Comparison of Cost Savings of Methods of Prevention of Orthopedic Implant-Associated Infection in Arthroplasty and Closed Fracture Surgery Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Cohort and Surgical Procedure Distribution
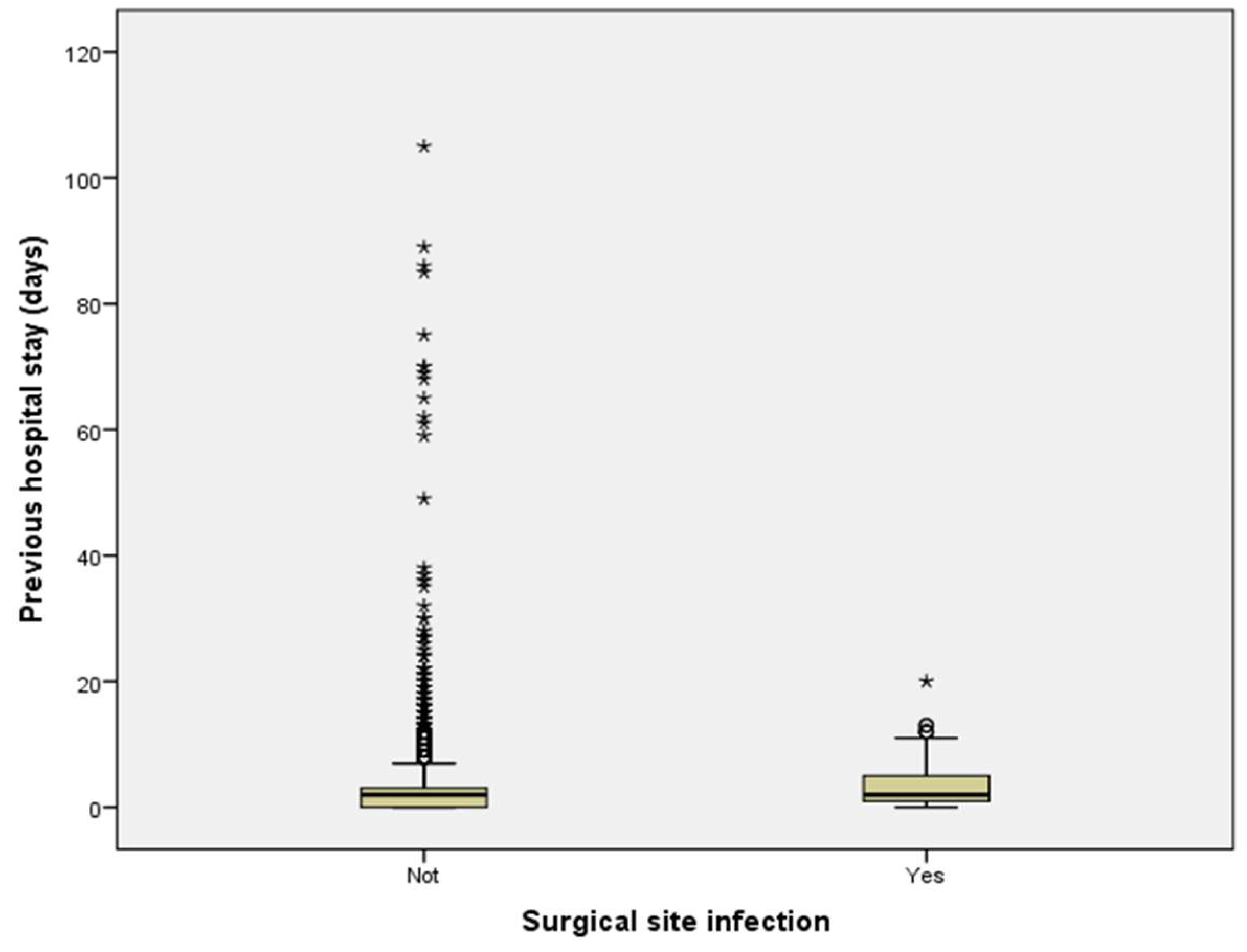
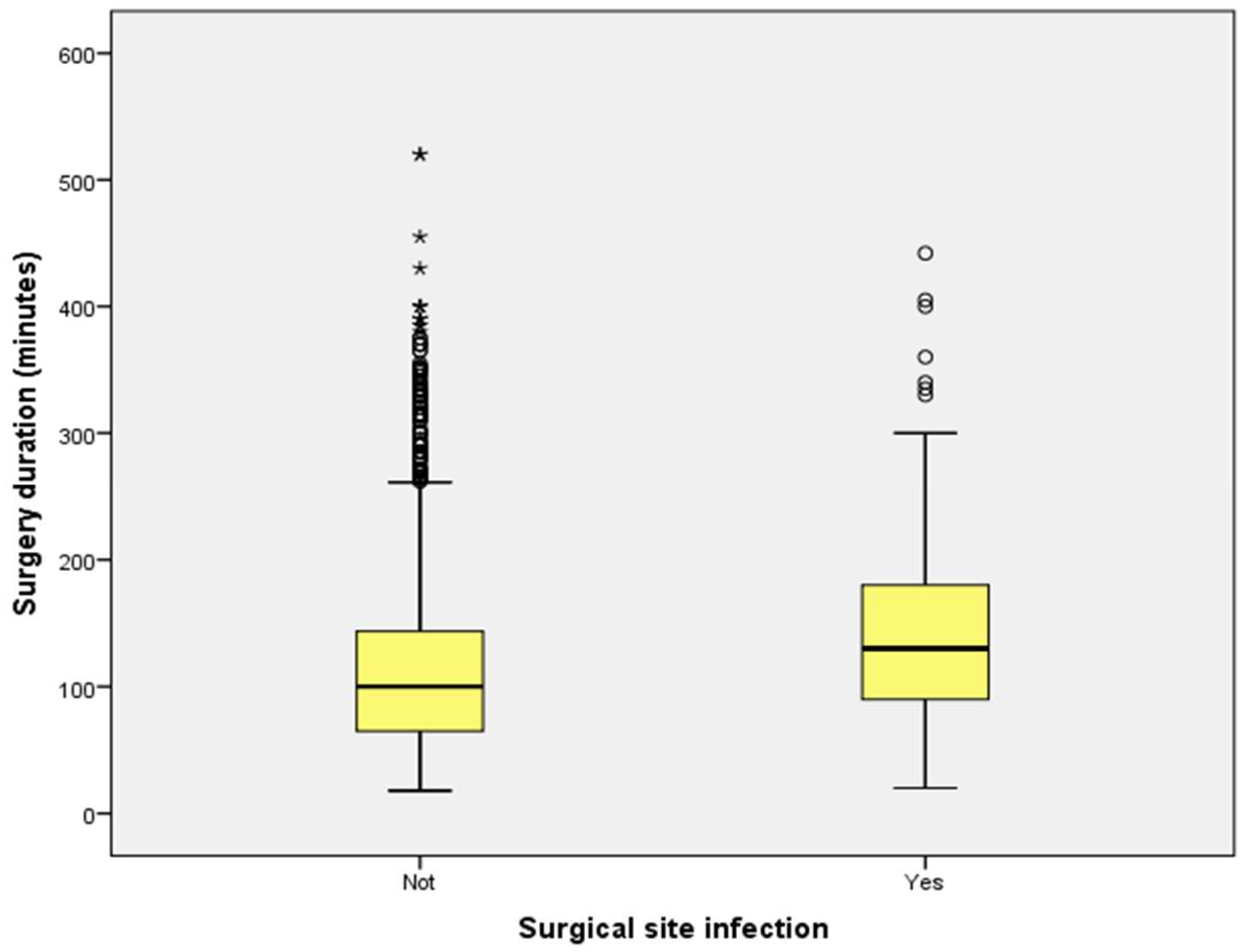
2.2. Incidence and Impact of Surgical Site Infections
2.3. Length of Hospitalization and Surgical Duration
2.4. Effectiveness of Preventive Measures
2.5. Economic Evaluation of Preventive Strategies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design, Population, and Definitions
4.2. Preventive Measures Implemented
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AO | AO Foundation |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists (score) |
| CAD | Canadian Dollar |
| CCI | Charlson Comorbidity Index |
| EBJIS | European Bone and Joint Infection Society |
| FRIs | Fracture-Related Infections |
| HA | Hip Arthroplasty |
| HAIs | Hospital-Acquired Infections |
| IOM | Intraoperative Measures |
| IPC | Infection Prevention and Control |
| KA | Knee Arthroplasty |
| MRSA | Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| ORIF | Open Reduction and Internal Fixation |
| PAP | Perioperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis |
| PJIs | Periprosthetic Joint Infections |
| PMs | Preventive Measures |
| PoOM | Postoperative Measure |
| PrOM | Preoperative Measure |
| SSI | Surgical Site Infection |
| THA | Total Hip Arthroplasty |
| TKA | Total Knee Arthroplasty |
| TLA | Three-Letter Acronym |
| USD | United States Dollar |
References
- Yao, J.J.; Hevesi, M.; Visscher, S.L.; Ransom, J.E.; Lewallen, D.G.; Berry, D.J.; Kremers, H.M. Direct inpatient medical costs of operative treatment of periprosthetic hip and knee infections are twofold higher than those of aseptic revisions. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2021, 103, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, A.; Kolin, D.A.; Farley, K.X.; Wilson, J.M.; McLawhorn, A.S.; Cross, M.B.; Sculco, P.K.; Sculco, P.K. Projected economic burden of periprosthetic joint infection of the hip and knee in the United States. J. Arthroplasty. 