Dose-Dependent Physiological Response to Transient Bioaccumulation of Tetracycline in Kimchi Cabbage (Brassica campestris L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
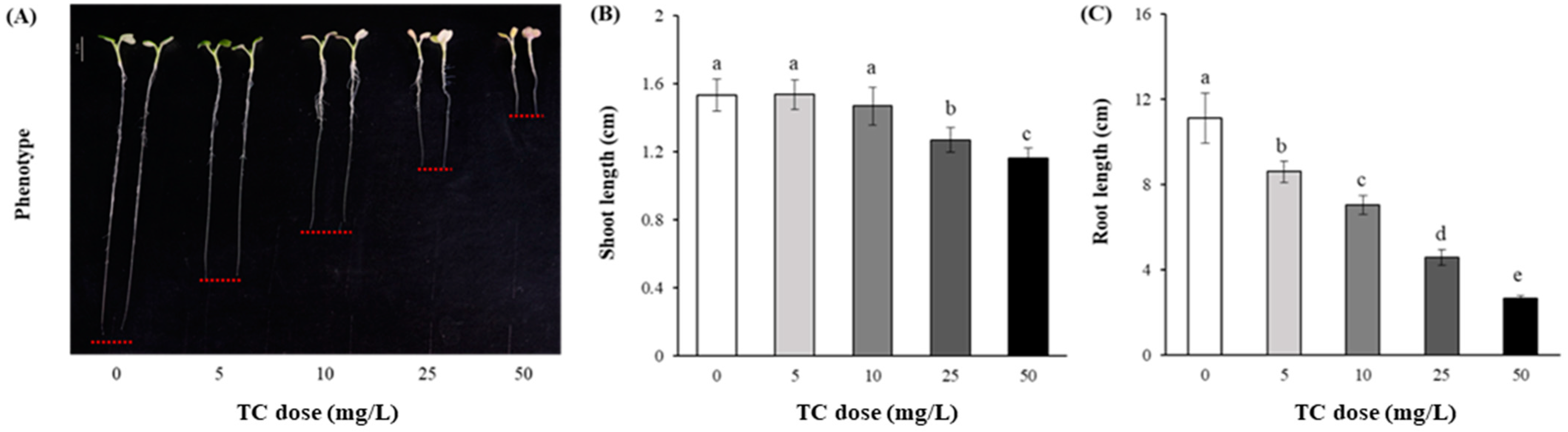
2.1. Germination and Early Seedling Growth
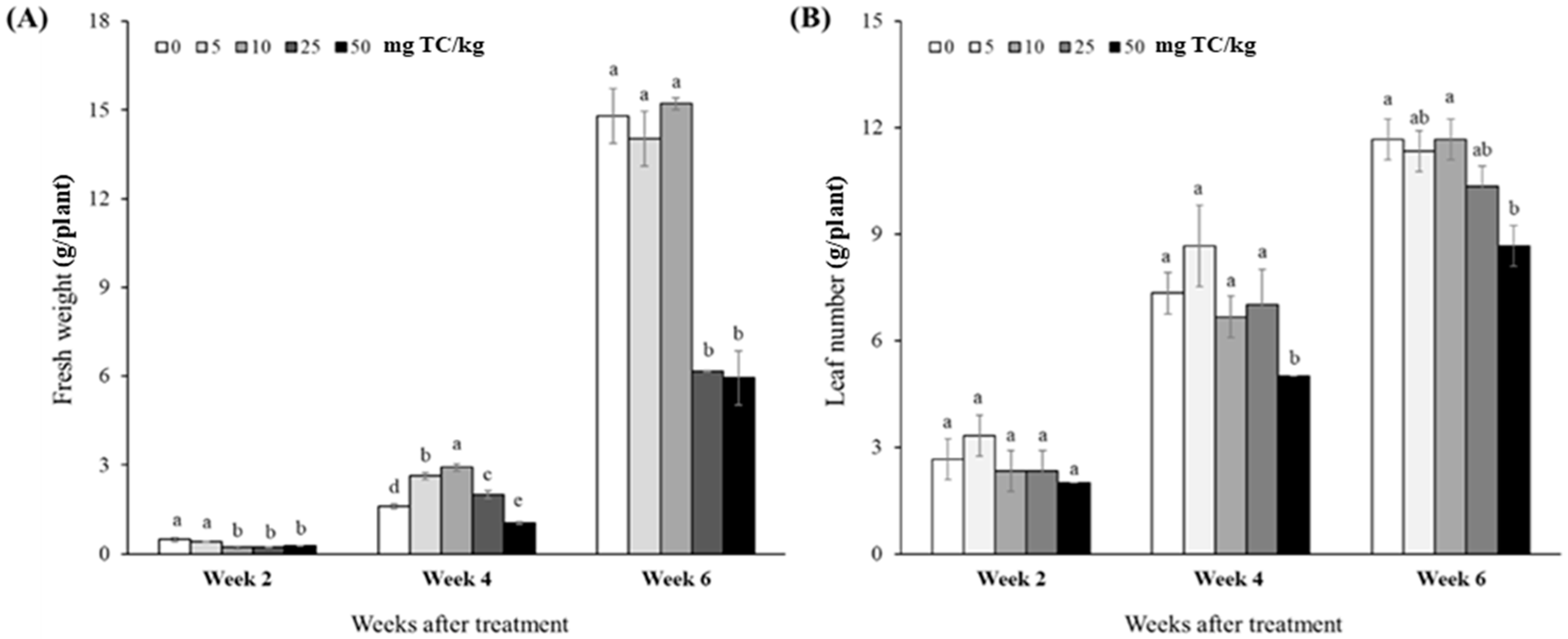
2.2. Growth and Physiological Responses at the Vegetative Stage
2.2.1. Plant Growth and Development
2.2.2. Photosynthetic Performance and Pigmentation
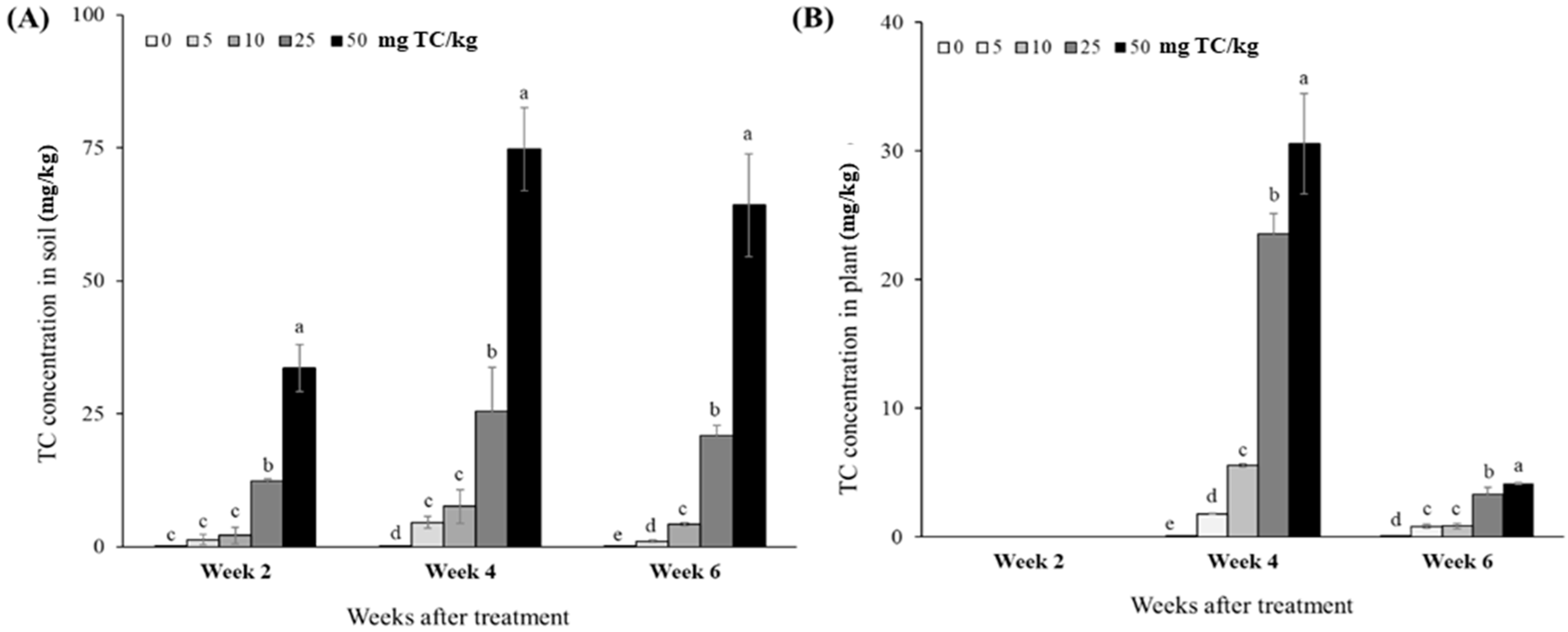
2.2.3. Tetracycline Concentrations in Soil and Plant
2.2.4. Bioconcentration Factor and Accumulation
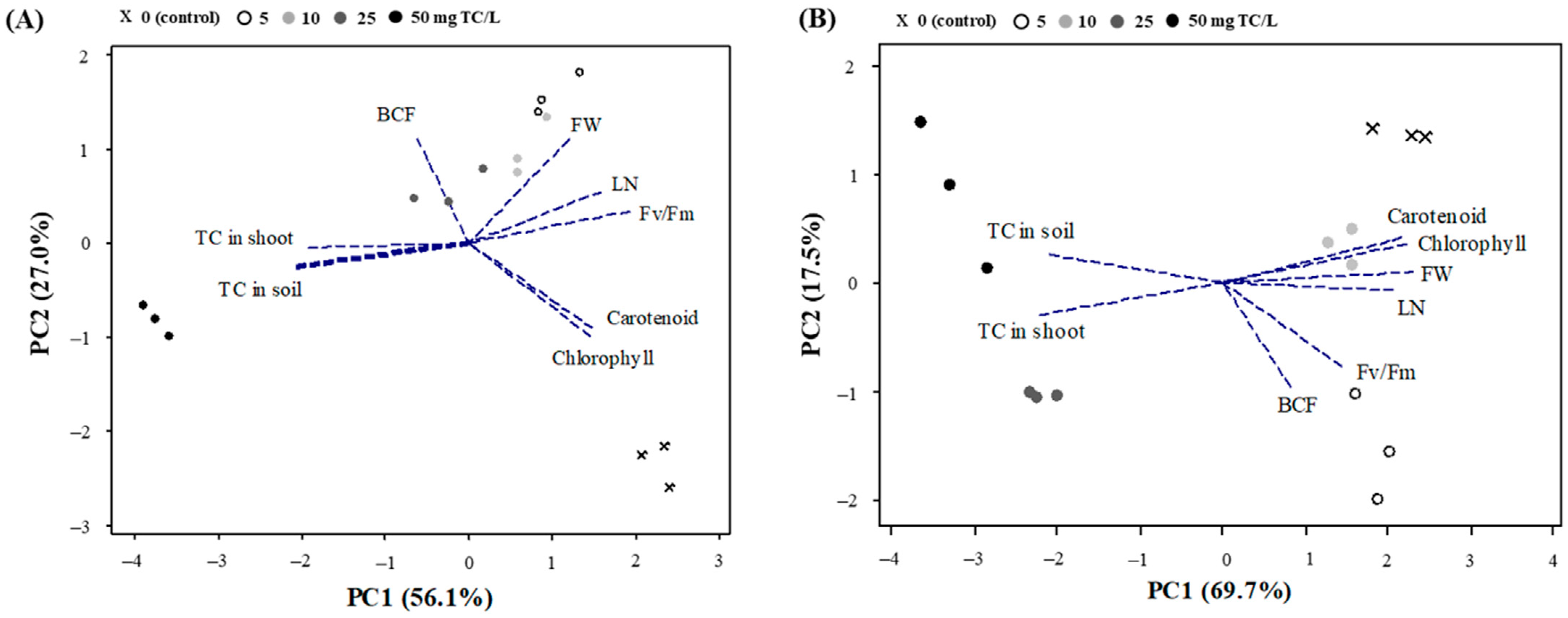
2.2.5. PCA Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Chemical Agents
4.2. Germination Test
4.3. Pot Experiment
4.4. Analytical
4.5. Bioconcentration Factor and Total Accumulation Content
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TC | Tetracycline |
| GP | Germination percentage |
| BCF | Bio-concentration factor |
| VAs | Veterinary antibiotics |
| FW | Fresh weight |
| DW | Dry weight |
| LN | Leaf number |
| Fv/Fm | The maximum photosystem II quantum yield |
| SPE | Solid phase extraction |
| PS | Photosystem |
References
- Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Balan, B.; Dhaulaniya, A.S.; Shree, P.; Sharma, N.; Singh, D.K. Perspectives on the antibiotic contamination, resistance, metabolomics, and systemic remediation. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.T.H.; Yidana, Z.; Smooker, P.M.; Coloe, P.J. Antibiotic use in food animals worldwide, with a focus on Africa: Pluses and minuses. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 20, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WOAH. The 6th Annual Report on Antimicrobial Agents Intended for Use in Animals; WOAH: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Gao, Z.; Yu, Z. The spread of antibiotic resistance to humans and potential protection strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasho, R.P.; Cho, J.Y. Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, H.Q.; Le, T.P.Q.; Da Le, N.; Lu, X.X.; Duong, T.T.; Garnier, J.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Zhang, S.; Oh, N.H.; Oeurng, C.; et al. Antibiotics in surface water of East and Southeast Asian countries: A focused review on contamination status, pollution sources, potential risks, and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamscher, G.; Sczesny, S.; Höper, H.; Nau, H. Determination of persistent tetracycline residues in soil fertilized with liquid manure by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ke, J.; Show, P.L.