Antimicrobial Activity of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extracts Against Community- and Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Activity of Lcb. rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extract Against MRSA Strains
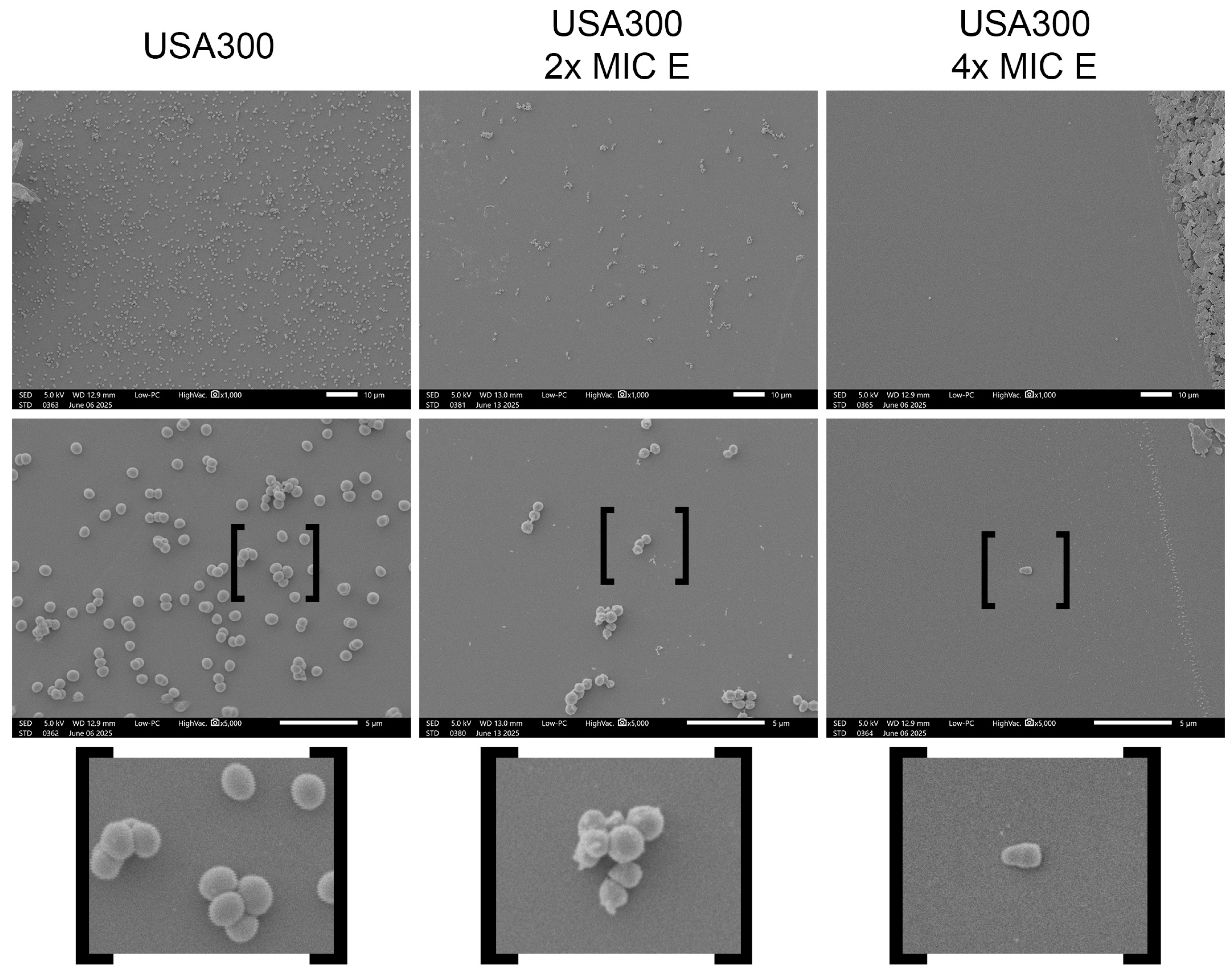
2.2. Morphological Changes Induced by Lcb. rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extract on S. aureus Cells
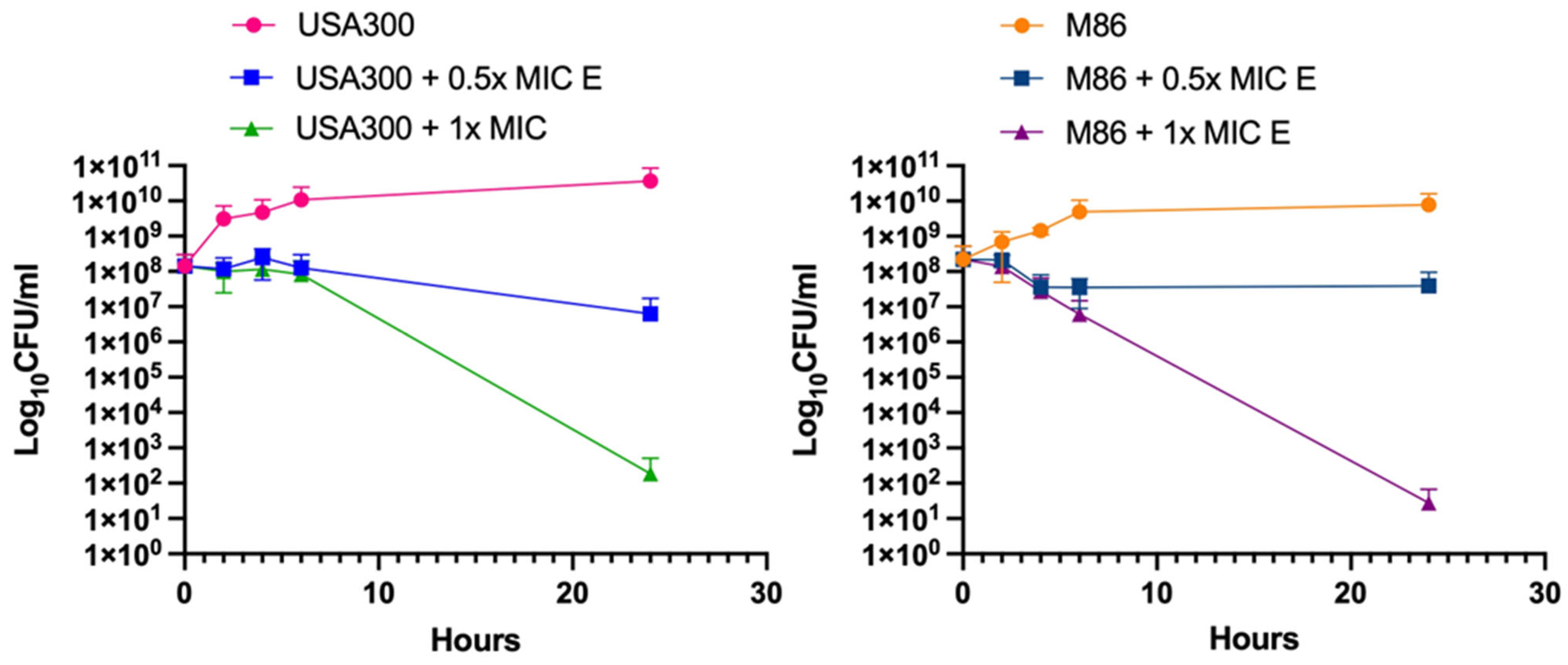
2.3. Bactericidal Effect of Lcb. rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extract Against MRSA Strains
2.4. MRSA Transcriptional Changes Triggered by the Extract from Lcb. rhamnosus CRL 2244
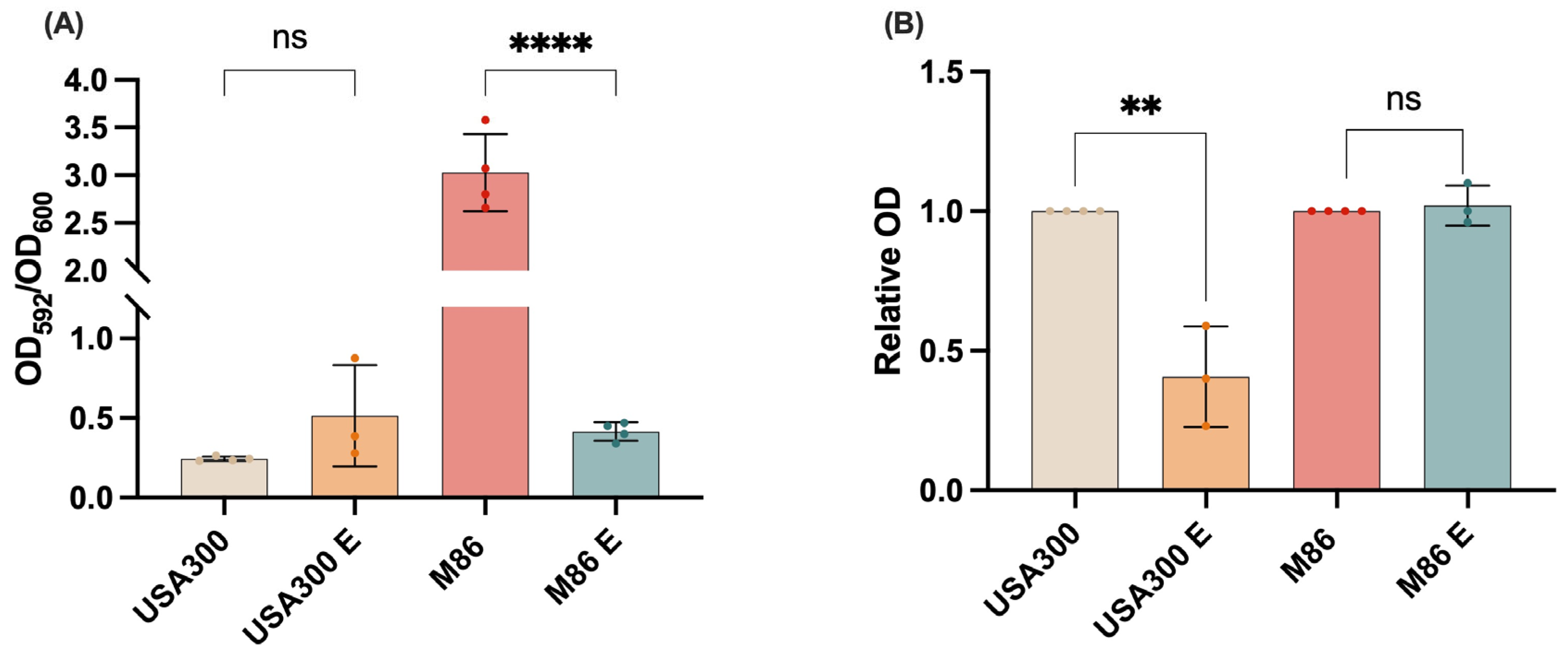
2.5. Effect of the Extract on MRSA Virulence: Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Staphyloxanthin Production
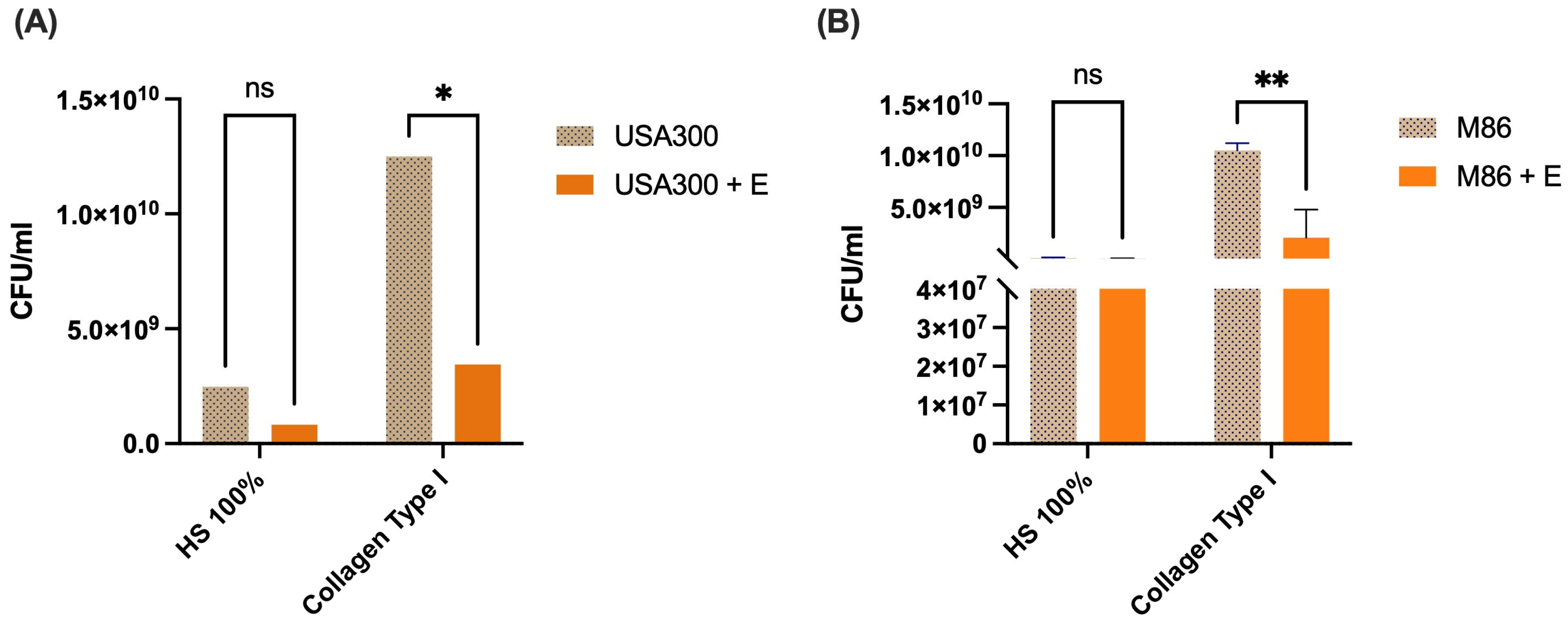
2.6. Impact of the Lcb. rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extract on MRSA Viability in Host-Mimicking Conditions
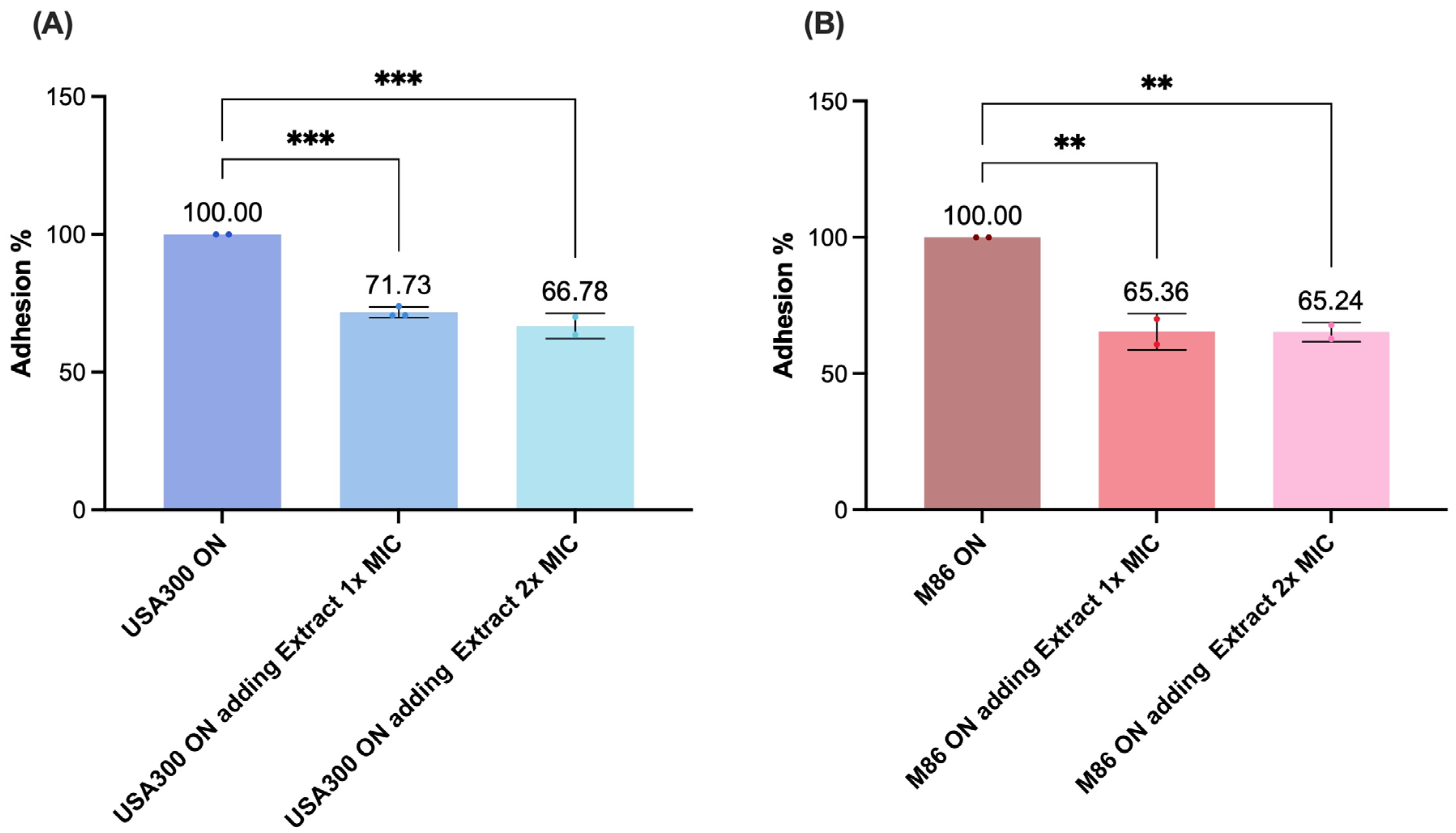
2.7. Effect of the Lcb. rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extract on Bacterial Adhesion of MRSA Strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Preparation of Extracts from Lcb. rhamnosus CRL 2244
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Assays
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Time-Killing Assay
4.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Assays
4.7. Biofilm Formation Assay
4.8. Staphyloxanthin Production Assay
4.9. Human Fluids Survival Assay
4.10. Adhesion Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Defres, S.; Marwick, C.; Nathwani, D. MRSA as a cause of lung infection including airway infection, community-acquired pneumonia and hospital-acquired pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, E.F.; Johnson, J.K.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Enemy amidst Us. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.C.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, N.; Wu, Z.D.; Wang, J.; Yu, Q.H.; Hong, L.; Shi, K.; Yu, J.A. Complicated Posterior Cervical Skin and Soft Tissue Infections at a Single Referral Center. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5230763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.Y.; Wagner, N.J.; Velez, A.Z.; Ceppe, A.; Conlon, B.P.; Muhlebach, M.S. Antibiotic Tolerance and Treatment Outcomes in Cystic Fibrosis Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0406122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Pierre, V.; Boudet, A.; Sorlin, P.; Menetrey, Q.; Chiron, R.; Lavigne, J.P.; Marchandin, H. Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus aureus in the Specific Context of Cystic Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Ganesh, V.K.; Hook, M. Adhesion, invasion and evasion: The many functions of the surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.A.; Hurford, I.M.; Cassat, J.E. Antivirulence Strategies for the Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infections: A Mini Review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 632706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinski, J.M.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections: Pathogenesis and regulatory mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 53, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, I.N.; Latorre-Fernandez, J.; Reuben, R.C.; Trabelsi, I.; Gonzalez-Azcona, C.; Arfaoui, A.; Usman, Y.; Lozano, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Beyond the Wild MRSA: Genetic Features and Phylogenomic Review of mecC-Mediated Methicillin Resistance in Non-aureus Staphylococci and Mammaliicocci. Microorganisms 2023, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.L.; Jia, Q.; Gao, J.; Cao, L.; Yan, J.; Li, B.L.; Xie, X.J.; Xu, Y.H.; et al. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a Hospital Setting: A Retrospective Study from 2018 to 2022. Indian J. Microbiol. 2024, 64, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazorla, S.I.; Maldonado-Galdeano, C.; Weill, R.; De Paula, J.; Perdigon, G.D.V. Oral Administration of Probiotics Increases Paneth Cells and Intestinal Antimicrobial Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, F.; Pasolli, E.; Ercolini, D. The food-gut axis: Lactic acid bacteria and their link to food, the gut microbiome and human health. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 454–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladha, G.; Jeevaratnam, K. A novel antibacterial compound produced by Lactobacillus plantarum LJR13 isolated from rumen liquor of goat effectively controls multi-drug resistant human pathogens. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 241, 126563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Mittal, V.; Singh, A. Selection of Potential Probiotic Bacteria from Exclusively Breastfed Infant Faeces with Antagonistic Activity Against Multidrug-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlambo, L.K.; Abbasiliasi, S.; Tang, H.W.; Ng, Z.J.; Parumasivam, T.; Hanafiah, K.M.; Al-Shammary, A.A.K.; Tan, J.S. Bioactive Metabolites of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum K014 Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ATCC43300 and In Vitro Evaluation of Its Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Ramlaoui, D.; Gasca, B.; Azis, A.; Leal, C.; Lopez, C.; Merzcord, V.; McManus, K.S.; Jo, J.; Cazorla, S.I.; et al. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL 2244 secreted metabolites display killing and antibiotic synergistic activity against multi-drug resistant pathogens. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekema, D.J.; Richter, S.S.; Heilmann, K.P.; Dohrn, C.L.; Riahi, F.; Tendolkar, S.; McDanel, J.S.; Doern, G.V. Continued emergence of USA300 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the United States: Results from a nationwide surveillance study. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.H.; Cameron, D.R.; Nethercott, C.; Aires-de-Sousa, M.; Peleg, A.Y. Virulence attributes of successful methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 36, e0014822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endimiani, A.; Blackford, M.; Dasenbrook, E.C.; Reed, M.D.; Bajaksouszian, S.; Hujer, A.M.; Rudin, S.D.; Hujer, K.M.; Perreten, V.; Rice, L.B.; et al. Emergence of linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus aureus after prolonged treatment of cystic fibrosis patients in Cleveland, Ohio. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.P.; Capozzi, V.; Russo, P.; Drider, D.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Immunobiosis and probiosis: Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria with a focus on their antiviral and antifungal properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9949–9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, G.; Ahmad, T.; Kaur, B.; Hakeem, K.R. Tailoring cellular metabolism in lactic acid bacteria through metabolic engineering. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 170, 105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Roman, R.; Last, A.; Mirhakkak, M.H.; Sprague, J.L.; Moller, L.; Grossmann, P.; Graf, K.; Gratz, R.; Mogavero, S.; Vylkova, S.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus colonisation antagonizes Candida albicans by forcing metabolic adaptations that compromise pathogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azami, S.; Arefian, E.; Kashef, N. Postbiotics of Lactobacillus casei target virulence and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by modulating quorum sensing. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Hamadou, W.S.; Surti, M.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; Ashraf, S.A.; Alreshidi, M.; Snoussi, M.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Bardakci, F.; et al. Inhibition of Bacterial Adhesion and Antibiofilm Activities of a Glycolipid Biosurfactant from Lactobacillus rhamnosus with Its Physicochemical and Functional Properties. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, E.; De Paepe, K.; Van de Wiele, T. Postbiotics and Their Health Modulatory Biomolecules. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Shi, J.; Fang, C.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Du, Q.; Tu, M.; Pan, D. Elimination of Pathogen Biofilms via Postbiotics from Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Promising Method in Food and Biomedicine. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. Author Correction: The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, G.; Sanders, M.E.; Cunningham, M.; Hill, C. Frequently asked questions about the ISAPP postbiotic definition. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1324565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Ramlaoui, D.; Georgeos, N.; Gasca, B.; Leal, C.; Subils, T.; Tuttobene, M.R.; Sieira, R.; Salzameda, N.T.; Bonomo, R.A.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of the Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL 2244 and its impact on the phenotypic and transcriptional responses in carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klancnik, A.; Piskernik, S.; Jersek, B.; Mozina, S.S. Evaluation of diffusion and dilution methods to determine the antibacterial activity of plant extracts. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 81, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, T.J. Methods for screening and evaluation of antimicrobial activity: A review of protocols, advantages, and limitations. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2024, 14, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaumer-Proll, A.K.; Knotzer, S.; Eberl, S.; Reiter, B.; Stimpfl, T.; Jager, W.; Poschner, S.; Zeitlinger, M. Impact of erythrocytes on bacterial growth and antimicrobial activity of selected antibiotics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berube, B.J.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin: Nearly a century of intrigue. Toxins 2013, 5, 1140–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus aureus toxins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, A.C.; Thurlow, L.R.; Richardson, A.R. Mechanisms Behind the Indirect Impact of Metabolic Regulators on Virulence Factor Production in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0206322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauditz, A.; Resch, A.; Wieland, K.P.; Peschel, A.; Gotz, F. Staphyloxanthin plays a role in the fitness of Staphylococcus aureus and its ability to cope with oxidative stress. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4950–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.Y.; Essex, A.; Buchanan, J.T.; Datta, V.; Hoffman, H.M.; Bastian, J.F.; Fierer, J.; Nizet, V. Staphylococcus aureus golden pigment impairs neutrophil killing and promotes virulence through its antioxidant activity. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmesseri, R.A.; Saleh, S.E.; Elsherif, H.M.; Yahia, I.S.; Aboshanab, K.M. Staphyloxanthin as a Potential Novel Target for Deciphering Promising Anti-Staphylococcus aureus Agents. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmesseri, R.A.; Saleh, S.E.; Ghobish, S.A.; Majrashi, T.A.; Elsherif, H.M.; Aboshanab, K.M. Diclofenac and Meloxicam Exhibited Anti-Virulence Activities Targeting Staphyloxanthin Production in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yan, Z.; Lu, W.; Wan, D.; Zhu, H. Staphyloxanthin: A potential target for antivirulence therapy. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambanthamoorthy, K.; Feng, X.; Patel, R.; Patel, S.; Paranavitana, C. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm potential of biosurfactants isolated from lactobacilli against multi-drug-resistant pathogens. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.M.; Mergulhao, F.J.M.; Gomes, L.C. Using Lactobacilli to Fight Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms on Urinary Tract Devices. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindieh, P.; Yaghi, J.; Assaf, J.C.; Chokr, A.; Atoui, A.; Louka, N.; Khoury, A.E. Unlocking the potential of lactic acid bacteria mature biofilm extracts as antibiofilm agents. AMB Express 2024, 14, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Zhang, W.; Su, J.; Li, F.; Chen, D.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Gu, R.; Zhang, C. Antibacterial and antibiofilm potential of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus YT and its cell-surface extract. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiedrowski, M.R.; Kavanaugh, J.S.; Malone, C.L.; Mootz, J.M.; Voyich, J.M.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Bayles, K.W.; Horswill, A.R. Nuclease modulates biofilm formation in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Horswill, A.R. The role of human extracellular matrix proteins in defining Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infections. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 48, fuae002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhou, G.; Yang, X.M.; Chen, G.J.; Chen, H.B.; Liao, Z.L.; Zhong, Q.P.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Wang, J. Transcriptomic Analysis Revealed Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Lactobacillus rhamnosus SCB0119 against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenover, F.C.; Goering, R.V. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain USA300: Origin and epidemiology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, T.K.; Pallister, K.B.; DuMont, A.L.; DeWald, M.; Watkins, R.L.; Pallister, E.Q.; Malone, C.; Griffith, S.; Horswill, A.R.; Torres, V.J.; et al. Alpha-toxin induces programmed cell death of human T cells, B cells, and monocytes during USA300 infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, D.; Mandal, M.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Pal, N.K.; Mandal, S. Indigenous Probiotic Lactobacillus Isolates Presenting Antibiotic like Activity against Human Pathogenic Bacteria. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Thirty Edition Informational Supplement; CLSI Document M100-S30:2020; Clinical Lab Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, B.; Escalante, J.; Mezcord, V.; Tuttobene, M.R.; Subils, T.; Actis, L.A.; Pasteran, F.; Tolmasky, M.E.; Bonomo, R.A.; Ramirez, M.S. Human serum albumin-induced modification of Ton-B-dependent receptor expression in cefiderocol-exposed carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezcord, V.; Traglia, G.M.; Pasteran, F.; Escalante, J.; Lopez, C.; Wong, O.; Rojas, L.; Marshall, S.H.; Tolmasky, M.E.; Bonomo, R.A.; et al. Characterisation of cefiderocol-resistant spontaneous mutant variants of Klebsiella pneumoniae-producing NDM-5 with a single mutation in cirA. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, K.; Maruyama, A.; Inose, Y.; Higashide, M.; Hayashi, H.; Ohta, T. Overexpression of sigma factor, sigma(B), urges Staphylococcus aureus to thicken the cell wall and to resist beta-lactams. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, S.J.; Day, N.P.; Thomas, M.G.; Berendt, A.R.; Foster, T.J. Clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus exhibit diversity in fnb genes and adhesion to human fibronectin. J. Infect. 