2021, 36, 1484–1493.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Guidelines for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-92-4-154988-2. [Google Scholar]
- Manivannan, S.; Karnan, S.; Thangavel, A. Surveillance, auditing, and feedback can reduce surgical site infection dramatically: Toward zero surgical site infection. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, T.J.; Konopka, J.F.; Bedair, H.S. What is the long-term economic societal effect of periprosthetic infections after THA? A Markov analysis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymski, D.; Walter, N.; Hierl, K.; Rupp, M.; Alt, V. Direct hospital costs per case of periprosthetic hip and knee joint infections in Europe: A systematic review. J. Arthroplast. 2024, 39, 1876–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsemakers, W.; Morgenstern, M.; McNally, M.; Moriarty, T.; McFadyen, I.; Scarborough, M.; Athanasou, N.; Ochsner, P.; Kuehl, R.; Raschke, M.; et al. Fracture-related infection: A consensus on definition from an international expert group. Injury 2018, 49, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casenaz, A.; Piroth, L.; Labattut, L.; Sixt, T.; Magallon, A.; Guilloteau, A.; Neuwirth, C.; Amoureux, L. Epidemiology and antibiotic resistance of prosthetic joint infections according to time of occurrence: A 10-year study. J. Infect. 2022, 85, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). National Consumer Price Index (IPCA). Rio de Janeiro: IBGE. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Statistics Canada. Consumer Price Index (CPI). Ottawa: Statistics Canada. Available online: https://www.statcan.gc.ca (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Consumer Price Index (CPI-U). Washington (DC): U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Available online: https://www.bls.gov (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- World Bank. Official Exchange Rates and Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Conversion Factors. Washington (DC): World Bank. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Starling, C.E.F.; Couto, B.R.G.M.; Fialho, A.S.; Alves, A.A. Impacto das infecções hospitalares na lucratividade de hospitais privados brasileiros. Prática. Hosp. Urgências. 2004, 34, 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- AlBuhairan, B.; Hind, D.; Hutchinson, A. Antibiotic prophylaxis for wound infections in total joint arthroplasty: A systematic review. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.; Sohr, D.; Behnke, M.; Daschner, F.; Rüden, H.; Gastmeier, P. Operating room ventilation with laminar airflow shows no benefit for preventing surgical site infection. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2008, 29, 302–308. [Google Scholar]
- Gastmeier, P.; Breier, A.C.; Brandt, C. Influence of laminar airflow on prosthetic joint infections: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2012, 81, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, P.; Gopalan, H.; Sprague, S.; Pradhan, C.; Kulkarni, S.; Bhandari, M. Incidence of infection following internal fixation of open and closed fractures. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, G.A.S.; Sawada, P.Y.; Ribeiro, E.S.; Godoy, G.M.S.; Mota, W.R.F.V.; Zago, P.L.; Almeida Neto, E.; Silva Neto, L.A.; Leite, A.F.F.O.; Santos, S.G.; et al. Economic and performance impact of surgical site infections in patients undergoing cardiac surgery in a tertiary emergency hospital. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 26, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Chang, C.J.; Hsieh, P.H. Increased periprosthetic hip and knee infection projected with longer life expectancy in the USA. Arthroplast. Today 2020, 6, 421–427. [Google Scholar]
