Transcriptomic Analysis of Biofilm Formation Inhibition by PDIA Iminosugar in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Biofilm Structure by SEM
2.2. Transcriptomic Analysis of PDIA-Induced Gene Expression Changes
2.3. GO Term Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
2.4. qPCR Validation of RNA-Seq Results
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
4.2. Iminosugar
4.3. Biofilm Assay on Polystyrene Plate by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4. Experimental Design
4.5. RNA Isolation
4.6. Sequencing
4.7. Data Analysis
4.8. Real-Time PCR Validation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hassoun-Kheir, N.; Guedes, M.; Ngo Nsoga, M.T.; Argante, L.; Arieti, F.; Gladstone, B.P.; Kingston, R.; Naylor, N.R.; Pezzani, M.D.; Pouwels, K.B.; et al. A systematic review on the excess health risk of antibiotic-resistant bloodstream infections for six key pathogens in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2024, 1, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, Y.C.; Cheug, C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar]
- Thurlow, L.R.; Hanke, M.L.; Fritz, T.; Angle, A.; Aldrich, A.; Williams, S.H.; Engebretsen, I.L.; Bayles, K.W.; Horswill, A.R.; Kielian, T. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms prevent macrophage phagocytosis and attenuate inflammation in vivo. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6585–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Ganesh, V.K.; Hook, M. Adhesion, invasion and evasion: The many functions of the surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, J.L.; Horswill, H.R. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compain, P.; Martin, O.R. Iminosugars: From Synthesis to Therapeutic Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007; ISBN 9780470517437. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, R.J.; Kato, A.; Yu, C.-Y.; Fleet, G.W. Iminosugars as therapeutic agents: Recent advances and promising trends. Futur. Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans DeWald, L.; Starr, C.; Butters, T.; Treston, A.; Warfield, K.L. Iminosugars: A host-targeted approach to combat Flaviviridae infections. Antivir. Res. 2020, 184, 104881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fenza, M.; D’Alonzo, D.; Esposito, A.; Munari, S.; Loberto, N.; Santangelo, A.; Lampronti, I.; Tamanini, A.; Rossi, A.; Ranucci, S.; et al. Exploring the effect of chirality on the therapeutic potential of N-alkyl-deoxyiminosugars: Anti-inflammatory response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections for application in CF lung disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 175, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gregorio, E.; Esposito, A.; Vollaro, A.; De Fenza, M.; D’Alonzo, D.; Migliaccio, A.; Iula, V.D.; Raffaele Zarrilli, R.; Guaragna, A. N-Nonyloxypentyl-l-Deoxynojirimycin inhibits growth, biofilm formation and virulence factors expression of Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, B.; Khan, S.N.; Haque, I.; Alam, M.; Mushfiq, M.; Khan, A.U. Novel anti-adherence activity of mulberry leaves: Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilm by 1-deoxynojirimycin isolated from Morus alba. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strus, M.; Mikołajczyk, D.; Machul, A.; Heczko, P.; Chronowska, A.; Stochel, G.; Gallienne, E.; Nicolas, C.; Martin, O.R.; Kyzioł, A. Effects of the selected iminosugar derivatives on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozień, Ł.; Gallienne, E.; Martin, O.; Front, S.; Strus, M.; Heczko, P. PDIA, an Iminosugar Compound with a Wide Biofilm Inhibitory Spectrum Covering Both Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Human Bacterial Pathogens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozień, Ł.; Policht, A.; Heczko, P.; Arent, Z.; Bracha, U.; Pardyak, L.; Pietsch-Fulbiszewska, A.; Gallienne, E.; Piwowar, P.; Okoń, K. PDIA iminosugar influence on subcutaneous Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in mice. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1395577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, C.; Martin, O.R. Glycoside Mimics from Glycosylamines: Recent Progress. Molecules 2018, 23, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, S.; Chung, S.J.; Igarashi, Y.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sepp, A.; Lechler, R.I.; Wu, J.; Hayashi, T.; Siuzdak, G.; Wong, C.H. Selective inhibition of beta-1,4- and alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferases: Donor sugar-nucleotide based approach. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.L.; Tyrrell, B.E.; Zitzmann, N. Mechanisms of Antiviral Activity of Iminosugars Against Dengue Virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1062, 277–301. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, M.; Cheng, J.; Lee, Y.G.; Cho, J.H.; Suh, J.W. Discovery of Novel Iminosugar Compounds Produced by Lactobacillus paragasseri MJM60645 and Their Anti-Biofilm Activity against Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0112222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluj, R.M.; Ebner, P.; Adamek, M.; Ziemert, N.; Mayer, C.; Borisova, M. Recovery of the Peptidoglycan Turnover Product Released by the Autolysin Atl in Staphylococcus aureus Involves the Phosphotransferase System Transporter MurP and the Novel 6-phospho-N-acetylmuramidase MupG. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, N.; Mukai, T. Production profile of the soluble lytic transglycosylase homologue in Staphylococcus aureus during bacterial proliferation. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saier, M.H.; Reddy, B.L. Holins in bacteria, eukaryotes, and archaea: Multifunctional xenologues with potential biotechnological and biomedicalications. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, N.; Yan, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Sun, J. Combined antibacterial activity of phage lytic proteins holin and lysin from Streptococcus suis bacteriophage SMP. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Xie, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; Geng, W.; Wu, X.