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, J. Antibiotics: An overview on the environmental occurrence, toxicity, degradation, and removal methods. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7376–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Sun, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, M.; Deng, R.; Bi, L. Plant growth, antibiotic uptake, and prevalence of antibiotic resistance in an endophytic system of pakchoi under antibiotic exposure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Ge, F.; Zhang, L.; Hou, X.; Cao, Y.; Gong, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, R.; Bao, E. Occurrence of 13 veterinary drugs in animal manure-amended soils in Eastern China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparrini, A.J.; Markley, J.L.; Kumar, H.; Wang, B.; Fang, L.; Irum, S.; Symister, C.T.; Wallace, M.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Andleeb, S.; et al. Tetracycline-inactivating enzymes from environmental, human commensal, and pathogenic bacteria cause broad-spectrum tetracycline resistance. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Q.; Eitzer, B.; Wang, Z.; Cai, W.; Newman, L.A.; White, J.C.; Dhankher, O.P.; et al. Effects of titanium oxide nanoparticles on tetracycline accumulation and toxicity in Oryza sativa (L.). Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 827–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagoubi, A.; Mahjoubi, Y.; Giannakis, S.; Rzigui, T.; Djebali, W.; Chouari, R. The silver lining of antibiotic resistance: Bacterial-mediated reduction of tetracycline plant stress via antibiotrophy. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 204, 108093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, L.; Cai, B. Characteristics of tetracycline antibiotic resistance gene enrichment and migration in soil–plant system. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, H.; Kantharaj, V.; Lee, K.-A.; Shin, Y.; Chohra, H.; Yoon, Y.-E.; Kim, Y.-N.; Lee, Y.B. Morpho-physiological, biochemical, and molecular responses of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) seedlings to chlortetracycline stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 219, 105615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minden, V.; Deloy, A.; Volkert, A.M.; Leonhardt, S.D.; Pufal, G. Antibiotics impact plant traits, even at small concentrations. AoB Plants 2017, 9, plx010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Kakarla, D.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M.; Yoon, Y.E.; Lee, Y.B. Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) contamination as a global agro-ecological issue: A critical view. