Repurposing Anthelmintic Drugs for COVID-19 Treatment: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials on Ivermectin and Mebendazole
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantitative Findings
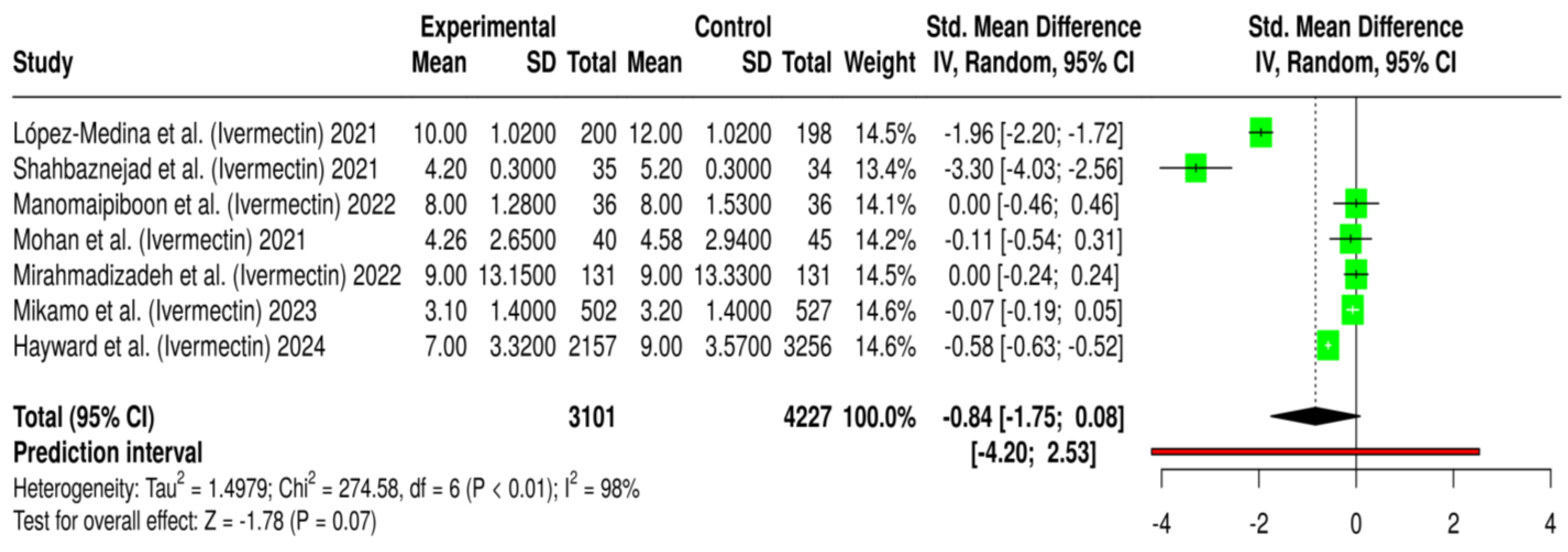
2.1.1. Impact on COVID-19 Viral Clearance
2.1.2. Effect on COVID-19 Hospitalization Duration
2.1.3. Effect on COVID-19 Symptom Resolution
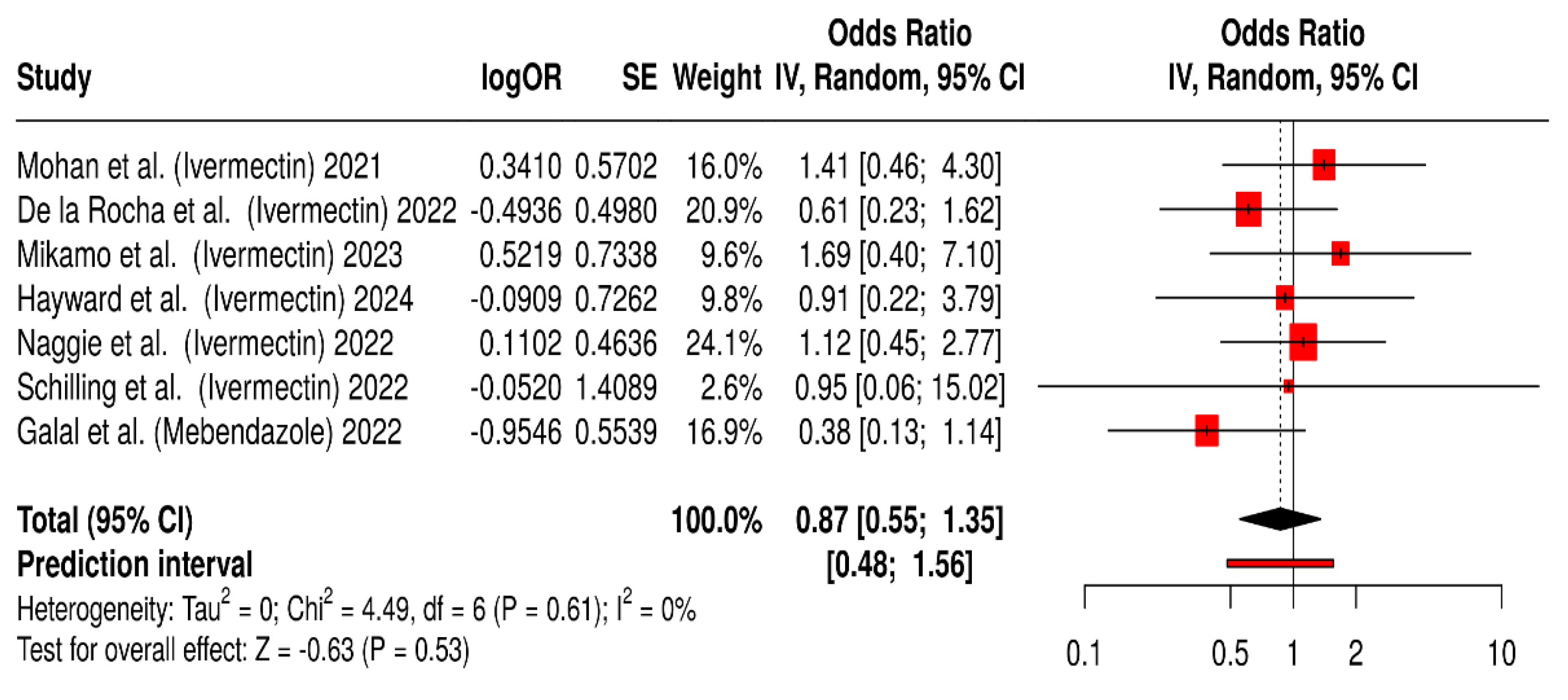
2.1.4. Safety and Tolerability of Ivermectin and Mebendazole Used During COVID-19 Treatment
2.1.5. Summary of Quantitative Findings
2.2. Qualitative Findings
2.2.1. COVID-19 Virological Clearance and Viral Load Reduction
2.2.2. COVID-19 Symptom Resolution and Clinical Improvement
2.2.3. COVID-19 Hospitalization and Mortality
2.2.4. Safety and Tolerability
2.2.5. Summary of Qualitative Findings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
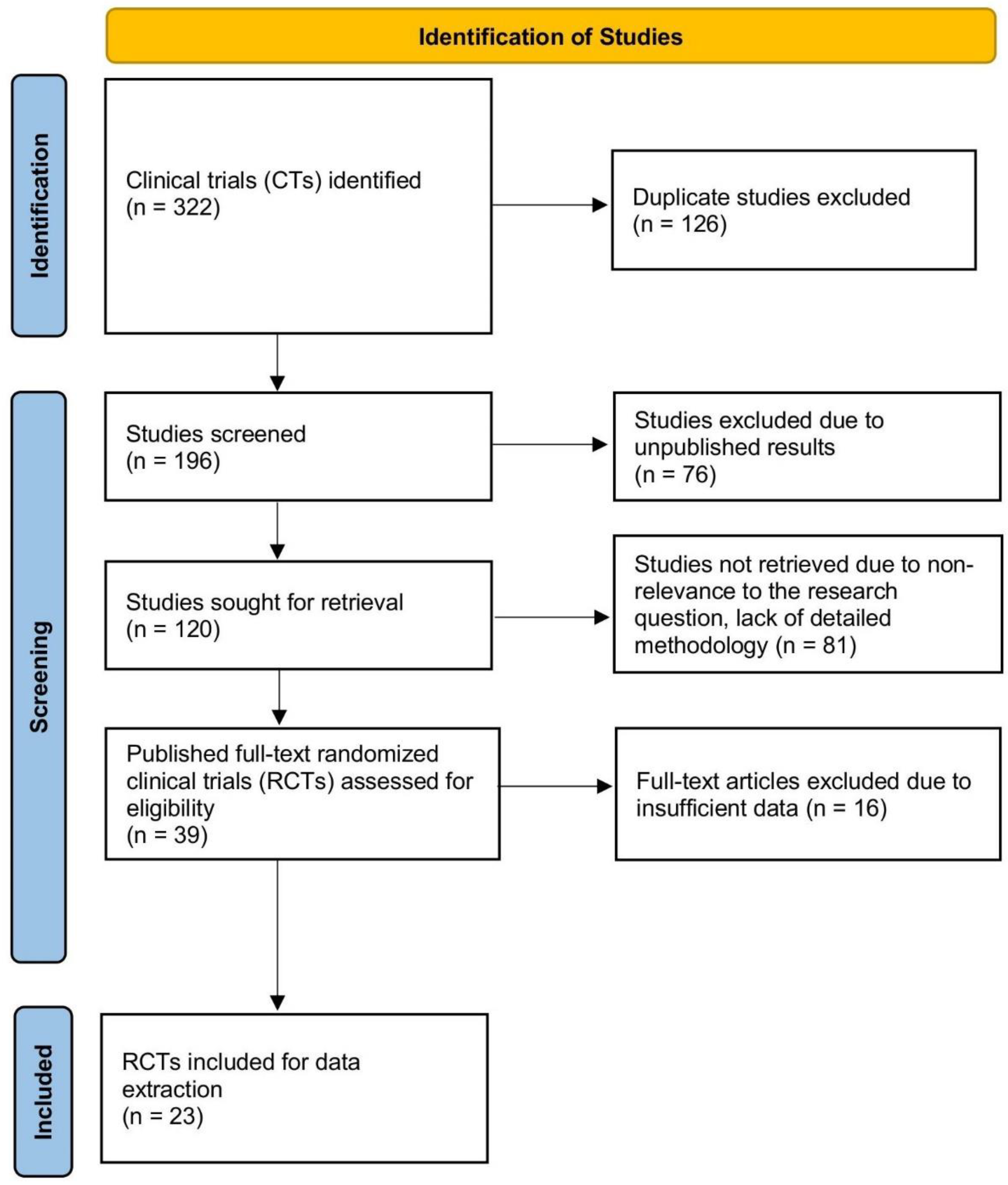
4.1. Search Strategy
4.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
4.2.1. Randomization Process
4.2.2. Deviations from Intended Interventions
4.2.3. Missing Outcome Data
4.2.4. Measurement of Outcomes
4.2.5. Selection of the Reported Results
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakraborty, I.; Maity, P. COVID-19 outbreak: Migration, effects on society, global environment and prevention. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljevic, M.; Bjedov, S.; Jaksic, N.; Jakovljevic, I. COVID-19 pandemia and public and global mental health from the perspective of global health security. Psychiatr. Danub. 2020, 32, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoumpourlis, V.; Goulielmaki, M.; Rizos, E.; Baliou, S.; Spandidos, D.A. The COVID-19 pandemic as a scientific and social challenge in the 21st century. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3035–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gołębiowska, A.; Prokopowicz, D. The impact of the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronavirus pandemic on ecological security and the development of international environmental policy. Zesz. Nauk. Szkoły Głównej Służby Pożarniczej 2021, 2, 179–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurjak, A.; Stanojevic, M.; Jakovljevic, M.; Gaber, G.; Porovic, S.; Medjedovic, E.; Vacek, V. Coronavirus Disease-2019 or the End of a Happy Globalization. Donald Sch. J. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 14, 279–287. [Google Scholar]
- Mekala, R. Global Epidemics and Pandemics in the Light of Civilization, Colonization and Globalization Its Impact on Environmental Health to Contain COVID-19 One Heath Approach is Mandate: A Review. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341180553_One_Health_Review_Article (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Bakshi, A.; Gangopadhyay, K.; Basak, S.; De, R.K.; Sengupta, S.; Dasgupta, A. Integrating state-space modeling, parameter estimation, deep learning, and docking techniques in drug repurposing: A case study on COVID-19 cytokine storm. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2025, ocaf035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusinato, J.; Cau, Y.; Calvani, A.M.; Mori, M. Repurposing drugs for the management of COVID-19. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2021, 31, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, T.L.; Devi, M.M.; Okram, M.; Singh, O.M. Repurposed Drugs during the Outbreak of Pandemic COVID-19: A Mini-Review on Their Molecular Structures and Hit-and-Trial Results. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 36858–36864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, R.K.; DiPaola, R.S.; Romanelli, F.; Dutch, R.E. Rapid repurposing of drugs for COVID-19. Science 2020, 368, 829–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathaneni, V.; Gupta, V. Utilizing drug repurposing against COVID-19–efficacy, limitations, and challenges. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, S.L. Drug repurposing strategies for COVID-19. Future Drug Discov. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.U.; Parida, S.; Lingaraju, M.C.; Kesavan, M.; Kumar, D.; Singh, R.K. Drug repurposing approach to fight COVID-19. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 1479–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P. Repurposing drugs for treatment of COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Blavo, C.; Parmar, M.S. Ivermectin: A multifaceted drug with a potential beyond anti-parasitic therapy. Cureus 2024, 16, e56025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.C.d.N.; Porto, J.C.S.; dos Santos, I.L.; Filho, J.I.A.B.; Ferreira, P.M.P. Repositioning anthelmintics for the treatment of inflammatory-based pathological conditions. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 33, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Rápalo, S.N.; Cordero-Rivera, C.D.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; Benitez-Vega, M.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Del Angel, R.M. Drug Repositioning as an Antiviral Strategy Against Emerging Viruses. In Emerging Viruses in Latin America: Contemporary Virology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 273–317. [Google Scholar]
- Almulhim, M.; Ghasemian, A.; Memariani, M.; Karami, F.; Yassen, A.S.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Drug repositioning as a promising approach for the eradication of emerging and re-emerging viral agents. Mol. Divers. 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengu, N.S.; Raheem, A.; Pons, A.G.; Ho, W.L.; Ali, S.M.S.; Haseeb, A.; Ahmad, T.K.F.; Mustafa, M.S. The impact of ivermectin on COVID-19 outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2025, 87, 809–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Pathak, K.; Saikia, R.; Pramanik, P.; Das, A.; Talukdar, P.; Shakya, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Singh, U.P.; Bhat, H.R. An in-depth analysis of COVID-19 treatment: Present situation and prospects. Arch. Der Pharm. 