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Cheng, L.; Qiu, L.; Cheng, C. Artificial Phages with Biocatalytic Spikes for Synergistically Eradicating Antibiotic-Resistant Biofilms. Adv. Mat. 2024, 16, 2404411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.J.; Vold, B.S. Staphylococus aureus has Clustered tRNA Genes. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 5091–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElvania TeKippe, E.; Burnham, C.-A.D. Evaluation of the Bruker Biotyper and VITEK MS MALDI-TOF MS systems for the identification of unusual and/or difficult-to-identify microorganisms isolated from clinical specimens. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-Based Genome Alignment and Genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-Genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq: A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenfuhrer, J. TopGO: Enrichment Analysis for Gene Ontology, R Package Version 2.58.0. 2024. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/topGO.html (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2002, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
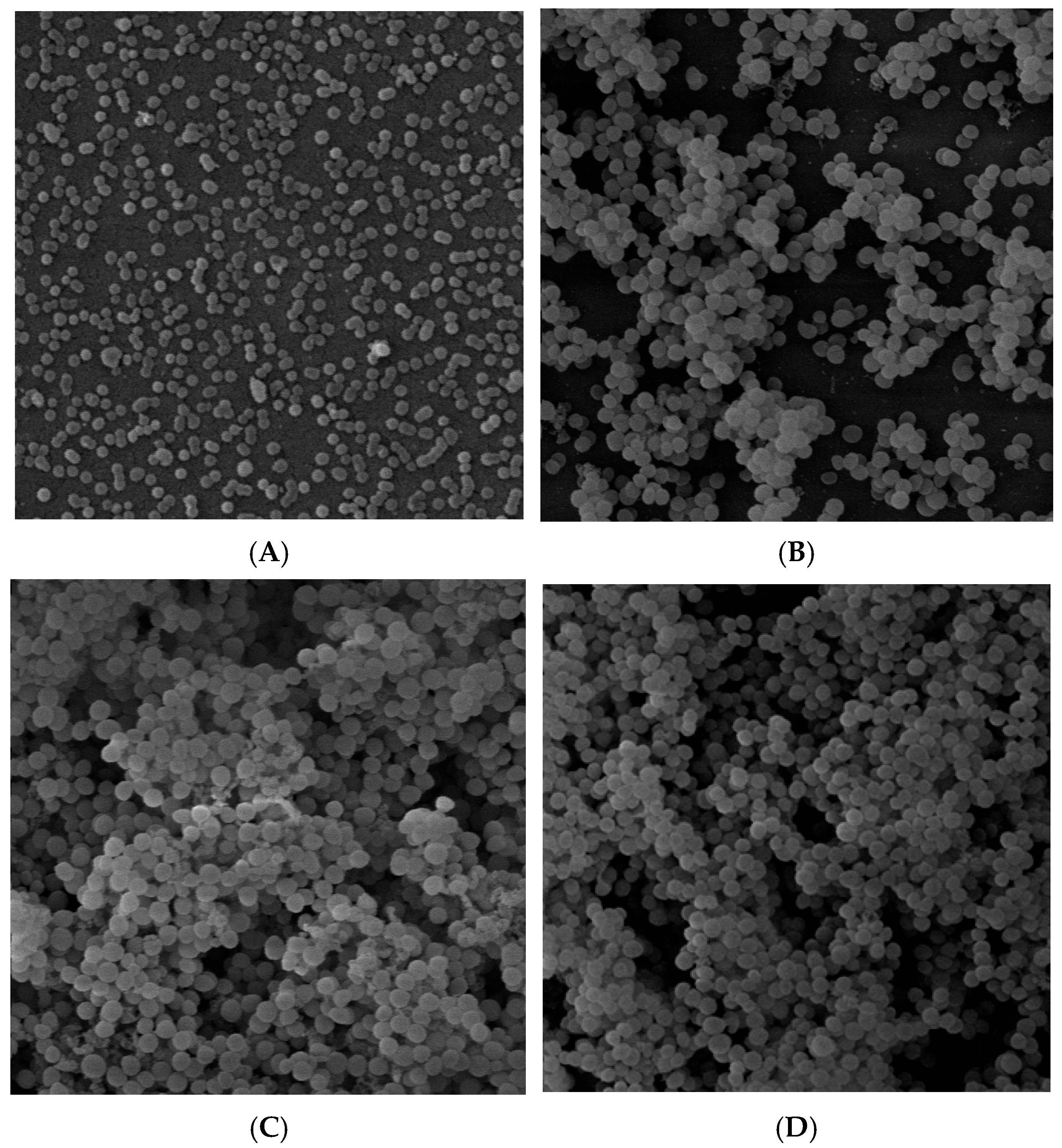
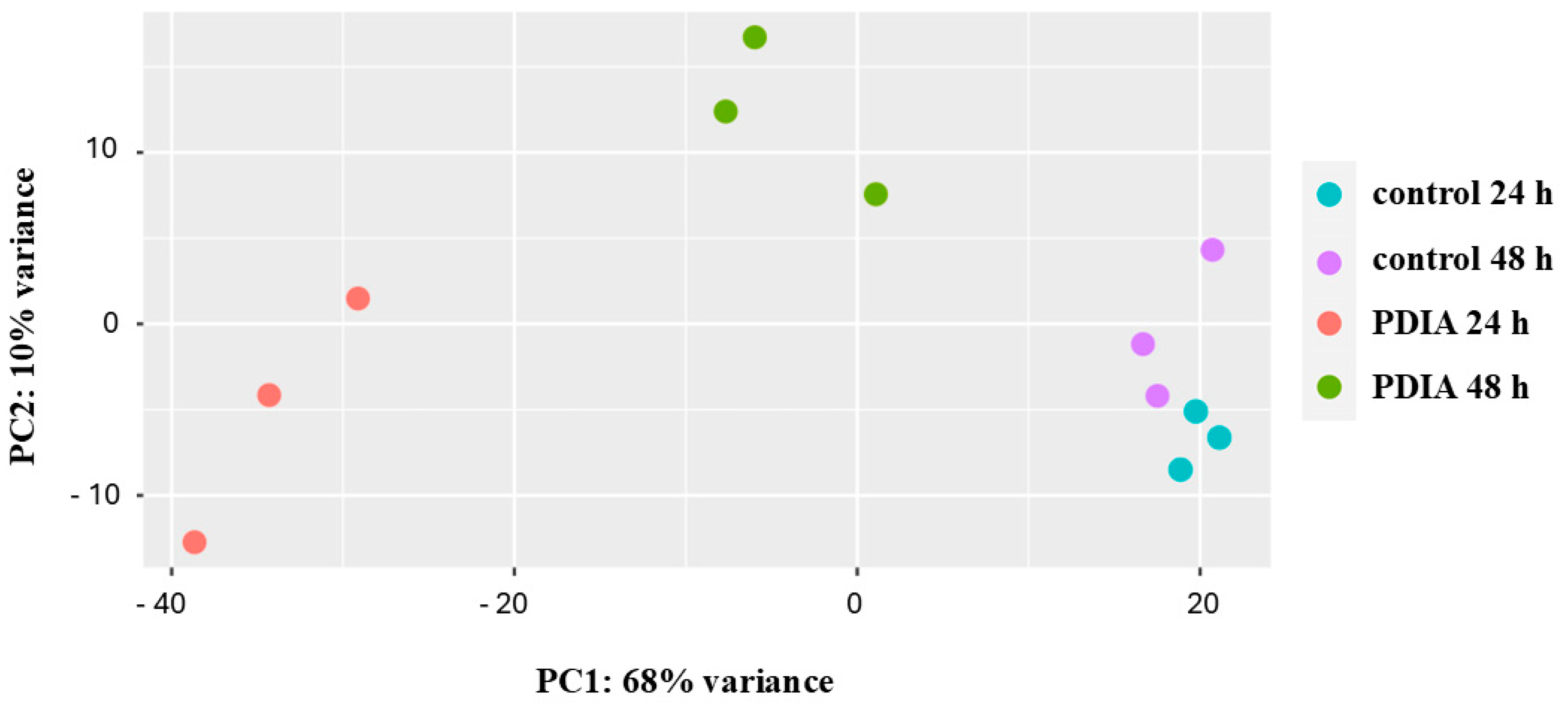
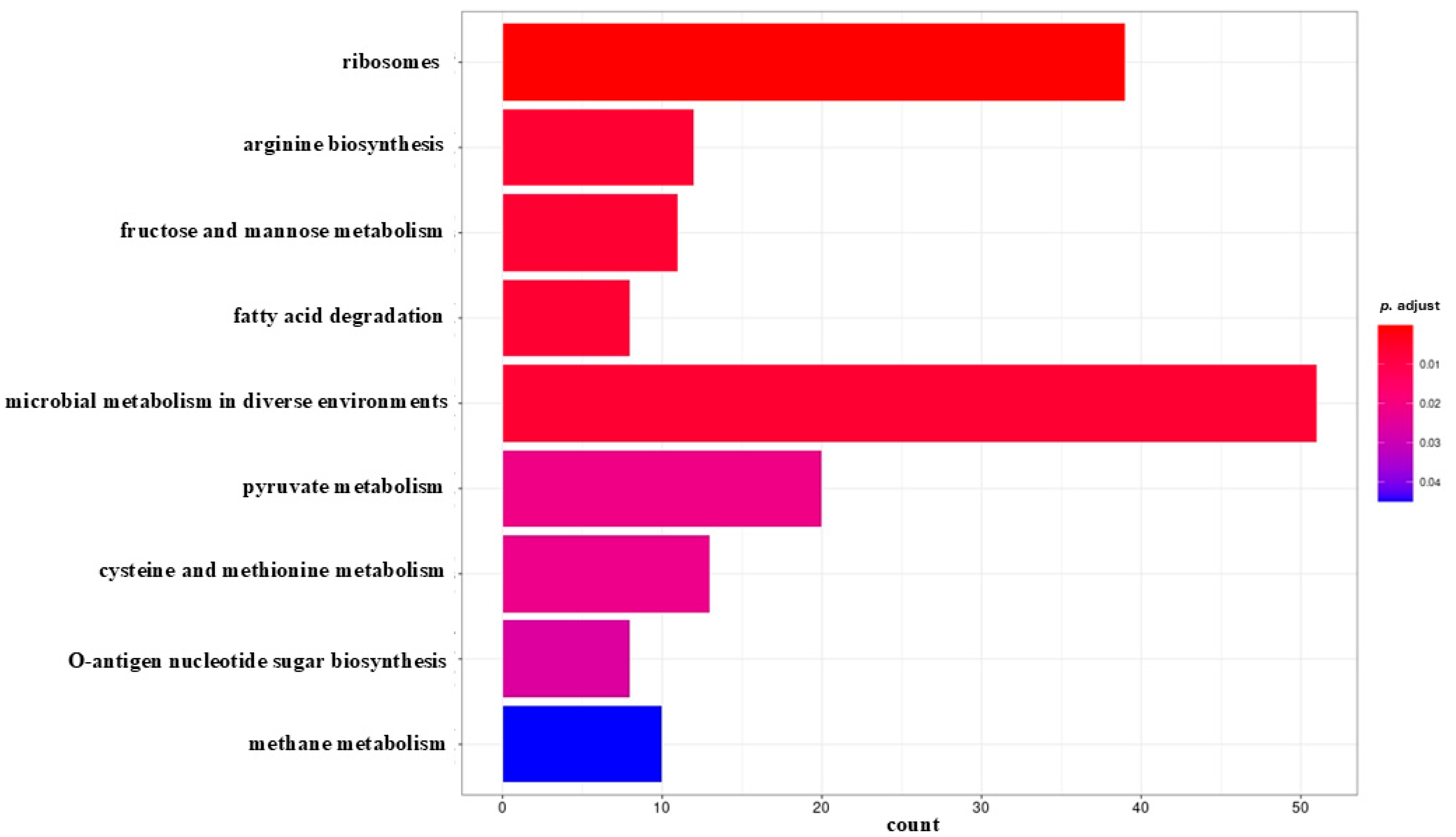
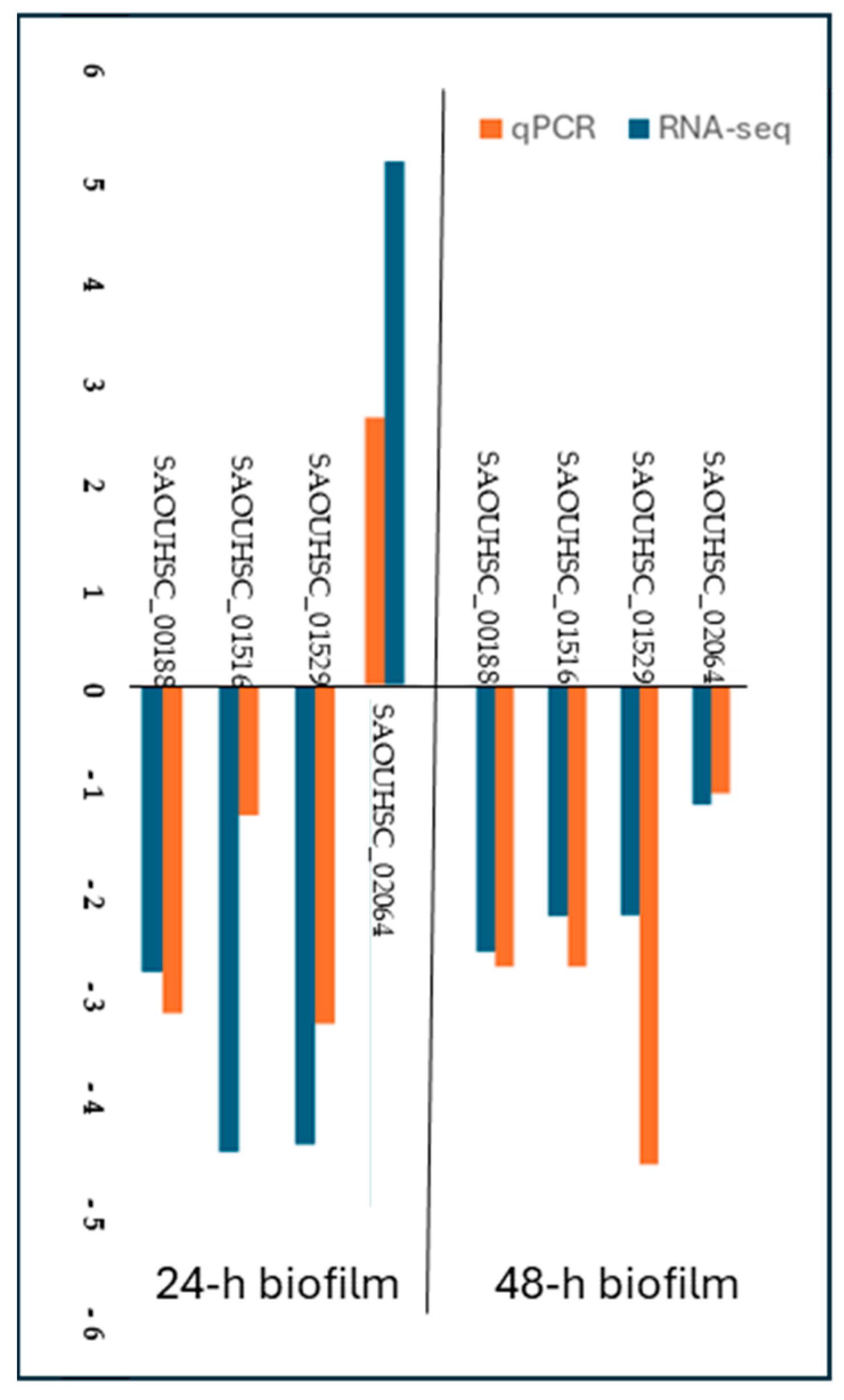
| Gene | log2 Fold Change | FDR Adjusted p-Value | Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAOUHSC_02260 | −9.39 | 3.46 × 10−279 | delta-hemolysin |
| SAOUHSC_01532 | −5.23 | 3.80 × 10−30 | SLT orf 110-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01536 | −4.86 | 8.86 × 10−69 | scaffolding protease |
| SAOUHSC_01531 | −4.83 | 5.88 × 10−54 | SLT orf 123-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01516 | −4.74 | 8.96 × 10−33 | holin protein |
| SAOUHSC_01529 | −4.67 | 1.39 × 10−57 | major tail protein |
| SAOUHSC_01451 | −4.63 | 7.64 × 10−58 | threonine dehydratase |
| SAOUHSC_01528 | −4.62 | 7.94 × 10−59 | bacteriophage L54aIg-like domain |
| SAOUHSC_02969 | −4.56 | 7.74 × 10−47 | arginine deiminase |
