Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Diversity and Safety Assessment of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from European Hakes (Merluccius merluccius, L.) Caught in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Activity and Taxonomic Identification of Bacteria Isolated from European Hakes
2.2. Genetic Diversity Analysis by ERIC-PCR
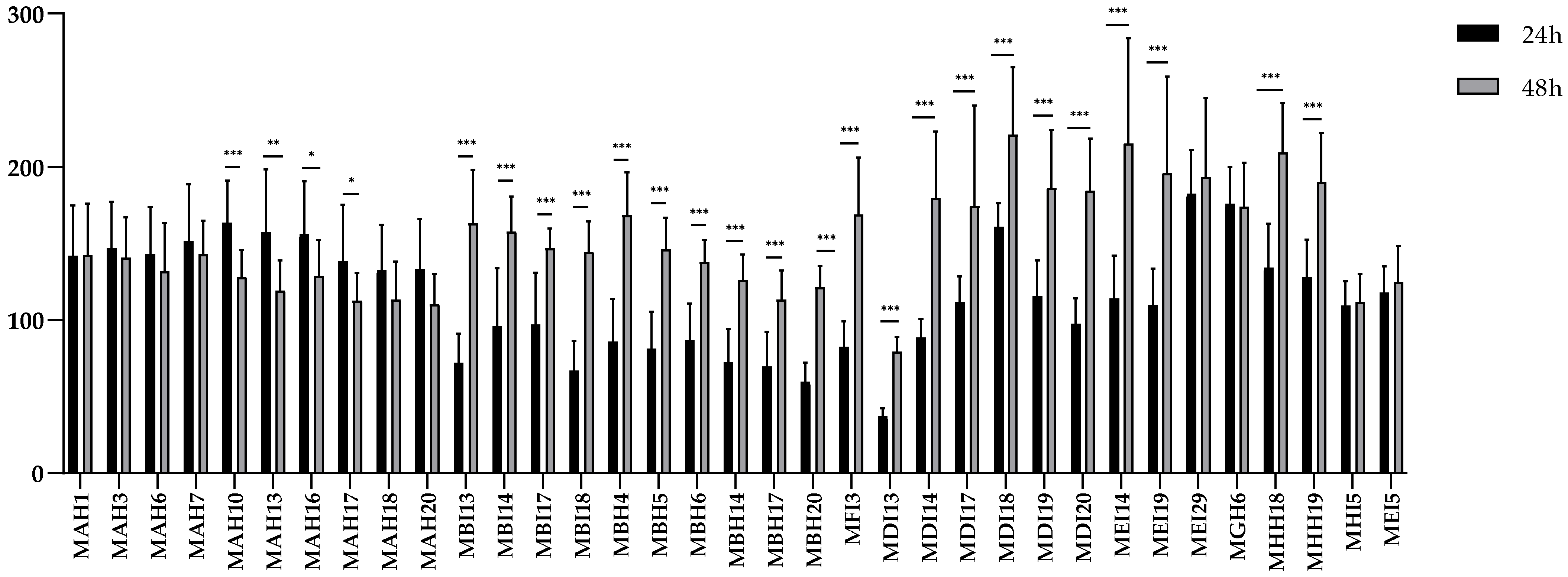
2.3. Biofilm Formation
2.4. LAB Susceptibility to Antibiotics
2.5. Haemolytic and Gelatinase Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area, Sample Collection and Bacterial Isolation
4.2. Screening of Bacteria with Antimicrobial Activity Against Ichthyopathogens
4.3. Taxonomic Identification of Bacterial Isolates
4.4. Genetic Diversity Analysis by Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus-PCR (ERIC-PCR)
4.5. Biofilm Formation and Quantification
4.6. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
4.7. Evaluation of Haemolytic and Gelatinase Activities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of WORLD Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.C.; Smith, R.G.; Schipanski, M.E.; Atwood, L.W.; Mortensen, D.A. Agriculture in 2050: Recalibrating targets for sustainable intensification. BioScience 2017, 67, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cc0461es (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Álvarez-Pellitero, P. Fish immunity and parasite infections: From innate immunity to immunity to immunoprophylactic prospects. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 126, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Cunha, A.; Gomes, N.C.; Alves, E.; Costa, L.; Faustino, M.A. Phage therapy and photodynamic therapy: Low environmental impact approaches to inactivate microorganisms in fish farming plants. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 268–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gui, J.F. Virus genomes and virus-host interactions in aquaculture animals. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibenge, F.S. Emerging viruses in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abowei, F.N.; Briyai, O.F.; Bassey, S.E. A review of some basic parasite diseases in culture fisheries: Flagellids, dinoflagellides and ichthyophthriasis, ichtyobodiasis, coccidiosis trichodiniasis, heminthiasis, hirudinea infestation, crustacean parsite and ciliates. Br. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 2, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Bateman, I.J.; Hinchliffe, S.J.; Bass, D.; Hartnell, R.; Santos, E.M.; Devlin, M.J.; Feist, S.W.; Taylor, N.G.H.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; et al. Sustainable aquaculture through the One Health lens. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, A.; Leiro, J.M.; Pereiro, P.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B.; Dirks, R.P.H.; Lamas, J. Interactions between the parasite Philasterides dicentrarchi and the immune system of the turbot Scophthalmus maximus. A transcriptomic analysis. Biology 2020, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.; Schrama, D.; Farinha, A.P.; Cerqueira, M.; Raposo de Magalhães, C.; Carrilho, R.; Rodrigues, P. Fish pathology research and diagnosis in aquaculture of farmed fish; a proteomics perspective. Animals 2021, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024. Blue Transformation in Action. 2024. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/06690fd0-d133-424c-9673-1849e414543d (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Chen, J.; Sun, R.; Pan, C.; Sun, Y.; Mai, B.; Li, Q.X. Antibiotics and Food Safety in Aquaculture. J Agric Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11908–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Gómez-Sala, B.; Araújo, C.; Campanero, C.; del Campo, R.