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ying, G.-G.; Tao, R.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, J.-F.; Zhao, L.-F. Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liang, J.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, L.; Xing, W.; Tang, N. Revealing the active period and type of tetracycline stress on Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.) during seed germination and post-germination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11443–11449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lu, L.; Wang, M.; Hussain, B.; Tian, S.; Luo, W.; Zhou, J.; Yang, X. Tetracycline uptake by pak choi grown on contaminated soils and its toxicity in human liver cell line HL-7702. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, F.; Almugbel, R.; Maher, H.M.; Alodaib, F.M.; Alzoman, N.Z. Determination of tetracycline, oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline residues in seafood products of Saudi Arabia using high performance liquid chromatography–Photo diode array detection. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S. Accumulation and risk assessment of antibiotics in edible plants grown in contaminated farmlands: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.A.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, K.M. Endophytic bacterial diversity in Korean kimchi made of Chinese cabbage leaves and their antimicrobial activity against pathogens. Food Control 2015, 56, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Kim, G.H. GC-MS Analysis of the extracts from Korean cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis) and its seed. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2013, 18, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RDA. Vegetable Basic Statistics. 2024. Available online: https://www.nihhs.go.kr/farmer/statistics/statistics.do?t_cd=0202 (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Luo, Y.; Liang, J.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Chen, M.; Jiang, L.; Xing, W.; Tang, N. Responses of seeds of typical Brassica crops to tetracycline stress: Sensitivity difference and source analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Koukoulakis, P.H.; Vasquez, M.I. The risks associated with wastewater reuse and xenobiotics in the agroecological environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3555–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, H. Antibiotic of tetracycline can delay water absorption and germination of Brassica seeds even at low concentrations and it is dependent on