| SAOUHSC_01519 | −4.45 | 3.99 × 10−35 | SLT orf 129-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01515 | −4.39 | 1.75 × 10−65 | peptidoglycan hydrolase |
| SAOUHSC_01539 | −4.21 | 3.33 × 10−16 | terminase small subunit |
| SAOUHSC_01521 | −4.19 | 5.90 × 10−52 | SLT orf 636-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01520 | −4.19 | 2.91 × 10−46 | SLT orf 488-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_02968 | −4.11 | 2.80 × 10−46 | ornithine carbamoyltransferase |
| SAOUHSC_01537 | −4.07 | 1.55 × 10−41 | HK97 family phage portal protein |
| SAOUHSC_01452 | −4.07 | 4.61 × 10−34 | alanine dehydrogenase |
| SAOUHSC_00533 | −4.04 | 2.96 × 10−53 | chaperone protein HchA |
| SAOUHSC_01524 | −3.96 | 6.66 × 10−40 | holin-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01538 | −3.95 | 1.04 × 10−39 | phage terminase large subunit |
| SAOUHSC_00608 | −3.81 | 3.37 × 10−36 | alcohol dehydrogenase |
| SAOUHSC_01788 | −3.77 | 1.36 × 10−59 | threonyl-tRNA synthetase |
| SAOUHSC_01278 | −3.74 | 2.45 × 10−68 | aerobic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| SAOUHSC_01525 | −3.73 | 4.46 × 10−58 | phage tail tape meausure protein |
| SAOUHSC_01523 | −3.72 | 1.54 × 10−36 | SLT orf 527-like protein |
| Gene | log2 Fold Change | FDR Adjusted p-Value | Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAOUHSC_T00021 | 11.92 | 2.18 × 10−5 | tRNA-Gly |
| SAOUHSC_T00041 | 7.14 | 1.75 × 10−7 | tRNA-Met |
| SAOUHSC_T00058 | 6.55 | 5.79 × 10−5 | tRNA-Tyr |
| SAOUHSC_T00053 | 6.36 | 3.97 × 10−5 | tRNA-Thr |
| SAOUHSC_T00035 | 5.5 | 3.48 × 10−6 | tRNA-Lys |
| SAOUHSC_02064 | 5.3 | 2.04 × 10−7 | phi ETA orf 25-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_T00051 | 5.25 | 1.80 × 10−14 | tRNA-Ser |
| SAOUHSC_02050 | 5.16 | 0.005511766 | terminase small subunit |
| SAOUHSC_T00016 | 4.96 | 0.012930175 | tRNA-Gln |
| SAOUHSC_T00014 | 4.75 | 3.23 × 10−16 | tRNA-Asp |
| SAOUHSC_T00022 | 4.7 | 0.005922209 | tRNA-Gly |
| SAOUHSC_T00056 | 4.67 | 0.024895614 | tRNA-Trp |
| SAOUHSC_02217 | 4.59 | 3.15 × 10−53 | phi ETA orf 22-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_02216 | 4.53 | 2.31 × 10−66 | phage DnaC-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_02080 | 4.4 | 5.02 × 10−57 | bacteriophage L54a antirepressor |