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Antimicrobial activity, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence factors of Lactic Acid Bacteria of aquatic origin intended for use as probiotics in aquaculture. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Ramírez, M.; Poeta, P.; Igrejas, G.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Safety assessment, genetic relatedness and bacteriocin activity of potential probiotic Lactococcus lactis strains from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and rearing environment. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Resistencia a Los Antimicrobianos. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Alagawany, M.; Patra, A.K.; Kar, I.; Tiwari, R.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Dhama, K.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. The functionality of probiotics in aquaculture: An overview. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Current prospects and challenges in fish vaccine development in India with special reference to Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Middha, S.K.; Menon, S.V.; Paital, B.; Gokarn, S.; Nelli, M.; Rajanikanth, R.B.; Chandra, H.M.; Mugunthan, S.P.; Kantwa, S.M.; et al. Current challenges of vaccination in fish health management. Animals 2024, 14, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toranzo, A.; Magariños, B.; Romalde, J.L.; Barja, J.L. Present and future of aquaculture vaccines against fish bacterias diseases. Options Méditerranéennes 2009, 86, 155–176. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, A. Progress, challenges and opportunities in fish vaccine development. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.; Lorenzen, N.; Collet, B. DNA vaccination for finfish aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 85, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; de Blas, I.; Balcázar, J.L. Probiotics in aquaculture: A current assessment. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 6, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sala, B.; Feito, J.; Hernández, P.E.; Cintas, L.M. Lactic Acid Bacteria in aquatic Environments and Their Applications, 5th ed.; Vinderola, G., Ouwehand, A.C., Salminen, S., von Wright, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 555–570. [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher, C.; Høj, L.; Bourne, D.G. Probiotics for coral aquaculture: Challenges and considerations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 73, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Statement on the requirements for whole genome sequence analysis of microorganisms intentionally used in the food chain. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU). 2020/151 of 4 February 2020 concerning the authorisation of Pediococcus acidilactici CNCM I-4622 as a feed additive for all porcine species for fattening and for breeding other than sows, all avian species, all fish species and all crustaceans and repealing Regulations (EC) No 911/2009, (EU) No 1120/2010 and (EU) No 212/2011 and Implementing Regulations (EU) No 95/2013, (EU) No 413/2013 and (EU) 2017/2299 (holder of authorisation Danstar Ferment AG represented in the Union by Lallemand SAS). Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, 33, 12–15. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2020/151/oj (accessed on 8 November 2024).