seed inherent characteristics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 46885–46897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, L.; Sun, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; Bai, Z.; et al. Seed priming with melatonin promotes seed germination and seedling growth of Triticale hexaploide L. under PEG-6000 induced drought stress. Front. Plant. Sci. 2022, 13, 932912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Guo, W.; Jiang, L.; Pan, F.; et al. Effects of tetracycline on growth, oxidative stress response, and metabolite pattern of ryegrass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasooli, Z.; Barzin, G.; Mahabadi, T.D.; Entezari, M. Stimulating effects of cold plasma seed priming on germination and seedling growth of cumin plant. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 142, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, F.; Zhang, L. Ecotoxicological effects of paracetamol on seed germination and seedling development of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Q.X. Ecological toxicity of reactive X-3 Bred dye and cadmium acting on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Environ. Sci. 2002, 14, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.; Chu, L.M. Phytotoxicity of veterinary antibiotics to seed germination and root elongation of crops. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ryu, D.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Auwerx, J. Antibiotic use and abuse: A threat to mitochondria and chloroplasts with impact on research, health, and environment. BioEssays 2015, 37, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, D.; Guo, J.; Bao, Y. Toxic effect of tetracycline exposure on growth, antioxidative and genetic indices of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupka, M.; Piotrowicz-Cieślak, A.I.; Michalczyk, D.J. Effects of antibiotics on the photosynthetic apparatus of plants. J. Plant Interact. 2022, 17, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.Y.; Ali, B.; Zhang, S.; Stoffella, P.J.; Yuan, S.; Xia, Q.; Qu, H.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Guo, Y. Effects of antibiotics stress on growth variables, ultrastructure, and metabolite pattern of Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margas, M.; Piotrowicz-Cieślak, A.; Orzoł, A.; Adomas, B. Tetracycline accumulation in pea seedlings and its effects on proteome and enzyme activities. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2016, 18, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baciak, M.; Sikorski, Ł.; Piotrowicz-Cieślak, A.I.; Adomas, B. Content of biogenic amines in Lemna minor (common duckweed) growing in medium contaminated with tetracycline. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 180, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydzyński, D.; Piotrowicz-Cieślak, A.I.; Grajek, H.; Michalczyk, D.J. Instability of chlorophyll in yellow lupin seedlings grown in soil contaminated with ciprofloxacin and tetracycline. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydzyński, D.; Piotrowicz-Cieślak, A.I.; Grajek, H.; Wasilewski, J. Investigation of chlorophyll degradation by tetracycline. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, G.; Gismondi, A.; Canuti, L.; Scimeca, M.; Volpe, A.; Canini, A. Tetracycline accumulates in Iberis sempervirens L. through apoplastic transport inducing oxidative stress and growth inhibition. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Cozzolino, S.; Fiori, M. Phytotoxicity to and uptake of enrofloxacin in crop plants. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Song, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, H.; Bi, W.; Ni, Y. Reducing residues of tetracycline and its resistance genes in soil-maize system and improving plant growth: Selecting the best remediation substance. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczerzak, M.; Kudłak, B.; Namieśnik, J. Impact of selected drugs and their binary mixtures on the germination of Sorghum bicolor (sorgo) seeds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18717–18727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, Y. Occurrence and source analysis of typical veterinary antibiotics in manure, soil, vegetables and groundwater from organic vegetable bases, Northern China. Environl. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2992–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J. Environmental fate of tetracycline antibiotics: Degradation pathway mechanisms, challenges, and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorquodale-Bauer, K.; Grosshans, R.; Zvomuya, F.; Cicek, N. Critical review of phytoremediation for the removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Wu, Y.; Zou, B.; Lou, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, J.; Lu, L.; Dai, G. Simultaneous removal and degradation characteristics of sulfonamide, tetracycline, and quinolone antibiotics by laccase-mediated oxidation coupled with soil adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 307, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.; Varela Della Giustina, S.