2000, 41, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strains | Special Features | IDH (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLDE Agar | Blood Agar | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | |||
| M86 | Linezolid Resistance, PVL+ | 10 | 20 |
| USA 300 | mecA, PVL+ | 12 | 20 |
| SAUSA 300 mutants | |||
| 1992 | ΔagrA (accessory gene regulator protein A) | 16 | 19 |
| 0605 | ΔsarA (accessory regulator A) | 15 | nd |
| 1382 | ΔlukS-PV (Panton–Valentine leukocidin, LukS-PV | 16 | nd |
| 0772 | ΔclfA (clumping factor A) | 18 | nd |
| 2441 | ΔfnbA (fibronectin binding protein A) | 16 | nd |
| α-toxin | Δhla (α-toxin) | 20 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez, C.; Gasca, B.; Mezcord, V.; Bonomo, R.A.; Rao, G.; Salzameda, N.T.; Ramirez, M.S. Antimicrobial Activity of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extracts Against Community- and Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080812
Rodriguez C, Gasca B, Mezcord V, Bonomo RA, Rao G, Salzameda NT, Ramirez MS. Antimicrobial Activity of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extracts Against Community- and Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(8):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080812
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez, Cecilia, Briea Gasca, Vyanka Mezcord, Robert A. Bonomo, Gauri Rao, Nicholas T. Salzameda, and Maria Soledad Ramirez. 2025. "Antimicrobial Activity of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extracts Against Community- and Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus" Antibiotics 14, no. 8: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080812
APA StyleRodriguez, C., Gasca, B., Mezcord, V., Bonomo, R. A., Rao, G., Salzameda, N. T., & Ramirez, M. S. (2025). Antimicrobial Activity of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CRL 2244 Extracts Against Community- and Hospital-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics, 14(8), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080812