- Todorov, S.D.; Lima, J.M.S.; Bucheli, J.E.V.; Popov, I.V.; Tiwari, S.K.; Chikindas, M.L. Probiotics for Aquaculture: Hope, Truth, and Reality. Probiot. Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 2007–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillor, O.; Etzion, A.; Riley, M.A. The dual role of bacteriocins as anti- and probiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 81, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringø, E.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ghosh, K.; Doan, H.V.; Beck, B.R.; Song, S.K. Lactic acid bacteria in finfish-an update. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Van Doan, H.; Lee, S.H.; Soltani, M.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Harikrishnan, R.; Song, S.K. Probiotics, lactic acid bacteria and bacilli: Interesting supplementation for aquaculture. J. App. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorriehzahra, M.J.; Delshad, S.T.; Adel, M.; Tiwari, R.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K.; Lazado, C.C. Probiotics as beneficial microbes in aquaculture: An update on their multiple modes of action: A review. Vet Q. 2016, 36, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vine, N.G.; Leukes, W.D.; Kaiser, H. Probiotics in marine larviculture. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 404–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Løvmo, L.; Kristiansen, M.; Bakken, Y.; Salinas, I.; Myklebust, R.; Olsen, R.E.; Mayhew, T.M. Lactic acid bacteria vs. pathogens in the gastrointestinal tract of fish: A review. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.; Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Bacteriocin production: A probiotic trait? Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ołdak, A.; Zielińska, D. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria as an alternative to antibiotics. Postep. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2017, 71, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-González, J.C.; Martínez-Tapia, G.A.; Lazcano-Hernández, B.E.; García-Pérez Castrejón-Jiménez, N.S. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria. A powerful alternative as antimicrobials, probiotics, and immunomodulators in veterinary medicine. Animals 2021, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniacke-Lowe, S.; Collins, F.W.J.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Bioactivity screening and genomic analysis reveals deep-sea fish microbiome isolates as sources of novel antimicrobials. Mar. Drugs. 2023, 21, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación (MAPA). Estadísticas Pesqueras: Pesca Marítima. 2022. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/estadistica/temas/estadisticas-pesqueras/pesca-maritima/ (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Ringø, E.; Jutfelt, F.; Kanapathippillai, P.; Bakken, Y.; Sundell, K.; Glette, J.; Mayhew, T.M.; Myklebust, R.; Olsen, R.E. Damaging effect of the fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida ssp. salmonicida on intestinal enterocytes of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar, L.). Cell. Tissue. Res. 2004, 318, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabrok, M.; Algammal, A.M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Hetta, H.F.; Atwah, B.; Alghamdi, S.; Fawzy, A.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Rodkhum, C. Tenacibaculosis caused by Tenacibaculum maritimum: Updated knowledge of this marine bacterial fish pathogen. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1068000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nho, S.W.; Hikima, J.; Cha, I.S.; Park, S.B.; Jang, H.B.; del Castillo, C.S.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T.; Jung, T.S. Complete genome sequence and immunoproteomic analyses of the bacterial fish pathogen Streptococcus parauberis. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3356–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEEDAP. Guidance on the characterization of microorganisms used as feed additives or as production organisms. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05206. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). M45 Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria, 3rd ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). M100 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gónzalez, C.; Encinas, J.P.; García-López, L.M.; Otero, A. Characterisation and identification of lactic acid bacteria from freshwater fishes. Food Microbiol. 2020, 17, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Holzapfel, W. Identification and characterization of carnobacteria associated with the gills of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 23, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elidrissi, A.; Ezzaky, Y.; Boussif, K.; Achemchem, F. Isolation and characterization of bioprotective lactic acid bacteria from Moroccan fish and seafood. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheriet, S.; Lengliz, S.; Romdhani, A.; Hynds, P.; Abbassi, M.S.; Ghrairi, T. Selection and characterization of bacteriocinogenic Lactic Acid Bacteria from the intestine of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and whiting fish (Merlangius merlangus): Promising strains for aquaculture probiotic and food bio-preservation. Life 2023, 13, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppola, M.; Olsen, R.E.; Sandeker, E.; Kanapathippillai, P.; Holzapfel, W.; Ringø, E. Random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) typing of carnobacteria isolated from hindgur chamber and large intestine of atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 28, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Fernandes, L.; Pinto, C.; Albano, H.; Castillo, F.; Teixeira, P.; Gibbs, A. Characterization of anti-Listeria bacteriocins isolated from shellfish: Potencial antimicrobials to control non-fermented seafood. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2009, 129, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauzon, H.L.; Ringo, E. Prevalence and application of lactic acid bacteria in aquatic environments. In Lactic Acid Bacteria: Microbiological and Functional Aspects, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Sala, B.; Herranz, C.; Díaz-Freitas, B.; Hernández, P.E.; Sala, A.; Cintas, L.M. Strategies to increase the hygienic and economic value of fresh fish: Biopreservation using lactic acid bacteria of marine origin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 223, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, T.K.; Jena, P.K.; Nagar, N.; Patel, A.K.; Seshadri, S. In vitro evaluation of probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria from the gut of Labeo rohita and Catla catla. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2015, 7, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Patel, B.; Amaresan, N.; Joshi, B.; Shah, R.; Krishnamurthy, R. Isolation and characterization of Lactococcus garvieae from the fish gut for in vitro fermentation with carbohydrates from agro-industrial waste. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 28, e00555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Nahuelquín, Y.; Poeta, P.; Igrejas, G.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Inhibition of fish pathogens by the microbiota from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and rearing environment. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phupaboon, S.; Hashim, F.J.; Phumkhachorn, P.; Rattanachaikunsopon, P. Molecular and biotechnological characteristics of proteolytic activity from Streptococcus thermophiles as a proteolytic lactic acid bacteria to enhance protein-derived bioactive peptides. AIMS Microbiol. 2023, 9, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as means of diseases control in aquaculture, a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Li, X.; Doan, H.; Ghosh, K. Interesting probiotic bacteria other than the more widely used lactic acid bacteria and bacilliin finfish. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 848037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, R.; Docando, F.; Nu.ez-Ortiz, N.; Tafalla, C.; Díaz-Rosales, P. Mechanisms used by probiotics to confer pathogen resistance to teleost fish. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 653025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumon, M.A.A.; Molla, M.H.R.; Hakeem, I.J.; Ahammad, F.; Amran, R.H.; Jamal, M.T.; Gabr, M.H.; Islam, M.S.; Alam, M.T.; Brown, C.L.; et al. Epigenetics and probiotics application toward the modulation of fish reproductive performance. Fishes 2022, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintas, L.M.; Casaus, M.P.; Herranz, C.; Nes, I.F.; Hernández, P.E. Review: Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2001, 7, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Bacteriocins—A viable alternative to antibiotics? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Shi, L.; Cai, R.; Li, C.; Yan, H. Association between agr type, virulence factors, biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from pork production. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-López, P.; Filipello, V.; Di Ciccio, P.A.; Pitozzi, A.; Ghidini, S.; Scali, F.; Ianieri, A.; Zanardi, E.; Losio, M.N.; Simon, A.C.; et al. Assessment of the antibiotic resistance profile, genetic heterogeneity and biofilm production of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from the Italian swine production chain. Foods 2020, 9, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.A.; Roh, Y.J.; Son, H.R.; Choi, H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, C.H. Assessment of the biofilm-forming ability on solid surfaces of periprosthetic infection-associated pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contente, D.; Díaz-Formoso, L.; Feito, J.; Gómez-Sala, B.; Costas, D.; Hernández, P.E.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Borrero, J.; Poeta, P.; Cintas, L.M. Antimicrobial activity, genetic relatedness, and safety assessment of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria isolated from a rearing tank of rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) used as live feed in fish larviculture. Animals 2024, 14, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, Z.; Khanzadi, S.; Salari, A. Biofilm formation and antagonistic activity of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus (PTCC1712) and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (PTCC1745). AMB Express 2021, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzabekyan, S.; Harutyunyan, N.; Manvelyan, A.; Malkhasyan, L.; Balayan, M.; Miralimova, S.; Chikindas, M.L.; Chistyakov, V.; Pepoyan, A. Fish probiotics: Cell surface properties of fish intestinal lactobacilli and Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A review on formation, infection, antibiotic resistance, control measures, and innovative treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamignon, C.; Guéneau, V.; Medina, S.; Deschamps, J.