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Schoevaart, R.; Barceló, D.; de Cazes, M.; Belleville, M.P.; Sanchez-Marcano, J.; de Gunzburg, J.; Couillerot, O.; et al. Removal of antibiotics in wastewater by enzymatic treatment with fungal laccase—Degradation of compounds does not always eliminate toxicity. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Delgado, C.; Eymar, E.; Camacho-Arévalo, R.; Petruccioli, M.; Crognale, S.; D’Annibale, A. Degradation of tetracyclines and sulfonamides by stevensite- and biochar-immobilized laccase systems and impact on residual antibiotic activity. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 3394–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.T.; Lu, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Luo, F.; Yang, H. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) laccases involved in modification and detoxification of herbicides atrazine and isoproturon residues in plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6397–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-D.; Li, Q.-J.; Luo, B.; Chen, X.-Y. Ex planta phytoremediation of trichlorophenol and phenolic allelochemicals via an engineered secretory laccase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shohag, M.J.I.; Qiu, W.; Lu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Health risk assessment of tetracyclines contamination in soil-cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis) system. Agronomy 2025, 15, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Mrozik, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Antibiotics in the soil environment—Degradation and their impact on microbial activity and diversity. Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-N.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoon, Y.-E.; Choe, H.; Lee, K.-A.; Kantharaj, V.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, Y.B. Biostimulatory effects of Chlorella fusca CHK0059 on plant growth and fruit quality of strawberry. Plants 2023, 12, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.S.; Aga, D.S. Enhancing extraction and detection of veterinary antibiotics in solid and liquid fractions of manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time | Tetracycline Dose (mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 25 | 50 | |
| Day 1 | 91.7 ± 0 a | 88.9 ± 4.8 a | 88.9 ± 4.8 a | 75.0 ± 0 b | 69.4 ± 4.8 b |
| Day 2 | 100 ± 0 a | 94.4 ± 4.8 a | 91.7 ± 0 a | 94.4 ± 4.8 a | 97.2 ± 4.8 a |
| Day 3 | 100 ± 0 a | 100 ± 0 a | 100 ± 0 a | 100 ± 0 a | 100 ± 0 a |
| Treatment (mg TC/L) | The Maximum PSII Quantum Yield | Pigment Content | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fv/Fm | SPAD | Chlorophylls (mg/g) | Carotenoids (mg/g) | |||||