2024, 357, e2400307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, A.D.; Atari, N.; Meningher, T.; Erster, O.; Avni, D.; Schwartz, E.; Mandelboim, M. The selective effect of Ivermectin on different human coronaviruses; in-vitro study. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xuan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W.; Wen, Z. Ivermectin ameliorates acute myocarditis via the inhibition of importin-mediated nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 133, 112073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.S.; Malik, Y.S.; Saminathan, M.; Tripathi, B.N. Immunological Interventions for the Management of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). In Essentials of Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 453–482. [Google Scholar]
- Muheyuddeen, G.; Khan, M.Y.; Ahmad, T.; Srivastava, S.; Verma, S.; Ansari, M.S.; Sahu, N. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel imidazole derivatives as analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents: Experimental and molecular docking insights. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthick, K.; Abishek, K.; Angel Jemima, E. In Silico Study, Protein Kinase Inhibition and Molecular Docking Study of Benzimidazole Derivatives. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2024, 18, 11779322241247635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S. Back to the Future-Solutions for Parasitic Problems Rahime Şimşek1, Aqsa Farooqui2, Salah-Ud-Din Khan3 and. In Parasitic Infections: Immune Responses and Therapeutics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Baig, M.S.; Bhardwaj, K. Advancements in the development of antivirals against SARS-Coronavirus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1520811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, A.; Harmelin, G.; Lev, D.; Ram, L.; Shaham, A.; Nemet, I.; Kliker, L.; Erster, O.; Mandelboim, M.; Schwartz, E. The effect of ivermectin on the viral load and culture viability in early treatment of nonhospitalized patients with mild COVID-19–a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 122, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfrate, D.; Chesini, F.; Martini, D.; Roncaglioni, M.C.; Fernandez, M.L.O.; Alvisi, M.F.; De Simone, I.; Rulli, E.; Nobili, A.; Casalini, G. High-dose ivermectin for early treatment of COVID-19 (COVER study): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase II, dose-finding, proof-of-concept clinical trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 59, 106516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rocha, C.; Cid-López, M.A.; Venegas-López, B.I.; Gómez-Méndez, S.C.; Sánchez-Ortiz, A.; Pérez-Ríos, A.M.; Llamas-Velázquez, R.A.; Meza-Acuña, A.I.; Vargas-Íñiguez, B.; Rosales-Galván, D. Ivermectin compared with placebo in the clinical course in Mexican patients with asymptomatic and mild COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tanani, M.; Ahmed, K.A.