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Briandet, R.; Mousset, P.-Y.; Langella, P.; Lafay, S.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Evaluation of the probiotic properties and the capacity to form biofilms of various Lactobacillus strains. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, M.; Abd El-Rahman, O.A.; Al-Qaidi, B.; Ashour, H.M. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of probiotic Lactobacilli on antibiotic-resistant Proteus mirabilis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feito, J.; Araújo, C.; Arbulu, S.; Contente, D.; Gómez-Sala, B.; Díaz-Formoso, L.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Borrero, J.; Cintas, L.M.; Hernández, P.E. Design of Lactococcus lactis strains producing garvicin A and/or garvicin Q, either alone or together with nisin A or nisin Z and high antimicrobial activity against Lactococcus garvieae. Foods 2023, 12, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.A.; Facklam, R.R. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Lactococcus lactis and Lactococcus garvieae and a proposed method to discriminate between them. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, C.; Rossano, A.; Thomann, A.; Perreten, V. Antibiotic resistance in Lactococcus species from bovine milk: Presence of a mutated multidrug transporter mdt(A) gene in susceptible Lactococcus garvieae strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 131, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumed-Ferrer, C.; Barberio, A.; Franklin-Guild, R.; Werner, B.; McDonough, P.; Bennett, J.; Gioia, G.; Rota, N.; Welcome, F.; Nydam, D.V.; et al. Antimicrobial susceptibilities and random amplified polymorphic DNA-PCR fingerprint characterization of Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis and Lactococcus garvieae isolated from bovine intramammary infections. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6216–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortina, M.G.; Ricci, G.; Foschino, R.; Picozzi, C.; Dolci, P.; Zeppa, G.; Cocolin, L.; Manachini, P.L. Phenotypic typing, technological properties and safety aspects of Lactococcus garvieae strains from dairy environments. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissy, M.; Moumeni, M. Detection of antibiotic resistance genes in some Lactococcus garvieae strains isolated from infected rainbow trout. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2016, 15, 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, R.P.; Aragão, B.B.; de Melo, R.P.B.; da Silva, D.M.S.; de Carvalho, R.G.; Juliano, M.A.; Farias, M.P.O.; de Lira, N.S.C.; Mota, R.A. Bovine mastitis in northeastern Brazil: Occurrence of emergent bacteria and their phenotypic and genotypic profile of antimicrobial resistance. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 85, 101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Corral, Y.; Santos, Y. Predicting antimicrobial resistance of Lactococcus garvieae: PCR detection of resistance genes versus MALDI-TOF protein profiling. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, N.; Mallik, S.K. Emerging bacterial fish pathogen Lactococcus garvieae RTCLI04, isolated from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Genomic features and comparative genomics. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Han, J.; Barkema, H.W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Kastelic, J.P.; Han, B.; Qin, S.; Deng, Z. Comparative genomic analyses of Lactococcus garvieae isolated from bovine mastitis in China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0299522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffanel, F.; Charron-Bourgoin, F.; Libante, V.; Leblond-Bourget, N.; Payot, S. Resistance genes and genetic elements associated with antibiotic resistance in clinical and commensal isolates of Streptococcus salivarius. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4155–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, T.H.; Harth-Chú, E.N.; Scott, J.; Stipp, R.N.; Boisvert, H.; Salomão, M.F.; Theobaldo, J.D.; Possobon, R.F.; Nascimento, L.C.; McCafferty, J.W.; et al. Oral cavities of healthy infants harbour high proportions of Streptococcus salivarius strains with phenotypic and genotypic resistance to multiple classes of antibiotics. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doumith, M.; Mushtaq, S.; Martin, V.; Chaudhry, A.; Adkin, R.; Coelho, J.; Chalker, V.; MacGowan, A.; Woodford, N.; Livermore, D.M.; et al. Genomic sequences of Streptococcus agalactiae with high-level gentamicin resistance, collected in the BSAC bacteraemia surveillance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2704–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, R.R. Antimicrobial resistance among beta-hemolytic Streptococcus in Brazil: An Overview. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Lin, M.; Bao, J.; Wang, G.; Dong, R.; Zou, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, T.; et al. Maternal colonization with group B Streptococcus and antibiotic resistance in China: Systematic review and meta-analyses. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creti, R.; Imperi, M.; Khan, U.B.; Berardi, A.; Recchia, S.; Alfarone, G.; Gherardi, G. Emergence of high-level gentamicin resistance in Streptococcus agalactiae hypervirulent serotype IV ST1010 (CC452) strains by acquisition of a novel integrative and conjugative element. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Barroco, C.; Rivas-García, L.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V. Tackling multidrug resistance in streptococci—From novel biotherapeutic strategies to nanomedicines. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 579916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Lv, X.; Duan, D.; Wang, L.; Huang, J. Characterization of a linezolid- and vancomycin-resistant Streptococcus suis isolate that harbors optrA and vanG operons. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergova, R.; Boyanov, V.; Muhtarova, A.; Alexandrova, A. A review of the impact of streptococcal infections and antimicrobial resistance on human health. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, O.M.; Fayez, M.; Alswat, A.S.; Alkafafy, M.; Mahmoud, S.F.; Al-Marri, T.; Almuslem, A.; Ashfaq, H.; Yusuf, S. Antimicrobial resistance, biofilm formation, and virulence genes in Enterococcus species from small backyard chicken flocks. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, A.; Kawada-Matsuo, M.; Nguyen-Tra Le, M.; Masuda, K.; Tadera, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Nishihama, S.; Hisatsune, J.; Sugawara, Y.; Kashiyama, S.; et al. Antibiotic susceptibility and genome analysis of Enterococcus species isolated from inpatients in one hospital with no apparent outbreak of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus in Japan. Microbiol. Immunol. 2024, 68, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Paganelli, F.L.; Bierschenk, D.; Kuipers, A.; Bonten, M.J.; Willems, R.J.; van Schaik, W. Genome-wide identification of ampicillin resistance determinants in Enterococcus faecium. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Solache, M.; Rice, L.B. The Enterococcus: A model of adaptability to its environment. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00058-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagetti, P.; Bonofiglio, L.; García Gabarrot, G.; Kaufman, S.; Mollerach, M.; Vigliarolo, L.; von Specht, M.; Toresani, I.; Lopardo, H.A. Resistance to β-lactams in enterococci. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Meng, W.; Li, Q.; Fu, K.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; et al. Distribution and association of antimicrobial resistance and virulence characteristics in Enterococcus spp. isolates from captive Asian elephants in China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1277221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, N.; Momtaz, H.; Tajbakhsh, E. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Enterococcus faecalis isolated from seafood samples. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez, A.B.; Campedelli, I.; Delgado, S.; Alegría, Á.; Salvetti, E.; Felis, G.E.; Mayo, B.; Torriani, S. Antibiotic susceptibility profiles of dairy leuconostoc, analysis of the genetic basis of atypical resistances and transfer of genes in vitro and in a food matrix. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvetti, E.; Campedelli, I.; Larini, I.; Conedera, G.; Torriani, S. Exploring Antibiotic resistance diversity in Leuconostoc spp. by a genome-based approach: Focus on the lsaA gene. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, S.; Spampinato, G.; Candeliere, F.; Amaretti, A.; Brun, P.; Castagliuolo, I.; Rossi, M. Phenotypic traits and immunomodulatory properties of Leuconostoc carnosum isolated from meat products. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, S.; Blanquart, F.; Lipsitch, M.; Fraser, C. On the evolutionary ecology of multidrug resistance in bacteria. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardeu, M.; Vernoux, J.P.; Henri-Dubernet, S.; Gueguen, M. Safety assement of dairy organisms: The Lactobacillus genus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimee, G.; Halami, P.M. Emerging resistance to aminoglycosides in lactic acid bacteria of food origin-an impending menace. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuben, R.C.; Roy, P.C.; Sarkar, S.L.; Alam, R.U.; Jahid, I.K. Isolation, characterization, and assessment of lactic acid bacteria toward their selection as poultry probiotics. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, R.C.; Roy, P.C.; Sarkar, S.L.; Rubayet Ul Alam, A.S.M.; Jahid, I.K. Characterization and evaluation of lactic acid bacteria from indigenous raw milk for potential probiotic properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Nyaruaba, R.; Ita, R.E.; Okon, S.U.; Addey, C.I.; Ebido, C.C.; Opabunmi, A.O.; Okeke, E.S.; Chukwudozie, K.I. Antibiotic resistance in the aquatic environment: Analytical techniques and interactive impact of emerging contaminants. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 96, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, F.; Imtiaz, M.; Haq, I.U. Emergent crisis of antibiotic resistance: A silent pandemic threat to 21st century. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 174, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar, J.L.; de Blas, I.