| SAOUHSC_02078 | 4.35 | 3.57 × 10−40 | phi PV83 orf 10-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_T00057 | 4.35 | 0.00974457 | tRNA-Tyr |
| SAOUHSC_02219 | 4.33 | 7.93 × 10−42 | phi ETA orf 20-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01761a | 4.24 | 3.60 × 10−30 | membrane protein |
| SAOUHSC_02873 | 4.21 | 5.93 × 10−41 | cation transporter E1-E2 family ATPase |
| SAOUHSC_02213 | 4.15 | 1.59 × 10−15 | phi ETA orf 25-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_02450 | 4.14 | 7.53 × 10−80 | PTS system lactose-specific transporter |
| SAOUHSC_00097 | 4.06 | 7.82 × 10−42 | purine nucleoside phosphorylase |
| SAOUHSC_02449 | 4.04 | 5.44 × 10−56 | 6-phospho-beta-galactosidase |
| SAOUHSC_02452 | 3.97 | 2.45 × 10−66 | tagatose 1,6-diphosphate aldolase |
| Gene | log2 Fold Change | FDR Adjusted p-Value | Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAOUHSC_00188 | −2.79 | 2.73 × 10−17 | pyruvate formate-lyase 1 activating enzyme |
| SAOUHSC_01528 | −2.7 | 5.21 × 10−6 | bacteriophage L54aIg-like domain |
| SAOUHSC_01515 | −2.57 | 0.008840928 | peptidoglycan hydrolase |
| SAOUHSC_00187 | −2.53 | 8.45 × 10−13 | formate acetyltransferase |
| SAOUHSC_01516 | −2.41 | 0.000287074 | holin protein |
| SAOUHSC_01529 | −2.4 | 3.35 × 10−5 | major tail protein |
| SAOUHSC_01531 | −2.33 | 4.59 × 10−5 | SLT orf 123-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01536 | −2.33 | 0.000101285 | scaffolding protease |
| SAOUHSC_02260 | −2.3 | 4.58 × 10−7 | delta-hemolysin |
| SAOUHSC_01532 | −2.19 | 0.003732062 | SLT orf 110-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_02958 | −2.18 | 5.83 × 10−6 | alkaline phosphatase III |
| SAOUHSC_01537 | −2.08 | 0.000446571 | HK97 family phage portal protein |
| SAOUHSC_01521 | −2.07 | 0.038669542 | SLT orf 636-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01525 | −2.01 | 0.000109535 | phage tail tape meausure protein |
