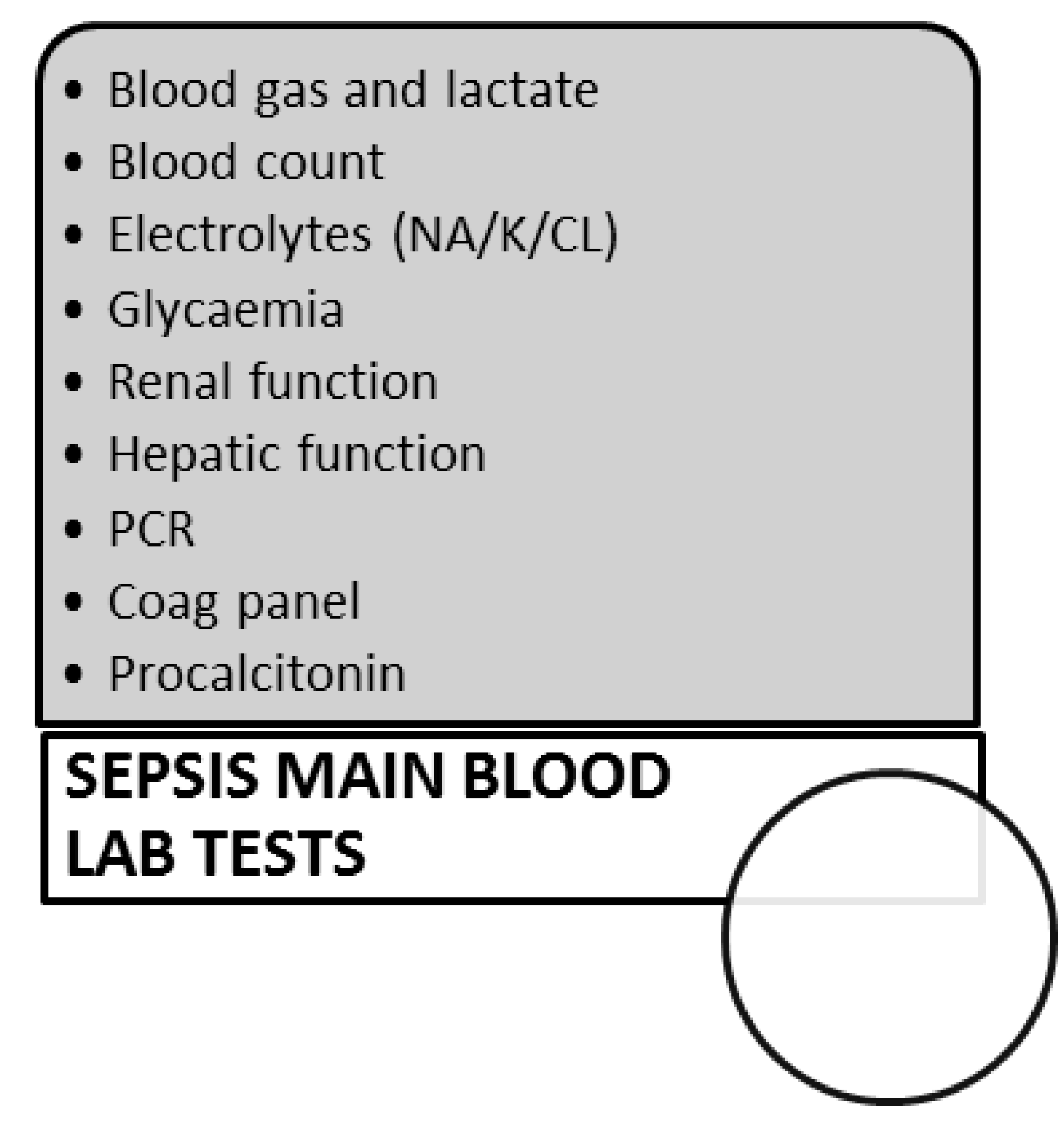
2. Recognition and Management of the Septic Patient at the Emergency Room
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, G.S. Sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock: Changes in incidence, pathogens and outcomes. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj, J.; Blaine, N.; Salavaci, J.; Jacoby, D. The “Centrality of Sepsis”: A Review on Incidence, Mortality, and Cost of Care. Healthcare 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, A.; Mare, A.; Toma, F.; Curticăpean, A.; Santacroce, L. Health Threats from Contamination of Spices Commercialized in Romania: Risks of Fungal and Bacterial Infections. Endocr. Metab. Immun. Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 16, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, F.; Abenavoli, F.M.; De Angelis, F.; Orefici, A.; Santacroce, L.; Dipalma, G. Conservative Surgical Approach to Restore Necrotic Columella in Patients Undergoing Neonatal Usage of Nasogastric Tube. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 7, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Bottalico, L.; Mangini, F. Dental hygiene procedure in a patient with Giardia lamblia infection. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2007, 5, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangini, F.; Santacroce, L.; Bottalico, L. Periodontitis and systemic diseases. Clin. Ther. 2006, 157, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Vermesan, D.; Vermesan, H.; Dragulescu, S.I.; Bera, I.; Di Giovanni, A.; Sabatini, R.; Santacroce, L.; Bottalico, L.; Flace, P.; Cagiano, R. Secondary pathologic fractures in osteosarcoma: Prognosis and evolution. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 13, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mervyn, S.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Gordon, R.B.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar]
- Bastoni, D.; Ticinesi, A.; Lauretani, F.; Calamai, S.; Catalano, M.L.; Catania, P.; Cecchia, M.; Cerundolo, N.; Galluzzo, C.; Giovini, M.; et al. Application of the Sepsis-3 Consensus Criteria in a Geriatric Acute Care Unit: A Prospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewersdorf, J.P.; Hautmann, O.; Kofink, D.; Khalil, A.; Imran, Z.; Loch, A. The SPEED (sepsis patient evaluation in the emergency department) score: A risk stratification and outcome prediction tool. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 24, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morr, M.; Lukasz, A.; Rübig, E.; Pavenstädt, H.; Kümpers, P. Sepsis recognition in the emergency department – impact on quality of care and outcome? BMC Emerg Med. 2017, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prejbeanu, R.; Vermesan, H.; Dragulescu, S.I.; Vermesan, D.; Motoc, A.; Sabatini, R.; Santacroce, L.; Cagiano, R. Thromboembolic risk after knee endoprosthesis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 11, 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ballini, A.; Cantore, S.; Farronato, D.; Cirulli, N.; Inchingolo, F.; Papa, F.; Malcangi, G.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Dipalma, G.; Sardaro, N.; et al. Periodontal disease and bone pathogenesis: The crosstalk between cytokines and porphyromonas gingivalis. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2015, 29, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Monea, A.; Santacroce, L.; Marrelli, M.; Man, A. Oral candidiasis and inflammatory response: A potential synergic contribution to the onset of type-2 diabetes mellitus. Australas. Med. J. 2017, 10, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Moon, H.G.; Kim, S.H. Efficacy of quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment with lactate concentration for predicting mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia in the emergency department. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2019, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Serio, F.; Lovero, R.; D’Agostino, D.; Nisi, L.; Miragliotta, G.; Contino, R.; Man, A.; Ciccone, M.M.; Santacroce, L. Evaluation of procalcitonin, Vitamin D and C-reactive protein levels in septic patients with positive emocoltures. Our preliminary experience. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2016, 32, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaella, T.; Fiore, F.; Fabrizia, M.; Francesco, P.; Arcangela, I.; Salvatore, S.; Luigi, S.; Nicola, B. Induction of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in human fibroblast cultures exposed to serum from septic patients. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Bottalico, L. The Alcmaeon’s School of Croton: Philosophy and Science. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; D’agostino, D.; Charitos, I.A.; Bottalico, L.; Ballini, A. A short review about electrophysiology and bioimpedance: History and perspectives. Indian J Public Health Res. Dev. 2018, 9, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosillo, G.; Di Venosa, N.; Ruggiero, F.M.; Pistolese, M.; D’Agostino, D.; Tiravanti, E.; Fiore, T.; Paradies, G. Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with cardiac ischemia/reperfusion can be attenuated by oxygen tension control. Role of oxygen-free radicals and cardiolipin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1710, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serviddio, G.; Di Venosa, N.; Federici, A.; D’Agostino, D.; Rollo, T.; Prigigallo, F.; Altomare, E.; Fiore, T.; Vendemiale, G. Brief hypoxia before normoxic reperfusion (postconditioning) protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury by preventing mitochondria peroxyde production and glutathione depletion. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, R.; Silva, J.R.L.E.; Bergmann, A.; de Oliveira Melo, U.; Calil, F.E.; Santos, R.C.; Salluh, J.I.F. Factors associated with mortality in severe community-acquired pneumonia: A multicenter cohort study. J. Crit. Care 2019, 50, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, K.; Walker, K.A.; Goodson, C.; Olson, E.; Maher, D.; Brown, C.H., 4th; Nyquist, P. Cerebral Autoregulation-Guided Optimal Blood Pressure in Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy: A Case Series. J. Intensiv. Care Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dai, X.; Guo, C. Crystalloid fluid administration was associated with outcomes in pediatric patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e12663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, J.S.T.; Akech, S.; Kissoon, N.; Wiens, M.O.; English, M.; Ansermino, J.M. Determining predictors of sepsis at triage among children under 5 years of age in resource-limited settings: A modified Delphi process. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hady, H.; Yahia, S.; Megahed, A.; Mosbah, A.; Seif, B.; Nageh, E.; Bhattacharjee, I.; Aly, H. Vitamin D and Inflammatory Mediators in Preterm Infants with Late-Onset Sepsis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrath, E.T.; Fortenberry, J.D.; Travers, C.; McCracken, C.E.; Hebbar, K.B. Resuscitation with Balanced Fluids Is Associated With Improved Survival in Pediatric Severe Sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shane, A.L.; Sánchez, P.J.; Stoll, B.J. Neonatal sepsis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Carlaio, R.G.; Bottalico, L. Does it make sense that diabetes is reciprocally associated with periodontal disease? Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets. 2010, 10, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Llorens, X.; Vargas, S.; Guerra, F.; Coronado, L. Application of new sepsis definitions to evaluate outcome of pediatric patients with severe systemic infections. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1995, 14, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, L.A. Interventions for Pediatric Sepsis and Their Impact on Outcomes: A Brief Review. Healthcare (Basel) 2019, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Hong, S.B. Sepsis and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Recent Update. Tuber. Respir. Dis. (Seoul) 2016, 79, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, R.J.; Chandler, B.D.; Stonestreet, B.S.; Oh, W. Early identification of sepsis in infants with respiratory distress. Pediatrics 1978, 62, 744–750. [Google Scholar]