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Vendrell, D.; Gironés, O.; Muzquiz, J.L. Enhancement of the immune response and protection induced by probiotic lactic acid bacteria against furunculosis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, K.T.; Skov, M.N.; Gill, S.; Kemp, M. Virulence factors associated with Enterococcus faecalis infective endocarditis: A mini review. Open Microbiol. J. 2017, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, C.M.; Antiporta, M.H.; Murray, B.E.; Dunny, G.M. Role of the Enterococcus faecalis GelE protease in determination of cellular chain length, supernatant pheromone levels, and degradation of fibrin and misfolded surface proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3613–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unión Europea. Denominaciones Comerciales. Mapa de las Zonas Pesqueras UE. Names of Sub-Areas and Divisions of FAO Fishing Areas 27 and 37. Available online: https://fish-commercial-names.ec.europa.eu/fish-names/fishing-areas_es (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Cintas, L.M.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fernández, M.F.; Sletten, K.; Nes, I.F.; Herández, P.E.; Holo, H. Isolation and characterization of pediocin L50, a new bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici with a broad inhibitory spectrum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2643–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffrès, E.; Sohier, D.; Leroi, F.; Pilet, M.F.; Prévost, H.; Joffraud, J.J.; Dousset, X. Study of the bacterial ecosystem in tropical cooked and peeled shrimps using a polyphasic approach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 131, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniciuc, E.-A.; Cerca, N.; Nicolau, A.I. Compositional Analysis of biofilms formed by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from food sources. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, E.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Comparison of multiple methods for quantification of microbial biofilms grown in microtiter plates. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 72, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA FEEDAP Panel (EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed); Rychen, G.; Aquilina, G.; Azimonti, G.; Bampidis, V.; Bastos, M.L.; Bories, G.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Flachowsky, G.; et al. El Plan de Acción de la FAO Sobre la Resistencia a los Antimicrobianos 2016–2020. 2016. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i5996s/i5996s.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Schar, D.; Klein, E.Y.; Laxminarayan, R.; Gilbert, M.; van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Rheman, S.; Debnath, N.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Akhtar, Z.; Ghosh, S.; Parveen, S.; Islam, K.; Islam, M.A.; Rashid, M.M.; et al. Antibiotics usage practices in aquaculture in Bangladesh and their associate factors. One Health 2022, 15, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; le Groumellec, M.; Li, A.; Surachetpong, W.; Karunasagar, I.; et al. Reviews of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1421–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Expected Phenotypes Version 1.0. 2022. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/expert_rules_and_expected_phenotypes/expected_phenotypes (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of Mics and Zone Diameters; Version 13.1. 2023. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_13.1_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). M31-A2 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals: Approved Standard, 2nd ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, T.J.; Gasson, M.J. Molecular screening of Enterococcus virulence determinants and potential for genetic exchange between food and medical isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Antibiotics | Species (Number of Tested Isolates) | Number of Strains with the Indicated MIC (µg/mL) a | EFSA/CLSI Cut-Off Values (µg/mL) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.062 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | |||
| Ampicillin | Lc. garvieae (21) | 6 | 15 | >2/≥4 | ||||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 2 | 1 | 3 | >2/≥8 | ||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 2 | 2 | 2 | >2/≥16 | ||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | >4/Na | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | >2/Na | ||||||||||||
| Vancomycin b | Lc. garvieae (21) | 21 | >4/≥32 | |||||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 6 | >4/Na | ||||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 4 | 2 | >4/≥32 | |||||||||||
| Gentamicin | Lc. garvieae (21) | 1 | 1 | 5 | 11 | 3 | >32/≥16 | |||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 1 | 4 | 1 | >32/≥16 | ||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 3 | 3 | >32/≥16 | |||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | >16/≥16 | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | >16/≥16 | ||||||||||||
| Kanamycin | Lc. garvieae (21) | 1 | 1 | 15 | 4 | >64/≥64 | ||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 1 | 2 | 3 | Nr/≥64 | ||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 2 | 3 | 1 | >1.024/≥64 | ||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | >64/≥64 | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | >16/≥64 | ||||||||||||