| SAOUHSC_01386 | −1.99 | 0.001324074 | phosphate ABC transporter permease |
| SAOUHSC_01566 | −1.97 | 8.77 × 10−5 | phi APSE P51-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_00142 | −1.9 | 7.03 × 10−10 | formate dehydrogenase |
| SAOUHSC_01538 | −1.88 | 0.001015173 | phage terminase large subunit |
| SAOUHSC_01570 | −1.87 | 0.000306708 | PVL orf 37-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_01539 | −1.83 | 0.011205785 | terminase small subunit |
| SAOUHSC_01523 | −1.81 | 0.00306758 | SLT orf 527-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_02606 | −1.79 | 9.95 × 10−6 | imidazolonepropionase |
| SAOUHSC_00608 | −1.76 | 2.94 × 10−8 | alcohol dehydrogenase |
| SAOUHSC_01524 | −1.76 | 0.002256919 | holin-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_00120 | −1.75 | 1.56 × 10−20 | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase |
| Gene | log2 Fold Change | FDR Adjusted p-Value | Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAOUHSC_00173 | 3.14 | 1.61 × 10−26 | azoreductase |
| SAOUHSC_00199 | 3.01 | 3.42 × 10−12 | acyl CoA:acetate/3-ketoacid CoA transferase |
| SAOUHSC_02450 | 2.63 | 1.06 × 10−34 | PTS system lactose-specific transporter subunit IIBC |
| SAOUHSC_02452 | 2.62 | 1.43 × 10−34 | tagatose 1,6-diphosphate aldolase |
| SAOUHSC_02455 | 2.45 | 1.34 × 10−17 | galactose-6-phosphate isomerase subunit LacA |
| SAOUHSC_02453 | 2.4 | 5.20 × 10−20 | tagatose-6-phosphate kinase |
| SAOUHSC_02451 | 2.4 | 6.33 × 10−16 | PTS system lactose-specific transporter subunit IIA |
| SAOUHSC_02662 | 2.4 | 1.04 × 10−10 | PTS system sucrose-specific transporter subunit IIBC |
| SAOUHSC_01761a | 2.36 | 2.57 × 10−5 | membrane protein |
| SAOUHSC_00132 | 2.31 | 0.02681717 | aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| SAOUHSC_02729 | 2.25 | 1.13 × 10−10 | amino acid ABC transporter-like protein |
| SAOUHSC_02454 | 2.23 | 1.99 × 10−12 | galactose-6-phosphate isomerase subunit LacB |
| SAOUHSC_02449 | 2.17 | 1.97 × 10−20 | 6-phospho-beta-galactosidase |
| SAOUHSC_01991 | 2.17 | 3.72 × 10−6 | ABC transporter permease |