- Kheir, M.M.; Tan, T.L.; Shohat, N.; Meneghini, R.M. Extended oral antibiotics prevent periprosthetic joint infection in high-risk cases: 3855 patients with 1-year follow-up (AAHKS Clinical Research Award). J. Arthroplast. 2021, 103, S18–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouiche, R.O.; Wall, M.J.; Itani, K.M.; Otterson, M.F.; Webb, A.L.; Carrick, M.M.; Miller, H.J.; Awad, S.S.; Crosby, C.T.; Mosier, M.C.; et al. Chlorhexidine–alcohol versus povidone–iodine for surgical-site antisepsis: A randomised trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabichi, S.; Chisari, E.; Van Nest, D.S.; Krueger, C.A.; Parvizi, J. Prevention of surgical site infection: A ten-step approach. Arthroplasty 2023, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busada, B.; El-Farargy, N.; Hammad, A. Auditing infection control practices to improve surgical outcomes in a resource-limited teaching hospital. J. Hosp. Infect. 2024, 142, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilskog, K.; Høvding, P.; Fenstad, A.M.; Inderhaug, E.; Fevang, J.M.; Dale, H. Risk factors for fracture-related infection after ankle fracture surgery. Injury 2023, 54, 111011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewick, A.; Makani, A.; Wu, C.; O’Donnell, J.; Baldwin, K.D.; Lee, G.C. Does dual antibiotic prophylaxis better prevent surgical site infections in total joint arthroplasty? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 2702–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osco, J.; Tejada, P.R.; Catanzano, A.; Stachel, A.; Phillips, M. Expanded Gram-negative antimicrobial prophylaxis reduces surgical site infections in hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 1620–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymski, D.; Walter, N.; Alt, V.; Rupp, M. Evaluation of comorbidities as risk factors for fracture-related infection and periprosthetic joint infection in Germany. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, M.; Vallejo, A.; McNally, M.A.; Moriarty, T.F.; Ferguson, J.Y.; Nijs, S.; Metsemakers, W.J. The effect of local antibiotic prophylaxis when treating open limb fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Jt. Res. 2018, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegranzi, B.; Bischoff, P.; de Jonge, S.; Kubilay, N.Z.; Zayed, B.; Gomes, S.M.; Abbas, M.; Atema, J.J.; Gans, S.; van Rijen, M.; et al. New WHO recommendations on preoperative measures for surgical site infection prevention: An evidence-based global perspective. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e276–e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegranzi, B.; Zayed, B.; Bischoff, P.; Kubilay, N.Z.; de Jonge, S.; de Vries, F.; Gomes, S.M.; Gans, S.; Wallert, E.D.; Wu, X.; et al. New WHO recommendations on intraoperative and postoperative measures for surgical site infection prevention: An evidence-based global perspective. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e288–e303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebše, R. The EBJIS definition of periprosthetic joint infection. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
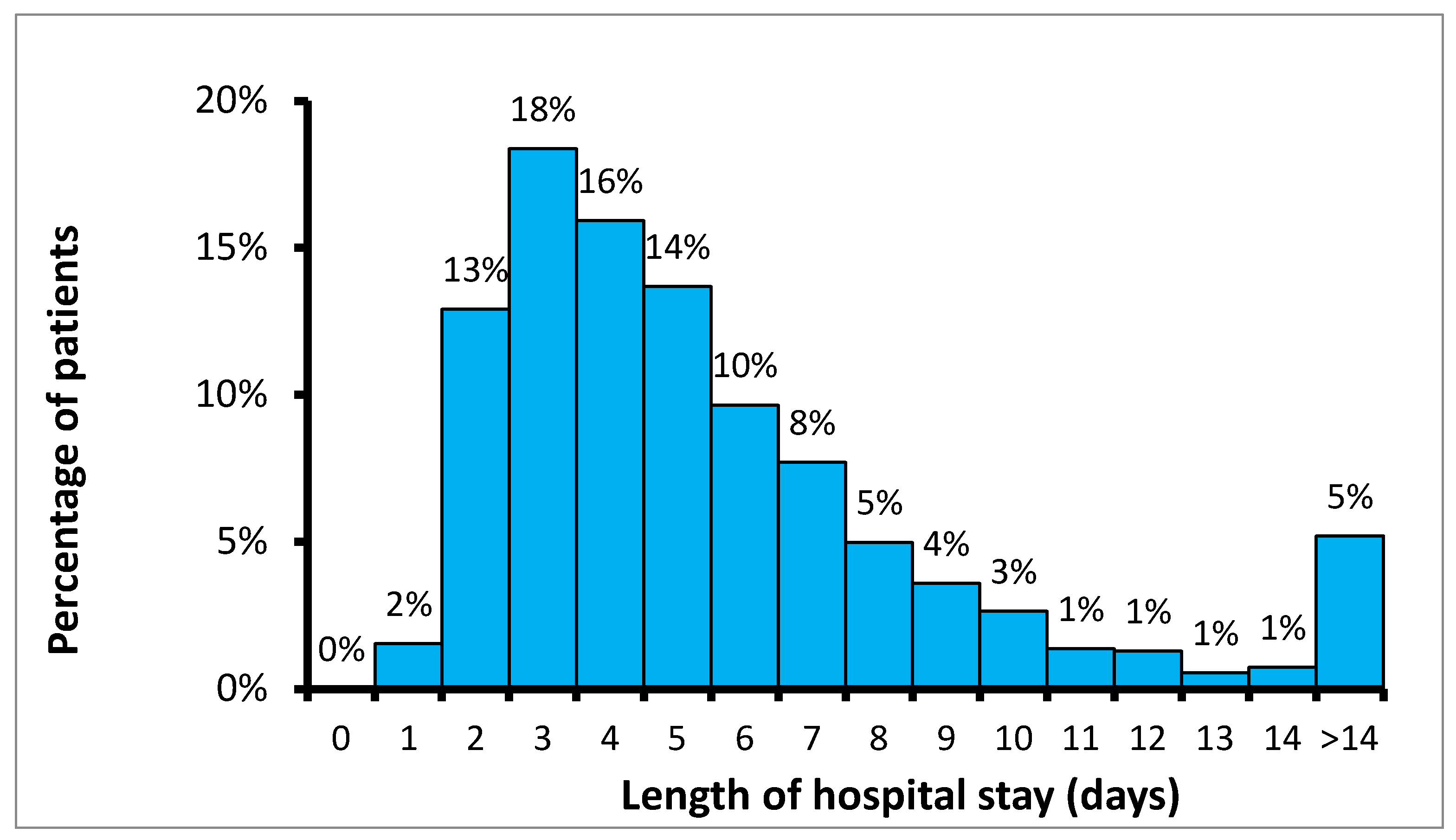


| Variable | Period | Mean | Median | Standard Deviation | 25th Percentile | 75th Percentile | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * ASA score | 2019–2022 2023–2024 | 1.6 1.7 | 2 2 | 0.59 0.91 | 1 1 | 2 2 | 0.482 |
| Age (years) | 2019–2022 2023–2024 | 51 48 | 51 49 | 20.7 19.9 | 34 32 | 67 64 | <0.001 |
| Operative time (minutes) | 2019–2022 2023–2024 | 103 104 | 100 120 | 55.4 55.6 | 65 60 | 145 120 | 0.131 |
| Pre-operative hospital stay (days) | 2019–2022 2023–2024 | 2.9 3.3 | 2 2 | 12.0 9.4 | 0 0 | 3 4 | 0.118 |
| Number of hospital admissions | 2019–2022 2023–2024 | 1.2 1.2 | 1 1 | 0.53 0.61 | 1 1 | 1 1 | 0.191 |
| Patient Group | Sample Size (n) | Total Deaths | Mortality Risk (%) | Relative Risk (RR) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infected patients | 239 | 9 | 3.8 | 2.5 | 0.014 |
| Non-infected patients | 3917 | 59 | 1.5 | ||
| Total | 4154 | 68 | 1.6 |