| Week 2 | Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 2 † | Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 4 | Week 6 | |
| 0 | 619.5 ± 14.5 a | 794.0 ± 6.0 a | 577.0 ± 4.0 ab | 20.7 ± 1.7 a | 355.5 ± 10.5 a | 356.3 ± 0.6 a | 49.8 ± 3.2 a | 56.3 ± 3.4 a |
| 5 | 641.5 ± 0.5 a | 790.5 ± 7.5 a | 610.5 ± 1.5 a | 20.6 ± 0.6 a | 209.0 ± 0.1 d | 318.7 ± 0.3 c | 27.4 ± 1.9 c | 49.0 ± 0.1 b |
| 10 | 635.0 ± 8.0 a | 743.0 ± 42.0 a | 583.0 ± 0.0 ab | 20.5 ± 0.3 a | 248.0 ± 0.9 c | 322.7 ± 0.2 b | 35.4 ± 1.0 b | 48.6 ± 0.4 b |
| 25 | 628.5 ± 15.5 a | 794.5 ± 12.5 a | 583.0 ± 0.0 ab | 21.1 ± 1.0 a | 261.2 ± 0.6 b | 211.3 ± 0.5 e | 36.3 ± 0.6 b | 35.9 ± 0.2 d |
| 50 | 644.5 ± 4.5 a | 501.0 ± 23.0 b | 536.0 ± 47.0 b | 19.2 ± 0.3 a | 197.5 ± 0.4 e | 236.5 ± 0.2 d | 25.3 ± 0.4 c | 38.8 ± 0.1 c |
| Treatment (mg TC/L) | BCF | Accumulation Amount (g/plant) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 4 | Week 6 | |
| 0 | 0.091 ± 0.030 c | 0.213 ± 0.110 b | 0.003 ± <0.001 d | 0.003 ± 0.001 d |
| 5 | 0.458 ± 0.011 b | 0.636 ± 0.037 a | 1.638 ± 0.344 cd | 0.834 ± 0.155 c |
| 10 | 0.610 ± 0.093 ab | 0.205 ± 0.091 b | 5.623 ± 0.119 c | 0.862 ± 0.225 c |
| 25 | 0.780 ± 0.023 a | 0.159 ± 0.018 b | 23.980 ± 1.677 b | 3.307 ± 0.578 b |
| 50 | 0.424 ± 0.136 b | 0.066 ± 0.021 b | 31.485 ± 3.735 a | 4.179 ± 0.062 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chohra, H.; Lee, K.-A.; Choe, H.; Cho, J.Y.; Kantharaj, V.; Cheong, M.S.; Kim, Y.-N.; Lee, Y.B. Dose-Dependent Physiological Response to Transient Bioaccumulation of Tetracycline in Kimchi Cabbage (Brassica campestris L.). Antibiotics 2025, 14, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050501
Chohra H, Lee K-A, Choe H, Cho JY, Kantharaj V, Cheong MS, Kim Y-N, Lee YB. Dose-Dependent Physiological Response to Transient Bioaccumulation of Tetracycline in Kimchi Cabbage (Brassica campestris L.). Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050501
Chicago/Turabian StyleChohra, Hadjer, Keum-Ah Lee, Hyeonji Choe, Ju Young Cho, Vimalraj Kantharaj, Mi Sun Cheong, Young-Nam Kim, and Yong Bok Lee. 2025. "Dose-Dependent Physiological Response to Transient Bioaccumulation of Tetracycline in Kimchi Cabbage (Brassica campestris L.)" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050501
APA StyleChohra, H., Lee, K.-A., Choe, H., Cho, J. Y., Kantharaj, V., Cheong, M. S., Kim, Y.-N., & Lee, Y. B. (2025). Dose-Dependent Physiological Response to Transient Bioaccumulation of Tetracycline in Kimchi Cabbage (Brassica campestris L.). Antibiotics, 14(5), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050501