| Streptomycin | Lc. garvieae (21) | 1 | 3 | 17 | >32/Na | |||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 1 | 5 | >64/Na | |||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 5 | 1 | >128/Na | |||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | >64/Na | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | >64/Na | ||||||||||||
| Erythromycin | Lc. garvieae (21) | 6 | 15 | >1/≥8 | ||||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 2 | 2 | 2 | >2/≥1 | ||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 2 | 4 | >4/≥8 | |||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | >1/≥8 | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | >1/≥8 | ||||||||||||
| Clindamycin | Lc. garvieae (21) | 21 | >1/≥4 | |||||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 6 | >2/≥4 | ||||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 1 | 4 | 1 | >4/≥4 | ||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | >4/≥2 | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | >1/≥4 | ||||||||||||
| Tetracycline | Lc. garvieae (21) | 2 | 9 | 9 | 1 | >4/≥8 | ||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 4 | 2 | >4/≥8 | |||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 6 | >4/≥16 | ||||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | >8//≥16 | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | >8/≥16 | ||||||||||||
| Chloramphenicol | Lc. garvieae (21) | 1 | 1 | 17 | 2 | >8/≥32 | ||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 4 | 2 | >8/≥16 | |||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 4 | 2 | >16/≥32 | |||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | >4/≥32 | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | >4/≥32 | ||||||||||||
| Florfenicol | Lc. garvieae (21) | 10 | 11 | Na/≥8 | ||||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 4 | 2 | Na/≥8 | |||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Na/≥8 | |||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | Na/≥8 | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | Na/≥8 | ||||||||||||
| Oxytetracycline | Lc. garvieae (21) | 1 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 7 | Na/≥16 | ||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 5 | 1 | Na/≥8 | |||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 4 | 2 | Na/≥16 | |||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | Na/≥16 | ||||||||||||
| Lc. carnosum (1) | 1 | Na/≥16 | ||||||||||||
| Flumequine | Lc. garvieae (21) | 2 | 4 | 16 | Na | |||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 6 | Na | ||||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 1 | 3 | 2 | Na | ||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | Na | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | Na | ||||||||||||
| Amoxicillin | Lc. garvieae (21) | 3 | 8 | 10 | Na/≥8 | |||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 5 | 1 | Na/≥16 | |||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 2 | 1 | 3 | Na | ||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | Na | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | Na | ||||||||||||
| Antibiotics | Species (Number of Tested Isolates) | Number of Strains with the Indicated MIC (µg/mL) a | EFSA/CLSI Cut-off Values (µg/mL) | |||||||||||
| 0.0625/1.1875 | 0.125/2.375 | 0.25/4.75 | 0.5/9.5 | 1/19 | 2/38 | 4/76 | ||||||||
| Trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole | Lc. garvieae (21) | 21 | Na/≥4–76 | |||||||||||
| St. salivarius (6) | 5 | 1 | Na/≥4–76 | |||||||||||
| E. avium (6) | 6 | Na/≥4–76 | ||||||||||||
| Lb. sakei (1) | 1 | Na/≥4–76 | ||||||||||||
| Lt. carnosum (1) | 1 | Na/≥4–76 | ||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Formoso, L.; Contente, D.; Feito, J.; Orgaz, B.; Hernández, P.E.; Borrero, J.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Cintas, L.M. Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Diversity and Safety Assessment of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from European Hakes (Merluccius merluccius, L.) Caught in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050469
Díaz-Formoso L, Contente D, Feito J, Orgaz B, Hernández PE, Borrero J, Muñoz-Atienza E, Cintas LM. Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Diversity and Safety Assessment of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from European Hakes (Merluccius merluccius, L.) Caught in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050469
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Formoso, Lara, Diogo Contente, Javier Feito, Belén Orgaz, Pablo E. Hernández, Juan Borrero, Estefanía Muñoz-Atienza, and Luis M. Cintas. 2025. "Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Diversity and Safety Assessment of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from European Hakes (Merluccius merluccius, L.) Caught in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050469
APA StyleDíaz-Formoso, L., Contente, D., Feito, J., Orgaz, B., Hernández, P. E., Borrero, J., Muñoz-Atienza, E., & Cintas, L. M. (2025). Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Diversity and Safety Assessment of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from European Hakes (Merluccius merluccius, L.) Caught in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean. Antibiotics, 14(5), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050469