- Poland, R.L.; Watterberg, K.L. Sepsis in the newborn. Pediatr. Rev. 1993, 14, 262–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, M.Y.; Klompas, M.; Evans, L. Early Administration of Antibiotics for Suspected Sepsis February 7, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, R.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Phillips, G.; Osborn, T.M.; Townsend, S.; Dellinger, R.P.; Artigas, A.; Schorr, C.; Levy, M.M. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: Results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Losacco, T. Abdominal sepsis in surgical patients. Pathophysiology and prevention. Recent. Prog. Med. 2006, 97, 411–416. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino, D.; Bottalico, L.; Santacroce, L. Infective endocarditis: What is changed in epidemiology and prophylaxis. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2012, 28, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino, D.; Man, A.; Santacroce, L. Current trends in cardiac surgery: Clinical experience in the treatment of mediastinitis with sternal wound infection through negative pressure therapy. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2016, 32, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’agostino, D.; Lacatena, C.; Santacroce, L. Postoperative mediastinitis in cardiac surgery—Pathophysiology, risk factors and prevention. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2015, 31, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Giudice, G.; Cutrignelli, D.A.; Sportelli, P.; Limongelli, L.; Tempesta, A.; Di Gioia, G.; Santacroce, L.; Maiorano, E.; Favia, G. Rhinocerebral mucormycosis with orosinusal involvement: Diagnostic and surgical treatment guidelines. Endocr. Metab. Immun. Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 16, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, D.; Losacco, T.; Santacroce, L. Clinical management of the infective endocarditis today. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2012, 28, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Bottalico, L.; Tatullo, M.; Marrelli, M.; Santacroce, L. Lights and shadows of dental implants: Focus on mucositis and perimplantitis and their biological markers. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 859–861. [Google Scholar]
- Rello, J.; Kalwaje Eshwara, V.; Conway-Morris, A.; Lagunes, L.; Alves, J.; Alp, E.; Zhang, Z.; Mer, M. TOTEM Study Investigators. Perceived differences between intensivists and infectious diseases consultants facing antimicrobial resistance: A global cross-sectional survey. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemkere, G.; Tenna, A.; Engidawork, E. Antibiotic use practice and predictors of hospital outcome among patients with systemic bacterial infection: Identifying targets for antibiotic and health care resource stewardship. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miragliotta, G.; Del Prete, R.; Santacroce, L. The role of the clinical microbiologist in the management of the respiratory infections today [II ruolo attuale del microbiologo clinico nella gestione delle infezioni respiratorie]. Rassegna di Patologia dell’Apparato Respiratorio 2008, 23, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Santacroce, L.; Cagiano, R.; Del Prete, R.; Bottalico, L.; Sabatini, R.; Carlaio, R.G.; Prejbeanu, R.; Vermesan, H.; Dragulescu, S.I.; Vermesan, D.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric MALTomas: An up-to-date and therapy highlight. Clin. Ter. 2008, 159, 457–462. [Google Scholar]
- Santacroce, L.; Cagiano, R.; Carlaio, R.G.; Del Prete, R.; Bottalico, L. Dentistry oral hygiene and endocarditis. Pathophysiology and prophylactic therapy. Recent. Prog. Med. 2008, 99, 516–521. [Google Scholar]