| SAOUHSC_01012 | 2.17 | 0.036879081 | phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase I |
| SAOUHSC_01327 | 1.96 | 0.000190593 | catalase |
| SAOUHSC_00992 | 1.93 | 7.28 × 10−8 | MarR family transcriptional regulator |
| SAOUHSC_01691 | 1.89 | 2.31 × 10−6 | DNA internalization-related competence protein |
| SAOUHSC_00624 | 1.84 | 1.13 × 10−5 | integrase/recombinase |
| SAOUHSC_02270 | 1.84 | 0.032778238 | ammonium transporter |
| SAOUHSC_00871 | 1.83 | 0.009866049 | D-alanine-poly(phosphoribitol) ligase subunit 2 |
| SAOUHSC_00195 | 1.82 | 0.0003095 | acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase |
| SAOUHSC_00221 | 1.79 | 0.004285467 | alcohol dehydrogenase |
| SAOUHSC_01990 | 1.76 | 0.000106789 | amino acid ABC transporter ATP-binding protein |
| SAOUHSC_00899 | 1.74 | 7.79 × 10−5 | argininosuccinate synthase |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomusiak-Plebanek, A.; Kozień, Ł.; Gallienne, E.; Florczyk, M.; Ciesielski, S.; Heczko, P.; Strus, M. Transcriptomic Analysis of Biofilm Formation Inhibition by PDIA Iminosugar in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070668
Tomusiak-Plebanek A, Kozień Ł, Gallienne E, Florczyk M, Ciesielski S, Heczko P, Strus M. Transcriptomic Analysis of Biofilm Formation Inhibition by PDIA Iminosugar in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(7):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070668
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomusiak-Plebanek, Anna, Łucja Kozień, Estelle Gallienne, Maciej Florczyk, Sławomir Ciesielski, Piotr Heczko, and Magdalena Strus. 2025. "Transcriptomic Analysis of Biofilm Formation Inhibition by PDIA Iminosugar in Staphylococcus aureus" Antibiotics 14, no. 7: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070668
APA StyleTomusiak-Plebanek, A., Kozień, Ł., Gallienne, E., Florczyk, M., Ciesielski, S., Heczko, P., & Strus, M. (2025). Transcriptomic Analysis of Biofilm Formation Inhibition by PDIA Iminosugar in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics, 14(7), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070668