-A.; Shakya, A.K.; Ammari, W.G.; Al-Shudifat, A.-E. Phase II, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial investigating the efficacy of mebendazole in the management of symptomatic COVID-19 patients. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manomaipiboon, A.; Pholtawornkulchai, K.; Poopipatpab, S.; Suraamornkul, S.; Maneerit, J.; Ruksakul, W.; Phumisantiphong, U.; Trakarnvanich, T. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin in the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 infection: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Trials 2022, 23, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Tiwari, P.; Suri, T.M.; Mittal, S.; Patel, A.; Jain, A.; Velpandian, T.; Das, U.S.; Boppana, T.K.; Pandey, R.M. Single-dose oral ivermectin in mild and moderate COVID-19 (RIVET-COV): A single-centre randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, W.H.; Jittamala, P.; Watson, J.A.; Ekkapongpisit, M.; Siripoon, T.; Ngamprasertchai, T.; Luvira, V.; Pongwilai, S.; Cruz, C.V.; Callery, J.J. Pharmacometrics of high dose ivermectin in early COVID-19: An open label, randomized, controlled adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV). eLife 2023, 12, e83201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewickrema, A.; Banneheke, H.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Refai, F.W.; Kauranaratne, M.; Malavige, N.; Jeewandara, C.; Ekanayake, M.; Samaraweera, D.; Thambavita, D. Efficacy and safety of oral ivermectin in the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 patients: A multi-centre double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaccour, C.; Hammann, F.; Ramón-García, S.; Rabinovich, N.R. Ivermectin and COVID-19: Keeping rigor in times of urgency. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 102, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Medina, E.; López, P.; Hurtado, I.C.; Dávalos, D.M.; Ramirez, O.; Martínez, E.; Díazgranados, J.A.; Oñate, J.M.; Chavarriaga, H.; Herrera, S. Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. Jama 2021, 325, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajter, J.C.; Sherman, M.S.; Fatteh, N.; Vogel, F.; Sacks, J.; Rajter, J.-J. Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: The ivermectin in COVID nineteen study. Chest 2021, 159, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejos, J.; Zoni, R.; Bangher, M.; Villamandos, S.; Bobadilla, A.; Plano, F.; Campias, C.; Chaparro Campias, E.; Medina, M.F.; Achinelli, F. Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsalam, S.; Noor, R.A.; Badawi, R.; Khalaf, M.; Esmail, E.S.; Soliman, S.; Abd El Ghafar, M.S.; Elbahnasawy, M.; Moustafa, E.F.; Hassany, S.M. Clinical study evaluating the efficacy of ivermectin in COVID-19 treatment: A randomized controlled study. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 5833–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Karim, M.M.; Ross, A.G.; Hossain, M.S.; Clemens, J.D.; Sumiya, M.K.; Phru, C.S.; Rahman, M.; Zaman, K.; Somani, J. A five-day course of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 may reduce the duration of illness. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 103, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, M.W.; Ahmed, M.; Shao, Y.; Xing, C.; Ali, W.; Baly, A.E.; Elfiky, A.; Amer, K.; Schoggins, J.; Sadek, H.A. The Use of Mebendazole in COVID-19 Patients: An Observational Retrospective Single Center Study. Adv. Virol. 2022, 2022, 3014686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naggie, S.; Boulware, D.R.; Lindsell, C.J.; Stewart, T.G.; Gentile, N.; Collins, S.; McCarthy, M.W.; Jayaweera, D.; Castro, M.; Sulkowski, M. Effect of ivermectin vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2022, 328, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, G.; Silva, E.A.; Silva, D.C.; Thabane, L.; Milagres, A.C.; Ferreira, T.S.; Dos Santos, C.V.; Campos, V.H.; Nogueira, A.M.; de Almeida, A.P. Effect of early treatment with ivermectin among patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaznejad, L.; Davoudi, A.; Eslami, G.; Markowitz, J.S.; Navaeifar, M.R.; Hosseinzadeh, F.; Movahedi, F.S.; Rezai, M.S. Effects of ivermectin in patients with COVID-19: A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayward, G.; Yu, L.-M.; Little, P.; Gbinigie, O.; Shanyinde, M.; Harris, V.; Dorward, J.; Saville, B.R.; Berry, N.; Evans, P.H. Ivermectin for COVID-19 in adults in the community (PRINCIPLE): An open, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial of short-and longer-term outcomes. J. Infect. 2024, 88, 106130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikamo, H.; Takahashi, S.; Yamagishi, Y.; Hirakawa, A.; Harada, T.; Nagashima, H.; Noguchi, C.; Masuko, K.; Maekawa, H.; Kashii, T. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin in patients with mild COVID-19 in Japan and Thailand. J. Infect. Chemother. 2024, 30, 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Mirahmadizadeh, A.; Semati, A.; Heiran, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Hemmati, A.; Karimi, M.; Basir, S.; Zare, M.; Charlys da Costa, A.; Zeinali, M. Efficacy of single-dose and double-dose ivermectin early treatment in preventing progression to hospitalization in mild COVID-19: A multi-arm, parallel-group randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Respirology 2022, 27, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, M.; Stegemann, M.; Metzendorf, M.-I.; Gould, S.; Kranke, P.; Meybohm, P.; Skoetz, N.; Weibel, S. Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 7, CD015017. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roman, Y.M.; Burela, P.A.; Pasupuleti, V.; Piscoya, A.; Vidal, J.E.; Hernandez, A.V. Ivermectin for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, A.; Lawrie, T.A.; Dowswell, T.; Fordham, E.J.; Mitchell, S.; Hill, S.R.; Tham, T.C. Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines. Am. J. Ther. 2021, 28, e434–e460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, T. Ivermectin Reduces the Risk of Death from COVID-19—A Rapid Review and Meta-Analysis in Support of the Recommendation of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348230894_Ivermectin_reduces_the_risk_of_death_from_COVID-19_-a_rapid_review_and_meta-analysis_in_support_of_the_recommendation_of_the_Front_Line_COVID-19_Critical_Care_Alliance (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Moqaddasi, H.R. Pharmacology of Drugs for Treatment of COVID-19. In COVID 19: A Deteriorative Conundrum of Human Health; Selective & Scientific Books: Delhi, India, 2022; p. 134. [Google Scholar]
- Negi, K.; Agarwal, M.; Pahuja, I.; Bhardwaj, B.; Rawat, M.; Bhaskar, A.; Dwivedi, V.P. Combating the challenges of COVID-19 pandemic: Insights into molecular mechanisms, immune responses and therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2. Oxf. Open Immunol. 2023, 4, iqad001. [Google Scholar]
- Eskandari, M.; Asgharzadeh, F.; Askarnia-Faal, M.M.; Naimi, H.; Avan, A.; Ahadi, M.; Vossoughinia, H.; Gharib, M.; Soleimani, A.; Naghibzadeh, N. Mebendazole, an anti-helminth drug, suppresses inflammation, oxidative stress and injury in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Satyam, S.M.; El-Tanani, M.; Patni, M.A.; Rehman, A.; Wali, A.F.; Rangraze, I.R.; Babiker, R.; Rabbani, S.A.; El-Tanani, Y.; Rizzo, M. Repurposing Anthelmintic Drugs for COVID-19 Treatment: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials on Ivermectin and Mebendazole. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050459
Satyam SM, El-Tanani M, Patni MA, Rehman A, Wali AF, Rangraze IR, Babiker R, Rabbani SA, El-Tanani Y, Rizzo M. Repurposing Anthelmintic Drugs for COVID-19 Treatment: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials on Ivermectin and Mebendazole. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050459
Chicago/Turabian StyleSatyam, Shakta Mani, Mohamed El-Tanani, Mohamed Anas Patni, Abdul Rehman, Adil Farooq Wali, Imran Rashid Rangraze, Rasha Babiker, Syed Arman Rabbani, Yahia El-Tanani, and Manfredi Rizzo. 2025. "Repurposing Anthelmintic Drugs for COVID-19 Treatment: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials on Ivermectin and Mebendazole" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050459
APA StyleSatyam, S. M., El-Tanani, M., Patni, M. A., Rehman, A., Wali, A. F., Rangraze, I. R., Babiker, R., Rabbani, S. A., El-Tanani, Y., & Rizzo, M. (2025). Repurposing Anthelmintic Drugs for COVID-19 Treatment: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials on Ivermectin and Mebendazole. Antibiotics, 14(5), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050459