- Mosca, A.; Carucci, A.; Santacroce, L.; Schettini, F.; De Mattia, D.; Miragliotta, G. Streptococcus pneumoniae nasopharyngeal colonization in young healthy children: Rate of carriage, serotype distribution, and antibiotic resistance. New Microbiol. 2003, 26, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, F.C.F.; Brenner, T.; Uhle, F.; Loesch, S.; Hackert, T.; Ulrich, A.; Hofer, S.; Dalpke, A.H.; Weigand, M.A.; Boutin, S. Gut microbiome patterns correlate with higher postoperative complication rates after pancreatic surgery. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.D.; Zhu, R.X.; Wu, Z.Q.; Lyu, S.Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Du, Z.J.; Pan, X.T. Gut Microbiota Disruption in Septic Shock Patients: A Pilot Study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 8639–8646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Yamada, T.; Ogura, H.; Mohri, T.; Kiguchi, T.; Fujimi, S.; Asahara, T.; Yamada, T.; Ojima, M.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Synbiotics modulate gut microbiota and reduce enteritis and ventilator-associated pneumonia in patients with sepsis: A randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, B.W.; Prescott, H.C.; Wiersinga, W.J. Therapeutic Potential of the Gut Microbiota in the Prevention and Treatment of Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukovic, E.; Moitra, V.K.; Freedberg, D.E. The microbiome: Implications for perioperative and critical care. Curr. Opin Anaesthesiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.C.; Vasconcelos, Y.A.G.; de Santana Souza, M.T.; Oliveira, A.S.; Bomfim, R.R.; de Albuquerque Júnior, R.L.C.; Camargo, E.A.; Portella, V.G.; Coelho-de-Souza, A.N.; Diniz, L.R.L. Hepatoprotective Effect of Essential Oils from Hyptis crenata in Sepsis-Induced Liver Dysfunction. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, A.; Santacroce, L.; Jacob, R.; Mare, A.; Man, L. Antimicrobial activity of six essential oils against a group of human pathogens: A comparative study. Pathogens 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Hsu, J.S.; Li, C.C.; Chen, K.M.; Liu, C.T. Protective effect of leaf essential oil from Cinnamomum osmophloeum Kanehira on endotoxin-induced intestinal injury in mice associated with suppressed local expression of molecules in the signaling pathways of TLR4 and NLRP3. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, V.; Saranya, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Antibacterial microemulsion prevents sepsis and triggers healing of wound in wistar rats. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 105, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatullo, M.; Simone, G.M.; Tarullo, F.; Irlandese, G.; Vito, D.; Marrelli, M.; Santacroce, L.; Cocco, T.; Ballini, A.; Scacco, S. Antioxidant and Antitumor Activity of a Bioactive Polyphenolic Fraction Isolated from the Brewing Process. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Boone, L.; Alvarez-Román, R.; Salazar-Aranda, R.; Torres-Cirio, A.; Rivas-Galindo, V.M.; Waksman de Torres, N.; González González, G.M.; Pérez-López, L.A. Chemical compositions and antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the essential oils from Magnolia grandiflora, Chrysactinia mexicana, and Schinus molle found in northeast Mexico. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, A.; Lehmann, C. Betacaryophyllene—A phytocannabinoid as potential therapeutic modality for human sepsis? Med. Hypotheses 2018, 110, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Cao-Danh, H.; Friehs, I.; Glynn, P.; D’Agostino, D.; Simplaceanu, E.; McGowan, F.X.; del Nido, P.J. Administration of fructose 1,6-diphosphate during early reperfusion significantly improves recovery of contractile function in the postischemic heart. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1998, 116, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentadue, R.; Fiore, F.; Massaro, F.; Papa, F.; Iuso, A.; Scacco, S.; Santacroce, L.; Brienza, N. Erratum: Induction of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in human fibroblast cultures exposed to serum from septic patients. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losacco, T.; Cagiano, R.; Bottalico, L.; Carlaio, R.G.; Prejbeanu, R.; Vermesan, H.; Dragulescu, S.I.; Vermesan, D.; Motoc, A.; Santacroce, L. Our experience in Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric MALToma. Clin. Ter. 2008, 159, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Inchingolo, F.; Dipalma, G.; Cirulli, N.; Cantore, S.; Saini, R.S.; Altini, V.; Santacroce, L.; Ballini, A.; Saini, R. Microbiological results of improvement in periodontal condition by administration of oral probiotics. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Stadlbauer, V.; Horvath, A.; Komarova, I.; Schmerboeck, B.; Feldbacher, N.; Klymiuk, I.; Durdevic, M.; Rainer, F.; Blesl, A.; Stiegler, P.; et al. Dysbiosis in early sepsis can be modulated by a multispecies probiotic: A randomised controlled pilot trial. Benef. Microbes 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Santacroce, L.; Cantore, S.; Bottalico, L.; Dipalma, G.; Vito, D.; Saini, R.; Inchingolo, F. Probiotics Improve Urogenital Health in Women. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Rao, S.; Nathan, E.A.; Patole, S. Effect of probiotics on C-reactive protein levels in preterm infants: Secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. J. Neonatal Perinat. Med. 2018, 11, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, V.; Syed, J.; Santacroce, L.; Saini, R.; Ballini, A.; Inchingolo, F. Oral probiotics influence oral and respiratory tract infections in pediatric population: A randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8034–8041. [Google Scholar]
- Gunduz, M.; Murakami, D.; Gunduz, I.; Tamagawa, S.; Hiraoka, M.; Sugita, G.; Hotomi, M.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Li, J.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment improves intestinal permeability and modulates microbiota dysbiosis in an experimental model of sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Santacroce, L.; Cantore, S.; Bottalico, L.; Dipalma, G.; Topi, S.; Saini, R.; De Vito, D.; Inchingolo, F. Probiotics Efficacy on Oxidative Stress Values in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Endocr. Metab. Immun. Disord. Drug Targets 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.; Murakami, D.; Gunduz, I.; Tamagawa, S.; Hiraoka, M.; Sugita, G.; Hotomi, M. Recurrent bacterial translocation from gut and sepsis in Head and neck cancer patients and its prevention by probiotics. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 120, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angurana, S.K.; Bansal, A.; Singhi, S.; Aggarwal, R.; Jayashree, M.; Salaria, M.; Mangat, N.K. Evaluation of Effect of Probiotics on Cytokine Levels in Critically Ill Children With Severe Sepsis: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Points |
|---|---|
| Respiratory rate ≥22 | 1 |
| Change in mental status | 1 |
| Systolic blood pressure ≤100 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Castellaneta, F.; D’Agostino, D. Current Issues and Perspectives in Patients with Possible Sepsis at Emergency Departments. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8020056
Charitos IA, Topi S, Castellaneta F, D’Agostino D. Current Issues and Perspectives in Patients with Possible Sepsis at Emergency Departments. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharitos, Ioannis Alexandros, Skender Topi, Francesca Castellaneta, and Donato D’Agostino. 2019. "Current Issues and Perspectives in Patients with Possible Sepsis at Emergency Departments" Antibiotics 8, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8020056
APA StyleCharitos, I. A., Topi, S., Castellaneta, F., & D’Agostino, D. (2019). Current Issues and Perspectives in Patients with Possible Sepsis at Emergency Departments. Antibiotics, 8(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8020056