| Surgical Procedure | Baseline SSI Rate (2019–2022) | Intervention SSI Rate (2023–2024) | Relative Risk (RR) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Knee Arthroplasty | 4.8% | 1.2% | 4.1 | 0.013 |
| Open Reduction | 5.2% | 1.0% | 5.4 | <0.001 |
| Total Hip Arthroplasty | 9.2% | 2.4% | 3.8 | <0.001 |
| Overall | 5.6% | 1.1% | 5.1 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, P.A.M.; Gontijo, T.d.C.; Colen, G.C.; Morganti, A.C.; Ulloa Gómez, F.I.; Mourão, P.A.; Mota, G.A.R.; Couto, B.R.G.M.; Rocha, P.A.d.V.; Machado, L.G.; et al. Comparison of Cost Savings of Methods of Prevention of Orthopedic Implant-Associated Infection in Arthroplasty and Closed Fracture Surgery Patients. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090900
Moreira PAM, Gontijo TdC, Colen GC, Morganti AC, Ulloa Gómez FI, Mourão PA, Mota GAR, Couto BRGM, Rocha PAdV, Machado LG, et al. Comparison of Cost Savings of Methods of Prevention of Orthopedic Implant-Associated Infection in Arthroplasty and Closed Fracture Surgery Patients. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090900
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Pedro Augusto Maciel, Thiago de Carvalho Gontijo, Gabriel Costa Colen, Ana Carolina Morganti, Felipe Ismael Ulloa Gómez, Pedro Assis Mourão, Gabrielle Adriane Rodrigues Mota, Braulio R. G. M. Couto, Patrícia Almeida de Vasconcellos Rocha, Laila Gonçalves Machado, and et al. 2025. "Comparison of Cost Savings of Methods of Prevention of Orthopedic Implant-Associated Infection in Arthroplasty and Closed Fracture Surgery Patients" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090900
APA StyleMoreira, P. A. M., Gontijo, T. d. C., Colen, G. C., Morganti, A. C., Ulloa Gómez, F. I., Mourão, P. A., Mota, G. A. R., Couto, B. R. G. M., Rocha, P. A. d. V., Machado, L. G., Silva, R. B. d., & Salles, M. J. (2025). Comparison of Cost Savings of Methods of Prevention of Orthopedic Implant-Associated Infection in Arthroplasty and Closed Fracture Surgery Patients. Antibiotics, 14(9), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090900







